Identification of Site-Specific Stroke Biomarker Candidates by Laser Capture Microdissection and Labeled Reference Peptide
Abstract
:1. Introduction

2. Results and Discussion
2.1. The Focal Cerebral Ischemic Model in Rats
2.2. Laser Capture Microdissection (LCM) of Intact and Infarcted Tissue in the Cerebral Cortex
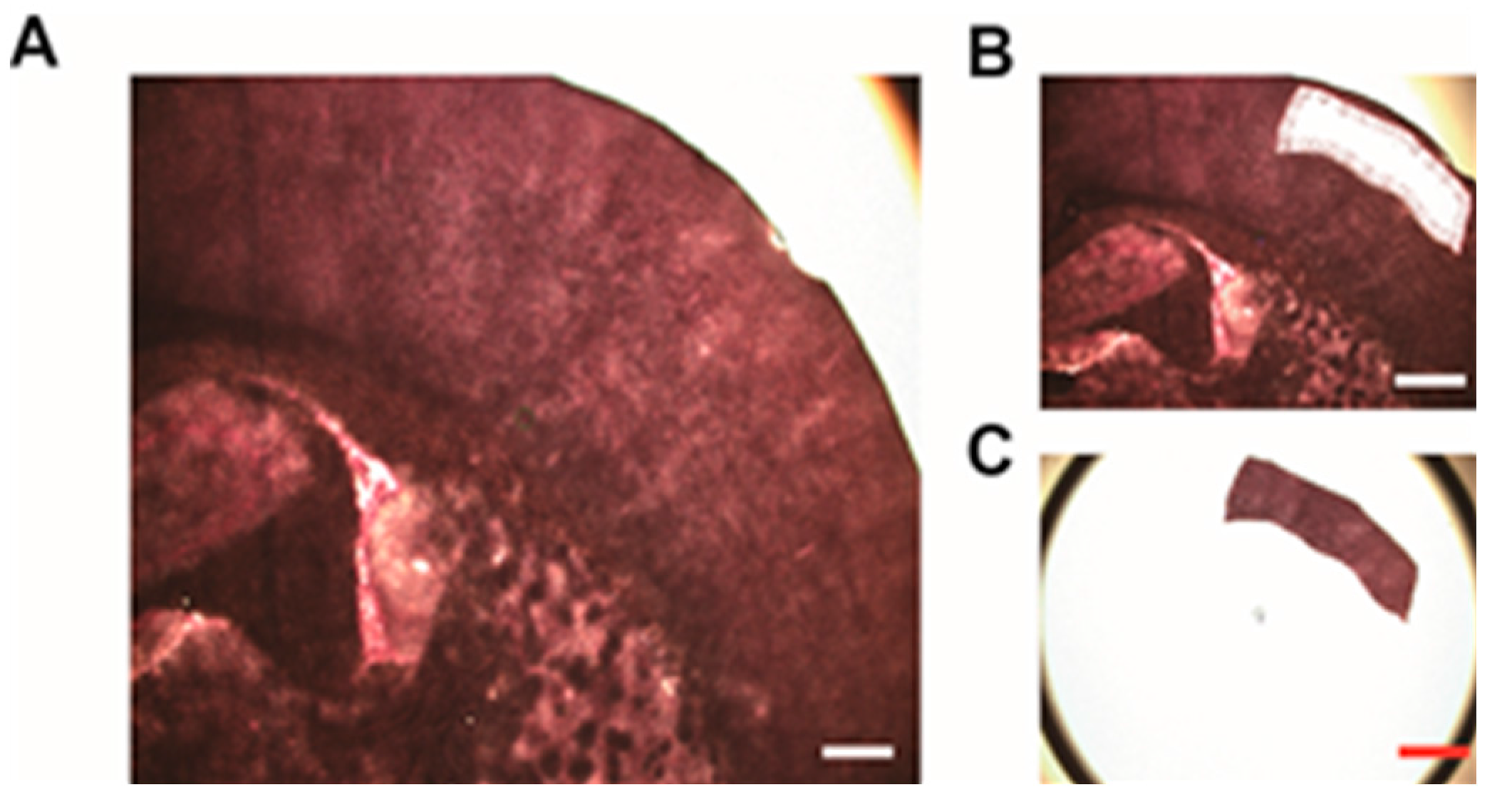
| Sample Size | Zone 1 | Zone 2 | Zone 3 | Zone 4 | Zone 5 | Zone 6 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LCM Area (mm2) | 10.36 ± 0.07 | 9.96 ± 0.08 | 9.67 ± 0.05 | 10.47 ± 0.07 | 9.87 ± 0.07 | 9.71 ± 0.07 |
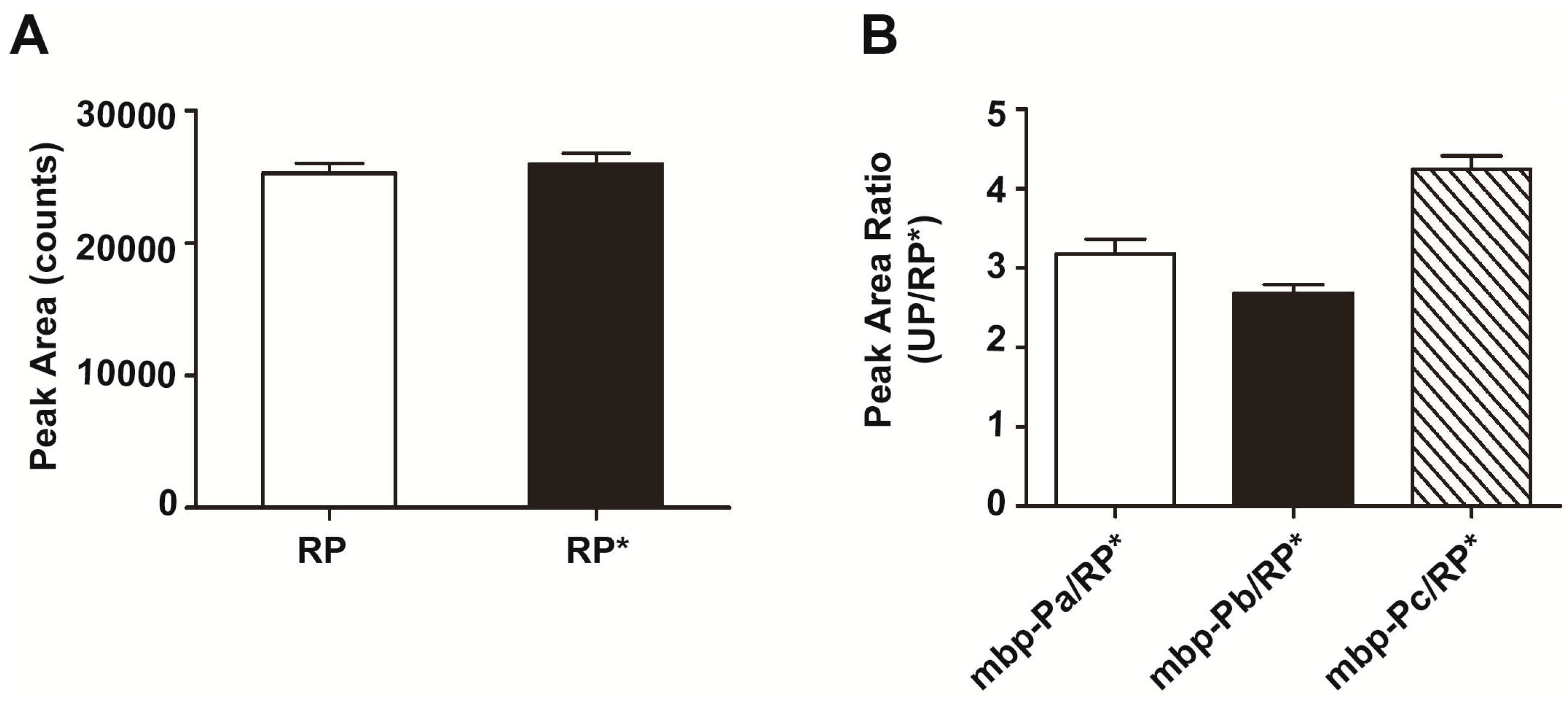
2.3. Semi-Quantification of Quality Control Protein by Labeled Reference Peptide (LRP) Analysis
| Peptide | Sequence | Molecular Weight (Da) | Peak Area | Peak Area Ratio (RP*) | Theoretical Amount (ng) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RP | APGLTQALNTK | 1113.261 | 25,237 ± 766.7 | 0.9959 ± 0.02496 | 1 |
| RP* | APGLTQALNTK* | 1121.261 | 25,952 ± 815.9 | 1.0000 | 1 |
| mbp-Pa | DVGVDNAGAK | 944.979 | 77,202 ± 5126 | 3.182 ± 0.1818 | 3.336641 |
| mbp-Pb | AGLTFLVDLIK | 1189.442 | 65,117 ± 3118 | 2.687 ± 0.1039 | 4.199819 |
| mbp-Pc | VNYGVTVLPTFK | 1337.562 | 103,733 ± 5828 | 4.242 ± 0.1669 | 4.722818 |
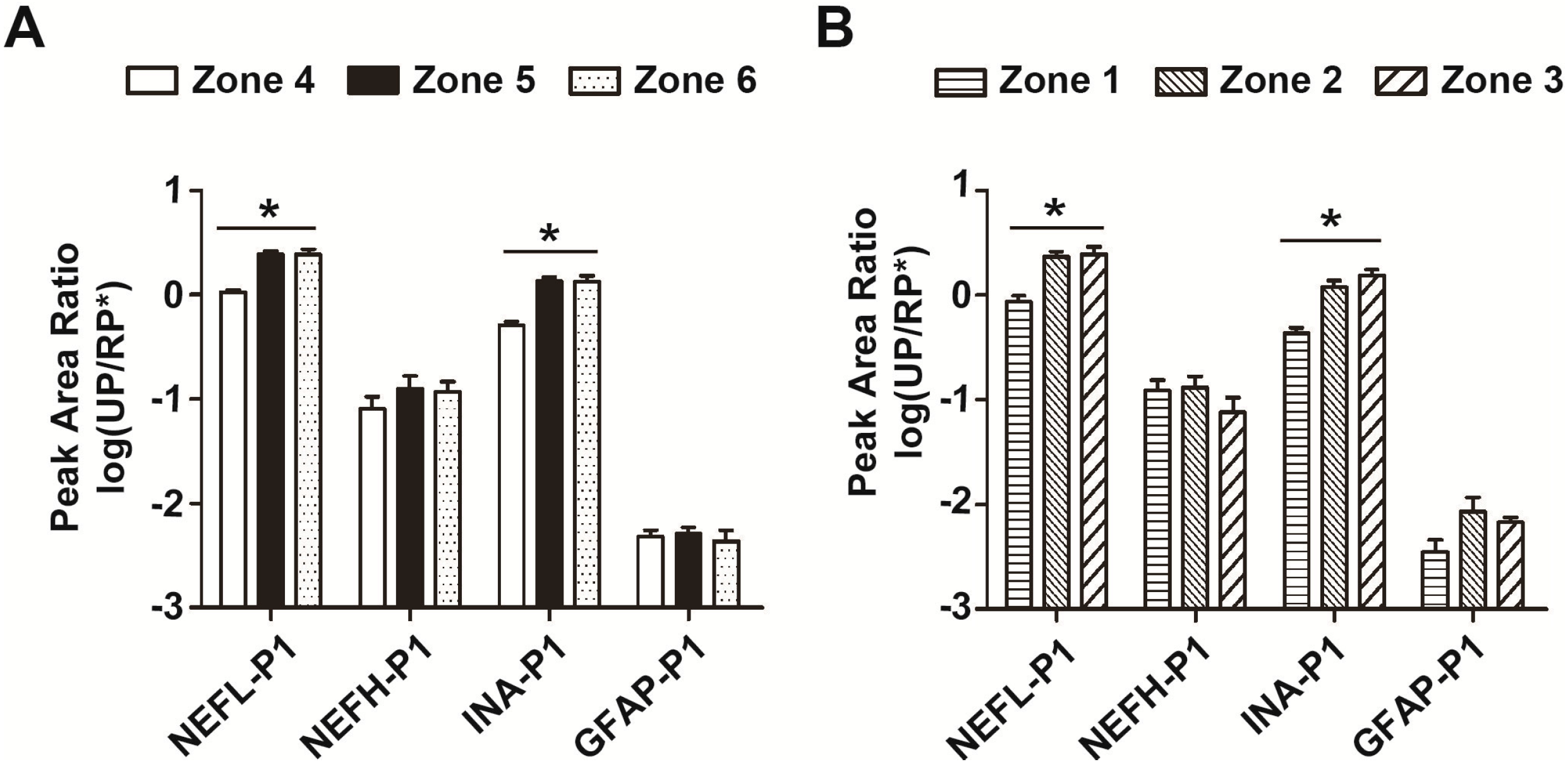
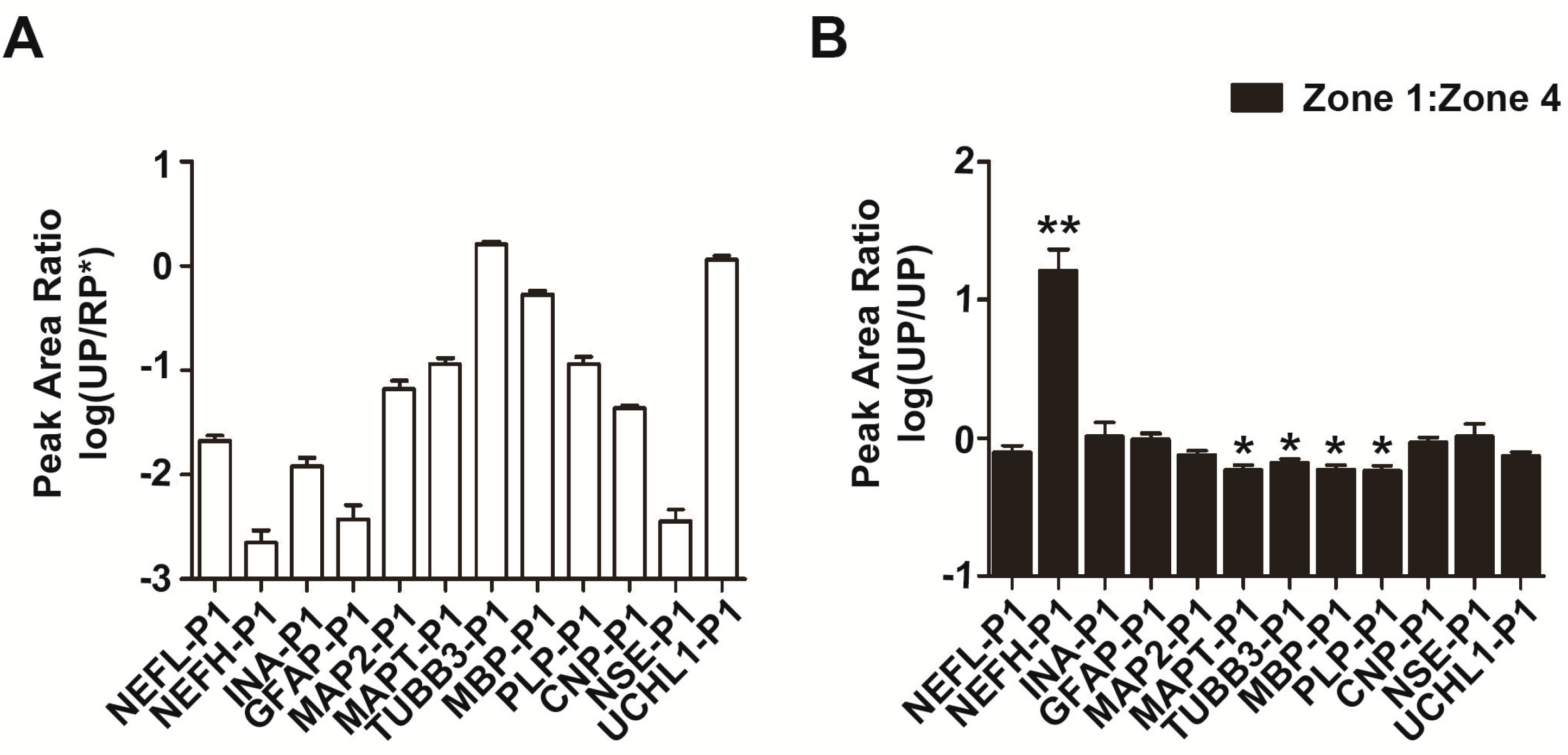
2.4. Distribution of Neurofilament- and Microtubule-Related Proteins in both Intact and Infarcted Brain Tissues
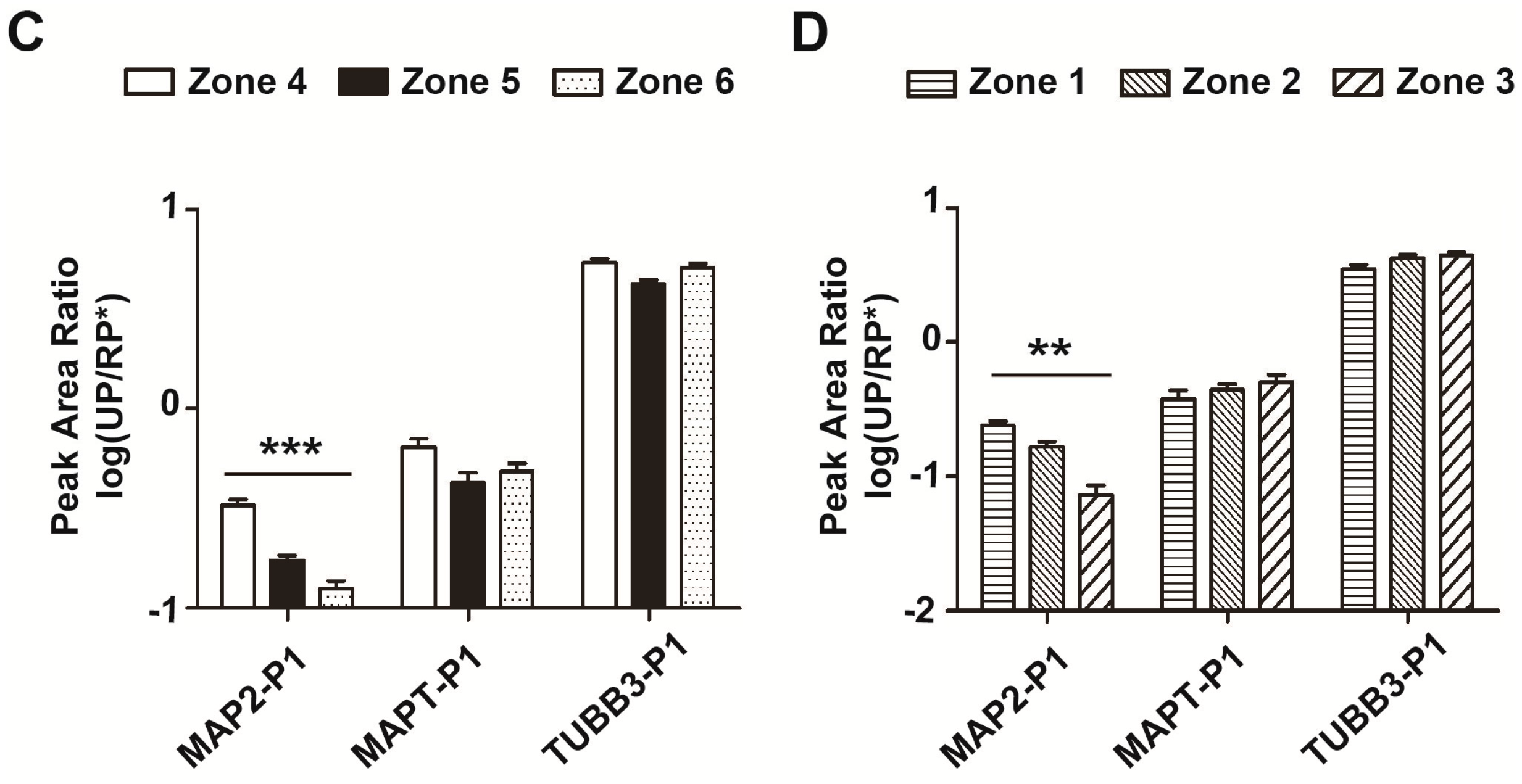
2.5. Site-Specificity of Myelin-Related Proteins in Intact and Infarcted Brain Tissues
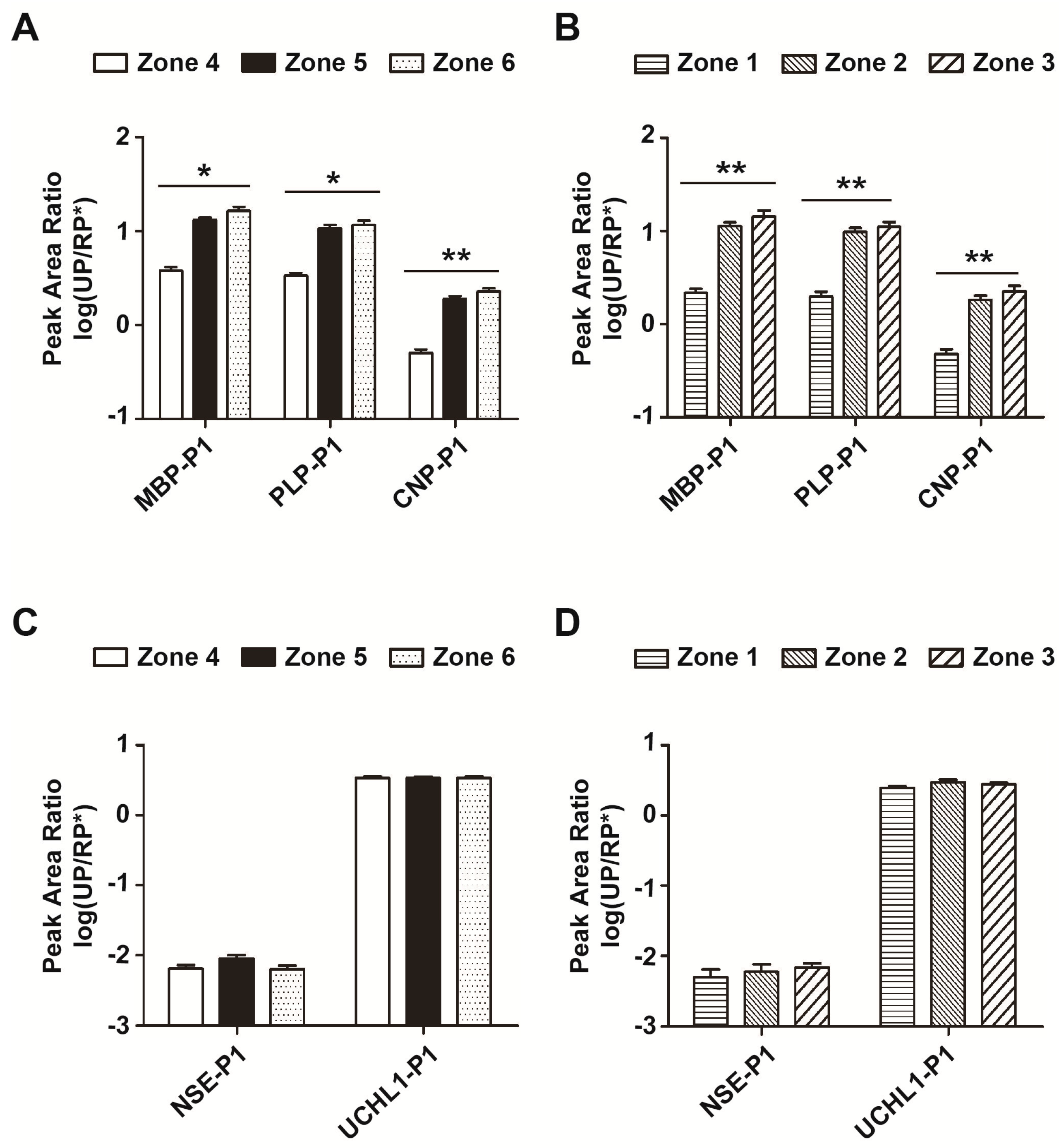
2.6. Abundance and Stability Analysis of Protein Biomarker Candidates by LCM–LRP
3. Experimental Section
3.1. Materials
3.2. Animals
3.3. Intraluminal Middle Cerebral Artery Occlusion (MCAO) Model
3.4. Brain Tissue Collection and Preparation
3.5. On-Film Digestion
3.6. Selection of Unique Peptides, Reference Peptides and Q1/Q3 Transition
3.7. LC-Multiple Reaction Monitoring (MRM) MS Analysis
3.8. Data Analysis
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jickling, G.C.; Sharp, F.R. Blood biomarkers of ischemic stroke. Neurotherapeutics 2011, 8, 349–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernandez-Lopez, D.; Faustino, J.; Daneman, R.; Zhou, L.; Lee, S.Y.; Derugin, N.; Wendland, M.F.; Vexler, Z.S. Blood-brain barrier permeability is increased after acute adult stroke but not neonatal stroke in the rat. J. Neurosci. 2012, 32, 9588–9600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, X.; Chopp, M.; Zacharek, A.; Karasinska, J.M.; Cui, Y.; Ning, R.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Chen, J. Deficiency of brain ATP-binding cassette transporter A-1 exacerbates blood-brain barrier and white matter damage after stroke. Stroke 2015, 46, 827–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saenger, A.K.; Christenson, R.H. Stroke biomarkers: Progress and challenges for diagnosis, prognosis, differentiation, and treatment. Clin. Chem. 2010, 56, 21–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jensen, M.B.; Chacon, M.R.; Sattin, J.A.; Aleu, A.; Lyden, P.D. The promise and potential pitfalls of serum biomarkers for ischemic stroke and transient ischemic attack. Neurologist 2008, 14, 243–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hill, M.D.; Jackowski, G.; Bayer, N.; Lawrence, M.; Jaeschke, R. Biochemical markers in acute ischemic stroke. Can. Med. Assoc. J. 2000, 162, 1139–1140. [Google Scholar]
- Emmert-Buck, M.R.; Wulfkuhle, J.D.; Calvert, V.S.; van Meter, A.; Zhou, W.; Coukos, G.; Geho, D.H.; Petricoin, E.F., 3rd.; Liotta, L.A. Laser capture microdissection. Science 1996, 274, 998–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Subramanian, M.; Holt, A.G.; Mueller, P.J. Physical activity correlates with glutamate receptor gene expression in spinally-projecting RVLM neurons: A laser capture microdissection study. Brain Res. 2014, 1585, 51–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hebbar, S.; Schulz, W.D.; Sauer, U.; Schwudke, D. Laser capture microdissection coupled with on-column extraction LC–MS(n) enables lipidomics of fluorescently labeled Drosophila neurons. Anal. Chem. 2014, 86, 5345–5352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bagnato, C.; Thumar, J.; Mayya, V.; Hwang, S.I.; Zebroski, H.; Claffey, K.P.; Haudenschild, C.; Eng, J.K.; Lundgren, D.H.; Han, D.K. Proteomics analysis of human coronary atherosclerotic plaque: A feasibility study of direct tissue proteomics by liquid chromatography and tandem mass spectrometry. Mol. Cell. Proteomics 2007, 6, 1088–1102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guzel, C.; Ursem, N.T.; Dekker, L.J.; Derkx, P.; Joore, J.; van Dijk, E.; Ligtvoet, G.; Steegers, E.A.; Luider, T.M. Multiple reaction monitoring assay for pre-eclampsia related calcyclin peptides in formalin fixed paraffin embedded placenta. J. Proteome Res. 2011, 10, 3274–3282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Liu, Q.; Zimmerman, L.J.; Ham, A.J.; Slebos, R.J.; Rahman, J.; Kikuchi, T.; Massion, P.P.; Carbone, D.P.; Billheimer, D.; et al. Methods for peptide and protein quantitation by liquid chromatography-multiple reaction monitoring mass spectrometry. Mol. Cell. Proteomics 2011, 10, M110 006593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Longa, E.Z.; Weinstein, P.R.; Carlson, S.; Cummins, R. Reversible middle cerebral artery occlusion without craniectomy in rats. Stroke 1989, 20, 84–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krueger, M.; Bechmann, I.; Immig, K.; Reichenbach, A.; Härtig, W.; Michalski, D. Blood-brain barrier breakdown involves four distinct stages of vascular damage in various models of experimental focal cerebral ischemia. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 2014, 35, 292–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herrmann, M.; Vos, P.; Wunderlich, M.T.; de Bruijn, C.H.; Lamers, K.J. Release of glial tissue-specific proteins after acute stroke: A comparative analysis of serum concentrations of protein S-100B and glial fibrillary acidic protein. Stroke 2000, 31, 2670–2677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Foerch, C.; Curdt, I.; Yan, B.; Dvorak, F.; Hermans, M.; Berkefeld, J.; Raabe, A.; Neumann-Haefelin, T.; Steinmetz, H.; Sitzer, M. Serum glial fibrillary acidic protein as a biomarker for intracerebral haemorrhage in patients with acute stroke. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2006, 77, 181–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laser-Azogui, A.; Kornreich, M.; Malka-Gibor, E.; Beck, R. Neurofilament assembly and function during neuronal development. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 2015, 32C, 92–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Staal, J.A.; Canty, A.J.; Kirkcaldie, M.T.; King, A.E.; Bibari, O.; Mitew, S.T.; Dickson, T.C.; Vickers, J.C. Cytoskeletal changes during development and aging in the cortex of neurofilament light protein knockout mice. J. Comp. Neurol. 2013, 521, 1817–1827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Delacourte, A.; Defossez, A. Alzheimer’s disease: Tau proteins, the promoting factors of microtubule assembly, are major components of paired helical filaments. J. Neurol. Sci. 1986, 76, 173–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yushmanov, V.E.; Kharlamov, A.; Simplaceanu, E.; Williams, D.S.; Jones, S.C. Differences between arterial occlusive and cortical photothrombosis stroke models with magnetic resonance imaging and microtubule-associated protein-2 immunoreactivity. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2006, 24, 1087–1093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trotter, J.L.; Clark, H.B.; Collins, K.G.; Wegeschiede, C.L.; Scarpellini, J.D. Myelin proteolipid protein induces demyelinating disease in mice. J. Neurol. Sci. 1987, 79, 173–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheedlo, H.J.; Sprinkle, T.J. The distribution of 2′:3′-cyclic nucleotide 3′-phosphodiesterase (CNP) in the CNS of normal (+/+) and Shiverer (shi/shi) mice. J. Neurol. Sci. 1985, 67, 35–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jauch, E.C.; Lindsell, C.; Broderick, J.; Fagan, S.C.; Tilley, B.C.; Levine, S.R.; NINDS rt-PA Stroke Study Group. Association of serial biochemical markers with acute ischemic stroke: The National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke recombinant tissue plasminogen activator Stroke Study. Stroke 2006, 37, 2508–2513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Osaka, H.; Wang, Y.L.; Takada, K.; Takizawa, S.; Setsuie, R.; Li, H.; Sato, Y.; Nishikawa, K.; Sun, Y.J.; Sakurai, M.; et al. Ubiquitin carboxy-terminal hydrolase L1 binds to and stabilizes monoubiquitin in neuron. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2003, 12, 1945–1958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Erickson, H.S.; Albert, P.S.; Gillespie, J.W.; Rodriguez-Canales, J.; Marston Linehan, W.; Pinto, P.A.; Chuaqui, R.F.; Emmert-Buck, M.R. Quantitative RT-PCR gene expression analysis of laser microdissected tissue samples. Nat. Protoc. 2009, 4, 902–922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Qian, W.J.; Mottaz, H.M.; Clauss, T.R.; Anderson, D.J.; Moore, R.J.; Camp, D.G., 2nd.; Khan, A.H.; Sforza, D.M.; Pallavicini, M.; et al. Development and evaluation of a micro- and nano-scale proteomic sample preparation method. J. Proteome Res. 2005, 4, 2397–2403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sprung, R.W., Jr.; Brock, J.W.; Tanksley, J.P.; Li, M.; Washington, M.K.; Slebos, R.J.; Liebler, D.C. Equivalence of protein inventories obtained from formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded and frozen tissue in multidimensional liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry shotgun proteomic analysis. Mol. Cell. Proteomics 2009, 8, 1988–1998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lange, V.; Picotti, P.; Domon, B.; Aebersold, R. Selected reaction monitoring for quantitative proteomics: A tutorial. Mol. Syst. Biol. 2008, 4, 222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- MacLean, B.; Tomazela, D.M.; Shulman, N.; Chambers, M.; Finney, G.L.; Frewen, B.; Kern, R.; Tabb, D.L.; Liebler, D.C.; MacCoss, M.J. Skyline: An open source document editor for creating and analyzing targeted proteomics experiments. Bioinformatics 2010, 26, 966–968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2015 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lian, T.; Qu, D.; Zhao, X.; Yu, L.; Gao, B. Identification of Site-Specific Stroke Biomarker Candidates by Laser Capture Microdissection and Labeled Reference Peptide. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2015, 16, 13427-13441. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms160613427
Lian T, Qu D, Zhao X, Yu L, Gao B. Identification of Site-Specific Stroke Biomarker Candidates by Laser Capture Microdissection and Labeled Reference Peptide. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2015; 16(6):13427-13441. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms160613427
Chicago/Turabian StyleLian, Tingting, Daixin Qu, Xu Zhao, Lixia Yu, and Bing Gao. 2015. "Identification of Site-Specific Stroke Biomarker Candidates by Laser Capture Microdissection and Labeled Reference Peptide" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 16, no. 6: 13427-13441. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms160613427
APA StyleLian, T., Qu, D., Zhao, X., Yu, L., & Gao, B. (2015). Identification of Site-Specific Stroke Biomarker Candidates by Laser Capture Microdissection and Labeled Reference Peptide. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 16(6), 13427-13441. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms160613427





