Recent Advances in Stimuli-Responsive Microgels and Their Biomedical Applications
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Design Strategies of Stimuli-Responsive Microgels
2.1. Functional Monomer
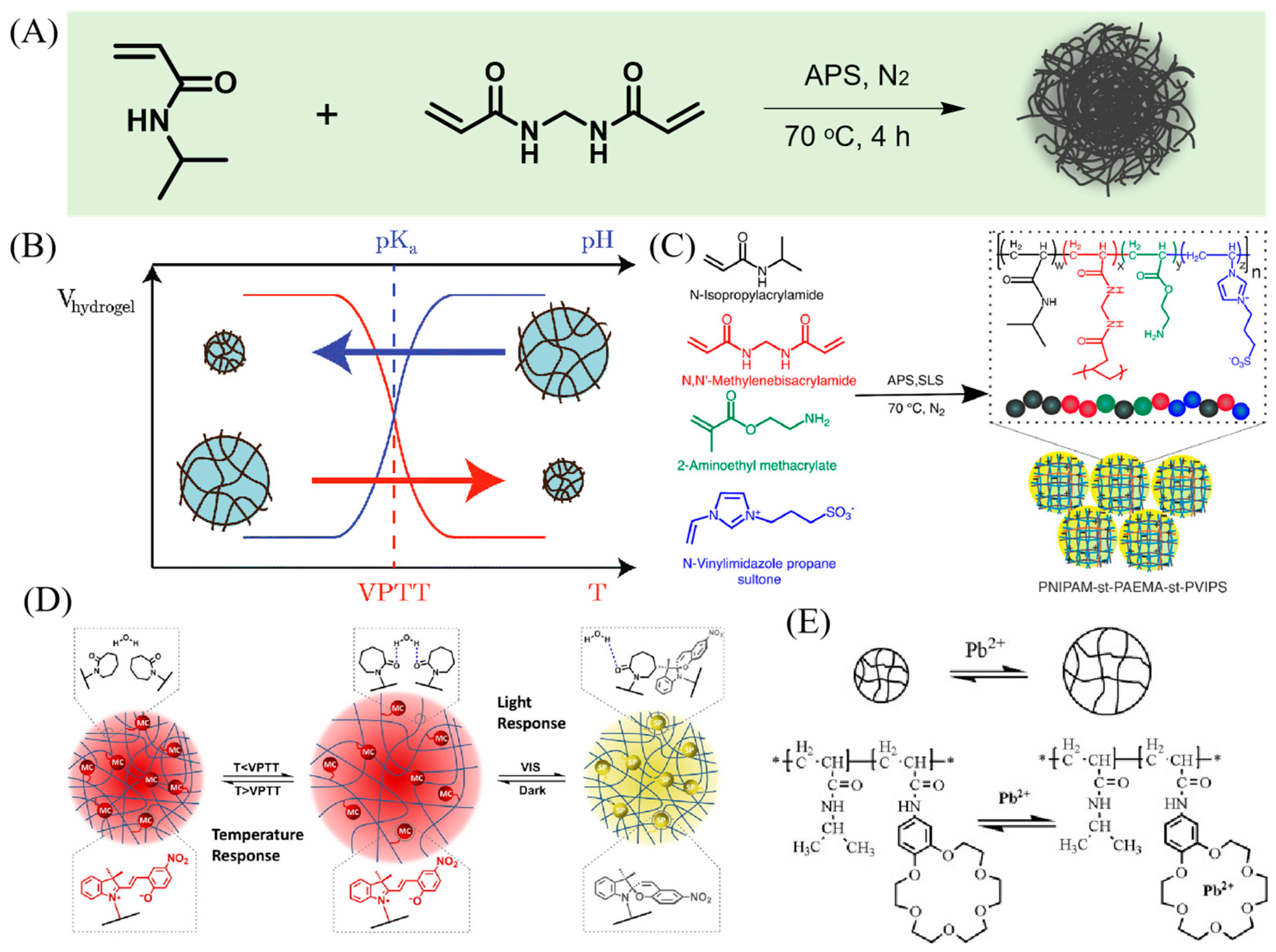
2.2. Cross-Linker Chemistry
2.2.1. Chemical Cross-Linking
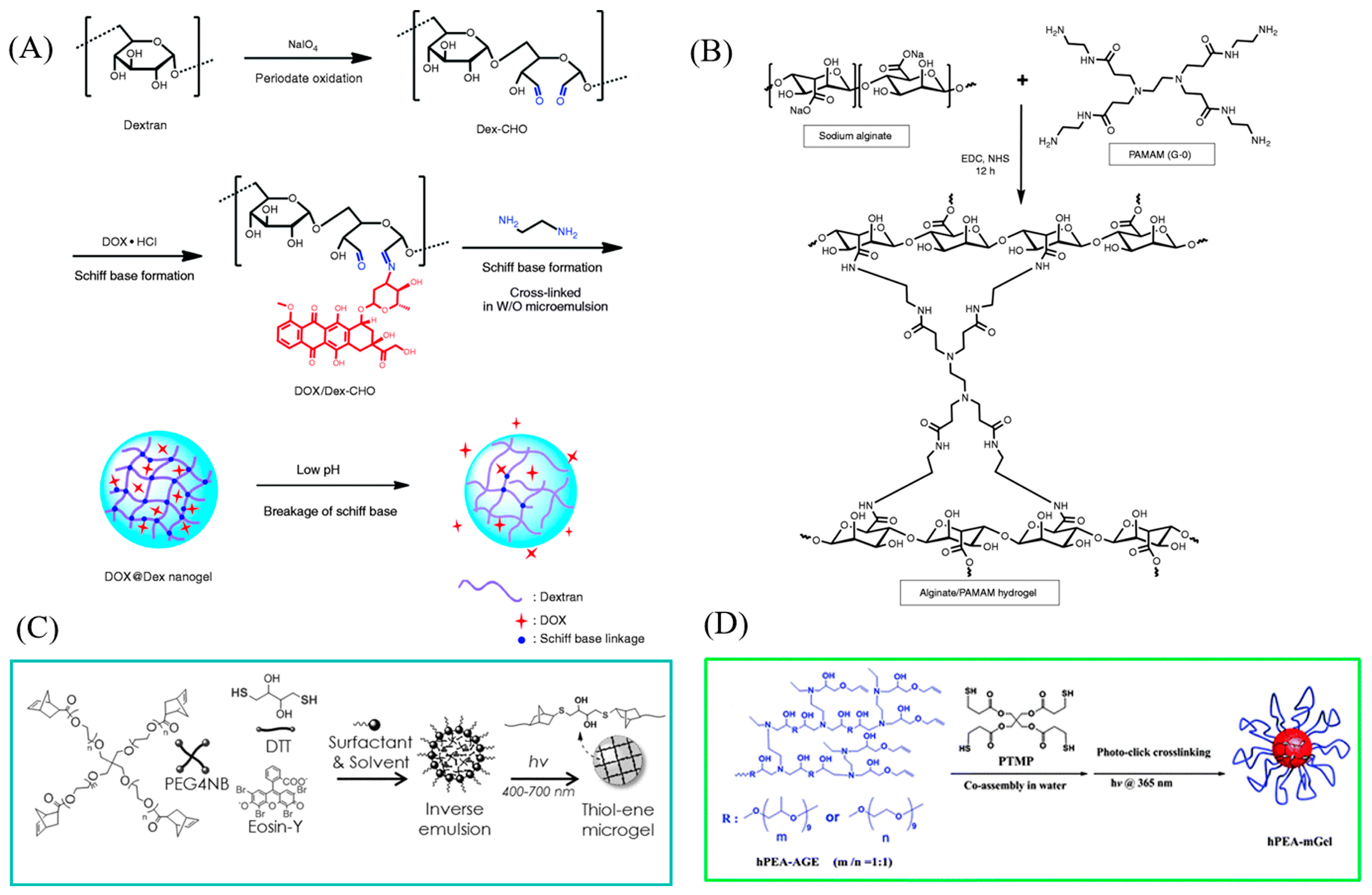
2.2.2. Physical Cross-Linking

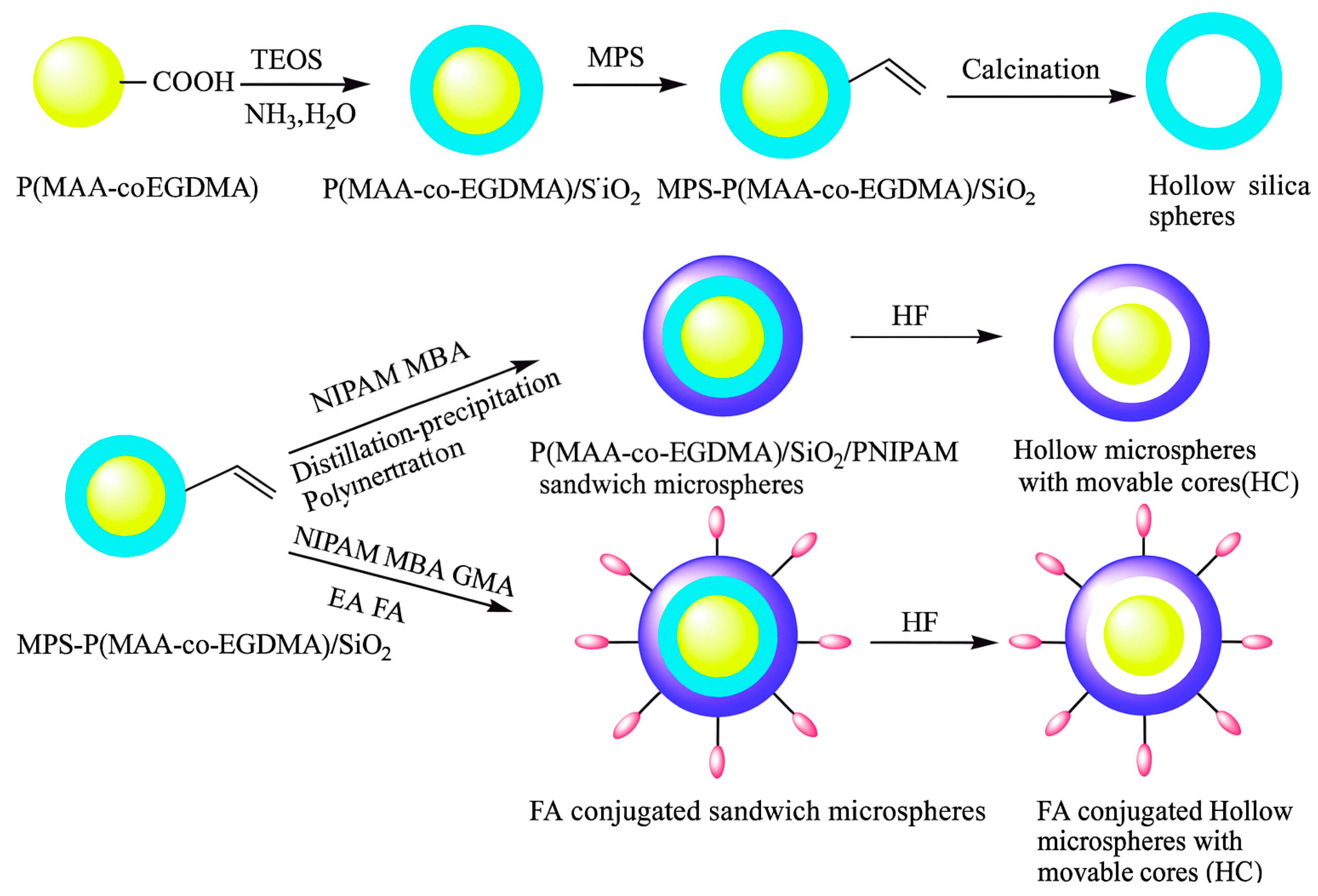
2.3. Microgels Post-Functionaliztion
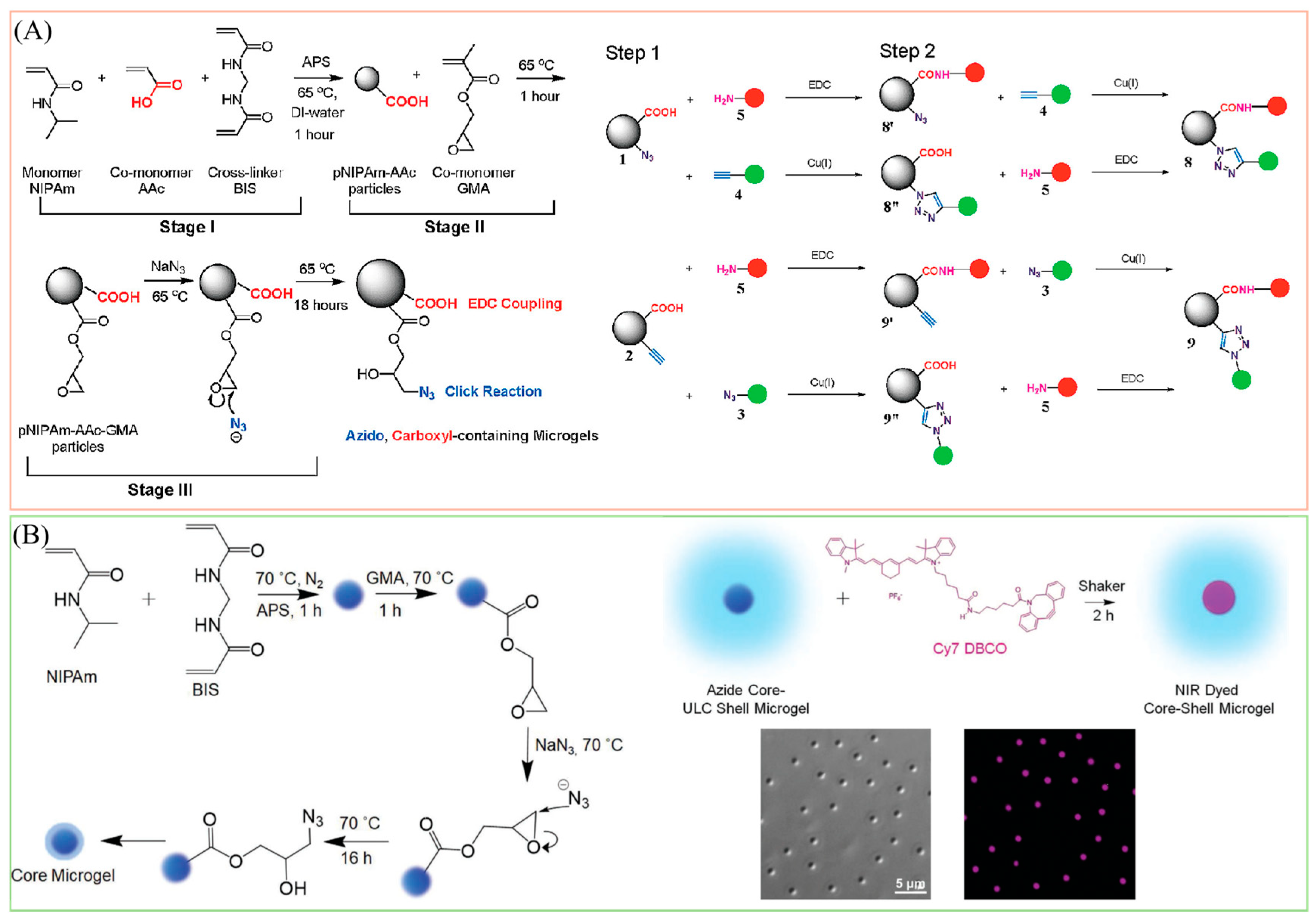
2.3.1. Carbodiimide Cross-Linking Chemistry
2.3.2. Click Chemistry
2.3.3. Enzyme-Mediated Conjugation
3. Conclusion and Perspective
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Das, M.; Zhang, H.; Kumacheva, E. Microgels: Old materials with new applications. Annu. Rev. Mater. Res. 2006, 36, 117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plamper, F.A.; Richtering, W. Functional microgels and microgel systems. Acc. Chem. Res. 2017, 50, 131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scheffold, F. Pathways and challenges towards a complete characterization of microgels. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 4315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, J.K.; Drumright, R.; Siegwart, D.J.; Matyjaszewski, K. The development of microgels/nanogels for drug delivery applications. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2008, 33, 448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, J.K.; Lee, D.I.; Park, J.M. Biopolymer-based microgels/nanogels for drug delivery applications. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2009, 34, 1261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uhrich, K.E.; Cannizzaro, S.M.; Langer, R.S.; Shakesheff, K.M. Polymeric systems for controlled drug release. Chem. Rev. 1999, 99, 3181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López Ruiz, A.; Ramirez, A.; McEnnis, K. Single and multiple stimuli-responsive polymer particles for controlled drug delivery. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thang, N.H.; Chien, T.B.; Cuong, D.X. Polymer-based hydrogels applied in drug delivery: An overview. Gels 2023, 9, 523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Luan, F.; Yue, H.; Song, C.; Wang, S.; Feng, J.; Zhang, X.; Yang, W.; Li, Y.; Wei, W. Recent Advances of Smart Materials for Ocular Drug Delivery. Adv. Drug Del. Rev. 2023, 200, 115006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Hetjens, L.; Wolter, N.; Li, H.; Shi, X.; Pich, A. Charge-reversible and biodegradable chitosan-based microgels for lysozyme-triggered release of vancomycin. J. Adv. Res. 2023, 43, 87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lévesque, S.G.; Shoichet, M.S. Synthesis of enzyme-degradable, peptide-cross-linked dextran hydrogels. Bioconjugate Chem. 2007, 18, 874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muggli, D.S.; Burkoth, A.K.; Keyser, S.A.; Lee, H.R.; Anseth, K.S. Reaction behavior of biodegradable, photo-cross-linkable polyanhydrides. Macromolecules 1998, 31, 4120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steinhilber, D.; Witting, M.; Zhang, X.; Staegemann, M.; Paulus, F.; Friess, W.; Küchler, S.; Haag, R. Surfactant free preparation of biodegradable dendritic polyglycerol nanogels by inverse nanoprecipitation for encapsulation and release of pharmaceutical biomacromolecules. J. Control. Release 2013, 169, 289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Gao, Y.; Serpe, M.J. Reductant-responsive poly (N-isopropylacrylamide) microgels and microgel-based optical materials. Can. J. Chem. 2015, 93, 685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murthy, N.; Thng, Y.X.; Schuck, S.; Xu, M.C.; Fréchet, J.M. A novel strategy for encapsulation and release of proteins: Hydrogels and microgels with acid-labile acetal cross-linkers. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2002, 124, 12398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neugebauer, D.; Rydz, J.; Goebel, I.; Dacko, P.; Kowalczuk, M. Synthesis of graft copolymers containing biodegradable poly (3-hydroxybutyrate) chains. Macromolecules 2007, 40, 1767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhuchar, N.; Sunasee, R.; Ishihara, K.; Thundat, T.; Narain, R. Degradable thermoresponsive nanogels for protein encapsulation and controlled release. Bioconjugate Chem. 2011, 23, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Debord, J.D.; Lyon, L.A. Synthesis and characterization of pH-responsive copolymer microgels with tunable volume phase transition temperatures. Langmuir 2003, 19, 7662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heckel, J.; Loescher, S.; Mathers, R.T.; Walther, A. Chemically fueled volume phase transition of polyacid microgels. Angew. Chem. 2021, 133, 7193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C. A comparison between thecoil-to-globule’transition of linear chains and the “volume phase transition” of spherical microgels. Polymer 1998, 39, 4609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agrawal, G.; Agrawal, R. Stimuli-responsive microgels and microgel-based systems: Advances in the exploitation of microgel colloidal properties and their interfacial activity. Polymers 2018, 10, 418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Echeverria, C.; Fernandes, S.N.; Godinho, M.H.; Borges, J.P.; Soares, P.I. Functional stimuli-responsive gels: Hydrogels and microgels. Gels 2018, 4, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Li, X.; Serpe, M.J. Stimuli-responsive microgel-based etalons for optical sensing. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 44074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, M.; Gao, Y.; Li, X.; Serpe, M.J. Stimuli-responsive polymers and their applications. Polym. Chem. 2017, 8, 127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gau, E.; Flecken, F.; Ksiazkiewicz, A.N.; Pich, A. Enzymatic synthesis of temperature-responsive poly (N-vinylcaprolactam) microgels with glucose oxidase. Green Chem. 2018, 20, 431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Q.; Katti, P.S.; Gu, Z. Enzyme-responsive nanomaterials for controlled drug delivery. Nanoscale 2014, 6, 12273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gong, X.; Qiao, Z.; Liao, Y.; Zhu, S.; Shi, L.; Kim, M.; Chen, Y.C. Enzyme-Programmable Microgel Lasers for Information Encoding and Anti-Counterfeiting. Adv. Mater. 2022, 34, 2107809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stuart, M.A.C.; Huck, W.T.; Genzer, J.; Müller, M.; Ober, C.; Stamm, M.; Sukhorukov, G.B.; Szleifer, I.; Tsukruk, V.V.; Urban, M. Emerging applications of stimuli-responsive polymer materials. Nat. Mater. 2010, 9, 101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhai, L. Stimuli-responsive polymer films. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2013, 42, 7148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De las Heras Alarcón, C.; Pennadam, S.; Alexander, C. Stimuli responsive polymers for biomedical applications. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2005, 34, 276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Pelton, R.; Hamielec, A.; Woods, D.; McPhee, W. The kinetics of poly (N-isopropylacrylamide) microgel latex formation. Colloid Polym. Sci. 1994, 272, 467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pelton, R.; Chibante, P. Preparation of aqueous latices with N-isopropylacrylamide. Colloids Surf. 1986, 20, 247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyon, L.A.; Meng, Z.; Singh, N.; Sorrell, C.D.; John, A.S. Thermoresponsive microgel-based materials. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2009, 38, 865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tobita, H.; Uemura, Y. Microgel formation in emulsion copolymerization. I. Polymerization without seed latex. J. Polym. Sci. Part B Polym. Phys. 1996, 34, 1403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seiffert, S. Small but smart: Sensitive microgel capsules. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2013, 52, 11462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irie, M.; Misumi, Y.; Tanaka, T. Stimuli-responsive polymers: Chemical induced reversible phase separation of an aqueous solution of poly (N-isopropylacrylamide) with pendent crown ether groups. Polymer 1993, 34, 4531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, X.; Lu, G.; Feng, C.; Li, Y.; Huang, X. Poly (acrylic acid)-graft-poly (N-vinylcaprolactam): A novel pH and thermo dual-stimuli responsive system. Polym. Chem. 2013, 4, 3876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scherzinger, C.; Lindner, P.; Keerl, M.; Richtering, W. Cononsolvency of Poly (N, N-diethylacrylamide) (PDEAAM) and poly (N-isopropylacrylamide) (PNIPAM) based microgels in water/methanol mixtures: Copolymer vs core−shell microgel. Macromolecules 2010, 43, 6829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pelton, R. Temperature-sensitive aqueous microgels. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2000, 85, 1–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fundueanu, G.; Constantin, M.; Bucatariu, S.; Ascenzi, P. Poly (N-isopropylacrylamide-co-N-isopropylmethacrylamide) Thermo-Responsive Microgels as Self-Regulated Drug Delivery System. Macromol. Chem. Phys. 2016, 217, 2525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cors, M.; Wiehemeier, L.; Oberdisse, J.; Hellweg, T. Deuteration-induced volume phase transition temperature shift of PNIPMAM microgels. Polymers 2019, 11, 620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wrede, O.; Bergmann, S.; Hannappel, Y.; Hellweg, T.; Huser, T. Smart microgels investigated by super-resolution fluorescence microscopy: Influence of the monomer structure on the particle morphology. Soft Matter 2020, 16, 8078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balaceanu, A.; Mayorga, V.; Lin, W.; Schürings, M.-P.; Demco, D.E.; Böker, A.; Winnik, M.A.; Pich, A. Copolymer microgels by precipitation polymerisation of N-vinylcaprolactam and N-isopropylacrylamides in aqueous medium. Colloid Polym. Sci. 2013, 291, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saha, P.; Santi, M.; Emondts, M.; Roth, H.; Rahimi, K.; Großkurth, J.; Ganguly, R.; Wessling, M.; Singha, N.K.; Pich, A. Stimuli-responsive zwitterionic core–shell microgels for antifouling surface coatings. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 58223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, M.R.; Serpe, M.J. Penetration of polyelectrolytes into charged poly (N-isopropylacrylamide) microgel layers confined between two surfaces. Macromolecules 2013, 46, 1599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinkrah, V.; Snowden, M.; Mitchell, J.; Seidel, J.; Chowdhry, B.; Fern, G. Physicochemical properties of poly (N-isopropylacrylamide-co-4-vinylpyridine) cationic polyelectrolyte colloidal microgels. Langmuir 2003, 19, 585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farooqi, Z.H.; Khan, H.U.; Shah, S.M.; Siddiq, M. Stability of poly (N-isopropylacrylamide-co-acrylic acid) polymer microgels under various conditions of temperature, pH and salt concentration. Arab. J. Chem. 2017, 10, 329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carvalho, W.S.; Lee, C.; Zhang, Y.; Czarnecki, A.; Serpe, M.J. Probing the response of poly (N-isopropylacrylamide) microgels to solutions of various salts using etalons. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2021, 585, 195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mackiewicz, M.; Dagdelen, S.; Waleka-Bargiel, E.; Karbarz, M. A polyampholyte core-shell microgel as an environmentally sensitive drug carrier. Arab. J. Chem. 2024, 17, 105464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mackiewicz, M.J.; Dagdelen, S.; Marcisz, K.; Waleka-Bargiel, E.; Stojek, Z.; Karbarz, M. Redox-degradable microgel based on poly(acrylic acid) as drug-carrier with very high drug-loading capacity and decreased toxicity against healthy cells. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2021, 190, 109652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mackiewicz, M.J.; Dagdelen, S.; Abubakar, M.; Romanski, K.; Waleka-Bargiel, E.; Karbarz, M. Stimuli-sensitive and degradable capsules as drug carriers with decreased toxicity against healthy cells. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2023, 212, 110349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phua, D.I.; Herman, K.; Balaceanu, A.; Zakrevski, J.; Pich, A. Reversible size modulation of aqueous microgels via orthogonal or combined application of thermo-and phototriggers. Langmuir 2016, 32, 3867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Fang, C.; Carvalho, W.S.; Gao, Y.; Serpe, M.J. Triggered Small-Molecule Release from Dual-Stimuli Responsive Microgels. ACS Appl. Polym. Mater. 2020, 3, 410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vleminckx, G.; Jofore, B.D.; Moldenaers, P.; Clasen, C. Effect of geometrical confinement on the flow of soft microgel particle pastes. Rheol. Acta 2020, 59, 435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, B.; Biswal, S.; Dubey, N.C.; Tripathi, B.P. Anti (-bio) fouling Nanostructured Membranes Based on the Cross-Linked Assembly of Stimuli-Responsive Zwitterionic Microgels. ACS Appl. Polym. Mater. 2022, 4, 4719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, C.; Xu, W.; Conrads, C.M.; Wu, J.; Pich, A. Visible light and temperature dual-responsive microgels by crosslinking of spiropyran modified prepolymers. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2021, 582, 1075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Q.; Guan, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Siddiq, M. Lead-sensitive PNIPAM microgels modified with crown ether groups. J. Polym. Sci. Part A Polym. Chem. 2010, 48, 4120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Annegarn, M.; Dirksen, M.; Hellweg, T. Importance of pH in synthesis of pH-responsive cationic nano-and microgels. Polymers 2021, 13, 827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, G.H.; Fukutomi, T. Studies on the preparation and characterization of poly (4-vinylpyridine) microgel. I. Preparation with polymer emulsifier. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 1991, 43, 1451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Tang, J.; Ji, F.; Lin, W.; Chen, S. Recent advances in zwitterionic hydrogels: Preparation, property, and biomedical application. Gels 2022, 8, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, C.; Sun, Y.; van Wissen, G.; Peng, Y.; Pich, A. Visible Light-Responsive Microgels Modified with Donor–Acceptor Stenhouse Adducts. Chem. Mater. 2022, 34, 4774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, C.; Pich, A. Multiresponsive Azobenzene-Modified Microgels with Polyampholyte Behavior. Macromolecules 2023, 56, 4910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.M.; Li, X.; Islam, M.R.; Wei, M.; Serpe, M.J. Light switchable optical materials from azobenzene crosslinked poly (N-isopropylacrylamide)-based microgels. J. Mater. Chem. C 2014, 2, 6961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ofridam, F.; Tarhini, M.; Lebaz, N.; Gagnière, É.; Mangin, D.; Elaissari, A. pH-sensitive polymers: Classification and some fine potential applications. Polym. Adv. Technol. 2021, 32, 1455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Liu, Z.; Xie, R.; Ju, X.-J.; Wang, W.; Pan, D.-W.; Chu, L.-Y. Poly (N-isopropylmethacrylamide-co-4-acrylamidobenzo-18-crown-6) microgels with expanded networks for excellent adsorption of lead (II) ions. Particuology 2023, 77, 105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonham, J.; Faers, M.; Van Duijneveldt, J. Non-aqueous microgel particles: Synthesis, properties and applications. Soft Matter 2014, 10, 9384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langley, N.R.; Polmanteer, K.E. Relation of elastic modulus to crosslink and entanglement concentrations in rubber networks. J. Polym. Sci. Polym. Phys. Ed. 1974, 12, 1023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maitra, J.; Shukla, V.K. Cross-linking in hydrogels-a review. Am. J. Polym. Sci. 2014, 4, 25. [Google Scholar]
- Ochiai, H.; Kurita, Y.; Murakami, I. Viscosity behavior of the polyelectrolyte poly (vinyl alcohol) having some intrachain crosslinks. Die Makromol. Chem. Macromol. Chem. Phys. 1984, 185, 167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolfe, M.; Scopazzi, C. Rheology of swellable microgel dispersions: Influence of crosslink density. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 1989, 133, 265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stutz, H.; Illers, K.H.; Mertes, J. A generalized theory for the glass transition temperature of crosslinked and uncrosslinked polymers. J. Polym. Sci. Part B Polym. Phys. 1990, 28, 1483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eichenbaum, G.M.; Kiser, P.F.; Dobrynin, A.V.; Simon, S.A.; Needham, D. Investigation of the swelling response and loading of ionic microgels with drugs and proteins: The dependence on cross-link density. Macromolecules 1999, 32, 4867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schild, H.G. Poly (N-isopropylacrylamide): Experiment, theory and application. Prog. Polym. Sci. 1992, 17, 163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hennink, W.E.; van Nostrum, C.F. Novel crosslinking methods to design hydrogels. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2012, 64, 223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, M.; Kim, J.-C. FITC-dextran releases from chitosan microgel coated with poly (N-isopropylacrylamide-co-methacrylic acid). Polym. Test. 2010, 29, 784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, H.; Zhang, W.; Wu, Y.; Han, X.; Liu, G.; Jia, Q.; Shan, S. Schiff base-containing dextran nanogel as pH-sensitive drug delivery system of doxorubicin: Synthesis and characterization. J. Biomater. Appl. 2018, 33, 170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eiselt, P.; Lee, K.Y.; Mooney, D.J. Rigidity of two-component hydrogels prepared from alginate and poly (ethylene glycol)−diamines. Macromolecules 1999, 32, 5561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hauck, N.; Seixas, N.; Centeno, S.P.; Schlüßler, R.; Cojoc, G.; Müller, P.; Guck, J.; Wöll, D.; Wessjohann, L.A.; Thiele, J. Droplet-assisted microfluidic fabrication and characterization of multifunctional polysaccharide microgels formed by multicomponent reactions. Polymers 2018, 10, 1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fraser, A.K.; Ki, C.S.; Lin, C.C. PEG-Based Microgels Formed by Visible-Light-Mediated Thiol-Ene Photo-Click Reactions. Macromol. Chem. Phys. 2014, 215, 507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patil, S.; Nune, K.; Misra, R. Alginate/poly (amidoamine) injectable hybrid hydrogel for cell delivery. J. Biomater. Appl. 2018, 33, 295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, B.; Jiang, X.; Yin, J. Multi-responsive microgel of hyperbranched poly (ether amine) (hPEA-mGel) for the selective adsorption and separation of hydrophilic fluorescein dyes. J. Mater. Chem. 2012, 22, 17976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Utech, S.; Prodanovic, R.; Mao, A.S.; Ostafe, R.; Mooney, D.J.; Weitz, D.A. Microfluidic generation of monodisperse, structurally homogeneous alginate microgels for cell encapsulation and 3D cell culture. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2015, 4, 1628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watanabe, T.; Ohtsuka, A.; Murase, N.; Barth, P.; Gersonde, K. NMR studies on water and polymer diffusion in dextran gels. Influence of potassium ions on microstructure formation and gelation mechanism. Magn. Reson. Med. 1996, 35, 697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Q.; Gao, Y.; Xu, J.-F.; Qin, B.; Serpe, M.J.; Zhang, X. Supramolecular microgels fabricated from supramonomers. ACS Macro Lett. 2016, 5, 1084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmitz, D.; Pich, A. Responsive microgels with supramolecular crosslinks: Synthesis and triggered degradation in aqueous medium. Polym. Chem. 2016, 7, 5687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López, C.M.; Pich, A. Supramolecular stimuli-responsive microgels crosslinked by tannic acid. Macromol. Rapid Commun. 2018, 39, 1700808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, J.; Ji, W.; Dong, S.; Zhang, Z.; Gao, J.; Yang, P.; Nie, J.; Du, B. Degradable and thermosensitive microgels with tannic acid as the sole cross-linker. Langmuir 2019, 35, 16353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeong, B.; Bae, Y.H.; Kim, S.W. Thermoreversible gelation of PEG−PLGA−PEG triblock copolymer aqueous solutions. Macromolecules 1999, 32, 7064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonacucina, G.; Cespi, M.; Mencarelli, G.; Giorgioni, G.; Palmieri, G.F. Thermosensitive self-assembling block copolymers as drug delivery systems. Polymers 2011, 3, 779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Güney, A.; Gardiner, C.; McCormack, A.; Malda, J.; Grijpma, D.W. Thermoplastic PCL-b-PEG-b-PCL and HDI polyurethanes for extrusion-based 3D-printing of tough hydrogels. Bioengineering 2018, 5, 99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gruber, A.; Navarro, L.; Klinger, D. Reactive precursor particles as synthetic platform for the generation of functional nanoparticles, nanogels, and microgels. Adv. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 7, 1901676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Q.; Li, D.; Li, Q.; Cao, X.; Dong, H. Microgel assembly: Fabrication, characteristics and application in tissue engineering and regenerative medicine. Bioact. Mater. 2022, 9, 105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nayak, S.; Lee, H.; Chmielewski, J.; Lyon, L.A. Folate-mediated cell targeting and cytotoxicity using thermoresponsive microgels. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2004, 126, 10258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, Z.; Hendrickson, G.R.; Lyon, L.A. Simultaneous orthogonal chemoligations on multiresponsive microgels. Macromolecules 2009, 42, 7664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, M.R.; Nguy, C.; Pandit, S.; Lyon, L.A. Design and Synthesis of Core–Shell Microgels with One-Step Clickable Crosslinked Cores and Ultralow Crosslinked Shells. Macromol. Chem. Phys. 2020, 221, 2000156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gau, E.; Mate, D.M.; Zou, Z.; Oppermann, A.; Töpel, A.; Jakob, F.; Wöll, D.; Schwaneberg, U.; Pich, A. Sortase-mediated surface functionalization of stimuli-responsive microgels. Biomacromolecules 2017, 18, 2789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fischer, M.J. Amine coupling through EDC/NHS: A practical approach. In Surface Plasmon Resonance: Methods and Protocols; Humana Press: Totowa, NJ, USA, 2010; pp. 55–73. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, T.; Liu, C.; Min, Z.; Cai, W.; Zhang, X.; Li, W.; Zhang, A. Microfluidic Fabrication of Gelatin Acrylamide Microgels through Visible Light Photopolymerization for Cell Encapsulation. ACS Appl. Bio Mater. 2023, 6, 2496–2504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Ren, J.; Qian, L.; He, Y.; Song, P.; Wang, R. Preparation of FK-SA conjugate gel beads with double cross-linking for pH-controllable drug releasing. Polym. Bull. 2023, 80, 331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, P.; Yang, H.; Zeng, J.; Liu, P. Folic acid-conjugated temperature and pH dual-responsive yolk/shell microspheres as a drug delivery system. J. Mater. Chem. B 2013, 1, 5298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, L.; Liu, Y.-X.; Zhong, H.; Li, X.-R.; Jun, Y.-L.; Wang, Q.-L.; Ding, L.-S.; Cheng, Z.-P.; Qian, H.-Y. Folic acid conjugated palygorskite/Au hybrid microgels: Temperature, pH and light triple-responsive and its application in drug delivery. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2023, 229, 113432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, Y.; Liu, W.; Wu, F. Novel multi-responsive polymer magnetic microgels with folate or methyltetrahydrofolate ligand as anticancer drug carriers. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 10333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolb, H.C.; Finn, M.; Sharpless, K.B. Click chemistry: Diverse chemical function from a few good reactions. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2001, 40, 2004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Xiong, Y. Application of “Click” Chemistry in Biomedical Hydrogels. ACS Omega 2022, 7, 36918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Battigelli, A.; Almeida, B.; Shukla, A. Recent advances in bioorthogonal click chemistry for biomedical applications. Bioconjugate Chem. 2022, 33, 263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Finn, M.; Kolb, H.C.; Sharpless, K.B. Click chemistry connections for functional discovery. Nat. Synth. 2022, 1, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Chen, J.; Deng, C.; Suuronen, E.J.; Zhong, Z. Click hydrogels, microgels and nanogels: Emerging platforms for drug delivery and tissue engineering. Biomaterials 2014, 35, 4969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeon, O.; Lee, Y.B.; Hinton, T.J.; Feinberg, A.W.; Alsberg, E. Cryopreserved cell-laden alginate microgel bioink for 3D bioprinting of living tissues. Mater. Today Chem. 2019, 12, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Li, N.; Qi, J.; Gao, D.; Zhou, M.; Wei, X.; Xing, C. Mild-Temperature Photothermal Effect Enhanced by Functional Conjugated Polymer Nanoparticles through Enzyme-Mediated Starvation. ACS Appl. Bio Mater. 2022, 5, 2536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, S.; Ahn, H.; Kim, S.H. Tyrosinase-mediated hydrogel crosslinking for tissue engineering. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2022, 139, 51887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zavada, S.; McHardy, N.; Scott, T. Oxygen-mediated enzymatic polymerization of thiol–ene hydrogels. J. Mater. Chem. B 2014, 2, 2598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zare, I.; Taheri-Ledari, R.; Esmailzadeh, F.; Salehi, M.M.; Mohammadi, A.; Maleki, A.; Mostafavi, E. DNA hydrogels and nanogels for diagnostics, therapeutics, and theragnostic of various cancers. Nanoscale 2023, 15, 10882–10903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, H.; Gao, Y. Recent Advances in Stimuli-Responsive Microgels and Their Biomedical Applications. Molecules 2025, 30, 4457. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30224457
Zhang H, Gao Y. Recent Advances in Stimuli-Responsive Microgels and Their Biomedical Applications. Molecules. 2025; 30(22):4457. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30224457
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Hongtao, and Yongfeng Gao. 2025. "Recent Advances in Stimuli-Responsive Microgels and Their Biomedical Applications" Molecules 30, no. 22: 4457. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30224457
APA StyleZhang, H., & Gao, Y. (2025). Recent Advances in Stimuli-Responsive Microgels and Their Biomedical Applications. Molecules, 30(22), 4457. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30224457







