Abstract
The present review offers a comprehensive synthesis of the structural diversity, natural occurrence, and therapeutic promise of key ellagitannins (punicalagin, sanguiin H-6, corilagin, geraniin, oenothein B, chebulagic, and chebulinic acids) within the hydrolyzable ellagitannin pool. Distributed in medicinal and dietary plants long used in traditional medicine, ellagitannin-rich species serve as sources of both complex polyphenolic scaffolds and their bioactive metabolites, urolithins, which mediate many of their health-promoting effects. Special emphasis is placed on the multifaceted mechanisms that contribute to their potent antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, antimicrobial, and anticancer effects, extending to both non-communicable and communicable diseases. Despite their broad therapeutic spectrum, clinical translation is limited by challenges such as poor bioavailability, host-gut microbiota variability, and a lack of robust in vivo evidence. The review highlights future directions aimed at unlocking ellagitannins’ potential, including microbiota-targeted strategies for urolithin production, the design of stable prodrugs and analogs, and innovative delivery platforms. By integrating phytochemical, mechanistic and translational insights, this article positions ellagitannins as promising candidates for the development of novel polyphenol-based interventions.
1. Introduction
Polyphenols constitute one of the most abundant and chemically versatile classes of plant secondary metabolites, encompassing flavonoids, stilbenes, phenolic acids, and tannins [1,2]. Flavonoid polyphenols, including quercetin, catechins, and anthocyanins, are ubiquitous in fruits, vegetables, tea, and wine, and have been the subject of extensive scientific investigation for their roles in oxidative stress modulation, inflammation, and metabolic regulation through established cellular mechanisms [3]. As a result, these constituents dominate the phytochemical literature, with extensive experimental and clinical research on their well-documented health-promoting effects.
In contrast, the class of polyphenols belonging to the hydrolysable tannins class has been far less investigated, despite emerging evidence of their distinctive chemical features and bioactivities. As representative plant metabolites with abundant hydroxyl groups, particularly tannins of the hydrolysable type, have recently attracted growing attention for their emerging significance in human health and diseases [4].
Hydrolysable tannins are a diverse group of plant polyphenols, encompassing ellagitannins, gallotannins, and various types of complex tannins, distinguished by their structural complexity, considerable molecular weight, and multifaceted bioactivities. They belong to the broader class of tannins, which, as major members of the secondary metabolite repertoire, hold significant ecological, nutritional, and pharmacological relevance [1]. Unlike condensed tannins, hydrolysable tannins readily undergo hydrolysis under acidic or enzymatic conditions, yielding sugars (typically glucose) and phenolic acids such as gallic or ellagic acid and their derivatives [2,5].
Within the hydrolyzable tannin pool, a subset of plant-specific ellagitannin derivatives—punicalagin, sanguiin H-6, corilagin, geraniin, oenothein B, chebulagic and chebulinic acids, is increasingly recognized as a promising area of research, yet still receives comparatively limited mechanistic and translational investigation, despite accumulating evidence of biological relevance [4]. These compounds exhibit considerable structural complexity, encompassing composite structures with distinctive monomeric, macrocyclic, or dimeric architectures. Their occurrence in plants long valued in traditional medicine, including Terminalia species in Ayurveda, Epilobium in European and Asian phytotherapy, as well as dietary sources such as pomegranate and raspberries, asserts their ethnopharmacological importance [4,6].
The present review consolidates recent findings relating to the molecular diversity, natural distribution, and multifaceted bioactivities of key derivatives within the ellagitannin family, selected based on their structural diversity, prevalence in ethnomedicinal and dietary sources, and their established or emerging significance in pharmacological and mechanistic studies. Special emphasis is placed on elucidating the cellular and molecular mechanisms that mediate their potent antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, antimicrobial (including antibacterial, antifungal, antiviral), anticancer, cardiovascular, metabolic, and neuroprotective properties. The review also addresses critical barriers to the clinical translation of ellagitannins, including poor bioavailability, the scarcity of in vivo and clinical studies, and the underappreciated role of gut microbiota in the metabolism and bioactivation of these compounds. We further outline future research directions, focused on facilitating bioactivation through urolithin-producing probiotics (e.g., Gordonibacter urolithinfaciens), developing more stable and permeable prodrugs or molecular conjugates, engineering semi-synthetic analogs with enhanced lipophilicity and metabolic resilience, and employing technological delivery approaches.
2. Natural Sources and Ethnopharmacological Background
Ellagitannins represent an expansive and chemically diverse group of high-molecular-weight polyphenols, widely distributed throughout the plant kingdom in nearly all tissues of plants, including roots, leaves, bark, wood, galls, fruits, and seeds [1,4,7]. In their ecological context, ellagitannins act as key defensive metabolites, deterring herbivores and conferring resistance to microbial pathogens, while their ethnopharmacological relevance is substantiated by their deep integration into diverse traditional medicine systems. More recently, a growing body of research has pointed to their promising therapeutic potential, encouraging further investigation into their natural sources and diverse biological activities [8]. Nevertheless, the body of evidence supporting their biological and pharmacological properties is unevenly distributed among individual compounds. The most comprehensive data concern punicalagin and the gut microbiota-derived metabolites urolithins, which have been extensively studied in the contexts of food science, pharmacology, and human health. By contrast, other ellagitannins remain comparatively underexplored, with limited insight into their bioavailability, metabolism, and mechanistic effects. Understanding this gap is key to interpreting current evidence and directing future research toward the lesser-studied members of this class.
Punicalagin is among the most extensively characterized ellagitannins, found in high abundance in the pericarp, rind, bark and heartwood of Punica granatum (pomegranate), but also present in members of the Myrtales order, including the Terminalia (T. myriocarpa, T. catappa, T. chebula, T. arjuna) and Combretum genera (Combretum molle), distributed in Africa, Asia, Australia and the Americas [9,10,11]. Notably, in T. chebula, punicalagin co-occurs with the hallmark ellagitannins of the species, namely chebulagic and chebulinic acids, as well as corilagin (a gallotannin-ellagitannin hybrid), constituting the principal hydrolyzable tannin pool of this species [6,12,13]. Accordingly, Terminalia chebula (“haritaki”) is highly esteemed in Ayurvedic practice for its central role in the triphala formulation, credited with supporting digestive function, facilitating tissue regeneration, and aiding in the removal of toxins, effects largely attributed to its abundant tannin constituents [14]. Corilagin is also a common constituent of Punica granatum and pomegranate extracts, and of other medicinal species across the Euphorbiaceae (e.g., Phyllanthus emblica, P. urinaria, P. tenellus, P. niruri, Acalypha australis), Geraniaceae (Geranium sibiricum), Polygonaceae (Polygonum chinense), and Saururaceae (Saururus chinensis) families [15].
Geraniin, a dehydroellagitannin, is exceptionally abundant in Phyllanthus species, particularly P. amarus, P. urinaria, and P. muellerianus, traditionally used to manage menstrual disorders, wound infections, fevers, pain, and inflammation [16,17,18], and is also present in significant amounts within certain Geranium taxa (such as G. bellum, G. wilfordii, and G. carolinianum). Moreover, geraniin constitutes a principal bioactive compound in the traditional Chinese medicine Herba Geranii et Erodii, which is valued for its efficacy in rheumatism, joint pain, infectious diseases, and dysentery. Notably, hydrolytic cleavage of geraniin yields the ellagitannin corilagin, further enhancing its therapeutic scope [19,20,21].
Sanguiin H-6, representative of the Rubus genus (raspberry, blackberry), and oenothein B, a dimeric ellagitannin occurring in Epilobium spp., further exemplify this group’s phytochemical diversity [4]. Importantly, ellagitannins significantly contribute to the polyphenolic profile of edible plants and foods, including strawberries, blackberries, cranberries, walnuts, and hazelnuts, broadening their dietary relevance beyond classical medicinal species [1,22]. In European phytotherapy, Epilobium teas (oenothein B-rich) are traditionally used for urinary and prostate disorders, while oak gall and pomegranate extracts are utilized as topical astringents for oral, gingival, and cutaneous inflammatory conditions [4,23,24].
3. Structural Diversity and Structure-Activity Relationships (SARs) of Representative Ellagitannins
Tannins are structurally diverse polyphenols, generally classified into hydrolyzable tannins (including ellagitannins and gallotannins), condensed tannins, complex tannins (fusing hydrolysable and condensed motifs), and the less prevalent phlorotannins found in marine algae [25,26,27,28]. Condensed tannins, also known as proanthocyanidins, well-studied for their potent antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties, are polymers of flavan-3-ol units that are resistant to hydrolysis [28].
Hydrolyzable tannins, on the other hand, are esters of a central sugar core (most commonly D-glucose) with gallic acid (in the lesser common gallotannins) or with oxidatively coupled galloyl units that form the hexahydroxydiphenoyl (HHDP) group, present in the widely distributed ellagitannins [25,26]. (Figure 1). The HHDP moieties typically undergo spontaneous lactonization, yielding ellagic acid upon hydrolysis, which is the chemical hallmark of ellagitannins [4,29]. This chemical distinction gives rise to pronounced differences in the physicochemical properties, metabolic fate, and biological properties of both subclasses; gallotannins are typically less complex and readily hydrolyzed to gallic acid, whereas ellagitannins, featuring macrocyclic or polymeric HHDP units, offer extensive structural variability and broad-spectrum bioactivities [25,29].
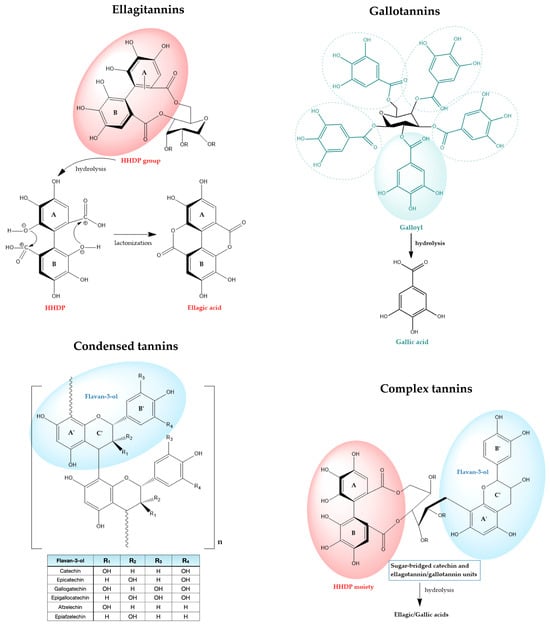
Figure 1.
Overview of tannin classes and their representative structures. Key functional groups are circled. Aromatic rings of the HHDP group in ellagitannins are identified as A and B, with the flavan-3-ol rings correspondingly labeled A’, B’ and C’.
Reflecting both subclasses, corilagin’s molecular structure features both a galloyl and an HHDP units esterified to the same sugar backbone [30,31]. Its unique structure accounts for its diverse extraction profiles, flexible pathways for enzymatic hydrolysis, and the ability to functionally mimic either gallotannin or ellagitannin characteristics according to context [27].
Complex tannins (hydrolysable flavono-ellagitannins) also exhibit bifunctional properties, containing both galloyl and HHDP esters on the glucose core alongside flavan-3-ol motifs, endowing them with features of both hydrolyzable and condensed tannins [27]. Unlike C-glycosidic tannins, they occur in a limited number of plant families, including Combretaceae, Myrtaceae, Melastomataceae, Fagaceae, and Theaceae [32].
The ellagitannin family spans a broad structural continuum, ranging from relatively simple monoesters such as corilagin, through highly substituted monomeric forms exemplified by geraniin, to complex oligomeric and macrocyclic architectures such as sanguiins and oenothein B (Figure 2). This molecular diversity underlies their wide-ranging biochemical mechanisms and physiological effects [4,33,34]. Within this review’s focus on representative ellagitannins (punicalagin, sanguiin H-6, corilagin, geraniin, oenothein B, chebulagic acid, and chebulinic acid), structure-activity relationship (SAR) analyses reveal that the number and distribution of galloyl, HHDP, and chebuloyl moieties modulate their capacities for metal chelation, radical scavenging, enzyme modulation, and molecular target specificity [35,36].
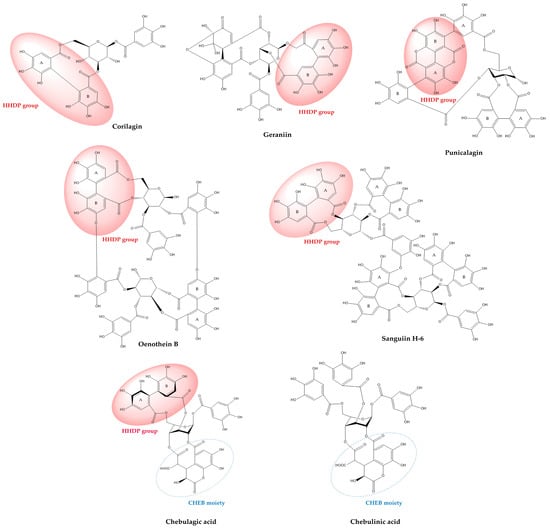
Figure 2.
Chemical structures of selected ellagitannins, showing characteristic HHDP and chebuloyl groups.
The high density of phenolic hydroxyl groups in the HHDP residue often increases in vitro antioxidant metrics of ellagitannins; however, it renders them too large and polar to cross the intestinal epithelium in their native form. Polymerization and macrocyclic topology (i.e., oenothein B, sanguiin-H6) are also decisive for protein interactions and metal chelation: multiple adjacent catechol- and pyrogallol-type hydroxyls bind metal ions (Fe, Cu) strongly and provide the chelation sites implicated in both antioxidant activity and, paradoxically, pro-oxidant Fenton chemistry in some settings. The spatial arrangement of these hydroxyls, whether on galloyl appendages, within HHDP rings, or distributed across oligomeric scaffolds, determines chelation geometry and redox potential. For instance, the HHDP unit tends to form a constrained biaryl diester that can stabilize radical intermediates and coordinate metals in a fashion not reproducible by isolated galloyl esters; this partially explains why HHDP-containing ellagitannins often outperform simple gallic acid in cell-free antioxidant assays and why HHDP stereochemistry affects ferroptosis-modulating activity observed for chebulagic/chebulinic acids [33,34,35,37,38,39,40].
On the other hand, the principal in vivo biological activities of dietary ellagitannins are mediated by their hydrolytic degradation products, namely ellagic acid and, foremostly, their final dibenzopyran-6-one metabolites, called urolithins, generated through sequential transformation by the gut microbiota. The microbial processing typically unfolds through a stepwise dehydroxylation, with ellagic acid first converted into intermediate products (i.e., urolithin D and C), and ultimately producing the final metabolites urolithin A and B. Urolithin A, in particular, is recognized as the principal circulating metabolite conferring the anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, and organoprotective effects characteristic of dietary ellagitannins in vivo [25,41,42]. Notably, interindividual variability in the abundance of urolithin-producing bacterial taxa (including Gordonibacter spp.) results in distinct metabotypes (A, B, and non-producers 0), with only subsets of the population efficiently converting precursors to bioactive urolithins [25,41,43].
Vice versa, ellagic acid and its gut-derived urolithin metabolites play a pivotal role in modulating the intestinal microbiota, reshaping both microbial diversity and function. These interactions foster an environment that promotes beneficial bacteria and suppresses potentially harmful species, contributing to strengthened intestinal barrier function, elevated antioxidant capacity and reduced inflammation. Recent animal studies and clinical interventions have demonstrated that ellagitannin supplementation leads to marked modulation of gut microbiota composition. For example, administration of ellagic acid at 0.3% of the daily diet in rodent models for 21 days resulted in increased jejunal villus height, elevated relative abundance of beneficial taxa such as Bacteroidetes, Lactobacillus, Ruminococcaceae and Clostridium ramosum, and reductions in potentially harmful groups including Firmicutes, Streptococcus, and Rothia [44]. Furthermore, a recent clinical study demonstrated that walnut supplementation caused notable shifts in gut microbiota composition, as revealed by 16S rRNA gene sequencing. Both beta diversity and Shannon’s alpha-diversity were significantly altered after walnut intake, independent of demographic factors and baseline urolithin metabotypes. Several bacterial genera showed differential enrichment pre- and post-supplementation; importantly, the abundance of Gordonibacter, a genus capable of producing urolithin A from ellagic acid, increased following walnut consumption, suggesting a link between dietary ellagitannin intake and enhancement of bacteria involved in urolithin production [45]. These microbial shifts strongly suggest that ellagitannin consumption can reprogram community composition toward a healthier profile, fostering a host environment characterized by increased production of protective short-chain fatty acids and metabolites, creating biochemical conditions that help counter the development and progression of cancer. For example, rodent studies administering ellagic acid or pomegranate extract (a rich source of ellagitannins) have shown decreased incidence and multiplicity of colon tumors, coinciding with increased abundance of urolithin-producing bacteria, lower inflammatory markers and improved gut integrity [25,46,47]. Other human intervention studies reveal similar trends: individuals with higher capacity for microbiome-mediated urolithin production exhibit greater systemic and colonic exposure to these metabolites and are hypothesized to derive enhanced chemopreventive benefits from ellagitannin-rich diets or supplements [47].
Punicalagin, a hallmark constituent of pomegranate, is among the highest molecular-weight monomeric ellagitannins identified in food, with a molecular weight of 1084.72 g/mol [48]. Importantly, it is among the few dietary ellagitannins that directly incorporate the actual dilactone ellagic acid moiety within their structure, rather than forming it upon hydrolysis. Modern structural revisions have reaffirmed its highly symmetrical and rigid macrocyclic dimeric nature, contributing to its known antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, anti-adipogenic, and anticancer activities. The SAR of punicalagin has been demonstrated to rely on the stereochemistry and spatial proximity of the HHDP and gallagyl groups, with maximal protein- and metal-binding afforded by the macrocyclic arrangements [11,49]. As with all high-molecular-weight ellagitannins, its solubility is low and membrane permeability is poor, accounting for rapid intestinal hydrolysis and decomposition to ellagic acid and, subsequently, urolithin [50].
Sanguiin H-6 is a dimeric casuarictin derivative consisting of repeating galloyl-glucose-HHDP units, and a major macrocyclic, polymeric ellagitannin in the Rosaceae and Rubus genera. The dimeric topology increases rigidity and yields high avidity for nucleic acids and nuclear enzymes (demonstrated as topoisomerase inhibition), potent in vitro cytotoxicity against transformed cell lines, and exceptional affinity for serum albumin and metal ions [51,52,53].
Corilagin, widely distributed in Phyllanthus and Terminalia species, is recognized for its hybrid structure exhibiting features of both gallotannins and ellagitannins: a gallic acid ester at one glucose hydroxyl, and a single HHDP at two others [31,54]. The SAR of corilagin is dominated by the capacity of both galloyl and HHDP groups to chelate metals, regulate enzyme activity (notably of pro-inflammatory COX and LOX isoforms), and scavenge ROS [55]. Despite its smaller molecular size, absorption studies show that corilagin itself is poorly transported across intestinal epithelia and displays enhanced hydrolytic breakdown compared to larger macrocyclic and polymeric ellagitannins [56]. Importantly, corilagin is also a typical hydrolysis product of larger ellagitannins (notably geraniin), which justifies its occurrence in decoctions and processed plant extracts.
Geraniin is paradigmatic of monomeric, highly substituted ellagitannins whose chemical lability determines both analytical behavior and biological fate: containing galloyl, hexahydroxydiphenoyl (HHDP) and dehydrohexahydroxydiphenoyl (DHHDP) groups, characteristic of ellagitannins, geraniin readily undergoes partial hydrolysis (e.g., on heating or in acidic media) to generate corilagin, brevifolin derivatives, gallic and ellagic acids—metabolites that have their own bioactivities and that complicate interpretation of crude-extract pharmacology. The hydrolysis is facilitated by the strategic positioning of the HHDP and DHHDP esters, both susceptible to enzymatic and chemical cleavage, particularly in the GI tract or during extended decoction. The hydrolytic susceptibility of geraniin also affects formulation choices and extraction yields and is a mechanistic basis for the frequent observation that decoctions or heated extracts display different biological profiles than cold extractions [57].
Oenothein B occupies a special place because it is a macrocyclic dimeric ellagitannin with a rigid, cyclic architecture that markedly alters its pharmacodynamics relative to linear monomers. Macrocyclization substantially increases molecular rigidity and creates a large, multivalent surface for interacting with proteins and receptors; accordingly, oenothein B exerts robust immunomodulatory effects (activation of phagocytes, modulation of cytokine release, and effects on innate lymphocytes), distinct enzyme-inhibitory profiles, and pronounced antioxidant capacity in vitro and in vivo. However, like other large ellagitannins, it is poorly permeable as an intact molecule and its in vivo actions likely reflect a combination of local (gastrointestinal) effects, modulation of microbiota, and generation of lower-molecular-weight metabolites [58].
Chebulagic and chebulinic acids, the most abundant hydrolyzable tannins in Terminalia fruits, exemplify how the stereochemistry of key moieties fundamentally shapes both chemical and biological profiles. Both compounds share a β-D-glucose backbone glycosylated with chebuloyl and galloyl esters, but structural differences arise from the number and arrangement of these groups, and especially from the absolute configuration and spatial orientation of the chiral axis in the HHDP motif [59]. Chebulagic acid incorporates a single galloyl, one chebuloyl, and one HHDP group, the latter two forming a macrocyclic (R)-configured ring, which imparts greater rigidity and spatial hindrance, translating to distinct enzyme affinities and kinetic properties. In contrast, chebulinic acid features three galloyl and one chebuloyl groups and adopts a more flexible “skew-boat” conformation, facilitating broader accessibility to active sites and more diverse binding interactions with biological targets. [37,59].
4. Biological Activities and Molecular Mechanisms of Ellagitannins
Despite the growing interest in the diverse class of ellagitannins, there is a pronounced disparity in the amount of experimental and clinical evidence available for different members of this group. The vast majority of mechanistic and translational studies, as well as published clinical trials, focus on punicalagin, ellagic acid, and urolithin derivatives found predominantly in pomegranate and widely investigated for their pharmacokinetics, bioactivities, and formulation strategies. In contrast, far fewer studies have examined the biological effects, biotransformation, or potential applications of other representative ellagitannins such as sanguiin H-6, corilagin, geraniin, oenothein B, chebulagic acid, and chebulinic acid (Table 1). Acknowledging these research gaps is essential for balanced interpretation and fostering future investigations that address the untapped potential of lesser-studied ellagitannin structures within this multifunctional compound class.
4.1. Antioxidant and Anti-Inflammatory Activities
Interception of oxidative stress and inflammatory signaling is fundamental to the health-protective effects of dietary polyphenols. Chronic oxidative damage, propelled by reactive oxygen species (ROS), underlies numerous human diseases, including cancer, cardiovascular, and inflammatory pathologies [60]. In vitro studies reveal that high-molecular-weight polyphenols, including ellagitannins, often display superior antioxidant potency compared to smaller phenolics and reference antioxidants such as ascorbic acid and α-tocopherol [60,61,62]. Their remarkable radical-scavenging ability enables disruption of free radical chain reactions, preventing lipid, protein, and DNA oxidative damage. Building on this, it is important to highlight that individual members of this group exhibit distinct yet complementary antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effects. Their complex polyphenolic structures confer the ability not only to neutralize free radicals directly but also to chelate transition metals and modulate redox-sensitive transcription factors. By attenuating oxidative stress at the molecular level, they further interrupt the activation of pro-inflammatory signaling cascades, including NF-κB and MAPK pathways, thereby reducing the production of cytokines, chemokines, and inflammatory enzymes. Furthermore, some ellagitannin derivatives can directly suppress key enzymes related to inflammation (e.g., COX and LOX), contributing to their anti-inflammatory profile. These multifaceted mechanisms underpin the therapeutic potential of ellagitannins in the prevention and management of inflammatory, cardiovascular, and neoplastic disorders [3,25,62].
A prime illustration of these bioactivities can be found in punicalagin, whose molecular characteristics and abundance in pomegranate make it a key subject in ellagitannin research. It demonstrates powerful antioxidant and anti-inflammatory activities, effectively neutralizing superoxide anions, hydroxyl radicals, and peroxynitrite while chelating transition metals and inhibiting lipid peroxidation, thereby protecting cellular membranes and nucleic acids. Numerous studies demonstrate its ability to upregulate endogenous antioxidant enzymes like superoxide dismutase (SOD) and catalase, thereby enhancing cellular defense mechanisms [50,63]. Punicalagin’s anti-inflammatory effect is underscored by inhibition of the NF-κB pathway, suppression of pro-inflammatory cytokines such as TNF-α, IL-6, IL-1β, and downregulation of COX-2 and iNOS—molecular actions that support its therapeutic potential in inflammatory diseases [11,49]. Importantly, it has been shown to inhibit vascular inflammation by reducing the expression of downstream pro-inflammatory cytokines and adhesion molecules (ICAM-1, VCAM-1), and blocking VEGF-induced endothelial signaling pathways [64].
Among sanguiins, sanguiin H-6 (SH6) is frequently identified as the principal compound responsible for antioxidant activity. Its antioxidant potential has been demonstrated in models of oxidative stress, such as lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced peroxynitrite (ONOO−) production and ischemia–reperfusion injury, where SH6 pre-treatment reduced ONOO−-mediated damage and improved kidney function [65]. Additionally, ellagitannins derived from Rubus berries, including dimeric forms such as SH6 and SH10, have been shown to act as effective radical scavengers in DPPH assays and inhibit lipid peroxidation in both bulk and emulsified methyl linoleate systems, as well as in human low-density lipoprotein in vitro [66]. SH6 significantly suppressed cytokine-induced neutrophil migration without exhibiting cytotoxicity toward neutrophils [67]. Furthermore, at a concentration of 2.5 μM, ellagitannin treatment completely inhibited both TNF-α- and IL-1β-induced IL-8 release and suppressed NF-κB transcriptional activity [68]. In another study, Sanguiin H-6 potently suppressed nitric oxide generation in a concentration-dependent manner and significantly downregulated the activity of inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS), preserving cellular viability. In addition, it effectively scavenged nitric oxide derived from sodium nitroprusside—a nitric oxide-releasing compound, demonstrating both inhibitory and direct neutralizing actions against NO-mediated cellular stress [69].
Corilagin, a prototypical gallotannin-ellagitannin hybrid, also possesses broad-spectrum antioxidant and anti-inflammatory activities. As demonstrated in both cellular and animal models, it acts as a powerful scavenger of hydroxyl and nitric oxide radicals, surpassing standard antioxidants in LDL and lipid protection assays, and effectively inhibits xanthine oxidase [31,70,71,72,73,74,75,76]. In LPS-activated RAW 264.7 cells, corilagin robustly inhibits the NF-κB pathway, restraining the release of TNF-α, IL-1β, IL-6, and COX-2 [31]. Moreover, in models of neuroinflammation and infection, it attenuates microglial activation and inflammatory injury of peripheral and central tissues by decreasing oxidative stress and pro-inflammatory mediator levels [31,77,78,79]. However, similarly to oenothein B, in the context of infection (Leishmania major-infected RAW 264.7 macrophages), Sanguiin H-6 has demonstrated preferential immune-stimulatory activity, boosting host defense mechanisms, most notably through the upregulation of cytokine expression. This context-dependent profile highlights its complex immunomodulatory activity: exerting anti-inflammatory actions under conditions of sterile inflammation, while enhancing immune response and antimicrobial defense under infectious conditions [80].
Geraniin-rich plant extracts have also consistently exhibited highly potent antioxidant activity, as evidenced across various model systems [17,81]. The ethanolic extract of Nephelium lappaceum peels demonstrated DPPH radical scavenging comparable to vitamin C, but with minimal pro-oxidant activity, paralleling commercial antioxidants [82]. Geraniin further displayed 5- to 6-fold greater FRAP activity than L-ascorbic acid and Trolox, efficiently neutralizing a spectrum of radicals, including DPPH, superoxide, hydroxyl, and nitric oxide, with IC50 values 7–14 times lower than conventional antioxidants such as ascorbic acid, BHA, and BHT [83,84,85]. Notably, geraniin mitigates cigarette smoke-induced oxidative stress in lung epithelial cells by reducing ROS accumulation and preserving cellular antioxidant defenses [86]. This exceptional capacity results from hydrogen atom transfer, generating resonance-stabilized phenoxyl radicals that terminate chain reactions. Geraniin also inhibits xanthine oxidase and lipid peroxidation, increases glutathione levels, and activates Nrf2 signaling, facilitating antioxidant gene expression [87,88,89]. In vivo studies reveal that geraniin mitigates liver injury in carbon tetrachloride-treated rats by enhancing hepatic glutathione and catalase, ameliorating oxidative damage, and improving liver function [17]. Its anti-inflammatory effects extend to inhibition of 5-lipoxygenase and iNOS in macrophages, suppression of NF-κB activation, and enhancement of macrophage phagocytosis [87,90].
Oenothein B, a dimeric macrocyclic ellagitannin prevalent in Epilobium and Oenothera species, is a well-characterized immunomodulator and antioxidant. Oenothein B-rich extracts are increasingly recognized for their potent anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, and tissue-protective properties. In a recent in vivo study by Simeonova et al., E. angustifolium extract significantly reduced colonic inflammation and oxidative stress in a DSS-induced ulcerative colitis mouse model, lowering myeloperoxidase and malondialdehyde levels, enhancing antioxidant enzyme activities, and improving hematological parameters with efficacy comparable to reference dexamethasone treatment [91]. Numerous independent in vivo studies confirm that oenothein B exerts protective effects in a variety of inflammatory models, including the amelioration of hepatic injury in alcoholic liver disease and intestinal remodeling in chemically induced ulcerative colitis [91,92,93,94]. These findings underscore the therapeutic relevance of oenothein B as a principal bioactive constituent in Epilobium-based preparations. The pharmacodynamic profile of this unique ellagitannin derivative includes reduced ROS production in stimulated neutrophils, inhibition of myeloperoxidase release with potency comparable to indomethacin, and attenuation of pro-inflammatory enzymes, including hyaluronidase and lipoxygenase [92,95]. In terms of immune responses, oenothein B activates phagocytes, induces intracellular calcium flux, ROS generation, NF-κB activation, and cytokine release in vitro [58,96]. In vivo, it triggers neutrophil infiltration and keratinocyte activation, and recent studies reveal significant neutrophil recruitment and induction of the chemokine KC [58,97,98]. Importantly, the intact dimeric macrocyclic structure is crucial for this activity, as smaller polyphenols lack similar immunostimulatory properties [58]. Further supporting its immunomodulatory profile, oenothein B dose-dependently suppresses iNOS gene and protein expression in LPS-stimulated macrophages, inhibits Toll-like receptor-mediated responses via NF-κB pathways, and stimulates γδ T and natural killer cells to produce IFN-γ, thereby enhancing anti-infective and antitumor immunity. It also regulates dendritic cell maturation and cytokine production through apoptosis-inducing mechanisms, establishing its role as a potent immune modulator with clear clinical and therapeutic relevance [97,99,100].
Chebulagic and chebulinic acids, principal ellagitannin components of Terminalia chebula extracts, demonstrate potent anti-inflammatory activity in both in vitro and in vivo models. Chebulagic acid attenuates LPS-induced inflammation in macrophage cell lines by downregulating iNOS and COX-2 expression, suppressing pro-inflammatory cytokines such as TNF-α and IL-6, and inhibiting nuclear translocation of NF-κB and STAT1/3 [101]. In a variety of animal models, chebulagic acid reduced edema, joint swelling, and inflammatory cell infiltration and mitigated symptoms in induced arthritis and colitis, supporting its therapeutic potential as an anti-inflammatory agent [13,102].
Chebulinic acid displays similar, albeit less pronounced effects. It has been demonstrated to efficiently inhibit nitric oxide production and COX-2 expression in activated macrophages, reduce pro-inflammatory chemokines and cytokines in vitro, and alleviate symptoms of acute inflammation and oxidative damage in mouse models [13,101,102]. Additionally, chebulinic acid acts as an anti-adhesive agent in bacterial inflammation, disrupting host–pathogen interactions, and provides protection against inflammatory bone loss, liver injury, and ulceration in various experimental settings [13].
The marked difference in anti-inflammatory potency between chebulagic acid and chebulinic acid is primarily attributable to their distinct structural features; specifically, chebulagic acid’s incorporation of a rigid hexahydroxydiphenoyl (HHDP) group in place of two galloyl moieties confers increased spatial hindrance and reduced flexibility, which enhances its interaction with biological targets and underlies its superior anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, and anti-infective effects compared to the more flexible, triple-galloyl chebulinic acid, as demonstrated in computational studies [59,103].
4.2. Antimicrobial Properties
The broad-spectrum antimicrobial activities of ellagitannins—including antibacterial, antiviral, and antiprotozoal effects, are well documented and continue to garner scientific interest as new drug-resistant pathogens emerge [26,104,105,106]. A compelling area of research concerns their synergistic potentiation of conventional antibiotics, which has been observed in the inhibition of key drug-resistant organisms such as methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) and carbapenem-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii, among others [107]. Importantly, their antiviral properties are equally significant; chebulagic acid and chebulinic acid, among others, have demonstrated potent inhibition of viruses including, SARS-CoV-2, herpes simplex virus (HSV-2) and influenza A virus (IAV), acting through mechanisms such as blocking viral entry, attachment, and progeny release [13,59,108,109]. Such attributes emphasize the relevance of representative ellagitannins as promising lead compounds in the ongoing search for novel, adjunctive anti-infective therapies, targeting both resistant bacterial pathogens and clinically significant viral infections in the face of escalating global antibiotic and antiviral resistance.
Pomegranate has emerged as a promising natural agent for the prevention and management of diverse respiratory disorders. Punicalagin, the principal ellagitannin in various parts of Punica granatum, demonstrates broad-spectrum antimicrobial activity against Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria, fungi, and significant respiratory viruses. Its mechanisms include disruption of microbial cell walls, inhibition of biofilm formation, modulation of quorum sensing, and interference with essential microbial enzymes. Notably, punicalagin is effective against antibiotic-resistant strains and clinically relevant respiratory and urinary pathogens, including gentamicin-resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Staphylococcus aureus, Escherichia coli, and Proteus mirabilis, supporting its role in addressing antimicrobial resistance [11,110].
In the context of viral infections, punicalagin exhibits virucidal activity against influenza viruses (A, H1N1, H3N2, B), herpesviruses, RSV, and SARS-CoV-2, acting through inhibition of viral entry, RNA replication, and progeny release [10,111,112,113]. Notably, ellagitanin-rich pomegranate extracts synergistically enhance the antiviral efficacy of oseltamivir, suppressing the replication of the influenza A virus [114]. More importantly, the ellagitannin has been found to act as an allosteric inhibitor of SARS-CoV-2 main protease (3CLpro), essential for viral polyprotein processing, and disrupt the interaction between the viral spike protein and the ACE2 receptor, potentially blocking viral entry [115]. Another recent study identified punicalagin as a potent inhibitor of the SARS-CoV-2 NSP13 helicase, a crucial enzyme for viral replication, demonstrating direct binding to the enzyme (KD = 21.6 nM), inhibiting ATP hydrolysis and DNA binding, and subsequently suppressing viral replication in A549-ACE2 and Vero cells with EC50 values of 347 nM and 196 nM, respectively [113]. According to the most recent findings, punicalagin potently inhibits the formation of liquid condensates between the nucleocapsid protein and viral RNA—a process essential for replication of multiple viruses, resulting in broad-spectrum antiviral activity. At nanomolar concentrations, it reduced tissue viral load and mitigated virus-induced inflammation and lethality in mice infected with SARS-CoV-2, vesicular stomatitis virus, and influenza A virus, by specifically targeting MAVS-dependent inflammatory pathways [116]. Punicalagin further attenuated inflammation-associated signaling in respiratory viral infections, alleviating airway inflammation and conferring protection in experimental models [117]. These multi-targeted activities are accompanied by a favorable safety profile, making punicalagin-rich extracts attractive candidates for adjunctive therapy, particularly in high-risk populations vulnerable to severe COVID-19, including the elderly and individuals with comorbidities like diabetes and cardiovascular disease [112].
Analogous to punicalagin’s antiviral effects, sanguiin H-6 (SH6) and related ellagitannins from Rubus species also exhibit significant antimicrobial and antiviral activities. Of particular note, recent in silico and in vitro studies have demonstrated that SH6 strongly binds to key SARS-CoV-2 targets, including the S1 and S2 subunits of the spike protein and the main protease (Mpro), with superior binding affinities compared to other polyphenols, inhibiting both viral entry and replication [52]. SH6′s potent antibacterial activity spans numerous Gram-positive and Gram-negative species, with minimum inhibitory concentrations reported for Streptococcus A, Streptococcus pneumoniae, Corynebacterium diphtheriae, Bacillus subtilis, Clostridium sporogenes, Staphylococcus aureus, Staphylococcus epidermidis, and Moraxella catarrhalis [118]. It also significantly inhibits Escherichia coli and Clostridium perfringens, and exerts fungistatic activity against Candida albicans [104,119].
Corilagin has demonstrated inhibitory effects against a broad spectrum of microorganisms, including bacteria, fungi, and viruses. While its activity against many pathogens such as Escherichia coli, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Klebsiella pneumoniae, and Bacillus subtilis is generally weaker, corilagin exhibits potent antibacterial effects against Staphylococcus aureus, with reported minimum inhibitory concentrations (MICs) ranging from 25 to 256 μg/mL [120,121]. Importantly, corilagin has shown the ability to significantly reduce the MICs of β-lactam antibiotics against both β-lactamase-positive and -negative methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) strains by inhibiting penicillin-binding protein 2′ (PBP2a), a key factor in MRSA antibiotic resistance [122,123,124]. Additionally, the ellagotannin displays strong antifungal activity, notably against Candida glabrata (MIC = 0.5 μg/mL) and inhibits chitin synthase II in Saccharomyces cerevisiae (IC50 = 25 μg/mL) [30,125]. It also effectively inhibits Helicobacter pylori (MIC = 4 μg/mL) and demonstrates substantial activity against multidrug-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii [126,127]. Corilagin’s broad-spectrum antiviral properties are equally noteworthy, as it inhibits key viral enzymes and entry processes for pathogens such as Epstein–Barr virus, HSV-2, hepatitis C virus, HIV-1, and notably SARS-CoV-2, where it blocks the interaction between the viral spike protein and ACE2 receptor, disrupts viral entry, and suppresses replication without cytotoxic effects, supporting its development as a multifaceted antiviral agent [128,129].
Geraniin-rich plant extracts exhibit notable antimicrobial effects against major human pathogens such as S. aureus, P. aeruginosa, S. pyogenes, and E. coli [130], and display strong antiviral activity, including the inhibition of dengue virus type 2 and enterovirus 71 by interfering with viral attachment and replication [131,132,133]. It has also been found to exert potent dose-dependent inhibition of viral entry and HIV-1 reverse transcriptase, impeding HIV infection by blocking gp120-CD4 interactions [134]. Additional studies confirm suppression of hepatitis B virus antigen release and inhibition of retroviral enzymes (protease, integrase, reverse transcriptase) [135,136,137]. In vivo, geraniin improves survival and reduces disease in EV71-infected mice, with evidence for dose-dependent efficacy [131]. Beyond antibacterial and antiviral effects, geraniin also exhibits antifungal activity against Candida species, and inhibits Plasmodium falciparum and Leishmania donovani, supporting its potential as a broad-spectrum agent against fungal and parasitic infections [138,139].
Ellagitannins, such as oenothein B have also demonstrated potent synergistic effects with β-lactam antibiotics against MRSA, reducing minimum inhibitory concentrations by several hundred-fold and potentially restoring antibiotic susceptibility [60]. In vitro studies on E. angustifolium and E. parviflorum extracts rich in oenothein B have shown strong antibacterial activity (MICs 4–512 µg/mL) against Gram-positive and Gram-negative prostatitis-causing pathogens, with efficacy comparable to levofloxacin [23]. The study also highlighted the importance of purification processes to enrich bioactive constituents, particularly oenothein B, thereby enhancing the antibacterial efficacy of the extracts. Ellagitannin-rich extracts from Epilobium hirsutum and Chamerion angustifolium (Onagraceae) effectively reduce HIV-1 release and selectively trigger apoptosis in HIV-1-infected T cells, sparing healthy cells. This activity was found to be driven by a synergistic interplay between oenothein B and quercetin, which jointly block viral replication and promote the elimination of infected cells. Moreover, extracts from C. angustifolium and Senna alexandrina further diminish the infectivity of progeny virions, supporting their utility as adjunctive agents targeting late stages of the HIV-1 lifecycle [140].
Chebulinic and chebulagic acids are also potent antiviral agents that inhibit the neuraminidase-mediated release of influenza A virus (IAV), maintaining efficacy even against oseltamivir-resistant NA/H274Y mutants, thus representing promising leads for novel neuraminidase inhibitors [59]. Both compounds also demonstrate significant antibacterial activities: Sapium baccatum-derived chebulinic acid acts against Ralstonia solanacearum and multidrug-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii, while Terminalia macroptera leaf extracts show strong effects against N. gonorrhoeae, including resistant strains [126,141]. Chebulinic acid also functions as a potent DNA gyrase inhibitor, effective against Mycobacterium tuberculosis, including quinolone-resistant strains, with molecular modeling confirming stable inhibition of the enzyme [142]. Similarly to punicalagin, it also exhibits anti-HIV activity, blocking gp120-CD4 binding to prevent viral entry and, along with chebulagic acid, inhibits HSV-2 infection by impairing viral attachment and penetration in a potent dose-dependent manner (IC50: 0.06–1.41 μg/mL) [109,143]. Finally, aqueous extracts of Terminalia chebula containing chebulinic acid reveal broad antifungal activity, particularly against dermatophytes and Candida spp. [144].
4.3. Therapeutic Potential in Cardiovascular Diseases (CVDs)
Ellagitannins have gained attention for their potential role in CVDs prevention and therapy. Increasing evidence from preclinical and clinical studies demonstrates that ellagitannins and their gut-derived metabolites, particularly urolithins, exert anti-inflammatory, anti-atherosclerotic, and endothelial-protective effects, improving cardiovascular risk factors such as lipid profile, vascular function, and oxidative stress. These emerging findings position ellagitannins as promising candidates for adjunctive dietary-based strategies to reduce the global burden of CVDs.
Punicalagin confers significant cardioprotective effects through multiple mechanisms: it enhances lipid metabolism, reduces LDL oxidation, and improves endothelial function, while its potent antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties slow atherosclerosis progression [50,145]. Studies demonstrate that pomegranate preparations rich in punicalagin improve lipid profiles in diabetes models, reduce cardiac fibrosis, and restore cardiac metabolic function by activating AMPK pathways, promoting mitochondrial health, and reducing oxidative stress [146,147]. Experimental models reveal that punicalagin pretreatment mitigates cardiac trauma during ischemia/reperfusion injury, decreases infarct size, lowers CK-MB and LDH levels, biomarkers of myocardial damage, and prevents apoptosis, effects attributed to AMPK activation and ACC phosphorylation [148]. Beyond maintaining antioxidant capacity and improving troponin T, it mitigates heart tissue apoptosis, inflammation, and DNA damage by regulating the apoptotic machinery, including caspase activity, p53, and the BCL-2 pathways [149]. Notably, clinical trials demonstrate that hydroxytyrosol and punicalagin supplementation results in reductions in oxidized LDL and improvements in vascular function and blood pressure among middle-aged adults with elevated cardiovascular risk. These findings support its potential as a cardioprotective nutraceutical, although solubility and bioavailability issues necessitate further clinical trials to establish optimal dosing regimens and delivery methods [50,150,151].
The cardioprotective effects of corilagin have also been studied in preclinical models of Ang II-induced atrial fibrosis and atrial fibrillation. By modulating the PI3K/Akt and NF-κB pathways, corilagin attenuated fibrotic tissue changes, reduced oxidative stress, and suppressed Ang II-induced upregulation of fibrotic markers, including smooth muscle alpha-actin (α-SMA), connective tissue growth factor (CTGF), collagen I, and collagen III, significantly reducing arrhythmogenic risk [152]. The ellagitannin additionally lowers blood pressure in hypertensive rats, likely through reduced noradrenaline release and vasorelaxation [153]. It also demonstrated thrombolytic potential by modulating plasminogen activators and inhibited atherosclerosis progression by reducing oxidative damage and vascular smooth muscle cell proliferation [154]. Moreover, it attenuated doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity via modulation of PI3K/Akt and NF-κB signaling pathways in a rat model [155].
Being a precursor to corilagin, geraniin has also demonstrated significant antihypertensive effects in vivo, primarily through inhibition of angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE), leading to vasodilation and blood pressure reduction [84]. It is also reported to modulate sympathetic activity by decreasing noradrenaline release at peripheral nerve terminals, independent of adrenal function. It is reported to decrease sympathetic neurotransmission by restraining noradrenaline liberation at peripheral nerve terminals [153]. Additionally, geraniin exhibits antithrombotic activity by inhibiting platelet aggregation in response to different activating stimuli and disrupting platelet-neutrophil interactions critical for thrombus formation. It also enhances fibrinolysis by inhibiting plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 (PAI-1), promoting clot breakdown, and offering potential benefits in thromboembolic and atherosclerotic conditions [17].
Similarly, chebuloyl-type ellagitannins have also been demonstrated to exert broad cardioprotective effects. Bag et al. reported that pre-administering T. chebula extract to rats reduced lipid peroxide formation and normalized marker enzyme activities in a model of isoproterenol-induced toxicity [156]. In a rat model, chebulinic acid effectively inhibited aortic contractile responses to serotonin and angiotensin II and competitively blocked prazosin binding to vascular receptors in a concentration-dependent manner. Binding assays reveal reversible, non-specific inhibition of adrenergic receptors, reducing receptor affinity and maximal binding sites, which collectively contribute to its vasodilatating properties. It also reversibly reduces maximal left ventricular pressure in isolated rat hearts at nanomolar concentrations, indicating its ability to modulate both vascular and cardiac contractility [157].
4.4. Therapeutic Potential in Metabolic Disorders
Metabolic disorders, such as diabetes, obesity, dyslipidemia, and metabolic syndrome, are tightly linked to the development and progression of cardiovascular diseases (CVDs), acting as key drivers of vascular dysfunction, atherosclerosis, and cardiac complications. The management and prevention of metabolic pathologies are therefore vital for reducing CVD morbidity and mortality. Both prior and recent studies suggest that ellagitannins and their gut-derived metabolites may positively influence metabolic pathways linked to both cardiovascular and metabolic disorders, offering a promising approach for the prevention and management of these overlapping conditions.
The antioxidant and anti-lipid peroxidation capacity of punicalagin, demonstrated in vitro, contributes to its ability to mitigate obesity-related oxidative stress and inflammation through activation of the Nrf2/Keap1 signaling axis and modulation of macrophage polarization [158]. Consistent with these findings, in vivo studies demonstrate that punicalagin supplementation regulates lipid homeostasis, enhances mitochondrial function, attenuates non-alcoholic fatty liver disease, strengthens pancreatic β-cell function and improves glycemic control in animal models [159,160]. It further supports metabolic health by inhibiting carbohydrate-digesting enzymes (α-amylase and α-glucosidase), enhancing insulin sensitivity, and reducing oxidative stress associated with hyperglycemia [9]. The ellagitannin has also demonstrated promising renoprotective effects in diabetes, cisplatin-induced acute kidney injury, and lupus nephritis models, supporting its potential as a therapeutic agent for diabetes-related complications [49,161]. In diabetic nephropathy, which affects up to 50% of end-stage renal disease patients, punicalagin showed therapeutic potential by downregulating NOX4 and inhibiting pyroptosis via the TXNIP/NLRP3 inflammasome pathway [162].
Corilagin’s antidiabetic effects are also well-documented. Functioning as a potent in vitro inhibitor of intestinal α-amylase and α-glucosidase, it effectively limits carbohydrate breakdown and glucose absorption. In animal studies, corilagin has been shown to improve insulin sensitivity by activating the PPARγ pathway, mirroring the mechanism of established antidiabetic medications such as rosiglitazone [163,164,165]. In diabetic rodent models, similar beneficial effects on glucose homeostasis have also been reported for geraniin and geraniin-rich extracts, restoring pancreatic β-cell function, enhancing insulin secretion, and improving insulin sensitivity in liver, adipose tissue, and skeletal muscles. Additionally, geraniin may alleviate serious diabetic complications such as nephropathy, retinopathy, encephalopathy, and cardiomyopathy. Many of its metabolites, including corilagin, ellagic acid, and urolithins, also exhibit anti-advanced glycation end-product (AGE) activity, reducing oxidative stress, inflammation, and fibrosis in affected organs [89].
Notable anti-obesity and anti-diabetic actions have also been demonstrated by macrocyclic ellagitannins, such as oenothein B. In a Caco-2 model, it has been shown to decrease fructose uptake by the intestinal GLUT5 transporter, which may help reduce de novo lipogenesis in the liver [166]. In vivo studies show that oenothein B supplementation reduces visceral fat, improves inflammatory markers associated with metabolic dysfunction, and boosts antioxidant defenses, including superoxide dismutase, catalase, and glutathione [92,166]. Experimental results in C. elegans indicate that oenothein B inhibits fat accumulation by modulating the expression of genes linked to lipid synthesis, oxidation, and storage (e.g., mdt-15, fat-5, and fasn-1), and upregulating key antioxidant enzymes, such as SOD and GSH-Px [167]. Although direct clinical trials for oenothein B remain limited, its safety profile and efficacy in preclinical models warrant further research as a well-tolerated adjuvant for managing metabolic disorders.
The metabolic attenuation and antidiabetic profile of chebulinic acid (Terminalia chebula), are also multifaceted and supported by both in vitro and animal studies. The ellagitannin has been shown to act as a dual inhibitor of protein tyrosine phosphatases PTPN9 and PTPN11 and promote glucose uptake through activation of the AMPK pathway [168,169]. Further evidence from studies on T. chebula extracts demonstrates α-glucosidase inhibition and improved insulin receptor signaling, which leads to upregulated GLUT4 translocation and better glucose handling in muscle tissue [170]. Additional benefits of chebulinic acids include suppression of aldose reductase activity and advanced glycation end product formation, key contributors to diabetic complications [171].
4.5. Anticancer Activity
Cancer ranks as the second leading cause of death globally after cardiovascular disease. Recent research highlights ellagitannins’ capacity to inhibit carcinogenesis and tumor progression through targeting multiple hallmarks of neoplastic diseases, affecting cell survival, apoptosis, invasion, and angiogenesis. Their key metabolites, namely ellagic acid and urolithins, execute these effects by reducing oxidative stress, modulating cellular signaling networks involved in tumor survival (PI3K/Akt, MAPK/ERK, Wnt/β-catenin and NF-κB), as well as direct regulation of apoptosis-related proteins (Bcl-XL, Bax, caspases, PARP) and EMT/migration markers (GOLPH3, MMP-2, MMP-9, N-cadherin, E-cadherin, TIMPs, Snail, Slug). Evidence from cell and animal studies further supports their ability to induce cell cycle arrest and apoptosis and suppress angiogenesis, pointing to their potential use as adjunctive, low-toxicity agents in cancer prevention and therapy.
Pomegranates, rich in ellagitannins, show considerable promise in cancer prevention and management [172]. Punicalagin’s anticancer activity is partially attributed to its capacity to selectively intensify oxidative stress, disrupt mitochondrial function, and promote senescence and apoptosis in malignant cells, while sparing normal cells. In breast cancer models, punicalagin substantially diminished the metastatic potential of MDA-MB-231 cells and reversed epithelial–mesenchymal transition (EMT) by downregulating GOLPH3, MMP-9, MMP-2, and N-cadherin levels [173]. Similarly, in prostate cancer models, the ellagitannin demonstrated significant inhibition of cell proliferation and induction of apoptosis with minimal toxicity to normal cells [174].
The anticancer activity of both punicalagin and pomegranate juice has also been studied in various colorectal cancer models. In HT-29 and HCT116 cells, treatment was found to effectively inhibit critical pro-inflammatory and survival pathways, including TNF-α-induced COX-2 expression, NF-κB nucleus translocation, AKT activity, and Anx-A1 expression, resulting in reduced proliferation and enhanced cell death [9,175,176]. Cervical cancer cells, including HeLa, exhibited dose-dependent reductions in proliferation and migration upon punicalagin treatment, mediated by multifaceted mechanisms. Besides suppressing NF-κB signaling, it downregulated matrix metalloproteinases (MMP-2, MMP-9), β-catenin, and the anti-apoptotic Bcl-2 protein, while upregulating the pro-apoptotic factors Bax and tissue inhibitors of metalloproteinases (TIMP-2, TIMP-3). In addition, punicalagin induced G1 cell cycle arrest and triggered mitochondrial apoptosis in malignant cells [177,178]. Lung carcinoma models also display marked sensitivity to punicalagin-induced cell death at low micromolar concentrations, related to a preferential G1/S arrest of the cell cycle and caspase activation in malignant populations [179]. In glioma, particularly the U87MG cell line, the ellagitannin activates both apoptotic and autophagic cytotoxic pathways. Thyroid cancers, including papillary, anaplastic, follicular, and medullary subtypes, respond to punicalagin via ATM-mediated DNA damage signaling and induction of senescence, as indicated by SA-β-gal staining and altered morphology. The anti-metastatic and tumor-suppressive actions of punicalagin have been further validated in vivo, with rat thyroid cancer models showing pronounced inhibition of tumor growth and metastatic progression [180,181].
Sanguiins have also garnered significant attention for their potential anticancer properties. Sanguiin H-6 has been shown to exert antineoplastic effects primarily through inhibition of DNA topoisomerases I and II. It demonstrated cytostatic activity against HeLa cells, suppressing proliferation at an effective concentration of 12 µM, with a dose-dependent reduction in topoisomerase activity. Additionally, SH6 exhibited notable antiangiogenic effects [53]. In studies involving HT1080 human fibrosarcoma cells, SH6 inhibited the binding of KDR/Flk-1-Fc to VEGF165 in a concentration-dependent manner and suppressed VEGF-induced proliferation of human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVECs) [182]. It has also been found to reduce metastatic potential of A549 lung cancer cells by modulating the TGF-β1-induced Smad 2/3 signaling pathway, enhancing epithelial E-cadherin expression and repressing mesenchymal markers Snail and N-cadherin during epithelial–mesenchymal transition [51]. In breast cancer models, SH6 exhibited antiproliferative cytotoxic effects in both tripple negative (MDA-MB-231) and adriamycin-resistant MCF-7/Adr cells and reduced the metastatic activity of MDA-MB-231 cells by downregulating VEGF, phosphorylated Akt, and ERK1/2 signaling pathways [183,184]. Moreover, SH6 increased the pro-apoptotic Bax/Bcl-2 ratio in both breast cancer models, shifting the fate of cancer cells toward programmed cell death. In A2780 human ovarian carcinoma cells, SH6 induced antiproliferative effects and morphological changes consistent with apoptosis without causing cell cycle arrest. It triggered early apoptotic events, including caspase activation, PARP cleavage, and activation of the MAPK signaling pathway. Increased levels of the truncated p15/BID proapoptotic protein were also reported, triggering cytochrome c release and activation of intrinsic apoptosis pathways [183,185,186].
Corilagin also displays strong antiproliferative activity across a wide range of human and murine tumor models, effectively inhibiting tumor growth and prolonging survival through a multifaceted array of molecular mechanisms. As a broadly acting antitumor agent, it consistently inhibited the proliferation and enhanced cellular sensitivity to cytotoxic agents of numerous human cancer cell lines, including nasopharyngeal, pancreatic (Bxpc-3), hepatocellular (Hep3B, SMMC7721, Bel7402, H22), laryngeal (Hep-2), gastric (SGC-7901), ovarian (SKOv3ip, Hey), lung adenocarcinoma, colon (HCT-8), glioblastoma multiforme (GBM), osteosarcoma (OS-732), metastatic carcinoma and cholangiocarcinoma [30]. It demonstrated potent antitumor activity against ovarian cancer by selectively inhibiting cancer cell growth and displaying minimal toxicity toward normal cells. It suppressed the expression of key cell cycle regulators such as Cyclin B1, Myt1, Phospho-cdc2, and Phospho-Weel, inducing cell cycle arrest at the G2/M phase and apoptosis signaling. In vivo, corilagin significantly reduces xenograft tumor growth and uniquely blocks TGF-β secretion and Snail stabilization, effectively inhibiting both canonical Smad and non-canonical ERK/AKT pathways [187]. The administration of corilagin markedly reduced tumor burden in models of Hep3B hepatocellular carcinoma, fibrosarcoma (sarcoma-180), Lewis lung carcinoma, lymphocytic leukemia (P388), hepatic carcinoma (H22), osteosarcoma, and colon carcinoma, resulting in significant prolongation of the overal survival across xenograft models [188,189]. Importantly, the synergistic interaction of corilagin with established chemotherapeutic drugs, such as cisplatin, doxorubicin, and temozolomide, has been shown to enhance chemosensitivity in hepatocellular carcinoma and glioma models, supporting its role in overcoming drug resistance [187,190].
The anticancer activity of geraniin is also validated in a broad range of human and murine malignancies, including colorectal, breast, melanoma, bladder, and lung cancer models, as well as Jurkat and HeLa carcinoma cell lines. In vitro, the ellagitannin reduces cell viability and proliferation in a dose- and time-dependent manner, inducing cell cycle arrest and triggering apoptosis through activation of the Fas death receptor and the downstream extrinsic pathway of apoptosis [20]. Additional mechanisms in orchestrating programmed cell death include targeted degradation of focal adhesion kinase, promotion of DNA fragmentation, and suppression of DNA repair processes. Moreover, geraniin disrupts oncoprotein stability through direct inhibition of both Hsp90 chaperone and ATPase functions, leading to profound decreases in Raf-1, phosphorylated Akt, and EGFR protein levels. These combined effects closely mirror the molecular actions of classical Hsp90 inhibitors, resulting in the abrogation of key prosurvival and proliferative signaling pathways within malignant cells [191]. Notably, in aggressive breast cancer 4T1 xenografts, daily geraniin administration attenuates primary tumor growth and hepatic metastasis and alters plasma protein expression profiles related to tumor aggressiveness [192]. In colorectal cancer, geraniin was shown to inhibit proliferation and induce catastrophic chromosomal instability, further promoting cytostasis and apoptosis, while selectively sparing normal mucosal cells [193,194]. Similarly to its active metabolite corilagin, geraniin has the capacity to effectively reverse TGF-β1-driven epithelial–mesenchymal transition and restore sensitivity to anoikis, resulting in disruption of the metastatic phenotype [195].
The antineoplastic activity of the ellagitannin family is also shared by macrocyclic representatives, including oenothein B. It has demonstrated strong antiproliferative and proapoptotic effects in a wide array of cancer models, including oral, cervical, prostate, hepatocellular, leukemia, and non-small cell lung cancer cell lines, while exhibiting lower cytotoxicity toward non-malignant cells compared to conventional chemotherapeutics [60,75,196,197]. In A549 lung adenocarcinoma cells, oenothein B induced G1 phase cell cycle arrest and activated mitochondria-mediated apoptosis, characterized by elevated intracellular ROS and increased expression of pro-apoptotic markers, including cleaved caspase-3, PARP, cytochrome c, and Bax. These effects appeared to be strongly dependent on ROS-driven downregulation of the PI3K/Akt/NF-κB pathway, as evidenced by the ability of ROS scavenger NAC and PI3K agonist IGF-1 to reverse both apoptosis and pathway inhibition induced by oenothein B. These findings point to oxidative stress serving as a critical upstream regulator of cell cycle arrest and intrinsic apoptotic signaling in the NSCLC model [75].
In prostate cancer studies, oenothein B and related compounds inhibit tumor cell growth and survival both in cell cultures and animal models, trigger mitochondria-driven apoptosis, and effectively inhibit enzymes critical to disease progression (e.g., 5α-reductase, aromatase, and neutral endopeptidase), validating the traditional application of Epilobium extracts for prostate health [198,199,200].
Further mechanistic insight reveals that oligomeric ellagitannins, including oenothein B, act as potent inhibitors of poly(ADP-ribose) glycohydrolase (PARG), regulating gene expression and apoptotic cell death [201]. Importantly, macrocyclic ellagitannins also function as inhibitors of viral DNA polymerases, as demonstrated in studies with Epstein–Barr virus (EBV). EBV, a member of the herpesvirus family, is strongly implicated in the pathogenesis of several human cancers, such as nasopharyngeal carcinoma, lymphomas, and certain gastric cancers. This oncogenic potential is mediated through the virus’s ability to disrupt normal cellular processes, including promoting uncontrolled cell proliferation, suppressing apoptosis, and remodeling the tumor microenvironment via oncogenic signaling networks [202].
Chebulinic acid functions as a natural multi-target antitumor agent across numerous cancer models, demonstrating particularly strong efficacy in human colorectal carcinoma. As a principal bioactive monomer within the Triphala polyherbal formulation, the T. chebula ellagitannin is essential for Triphala’s potent anticancer activity. [203].
Numerous independent studies report on the anti-proliferative, pro-apoptotic, and anti-migratory effects of chebulinic acid in this particular model, which are mechanistically linked to suppression of the PI3K/AKT and MAPK/ERK pathways, activation of caspase-3, DNA fragmentation, PARP cleavage, and mitochondrial membrane permeabilization [203,204,205]. Chebulinic acid also prevents VEGF-driven angiogenesis by inhibiting VEGFR-2 phosphorylation, supporting anti-angiogenic benefit in solid tumor malignancies where neovascularization is pivotal [206].
Furthermore, chebulinic acid has been shown to induce apoptosis in human leukemia cell lines HL-60 and NB4, and to suppress proliferation in cervical carcinoma (HeLa) cells. Uniquely, it selectively inhibits mitochondrial AAC2 (adenine nucleotide translocase) carrier activity, disrupting ATP/ADP exchange and imposing energy stress on cancer cells [205,207]. In erythroid and vascular models, it regulates transcriptional activity, inhibits PDGF-BB-induced MMP-2 expression, and blocks Akt/ERK signaling to suppress vascular remodeling and neovascularization [208].
4.6. Neuroprotective Properties
Although extensive evidence supports the neuroprotective potential of ellagitannins, it is primarily their microbial metabolites, urolithins, that can reach sufficient concentrations in brain tissue, given the limited permeability of parent ellagitannins through the blood–brain barrier (BBB) [209]. The neuroprotective properties of ellagitannins and their metabolites are intricately linked to the modulation of neuroinflammatory and oxidative stress pathways central to neurodegenerative disease pathology. They have also been reported to mitigate neuronal damage by suppressing pro-inflammatory cytokines, inhibiting NF-κB and ERK1/2 signaling, and attenuating the activation of microglia and astrocytes—key mediators of neuroinflammation in Alzheimer’s disease, traumatic brain injury, and other CNS disorders. Moreover, ellagitannins target amyloid-β toxicity, mitochondrial dysfunction, and blood–brain barrier integrity, addressing both inflammatory and pathology-specific mechanisms implicated in the progression of neurodegenerative conditions.
Punicalagin’s neuroprotective potential has been substantiated in both neuronal cell cultures and animal models, with experimental evidence supporting its capacity to inhibit amyloid-beta aggregation and microglial activation, preserve cognitive function, and reduce neuronal death through antioxidant and anti-inflammatory mechanisms. In Alzheimer’s transgenic mouse models and studies involving neonatal brain hypoxia, pomegranate-derived ellagitannins mitigate lipid oxidation and prevent neuronal death. The dietary enrichment in pregnant mothers confers a significant reduction in neonatal brain tissue loss and apoptosis via downregulation of caspase-3 activity. Furthermore, punicalagin enhances methionine-sulfoxide reductase activity and mitochondrial aldehyde dehydrogenase, regulates Bcl-xL protein stability, activates antiapoptotic pathways, and reduces neuroinflammation by suppressing TRAF-6 and NF-κB signaling [63,210,211,212].
In models of Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s diseases, corilagin has been found to inhibit amyloidogenic enzymes prolyl endopeptidase and β-secretase, modulate TLR4/Src/NOX2-driven ferroptotic pathways, and suppress oxidative stress, neuroinflammation, and iron accumulation in substantia nigra neurons, as confirmed in MPTP-induced mice and MPP+-treated N2a cells [213]. This multifaceted modulation of apoptotic, mitochondrial, and inflammatory pathways validates its promising application as a disease-modifying agent for neurodegenerative disorders.
Recent studies demonstrate that geraniin confers neuroprotection in both acute and chronic CNS injury models, further elucidating its mechanistic targets. In cerebral ischemia/reperfusion models, geraniin administration significantly reduces infarct volume, improves neurological deficits, and ameliorates neuronal pathology; these effects correlate with increased superoxide dismutase activity, decreased lipid peroxidation, and upregulation of the Nrf2/HO-1 signaling—hallmarks of antioxidant defense mechanisms in cytoprotection [214]. Moreover, rat models of spinal cord injury demonstrate that geraniin robustly attenuates oxidative stress, suppresses apoptotic activity, and mitigates neuroinflammation by restoring serum and tissue levels of the pro-inflammatory factors TNF-α, IL-1, IL-6 and COX-2 [215]. Geraniin administration also reversed haloperidol-induced neuronal damage in the striatum and ameliorated orofacial dyskinesia in rats [216]. Further experimental reports verify geraniin’s inhibitory activity on prolyl endopeptidase and β-secretase, facilitating preservation of neuropeptides and reduction in amyloid-β aggregation, implicated in Alzheimer’s pathogenesis [217,218].
Oenothein B confers neuroprotection in systemic inflammation models by dose-dependently suppressing pro-inflammatory cytokines IL-1β and IL-6, improving behavioral deficits, and reducing microglial activation and COX-2 expression in limbic brain regions. Due to its large, hydrophilic structure and limited ability to cross the BBB, it is likely that its neuroprotective effects are mediated indirectly through peripheral anti-inflammatory actions, or possibly via microbiota-derived metabolites that influence central neuroinflammatory responses [219,220].
Chebulagic and chebulinic acids, principal hydrolyzable tannins in Terminalia chebula and related species, exhibit substantial neuroprotective activity through multiple, complementary mechanisms. Chebulinic acid has shown significant efficacy against glutamate-induced excitotoxicity, a process characterized by excessive glutamate receptor activation, uncontrolled calcium influx, mitochondrial dysfunction, and ultimately neuronal death. Neuronal protection is mediated through inhibition of the MAPK pathway, restriction of calcium overload, and mitigation of oxidative stress. Additionally, chebulinic acid promotes neuronal survival by modulating the balance between pro- and anti-apoptotic factors and shifting the Bcl-2/Bax ratio [221]. Importantly, synergistic interactions with Boeravinone B further enhance antioxidant defenses and restore critical regulators of cellular redox homeostasis and aging [222]. The structurally related ellagitannin, chebulagic acid, extends these benefits by activating autophagy in SH-SY5Y human neuroblastoma cells. By engaging the AMPK–mTOR–Beclin-1–LC3 signaling axis, chebulagic acid facilitates the removal of dysfunctional proteins and rescues neurons in an MPP model of Parkinson’s disease [223]. Both chebulagic and chebulinic acids inhibit acetylcholinesterase, boost cholinergic activity, counter amyloid β aggregation, and reduce β-amyloid-driven toxicity, providing further mechanistic basis for their use in cognitive impairment and Alzheimer’s disease [12]. Recent reviews and in vivo findings further corroborate T. chebula extracts’ ability to reduce neuroinflammation, restore synaptic plasticity, improve memory and cognitive function, and confer safety in both animal and cellular models, consolidating the therapeutic potential of the plant in the prevention and potential treatment of neurodegenerative disorders [12,224].
4.7. Anti-Osteoporotic Effects
A growing body of evidence highlights the bone-protective efficacy of ellagitannin derivatives through complementary mechanisms targeting both osteoclastogenesis and inflammatory bone loss.
Punicalagin exhibits significant bone-sparing properties by inhibiting osteoclastogenesis and bone resorption in both in vitro and in vivo models. Mechanistically, punicalagin suppresses the differentiation of osteoclast precursor cells through downregulation of key osteoclast-specific marker genes, such as NFATc1, cathepsin K, c-Src, and TRAP. Its modulatory activity is also mediated through the targeted suppression of RANKL-induced activation of NF-κB and MAPK signaling cascades, which are fundamental for osteoclast maturation, survival, and bone-resorptive activity [225]. In animal models of estrogen deficiency (ovariectomized rodents) and diabetes, punicalagin administration not only preserved trabecular architecture and bone mineral density, but also attenuated systemic and local inflammation through suppression of pro-inflammatory cytokine production. Recent investigations further suggest that punicalagin may interfere with osteoclast actin-ring formation, macrophage fusion and multinucleation, critical processes in bone resorption, contributing to its therapeutic relevance in the treatment of osteoporosis and other bone metabolic disorders [225,226].
The in vitro anti-osteoporotic activity of sanguiin H-6 was demonstrated by its capacity to suppress osteoclast differentiation and bone loss, reduce reactive oxygen species production, and prevent the nuclear translocation of key transcription factors, including nuclear factor of activated T cells cytoplasmic-1 (NFATc1), c-Fos, and nuclear factor-κB (NF-κB). These mechanistic effects have also been validated in vivo, where ellagitannin supplementation inhibited osteoclast differentiation and prevented pathological bone loss [227]. Moreover, both sanguiin H-6 and R. coreanus extract have been shown to exhibit notable estrogenic activity, as evidenced by ERα-dependent proliferation in MCF-7 cells, suggesting potential benefits in postmenopausal osteoporosis [228].
Similarly to punicalagin, geraniin and its active metabolite corilagin have been found to suppress osteoclast differentiation and maturation and ameliorates osteolysis in mouse model by modulating RANKL-induced signaling pathways [229,230]. In ovariectomized rat models of postmenopausal osteoporosis, geraniin produced a marked increase in bone mineral density, trabecular bone volume, and overall bone microarchitecture, accompanied by improvement in key bone turnover (β-CTx, osteocalcin, ALP, BGP) and inflammatory (TNF-α, IL-1, and IL-6) markers in local and peripheral tissues. These effects are synergistically enhanced by the activation of the Wnt/β-catenin pathway and regulation of osteoblastic proliferation and differentiation, as well as upregulation of osteogenic transcription factors Runx2 and osterix [231].
Comparable pathways in punicalagin’s, corilagin’s, and geraniin’s antiosteoporotic activities suggest a shared structural and mechanistic basis for osteoprotection, strengthening the concept that their common metabolic products (i.e., urolithins A and B) act as the principal mediators of ellagitannins’ biological effects.
Reported biological activities, structural and mechanistic features of the representative ellagitannin derivatives are summarized in Table 1.

Table 1.
Structural specifics, distribution, and key molecular targets and biological activities of representative ellagitannins.
Table 1.
Structural specifics, distribution, and key molecular targets and biological activities of representative ellagitannins.
| Compound | Structural Specifics | Plant Species/Distribution | Key Molecular Mechanisms and Bioactivities | Refs. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sanguiin H-6 |
|
|
| [52,53,65,182,185,186,227,232] |
| Corilagin |
|
|
| [15,233,234,235,236,237,238,239] |
| Geraniin |
|
|
| [133,240,241,242] |
| Punicalagin |
|
|
| [158,243,244,245,246,247,248,249,250,251,252] |
| Oenothein B |
|
|
| [58,60,75,91,92,93,94,97,219,253,254,255,256,257,258] |
| Chebulagic acid |
|
|
| [37,59,259,260,261,262,263,264] |
| Chebulinic acid |
|
|
| [37,260,261,264] |
5. Limitations and Future Perspectives
5.1. Pharmacological and Translational Challenges
- Stability and pharmacokinetic issues
Solubility and permeability remain the major pharmacokinetic liabilities of ellagitannins. High molecular weight, extensive hydrogen-bonding capacity, and polar surface area severely limit passive diffusion across enterocyte membranes. Attempts to increase exposure by high oral dosing often founder on poor absorption and extensive first-pass metabolism or on unanticipated local gastrointestinal effects. Experimental permeability studies (e.g., on geraniin and its hydrolysis products) demonstrate low apparent permeability for intact ellagitannins, whereas smaller hydrolysis products (gallic and ellagic acids) and urolithins show improved transcellular passage. These physicochemical constraints underlie the contemporary shift from using crude extracts towards targeted delivery strategies (prodrugs, nanoencapsulation, colon-targeted systems) or towards direct administration of microbial metabolites when a systemic effect is desired [265,266].
After ingestion, ellagitannins rarely reach effective systemic concentrations; their absorption rates are low and highly variable, and their plasma half-lives are truncated by first-pass hepatic and microbial metabolism. The fate of these compounds is largely determined by extensive hydrolysis to ellagic acid and subsequent microbial transformation to urolithins—the actual bioactive metabolites in circulation [4,42,43,220]. For example, serum concentrations of ellagic acid and its precursor punicalagin observed in rodents were markedly lower than doses used in vitro. Interindividual variation in microbiota composition and metabolic capacity further exacerbates variability in urolithin production and pharmacodynamics, complicating pharmacokinetic prediction and clinical dosing [267,268]. In addition, the pharmacokinetic profile of ellagitannins appears to be complicated by the activity of efflux transporters, widely distributed in various tissues and organs (P-gp, MRPs, OATP, SGLT1). In a Caco-2 model, corilagin and its hydrolysis products, gallic acid and ellagic acid, all showed very low apparent permeability, consistent with poor intrinsic absorption. Uptake studies revealed that corilagin and gallic acid, in particular, were subject to pronounced efflux, which was markedly attenuated by inhibitors of P-glycoprotein and other multidrug-resistance proteins, indicating that these tannin-derived phenolics are substrates for intestinal efflux pumps. Ellagic acid, by contrast, appeared to rely partly on carrier-mediated influx via OATP and SGLT1, as its transport decreased in the presence of their inhibitors. These findings highlight efflux transporter phenomena as an additional variable in ellagitannins’ bioavailability, superimposed on their already low solubility and extensive metabolism [56].
- Extraction, characterization, and formulation issues
As with other high-molecular-weight polyphenols, ellagitannins exhibit substantial chemical lability, particularly under neutral to basic pH and elevated temperature, owing to multiple ester linkages and HHDP (hexahydroxydiphenoyl) groups that are prone to hydrolysis and oxidation. This instability significantly complicates their extraction, purification, and structural characterization. For example, sanguiin H-6 and lambertianin C degrade rapidly at pH 8, with half-lives dropping to ~2.5 h at 20 °C and even shorter at elevated temperatures [269]. Under more alkaline conditions (pH 10–11), many hydrolysable tannins display half-lives of under 10 min, driven by structural alterations where oxidation of phenolic groups can generate reactive quinones [270]. Similarly, studies have shown that under alkaline conditions, gallic acid undergoes oxidative dimerization, forming purpurogallin-8-carboxylic acid, which contributes to marked inhibition of xanthine oxidase activity. This illustrates how pH-dependent structural transformations can both compromise stability and, in some cases, yield new bioactive metabolites with distinct pharmacological properties [271].
In addition, isolation yields of ellagitannins can be low, and structural diversity (oligomerization, inter-ester and ether bonds, variable galloyl, HHDP and DHHDP substitutions) further complicates purification and can impede scale-up for clinical development. The formidable macrocyclic and oligomeric structures of some ellagitannins (such as oenothein B and sanguiin H-6) can pose analytical challenges, leading to signal overlap and line broadening in NMR spectroscopy and difficulties in purification and characterization [60].
- Toxicity and safety considerations
Ellagitannins are generally well-tolerated in preclinical models. For instance, chebulagic acid administered at doses up to 2000 mg/kg in Sprague-Dawley rats produced no observable toxicity [272]. Oenothein B, while not genotoxic, exhibited cytotoxic effects only following prolonged high-dose exposure over 48 h [273]. Some compounds, such as geraniin, may cause mild astringency that can reduce oral acceptability; nevertheless, overall toxicity in animal studies remains low, supporting their relative safety in preclinical contexts [134].
- Limited clinical evidence
Although large-scale clinical trials remain limited, clinical evidence for ellagitannins, ellagic acid, and their gut microbiota-derived metabolites (urolithins) in humans has been emerging across trials focused on metabolic syndrome, inflammation, muscle health, and cancer risk.
One representative randomized clinical trial tested whole pomegranate juice (rich in ellagitannins) in patients with inflammatory bowel disease (IBD). Over 12 weeks, regular intake of pomegranate juice led to significant changes in the gut microbiome and reduced fecal calprotectin, a surrogate marker for mucosal improvement, along with altered plasma cytokine profiles. The study also monitored urinary and plasma ellagitannin metabolites, confirming systemic uptake and bioconversion in humans [274].
In prostate cancer, a 4-week clinical trial examined black raspberry nectar and confectionary products standardized for ellagitannin content in men prior to prostatectomy. While focused on feasibility and safety, the trial detected dose-dependent increases in urinary urolithin A and dimethyl ellagic acid as biomarkers of ellagitannin metabolism, supporting the functional bioconversion of these polyphenols even in ill patients. These formulations have since been proposed for future cancer prevention trials [275].
A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials assessed the impact of ellagitannin-rich fruit consumption on blood pressure and vascular outcomes. Five randomized controlled trials collectively found that fruit intervention lowered diastolic blood pressure and improved endothelial function, although effects on systolic blood pressure were less robust. This reflects an anti-inflammatory and vasoprotective clinical fingerprint, consistent with mechanistic expectations [276].
Significant recent progress has come from trials on urolithin A, the direct microbial metabolite of ellagic acid. In a designed placebo-controlled study, older adults (mean age 71.7 years) given oral urolithin A daily for up to 4 months demonstrated measurable improvement in muscle endurance and mitochondrial function markers, with lower blood ceramide and C-reactive protein compared to placebo. Notably, adverse events did not differ between groups, confirming safety [277].
Additional clinical trials have shown positive effects for ellagic acid in metabolic syndrome and diabetes. Daily administration of 180 mg ellagic acid for 8 weeks led to modest but statistically significant reductions in some lipid profile variables and improved antioxidant status in adults, without serious adverse events [278]. Similar benefits have been reported for glycemic control, insulin resistance, and inflammatory markers, especially among patients with chronic disease backgrounds [279].
5.2. Emerging Research Perspectives
- Alternative routes and urolithins administration
Given their physicochemical and metabolic limitations, parenteral delivery strategies for ellagitannins and their bioactive metabolites are being actively investigated. Current preclinical studies have primarily employed oral and intraperitoneal routes for the administration of urolithins, bypassing microbial conversion, with urolithin A receiving particular attention. Evidence indicates that it can adequately cross the BBB, supporting its potential for targeting neurological conditions. Moreover, urolithin A displays a favorable pharmacokinetic profile: it is bioavailable across tested doses, does not accumulate over time, and demonstrates a relatively long half-life (17–22 h), most likely due to active enterohepatic recirculation. Administration routes should be optimized according to disease specifics, localization of organ and tissue targets, and pathophysiological context [280].
From a translational perspective, human studies on urolithin A remain limited and have thus far centered on its effects on mitochondrial and muscle health. A Phase I clinical trial confirmed the activation of mitochondrial biomarkers in both muscle and plasma, consistent with earlier findings in cell-based and in vivo models [280,281].
- Chemical modifications and formulation approaches
Chemical modification, prodrug and conjugation strategies, as well as formulation approaches, can offer substantial solutions to the bioavailability and delivery challenges faced by ellagitannins and their hydrolysis products.
For example, heat processing of strawberry purée minimally impacts the bioconversion of ellagitannins to urolithins by gut microbiota, as similar urolithin excretion profiles have been observed between fresh strawberries and thermally treated purées with equivalent ellagitannin content [282]. While processing may increase free ellagic acid, the type of food matrix and accessibility of ellagitannins do not substantially alter the microbial transformation to urolithins. Polyphenols generally occur in foods as esters, glycosides, and polymers, forms that require extensive hydrolysis by gastrointestinal enzymes and/or microbiota for absorption. It is estimated that about 48% of dietary polyphenols are transformed in the small intestine, 42% in the large intestine, and approximately 10% persist undigested [283].
Bioaccessibility of ellagic acid significantly increases throughout the digestive phases, rising during intestinal digestion due to progressive release from ellagitannins and food matrices, a process potentially facilitated by bile salts and pancreatin. Studies in diverse fruits confirm that liberation of ellagic acid is promoted by gastrointestinal digestion, enhancing its availability for microbial conversion and absorption [283]. Advances in delivery technology, notably the use of supersaturatable self-microemulsifying drug delivery systems (S-SMEDDS), have markedly increased the oral bioavailability of ellagic acid. Animal pharmacokinetic studies report a 4.7- to 5.8-fold higher area under the curve (AUC) with S-SMEDDS compared to suspensions, and reduced clearance rates [284].
Numerous micro- and nanotechnology-based delivery systems, including microspheres, nanoparticles, pH-sensitive microassemblies, and metalla-cages, have been developed to address the poor solubility and bioavailability of ellagic acid. These systems enhance aqueous solubility, membrane permeability, and targeted delivery, particularly for anticancer applications. Encapsulation methods, such as polymer-based nanoparticles, cyclodextrin complexes, and thermosensitive liposomes, have been shown to significantly elevate systemic ellagic acid concentrations, facilitate tumor-specific delivery, and potentiate cytotoxic effects on cancer cells [285].
Despite these advances, the oral bioavailability of ellagic acid remains limited by its poor solubility and membrane permeability, a consequence of its rigid structure and abundant hydroxyl groups. These characteristics classify ellagic acid as a class IV compound in the biopharmaceutical classification system, restricting its ability to reach therapeutic levels in plasma and tissues. Next-generation delivery technologies, including nanoformulations and surface-modified nanoparticles, offer promising strategies for overcoming these barriers by improving intestinal uptake and enabling lymphatic transport, thereby optimizing systemic exposure and therapeutic efficacy [286].
Multiple studies have now established that encapsulation in polymeric nanoparticles can significantly improve the oral bioavailability and therapeutic outcomes of ellagitannins and their derivative, ellagic acid. For example, poly(ε-caprolactone) nanoparticles produced by emulsion-diffusion-evaporation have been used to load ellagic acid, resulting in a 3.6-fold increase in area under the plasma concentration-time curve in rabbit models compared to free forms; oral administration protocols are typically utilized, with interventions lasting several weeks to permit both pharmacokinetic and efficacy assessments. Similarly, micro- and nanodevices using biocompatible polymers such as chitosan, soy phosphatidylcholine, maltodextrin, β-cyclodextrin, and PEGylated liposomes have been employed to provide improved stability, uptake, and retention in rodent and rabbit in vivo models, reflecting a move toward both systemic and tissue-targeted formulations. Chitosan nanoparticles, for instance, leverage their positive surface charge and biocompatibility to enhance site-specific delivery of ellagic acid to target organs, with nanoparticle sizes in the 20–60 nm range proving effective in cell models and animal studies. Routes of administration vary as appropriate to the pharmacological target, but oral, intravenous, and intraperitoneal interventions predominately prevail, depending on the tissue distribution and bioavailability objectives sought [287,288,289,290].
Intervention periods for these stabilization strategies typically range from single-dose pharmacokinetic analyses up to multi-week or even month-long regimens when evaluating sustained efficacy, antitumor, or organ-protective effects. Notably, advanced delivery devices such as pH-sensitive exosomes and dendrimer nanoparticles have now demonstrated enhanced brain delivery of urolithins in neuronal tumor models, while PEGylated liposomal platforms have been shown to prolong systemic circulation and facilitate tissue targeting for chronic disease applications [286].
Furthermore, recent advancements in micro- and nanodevices have garnered attention as promising drug delivery systems for ellagic acid, designed to enhance its bioavailability, utilizing biocompatible materials such as biopolymers [285]. Formation of geraniin-soy phosphatidylcholine complexes has shown to significantly enhance oral bioavailability and plasma retention of active metabolites, as confirmed by higher entrapment and complexation efficiencies, superior physicochemical stability, and an 11-fold increase in ellagic acid exposure compared to free geraniin [290]. In addition, encapsulation of urolithins A, B, and IsoUro-A in milk-derived exosomes improves brain delivery efficiency by 3–4 times and achieves a marked increase in antiproliferative activity and cell death in neuronal tumor models versus free forms [291]. PEGylated liposome delivery has likewise boosted the circulation half-life, cellular uptake, and antitumor potency of urolithin A in vitro and in vivo [292].
Structural modifications, such as methylated urolithin A, produce a superior effect in vivo, mitigating neuroinflammation and oxidative damage and restoring mitochondrial function in aging models [293]. In addition, chemically conjugated urolithin A-NSAID prodrugs efficiently inhibit glucuronidation and improve mucosal bioavailability and tight junction integrity in intestinal cells, widening the therapeutic window of urolithin-based interventions [294].
Microbiome-targeted strategies are also gaining traction, such as pre- or probiotic co-administration to boost specific urolithin-producing taxa. Personalized microbiome profiling can identify metabotypes most likely to respond to ellagitannin supplementation, with potential for companion biomarker design in clinical studies [295].
6. Conclusions
In summary, this review consolidates the latest advances in understanding the structure, natural occurrence, and biological roles of representative ellagitannins—punicalagin, sanguiin H-6, corilagin, geraniin, oenothein B, chebulagic, and chebulinic acids, as well as their unique transformation into bioactive urolithins via gut microbial metabolism. Robust mechanistic and preclinical evidence highlights their antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, antimicrobial, and anticancer efficacy, spanning a broad spectrum of disease states. Nevertheless, core barriers such as poor bioavailability, variability in host microbiome metabolism, and limited clinical data still impede their full therapeutic translation. Encouragingly, recent advances are addressing these translational hurdles with novel approaches: microbiome-targeted interventions, innovative drug delivery systems, and metabolite-based strategies, all aiming to improve ellagitannin bioavailability and systemic exposure to urolithins and facilitate more consistent clinical outcomes.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization R.M. and R.S.; software, R.M.; investigation, R.M. and V.E.; resources, R.M. and V.E.; writing—original draft preparation, R.M. and V.E.; writing—review and editing, R.M. and R.S.; visualization, R.M.; supervision, R.M.; project administration, G.M.; funding acquisition, G.M. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the European Union-NextGenerationEU through the National Recovery and Resilience Plan of the Republic of Bulgaria, project BG-RRP-2.004-0004-C01, “Strategic Research and Innovation Program for Development of the Medical University of Sofia”.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
All data is available in the manuscript.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Smeriglio, A.; Barreca, D.; Bellocco, E.; Trombetta, D. Proanthocyanidins and hydrolysable tannins: Occurrence, dietary intake and pharmacological effects. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2017, 174, 1244–1262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Makkar, H.P.S.; Siddhuraju, P.; Becker, K. Tannins. In Plant Secondary Metabolites; Methods in Molecular Biology™; Humana Press: Totowa, NJ, USA, 2007; Volume 393, pp. 67–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciupei, D.; Colişar, A.; Leopold, L.; Stănilă, A.; Diaconeasa, Z.M. Polyphenols: From Classification to Therapeutic Potential and Bioavailability. Foods 2024, 13, 4131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamada, H.; Wakamori, S.; Hirokane, T.; Ikeuchi, K.; Matsumoto, S. Structural Revisions in Natural Ellagitannins. Molecules 2018, 23, 1901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wall-Medrano, A. Taninos Hidrolizables; Bioquímica, Aspectos Nutricionales Y Analíticos Y. Nutr. Hosp. 2015, 31, 55–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raya-Morquecho, E.M.; Aguilar-Zarate, P.; Sepúlveda, L.; Michel, M.R.; Iliná, A.; Aguilar, C.N.; Ascacio-Valdés, J.A. Ellagitannins and Their Derivatives: A Review on the Metabolization, Absorption, and Some Benefits Related to Intestinal Health. Microbiol. Res. 2025, 16, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, J.; Wang, H.; Zhong, L.; Wei, S.; Min, X.; Deng, H.; Zhang, X.; Zhong, M.; Huang, Y. Bioactivity and biomedical applications of pomegranate peel extract: A comprehensive review. Front. Pharmacol. 2025, 16, 1569141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shabbir, M.; Rather, L.J.; Shahid-Ul-Islam Bukhari, M.N.; Shahid, M.; Ali Khan, M.; Mohammad, F. An eco-friendly dyeing of woolen yarn by Terminalia chebula extract with evaluations of kinetic and adsorption characteristics. J. Adv. Res. 2016, 7, 473–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hassan, M.H.U.; Shahbaz, M.; Momal, U.; Naeem, H.; Imran, M.; Abdelgawad, M.A.; Ghoneim, M.M.; Mostafa, E.M.; El-Ghorab, A.H.; Alsagaby, S.A.; et al. Exploring Punicalagin Potential Against Cancers: A Comprehensive Review. Food Sci. Nutr. 2025, 13, e70072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, L.T.; Chen, T.Y.; Chung, C.Y.; Noyce, R.S.; Grindley, T.B.; McCormick, C.; Lin, T.C.; Wang, G.H.; Lin, C.C.; Richardson, C.D. Hydrolyzable Tannins (Chebulagic Acid and Punicalagin) Target Viral Glycoprotein-Glycosaminoglycan Interactions to Inhibit Herpes Simplex Virus 1 Entry and Cell-to-Cell Spread. J. Virol. 2011, 85, 4386–4398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rozadi, N.; Oktavia, S.; Fauziah, F. Pharmacological Activities of Punicalagin: A Review. J. Drug Deliv. Ther. 2022, 12, 148–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afshari, A.R.; Sadeghnia, H.R.; Mollazadeh, H. A Review on Potential Mechanisms of Terminalia chebula in Alzheimer’s Disease. Adv. Pharmacol. Sci. 2016, 2016, 8964849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhingra, A.K.; Chopra, B.; Grewal, A.S.; Guarve, K. Pharmacological properties of Chebulinic acid and related ellagitannins from nature: An emerging contemporary bioactive entity. Pharmacol. Res. Mod. Chin. Med. 2022, 5, 100163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hegde, S.N.; K, L.D.; Choudhary, M.; Menon, N.; Singh, G. A comprehensive metabolome profiling of Terminalia chebula, Terminalia bellerica, and Phyllanthus emblica to explore the medicinal potential of Triphala. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 31635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, A.; Singh, A.K.; Kumar, R.; Ganguly, R.; Rana, H.K.; Pandey, P.K.; Sethi, G.; Bishayee, A.; Pandey, A.K. Corilagin in Cancer: A Critical Evaluation of Anticancer Activities and Molecular Mechanisms. Molecules 2019, 24, 3399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Londhe, J.S.; Devasagayam, T.P.A.; Foo, L.Y.; Shastry, P.; Ghaskadbi, S.S. Geraniin and amariin, ellagitannins from Phyllanthus amarus, protect liver cells against ethanol induced cytotoxicity. Fitoterapia 2012, 83, 1562–1568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, H.S.; Ton, S.H.; Kadir, K.A. Ellagitannin geraniin: A review of the natural sources, biosynthesis, pharmacokinetics and biological effects. Phytochem. Rev. 2017, 16, 159–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boakye, Y.D.; Agyare, C.; Abotsi, W.K.M.; Ayande, P.G.; Ossei, P.P.S. Anti-inflammatory activity of aqueous leaf extract of Phyllanthus muellerianus (Kuntze) Exell. and its major constituent, geraniin. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2016, 187, 17–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loaiza-Cano, V.; Monsalve-Escudero, L.M.; Filho, C.D.S.M.B.; Martinez-Gutierrez, M.; Sousa, D.P.D. Antiviral Role of Phenolic Compounds against Dengue Virus: A Review. Biomolecules 2020, 11, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.C.; Tsai, C.Y.; Kao, J.Y.; Kao, M.C.; Tsai, S.C.; Chang, C.S.; Huang, L.J.; Kuo, S.C.; Lin, J.K.; Way, T.D. Geraniin-mediated apoptosis by cleavage of focal adhesion kinase through up-regulation of Fas ligand expression in human melanoma cells. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2008, 52, 655–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kong, C.; Pang, X.; Su, Z.; Liu, Y. Botany, ethnopharmacology, phytochemistry and pharmacology of Erodii Herba Geranii Herba-An review. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2023, 302, 115858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amarowicz, R.; Janiak, M. Hydrolysable Tannins. In Encyclopedia of Food Chemistry; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019; pp. 337–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbarossa, A.; Rosato, A.; Carocci, A.; Arpini, S.; Bosisio, S.; Pagni, L.; Piatti, D.; Spinozzi, E.; Angeloni, S.; Sagratini, G.; et al. Efficacy of Willow Herb (Epilobium angustifolium L. and E. parviflorum Schreb.) Crude and Purified Extracts and Oenothein B Against Prostatic Pathogens. Antibiotics 2025, 14, 117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vadaga, A.K.; Gudla, S.S. Phytochemical composition and pharmacological benefits of Majuphal. Pharmacol. Res. Nat. Prod. 2025, 8, 100342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Harbi, S.A.; Abdulrahman, A.O.; Zamzami, M.A.; Khan, M.I. Urolithins: The Gut Based Polyphenol Metabolites of Ellagitannins in Cancer Prevention, a Review. Front. Nutr. 2021, 8, 647582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.-C.; Chou, I.-W.; Hung, M.-C. Natural tannins as anti-SARS-CoV-2 compounds. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2022, 18, 4669–4676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cosme, F.; Aires, A.; Pinto, T.; Oliveira, I.; Vilela, A.; Gonçalves, B. A Comprehensive Review of Bioactive Tannins in Foods and Beverages: Functional Properties, Health Benefits, and Sensory Qualities. Molecules 2025, 30, 800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Romero, R.; Gonzalez, T.; Urbano, B.F.; Segura, C.; Pellis, A.; Vera, M. Exploring tannin structures to enhance enzymatic polymerization. Front. Chem. 2025, 13, 1555202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De León-Medina, J.C.; Sepúlveda, L.; Buenrostro-Figueroa, J.J.; Mata-Gómez, M.A.; Flores-Gallegos, A.C.; Rodríguez-Herrera, R.; Aguilar, C.N.; Ascacio-Valdes, J.A. Production and evaluation of ellagitannase activity using a pure geraniin substrate. Food Bioprod. Process. 2025, 149, 112–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Deng, Y.; Zheng, Z.; Huang, W.; Chen, L.; Tong, Q.; Ming, Y. Corilagin, a promising medicinal herbal agent. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2018, 99, 43–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Zhang, S.L.; Tao, J.Y.; Pang, R.; Jin, F.; Guo, Y.J.; Dong, J.H.; Ye, P.; Zhao, H.Y.; Zheng, G.H. Preliminary exploration on anti-inflammatory mechanism of Corilagin (beta-1-O-galloyl-3,6-(R)-hexahydroxydiphenoyl-d-glucose) in vitro. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2008, 8, 1059–1064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshida, T.; Amakura, Y.; Yoshimura, M. Structural Features and Biological Properties of Ellagitannins in Some Plant Families of the Order Myrtales. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2010, 11, 79–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engström, M.T.; Virtanen, V.; Salminen, J.-P. Influence of the Hydrolyzable Tannin Structure on the Characteristics of Insoluble Hydrolyzable Tannin–Protein Complexes. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2022, 70, 13036–13048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lipińska, L.; Klewicka, E.; Sójka, M. The structure, occurrence and biological activity of ellagitannins: A general review. Acta Sci. Pol. Technol. Aliment. 2014, 13, 289–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moilanen, J.; Salminen, J.-P. Ecologically neglected tannins and their biologically relevant activity: Chemical structures of plant ellagitannins reveal their in vitro oxidative activity at high pH. Chemoecology 2008, 18, 73–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baert, N.; Pellikaan, W.F.; Karonen, M.; Salminen, J.-P. A study of the structure-activity relationship of oligomeric ellagitannins on ruminal fermentation in vitro. J. Dairy Sci. 2016, 99, 8041–8052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, L.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, W.; Hua, Y.; Chen, B.; Wu, Q.; Chen, D.; Liu, S.; Li, X. Ferroptosis-Inhibitory Difference between Chebulagic Acid and Chebulinic Acid Indicates Beneficial Role of HHDP. Molecules 2021, 26, 4300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Villalba, K.J.O.; Barka, F.V.; Pasos, C.V.; Rodríguez, P.E. Food Ellagitannins: Structure, Metabolomic Fate, and Biological Properties. In Tannins—Structural Properties, Biological Properties and Current Knowledge; Aires, A., Ed.; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguilar-Zarate, P.; Wong-Paz, J.E.; Buenrostro-Figueroa, J.J.; Ascacio, J.A.; Contreras-Esquivel, J.C.; Aguilar, C.N. Ellagitannins: Bioavailability, Purification and Biotechnological Degradation. Mini-Rev. Med. Chem. 2018, 18, 1244–1252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karonen, M.; Oraviita, M.; Mueller-Harvey, I.; Salminen, J.-P.; Green, R.J. Ellagitannins with Glucopyranose Cores Have Higher Affinities to Proteins than Acyclic Ellagitannins by Isothermal Titration Calorimetry. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2019, 67, 12730–12740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pidgeon, R.; Mitchell, S.; Shamash, M.; Suleiman, L.; Dridi, L.; Maurice, C.F.; Castagner, B. Diet-derived urolithin A is produced by a dehydroxylase encoded by human gut Enterocloster species. Nat. Commun. 2025, 16, 999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Villalba, R.; Giménez-Bastida, J.A.; Cortés-Martín, A.; Ávila-Gálvez, M.Á.; Tomás-Barberán, F.A.; Selma, M.V.; Espín, J.C.; González-Sarrías, A. Urolithins: A Comprehensive Update on their Metabolism, Bioactivity, and Associated Gut Microbiota. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2022, 66, 2101019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribeiro, M.; Alvarenga, L.; Cardozo, L.F.M.F.; Baptista, B.G.; Nascimento, D.; Esgalhado, M.; Mafra, D. Urolithin as a Metabolite of Ellagitannins and Ellagic Acid from Fruits and Nuts Produced by the Gut Microbiota: Its Role on Non-Communicable Diseases. Curr. Nutr. Rep. 2025, 14, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leng, P.; Wang, Y.; Xie, M. Ellagic Acid and Gut Microbiota: Interactions, and Implications for Health. Food Sci. Nutr. 2025, 13, e70133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Birk, J.W.; Provatas, A.A.; Vaziri, H.; Fan, N.; Rosenberg, D.W.; Gharaibeh, R.Z.; Jobin, C. Correlation between intestinal microbiota and urolithin metabolism in a human walnut dietary intervention. BMC Microbiol. 2024, 24, 476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, X.; Shang, F.-S.; Wang, T.-F.; Wu, D.-J.; Chen, D.-G.; Zhuang, B. Ellagic acid induces apoptosis and autophagy in colon cancer through the AMPK/mTOR pathway. Tissue Cell 2023, 81, 102032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kujawska, M.; Jodynis-Liebert, J. Potential of the ellagic acid-derived gut microbiota metabolite—Urolithin A in gastrointestinal protection. World J. Gastroenterol. 2020, 26, 3170–3181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramlagan, P.; Labib, R.M.; Farag, M.A.; Neergheen, V.S. Advances towards the analysis, metabolism and health benefits of punicalagin, one of the largest ellagitannin from plants, with future perspectives. Phytomedicine Plus 2022, 2, 100313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shabir, I.; Dar, A.H.; Dash, K.K.; Manzoor, S.; Srivastava, S.; Pandey, V.K.; Shams, R.; Bashir, I.; Khan, S.A.; Mukar, S.A. Bioactive potential of punicalagin: A comprehensive review. Appl. Food Res. 2024, 4, 100572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venusova, E.; Kolesarova, A.; Horky, P.; Slama, P. Physiological and Immune Functions of Punicalagin. Nutrients 2021, 13, 2150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ko, H.; Jeon, H.; Lee, D.; Choi, H.-K.; Kang, K.S.; Choi, K.-C. Sanguiin H6 suppresses TGF-β induction of the epithelial–mesenchymal transition and inhibits migration and invasion in A549 lung cancer. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2015, 25, 5508–5513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gesek, J.; Jakimiuk, K.; Atanasov, A.G.; Tomczyk, M. Sanguiins—Promising Molecules with Broad Biological Potential. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 12972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bastow, K.F.; Bori, I.D.; Fukushima, Y.; Kashiwada, Y.; Tanaka, T.; Nonaka, G.; Nishioka, I.; Lee, K.H. Inhibition of DNA Topoisomerases by Sanguiin H-6, a Cytotoxic Dimeric Ellagitannin from Sanguisorba officinalis. Planta Med. 1993, 59, 240–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gandhi, G.R.; Antony, P.J.; Lana, M.J.M.P.; da Silva, B.F.X.; Oliveira, R.V.; Jothi, G.; Hariharan, G.; Mohana, T.; Gan, R.Y.; Gurgel, R.Q.; et al. Natural products modulating interleukins and other inflammatory mediators in tumor-bearing animals: A systematic review. Phytomedicine 2022, 100, 154038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barboza, J.R.; Pereira, F.A.N.; Fernandes, R.A.; Vasconcelos, C.C.; Cartágenes, M.D.S.S.; Oliveira Lopes, A.J.; Melo, A.C.; Guimarães, I.D.S.; Rocha, C.Q.D.; Ribeiro, M.N.S. Cytotoxicity and Pro-Apoptotic, Antioxidant and Anti-Inflammatory Activities of Geopropolis Produced by the Stingless Bee Melipona fasciculata Smith. Biology 2020, 9, 292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mao, X.; Wu, L.F.; Zhao, H.J.; Liang, W.Y.; Chen, W.J.; Han, S.X.; Qi, Q.; Cui, Y.P.; Li, S.; Yang, G.H.; et al. Transport of Corilagin, Gallic Acid, and Ellagic Acid from Fructus Phyllanthi Tannin Fraction in Caco-2 Cell Monolayers. Evid.-Based Complement. Alternat. Med. 2016, 2016, 9205379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bastian, F.; Ito, Y.; Ogahara, E.; Ganeko, N.; Hatano, T.; Ito, H. Simultaneous Quantification of Ellagitannins and Related Polyphenols in Geranium thunbergii Using Quantitative NMR. Molecules 2018, 23, 1346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schepetkin, I.A.; Kirpotina, L.N.; Jakiw, L.; Khlebnikov, A.I.; Blaskovich, C.L.; Jutila, M.A.; Quinn, M.T. Immunomodulatory Activity of Oenothein B Isolated from Epilobium angustifolium. J. Immunol. 2009, 183, 6754–6766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, P.; Du, R.; Wang, Y.; Hou, X.; Wang, L.; Zhao, X.; Zhan, P.; Liu, X.; Rong, L.; Cui, Q. Identification of Chebulinic Acid and Chebulagic Acid as Novel Influenza Viral Neuraminidase Inhibitors. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoshida, T.; Yoshimura, M.; Amakura, Y. Chemical and Biological Significance of Oenothein B and Related Ellagitannin Oligomers with Macrocyclic Structure. Molecules 2018, 23, 552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okuda, T.; Yoshida, T.; Hatano, T. Hydrolyzable Tannins and Related Polyphenols. In Fortschritte der Chemie Organischer Naturstoffe/Progress in the Chemistry of Organic Natural Products; Herz, W., Kirby, G.W., Moore, R.E., Steglich, W., Tamm, C., Eds.; Springer: Vienna, Austria, 1995; Volume 66, pp. 1–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haslam, E. Natural Polyphenols (Vegetable Tannins) as Drugs: Possible Modes of Action. J. Nat. Prod. 1996, 59, 205–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viladomiu, M.; Hontecillas, R.; Lu, P.; Bassaganya-Riera, J. Preventive and Prophylactic Mechanisms of Action of Pomegranate Bioactive Constituents. Evid.-Based Complement. Alternat. Med. 2013, 2013, 789764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Ou, Y.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Huang, L.; Wang, X.; Wu, B.; Huang, M. Inhibitory Effect of Punicalagin on Inflammatory and Angiogenic Activation of Human Umbilical Vein Endothelial Cells. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 727920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yokozawa, T.; Chen, C.P.; Rhyu, D.Y.; Tanaka, T.; Park, J.C.; Kitani, K. Potential of Sanguiin H-6 against Oxidative Damage in Renal Mitochondria and Apoptosis Mediated by Peroxynitrite in vivo. Nephron 2002, 92, 133–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kähkönen, M.; Kylli, P.; Ollilainen, V.; Salminen, J.-P.; Heinonen, M. Antioxidant Activity of Isolated Ellagitannins from Red Raspberries and Cloudberries. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2012, 60, 1167–1174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konishi, K.; Urada, M.; Adachi, I.; Tanaka, T. Inhibitory Effect of Sanguiin H-11 on Chemotaxis of Neutrophil. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2000, 23, 213–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sangiovanni, E.; Vrhovsek, U.; Rossoni, G.; Colombo, E.; Brunelli, C.; Brembati, L.; Trivulzio, S.; Gasperotti, M.; Mattivi, F.; Bosisio, E.; et al. Ellagitannins from Rubus Berries for the Control of Gastric Inflammation: In Vitro and In Vivo Studies. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e71762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yokozawa, T.; Chen, C.P.; Tanaka, T.; Kitani, K. Effects of sanguiin H-6, a component of Sanguisorbae Radix, on lipopolysaccharide-stimulated nitric oxide production. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2002, 63, 853–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tabata, H.; Katsube, T.; Tsuma, T.; Ohta, Y.; Imawaka, N.; Utsumi, T. Isolation and evaluation of the radical-scavenging activity of the antioxidants in the leaves of an edible plant, Mallotus japonicus. Food Chem. 2008, 109, 64–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, N.; Zu, Y.; Fu, Y.; Kong, Y.; Zhao, J.; Li, X.; Li, J.; Wink, M.; Efferth, T. Antioxidant Activities and Xanthine Oxidase Inhibitory Effects of Extracts and Main Polyphenolic Compounds Obtained from Geranium sibiricum L. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2010, 58, 4737–4743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabata, H.; Katsube, T.; Moriya, K.; Utsumi, T.; Yamasaki, Y. Protective activity of components of an edible plant, Mallotus japonicus, against oxidative modification of proteins and lipids. Food Chem. 2010, 118, 548–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pham, A.T.; Malterud, K.E.; Paulsen, B.S.; Diallo, D.; Wangensteen, H. DPPH Radical Scavenging and Xanthine Oxidase Inhibitory Activity of Terminalia macroptera Leaves. Nat. Prod. Commun. 2011, 6, 1125–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, C.-W.; Lee, Y.-C.; Hung, H.-F.; Fu, H.-W.; Jeng, K.-C. Longan Seed Extract Reduces Hyperuricemia via Modulating Urate Transporters and Suppressing Xanthine Oxidase Activity. Am. J. Chin. Med. 2012, 40, 979–991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pei, X.; Xiao, J.; Wei, G.; Zhang, Y.; Lin, F.; Xiong, Z.; Lu, L.; Wang, X.; Pang, G.; Jiang, Y.; et al. Oenothein B inhibits human non-small cell lung cancer A549 cell proliferation by ROS-mediated PI3K/Akt/NF-κB signaling pathway. Chem. Biol. Interact. 2019, 298, 112–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, X.-R.; Luo, M.; Fan, L.; Zhang, T.; Liu, L.; Dong, J.-H.; Wu, G. Corilagin inhibits the double strand break-triggered NF-κB pathway in irradiated microglial cells. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2010, 25, 531–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, Y.J.; Zhao, L.; Li, X.F.; Mei, Y.W.; Zhang, S.L.; Tao, J.Y.; Zhou, Y.; Dong, J.H. Effect of Corilagin on anti-inflammation in HSV-1 encephalitis and HSV-1 infected microglias. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2010, 635, 79–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Chen, C. Corilagin prevents tert-butyl hydroperoxide-induced oxidative stress injury in cultured N9 murine microglia cells. Neurochem. Int. 2011, 59, 290–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Youn, K.; Lee, S.; Jeong, W.-S.; Ho, C.-T.; Jun, M. Protective Role of Corilagin on A β25–35 -Induced Neurotoxicity: Suppression of NF- κ B Signaling Pathway. J. Med. Food 2016, 19, 901–911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kolodziej, H.; Burmeister, A.; Trun, W.; Radtke, O.A.; Kiderlen, A.F.; Ito, H.; Hatano, T.; Yoshida, T.; Foo, L.Y. Tannins and related compounds induce nitric oxide synthase and cytokines gene expressions in Leishmania major-infected macrophage-like RAW 264.7 cells. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2005, 13, 6470–6476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ito, H. Metabolites of the Ellagitannin Geraniin and Their Antioxidant Activities. Planta Med. 2011, 77, 1110–1115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mistriyani, M.; Riyanto, S.; Windarsih, A.; Rohman, A. Antioxidant Activities and Identification of an Active Compound from Rambutan (Nephelium lappaceum L.) Peel. Indones. J. Chem. 2020, 21, 259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Ma, Y.; Wang, Y.; Su, Z.; Gu, M.; Janson, J. One-step separation and purification of hydrolysable tannins from Geranium wilfordii Maxim by adsorption chromatography on cross-linked 12% agarose gel. J. Sep. Sci. 2011, 34, 995–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, S.-Y.; Wang, C.-C.; Lu, Y.-L.; Wu, W.-C.; Hou, W.-C. Antioxidant, anti-semicarbazide-sensitive amine oxidase, and anti-hypertensive activities of geraniin isolated from Phyllanthus urinaria. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2008, 46, 2485–2492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Cui, C.; Zhao, M.; Wang, J.; Luo, W.; Yang, B.; Jiang, Y. Identification of phenolics in the fruit of emblica (Phyllanthus emblica L.) and their antioxidant activities. Food Chem. 2008, 109, 909–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muresan, X.M.; Cervellati, F.; Sticozzi, C.; Belmonte, G.; Chui, C.H.; Lampronti, I.; Borgatti, M.; Gambari, R.; Valacchi, G. The Loss of Cellular Junctions in Epithelial Lung Cells Induced by Cigarette Smoke Is Attenuated by Corilagin. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2015, 2015, 631758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.; Han, S.; Lee, K.; Park, K.H.; Cho, S.W.; Hahm, K. 5-LOX Inhibitor Modulates the Inflammatory Responses Provoked by Helicobacter pylori Infection. Helicobacter 2007, 12, 49–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, M.-H.; Lin-Shiau, S.-Y.; Ho, C.-T.; Lin, J.-H.; Lin, J.-K. Suppression of lipopolysaccharide-induced nuclear factor-κB activity by theaflavin-3,3′-digallate from black tea and other polyphenols through down-regulation of IκB kinase activity in macrophages. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2000, 59, 357–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goh, B.H.; Tan, J.B.L. Geraniin: A Promising Multifunctional Nutraceutical for Diabetes Management. Food Rev. Int. 2025, 41, 578–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haj Ali, D.; Dărăban, A.M.; Ungureanu, D.; Căta, A.; Ienașcu, I.M.C.; Dinu, S.; Dehelean, C.A.; Danciu, C. An Up-to-Date Review Regarding the Biological Activity of Geranium robertianum L. Plants 2025, 14, 918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simeonova, R.; Mihaylova, R.; Gevrenova, R.; Savov, Y.; Zheleva-Dimitrova, D. Ulceroprotective Effects of Epilobium angustifolium Extract in DSS-Induced Colitis in Mice. Curr. Issues Mol. Biol. 2025, 47, 444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Li, W.; Chen, S.Y.; Deng, X.W.; Deng, W.F.; Liu, G.; Chen, Y.J.; Cao, Y. Oenothein B ameliorates hepatic injury in alcoholic liver disease mice by improving oxidative stress and inflammation and modulating the gut microbiota. Front. Nutr. 2022, 9, 1053718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiss, A.K.; Bazylko, A.; Filipek, A.; Granica, S.; Jaszewska, E.; Kiarszys, U.; Kośmider, A.; Piwowarski, J. Oenothein B’s contribution to the anti-inflammatory and antioxidant activity of Epilobium sp. Phytomedicine 2011, 18, 557–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martins, J.L.R.; da Silva, D.M.; Florentino, I.F.; Fajemiroye, J.O.; Pinto, E.M.H.; de Oliveira, T.S.; da Rocha, F.F.; de Souza Gil, E.; Ferreira, A.L.; da Costa Santos, S.; et al. Gastroprotective Effect of oenothein B: A Romising Macrocyclic Ellagitannin. Front. J. Soc. Technol. Environ. Sci. 2024, 13, 152–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tóth, B.H.; Blazics, B.; Kéry, Á. Polyphenol composition and antioxidant capacity of Epilobium species. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2009, 49, 26–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pizzi, A. Tannins medical / pharmacological and related applications: A critical review. Sustain. Chem. Pharm. 2021, 22, 100481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramstead, A.G.; Schepetkin, I.A.; Quinn, M.T.; Jutila, M.A. Oenothein B, a Cyclic Dimeric Ellagitannin Isolated from Epilobium angustifolium, Enhances IFNγ Production by Lymphocytes. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e50546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schepetkin, I.A.; Kirpotina, L.N.; Jakiw, L.; Blaskovich, C.L.; Jutila, M.A.; Quinn, M.T. Phagocyte Immunomodulatory Activity of Oenothein B, A Macrocyclic Elligatannin Isolated from Epilobium angustifolium. FASEB J. 2010, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramstead, A.G.; Schepetkin, I.A.; Todd, K.; Loeffelholz, J.; Berardinelli, J.G.; Quinn, M.T.; Jutila, M.A. Aging influences the response of T cells to stimulation by the ellagitannin, oenothein B. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2015, 26, 367–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmid, D.; Gruber, M.; Piskaty, C.; Woehs, F.; Renner, A.; Nagy, Z.; Kaltenboeck, A.; Wasserscheid, T.; Bazylko, A.; Kiss, A.K.; et al. Inhibition of NF-κB-Dependent Cytokine and Inducible Nitric Oxide Synthesis by the Macrocyclic Ellagitannin Oenothein B in TLR-Stimulated RAW 264.7 Macrophages. J. Nat. Prod. 2012, 75, 870–875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, D.B.; Reddanna, P. Chebulagic acid (CA) attenuates LPS-induced inflammation by suppressing NF-κB and MAPK activation in RAW 264.7 macrophages. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2009, 381, 112–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, M.H.; Ali, Z.; Khan, I.A.; Khan, S.I. Anti-inflammatory Activity of Constituents Isolated from Terminalia chebula. Nat. Prod. Commun. 2014, 9, 965–968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.-Y.; Huang, S.-L.; Zhang, Y.-W.; Huang, X.-X.; Sun, F.-T.; Fu, Y.-W.; Zhang, Q.-Z. Antibacterial effects of chebulagic acid and chebulinic acid isolated from Terminalia chebula against Vibrio parahaemolyticus. Aquac. Rep. 2025, 45, 103085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puljula, E.; Walton, G.; Woodward, M.J.; Karonen, M. Antimicrobial Activities of Ellagitannins against Clostridiales perfringens, Escherichia coli, Lactobacillus plantarum and Staphylococcus aureus. Molecules 2020, 25, 3714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kolodziej, H.; Kayser, O.; Kiderlen, A.F.; Ito, H.; Hatano, T.; Yoshida, T.; Foo, L.Y. Antileishmanial Activity of Hydrolyzable Tannins and their Modulatory Effects on Nitric Oxide and Tumour Necrosis Factor-α Release in Macrophages in Vitro. Planta Med. 2001, 67, 825–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.-Q.; Wang, Y.-F.; Yang, B.-Y.; He, R.-J.; Liu, Z.-B.; Huang, Y.-L. Plant polyphenols: Antibacterial activity and structural insights. Fitoterapia 2025, 185, 106763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okwu, M.U.; Olley, M.; Akpoka, A.O.; Izevbuwa, O.E. Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) and anti-MRSA activities of extracts of some medicinal plants: A brief review. AIMS Microbiol. 2019, 5, 117–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duncan, M.C.; Onguéné, P.A.; Kihara, I.; Nebangwa, D.N.; Naidu, M.E.; Williams, D.E.; Balgi, A.D.; Andrae-Marobela, K.; Roberge, M.; Andersen, R.J.; et al. Virtual Screening Identifies Chebulagic Acid as an Inhibitor of the M2(S31N) Viral Ion Channel and Influenza A Virus. Molecules 2020, 25, 2903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kesharwani, A.; Polachira, S.K.; Nair, R.; Agarwal, A.; Mishra, N.N.; Gupta, S.K. Anti-HSV-2 activity of Terminalia chebula Retz extract and its constituents, chebulagic and chebulinic acids. BMC Complement. Altern. Med. 2017, 17, 110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abutayeh, R.F.; Ayyash, M.A.K.; Alwany, R.A.; Abuodeh, A.; Jaber, K.; Al-Najjar, M.A.A. Exploring the antimicrobial potential of pomegranate peel extracts (PPEs): Extraction techniques and bacterial susceptibility. PLoS ONE 2024, 19, e0315173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jalal, Z.; Bakour, M.; Lyoussi, B. Medicinal Plants and Zinc: Impact on COVID-19 Pandemic. Sci. World J. 2021, 2021, 9632034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suručić, R.; Tubić, B.; Stojiljković, M.P.; Djuric, D.M.; Travar, M.; Grabež, M.; Šavikin, K.; Škrbić, R. Computational study of pomegranate peel extract polyphenols as potential inhibitors of SARS-CoV-2 virus internalization. Mol. Cell. Biochem. 2021, 476, 1179–1193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, L.; Peng, Y.; Yao, H.; Wang, Y.; Li, J.; Yang, Y.; Lin, Z. Punicalagin as an allosteric NSP13 helicase inhibitor potently suppresses SARS-CoV-2 replication in vitro. Antivir. Res. 2022, 206, 105389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haidari, M.; Ali, M.; Casscells, S.W.; Madjid, M. Pomegranate (Punica granatum) purified polyphenol extract inhibits influenza virus and has a synergistic effect with oseltamivir. Phytomedicine 2009, 16, 1127–1136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saadh, M.J.; Almaaytah, A.M.; Alaraj, M.; Dababneh, M.F.; Sa’adeh, I.; Aldalaen, S.M.; Kharshid, A.M.; Alboghdadly, A.; Hailat, M.; Khaleel, A.; et al. Punicalagin and zinc (II) ions inhibit the activity of SARS-CoV-2 3CL-protease in vitro. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2021, 25, 3908–3913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, S.-Z.; Yu, L.-B.; Shen, B.; Pan, J.; Li, X.-W.; Luo, R.-B.; Fan, L.-J.; Qian, B.-S.; Zhu, Y.; Wang, Z.; et al. Disruption of the nucleocapsid-RNA condensation by punicalagin is a broad-spectrum antiviral approach. Fundam. Res. 2025, S266732582500336X. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aghaei, F.; Moradi, M.T.; Karimi, A. Punicalagin inhibits pro-inflammatory cytokines induced by influenza A virus. Eur. J. Integr. Med. 2021, 43, 101324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krauze-Baranowska, M.; Majdan, M.; Hałasa, R.; Głód, D.; Kula, M.; Fecka, I.; Orzeł, A. The antimicrobial activity of fruits from some cultivar varieties of Rubus idaeus and Rubus occidentalis. Food Funct. 2014, 5, 2536–2541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Silva, L.P.; Pereira, E.; Pires, T.C.S.P.; Alves, M.J.; Pereira, O.R.; Barros, L.; Ferreira, I.C.F.R. Rubus ulmifolius Schott fruits: A detailed study of its nutritional, chemical and bioactive properties. Food Res. Int. 2019, 119, 34–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burapadaja, S.; Bunchoo, A. Antimicrobial Activity of Tannins from Terminalia citrina. Planta Med. 1995, 61, 365–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adesina, S.K.; Idowu, O.; Ogundaini, A.O.; Oladimeji, H.; Olugbade, T.A.; Onawunmi, G.O.; Pais, M. Antimicrobial constituents of the leaves of Acalypha wilkesiana and Acalypha hispida. Phytother. Res. 2000, 14, 371–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimizu, M.; Shiota, S.; Mizushima, T.; Ito, H.; Hatano, T.; Yoshida, T.; Tsuchiya, T. Marked Potentiation of Activity of β-Lactams against Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus by Corilagin. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2001, 45, 3198–3201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lam, P.L.; Gambari, R.; Ho, Y.W.; Wong, W.Y.; Hau, D.K.; Leung, T.W.; Leung, P.H.; Chui, C.H. Anti-methicillin resistance Staphylococcus aureus and in vitro toxicology evaluation of corilagin-loaded gelatin/agar microspheres with potential biotextile applications. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 237, 123982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shiota, S.; Shimizu, M.; Sugiyama, J.; Morita, Y.; Mizushima, T.; Tsuchiya, T. Mechanisms of Action of Corilagin and Tellimagrandin I That Remarkably Potentiate the Activity of β-Lactams against Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Microbiol. Immunol. 2004, 48, 67–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, E.I.; Ahn, B.T.; Lee, H.B.; Kim, Y.K.; Lee, K.S.; Bok, S.H.; Kim, Y.T.; Kim, S.U. Inhibitory Activity for Chitin Synthase II from Saccharomyces cerevisiae by Tannins and Related Compounds. Planta Med. 2004, 67, 501–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyasaki, Y.; Rabenstein, J.D.; Rhea, J.; Crouch, M.L.; Mocek, U.M.; Kittell, P.E.; Morgan, M.A.; Nichols, W.S.; Van Benschoten, M.M.; Hardy, W.D.; et al. Isolation and Characterization of Antimicrobial Compounds in Plant Extracts against Multidrug-Resistant Acinetobacter baumannii. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e61594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.-Q.; Gu, H.-M.; Li, X.-Z.; Xu, Z.-N.; Chen, Y.-S.; Li, Y. Anti-Helicobacter pylori compounds from the ethanol extracts of Geranium wilfordii. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2013, 147, 204–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Li, Z.; Li, C.; Chen, R.; Liu, T.; Jiang, Y. Antiviral Effect of Polyphenolic Substances in Geranium wilfordii Maxim against HSV-2 Infection Using in vitro and in silico Approaches. Evid.-Based Complement. Alternat. Med. 2022, 2022, 7953728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.J.; Chen, R.H.; Hamdoun, S.; Coghi, P.; Ng, J.P.L.; Zhang, D.W.; Guo, X.; Xia, C.; Law, B.Y.K.; Wong, V.K.W. Corilagin prevents SARS-CoV-2 infection by targeting RBD-ACE2 binding. Phytomedicine 2021, 87, 153591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boakye, Y.; Agyare, C. Antimicrobial and antioxidant activities of geraniin and aqueous leaf extract of Phyllanthus muellerianus (Kuntze) Exell. Planta Med. 2013, 79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Zhang, L.; Fan, X.; Qin, C.; Liu, J. Antiviral effect of geraniin on human enterovirus 71 in vitro and in vivo. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2012, 22, 2209–2211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.H.; Tang, Y.Q.; Rathkrishnan, A.; Wang, S.M.; Ong, K.C.; Manikam, R.; Payne, B.J.; Jaganath, I.B.; Sekaran, S.D. Effects of cocktail of four local Malaysian medicinal plants (Phyllanthus spp.) against dengue virus 2. BMC Complement. Altern. Med. 2013, 13, 192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmad, S.A.A.; Palanisamy, U.D.; Khoo, J.J.; Dhanoa, A.; Hassan, S.S. Efficacy of geraniin on dengue virus type-2 infected BALB/c mice. Virol. J. 2019, 16, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perera, A.; Ton, S.H.; Palanisamy, U.D. Perspectives on geraniin, a multifunctional natural bioactive compound. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2015, 44, 243–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, R.; Huang, Y.; Ou, J.; Chen, C.; Hsu, F.; Chang, C. Screening of 25 compounds isolated from Phyllanthus species for anti-human hepatitis B virus in vitro. Phytother. Res. 2003, 17, 449–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Huang, H.; Zhou, W.; Feng, M.; Zhou, P. Anti-hepatitis B Virus Activities of Geranium carolinianum L. Extracts and Identification of the Active Components. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2008, 31, 743–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Notka, F.; Meier, G.; Wagner, R. Concerted inhibitory activities of on HIV replication in vitro and ex vivo. Antivir. Res. 2004, 64, 93–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gohar, A.A.; Lahloub, M.F.; Niwa, M. Antibacterial Polyphenol from Erodium glaucophyllum. Z. Für Naturforschung C 2003, 58, 670–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ndjonka, D.; Bergmann, B.; Agyare, C.; Zimbres, F.M.; Lüersen, K.; Hensel, A.; Wrenger, C.; Liebau, E. In vitro activity of extracts and isolated polyphenols from West African medicinal plants against Plasmodium falciparum. Parasitol. Res. 2012, 111, 827–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tahara, Y.; Fujita, M.; Zhang, T.; Wang, D.; Tateishi, H.; Togami, A.; Nyame, P.; Terasawa, H.; Monde, N.; Appiah-Kubi, J.; et al. Turkish Plants, Including Quercetin and Oenothein B, Inhibit the HIV-1 Release and Accelerate Cell Apoptosis. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2023, 46, 1535–1547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vu, T.T.; Kim, H.; Tran, V.K.; Vu, H.D.; Hoang, T.X.; Han, J.W.; Choi, Y.H.; Jang, K.S.; Choi, G.J.; Kim, J.C. Antibacterial activity of tannins isolated from Sapium baccatum extract and use for control of tomato bacterial wilt. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0181499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, K.; Tyagi, C.; Goyal, S.; Jamal, S.; Wahi, D.; Jain, R.; Bharadvaja, N.; Grover, A. Identification of chebulinic acid as potent natural inhibitor of M. tuberculosis DNA gyrase and molecular insights into its binding mode of action. Comput. Biol. Chem. 2015, 59, 37–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weaver, J.L.; Pine, P.S.; Dutschman, G.; Cheng, Y.-C.; Lee, K.-H.; Aszalos, A. Prevention of binding of rgp120 by anti-HIV active tannins. Biochem. Pharmacol. 1992, 43, 2479–2480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vonshak, A.; Barazani, O.; Sathiyamoorthy, P.; Shalev, R.; Vardy, D.; Golan-Goldhirsh, A. Screening South Indian medicinal plants for antifungal activity against cutaneous pathogens. Phytother. Res. 2003, 17, 1123–1125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.N.; Meng, X.; Li, Y.; Li, S.; Liu, Q.; Tang, G.Y.; Li, H.B. Fruits for Prevention and Treatment of Cardiovascular Diseases. Nutrients 2017, 9, 598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giamogante, F.; Marrocco, I.; Cervoni, L.; Eufemi, M.; Chichiarelli, S.; Altieri, F. Punicalagin, an active pomegranate component, is a new inhibitor of PDIA3 reductase activity. Biochimie 2018, 147, 122–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.; Zou, M.-H. AMPK, Mitochondrial Function, and Cardiovascular Disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 4987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, M.; Wang, Y.; Sun, D.; Liu, Z.; Wang, J.; Li, X.; Huo, C.; Jia, X.; Chen, W.; Fu, F.; et al. Punicalagin Pretreatment Attenuates Myocardial Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury via Activation of AMPK. Am. J. Chin. Med. 2017, 45, 53–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Missiry, M.A.; Amer, M.A.; Hemieda, F.A.E.; Othman, A.I.; Sakr, D.A.; Abdulhadi, H.L. Cardioameliorative effect of punicalagin against streptozotocin-induced apoptosis, redox imbalance, metabolic changes and inflammation. Egypt. J. Basic Appl. Sci. 2015, 2, 247–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quirós-Fernández, R.; López-Plaza, B.; Bermejo, L.M.; Palma-Milla, S.; Gómez-Candela, C. Supplementation with Hydroxytyrosol and Punicalagin Improves Early Atherosclerosis Markers Involved in the Asymptomatic Phase of Atherosclerosis in the Adult Population: A Randomized, Placebo-Controlled, Crossover Trial. Nutrients 2019, 11, 640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alalawi, S.; Albalawi, F.; Ramji, D.P. The Role of Punicalagin and Its Metabolites in Atherosclerosis and Risk Factors Associated with the Disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 8476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Tian, B.; Cong, X.; Ning, Z. Corilagin inhibits angiotensin II-induced atrial fibrosis and fibrillation in mice through the PI3K-Akt pathway. Iran. J. Basic Med. Sci. 2024, 27, 717–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, J.-T.; Lin, T.-C.; Hsu, F.-L. Antihypertensive effect of corilagin in the rat. Can. J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 1995, 73, 1425–1429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, W.; Yu, Y.; Zhang, L. Antiatherogenic Effects of Phyllanthus Emblica Associated with Corilagin and its Analogue. Yakugaku Zasshi 2005, 125, 587–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szponar, J.; Niziński, P.; Dudka, J.; Kasprzak-Drozd, K.; Oniszczuk, A. Natural Products for Preventing and Managing Anthracycline-Induced Cardiotoxicity: A Comprehensive Review. Cells 2024, 13, 1151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bag, A.; Bhattacharyya, S.K.; Chattopadhyay, R.R. The development of Terminalia chebula Retz. (Combretaceae) in clinical research. Asian Pac. J. Trop. Biomed. 2013, 3, 244–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, Y.; Kwan, C.; Hsu, F.; Cheng, J. In vitro inhibitory effects of Cheubulinic acid on the contractile responses of cardiovascular muscles. Clin. Exp. Pharmacol. Physiol. 1996, 23, 747–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, B.; Kim, C.Y.; Hwang, J.; Jo, K.; Kim, S.; Suh, H.J.; Choi, H.S. Punicalagin, a Pomegranate-Derived Ellagitannin, Suppresses Obesity and Obesity-Induced Inflammatory Responses Via the Nrf2/Keap1 Signaling Pathway. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2019, 63, 1900574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, C.; Zhang, W.; Li, J.; Du, L.; Lv, O.; Zhao, S.; Li, J. Beneficial Effects of Pomegranate on Lipid Metabolism in Metabolic Disorders. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2019, 63, 1800773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Tan, X.; Cao, Y.; An, X.; Chen, J.; Yang, L. Punicalagin Protects against Diabetic Liver Injury by Upregulating Mitophagy and Antioxidant Enzyme Activities. Nutrients 2022, 14, 2782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aladaileh, S.H.; Al-Swailmi, F.K.; Abukhalil, M.H.; Ahmeda, A.F.; Mahmoud, A.M. Punicalagin prevents cisplatin-induced nephrotoxicity by attenuating oxidative stress, inflammatory response, and apoptosis in rats. Life Sci. 2021, 286, 120071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, X.; Zhang, Y.; Cao, Y.; Chen, J.; Qin, H.; Yang, L. Punicalagin Protects Diabetic Nephropathy by Inhibiting Pyroptosis Based on TXNIP/NLRP3 Pathway. Nutrients 2020, 12, 1516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.N.; Zhao, Y.L.; Gao, X.L.; Zhao, Z.F.; Jing, Z.; Zeng, W.C.; Yang, R.; Peng, R.; Tong, T.; Wang, L.F.; et al. Intestinal α-glucosidase inhibitory activity and toxicological evaluation of Nymphaea stellata flowers extract. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2010, 131, 306–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gunawan-Puteri, M.D.; Kato, E.; Kawabata, J. α-Amylase inhibitors from an Indonesian medicinal herb, Phyllanthus urinaria. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2012, 92, 606–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, M.H.; Vasquez, Y.; Ali, Z.; Khan, I.A.; Khan, S.I. Constituents from Terminalia species increase PPARα and PPARγ levels and stimulate glucose uptake without enhancing adipocyte differentiation. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2013, 149, 490–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sugimoto, K.; Amako, M.; Takeuchi, H.; Nakagawa, K.; Yoshimura, M.; Amakura, Y.; Fujita, T.; Takenaka, S.; Inui, H. Oenothein B in Eucalyptus Leaf Extract Suppresses Fructose Absorption in Caco-2 Cells. Molecules 2021, 27, 122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Liu, Q.; Chen, Y.; Li, W.; Feng, K.; Xiao, J.; Cao, Y.; Su, Z.; Wang, G.; Chen, Y. Regulatory Effect and Mechanism of Oenothein B in Reducing Fat Accumulation in Caenorhabditis Elegans. Eur. J. Lipid Sci. Technol. 2023, 125, 2200077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.-S.; Koo, Y.-C.; Suh, H.J.; Kim, K.-Y.; Lee, K.-W. Preventive effects of chebulic acid isolated from Terminalia chebula on advanced glycation endproduct-induced endothelial cell dysfunction. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2010, 131, 567–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, S.-Y.; Kang, H.J.; Ahn, D.; Hwang, J.Y.; Kwon, S.J.; Chung, S.J. Identification of chebulinic acid as a dual targeting inhibitor of protein tyrosine phosphatases relevant to insulin resistance. Bioorg. Chem. 2019, 90, 103087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan Bulbul, M.R.; Uddin Chowdhury, M.N.; Naima, T.A.; Sami, S.A.; Imtiaj, M.S.; Huda, N.; Uddin, M.G. A comprehensive review on the diverse pharmacological perspectives of Terminalia chebula Retz. Heliyon 2022, 8, e10220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Oh, J.-G.; Kim, J.S.; Lee, K.-W. Effects of Chebulic Acid on Advanced Glycation Endproducts-Induced Collagen Cross-Links. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2014, 37, 1162–1167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, T.L.; Strandberg, K.R.; Croley, C.R.; Fraser, S.E.; Nagulapalli Venkata, K.C.; Fimognari, C.; Sethi, G.; Bishayee, A. Pomegranate bioactive constituents target multiple oncogenic and oncosuppressive signaling for cancer prevention and intervention. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2021, 73, 265–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, L.; Duan, Y.; Ma, F.; Lou, L. Punicalagin inhibits the viability, migration, invasion, and EMT by regulating GOLPH3 in breast cancer cells. J. Recept. Signal Transduct. 2020, 40, 173–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adaramoye, O.; Erguen, B.; Nitzsche, B.; Höpfner, M.; Jung, K.; Rabien, A. Punicalagin, a polyphenol from pomegranate fruit, induces growth inhibition and apoptosis in human PC-3 and LNCaP cells. Chem. Biol. Interact. 2017, 274, 100–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, P.; McClees, S.; Afaq, F. Pomegranate for Prevention and Treatment of Cancer: An Update. Molecules 2017, 22, 177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Cao, K.; Liu, X.; Zhao, L.; Feng, Z.; Liu, J. Punicalagin Regulates Signaling Pathways in Inflammation-Associated Chronic Diseases. Antioxidants 2021, 11, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, J.; Li, B.; Hong, S.; Liu, C.; Min, J.; Hu, M.; Li, Y.; Liu, Y.; Hong, L. Punicalagin suppresses the proliferation and invasion of cervical cancer cells through inhibition of the β-catenin pathway. Mol. Med. Rep. 2017, 16, 1439–1444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Chinnathambi, A.; Alharbi, S.A.; Veeraraghavan, V.P.; Mohan, S.K.; Zhang, G. Punicalagin promotes the apoptosis in human cervical cancer (ME-180) cells through mitochondrial pathway and by inhibiting the NF-kB signaling pathway. Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 2020, 27, 1100–1106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berköz, M.; Krośniak, M. Punicalagin induces apoptosis in A549 cell line through mitochondria-mediated pathway. Gen. Physiol. Biophys. 2020, 39, 557–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, X.; Cheng, X.; Zhang, L.; Yu, H.; Bao, J.; Guan, H.; Lu, R. Punicalagin from pomegranate promotes human papillary thyroid carcinoma BCPAP cell death by triggering ATM-mediated DNA damage response. Nutr. Res. 2017, 47, 63–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, X.; Yao, X.; Xu, S.; Pan, J.; Yu, H.; Bao, J.; Guan, H.; Lu, R.; Zhang, L. Punicalagin induces senescent growth arrest in human papillary thyroid carcinoma BCPAP cells via NF-κB signaling pathway. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2018, 103, 490–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.-J.; Lee, H.-K. Sanguiin H-6 blocks endothelial cell growth through inhibition of VEGF binding to VEGF receptor. Arch. Pharm. Res. 2005, 28, 1270–1274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berdowska, I.; Zieliński, B.; Saczko, J.; Sopel, M.; Gamian, A.; Fecka, I. Modulatory impact of selected ellagitannins on the viability of human breast cancer cells. J. Funct. Foods 2018, 42, 122–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, E.-H.; Park, J.Y.; Yoo, H.-S.; Yoo, J.-E.; Lee, H.L. Assessment of the anti-metastatic properties of sanguiin H-6 in HUVECs and MDA-MB-231 human breast cancer cells. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2016, 26, 3291–3294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, E.J.; Lee, D.; Baek, S.E.; Kim, K.H.; Kang, K.S.; Jang, T.S.; Lee, H.L.; Song, J.H.; Yoo, J.E. Cytotoxic effect of sanguiin H-6 on MCF-7 and MDA-MB-231 human breast carcinoma cells. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2017, 27, 4389–4392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, D.; Ko, H.; Kim, Y.J.; Kim, S.N.; Choi, K.C.; Yamabe, N.; Kim, K.H.; Kang, K.S.; Kim, H.Y.; Shibamoto, T. Inhibition of A2780 Human Ovarian Carcinoma Cell Proliferation by a Rubus Component, Sanguiin H-6. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2016, 64, 801–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milani, R.; Brognara, E.; Fabbri, E.; Finotti, A.; Borgatti, M.; Lampronti, I.; Marzaro, G.; Chilin, A.; Lee, K.K.; Kok, S.H.; et al. Corilagin Induces High Levels of Apoptosis in the Temozolomide-Resistant T98G Glioma Cell Line. Oncol. Res. Featur. Preclin. Clin. Cancer Ther. 2018, 26, 1307–1315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miyamoto, K.; Kishi, N.; Koshiura, R.; Yoshida, T.; Hatano, T.; Okuda, T. Relationship between the structures and the antitumor activities of tannins. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 1987, 35, 814–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hau, D.K.; Zhu, G.Y.; Leung, A.K.; Wong, R.S.; Cheng, G.Y.; Lai, P.B.; Tong, S.W.; Lau, F.Y.; Chan, K.W.; Wong, W.Y. In vivo anti-tumour activity of corilagin on Hep3B hepatocellular carcinoma. Phytomedicine 2010, 18, 11–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gambari, R.; Hau, D.K.-P.; Wong, W.-Y.; Chui, C.-H. Sensitization of Hep3B hepatoma Cells to Cisplatin and Doxorubicin by Corilagin: Sensitization of Hep3B hepatoma Cells to CDDP and DOX by Corilagin. Phytother. Res. 2014, 28, 781–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vassallo, A.; Vaccaro, M.C.; De Tommasi, N.; Piaz, F.D.; Leone, A. Identification of the Plant Compound Geraniin as a Novel Hsp90 Inhibitor. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e74266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hui, H.J.; Xin, C.N.Z.; Anuar, N.D.; Rao, J.S.A.; Rutt, N.H.; Rosli, N.S.M.; Venkateswaran, S.P.; Radhakrishnan, A.K. Evaluating anticancer effects of geraniin supplementation in a syngeneic mouse model of breast cancer: Identification of differentially regulated plasma proteins. Cancer Plus 2025, 7, 83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.; Wang, H.; Ni, J.; Liang, Z.; Wu, X.; Xue, J.; Wang, X. Geraniin selectively promotes cytostasis and apoptosis in human colorectal cancer cells by inducing catastrophic chromosomal instability. Mutagenesis 2018, 33, 271–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Liu, T.; Lü, H. Geraniin inhibits proliferation and induces apoptosis through inhibition of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/Akt pathway in human colorectal cancer in vitro and in vivo. Anticancer Drugs 2020, 31, 575–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ko, H. Geraniin inhibits TGF-β1-induced epithelial–mesenchymal transition and suppresses A549 lung cancer migration, invasion and anoikis resistance. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2015, 25, 3529–3534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.-C.; Chen, L.-G.; Yang, L.-L. Antitumor activity of four macrocyclic ellagitannins from Cuphea hyssopifolia. Cancer Lett. 1999, 140, 195–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sakagami, H.; Jiang, Y.; Kusama, K.; Atsumi, T.; Ueha, T.; Toguchi, M.; Iwakura, I.; Satoh, K.; Ito, H.; Hatano, T.; et al. Cytotoxic activity of hydrolyzable tannins against human oral tumor cell lines—A possible mechanism. Phytomedicine 2000, 7, 39–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piwowarski, J.P.; Bobrowska-Korczak, B.; Stanisławska, I.; Bielecki, W.; Wrzesien, R.; Granica, S.; Krupa, K.; Kiss, A.K. Evaluation of the Effect of Epilobium angustifolium Aqueous Extract on LNCaP Cell Proliferation in In Vitro and In Vivo Models. Planta Med. 2017, 83, 1159–1168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kiss, A.; Kowalski, J.; Melzig, M.F. Induction of neutral endopeptidase activity in PC-3 cells by an aqueous extract of Epilobium angustifolium L. and oenothein B. Phytomedicine 2006, 13, 284–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ducrey, B.; Marston, A.; Göhring, S.; Hartmann, R.; Hostettmann, K. Inhibition of 5α-Reductase and Aromatase by the Ellagitannins Oenothein A and Oenothein B from Epilobium Species. Planta Med. 1997, 63, 111–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blenn, C.; Wyrsch, P.; Althaus, F.R. The Ups and Downs of Tannins as Inhibitors of Poly(ADP-Ribose)glycohydrolase. Molecules 2011, 16, 1854–1877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, M.-H.; Chiou, J.-F.; Yen, K.-Y.; Yang, L.-L. EBV DNA polymerase inhibition of tannins from Eugenia uniflora. Cancer Lett. 2000, 154, 131–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshida, T.; Haba, K.; Arata, R.; Nakata, F.; Shingu, T.; Okuda, T. Tannins and Related Polyphenols of Melastomataceous Plants. VII. Nobotanins J and K, Trimeric and Tetrameric Hydrolyzable Tannins from Heterocentron roseum. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 1995, 43, 1101–1106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Li, Y.; Hu, X. Chebulinic acid derived from triphala is a promising antitumour agent in human colorectal carcinoma cell lines. BMC Complement. Altern. Med. 2018, 18, 342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- odisco, S.; Di Noia, M.A.; Onofrio, A.; Parisi, G.; Punzi, G.; Redavid, G.; De Grassi, A.; Pierri, C.L. Identification of new highly selective inhibitors of the human ADP/ATP carriers by molecular docking and in vitro transport assays. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2016, 100, 112–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, K.; Chakroborty, D.; Sarkar, C.; Lu, T.; Xie, Z.; Liu, Z.; Basu, S. Triphala and Its Active Constituent Chebulinic Acid Are Natural Inhibitors of Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor-A Mediated Angiogenesis. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e43934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chhabra, S.; Mishra, T.; Kumar, Y.; Thacker, G.; Kanojiya, S.; Chattopadhyay, N.; Narender, T.; Trivedi, A.K. Chebulinic Acid Isolated from the Fruits of Terminalia chebula Specifically Induces Apoptosis in Acute Myeloid Leukemia Cells. Phytother. Res. 2017, 31, 1849–1857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, I.-S.; Jeong, Y.J.; Park, J.-H.; Shim, S.; Jang, S.-W. Chebulinic acid inhibits smooth muscle cell migration by suppressing PDGF-Rβ phosphorylation and inhibiting matrix metalloproteinase-2 expression. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 11797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, T.; Ma, H.; Liu, W.; Niesen, D.B.; Shah, N.; Crews, R.; Rose, K.N.; Vattem, D.A.; Seeram, N.P. Pomegranate’s Neuroprotective Effects against Alzheimer’s Disease Are Mediated by Urolithins, Its Ellagitannin-Gut Microbial Derived Metabolites. ACS Chem. Neurosci. 2016, 7, 26–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morzelle, M.C.; Salgado, J.M.; Telles, M.; Mourelle, D.; Bachiega, P.; Buck, H.S.; Viel, T.A. Neuroprotective Effects of Pomegranate Peel Extract after Chronic Infusion with Amyloid-β Peptide in Mice. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0166123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, P.; Guo, Z.; Zhou, B. Neuroprotective Potential of Punicalagin, a Natural Component of Pomegranate Polyphenols: A Review. J. Integr. Neurosci. 2023, 22, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kujawska, M.; Jourdes, M.; Kurpik, M.; Szulc, M.; Szaefer, H.; Chmielarz, P.; Kreiner, G.; Krajka-Kuźniak, V.; Mikołajczak, P.Ł.; Teissedre, P.L.; et al. Neuroprotective Effects of Pomegranate Juice against Parkinson’s Disease and Presence of Ellagitannins-Derived Metabolite—Urolithin A—In the Brain. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 21, 202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, Y.; Zhou, J.; Xu, D.; Chai, S.; Xiong, N. Corilagin Attenuates Neuronal Apoptosis and Ferroptosis of Parkinson’s Disease through Regulating the TLR4/Src/NOX2 Signaling Pathway. ACS Chem. Neurosci. 2025, 16, 968–980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; He, B.; Zhang, X.; Yang, R.; Xia, X.; Chen, L.; Li, R.; Shen, Z.; Chen, P. Geraniin Protects against Cerebral Ischemia/Reperfusion Injury by Suppressing Oxidative Stress and Neuronal Apoptosis via Regulation of the Nrf2/HO-1 Pathway. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2022, 2022, 2152746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Chu, X.; Hu, G.; Chang, J. Anti-oxidant, anti-apoptotic and anti-inflammatory effects of geraniin in spinal cord injury in rats: Role of COX-2. Folia Morphol. 2025, 84, 342–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, C.-P.; Tseng, H.-C.; Fang, C.-H.; Lin, Y.-W.; Soung, H.-S. Geraniin Ameliorates Haloperidol-Induced Orofacial Dyskinesia in Rats Through Mitigating Neuronal Oxidative Stress, Neuroinflammation, and Apoptosis via Modulation of the Nrf2 Signaling Pathway. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 5458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.H.; Jun, M.; Choi, J.Y.; Yang, E.J.; Hur, J.M.; Bae, K.; Seong, Y.H.; Huh, T.L.; Song, K.S. Plant phenolics as prolyl endopeptidase inhibitors. Arch. Pharm. Res. 2007, 30, 827–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Youn, K.; Jun, M. In Vitro BACE1 Inhibitory Activity of Geraniin and Corilagin from Geranium thunbergii. Planta Med. 2013, 79, 1038–1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okuyama, S.; Makihata, N.; Yoshimura, M.; Amakura, Y.; Yoshida, T.; Nakajima, M.; Furukawa, Y. Oenothein B Suppresses Lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-Induced Inflammation in the Mouse Brain. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2013, 14, 9767–9778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piwowarski, J.P.; Granica, S.; Stefańska, J.; Kiss, A.K. Differences in Metabolism of Ellagitannins by Human Gut Microbiota ex Vivo Cultures. J. Nat. Prod. 2016, 79, 3022–3030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, J.H.; Shin, M.-S.; Hwang, G.S.; Oh, S.T.; Hwang, J.J.; Kang, K.S. Chebulinic acid attenuates glutamate-induced HT22 cell death by inhibiting oxidative stress, calcium influx and MAPKs phosphorylation. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2018, 28, 249–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biradar, S.P.; Tamboli, A.S.; Khandare, R.V.; Pawar, P.K. Chebulinic acid and Boeravinone B act as anti-aging and anti-apoptosis phyto-molecules during oxidative stress. Mitochondrion 2019, 46, 236–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.J.; Kim, J.; Kang, K.S.; Lee, K.T.; Yang, H.O. Neuroprotective Effect of Chebulagic Acid via Autophagy Induction in SH-SY5Y Cells. Biomol. Ther. 2014, 22, 275–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, H.; Lu, H.; Fang, N.; Su, J.; Li, R.; Wang, W.; Zhang, Y. The potential of Terminalia chebula in alleviating mild cognitive impairment: A review. Front. Pharmacol. 2024, 15, 1484040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Bai, J.; Zhang, W.; Ge, G.; Wang, Q.; Liang, X.; Li, N.; Gu, Y.; Li, M.; Xu, W.; et al. Protective Effects of Punicalagin on Osteoporosis by Inhibiting Osteoclastogenesis and Inflammation via the NF-κB and MAPK Pathways. Front. Pharmacol. 2020, 11, 696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.; Hua, Q.; Chen, L.; Zhang, J.; Zhao, H.; Meng, X.; Zhong, F.; Gao, T. Punicalagin prevents the bone loss of diabetic mice induced by high-fat diet via the metabolism of gut microbiota. eFood 2024, 5, e186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakai, E.; Aoki, Y.; Yoshimatsu, M.; Nishishita, K.; Iwatake, M.; Fukuma, Y.; Okamoto, K.; Tanaka, T.; Tsukuba, T. Sanguiin H-6, a constituent of Rubus parvifolius L., inhibits receptor activator of nuclear factor-κB ligand-induced osteoclastogenesis and bone resorption in vitro and prevents tumor necrosis factor-α-induced osteoclast formation in vivo. Phytomedicine 2016, 23, 828–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trinh, T.A.; Park, E.-J.; Lee, D.; Song, J.H.; Lee, H.L.; Kim, K.H.; Kim, Y.; Jung, K.; Kang, K.S.; Yoo, J.-E. Estrogenic Activity of Sanguiin H-6 through Activation of Estrogen Receptor α Coactivator-binding Site. Nat. Prod. Sci. 2019, 25, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Xiao, F.; Zhai, Z.; Jiang, C.; Liu, X.; Li, H.; Qu, X.; Ouyang, Z.; Fan, Q.; Tang, T.; Qin, A.; et al. Geraniin suppresses RANKL-induced osteoclastogenesis in vitro and ameliorates wear particle-induced osteolysis in mouse model. Exp. Cell Res. 2015, 330, 91–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, S.; Su, Y.; Huang, L.; Deng, S.; Yan, G.; Yang, X.; Chen, R.; Xian, Y.; Liang, J.; Liu, Q.; et al. Corilagin attenuates osteoclastic osteolysis by enhancing HO-1 and inhibiting ROS. J. Biochem. Mol. Toxicol. 2022, 36, e23049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Wang, M.; Cui, X.; Li, Z.; Guo, S.; Gao, F.; Ma, M.; Wang, Z. Antiosteoporosis effect of geraniin on ovariectomy-induced osteoporosis in experimental rats. J. Biochem. Mol. Toxicol. 2021, 35, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguilera-Correa, J.J.; Fernández-López, S.; Cuñas-Figueroa, I.D.; Pérez-Rial, S.; Alakomi, H.L.; Nohynek, L.; Oksman-Caldentey, K.M.; Salminen, J.P.; Esteban, J.; Cuadros, J.; et al. Sanguiin H-6 Fractionated from Cloudberry (Rubus chamaemorus) Seeds Can Prevent the Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus Biofilm Development during Wound Infection. Antibiotics 2021, 10, 1481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Qin, X.; Ma, W.; Jia, S.; Zhang, X.; Yang, X.; Pan, D.; Jin, F. Corilagin induces apoptosis and autophagy in NRF2-addicted U251 glioma cell line. Mol. Med. Rep. 2021, 23, 320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, M.H.; Baek, S.H.; Hwang, S.T.; Um, J.; Ahn, K.S. Corilagin exhibits differential anticancer effects through the modulation of STAT3 /5 and MAPKs in human gastric cancer cells. Phytother. Res. 2022, 36, 2449–2462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, Y.; Zhang, G.; Li, Y.; Xu, J.; Yuan, J.; Zhang, B.; Hu, T.; Song, G. Corilagin inhibits breast cancer growth via reactive oxygen species-dependent apoptosis and autophagy. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2018, 22, 3795–3807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, L.; Jin, H.; Zhou, J.; Chen, L.; Lu, Y.; Ming, Y.; Yu, Y. A potential anti-tumor herbal medicine, Corilagin, inhibits ovarian cancer cell growth through blocking the TGF-β signaling pathways. BMC Complement. Altern. Med. 2013, 13, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, F.; Liu, L.; Lin, Y.; Yang, Z.; Qiu, F. Corilagin Inhibits Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma by Inducing DNA Damage and Down-Regulation of RNF8. Anticancer Agents Med. Chem. 2019, 19, 1021–1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreira, J.; Klein-Júnior, L.C.; Filho, V.C.; Buzzi, F.D.C. Anti-hyperalgesic activity of corilagin, a tannin isolated from Phyllanthus niruri L. (Euphorbiaceae). J. Ethnopharmacol. 2013, 146, 318–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, M.; Jiang, Y.; Wang, J.; Luo, T.; Yi, Y.; Wang, H.; Wang, L. The Effect and Mechanism of Corilagin from Euryale Ferox Salisb Shell on LPS-Induced Inflammation in Raw264.7 Cells. Foods 2023, 12, 979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okuda, T.; Mori, K.; Hatano, T. The distribution of geraniin and mallotusinic acid in the order geraniales. Phytochemistry 1980, 19, 547–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palanisamy, U.D.; Ling, L.T.; Manaharan, T.; Appleton, D. Rapid isolation of geraniin from Nephelium lappaceum rind waste and its anti-hyperglycemic activity. Food Chem. 2011, 127, 21–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okuda, T.; Yoshida, T.; Hatano, T. Constituents of Geranium thunbergii Sieb. et Zucc. Part 12. Hydrated stereostructure and equilibration of geraniin. J. Chem. Soc. Perkin 1982, 1, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, J.-P.; Kim, D.; Song, X.; Chater, J.M.; Heinitz, C.C.; Wang, Y. Uncovering the biosynthetic pathways of key flavor and color compounds in pomegranate using pathway-based metabolomics. RSC Adv. 2025, 15, 22831–22842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marzouk, M.S.A.; El-Toumy, S.A.A.; Moharram, F.A. Pharmacologically Active Ellagitannins from Terminalia myriocarpa. Planta Med. 2002, 68, 523–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, D.P.; Huang, H.Y.; Chou, C.L.; Cheng, L.C.; Wang, W.C.; Tian, Y.F.; Fang, C.L.; Lin, K.Y. Punicalagin is cytotoxic to human colon cancer cells by modulating cell proliferation, apoptosis, and invasion. Hum. Exp. Toxicol. 2023, 42, 09603271231213979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, D.P.; Uen, Y.H.; Kang, N.W.; Chang, C.C.; Tian, Y.F.; Fang, C.L.; Lin, K.Y. Punicalagin Restricts Growth, Promotes Apoptosis, and Reduces Invasion in Human Gastric Cancer Cells. Dose-Response 2024, 22, 15593258241264954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subkorn, P.; Norkaew, C.; Deesrisak, K.; Tanyong, D. Punicalagin, a pomegranate compound, induces apoptosis and autophagy in acute leukemia. PeerJ 2021, 9, e12303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, T.; Zhang, X.; Wang, H. Punicalagin inhibited proliferation, invasion and angiogenesis of osteosarcoma through suppression of NF-κB signaling. Mol. Med. Rep. 2020, 22, 2386–2394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brighenti, V.; Iseppi, R.; Pinzi, L.; Mincuzzi, A.; Ippolito, A.; Messi, P.; Sanzani, S.M.; Rastelli, G.; Pellati, F. Antifungal Activity and DNA Topoisomerase Inhibition of Hydrolysable Tannins from Punica granatum L. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 4175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, J.; Long, Y.; Ren, G.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, J.; Huang, R.; Yang, L. Punicalagin Reversed the Hepatic Injury of Tetrachloromethane by Antioxidation and Enhancement of Autophagy. J. Med. Food 2019, 22, 1271–1279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Kong, K.W.; Wu, D.T.; Liu, H.Y.; Li, H.B.; Zhang, J.R.; Gan, R.Y. Pomegranate peel-derived punicalagin: Ultrasonic-assisted extraction, purification, and its α-glucosidase inhibitory mechanism. Food Chem. 2022, 374, 131635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganesan, T.; Sinniah, A.; Chik, Z.; Alshawsh, M.A. Punicalagin Regulates Apoptosis-Autophagy Switch via Modulation of Annexin A1 in Colorectal Cancer. Nutrients 2020, 12, 2430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Qin, Q.; Chen, H.; Huang, Q.; Song, M.; Xiao, S.; Cao, L.; Cao, Y. The anti-proliferative activity and cellular antioxidant activity of oenothein B and its content in different Eucalyptus species and region. J. Future Foods 2023, 3, 392–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshimura, M.; Akiyama, H.; Kondo, K.; Sakata, K.; Matsuoka, H.; Amakura, Y.; Teshima, R.; Yoshida, T. Immunological Effects of Oenothein B, an Ellagitannin Dimer, on Dendritic Cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2012, 14, 46–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esposito, C.; Santarcangelo, C.; Masselli, R.; Buonomo, G.; Nicotra, G.; Insolia, V.; D’Avino, M.; Caruso, G.; Buonomo, A.R.; Sacchi, R.; et al. Epilobium angustifolium L. extract with high content in oenothein B on benign prostatic hyperplasia: A monocentric, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical trial. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2021, 138, 111414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyamoto, K.; Nomura, M.; Sasakura, M.; Matsui, E.; Koshiura, R.; Murayama, T.; Furukawa, T.; Hatano, T.; Yoshida, T.; Okuda, T. Antitumor Activity of Oenothein B, a Unique Macrocyclic Ellagitannin. Jpn. J. Cancer Res. 1993, 84, 99–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okuyama, S.; Furukawa, Y.; Yoshimura, M.; Amakura, Y.; Nakajima, M.; Yoshida, T.; Oenothein, B.; Ellagitannin, B. Activates the Extracellular Signal-Regulated Kinase 2 Signaling Pathway in the Mouse Brain. Plants 2021, 10, 1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lesuisse, D.; Berjonneau, J.; Ciot, C.; Devaux, P.; Doucet, B.; Gourvest, J.F.; Khemis, B.; Lang, C.; Legrand, R.; Lowinski, M.; et al. Determination of Oenothein B as the Active 5-α-Reductase-Inhibiting Principle of the Folk Medicine Epilobium parviflorum. J. Nat. Prod. 1996, 59, 490–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshida, T.; Fujii, R.; Okuda, T. Revised structures of chebulinic acid and chebulagic acid. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 1980, 28, 3713–3715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Yan, H.; Teng, S.; Yang, X. A liquid chromatography–tandem mass spectrometry method for preclinical pharmacokinetics and tissue distribution of hydrolyzable tannins chebulinic acid and chebulagic acid in rats. Biomed. Chromatogr. 2019, 33, e4425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Q.; Song, J.; Qiao, C.; Wong, L.; Xu, H. Preparative isolation of hydrolysable tannins chebulagic acid and chebulinic acid from Terminalia chebula by high-speed counter-current chromatography. J. Sep. Sci. 2006, 29, 1653–1657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.G.; Lee, J.Y.; Gallo, R.A.; Tao, W.; Tse, D.; Doddapaneni, R.; Pelaez, D. Therapeutic targeting of oncogenic transcription factors by natural products in eye cancer. Pharmacol. Res. 2018, 129, 365–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Ju, C.; Zhu, Q.; An, Y.; Hao, J.; Yang, W.; Wang, W.; Meng, X. Preparation and stability of chebulagic acid and chebulinic acid from Terminalia chebula and their biological activity. Pak. J. Pharm. Sci. 2024, 37, 1289–1301. [Google Scholar]
- Chuang, H.Y.; Ng, L.T.; Lin, L.T.; Chang, J.S.; Chen, J.Y.; Lin, T.C.; Lin, C.C. Hydrolysable tannins of tropical almond show antifibrotic effects in TGF-β1-induced hepatic stellate cells. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2011, 91, 2777–2784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elendran, S.; Muniyandy, S.; Lee, W.W.; Palanisamy, U.D. Permeability of the ellagitannin geraniin and its metabolites in a human colon adenocarcinoma Caco-2 cell culture model. Food Funct. 2019, 10, 602–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Llorach, R.; Cerdá, B.; Cerón, J.J.; Espín, J.C.; Tomás-Barberán, F.A. Evaluation of the bioavailability and metabolism in the rat of punicalagin, an antioxidant polyphenol from pomegranate juice. Eur. J. Nutr. 2003, 42, 18–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Sarrías, A.; García-Villalba, R.; Núñez-Sánchez, M.Á.; Tomé-Carneiro, J.; Zafrilla, P.; Mulero, J.; Tomás-Barberán, F.A.; Espín, J.C. Identifying the limits for ellagic acid bioavailability: A crossover pharmacokinetic study in healthy volunteers after consumption of pomegranate extracts. J. Funct. Foods 2015, 19, 225–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alfei, S.; Marengo, B.; Zuccari, G. Oxidative Stress, Antioxidant Capabilities, and Bioavailability: Ellagic Acid or Urolithins? Antioxidants 2020, 9, 707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sójka, M.; Janowski, M.; Grzelak-Błaszczyk, K. Stability and transformations of raspberry (Rubus idaeus L.) ellagitannins in aqueous solutions. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2019, 245, 1113–1122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuominen, A.; Sundman, T. Stability and Oxidation Products of Hydrolysable Tannins in Basic Conditions Detected by HPLC/DAD–ESI/QTOF/MS. Phytochem. Anal. 2013, 24, 424–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Honda, S.; Ishida, R.; Hidaka, K.; Masuda, T. Stability of Polyphenols under Alkaline Conditions and the Formation of a Xanthine Oxidase Inhibitor from Gallic Acid in a Solution at pH 7.4. Food Sci. Technol. Res. 2019, 25, 123–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aamir, K.; Sugumar, V.; Khan, H.U.; Looi, C.Y.; Juneja, R.; Waqas, M.; Arya, A. Non-toxic nature of chebulinic acid on biochemical, hematological and histopathological analysis in normal Sprague Dawley rats. Toxicol. Res. 2022, 38, 159–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, C.A.; Silva, C.R.; Véras, J.H.; Chen-Chen, L.; Ferri, P.H.; Santos, S.D.C. Genotoxicity and cytotoxicity evaluation of oenothein B and its protective effect against mitomycin C-induced mutagenic action. Mutat. Res. Toxicol. Environ. Mutagen. 2014, 767, 8–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minato, I.; Mena, P.; Ricciardiello, L.; Scaioli, E.; Belluzzi, A.; Rotondo, E.; Derlindati, E.; Montanini, B.; Michelini, C.; Tosi, N.; et al. Evidence for a Modulatory Effect of a 12-Week Pomegranate Juice Intervention on the Transcriptional Response in Inflammatory Bowel Disease Patients Reducing Fecal Calprotectin Levels: Findings From a Proof-of-Principle Study. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2025, 69, e70067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberts, K.M.; Grainger, E.M.; Thomas-Ahner, J.M.; Hinton, A.; Gu, J.; Riedl, K.; Vodovotz, Y.; Abaza, R.; Schwartz, S.J.; Clinton, S.K. Dose-Dependent Increases in Ellagitannin Metabolites as Biomarkers of Intake in Humans Consuming Standardized Black Raspberry Food Products Designed for Clinical Trials. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2020, 64, 1900800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Looi, D.; Moorthy, M.; Chaiyakunapruk, N.; Palanisamy, U.D. Impact of ellagitannin-rich fruit consumption on blood pressure: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. J. Funct. Foods 2022, 99, 105320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; D’Amico, D.; Shankland, E.; Bhayana, S.; Garcia, J.M.; Aebischer, P.; Rinsch, C.; Singh, A.; Marcinek, D.J. Effect of Urolithin A Supplementation on Muscle Endurance and Mitochondrial Health in Older Adults: A Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA Netw. Open 2022, 5, e2144279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mighani, S.; Samimi, R.; Nooshabadi, M.R.; Farzam, S.A.; Haghighian, H.K.; Javadi, M. A randomized double-blind clinical trial investigating the effects of ellagic acid on glycemic status, liver enzymes, and oxidative stress in patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. BMC Complement. Med. Ther. 2025, 25, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amor, A.J.; Gómez-Guerrero, C.; Ortega, E.; Sala-Vila, A.; Lázaro, I. Ellagic Acid as a Tool to Limit the Diabetes Burden: Updated Evidence. Antioxidants 2020, 9, 1226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Amico, D.; Andreux, P.A.; Valdés, P.; Singh, A.; Rinsch, C.; Auwerx, J. Impact of the Natural Compound Urolithin A on Health, Disease, and Aging. Trends Mol. Med. 2021, 27, 687–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A.; D’Amico, D.; Andreux, P.A.; Fouassier, A.M.; Blanco-Bose, W.; Evans, M.; Aebischer, P.; Auwerx, J.; Rinsch, C. Urolithin A improves muscle strength, exercise performance, and biomarkers of mitochondrial health in a randomized trial in middle-aged adults. Cell Rep. Med. 2022, 3, 100633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polia, F.; Pastor-Belda, M.; Martínez-Blázquez, A.; Horcajada, M.-N.; Tomás-Barberán, F.A.; García-Villalba, R. Technological and Biotechnological Processes to Enhance the Bioavailability of Dietary (Poly)phenols in Humans. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2022, 70, 2092–2107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akter, S.; Addepalli, R.; Netzel, M.; Tinggi, U.; Fletcher, M.; Sultanbawa, Y.; Osborne, S. In vitro Bioaccessibility and Intestinal Absorption of Selected Bioactive Compounds in Terminalia ferdinandiana. Front. Nutr. 2022, 8, 818195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Fan, L.; Zhang, L.; Zheng, D.; Wang, Y.; Sun, X.; Ji, Y. Pharmacokinetics study of a supersaturatable self-microemulsifying drug delivery system for ellagic acid by UHPLC-Q-TOF-MS. Acta Pharm. 2021, 71, 679–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ceci, C.; Graziani, G.; Faraoni, I.; Cacciotti, I. Strategies to improve ellagic acid bioavailability: From natural or semisynthetic derivatives to nanotechnological approaches based on innovative carriers. Nanotechnology 2020, 31, 382001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manzari-Tavakoli, A.; Babajani, A.; Tavakoli, M.M.; Safaeinejad, F.; Jafari, A. Integrating natural compounds and nanoparticle-based drug delivery systems: A novel strategy for enhanced efficacy and selectivity in cancer therapy. Cancer Med. 2024, 13, e7010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paruvu, Y.; Reddemma, B.; Vangalapati, M. A Comprehensive Review on Pharmacological Activities of Ellagic Acid and its Applications. Nano Part. 2025, 6, 1–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sobhy, L.; Mostafa, M.; Fathalla, Z.; Hussein, A.K. Ellagic acid-loaded chitosan nanoparticles as an approach for mitigating oxidative stress and liver damage in Poloxamer-407-induced hyperlipidemia in mice: Development and optimization through 3 level full factorial design. Int. J. Pharm. 2025, 677, 125659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mady, F.; Shaker, M. Enhanced anticancer activity and oral bioavailability of ellagic acid through encapsulation in biodegradable polymeric nanoparticles. Int. J. Nanomed. 2017, 12, 7405–7417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elendran, S.; Kumar, V.S.; Sundralingam, U.; Tow, W.-K.; Palanisamy, U.D. Enhancing the Bioavailability of the Ellagitannin, Geraniin: Formulation, Characterization, and in vivo Evaluation. Int. J. Pharm. 2024, 660, 124333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ávila-Gálvez, M.Á.; Romero-Reyes, S.; del Carmen López de las Hazas, M.; del Saz-Lara, A.; Dávalos, A.; Espín, J.C.; González-Sarrías, A. Loading milk exosomes with urolithins boosts their delivery to the brain: Comparing the activity of encapsulated vs. free urolithins in SH-SY5Y neuroblastoma cells. Food Biosci. 2024, 61, 104888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, S.; Zhang, C.; Hu, J.; Meng, Y.; Chen, L.; Yu, H.; Li, S.; Wang, G.; Zheng, G.; Qiu, Z. Preparation, Characterization, and In Vitro Pharmacodynamics and Pharmacokinetics Evaluation of PEGylated Urolithin A Liposomes. AAPS PharmSciTech 2021, 22, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, P.; Wang, Y.; Xie, J.; Lei, J.; Zhou, B. Methylated urolithin A, mitigates cognitive impairment by inhibiting NLRP3 inflammasome and ameliorating mitochondrial dysfunction in aging mice. Neuropharmacology 2024, 252, 109950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korczak, M.; Roszkowski, P.; Skowrońska, W.; Żołdak, K.M.; Popowski, D.; Granica, S.; Piwowarski, J.P. Urolithin A conjugation with NSAIDs inhibits its glucuronidation and maintains improvement of Caco-2 monolayers’ barrier function. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2023, 169, 115932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iglesias-Aguirre, C.E.; García-Villalba, R.; Beltrán, D.; Frutos-Lisón, M.D.; Espín, J.C.; Tomás-Barberán, F.A.; Selma, M.V. Gut Bacteria Involved in Ellagic Acid Metabolism to Yield Human Urolithin Metabotypes Revealed. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2023, 71, 4029–4035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).