Simultaneous Development and Validation of an HPLC Method for the Determination of Furosemide and Its Degraded Compound in Pediatric Extemporaneous Furosemide Oral Solution
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. System Suitability
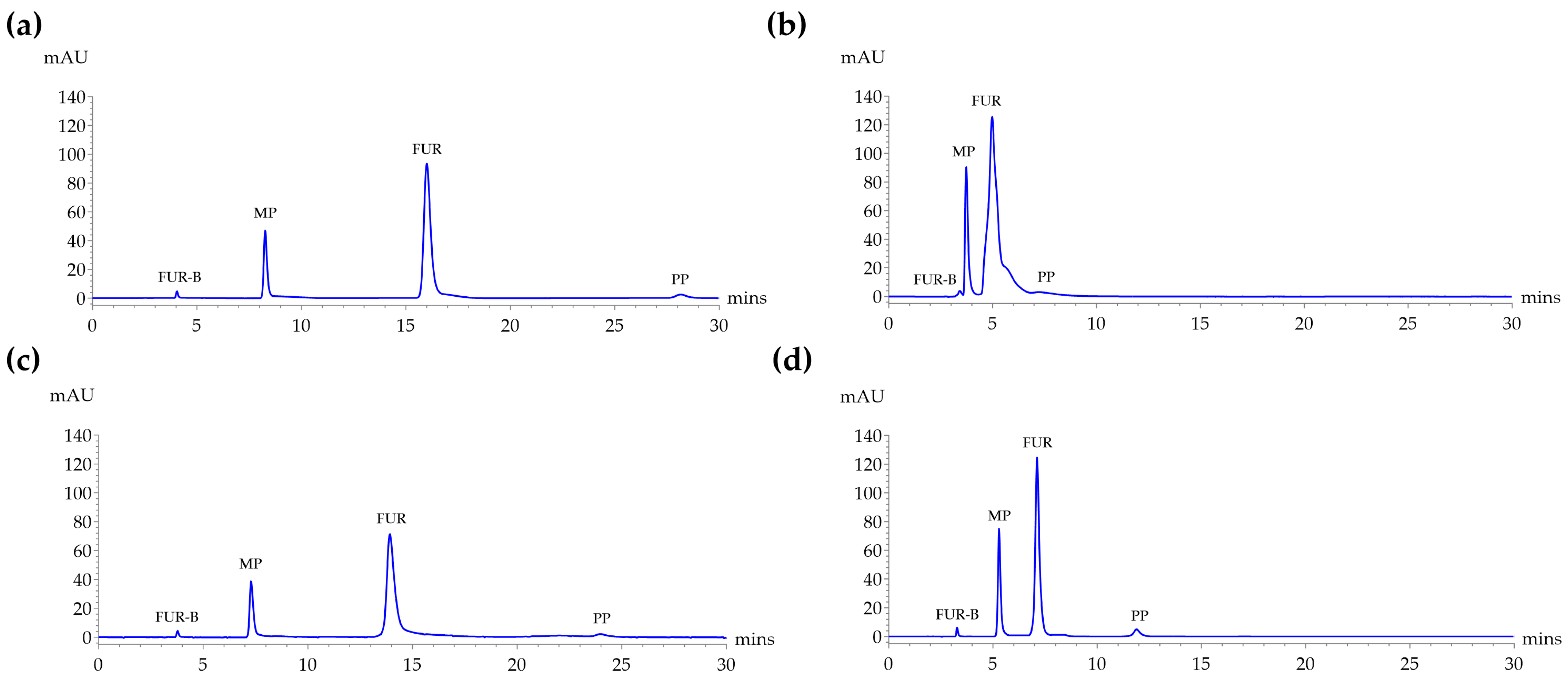
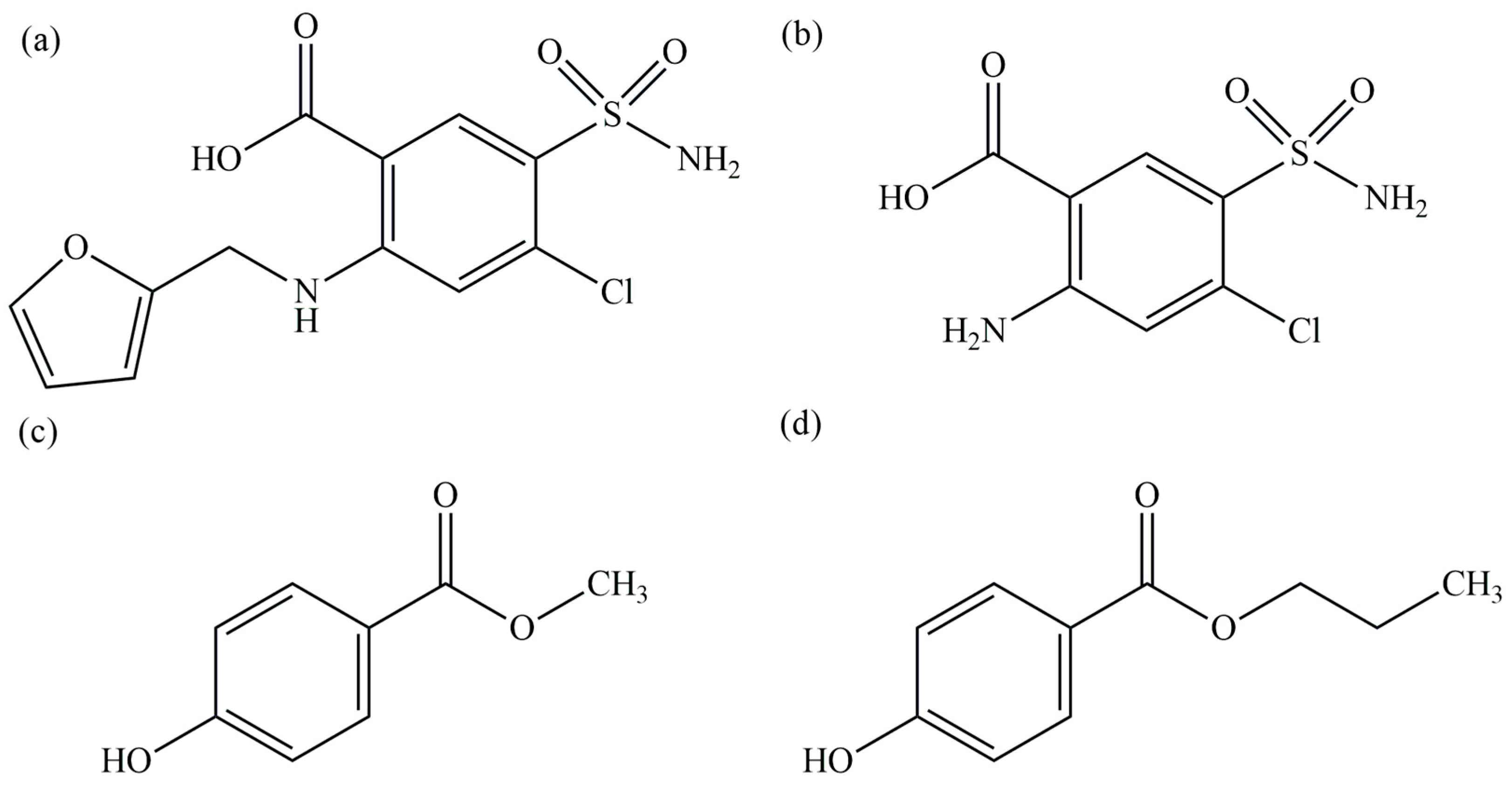
2.2. The Forced Degradation Studies
2.3. Method Validation
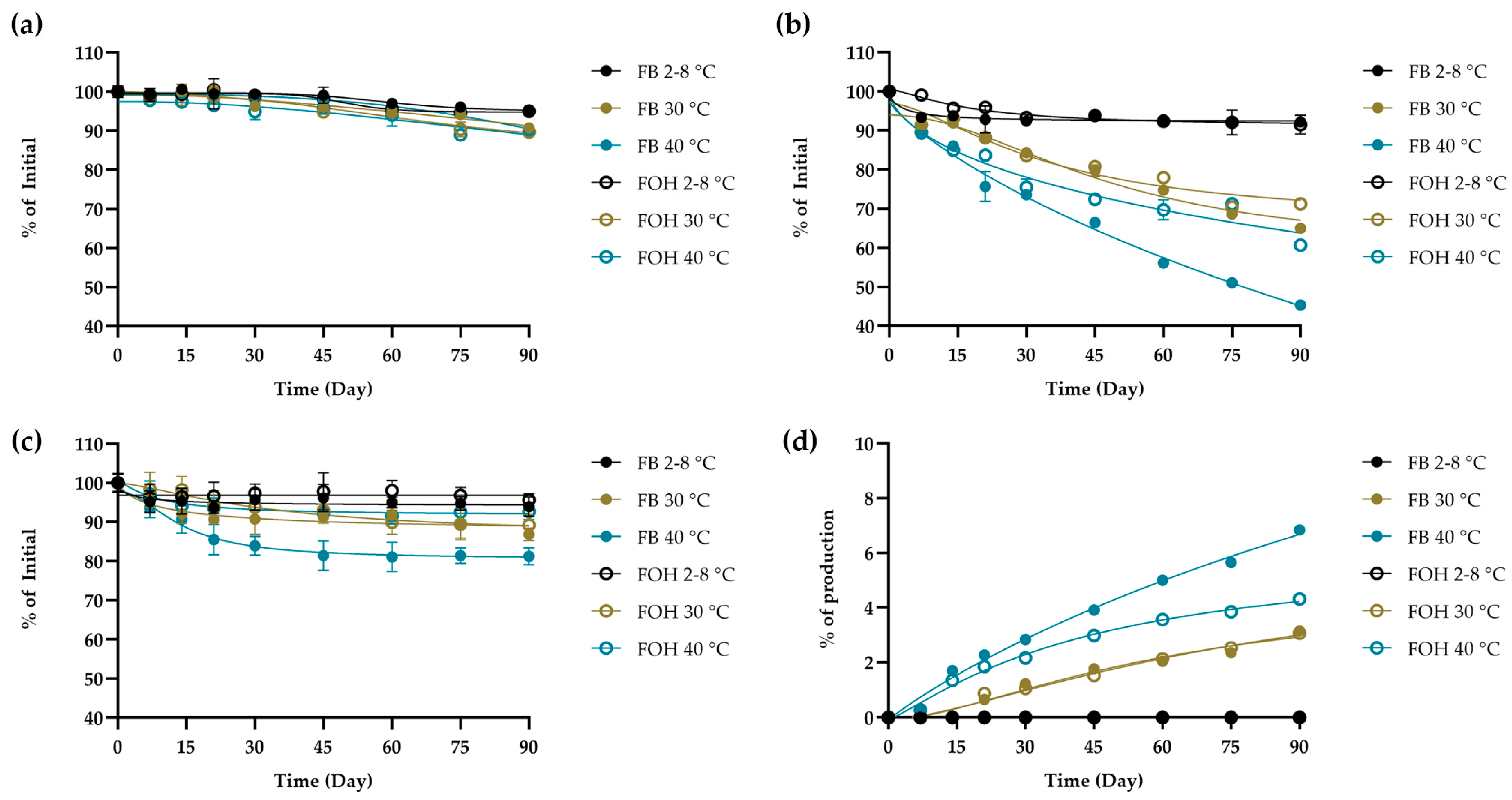
2.4. Application of the Validated HPLC Method
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Chemicals and Reagents
4.2. HPLC System and Method Optimization
4.3. The Forced Degradation Studies
4.4. Method Validation
4.4.1. Linearity, LOD, and LOQ
4.4.2. Methods of Accuracy and Precision
4.4.3. Method Robustness and Ruggedness Assessment
4.5. Application of a Validated HPLC Method for Demonstration of Method Suitability of Extemporaneous Furosemide Oral Solution
4.5.1. Preparation of Standard and Sample Solutions
4.5.2. Chemical Assessment During Short-Term Storage
4.5.3. Microbial Assessment During Short-Term Storage
4.5.4. pH Measurement
4.6. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wu, L.; Rodriguez, M.; El Hachem, K.; Krittanawong, C. Diuretic Treatment in Heart Failure: A Practical Guide for Clinicians. J. Clin. Med. 2024, 13, 4470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jayaprasad, N. Heart Failure in Children. Heart Views 2016, 17, 92–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kearns, G.L.; Abdel-Rahman, S.M.; Alander, S.W.; Blowey, D.L.; Leeder, J.S.; Kauffman, R.E. Developmental Pharmacology—Drug Disposition, Action, and Therapy in Infants and Children. N. Engl. J. Med. 2003, 349, 1157–1167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaya Shree, P.B.S.; Vivek, A.; Akshaya, S.B.; Rakshana, V.; Srinivasan, R. Recent Advances and Challenges in the Development of Pediatric Formulations: Review Article. J. Pharma Insight Res. 2024, 2, 028–038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopalco, A.; Denora, N. Paediatric Formulation: Design and Development. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 7118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, D.; Kirby, D.; Bryson, S.; Shah, M.; Rahman Mohammed, A. Paediatric specific dosage forms: Patient and formulation considerations. Int. J. Pharm. 2022, 616, 121501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- United States Pharmacopeia. Furosemide Oral Solution; United States Pharmacopeia: Rockville, MD, USA, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Ghanekar, A.G.; Das Gupta, V.; Gibbs, C.W., Jr. Stability of Furosemide in Aqueous Systems. J. Pharm. Sci. 1978, 67, 808–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giannetti, M.; Canale, V.; Micheli, L.; Fiori, M.; Mazzuca, C.; Palleschi, A. An Insight into the Degradation Processes of the Anti-Hypertensive Drug Furosemide. Molecules 2023, 28, 381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, D.P.; Antoine, D.J.; Butler, P.J.; Jones, R.; Randle, L.; Payne, A.; Howard, M.; Gardner, I.; Blagg, J.; Park, B.K. The metabolism and toxicity of furosemide in the Wistar rat and CD-1 mouse: A chemical and biochemical definition of the toxicophore. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2007, 322, 1208–1220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lincho, J.; Martins, R.C.; Gomes, J. Paraben Compounds—Part I: An Overview of Their Characteristics, Detection, and Impacts. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 2307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EMA/CHMP/SWP/272921/2012; Reflection Paper on the Use of Methyl- and Propylparaben as Excipients in Human Medicinal Products for Oral Use. Committee for Medicinal Products for Human Use (CHMP): London, UK, 2015.
- Zahalka, L.; Klovrzova, S.; Matysova, L.; Sklubalova, Z.; Solich, P. Furosemide ethanol-free oral solutions for paediatric use: Formulation, HPLC method and stability study. Eur. J. Hosp. Pharm. 2018, 25, 144–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, A.; Xue, Y.; Zeng, Y.; Li, J.; Zhou, H.; Wang, Z.; Chen, Y.; Chen, H.; Jin, J.; Zhuang, T. Isolation and Characterization of an Unknown Process-Related Impurity in Furosemide and Validation of a New HPLC Method. Molecules 2023, 28, 2415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thean, F.S.Y.; Yeoh, L.; Ng, R.C.; Thong, K.X. Stability study of an extemporaneous furosemide oral suspension prepared using commercially available tablets with X-Temp® Oral Suspension System. Malays. J. Pharm. 2024, 10, 56–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FDA. Reviewer Guidance: Validation of Chromatographic Methods; FDA Office of Enforcement, HFC-200: Rockville, MD, USA, 1994.
- AOAC International. AF-1 Guidelines for Standard Method Performance Requirements. In Official Methods of Analysis of AOAC International, 22nd ed.; Latimer, G.W., Jr., Ed.; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2023; Appendix F. [Google Scholar]
- ICH. Validation of Analytical Procedures Q2(R2); ICH: Geneva, Switzerland, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Karunakaran, A.; Sudharsan, S.; Jayaprakash, S.; Raju, S.K.; Sindhuja, V.; Elampulakkadu, A. Analytical method development and validation for the estimation of Furosemide an anti-diuretic in Furosemide injection diluted with normal saline in presence of impurities by RP-HPLC. Braz. J. Biol. Sci. 2021, 8, 35–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Youm, I.; Youan, B.-B.C. Validated Reverse-Phase High-Performance Liquid Chromatography for Quantification of Furosemide in Tablets and Nanoparticles. J. Anal. Methods Chem. 2013, 2013, 207028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naveed, D.S.; Qamar, F.; Zainab, S. Simple UV Spectrophotometric Assay Of Furosemide. J. Innov. Pharm. Biol. Sci. 2014, 1, 97–101. [Google Scholar]
- Espinosa Bosch, M.; Ruiz-Sanchez, A.; Rojas, F.; Bosch-Ojeda, C. Analytical determination of furosemide: The last researches. Int. J. Pharm. Biol. Sci. 2013, 3, 168–181. [Google Scholar]
- Hassouna, M. Spectrophotometric Determination of Furosemide Drug in Different Formulations using Schiff ’s Bases. Forensic Res. Criminol. Int. J. 2016, 1, 214–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Center for Biotechnology Information. PubChem Compound Summary for CID 23663626, Methylparaben Sodium. 2025. Available online: https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/Methylparaben (accessed on 16 September 2025).
- National Center for Biotechnology Information. PubChem Compound Summary for CID 23679044, Propylparaben Sodium. 2025. Available online: https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/Propylparaben (accessed on 16 September 2025).
- United States Pharmacopeia. Methylparaben Monograph; USP 47-NF 42; United States Pharmacopeia: Rockville, MD, USA, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- United States Pharmacopeia. Propylparaben Monograph; USP 47-NF 42; United States Pharmacopeia: Rockville, MD, USA, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- United States Pharmacopeial Convention (USP). Chromatography <621>. In United States Pharmacopeia and National Formulary (USP 47–NF 42), 47th ed.; United States Pharmacopeial Convention: Rockville, MD, USA, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Kowalska, M.; Woźniak, M.; Kijek, M.; Mitrosz, P.; Szakiel, J.; Turek, P. Management of validation of HPLC method for determination of acetylsalicylic acid impurities in a new pharmaceutical product. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katsura, S.; Yamada, N.; Nakashima, A.; Shiraishi, S.; Furuishi, T.; Ueda, H. Identification of Furosemide Photodegradation Products in Water–Acetonitrile Mixture. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 2015, 63, 617–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santoveña-Estévez, A.; Suárez-González, J.; Vera, M.; González-Martín, C.; Soriano, M.; Fariña, J.B. Effectiveness of Antimicrobial Preservation of Extemporaneous Diluted Simple Syrup Vehicles for Pediatrics. J. Pediatr. Pharmacol. Ther. 2018, 23, 405–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- United States Pharmacopeial Convention (USP). Microbiological Examination of Nonsterile Products: Microbial Enumeration Tests <61> and Tests for Specified Microorganisms <62>. In United States Pharmacopeia and National Formulary (USP 39–NF 34); United States Pharmacopeial Convention: Rockville, MD, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
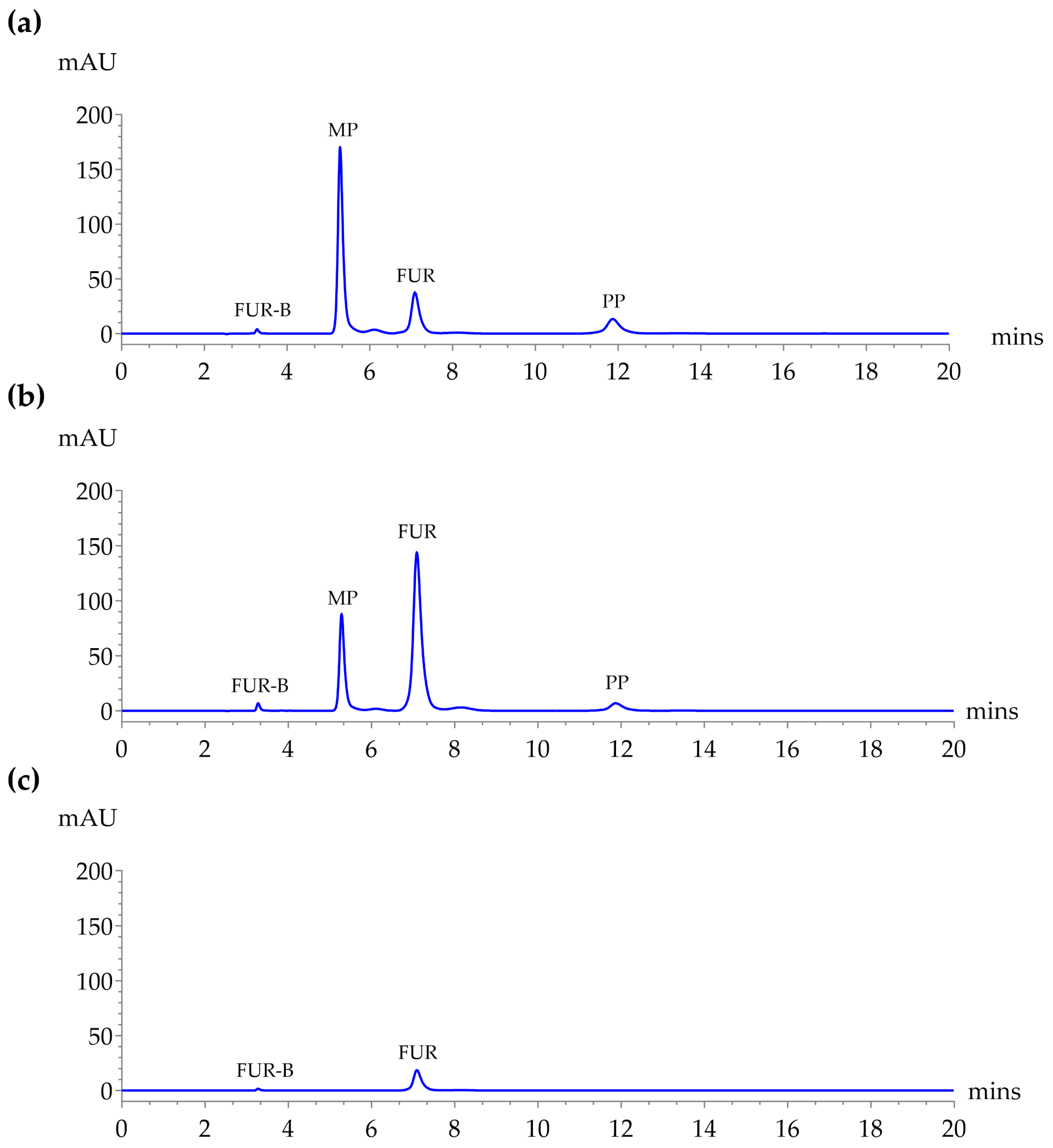

| Column | Mobile Phase | Flow Rate (mL/min) | Resolution | Symmetry Factor | Number of Theoretical Plates | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FUR-B→MP | MP→FUR | FUR→PP | FUR-B | MP | FUR | PP | FUR-B | MP | FUR | PP | |||
| Kinetex C18 | 0.1% Acetic acid in DI:ACN (70:30) | 0.5 | 31.68 | 30.12 | 45.44 | 0.73 | 0.99 | 1.20 | 1.20 | 26,572 | 38,926 | 34,123 | 45,404 |
| 0.1% Acetic acid in DI:ACN (60:40) | 0.5 | 1.85 | 3.87 | 4.14 | 0.8 | 1.43 | 2.00 | 1.58 | 5733 | 8222 | 1782 | 2835 | |
| Symmetry® C18 | 0.1% Acetic acid in DI:ACN (70:30) | 1 | 20.77 | 21.43 | 18.83 | 1.17 | 2.94 | 2.17 | 1.15 | 11,855 | 21,424 | 17,485 | 22,347 |
| 0.1% Acetic acid in DI:ACN (60:40) | 1 | 17.52 | 10.24 | 16.81 | 1.18 | 1.45 | 1.12 | 0.99 | 20,745 | 23,447 | 17,224 | 18,200 | |
| Degradation Condition | Degradation (% Assay Loss) | Major Degradant (FUR-B) (% Area) | Minor Degradants (% Area) | %Mass Balance | Peak Purity Index |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Acid stress | 8.93 | 7.03 | 1.81 | 99.91 | 0.930598 |
| Base stress | 0.82 | 0.10 | 0.62 | 99.90 | 0.958154 |
| Oxidation stress | 15.58 | 8.86 | 6.64 | 99.91 | 0.957837 |
| Thermal stress | 0.90 | 0.11 | 0.69 | 99.90 | 0.958991 |
| Photolysis | 0.37 | 0.10 | 0.17 | 99.90 | 0.960242 |
| Analytical Characteristics | FUR | FUR-B | MP | PP |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Linear Range (µg/mL) | 2.50–100.0 | 0.25–2.00 | 0.31–30.00 | 0.25–7.50 |
| R2 | 0.9992 | 0.9997 | 0.9997 | 0.9995 |
| LOD (µg/mL) | 1.14 | 0.12 | 0.15 | 0.08 |
| LOQ (µg/mL) | 3.45 | 0.36 | 0.44 | 0.24 |
| Compound | Concentration (µg/mL) | Intra-Day (n = 9) | Inter-Day (n = 27) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Measured Concentration (µg/mL) | Accuracy | Repeatability | Measured Concentration (µg/mL) | Accuracy | Intermediate Precision | ||
| Recovery (%) | RSD (%) | Recovery (%) | RSD (%) | ||||
| FUR | 25.00 | 24.87 ± 0.24 | 99.5 ± 1.0 | 1.0 | 24.89 ± 0.24 | 99.6 ± 1.0 | 1.0 |
| 50.00 | 49.93 ± 0.28 | 99.9 ± 0.6 | 0.6 | 49.95 ± 0.25 | 99.9 ± 0.5 | 0.5 | |
| 75.00 | 74.58 ± 0.44 | 99.4 ± 0.6 | 0.6 | 74.36 ± 0.49 | 99.2 ± 0.7 | 0.7 | |
| FUR-B | 0.75 | 0.75 ± 0.01 | 100.2 ± 1.5 | 1.5 | 0.75 ± 0.01 | 100.6 ± 1.8 | 1.8 |
| 1.00 | 1.01 ± 0.01 | 101.0 ± 0.8 | 0.8 | 1.01 ± 0.02 | 100.9 ± 1.5 | 1.5 | |
| 1.50 | 1.50 ± 0.02 | 100.0 ± 1.1 | 1.1 | 1.50 ± 0.02 | 99.9 ± 1.0 | 1.1 | |
| MP | 5.00 | 4.95 ± 0.01 | 99.1 ± 0.1 | 0.1 | 4.99 ± 0.06 | 99.7 ± 1.2 | 1.3 |
| 10.00 | 10.00 ± 0.06 | 100.0 ± 0.6 | 0.6 | 10.02 ± 0.06 | 100.2 ± 0.6 | 0.6 | |
| 15.00 | 14.92 ± 0.04 | 99.5 ± 0.3 | 0.3 | 14.97 ± 0.12 | 99.8 ± 0.8 | 0.8 | |
| PP | 1.00 | 1.00 ± 0.01 | 100.4 ± 0.9 | 0.9 | 1.01 ± 0.02 | 100.5 ± 1.8 | 1.7 |
| 2.00 | 1.98 ± 0.03 | 99.2 ± 1.4 | 1.4 | 1.96 ± 0.03 | 98.2 ± 1.6 | 1.6 | |
| 3.00 | 2.96 ± 0.04 | 98.8 ± 1.2 | 1.2 | 2.99 ± 0.06 | 99.8 ± 2.0 | 2.0 | |
| Column | Mobile Phase Composition | Flow Rate | Detection Wavelength |
|---|---|---|---|
| Kinetex C18 (2.6 μm, 4.6 × 150 mm) | 0.1% acetic acid in DI water: acetonitrile (70:30) | 0.5 mL/min | 254, 272, and 330 nm |
| 0.1% acetic acid in DI water: acetonitrile (60:40) | 0.5 mL/min | 254, 272, and 330 nm | |
| Symmetry® C18 (5 μm, 4.6 × 250 mm) | 0.1% acetic acid in DI water: acetonitrile (70:30) | 1.0 mL/min | 254, 272, and 330 nm |
| 0.1% acetic acid in DI water: acetonitrile (60:40) | 1.0 mL/min | 254, 272, and 330 nm |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Srejomthong, K.; Pattananandecha, T.; Apichai, S.; Charumanee, S.; Sirithunyalug, B.; Ogata, F.; Kawasaki, N.; Saenjum, C. Simultaneous Development and Validation of an HPLC Method for the Determination of Furosemide and Its Degraded Compound in Pediatric Extemporaneous Furosemide Oral Solution. Molecules 2025, 30, 4031. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30194031
Srejomthong K, Pattananandecha T, Apichai S, Charumanee S, Sirithunyalug B, Ogata F, Kawasaki N, Saenjum C. Simultaneous Development and Validation of an HPLC Method for the Determination of Furosemide and Its Degraded Compound in Pediatric Extemporaneous Furosemide Oral Solution. Molecules. 2025; 30(19):4031. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30194031
Chicago/Turabian StyleSrejomthong, Katsanee, Thanawat Pattananandecha, Sutasinee Apichai, Suporn Charumanee, Busaban Sirithunyalug, Fumihiko Ogata, Naohito Kawasaki, and Chalermpong Saenjum. 2025. "Simultaneous Development and Validation of an HPLC Method for the Determination of Furosemide and Its Degraded Compound in Pediatric Extemporaneous Furosemide Oral Solution" Molecules 30, no. 19: 4031. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30194031
APA StyleSrejomthong, K., Pattananandecha, T., Apichai, S., Charumanee, S., Sirithunyalug, B., Ogata, F., Kawasaki, N., & Saenjum, C. (2025). Simultaneous Development and Validation of an HPLC Method for the Determination of Furosemide and Its Degraded Compound in Pediatric Extemporaneous Furosemide Oral Solution. Molecules, 30(19), 4031. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30194031






