Abstract
Two new decalin-tetramic acid hybrid metabolites, zopfiellamides C (1) and D (2) were isolated from the marine-derived fungus Aspergillus sp. NF666. The structure determination was accomplished on the basis of HRESIMS and NMR spectral data analyses including COSY, HSQC, HMBC, and NOESY experiments. Both isolated metabolites (1 and 2) exhibited significant growth inhibition against four clinically relevant bacterial strains with minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) values of about 12.5 μΜ. Moreover, we proposed a plausible biosynthetic pathway of zopfiellamide D (2) in this work.
1. Introduction
Natural products derived from the secondary metabolism of microorganisms (bacteria and fungi) represent a large family of chemical molecules, and their structural diversity and attractive biological activities make them interesting as a source for the identification of novel antibiotics and other drug leads [1,2,3]. Marine-derived fungi have been considered as an abundant and important microbial resource for producing novel natural products [4,5]. As an essential part of marine microorganisms, Aspergillus is a diverse genus of filamentous fungi with approximately 446 known species. Species of this genus are known to be a rich source of secondary metabolites, including polyketides, alkaloids, terpenoids, peptides, sterols, fatty acids, and other compounds, displaying a variety of pharmacological activities such as antimicrobial, cytotoxic, anti-inflammatory, and antioxidant activities [6,7,8]. A typical example is lovastatin, produced by Aspergillus terreus, which is a well-known cholesterol-lowering drug on the market [9]. Even after much attention and investigations spanning over two decades, this genus still holds great potential to provide metabolites with new structures and remarkable biological activities.
Natural products that contain the decalin-tetramic acid motif have been studied extensively, and many of them possess excellent biological activities, for example, the HIV-1 integrase inhibitors equisetin and phomasetin [10,11,12]. Partial decalin-tetramic acid derivatives featuring an unnatural 4,4-disubstituted glutamic acid unit, such as Sch 210971 [13,14], Sch 210972 [15], and JBIR-22 [16,17], usually act as protein–protein interaction inhibitors that are of relevance to proteasome assembly. The complex chemical structures and stereochemistry of decalin-type tetramic acid compounds have prompted extensive synthetic and biosynthetic studies. Marine-derived Aspergillus sp. NF666, which was isolated from marine mud in the South China Sea, was found to produce novel azaspirenes A–E and siderophores in our previous study [18]. In our ongoing investigations, two new peaks with characteristic UV absorption bands around 280 nm were detected by HPLC analysis of the EtOAc extract. Subsequent chemical investigation led to the identification of two novel antibacterial decalin-type tetramic acid metabolites, zopfiellamides C (1) and D (2) (Figure 1). Details of the isolation, structural elucidation, antibacterial activity, and proposed biosynthetic pathway of zopfiellamides C (1) and D (2) are reported herein.
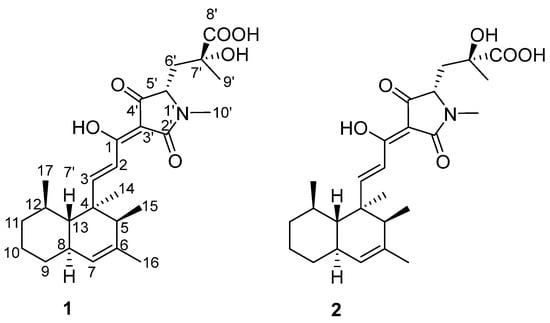
Figure 1.
Structures of the isolated compounds 1 and 2.
2. Results
2.1. Structural Elucidation of the Compounds
Compound 1 was isolated as a colorless, amorphous powder, and the molecular formula was determined to be C26H37NO6 on the basis of the HRESIMS ion peak at m/z [M + H]+ 460.2708 (calcd. for C26H38NO6, 460.2699), indicating nine degrees of unsaturation. The direct connectivity between each proton and carbon was established by the HSQC spectrum; the 13C and 1H NMR data for 1 are shown in Table 1. The NMR spectral data of 1 revealed characteristic signals of four methylenes [δH 1.17 (1H, m, H-9), 1.79 (1H, m, H-9), 1.73 (2H, m, H-10), 1.22 (1H, m, H-11), 1.68 (1H, m, H-11), 2.02 (1H, m, H-6′), and 2.39 (1H, dd, J = 2.3, 14.7 Hz, H-6′); δC 34.8 (C-9), 27.6 (C-10), 39.0 (C-11), and 39.2 (C-6′)], six methyls [δH 1.18 (3H, s, H-14), 1.01 (3H, d, J = 7.0 Hz, H-15), 1.67 (3H, s, H-16), 0.82 (3H, d, J = 5.7 Hz, H-17), 1.47 (3H, s, H-9′), and 2.98 (3H, s, H-10′); δC 17.9 (C-14), 16.8 (C-15), 22.3 (C-16), 23.1 (C-17), 27.2 (C-9′), and 27.1 (C-10′)], five methines [δH 1.56 (1H, q, J = 6.8 Hz, H-5), 1.83 (1H, m, H-8), 1.44 (1H, m, H-12), 1.44 (1H, m, H-13), and 3.93 (1H, d, J = 6.7 Hz, H-5′); δC 50.9 (C-5), 41.4 (C-8), 36.5 (C-12), 49.3 (C-13), and 65.0 (C-5′)], as well as two trans olefinic methine protons [δH 7.11 (d, J = 16.1 Hz, H-2), 7.62 (1H, d, J = 16.1 Hz, H-3); δC 115.7 (C-2), and 164.9 (C-3)] and a single olefinic methine proton [δH 5.13 (1H, s, H-7); δC 126.0 (C-7)].

Table 1.
The 1H NMR (400 MHz) and 13C NMR (100 MHz) data of 1 and 2 in acetone-d6 (J in Hz).
The continuous correlations in 1H-1H couplings revealed the presence of the 4, 5, 6, 12-tetramethyldecalin moiety. In the HMBC spectrum of 1, the correlations from olefinic methine protons H-3 (δH 7.62) to C-4 (δC 43.6) and H-2 (δH 7.11) to C-1 (δC 174.8) suggested that the α, β-unsaturated carbonyl moiety was substituted on the decalin moiety. An N-methyl proton H-10′ (δH 2.98) displayed HMBC correlations to an amide carbonyl carbon C-2′ (δC 174.2) and a methine carbon C-5′ (δC 65.0), which was 1H-1H spin-coupled to methylene protons H-6′ (δH 2.02, 2.39). The methyl protons H-9′ (δH 1.47) as well as methylene protons H-6′ respectively had HMBC correlations to a quaternary carbon C-7′ (δC 74.0) and a carboxylic carbonyl carbon C-8′ (δC 177.3), showing that the carboxylic acid residue was located at C-7′. The HMBC correlations from H-5′ and H-6′ to C-4′ (δC 197.4) revealed that C-4′ was connected to C-5′. By taking into consideration a remaining quaternary olefinic carbon C-3′ (δC 100.1) together with the typical 13C NMR chemical shifts of C-4′ and the α, β-unsaturated carbonyl carbon C-1, the unit from N-1′ to C-5′ forms a pyrrolidinone moiety (Figure 2). According to the molecular formula of 1, we established the planar structure of 1 as shown in Figure 1. Compound 1 has a very similar structure to the other pyrrolidinone derivatives zopfiellamides A and B [19], so this compound was named as zopfiellamide C.
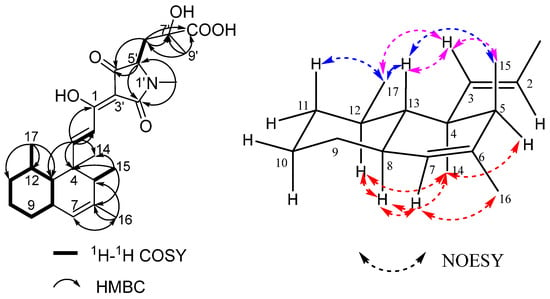
Figure 2.
The key 1H-1H COSY, HMBC (left), and NOESY (H→H, (right)) correlations of compound 1.
The relative configuration of the decalin part was found to be the same as that of zopfiellamide A as deduced from the NOESY spectra. The NOESY correlations observed between H-8 (δH 1.83, m)/H-12 (δH 1.44, m), H-8/H-7 (δH 5.13, s), H-8/Me-14 (δH 1.18, s), H-7/Me-16 (δH 1.67, s), H-5 (δH 1.56, q)/Me-14, and Me-14/H-12 revealed that these protons were directed toward the same face (α); while H-13 (δH 1.44, m) correlated with Me-15 (δH 1.01, d) and Me-17 (δH 0.82, d), Me-17 correlated with H-11ax (δH 1.22, m), and thus they were β-oriented. In addition, the strong NOESY correlations from trans olefinic H-3 (δH 7.62, d) to H-13, Me-17, and Me-15 showed that they are close to each other in spatial position (Figure 2).
The molecular formula of compound 2 was determined to be C26H37NO6 according to the [M + H]+ ion at m/z 460.2699 (calcd. for C26H38NO6, 460.2699) in its HRESIMS, which had the same molecular formula as 1. The similar 1H and 13C NMR spectra provided further supportive evidence for the structure of 2, and the only noticeable differences were found in the side chain of the tetramic acid part. The significant differences of chemical shifts at C-7′, C-9′, and C-10′ (+0.8 ppm) in comparison to 1 indicated a change of the side chain attached to the tetramic acid ring in 2. Scrutiny of the NOESY data for the tetramic acid part revealed that H-5′ has stronger NOESY correlation with Me-10′ than Me-9′ in both compounds, indicating that the relative configurations of C-5′ are both S. In addition, one H-6′ [2.48 (dd, J = 6.0, 15.0 Hz)] was shifted downfield (+0.46 ppm), with the other [δH 2.25 (dd, J = 2.9, 15.0 Hz)] shifting upfield (−0.14 ppm). Meanwhile, H-5′ (δH 3.86) was also shifted upfield (−0.07 ppm) in 2 (Figure 3A). The observation of a large chemical shift difference at H-6′ and H-5′ due to the steric effects of hydroxyl and carboxylic acid strongly suggested the opposite stereochemistry arrangements of hydroxyl and carboxylic acid groups at C-7′ in 2. Combined with chemical simulation (Figure 3B), only when the configuration of C-7′ changes from R to S will the above changes in chemical shift occur. The discrepancy in NMR spectra could only be explained by a different configuration at C-7′, so they should be 7′-epimers of each other. Hence, compound 1 was determined to have 5′S, 7′R stereochemistry, while compound 2 has 5′S, 7′S stereochemistry, as shown in Figure 1.
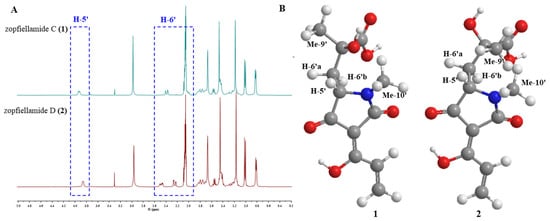
Figure 3.
(A) The chemical shift discrepancy of CH-5′ and CH2-6′ in 1H NMR spectrum in zopfiellamides C (1) and D (2); (B) the chemical simulation of tetramic acid moiety in zopfiellamides C (1) and D (2) with Chem 3D.
2.2. Antibacterial Activities
The isolated metabolites were evaluated for their antibacterial activities. Compounds 1 and 2 exhibit good antibacterial activities against a panel of bacterial pathogens including Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Staphylococcus aureus, Escherichia coli, and Pectobacterium carotovorum subsp. Carotovorum with MIC values of about 12.5 μΜ (Table 2). It seems that the configuration at C-5′ has strong correlation with the antibacterial activities, as the epimer of 1 (i.e., 2) was less active than 1.

Table 2.
Antibacterial activities of zopfiellamides C (1) and D (2) against a panel of bacterial pathogens.
2.3. Proposed Biosynthesis Pathway
At last, we proposed the biosynthetic pathway of zopfiellamide D (2). As proposed, the core decalin-tetramic acid structure is synthesized by dual-modular polyketide synthase–nonribosomal peptide synthetase (PKS-NRPS) proteins [20]. In this large hybrid enzyme, the PKS utilizes malonyl-CoA and S-adenosyl-L-methionine (SAM) to synthesize the linear polyketide intermediate (5) with the assistance of stand-alone enoyl reductase (ER), which could specifically reduce a nascent polyketide backbone double bond [21]. Then, the NRPS adds an unusual amino acid, γ-hydroxymethyl-L-glutamic acid (6), which is derived from two molecules of pyruvic acid (8) to form intermediate 7; different configurations of 7 may be formed by an aldolase. Then, a Diels–Alderase would bind to and lock the straight-chain polyketide intermediate 4 in a specific conformation to promote the [4+2] cycloaddition reaction and control the stereoselectivity of the reaction [22,23]. The terminal reductase domain (R) is proposed to catalyze the tetramate moiety-forming via Dieckmann-type condensation and release the product [24]. Finally, N-methylation could yield zopfiellamides C (1) and D (2) (Figure 4).
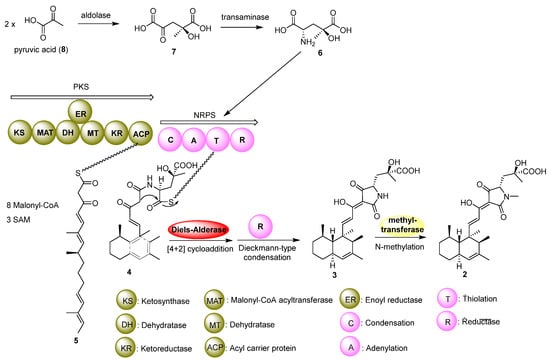
Figure 4.
Proposed biosynthetic pathway of zopfiellamide D (2).
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. General Experiment Procedure
All analytical and semi-preparative HPLC processes were carried out on an Agilent 1220 HPLC system with a DAD detector equipped with a Poroshell 120 EC-C18 column (Agilent Technologies, Waldbronn, Germany) and a Zorbax Eclipse XDB column (C-18, 9.4 × 250 mm, 5 μm, Agilent Technologies, Waldbronn, Germany), respectively. NMR spectra were obtained on a Bruker Avance III 400 spectrometer at 400 MHz for 1H and 100 MHz for 13C nuclei (Bruker, Zurich, Switzerland). HRESIMS data were measured on an Agilent 6530 TOF LC-MS spectrometer with a Porshell 120 EC-C18 column (4.5 × 50 mm, 2.7 μm, Agilent Technologies, Waldbronn, Germany). Column chromatography (CC) was performed using silica gel, 200–300 mesh (Qingdao Marine Chemical Company, Qingdao, China), and Sephadex LH-20 (YMC. CO., LTD, Kyoto, Japan). Precoated silica gel GF-254 plates (Qingdao Marine Chemical Company, Qingdao, China) were used for analytical TLC. NMR solvents were purchased from Sigma-Aldrich (Merck, Shanghai, China).
3.2. Fungal Material
The strain NF666 was isolated from seaweed collected in August 2020 from the South China Sea, Hainan Province, China. The identification of the NF666 stain was achieved by analyzing the 18S rDNA sequences that showed a great similarity to those accessible via the BLAST+2.16.0 of Aspergillus. The live culture of the NF666 strain was kept at the School of Medicine, Nanjing University of Chinese Medicine (China).
3.3. Fermentation, Extraction and Isolation
The fungus was cultured in potato dextrose broth (PDB) at 25 °C on a rotary shaker (220 rpm) for 3 days to obtain the seed culture. Large-scale fermentation proceeded in rice medium (80 g rice and 120 mL distilled water) at room temperature for 20 days after inoculation with 10 mL seed culture. The culture medium including the mycelium was extracted three times with EtOAc. After removal of the organic solvent, the crude extract (20 g) was subjected to silica gel CC using gradient elution with a mixture of CH2Cl2/MeOH (100:0, 100:1, 100:2, 100:4, 100:8, 100:16, 0:100, v/v) to yield seven fractions (Fr.1–Fr.7), respectively. Fr.3 was subjected to further CC (SiO2; petroleum ether (PE)/AcOEt (10:1, 8:1, 5:1, 3:1, 1:1, 0:1, (v/v)) to yield subfractions Fr.5.1-5.6. Fraction 5.2 was fractionated by Sephadex LH-20 with CH2Cl2-MeOH (1:1) and further purified by semi-preparative HPLC to yield 1 (76% MeOH-H2O, 2.5 mL/min, 5.5mg, tR = 18.0 min) and 2 (76% MeOH-H2O, 2.5 mL/min, 3.0 mg, tR = 22.0 min).
3.4. Antibacterial Assay
Minimum inhibitory concentrations (MIC) were determined for the antibacterial activity against a series of pathogens including Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Escherichia coli, Staphylococcus aureus, Bacillus subtilis, and Pectobacterium carotovorum subsp. Carotovorum. The compounds were prepared in a 10 mM solution and successively diluted in a gradient to obtain 5 mM, 2.5 mM, and 1.25 mM solutions. All tested bacteria were activated and cultured in LB broth at 37 °C for 12 h. The assays were performed in 96-well plates, wherein a 198 µL suspension (log phase) of bacteria was supplied with 2 µL of diluted compounds. DMSO and apramycin were used as the negative and positive controls, respectively. The MIC was defined as the lowest concentration of a compound that inhibited visible bacterial growth [25].
4. Conclusions
Two new decalin-tetramic acid hybrid metabolites, zopfiellamides C (1) and D (2) were isolated from the marine-derived fungus Aspergillus sp. NF666. Their structures were unambiguously determined by an extensive analysis of HRESIMS and NMR data. Compounds 1 and 2 exhibited potent antibacterial activity against four pathogens, with MIC values of about 12.5 μΜ. Moreover, we proposed a plausible biosynthetic pathway for zopfiellamide D (2).
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/molecules30071502/s1: Figures S1–S8: HRESIMS, 1H NMR, 13C NMR, DEPT, COSY, HSQC, HMBC, and NOESY spectra for compound 1; Figures S9–S16: HRESIMS, 1H NMR, 13C NMR, DEPT, COSY, HSQC, HMBC, and NOESY spectra for compound 2.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, F.J. and W.L.; methodology and investigation, F.J. and T.L.; data curation, F.J. and K.W.; data analysis, F.J., T.L. and S.L.; writing—original draft preparation, F.J. and T.L.; writing—review and editing F.J. and R.J.; supervision, W.L.; project administration and funding acquisition, F.J. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 82404481), Key project at central government level: The ability establishment of sustainable use for valuable Chinese medicine resources (No. 2060302-2302-02), the Natural Science Foundation of the Jiangsu Higher Education Institutions of China (No. 24KJB350006), and the Postgraduate Research & Practice Innovation Program of Jiangsu Province.
Data Availability Statement
Data are contained within the article and Supplementary Materials.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Genilloud, O. Natural products discovery and potential for new antibiotics. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 2019, 51, 81–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hutchings, M.I.; Truman, A.W.; Wilkinson, B. Antibiotics: Past, present and future. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 2019, 51, 72–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Newman, D.J.; Cragg, G.M. Natural Products as Sources of New Drugs over the Nearly Four Decades from 01/1981 to 09/2019. J. Nat. Prod. 2020, 83, 770–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, W.; Wu, W.; Liu, X.; Zaleta-Pinet, D.A.; Clark, B.R. Bioactive Compounds Isolated from Marine-Derived Microbes in China: 2009–2018. Mar. Drugs 2019, 17, 339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Sá, J.D.M.; Kumla, D.; Dethoup, T.; Kijjoa, A. Bioactive Compounds from Terrestrial and Marine-Derived Fungi of the Genus Neosartorya. Molecules 2022, 27, 2351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orfali, R.; Aboseada, M.A.; Abdel-Wahab, N.M.; Hassan, H.M.; Perveen, S.; Ameen, F.; Alturki, E.; Abdelmohsen, U.R. Recent updates on the bioactive compounds of the marine-derived genus Aspergillus. RSC Adv. 2021, 11, 17116–17150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ha, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Ma, M.; Wang, N.; Wang, P.; Zhang, Z. Antimicrobial metabolites from the marine-derived fungus Aspergillus sp. ZZ1861. Phytochemistry 2024, 224, 114164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.; Wang, H.; Yan, M.; Sai, C.; Zhang, Z. Research Advances of Bioactive Sesquiterpenoids Isolated from Marine-Derived Aspergillus sp. Molecules 2022, 27, 7376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butler, M.S. The role of natural product chemistry in drug discovery. J. Nat. Prod. 2004, 67, 2141–2153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mo, X.; Li, Q.; Ju, J. Naturally occurring tetramic acid products: Isolation, structure elucidation and biological activity. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 50566–50593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Kusari, S.; Spiteller, M. Natural products containing ’decalin’ motif in microorganisms. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2014, 31, 1175–1201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, S.B.; Zink, D.L.; Goetz, M.A.; Dombrowski, A.W.; Polishook, J.D.; Hazuda, D.J. Equisetin and a Novel Opposite Stereochemical Homolog Phomasetin, Two Fungal Metabolites as Inhibitors of HIV-1 Integrase. Tetrahedron Lett. 1998, 39, 2243–2246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.W.; Mierzwa, R.; Terracciano, J.; Patel, M.; Gullo, V.; Wagner, N.; Baroudy, B.; Puar, M.; Chan, T.M.; McPhail, A.T.; et al. Chemokine receptor CCR-5 inhibitors produced by Chaetomium globosum. J. Nat. Prod. 2006, 69, 1025–1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, S.; Kaushik, N.; Proksch, P. Identification of antifungal principle in the solvent extract of an endophytic fungus Chaetomium globosum from Withania somnifera. Springerplus 2013, 2, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kakule, T.B.; Zhang, S.; Zhan, J.; Schmidt, E.W. Biosynthesis of the tetramic acids Sch210971 and Sch210972. Org. Lett. 2015, 17, 2295–2297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Izumikawa, M.; Hashimoto, J.; Hirokawa, T.; Sugimoto, S.; Kato, T.; Takagi, M.; Shin-Ya, K. JBIR-22, an inhibitor for protein-protein interaction of the homodimer of proteasome assembly factor 3. J. Nat. Prod. 2010, 73, 628–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Healy, A.R.; Izumikawa, M.; Slawin, A.M.; Shin-Ya, K.; Westwood, N.J. Stereochemical assignment of the protein-protein interaction inhibitor JBIR-22 by total synthesis. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 2015, 54, 4046–4050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, F.W.; Xing, Y.N.; Liu, T.Y.; Wu, F.; Li, W.; Jiao, R.H. New azaspirene derivatives from marine-derived fungus Aspergillus micronesiensis NF666. Tetrahedron Lett. 2023, 123, 154566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daferner, M.; Anke, T.; Sterner, O. Zopfiellamides A and B, antimicrobial pyrrolidinone derivatives from the marine fungus Zopfiella latipes. Tetrahedron 2002, 58, 7781–7784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boettger, D.; Hertweck, C. Molecular diversity sculpted by fungal PKS-NRPS hybrids. Chembiochem 2013, 14, 28–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hertweck, C. The biosynthetic logic of polyketide diversity. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 2009, 48, 4688–4716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sato, M.; Yagishita, F.; Mino, T.; Uchiyama, N.; Patel, A.; Chooi, Y.H.; Goda, Y.; Xu, W.; Noguchi, H.; Yamamoto, T.; et al. Involvement of Lipocalin-Like CghA in Decalin-Forming Stereoselective Intramolecular [4+2] Cycloaddition. Chembiochem 2015, 16, 2294–2298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fujiyama, K.; Kato, N.; Re, S.; Kinugasa, K.; Watanabe, K.; Takita, R.; Nogawa, T.; Hino, T.; Osada, H.; Sugita, Y.; et al. Molecular Basis for Two Stereoselective Diels-Alderases that Produce Decalin Skeletons. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 2021, 60, 22401–22410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kishimoto, S.; Tsunematsu, Y.; Sato, M.; Watanabe, K. Elucidation of Biosynthetic Pathways of Natural Products. Chem. Rec. 2017, 17, 1095–1108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maglangit, F.; Fang, Q.; Leman, V.; Soldatou, S.; Ebel, R.; Kyeremeh, K.; Deng, H. Accramycin A, a New Aromatic Polyketide, from the Soil Bacterium, Streptomyces sp. MA37. Molecules 2019, 24, 3384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).