Families of microRNAs Expressed in Clusters Regulate Cell Signaling in Cervical Cancer
Abstract
:1. Introduction
| Clusters | miRNAs in the Cluster | Family of miRNAs | Chromosome | Function |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| miR-133a-2~1-1 | miR-1-1 and miR-133a-2 | miR-1 (1-1, 1-2 and 206); miR-133 (133a and 133b) | 20 | A/O |
| miR-1-2~133a-1 | miR-1-2 and miR-133a-1 | 18 | A/O | |
| miR-133b~206 | miR-133b and miR-206 | 6 | O/? | |
| miR-17~92 | miR-17−, miR-18a, miR19a, miR-20a, miR-19b-1, miR-92-1 | miR-17 (17, 18a, 18b, 20a, 20b, 93, 106a and 106b); miR-19 (19a, 19b-1 and 19b-2); miR-363 (363); miR-25 (25, 92a-1, 92a-2 and 92b) | 13 | O |
| miR-106a~363 | miR-106a, miR-18b, miR-20b, miR-19b-2, miR-92-2 and miR-363 | X | O | |
| miR-106b~25 | miR-106b, miR-93 and miR-25 | 7 | O | |
| miR-23a~27a~24-2 | miR-23a, miR-27a and miR-24-2 | miR-23 (23a, 23b and 23c); miR-24 (24-1 and 24-2); miR-27 (27a and 27b) | 19 | O |
| miR-23b~27b~24-1 | miR-23b, miR-27b and miR-24-1 | 9 | A | |
| miR-29a~29b-1 | miR-29a and miR-29b-1 | miR-29 (29a, 29b-1, 29b-2 and 29c) | 7 | A |
| miR-29b-2~29c | miR-29b-2 and miR-29c | 1 | A | |
| miR-34b~34c | miR-34b and miR-34c | miR-34 (34a, 34b and 34c) | 11 | A |
| miR-183~96~182 | miR-183, miR-96 and miR-182 | miR-183 (183); miR-96 (96); miR-182 (182) | 7 | O |
| miR-125a~let-7c~99b | miR-125a, let-7e and miR-99b | Let-7 (a-1, a-2, a-3, b, c, d, e, f-1, f-2, g and i); miR-99 (99a, 99b and 100); miR-125 (125a, 125b-1 and 125b-2) | 19 | O/?/A |
| miR-let-7c~99a | let-7c and miR-99a | 21 | ?/A | |
| miR-100~let-7a-2 | miR-100 and let-7a-2 | 11 | A/? | |
| miR-181a-1~181b-1 | miR-181a-1 and miR-181b-1 | miR-181 (181a-1, 181a-2, 181b-1, 181b-2, 181c and 181d) | 1 | O |
| miR-181a-2~181b-2 | miR-181a-2 and miR-181b-2 | 9 | O | |
| miR-181c~181d | miR-181c and miR-181d | 19 | O | |
| miR-199a-2~214 | miR-199a-2 and miR-214 | miR-199 (199a-1, 199a-2 and 199b); miR-214 (214 and 3120) | 1 | A |
| miR-302s | miR-302a, miR-302b, miR-302c, miR-302d and miR-367 | miR-302 (302a, 302b, 302c, 302d, 302e and 302f) miR-367 (367) | 4 | A |
2. miRNAs Families Altered in Cervical Cancer
3. Cell-Signaling Pathways Regulated by Members of miRNA Families Expressed in Clusters
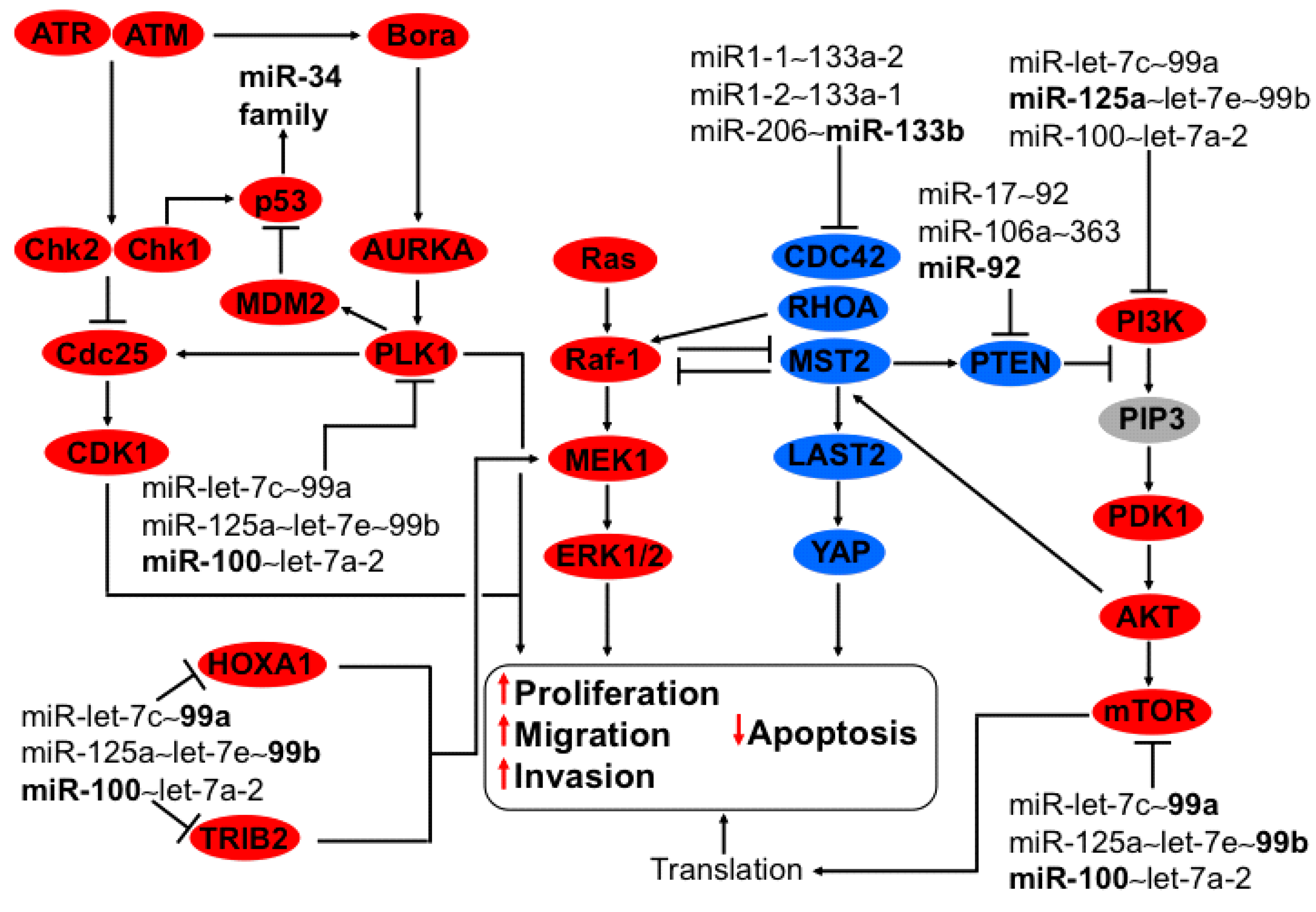
3.1. Regulation of PI3K-AKT and MAPK Axis by miR-133b from the Cluster miR-206~133b
3.2. Regulation of CUL5, NOTCH, TNKS2, PTEN-PI3K-AKT Axis by miR-17~92 and miR-106a~363 Clusters
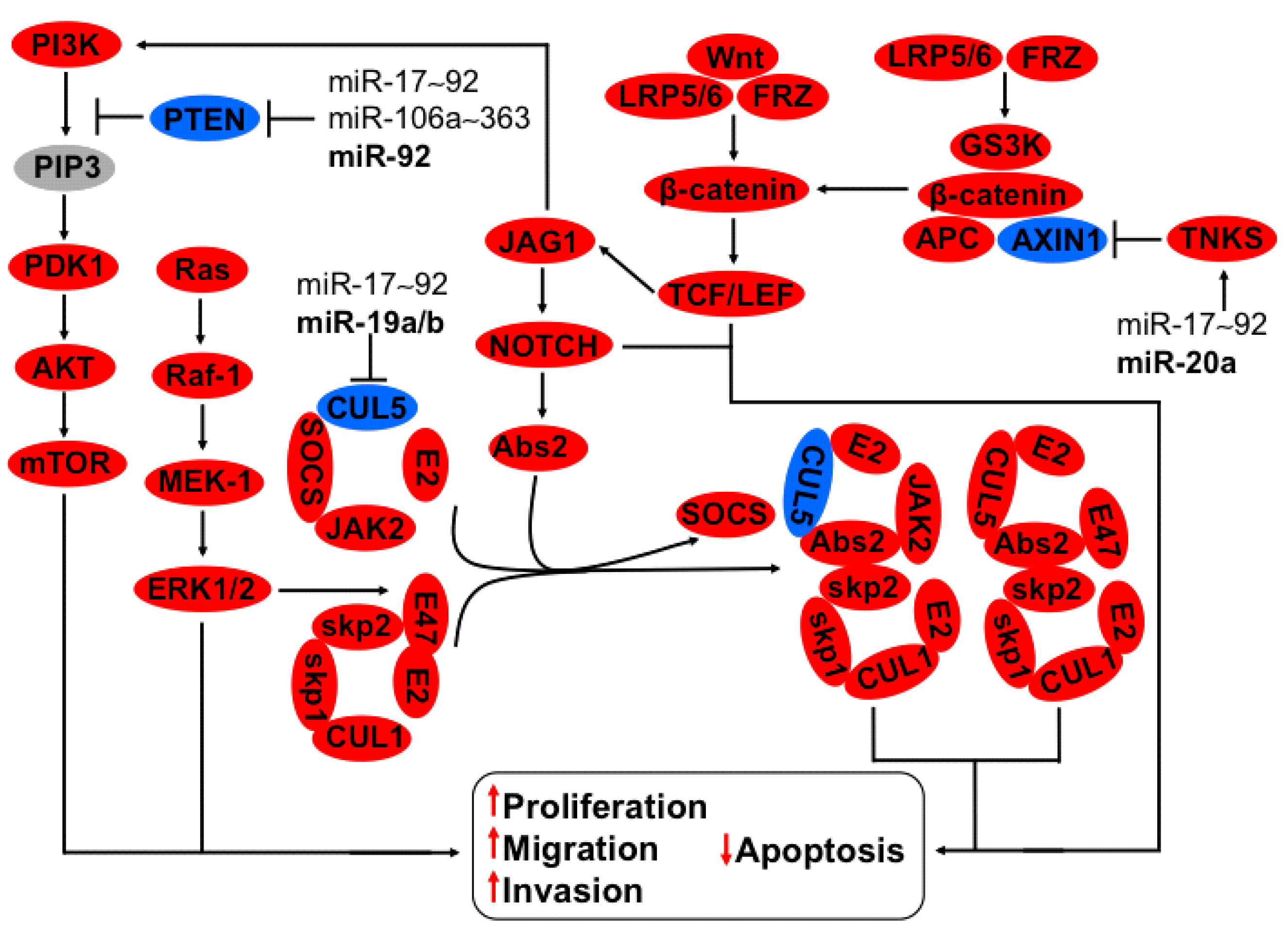
3.3. Regulation of uPA-PLG-MMP and JAG-NOTCH Axis by Members of miR-23b~27b~24-1 Cluster
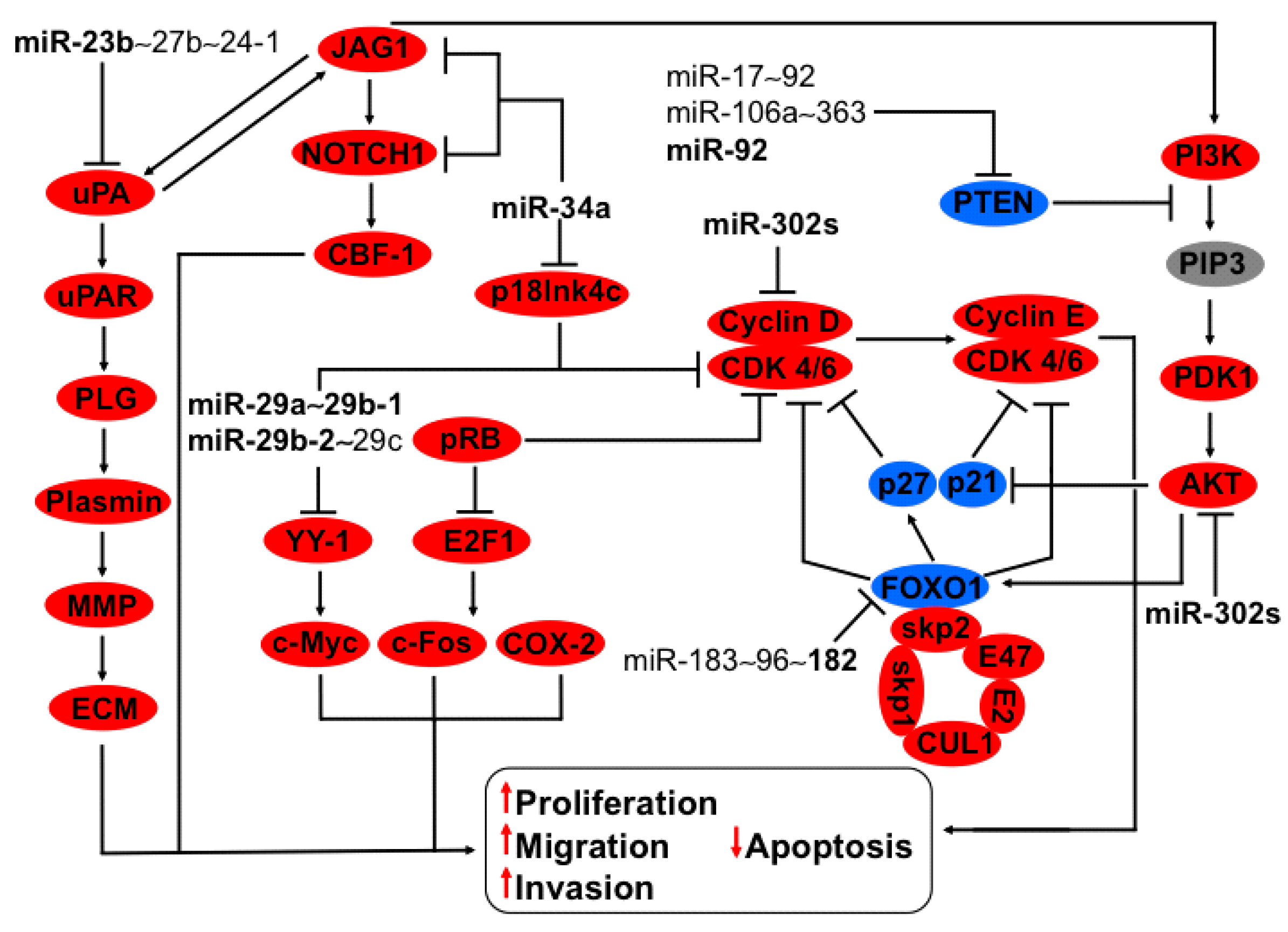
3.4. Regulation of HSP47, YY-1 and CDK6 Axis by miR-29a~29b-1 and miR-29b-2~29c Clusters
3.5. Regulation of P18Ink4c and JAG-NOTCH-uPA Axis by miR-34a
3.6. FOXO1-Cullin-Rings Axis Are Regulated by the Cluster miR183~96~182
3.7. Regulation of PI3K-AKT and MAPK Axis by miR-let-7c~99a, miR-125a~let-7e~99b, and miR-100~let-7a-2 Clusters
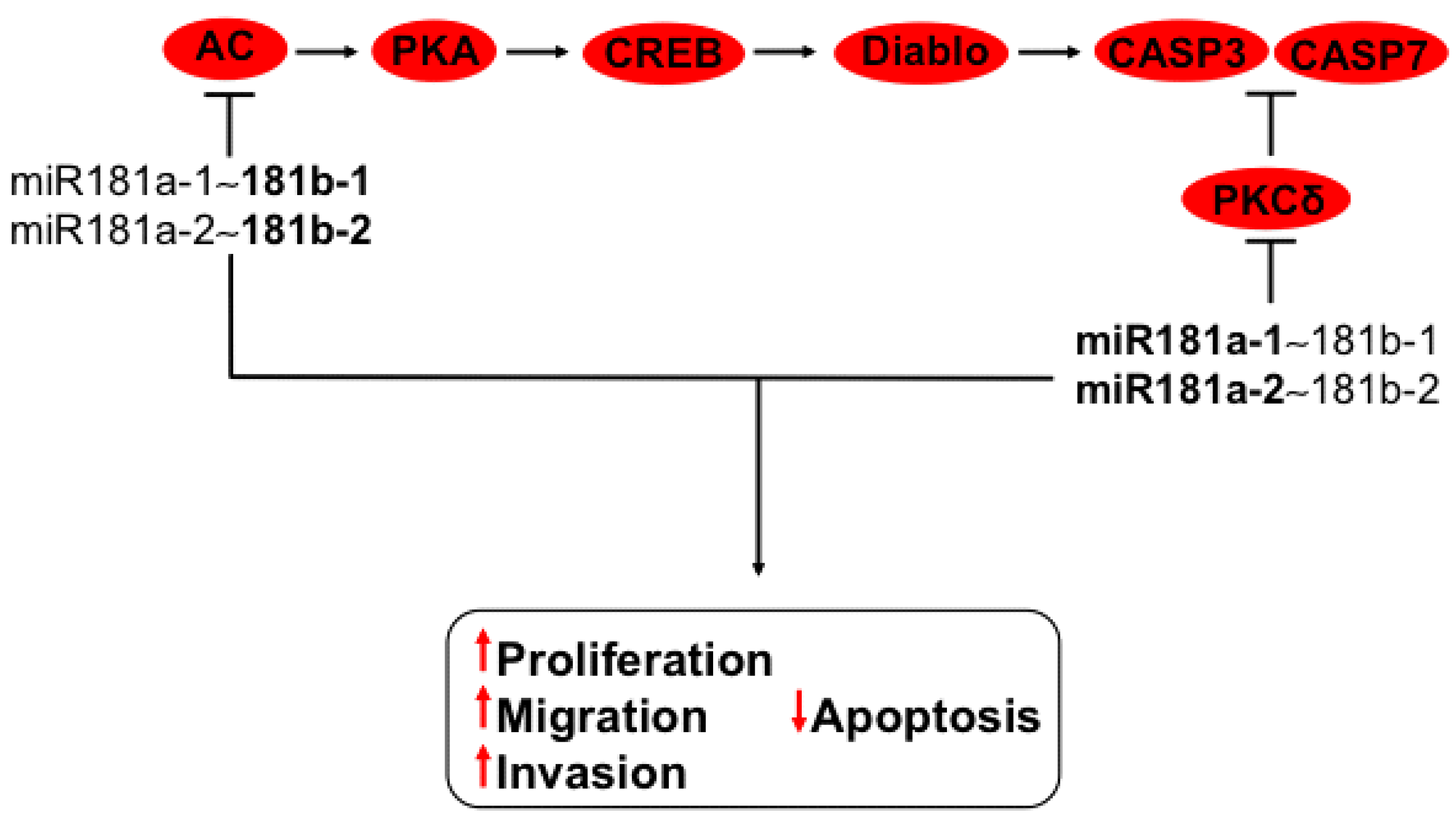
3.8. Regulation of PI3K-AKT and MAPK Axis by miR181a-1~181b-1 and miR181a-2~181b-2 Clusters
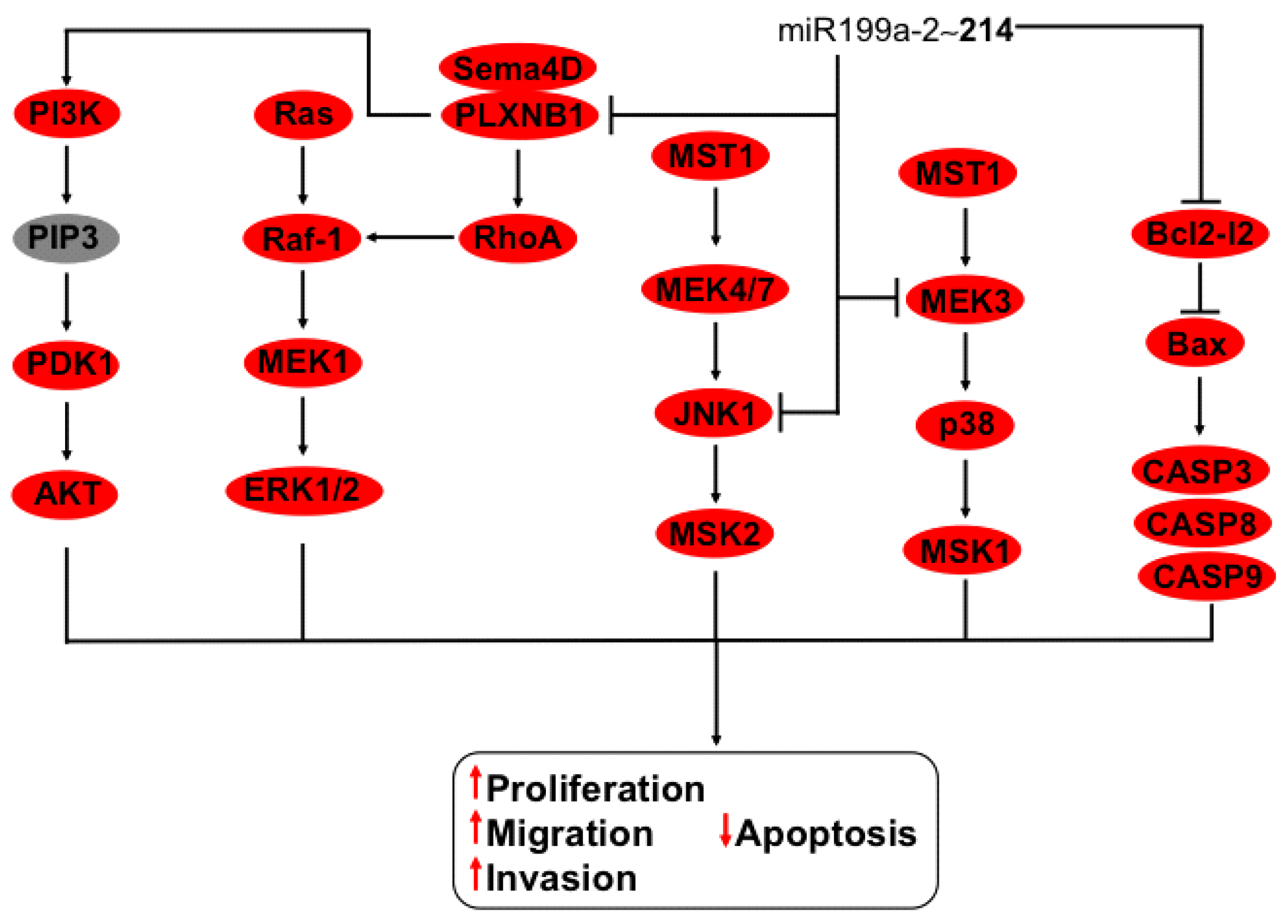
3.9. Regulation of MEK, JNK and Bcl2-l2 Axis by the miR-214~199a-2 Cluster
3.10. Regulation of Cyclin D and AKT Axis by the miR-302s Cluster
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, X.; Wang, H.K.; McCoy, J.P.; Banerjee, N.S.; Rader, J.S.; Broker, T.R.; Meyers, C.; Chow, L.T.; Zheng, Z.M. Oncogenic HPV infection interrupts the expression of tumor-suppressive miR-34a through viral oncoprotein E6. RNA 2009, 15, 637–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lopez, J.A.; Alvarez-Salas, L.M. Differential effects of miR-34c-3p and miR-34c-5p on SIHA cells proliferation apoptosis, migration and invasion. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2011, 409, 513–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Demuth, J.P.; de Bie, T.; Stajich, J.E.; Cristianini, N.; Hahn, M.W. The evolution of mammalian gene families. PLoS ONE 2006, 1, e85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, J.; Wang, F.; Yang, G.H.; Wang, F.L.; Ma, Y.N.; Du, Z.W.; Zhang, J.W. Human microRNA clusters: Genomic organization and expression profile in leukemia cell lines. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2006, 349, 59–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kriegel, A.J.; Liu, Y.; Fang, Y.; Ding, X.; Liang, M. The miR-29 family: Genomics, cell biology, and relevance to renal and cardiovascular injury. Physiol. Genomics 2012, 44, 237–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kozomara, A.; Griffiths-Jones, S. Mirbase: Annotating high confidence microRNAs using deep sequencing data. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014, 42, D68–D73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Altuvia, Y.; Landgraf, P.; Lithwick, G.; Elefant, N.; Pfeffer, S.; Aravin, A.; Brownstein, M.J.; Tuschl, T.; Margalit, H. Clustering and conservation patterns of human microRNAs. Nucleic Acids Res. 2005, 33, 2697–2706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chhabra, R.; Dubey, R.; Saini, N. Cooperative and individualistic functions of the microRNAs in the miR-23a~27a~24-2 cluster and its implication in human diseases. Mol. Cancer 2010, 9, 232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tehler, D.; Hoyland-Kroghsbo, N.M.; Lund, A.H. The miR-10 microRNA precursor family. RNA Biol. 2011, 8, 728–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, W.X.; Danaher, R.J.; Miller, C.S.; Berger, J.R.; Nubia, V.G.; Wilfred, B.S.; Neltner, J.H.; Norris, C.M.; Nelson, P.T. Expression of miR-15/107 family microRNAs in human tissues and cultured rat brain cells. Genomics Proteomics Bioinform. 2014, 12, 19–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, W.S.; Leung, C.M.; Pan, H.W.; Hu, L.Y.; Li, S.C.; Ho, M.R.; Tsai, K.W. Silencing of miR-1-1 and miR-133a-2 cluster expression by DNA hypermethylation in colorectal cancer. Oncol. Rep. 2012, 28, 1069–1076. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Granados Lopez, A.J.; Lopez, J.A. Multistep model of cervical cancer: Participation of miRNAs and coding genes. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2014, 15, 15700–15733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qin, W.; Dong, P.; Ma, C.; Mitchelson, K.; Deng, T.; Zhang, L.; Sun, Y.; Feng, X.; Ding, Y.; Lu, X.; et al. MicroRNA-133b is a key promoter of cervical carcinoma development through the activation of the ERK and AKT1 pathways. Oncogene 2012, 31, 4067–4075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leicht, D.T.; Balan, V.; Zhu, J.; Kaplun, A.; Bronisz, A.; Rana, A.; Tzivion, G. MEK-1 activates c-RAF through a RAS-independent mechanism. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2013, 1833, 976–986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Romano, D.; Matallanas, D.; Weitsman, G.; Preisinger, C.; Ng, T.; Kolch, W. Proapoptotic kinase MST2 coordinates signaling crosstalk between RASSF1A, RAF-1, and AKT. Cancer Res. 2010, 70, 1195–1203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, F.; Jiang, Q.; Shi, K.J.; Luo, H.; Yang, Y.; Xu, C.M. RhoA modulates functional and physical interaction between ROCK1 and ERK1/2 in selenite-induced apoptosis of leukaemia cells. Cell Death Dis. 2013, 4, e708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.; Dong, X.; Wang, Z.; Liu, W.; Deng, N.; Ding, Y.; Tang, L.; Hla, T.; Zeng, R.; Li, L.; et al. Regulation of PTEN by rho small GTPASES. Nat. Cell Biol. 2005, 7, 399–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zugasti, O.; Rul, W.; Roux, P.; Peyssonnaux, C.; Eychene, A.; Franke, T.F.; Fort, P.; Hibner, U. RAF-MEK-ERK cascade in ANOIKIS is controlled by RAC1 and CDC42 via AKT. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2001, 21, 6706–6717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Basile, J.R.; Gavard, J.; Gutkind, J.S. Plexin-b1 utilizes rhoA and rho kinase to promote the integrin-dependent activation of AKT and ERK and endothelial cell motility. J. Biol. Chem. 2007, 282, 34888–34895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aurandt, J.; Li, W.; Guan, K.L. Semaphorin 4d activates the MAPK pathway downstream of plexin-b1. Biochem. J. 2006, 394, 459–464. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Tanzer, A.; Stadler, P.F. Molecular evolution of a microRNA cluster. J. Mol. Biol. 2004, 339, 327–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, X.M.; Wang, X.B.; Chen, M.M.; Liu, T.; Li, Y.X.; Jia, W.H.; Liu, M.; Li, X.; Tang, H. MicroRNA-19a and -19b regulate cervical carcinoma cell proliferation and invasion by targeting cul5. Cancer Lett. 2012, 322, 148–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiba, T.; Tanaka, K. Cullin-based ubiquitin ligase and its control by NEDD8-conjugating system. Curr. Protein Pept. Sci. 2004, 5, 177–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petroski, M.D.; Deshaies, R.J. Mechanism of lysine 48-linked ubiquitin-chain synthesis by the cullin-ring ubiquitin-ligase complex SCF-CDC34. Cell 2005, 123, 1107–1120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nie, L.; Zhao, Y.; Wu, W.; Yang, Y.Z.; Wang, H.C.; Sun, X.H. Notch-induced ASB2 expression promotes protein ubiquitination by forming non-canonical E3 ligase complexes. Cell Res. 2011, 21, 754–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, W.; Sun, X.H. A mechanism underlying NOTCH-induced and ubiquitin-mediated JAK3 degradation. J. Biol. Chem. 2011, 286, 41153–41162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nie, L.; Xu, M.; Vladimirova, A.; Sun, X.H. NOTCH-induced E2A ubiquitination and degradation are controlled by map kinase activities. EMBO J. 2003, 22, 5780–5792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, H.W.; Wang, F.; Wei, Q.; Zhao, Y.F.; Liu, M.; Li, X.; Tang, H. miR-20a promotes migration and invasion by regulating TNKS2 in human cervical cancer cells. FEBS Lett. 2012, 586, 897–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- James, R.G.; Davidson, K.C.; Bosch, K.A.; Biechele, T.L.; Robin, N.C.; Taylor, R.J.; Major, M.B.; Camp, N.D.; Fowler, K.; Martins, T.J.; et al. WIKI4, a novel inhibitor of TANKYRASE and Wnt/SS-catenin signaling. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e50457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katoh, M.; Katoh, M. Notch ligand, JAG1, is evolutionarily conserved target of canonical Wnt signaling pathway in progenitor cells. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2006, 17, 681–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanahan, D.; Weinberg, R.A. Hallmarks of cancer: The next generation. Cell 2011, 144, 646–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, S. MicroRNA-92 regulates cervical tumorigenesis and its expression is upregulated by human papillomavirus-16 E6 in cervical cancer cells. Oncol. Lett. 2013, 6, 468–474. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ayaz, F.; Osborne, B.A. Non-canonical notch signaling in cancer and immunity. Front. Oncol. 2014, 4, 345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Veeraraghavalu, K.; Subbaiah, V.K.; Srivastava, S.; Chakrabarti, O.; Syal, R.; Krishna, S. Complementation of human papillomavirus type 16 E6 and E7 by JAGGED1-specific NOTCH1-phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase signaling involves pleiotropic oncogenic functions independent of CBF1;SU(H);LAG-1 activation. J. Virol. 2005, 79, 7889–7898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Q.; Gallagher, R.; Ufret-Vincenty, R.; Li, X.; Olson, E.N.; Wang, S. Regulation of angiogenesis and choroidal neovascularization by members of microRNA-23~27~24 clusters. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 8287–8292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Au Yeung, C.L.; Tsang, T.Y.; Yau, P.L.; Kwok, T.T. Human papillomavirus type 16 E6 induces cervical cancer cell migration through the p53/microRNA-23b/urokinase-type plasminogen activator pathway. Oncogene 2011, 30, 2401–2410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raghu, H.; Gondi, C.S.; Dinh, D.H.; Gujrati, M.; Rao, J.S. Specific knockdown of UPA/UPAR attenuates invasion in glioblastoma cells and Xenografts by inhibition of cleavage and trafficking of NOTCH-1 receptor. Mol. Cancer 2011, 10, 130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shimizu, M.; Cohen, B.; Goldvasser, P.; Berman, H.; Virtanen, C.; Reedijk, M. Plasminogen activator UPA is a direct transcriptional target of the JAG1-NOTCH receptor signaling pathway in breast cancer. Cancer Res. 2011, 71, 277–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bin Hafeez, B.; Adhami, V.M.; Asim, M.; Siddiqui, I.A.; Bhat, K.M.; Zhong, W.; Saleem, M.; Din, M.; Setaluri, V.; Mukhtar, H. Targeted knockdown of NOTCH1 inhibits invasion of human prostate cancer cells concomitant with inhibition of matrix metalloproteinase-9 and urokinase plasminogen activator. Clin. Cancer Res. 2009, 15, 452–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamamoto, N.; Kinoshita, T.; Nohata, N.; Yoshino, H.; Itesako, T.; Fujimura, L.; Mitsuhashi, A.; Usui, H.; Enokida, H.; Nakagawa, M.; et al. Tumor-suppressive microRNA-29a inhibits cancer cell migration and invasion via targeting HSP47 in cervical squamous cell carcinoma. Int. J. Oncol. 2013, 43, 1855–1863. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Wang, F.; Xu, J.; Ye, F.; Shen, Y.; Zhou, J.; Lu, W.; Wan, X.; Ma, D.; Xie, X. Progressive miRNA expression profiles in cervical carcinogenesis and identification of HPV-related target genes for miR-29. J. Pathol. 2011, 224, 484–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gong, J.; Li, J.; Wang, Y.; Liu, C.; Jia, H.; Jiang, C.; Wang, Y.; Luo, M.; Zhao, H.; Dong, L.; et al. Characterization of microRNA-29 family expression and investigation of their mechanistic roles in gastric cancer. Carcinogenesis 2014, 35, 497–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Q.; Stovall, D.B.; Inoue, K.; Sui, G. The oncogenic role of yin yang 1. Crit. Rev. Oncog. 2011, 16, 163–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Polager, S.; Ginsberg, D. E2f—At the crossroads of life and death. Trends Cell Biol. 2008, 18, 528–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Meyers, C.; Guo, M.; Zheng, Z.M. Upregulation of p18ink4c expression by oncogenic HPV E6 via p53-miR-34a pathway. Int. J. Cancer 2011, 129, 1362–1372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pang, R.T.; Leung, C.O.; Ye, T.M.; Liu, W.; Chiu, P.C.; Lam, K.K.; Lee, K.F.; Yeung, W.S. MicroRNA-34a suppresses invasion through downregulation of notch1 and JAGGED1 in cervical carcinoma and choriocarcinoma cells. Carcinogenesis 2010, 31, 1037–1044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, P.; Sheng, C.; Huang, L.; Zhang, H.; Huang, L.; Cheng, Z.; Zhu, Q. miR-183/-96/-182 cluster is up-regulated in most breast cancers and increases cell proliferation and migration. Breast Cancer Res. 2014, 16, 473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, T.; Wong, H.K.; Gu, W.; Yu, M.Y.; To, K.F.; Wang, C.C.; Wong, Y.F.; Cheung, T.H.; Chung, T.K.; Choy, K.W. MicroRNA-182 plays an onco-mirna role in cervical cancer. Gynecol. Oncol. 2013, 129, 199–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, H.; Wu, Y.L.; Wang, Y.X.; Zhu, F.F. Characterization of the microRNA expression profile of cervical squamous cell carcinoma metastases. Asian Pac. J. Cancer Prev. 2014, 15, 1675–1679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, H.; Regan, K.M.; Wang, F.; Wang, D.; Smith, D.I.; van Deursen, J.M.; Tindall, D.J. SKP2 inhibits FOXO1 in tumor suppression through ubiquitin-mediated degradation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 1649–1654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmidt, M.; Fernandez de Mattos, S.; van der Horst, A.; Klompmaker, R.; Kops, G.J.; Lam, E.W.; Burgering, B.M.; Medema, R.H. Cell cycle inhibition by FOXO forkhead transcription factors involves downregulation of cyclin D. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2002, 22, 7842–7852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xin, J.X.; Yue, Z.; Zhang, S.; Jiang, Z.H.; Wang, P.Y.; Li, Y.J.; Pang, M.; Xie, S.Y. miR-99 inhibits cervical carcinoma cell proliferation by targeting TRIB2. Oncol. Lett. 2013, 6, 1025–1030. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Grandinetti, K.B.; Stevens, T.A.; Ha, S.; Salamone, R.J.; Walker, J.R.; Zhang, J.; Agarwalla, S.; Tenen, D.G.; Peters, E.C.; Reddy, V.A. Over-expression of TRIB2 in human lung cancers contributes to tumorigenesis through downregulation of C/EBPα. Oncogene 2011, 30, 3328–3335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keeshan, K.; He, Y.; Wouters, B.J.; Shestova, O.; Xu, L.; Sai, H.; Rodriguez, C.G.; Maillard, I.; Tobias, J.W.; Valk, P.; et al. Tribbles homolog 2 inactivates C/EBPα and causes acute myelogenous leukemia. Cancer Cell 2006, 10, 401–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naiki, T.; Saijou, E.; Miyaoka, Y.; Sekine, K.; Miyajima, A. TRB2, a mouse tribbles ortholog, suppresses adipocyte differentiation by inhibiting AKT and C/EBPα. J. Biol. Chem. 2007, 282, 24075–24082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohankumar, K.M.; Xu, X.Q.; Zhu, T.; Kannan, N.; Miller, L.D.; Liu, E.T.; Gluckman, P.D.; Sukumar, S.; Emerald, B.S.; Lobie, P.E. Hoxa1-stimulated oncogenicity is mediated by selective upregulation of components of the p44/42 MAP kinase pathway in human mammary carcinoma cells. Oncogene 2007, 26, 3998–4008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, D.; Chen, Z.; Jin, Y.; Dragas, D.; Zhang, L.; Adjei, B.S.; Wang, A.; Dai, Y.; Zhou, X. MicroRNA-99 family members suppress homeobox A1 expression in epithelial cells. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e80625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, B.H.; Zhou, J.S.; Ye, F.; Cheng, X.D.; Zhou, C.Y.; Lu, W.G.; Xie, X. Reduced miR-100 expression in cervical cancer and precursors and its carcinogenic effect through targeting PLK1 protein. Eur. J. Cancer 2011, 47, 2166–2174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bahassi, E.M. Polo-like kinases and DNA damage checkpoint: Beyond the traditional mitotic functions. Exp. Biol. Med. 2011, 236, 648–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hyun, S.Y.; Hwang, H.I.; Jang, Y.J. Polo-like kinase-1 in DNA damage response. BMB Rep. 2014, 47, 249–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, F.; Li, X.; Zhu, X.; Huang, L.; Huang, Y.; Mao, C.; Yan, Q.; Zhu, J.; Zhao, W.; Shi, H. miR-125b inhibits tumor growth and promotes apoptosis of cervical cancer cells by targeting phosphoinositide 3-kinase catalytic subunit delta. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2012, 30, 1310–1318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ke, G.; Liang, L.; Yang, J.M.; Huang, X.; Han, D.; Huang, S.; Zhao, Y.; Zha, R.; He, X.; Wu, X. miR-181a confers resistance of cervical cancer to radiation therapy through targeting the pro-apoptotic PRKCD gene. Oncogene 2013, 32, 3019–3027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Ke, G.; Han, D.; Liang, S.; Yang, G.; Wu, X. MicroRNA-181a enhances the chemoresistance of human cervical squamous cell carcinoma to cisplatin by targeting PRKCD. Exp. Cell Res. 2014, 320, 12–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, L.; Wang, Y.L.; Liu, S.; Zhang, P.P.; Chen, Z.; Liu, M.; Tang, H. miR-181b promotes cell proliferation and reduces apoptosis by repressing the expression of adenylyl cyclase 9 (AC9) in cervical cancer cells. FEBS Lett. 2014, 588, 124–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martinez-Velazquez, M.; Melendez-Zajgla, J.; Maldonado, V. Apoptosis induced by camp requires SMAC/DIABLO transcriptional upregulation. Cell. Signal. 2007, 19, 1212–1220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, X.; Sit, A.; Feinberg, M.W. Role of miR-181 family in regulating vascular inflammation and immunity. Trends Cardiovasc. Med. 2014, 24, 105–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baumgarten, A.; Bang, C.; Tschirner, A.; Engelmann, A.; Adams, V.; von Haehling, S.; Doehner, W.; Pregla, R.; Anker, M.S.; Blecharz, K.; et al. Twist1 regulates the activity of ubiquitin proteasome system via the miR-199/214 cluster in human end-stage dilated cardiomyopathy. Int. J. Cardiol. 2013, 168, 1447–1452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, G.; Chen, R.; Alvero, A.B.; Fu, H.H.; Holmberg, J.; Glackin, C.; Rutherford, T.; Mor, G. Twisting stemness, inflammation and proliferation of epithelial ovarian cancer cells through miR199a2/214. Oncogene 2010, 29, 3545–3553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiang, R.; Wang, F.; Shi, L.Y.; Liu, M.; Chen, S.; Wan, H.Y.; Li, Y.X.; Li, X.; Gao, S.Y.; Sun, B.C.; et al. Plexin-b1 is a target of miR-214 in cervical cancer and promotes the growth and invasion of HELA cells. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2011, 43, 632–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Z.; Chen, S.; Luan, X.; Li, Y.; Liu, M.; Li, X.; Liu, T.; Tang, H. MicroRNA-214 is aberrantly expressed in cervical cancers and inhibits the growth of HELA cells. IUBMB Life 2009, 61, 1075–1082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, R.Q.; Wan, H.Y.; Li, H.F.; Liu, M.; Li, X.; Tang, H. MicroRNA-214 suppresses growth and invasiveness of cervical cancer cells by targeting UDP-N-acetyl-α-d-galactosamine: Polypeptide N-acetylgalactosaminyltransferase 7. J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 287, 14301–14309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, F.; Liu, M.; Li, X.; Tang, H. miR-214 reduces cell survival and enhances cisplatin-induced cytotoxicity via down-regulation of BCL2L2 in cervical cancer cells. FEBS Lett. 2013, 587, 488–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, N.; Wang, Y.D.; Zheng, P.S. The microRNA-302~367 cluster suppresses the proliferation of cervical carcinoma cells through the novel target AKT1. RNA 2013, 19, 85–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2015 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Servín-González, L.S.; Granados-López, A.J.; López, J.A. Families of microRNAs Expressed in Clusters Regulate Cell Signaling in Cervical Cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2015, 16, 12773-12790. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms160612773
Servín-González LS, Granados-López AJ, López JA. Families of microRNAs Expressed in Clusters Regulate Cell Signaling in Cervical Cancer. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2015; 16(6):12773-12790. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms160612773
Chicago/Turabian StyleServín-González, Luis Steven, Angelica Judith Granados-López, and Jesús Adrián López. 2015. "Families of microRNAs Expressed in Clusters Regulate Cell Signaling in Cervical Cancer" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 16, no. 6: 12773-12790. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms160612773
APA StyleServín-González, L. S., Granados-López, A. J., & López, J. A. (2015). Families of microRNAs Expressed in Clusters Regulate Cell Signaling in Cervical Cancer. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 16(6), 12773-12790. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms160612773





