Molecular and Immobilized Tripodal Phosphine Ligands and Their Trinuclear Palladium Complexes
Abstract
1. Introduction
General Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
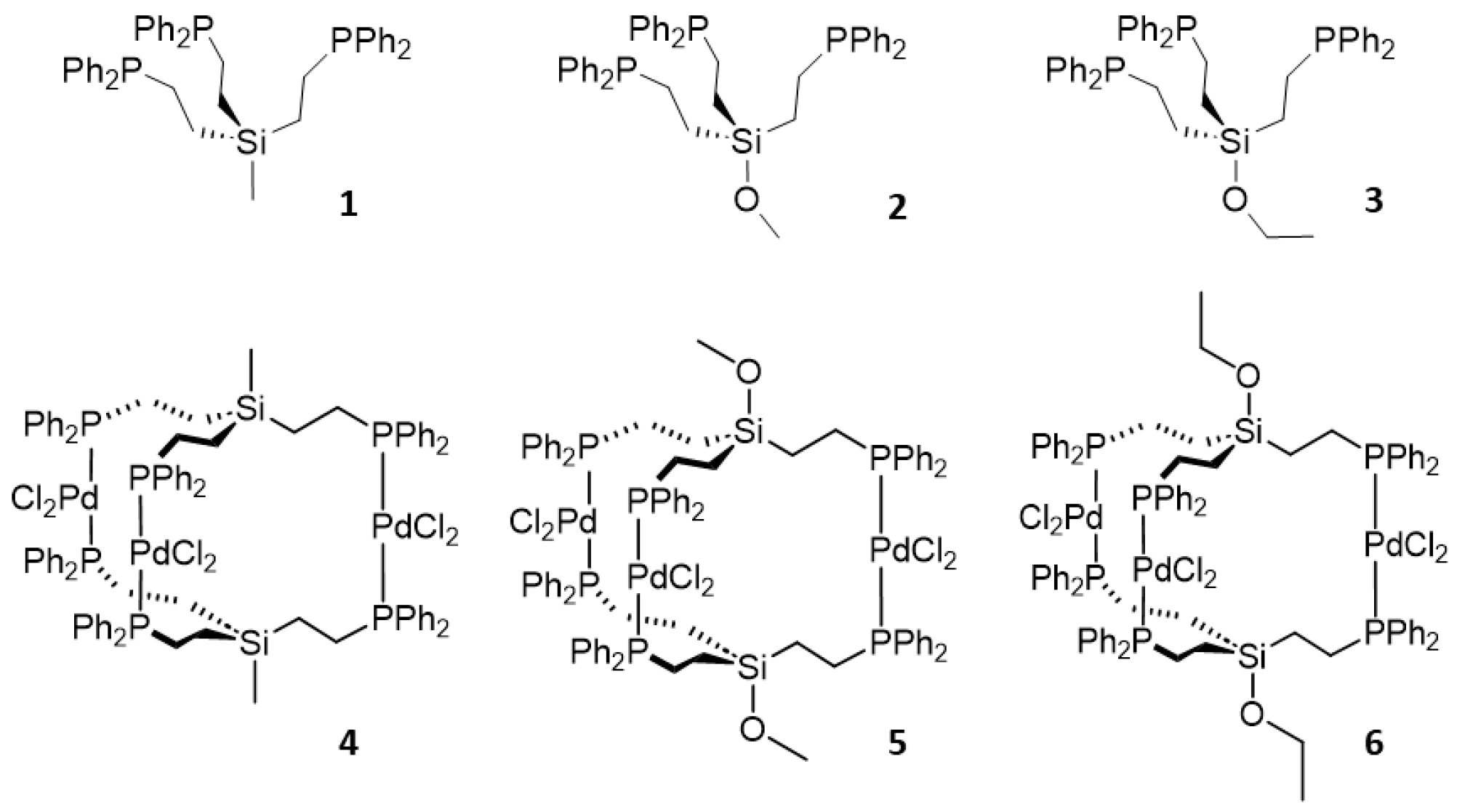
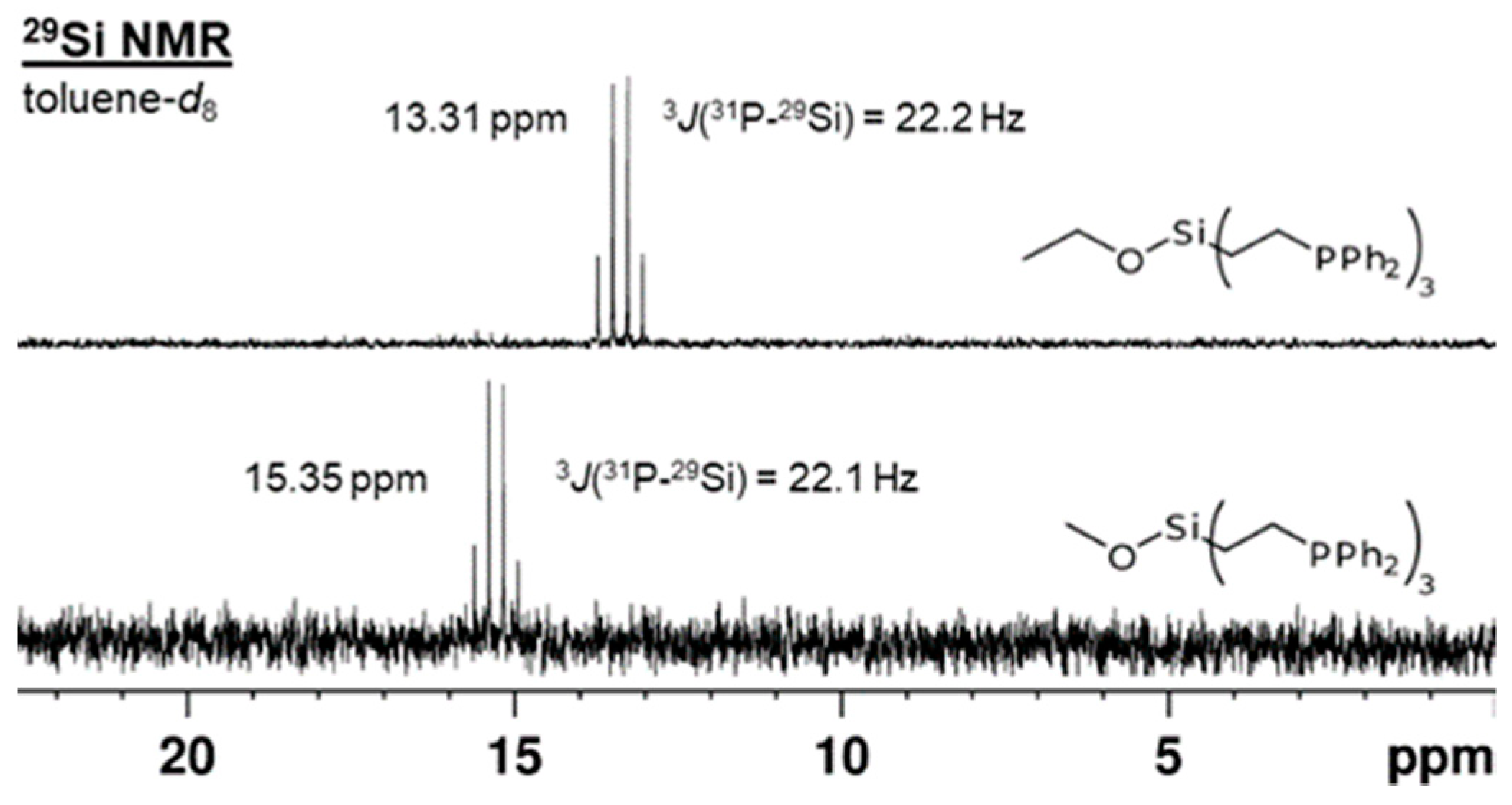
2.1. Tripodal Phosphine Ligands
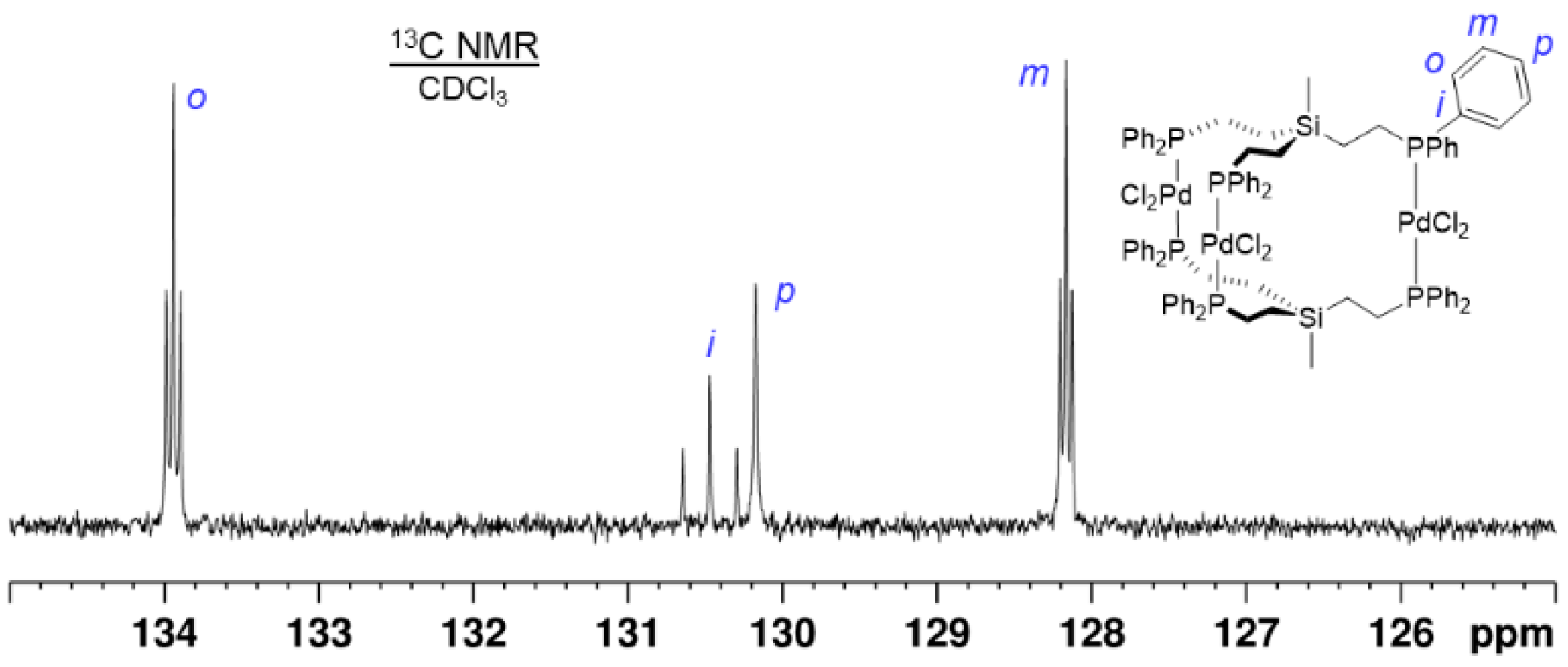
2.2. Trinuclear Palladium Complexes
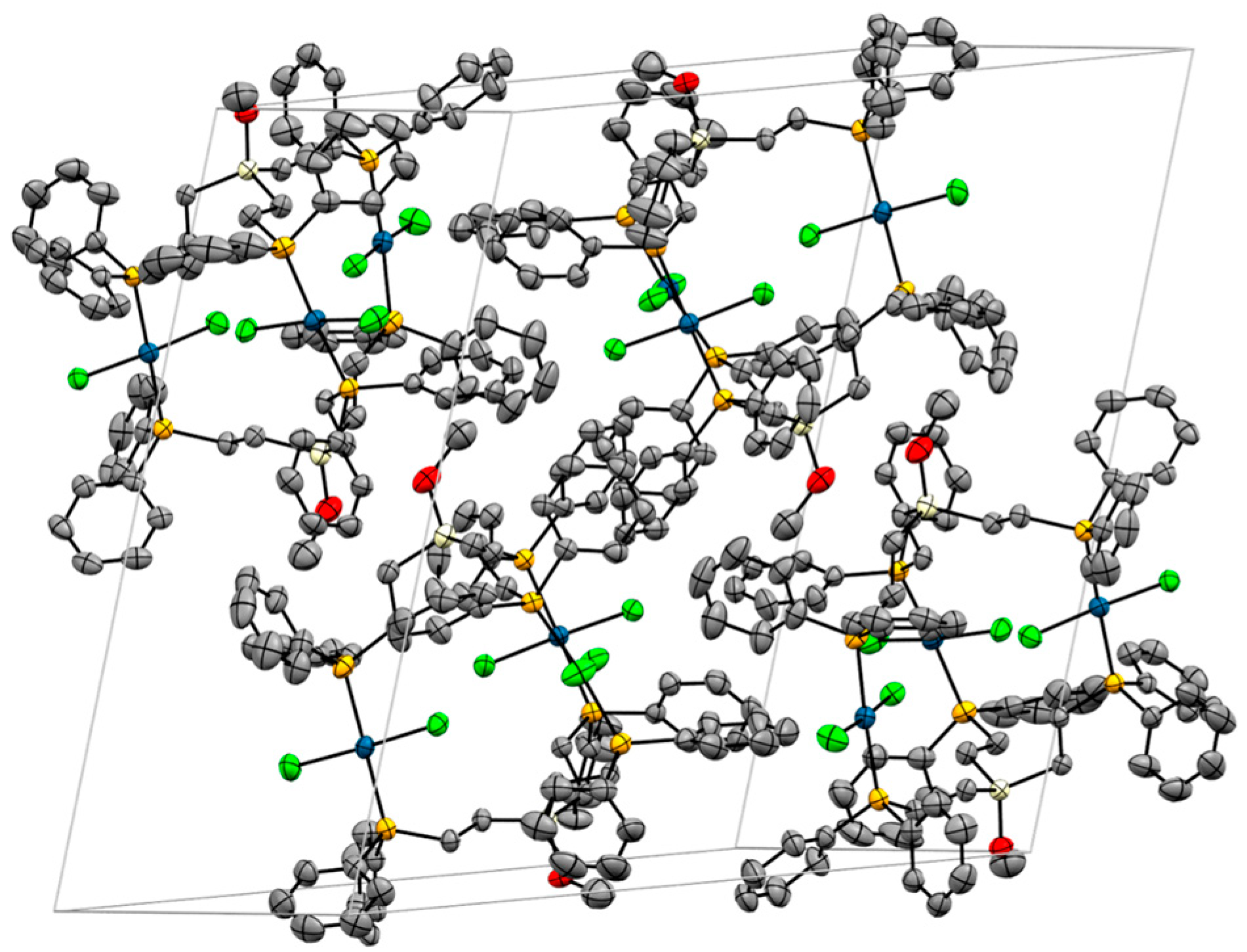
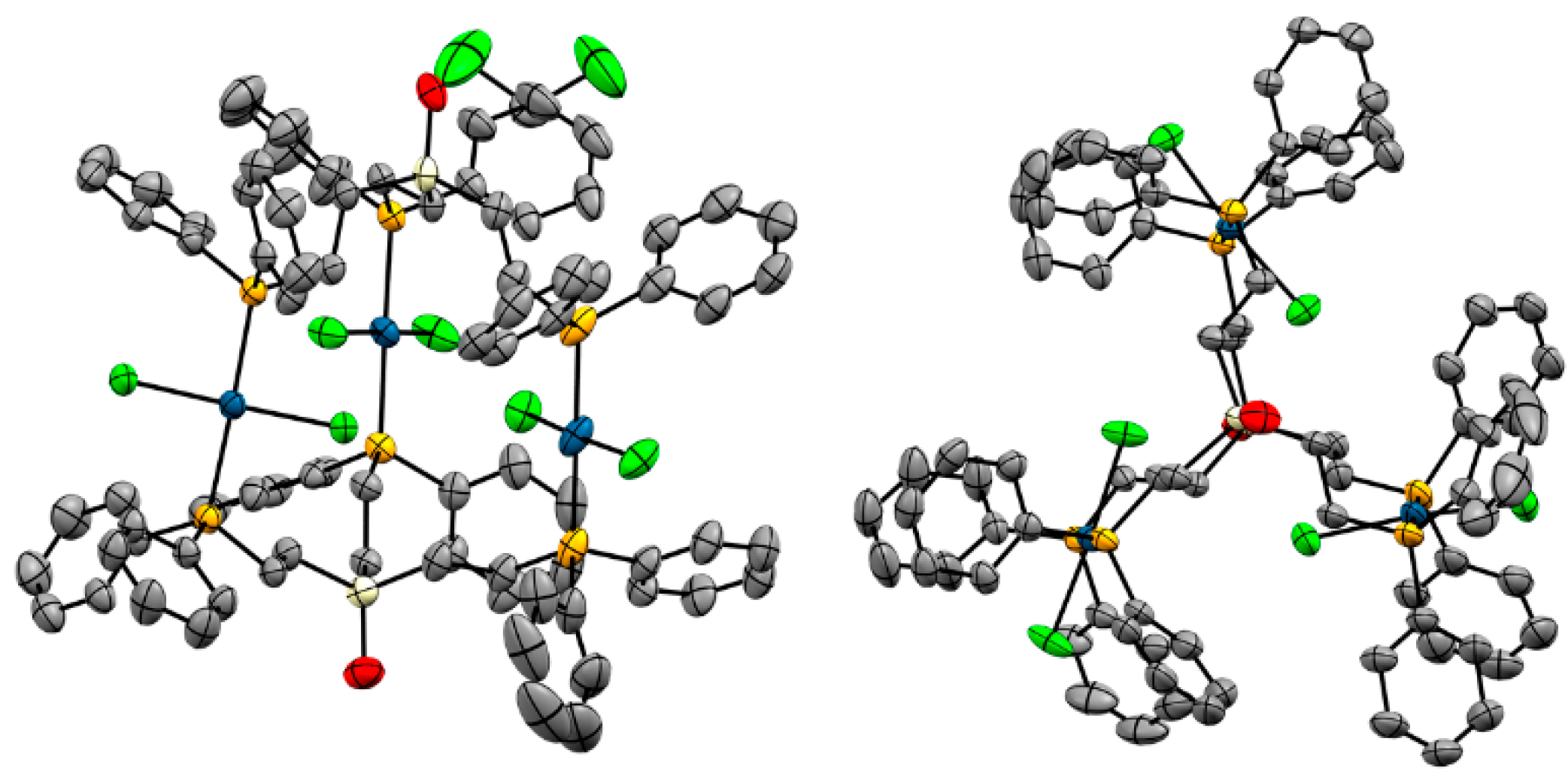
2.3. X-Ray Crystallography


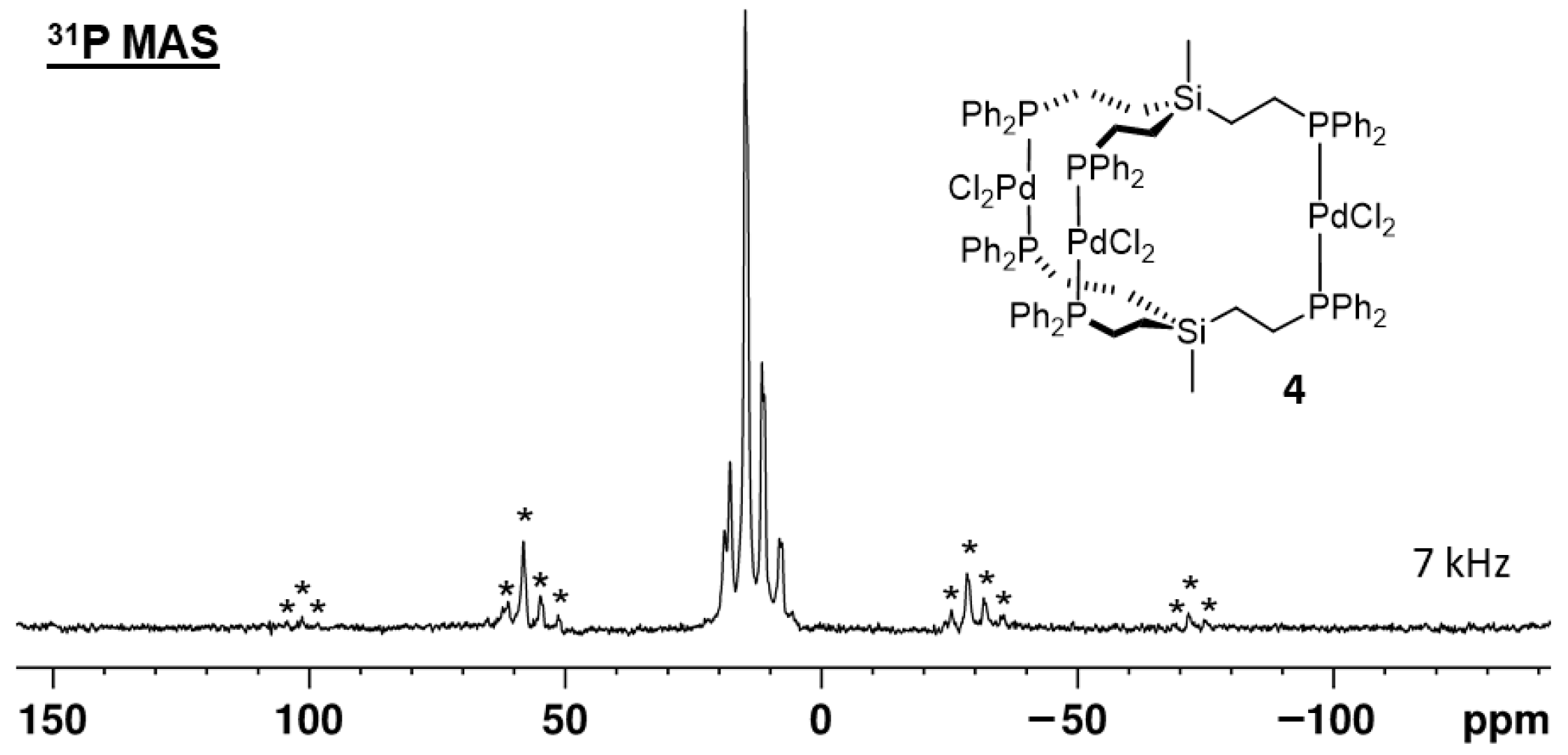

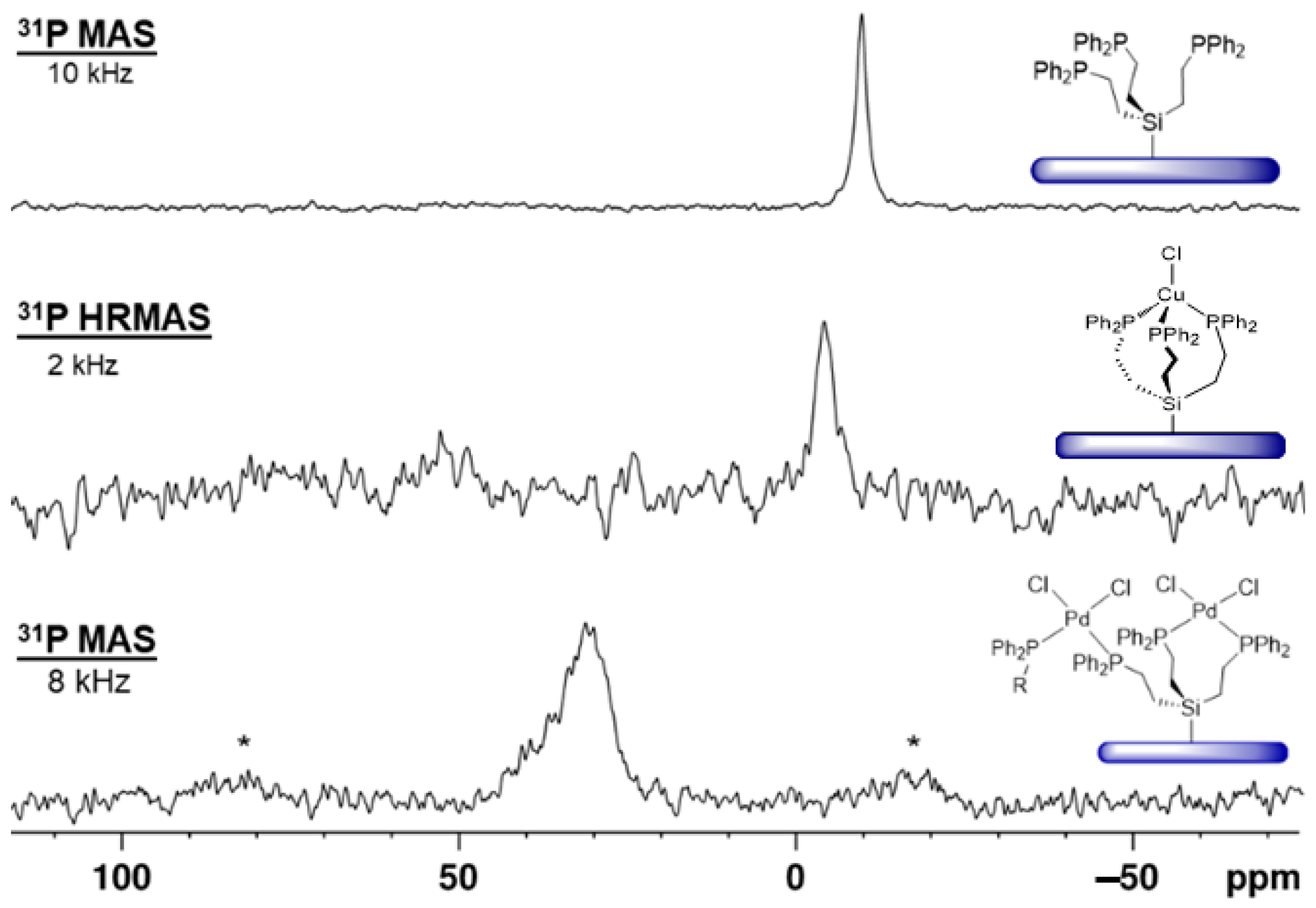
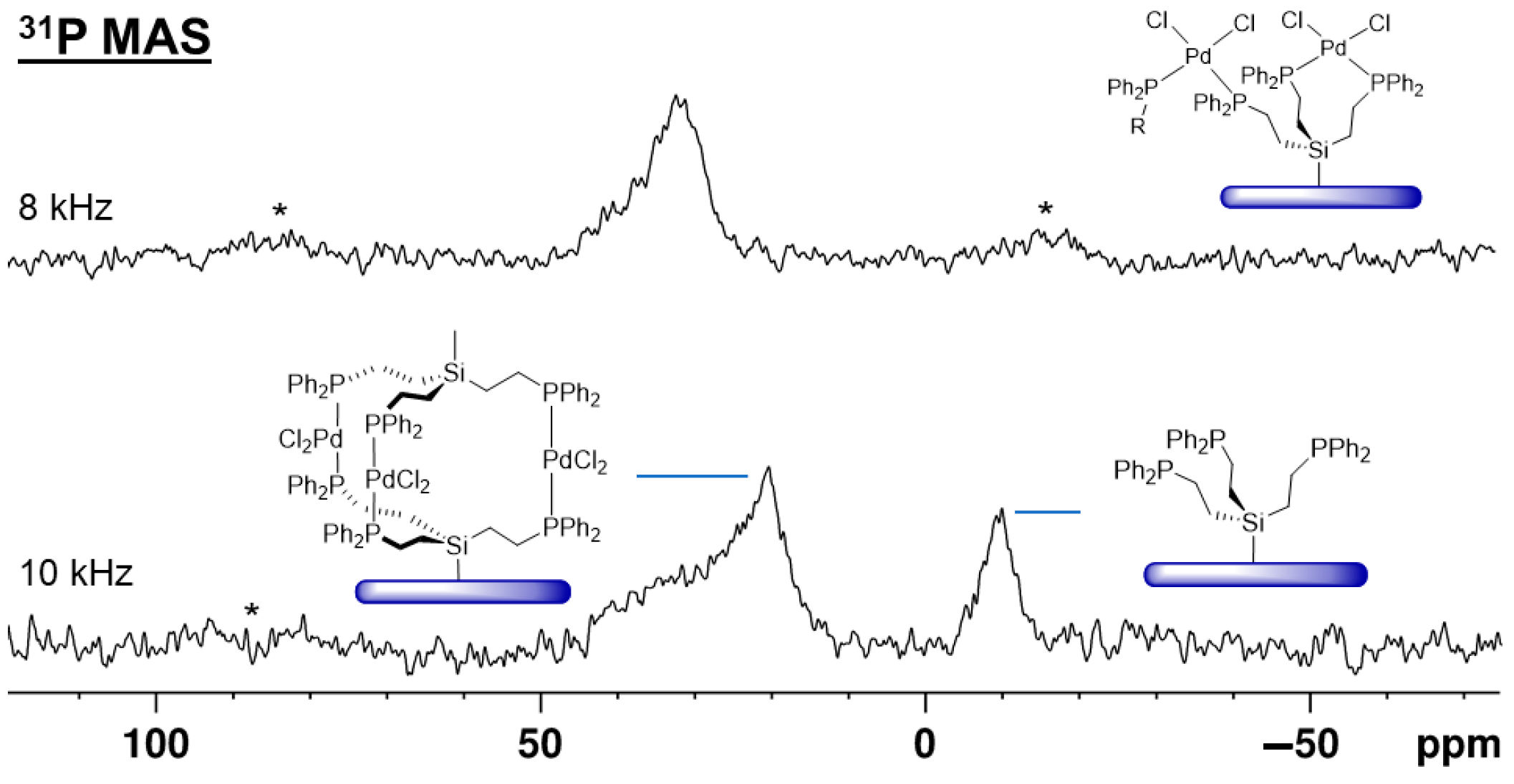
2.4. Immobilization on Silica
3. Conclusions
4. Experimental Section
4.1. General Information
4.2. NMR Spectroscopy
4.3. X-Ray Diffraction
4.4. Syntheses
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Blümel, J. Linkers and Catalysts Immobilized on Oxide Supports: New Insights by Solid-State NMR Spectroscopy. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2008, 252, 2410–2423. [Google Scholar]
- Guenther, J.; Reibenspies, J.; Blümel, J. Synthesis, Immobilization, CP- and HR-MAS NMR of a New Chelate Phosphine Linker System, and Catalysis by Rhodium Adducts thereof. Adv. Synth. Catal. 2011, 353, 443–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guenther, J.; Reibenspies, J.; Blümel, J. Synthesis and Characterization of Tridentate Phosphine Ligands Incorporating Long Methylene Chains and Ethoxysilane Groups for Immobilizing Molecular Rhodium Catalysts. Mol. Catal. 2019, 479, 110629. [Google Scholar]
- Baker, J.H.; Bhuvanesh, N.; Blümel, J. Tetraphosphines with Tetra(biphenyl)silane and -Stannane Cores as Rigid Scaffold Linkers for Immobilized Catalysts. J. Organomet. Chem. 2017, 847, 193–203. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Y.; Beele, B.; Blümel, J. Easily Immobilized Di- and Tetraphosphine Linkers: Rigid Scaffolds that Prevent Interactions of Metal Complexes with Oxide Supports. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2008, 30, 3771–3773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blümel, J. Reactions of Ethoxysilanes with Silica: A Solid-State NMR Study. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1995, 117, 2112–2113. [Google Scholar]
- Pope, J.C.; Posset, T.; Bhuvanesh, N.; Blümel, J. The Palladium Component of an Immobilized Sonogashira Catalyst System: New Insights by Multinuclear HRMAS NMR Spectroscopy. Organometallics 2014, 33, 6750–6753. [Google Scholar]
- Posset, T.; Guenther, J.; Pope, J.C.; Oeser, T.; Blümel, J. Immobilized Sonogashira Catalyst Systems: New Insights by Multinuclear HRMAS NMR Studies. Chem. Commun. 2011, 47, 2059–2061. [Google Scholar]
- Posset, T.; Blümel, J. New Mechanistic Insights Regarding Pd/Cu Catalysts for the Sonogashira Reaction: HRMAS NMR Studies of Silica-Immobilized Systems. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2006, 128, 8394–8395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cluff, K.J.; Bhuvanesh, N.; Blümel, J. Monometallic Ni(0) and Heterobimetallic Ni(0)/Au(I) Complexes of Tripodal Phosphine Ligands: Characterization in Solution and in the Solid State and Catalysis. Chem. Eur. J. 2015, 21, 10138–10148. [Google Scholar]
- Fetouaki, R.; Seifert, A.; Bogza, M.; Oeser, T.; Blümel, J. Synthesis, immobilization, and solid-state NMR of new phosphine linkers with long alkyl chains. Inorg. Chim. Acta 2006, 359, 4865–4873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bogza, M. New Dppm-, Dppp-, and Tripod-Type Linkers Containing Ethoxysilane Groups for Immobilization, and their Ni, Pd, W, and Rh Complexes. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Heidelberg, Heidelberg, Germany, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Hendriksen, D.E.; Oswald, A.A.; Ansell, G.B.; Leta, S.; Kastrup, R.V. Selective rhodium-catalyzed hydroformylation with the tri- and tetraphosphine ligands (CH3)1,0Si(CH2CH2PPh2)3,4. Formation of Rh[Si(CH2CH2PPh2)3](CO) via CH3-Si bond cleavage and structure of this Rh(I)-Si bonded complex. Organometallics 1989, 8, 1153–1157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grobe, J.; Wehmshulte, R. Alternativ-Liganden. XXX [1] Neue Tripod-Liganden XM’ (OCH2PMe2)n(CH2CH2PMe2)3-n (M’ = Si; Ge; n = 0–3) für Käfigstrukturen. Z. Anorg. Allg. Chem. 1993, 619, 563–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grobe, J.; Hildebrandt, W.; Martin, R.; Walter, A. Alternativ-Liganden. XXI. Neue Donor/Akzeptor-Liganden Me2PCH2CH2SiFnMe3-n, Me2PCH2CH2SiR(C6H4F)2 und (2-Me2PC6H4)SiXMe2. Z. Anorg. Allg. Chem. 1991, 592, 121–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joslin, F.L.; Stobart, S.R. (Phosphinoalkyl)silanes. 2. Synthesis and spectroscopic properties of the poly(phosphinoalkyl)silanes SiHR[(CH2)nPR’2]2 (R = Me or Ph; n = 2 or 3; R’ = Ph or cyclohexyl) and SiH[(CH2)nPR’2]3 (R = Me or Ph; n = 2, R’ = Ph or cyclohexyl; n = 3, R’ = Ph). Inorg. Chem. 1993, 32, 2221–2223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hersh, W.H. False AA’X Spin-Spin Coupling System in 13C NMR: Examples Involving Phosphorus and a 20-Year-Old Mystery in Off-Resonance Decoupling. J. Chem. Educ. 1997, 74, 1485–1488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hersh, W.H.; Xu, P.; Wang, B.; Yom, J.W.; Simpson, C.K. Synthesis of Tungsten Carbonyl and Nitrosyl Complexes of Monodentate and Chelating Aryl-N-sulfonylphosphoramides, the First Members of a New Class of Electron-Withdrawing Phosphine Ligands. Comparative IR and 13C and 31P NMR Study of Related Phosphorus Complexes. Inorg. Chem. 1996, 35, 5453–5459. [Google Scholar]
- Available online: www.ccdc.cam.ac.uk/data_request/cif (accessed on 1 January 2025).
- Zarcone, S.R.; Chu, G.M.; Ehnbom, A.; Cardenal, A.; Fiedler, T.; Bhuvanesh, N.; Hall, M.B.; Gladysz, J.A. Toward Frameworks with Multiple Aligned and Interactive Fe(CO)3 Rotators: Syntheses and Structures of Diiron Complexes Linked by Two trans-Diaxial α,ω-Diphosphine Ligands Ar2P(CH2)nPAr2. Inorg. Chem. 2021, 60, 3314–3330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aizawa, S.; Kawamoto, T.; Nishigaki, S.; Sasaki, A. Preparation and properties of sandwiched trinuclear palladium(II) complexes with tridentate phosphine and phosphine sulfide ligands. J. Organomet. Chem. 2011, 696, 2471–2476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cecconi, F.; Midollini, S.; Orlandini, A.; Sacconi, L. Trimeric nickel(II) complexes with bridging triphosphine ligand 1,1,1-tris(diphenylphosphinoethyl)ethane (etp3). X-ray structure of the complex [Ni3Cl6(etp3)2]·0.7CHCl3. Inorg. Chim. Acta. 1980, 42, 59–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shakeri, E.; Blümel, J. Creating Well-Defined Monolayers of Phosphine Linkers Incorporating Ethoxysilyl Groups on Silica Surfaces for Superior Immobilized Catalysts. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2023, 615, 156380–156387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merckle, C.; Blümel, J. Bifunctional Phosphines Immobilized on Inorganic Oxides. Chem. Mater. 2001, 13, 3617–3623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamahewage, S.N.S.; Dorn, R.W.; Atterberry, B.A.; Gi, E.; Kimball, M.R.; Blümel, J.; Vela, J.; Rossini, A.J. Accelerated acquisition of wideline solid-state NMR spectra of spin 3/2 nuclei by frequency-stepped indirect detection experiments. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2024, 26, 5081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoefler, J.C.; Vu, A.; Perez, A.J.; Blümel, J. Immobilized Di(hydroperoxy)propane Adducts of Phosphine Oxides as Traceless and Recyclable Oxidizing Agents. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2023, 629, 157333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behringer, K.D.; Blümel, J. Reactions of Ethoxysilanes with Silica: A Solid-State NMR Study. J. Liq. Chromatogr. Rel. Technol. 1996, 19, 2753–2765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guenther, J. Tridentate Phosphine Linkers for Immobilized Catalysts: Development and Characterization of Immobilized Rhodium Complexes and Solid-State NMR Studies of Polymers. Ph.D. Thesis, Texas A&M University, College Station, TX, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Bruker. APEX3; Bruker AXS Inc.: Madison, WI, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Bruker. SADABS; Bruker AXS Inc.: Madison, WI, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Sheldrick, G.M. A short history of SHELX. Acta Crystallogr. Sect. A 2008, A64, 112–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheldrick, G.M. SHELXT—Integrated space-group and crystal-structure determination. Acta Crystallogr. Sect. A Found. Adv. 2015, 71, 3–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheldrick, G.M. Crystal structure refinement with SHELXL. Acta Crystallogr. Sect. C Struct. Chem. 2015, 71, 3–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spek, A.L. Structure validation in chemical crystallography. Acta Crystallogr. Sect. D Struct. Biol. 2009, 65, 148–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dolomanov, O.V.; Bourhis, L.J.; Gildea, R.J.; Howard, J.A.K.; Puschmann, H. OLEX2: A complete structure solution, refinement and analysis program. J. Appl. Cryst. 2009, 42, 339–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, R.; Macrae, C.F. Rules governing the crystal packing of mono- and dialcohols. Acta Cryst. 2001, B57, 815–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| Complex | L–M–L (°) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| 4 | 165.68 (3) | 175.79 (3) | 176.09 (3) |
| 5a | 174.22 (3) | 174.71 (3) | 178.24 (3) |
| 5b | 165.45 (3) | 176.33 (3) | 176.45 (3) |
| 7 | 177.22 (4) | 179.02 (4) | 179.31 (5) |
| Pd3I6(pOp3)2 [21] | 175.8 (2) | 176.4 (2) | 178.2 (2) |
| Pd3Cl6(pOp3S3)2 [21] | 168.1 (1) | 168.1 (1) | 168.1 (1) |
| Ni3Cl6(etp)2 [22] | 167.62 | 171.80 | 176.54 |
| Complex | X–M–X | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| 4 | 178.76 (3) | 173.04 (4) | 171.76 (4) |
| 5a | 168.83 (5) | 176.18 (4) | 176.89 (4) |
| 5b | 179.23 (3) | 174.14 (3) | 172.24 (3) |
| 7 | 174.09 (5) | 176.63 (5) | 174.20 (5) |
| Pd3I6(pOp3)2 [21] | 160.26 (7) | 172.6 (2)/158.5 (2) | 169.38 (7) |
| Pd3Cl6(pOp3S3)2 [21] | 179.5 (1) | 179.5 (1) | 179.5 (1) |
| Ni3Cl6(etp)2 [22] | 161.97 | 166.85 | 166.31 |
| Complex | Dihedral Angles L–Center–Center–L (°) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| 4 | 2.11 (2) | 2.93 (3) | 8.14 (3) |
| 5a | 4.41 (3) | 8.95 (3) | 12.68 (3) |
| 5b | 2.91 (3) | 1.90 (2) | 7.40 (3) |
| 7 | 5.43 (3) | 6.27 (3) | 11.72 (3) |
| Pd3I6(pOp3)2 [21] | 2.0 (1) | 0.6 (1) | 0.8 (1) |
| Pd3Cl6(pOp3S3)2 [21] | 50.68 | 50.68 | 50.68 |
| Ni3Cl6(etp)2 [22] | 0.37 | 0.10 | 2.35 |
| Complex | Center–Center | M–M | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 4 | 7.364 (1) | 7.4963 (8) | 6.8894 (8) | 7.5769 (7) |
| 5a | 8.363 (1) | 7.0903 (6) | 7.2621 (7) | 7.1109 (6) |
| 5b | 7.453 (1) | 7.4188 (5) | 7.8960 (6) | 7.4932 (5) |
| 7 | 8.530 (2) | 7.1131 (8) | 6.8095 (7) | 7.1727 (7) |
| Pd3I6(pOp3)2 [21] | 6.882 (9) | 7.73 (1) | 7.35 (1) | 7.325 (8) |
| Pd3Cl6(pOp3S3)2 [21] | 4.85 (9) | 7.616 (8) | 7.62 (1) | 7.616 (7) |
| Ni3Cl6(etp)2 [22] | 6.051 | 7.783 | 6.893 | 7.27 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kimball, M.R.; Cluff, K.J.; Bhuvanesh, N.; Blümel, J. Molecular and Immobilized Tripodal Phosphine Ligands and Their Trinuclear Palladium Complexes. Molecules 2025, 30, 1616. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30071616
Kimball MR, Cluff KJ, Bhuvanesh N, Blümel J. Molecular and Immobilized Tripodal Phosphine Ligands and Their Trinuclear Palladium Complexes. Molecules. 2025; 30(7):1616. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30071616
Chicago/Turabian StyleKimball, Maxwell R., Kyle J. Cluff, Nattamai Bhuvanesh, and Janet Blümel. 2025. "Molecular and Immobilized Tripodal Phosphine Ligands and Their Trinuclear Palladium Complexes" Molecules 30, no. 7: 1616. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30071616
APA StyleKimball, M. R., Cluff, K. J., Bhuvanesh, N., & Blümel, J. (2025). Molecular and Immobilized Tripodal Phosphine Ligands and Their Trinuclear Palladium Complexes. Molecules, 30(7), 1616. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30071616






