Abstract
Honey bee (Apis mellifera) products have been extensively utilized in traditional medicine. Bee venom (BV) is one of the major bee products with a high concentration of the small peptide melittin (MEL) and exerts bioactivity ranging from anti-microbial to anti-inflammatory and anti-cancer. This scoping review aims to sum up research articles on the bioactivity exerted by BV and MEL published in PubMed and Scopus from 2010 onwards. PRISMA guidelines were implemented to analyze the relevant literature; we ended up with 425 research articles. Bioactivity of BV and MEL was grouped as (i) anti-inflammatory (85), (ii) immunomodulatory (37), (iii) anti-microbial (179), (iv) anti-cancer (170), and (v) anti-oxidant (32). Although there is a significant body of research on the anti-cancer and anti-microbial activity of BV and MEL, their anti-oxidant, anti-inflammatory and immunomodulatory properties have received comparatively less attention. Many studies on the immunomodulatory effects of BV or MEL have focused on cancer. However, the effects on Parkinson’s and Alzheimer’s disease have not been extensively studied regarding the anti-inflammatory effects. Given the critical role of the immune system and inflammatory response in cancer, neurodegenerative diseases, senescence and against infections, it is paramount to further explore the immunomodulatory and anti-inflammatory potential of BV and MEL.
1. Introduction
Bee venom (BV), also known as apitoxin, is a natural mixture produced in the venom glands of bees belonging to the order Hymenoptera, which are the type of insects that generally sting their adversaries to protect themselves [1,2]. Honey bees belong to the genus Apis and are important crop pollinators, especially Apis mellifera, the European Honey Bee [1]. BV has a long history as a therapeutic substance for thousands of years, from ancient Egypt to China [2,3]. Honey bee venom is a mixture of bioactive substances such as peptides, proteins, enzymes, and other small molecules in an odorless, translucent, acidic liquid form with an average pH of 5 [4,5,6]. It is estimated that BV contains more than 200 different compounds, and more than half of them are quantified [7]. BV is harvested from honeybees with continuous electro-simulation according to the Benton protocol [8]. The most abundant BV compound is the peptide melittin (MEL), which makes up approximately 60% of dry BV weight, varying between different bee species [9,10]. The enzyme phospholipase A2 (PLA2) makes up to 20% of dry BV weight (Table 1). Another peptide, apamin, is the third most abundant compound, though it makes up to only 1% of dry BV weight, followed by approximately 200 less abundant molecules (Table 1) [7,9,10]. Numerous in vivo and in vitro studies have demonstrated that BV exerts strong bioactivity, such as anti-cancer, anti-nociceptive, anti-oxidant, anti-bacterial, anti-fungal, anti-viral, anti-inflammatory, anti-arthritic, anti-metastatic, and hemolytic effects [5,6,11,12]. Especially in East Asia, BV is used for acupuncture to treat chronic pain, generally caused by inflammation or neuropathy [13,14].

Table 1.
Major compounds detected in bee venom [4,6,11,15].
2. Methodology
This scoping review focuses on the potentially therapeutic bioactivity exerted by the bee venom and its compounds, especially melittin, as described in original research articles. Our main goal was to implement the PRISMA guidelines to summarize and categorize the relevant scientific literature, to identify research gaps, and to suggest future perspectives on research relevant to the bioactivity exerted by BV and MEL.
The widely used Scopus and PubMed databases were searched in this review. The last search took place on 28 May 2025. Since both sites use different ID systems (EID for Scopus, PMID for PubMed), DOI links were used to store and compare the data of the documents obtained through browsing. According to our expertise on the topic, two search groups were formed, namely BV and MEL. We included general keywords to combine BV and MEL with specific types of bioactivities (Table 2). The keywords that were suggested by the databases were also considered (Table 2).

Table 2.
The search terms for the databases.
In PubMed, the search filter “best match” was applied, while in Scopus, it was “relevance”. Published articles from 2010 onwards were included. In Scopus, language was filtered with English; however, since PubMed is a US-based website, no language filter was applied. Original research and review articles were prioritized, and some literature items were considered not eligible, especially letters formatted as “letter to the editor, correction, correspondence,” etc., which don’t focus on detailed, complete research. Zotero was used as an automation program to recognize the documents and to remove duplicate results. The articles were read, categorized, and presented in tables and figures, according to their type and content.
The overall search yielded a total of 3145 items. After the 2016 duplicates and 6 publications that were marked unidentified by the automation tool were removed using Excel and Zotero, 1123 articles remained. After reviewing, 76 articles were removed because they were not original research or review articles. These publications were either letters to the editor, communications, corrections or editorials. Also, 5 articles were retracted, leaving 1044 articles for assessment for eligibility. After reviewing, the remaining 788 articles were identified as 761 research articles and 24 case reports. 425 articles were found to be relevant to our topic (Figure 1).
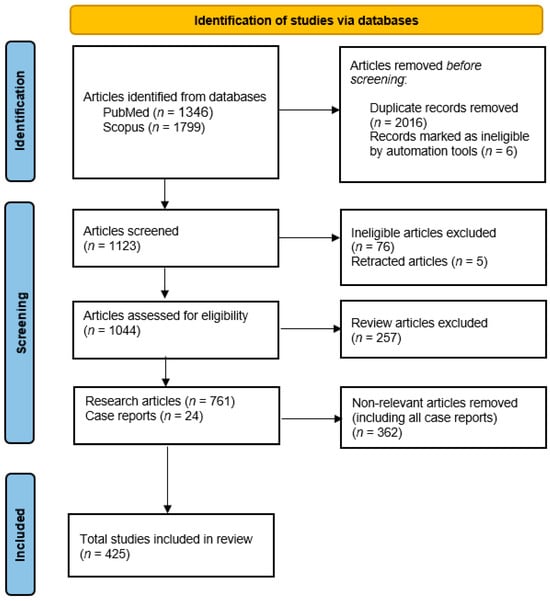
Figure 1.
PRISMA flowchart: Implementation of PRISMA guidelines followed during this review in order to include eligible studies [16].
The remaining articles were categorized based on their type of bioactivity. BV and MEL are both used in different types of in vivo studies (clinical and animal models) as well as in vitro (cell lines, microorganisms). Types of animal models (generally rats or mice), along with administration types (injection, topical, acupuncture), targeted microorganisms, cell lines and delivery systems are listed in the experimental design section. The “additional information” column in the table provides other types of bioactivity or other specific information regarding the experimental design. It also lists the types of substances used—such as bee venom (BV), melittin, and other components of BV—along with their sources, including Apis mellifera (honeybee), general references to bees, or other species. Overall, regarding the bioactivity described or studied, the relevant articles were categorized as follows: (i) anti-inflammatory, (ii) immunomodulatory, (iii) anti-microbial, (iv) anti-cancer, and (v) anti-oxidant and they are presented below.
3. Content of Bee Venom
Bee venom consists of a range of bioactive molecules. Bee venom compounds, including melittin, apamin, secapin, mast cell degranulating (MCD) peptide, tertiapin, hyaluronidase, and phospholipase A2, act synergistically, contributing to the overall bioactivity exerted by bee venom, inducing cytolytic, neurotoxic, pro-inflammatory, allergenic, and anti-microbial effects. The most bioactive compound, Melittin (MEL), is a small peptide of 26 amino acid residues with a weight of 2840 Da (GIGAVLKVLTTGLPALISWIKRKRQQ-CONH2) and is often described as an “anti-microbial peptide (AMP)” (Figure 2A). Alongside the asymmetrical distribution of polar and non-polar amino acid residues, melittin structure demonstrates an amphipathic nature, therefore making it a highly bioactive component, especially against membranes. Therefore, melittin disrupts the membranes of cancer cells, bacteria, and fungi. In many in vitro experiments, melittin is used as a positive control for such effects. Furthermore, melittin blocks metabolic pathway elements, including Tumor Necrosis Factor (TNF) receptors, cytokine signaling pathways, and Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor (EGFR), thus suggesting its role in promoting apoptosis [1,2,3,4]. Apamin is a neurotoxin that crosses the blood–brain barrier. It contains 18 amino acid residues with two disulfide bonds (Cys1-Cys11, Cys3-Cys15) in between (Figure 2B). Since animal venom toxins are often modified post-translationally, apamin C-terminal is amidated. In the early 1980s, apamin was used to identify certain Ca2− activated K ion channels due to its selective activity towards these channels. Moreover, it is known to demonstrate antimicrobial effects. Due to molecular stability, apamin is a possible drug delivery element. Tertiapin (Figure 2C) is a 21-amino-acid peptide that blocks potassium channels [5,6,7,8]. Phospholipase A2 from bee venom (BvPLA2) is a type of secreted PLA2. BvPLA2 is Ca2+-dependent, catalyzing the hydrolysis of sn-2 acyl phospholipid bonds often implicated in inflammation, leading to the production of lysophosphatidic acid and arachidonic acid (Figure 2D). However, these interactions also exert anti-inflammatory activity from a medical perspective. Similarly to melittin, it plays a role in membrane disruption [5,9,10]. Hyaluronidase (Figure 2E) promotes allergenic response. It cleaves hyaluronan of the connective tissue and accelerates absorption of the bee venom into the tissue [5,11]. Secapin (Figure 2F) is a potential neurotoxin with anti-fibrinolytic, anti-elastolytic, and anti-microbial effects [5,6,7,8]. Mast Cell Degranulating (MCD) peptide has a similar structure to apamin (Figure 2G) and might also act like a neurotoxin. At low concentrations, it induces mast cell degranulation; at high concentrations, it has anti-inflammatory effects.

Figure 2.
Chemical structure of major bee venom compounds: (A–G) show the secondary and 3D structures of melittin, apamin, tertiapin, phospholipase A2, hyaluronidase, secapin, and mast cell degranulation peptide, respectively. (A–E) Domain organization, sequence conservation, and predicted physicochemical features of principal bee venom proteins visualized using bioinformatics tools. (A) Melittin, a 26-amino-acid amphipathic peptide responsible for hemolytic and cytolytic activities, shows a characteristic α-helical conformation. (B) Apamin, a small neurotoxic peptide that blocks Ca2+-activated K+ channels, displays a compact disulfide-stabilized α-helical structure. (C) Tertiapin, known for its potassium channel inhibitory activity, presents a short α-helix with disulfide bridges. (D) Phospholipase A2 (PLA2), the primary enzymatic component of bee venom, possesses conserved catalytic and Ca2+-binding domains, which contribute to membrane degradation and inflammation. (E) Hyaluronidase, often termed the “spreading factor,” shows conserved glycosidic hydrolase motifs and facilitates venom diffusion through connective tissues. (F,G) Three-dimensional molecular structures of smaller venom-derived peptides, including Secapin (F) and the Mast Cell Degranulating (MCD) peptide (G), highlight the presence of loop and β-turn motifs important for their antimicrobial and immunomodulatory activities. Structural models were generated using protein databases and homology modeling algorithms to visualize functional domains and peptide folding patterns (obtained from pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov and www.rcsb.org databases).
4. Bioactivity Exerted by Bee Venom and Melittin
4.1. Anti-Inflammatory Effects
4.1.1. Anti-Inflammatory Bioactivity Targeting Various Diseases
Anti-inflammatory effects of BV and MEL targeting diverse diseases are a popular research topic. Both BV and MEL are used as therapeutic tools against diseases where inflammation is a major issue mediating morbidity, most of them being neurological or immunological disorders (Table 3). Much research is focused on BV and MEL effects on inflammatory cytokine pathways and gene expression related to inflammation and immunomodulation. Both chronic and acute diseases are subjects of anti-inflammatory action exerted by BV and MEL. Animal in vivo studies are the most common experimental design.

Table 3.
Anti-inflammatory bioactivity exerted by BV/MEL on targeted diseases/disorders.
Despite extensive evidence supporting the anti-inflammatory and therapeutic potential of bee venom (BV) and its components like melittin, apamin, and PLA2 across diverse disease models, several research gaps remain. Most studies are limited to preclinical models, with scarce clinical trials validating safety, efficacy, dosing, and delivery mechanisms in humans. Furthermore, the mechanisms underlying BV’s immunomodulatory and anti-oxidant effects require deeper molecular investigation, especially in chronic and complex diseases. Standardization of BV extraction, formulation, and administration methods is lacking, which hinders reproducibility and clinical translation. Future research should focus on large-scale, controlled clinical trials, advanced drug delivery systems (e.g., nanoparticles, hydrogels), and long-term toxicity studies. Additionally, exploring BV’s synergistic effects with conventional therapies and its potential against antibiotic resistance and neurological disorders warrants further exploration.
4.1.2. Rheumatoid Arthritis
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a conspicuous disease target of BV (as well as its compounds) therapy (Table 4). It is a chronic inflammatory autoimmune disease that manifests as pain all over the body and may escalate into permanent loss of function, mobility issues, and a dramatic decrease in the quality of life [75]. MEL and PLA2 anti-inflammatory therapeutic effects are hot research topics of traditional medicine (especially traditional Korean medicine), and acupuncture/acupoint injection is commonly practiced with animal and human clinical models.

Table 4.
Anti-inflammatory therapeutic research targeting rheumatoid arthritis.
Most findings are limited to animal models or in silico analyses, with minimal translation into well-designed clinical trials. Delivery methods such as nanoparticles, microneedles, and liposomes are emerging but require optimization for consistent dosing, safety, and patient compliance. Future research should prioritize mechanistic studies to elucidate molecular targets, long-term safety assessments, and randomized controlled trials in humans. Moreover, integrating nanotechnology-based delivery systems with immunomodulatory strategies may enhance therapeutic outcomes in RA management.
4.1.3. Non-Disease Targeted Anti-Inflammatory Activity
Rather than targeting diseases, many researchers are looking into the potentially protective aspects of BV/melittin, which involve pathways and membrane interactions. Some are in vivo with rats and mice, but some are in vitro studies using cell lines and microorganisms (Table 5).

Table 5.
Anti-inflammatory bioactivity of BV and melittin without a specific disease target.
The immune system evolved in multicellular organisms in order to fight infections and other disorders such as cancer. By modulating immunological responses, such as T cell and macrophage activation, certain immunological pathways help to combat diseases. Both BV and melittin are known for their immunomodulatory effects due to their bioactive potential (Table 6). Nevertheless, another less abundant BV compound, PLA2, is described to exert immunomodulatory activity in BV-related studies.

Table 6.
Immunomodulatory activity research articles (without cancer).
Bee venom and its components, such as melittin and PLA2, show strong immunomodulatory and anti-inflammatory effects across a range of non-cancerous conditions including autoimmune, respiratory, and neurological diseases. However, several research gaps are evident. Many studies are preclinical, lacking human trials that could confirm efficacy, safety, and optimal dosing. The long-term effects of repeated BV exposure, particularly regarding immune tolerance or hypersensitivity, are not well understood. Furthermore, while novel delivery systems (e.g., nanoparticles, microneedles, LNPs) are emerging standardized methods for formulation and administration are still underdeveloped. Future research should focus on (i) well-controlled clinical studies, (ii) elucidation of mechanistic insights regarding immune regulation pathways, and (iii) the development of safe, targeted delivery platforms to minimize toxicity and maximize therapeutic outcomes.
Cancer therapy is often associated with adverse effects and might be inefficient in certain cancer types. Minimizing the side effects of chemotherapy is an active research topic that explores many alternative therapy options, such as apitherapy. Immunomodulatory effects might be considered either enhancing (immunostimulation) or suppressing (immunosuppression) [108]. Immunomodulatory agents can alter the functions of immune cells, regulate cytokine production, or affect inflammatory responses. As a result, immunomodulation has emerged as a significant therapeutic target, particularly in the treatment of cancer, autoimmune diseases, and chronic inflammation. Natural compounds and their derivatives are of interest in immunomodulation interventions [109]. Bee venom and melittin have attracted increasing attention in recent years due to their immunomodulatory properties (Table 7). These natural products might promote immune response in immunocompromised patients or control excessive immune responses by restoring immune balance, thus leading to more efficient cancer therapy.

Table 7.
Immunomodulatory activity exerted by BV and MEL in cancer research.
4.2. Anti-Microbial Activity
Anti-microbial resistance (AMR) is an escalating global crisis. AMR is driven by the overuse and misuse of antibiotics, leading to the rise in healthcare-associated infections worldwide. It is projected that by 2050, 10 million people annually may die from infections that cannot be treated due to resistant bacteria and the ineffectiveness of current antibiotics [127]. In that respect, alternatives to classic antibiotics and anti-fungal agents are constantly investigated, and the use of anti-microbial peptides (AMPs) is one of them. These small molecules are abundant as part of the innate immunity in many insects, including Apis mellifera and other Apis and non-Apis types of bees [128,129]. Considering that AMPs are small amino acid chains that don’t require complex protein folding mechanisms, AMP synthesis in heterologous hosts such as bacteria or fungi is feasible, thus leading to therapeutic applications [130]. Melittin, the major protein detected in BV, is a well-studied bacterial membrane disruption agent, and it is often used as a reference in studies related to other AMPs. The anti-microbial activity of MEL and BV against diverse multidrug-resistant pathogens such as Staphylococcus aureus (S. aureus), Klebsiella pneumoniae (K. pneumoniae), Escherichia coli (E. coli), Pseudomonas aeruginosa (P. aeruginosa), and Candida albicans (C. albicans) is well studied. Numerous studies describing these results are presented in Table 8, whereas often melittin is referred to as an Anti-Microbial Peptide (AMP). Overall, the in vitro antimicrobial activity of BV and especially MEL has been sufficiently studied. However, there is scarce data regarding the anti-biofilm effect of BV and MEL, the attenuation of virulence factors of diverse pathogens, and especially the response of pathogens to BV and MEL using OMICS technologies (for example, RNA-sequencing). Future research should be focused on more preclinical studies regarding in vivo validation and therapeutic potential, as well as clinical trials to assess efficacy, feasibility, and optimal dosage.

Table 8.
Research articles describing the anti-bacterial (ABA), anti-fungal (AFA), and anti-viral (AVA) activity of bee venom and melittin.
4.3. Anti-Cancer Activity
Alternatives for cancer therapy search for the minimum side effects for the patients. The goal is to maintain the health of the non-cancerous tissue while eliminating cancerous cells; therefore, selectivity. Traditional methods of chemotherapy suffer from inducing toxic effects, aforementioned acute kidney injury, which further deteriorates the odds of patient survival. In addition, MDR (multi-drug resistance) is another reason for alternative approaches [139,213].
Cytotoxic effects and BV and melittin are directly responsible for the therapeutic potential for anti-cancer research [295,296,297,298,299,300]. As mentioned before, the anti-microbial effect of BV and melittin relies on membrane interactions and the subsequent cytotoxicity. Mammalian cancers are much more complex threats to overcome due to their resistance to follow the cell cycle, eventually cell death. By size and membrane composition, mammalian cells are different from microorganisms; therefore, a small molecule in the complexity of BV may interfere with several pathways generally overexpressed in various cancer types. With this possibility, many studies are focused on gene expression and pathways in cancers. But this exact cytotoxic potential clashes with the goal of selectivity. To reduce the cytotoxic and hemolytic activity against healthy tissue; deliveries of both BV and melittin are considered and designed extensively in obtained research articles.
The cytotoxic effect of bee venom and melittin has been shown in both human and murine cancer and a variety of cancer cells such as breast [300], hepatocellular [301], cervical [302], pancreatic [303], colorectal cancers [304], glioblastoma [88,305] and melanoma [306], and also in rat or mice animal models of cancer [125,307,308] (Table 9 and Table 10). The anti-cancer effects of bee venom and melittin are given separately.
4.3.1. Bee Venom in Cancer Research
The anti-cancer activity of bee venom (BV) has been studied in many cell lines and cancer types, alongside xenograft animal models (Table 9). The interactions of bee venom with pro-apoptotic pathways are a common study goal among these studies [256,309,310,311]. Delivery systems implementing nanoparticles are popular since BV may cause adverse effects such as unwanted hemolytic activity or allergic reactions [312,313].

Table 9.
Cancer research with bee venom.
Table 9.
Cancer research with bee venom.
| Article Name | Substance | Cancer Type | Experimental Design | Additional Information |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| (G. B. Jung et al., 2018) [295] | BV | Breast cancer | In vitro; MDA-MB-231, PBMLs cell lines | Anti-cancer effect |
| (A. A. Nagy et al., 2022) [296] | BV | Hepatocellular carcinoma | In vivo; Animal: rats Nano delivery of BV with iron oxide | Gene Expression-Pathway |
| (Sevin et al., 2023) [88] | BV (Apis m.) Apamin Melittin PLA2 | Glioblastoma | In vitro; U87MG cell line | Cytotoxicity Gene expression-pathway Immunomodulation |
| (Yaacoub et al., 2022) [297] | PLA2, Melittin from BV (Apis m.) | Cervical cancer | In vitro; HeLa cell line | Cytotoxicity, anti-coagulation, proteolytic activity |
| (M. Sharaf et al., 2024) [209] | Nanoparticles loaded with apitoxin from BV (Apis m.) | Hepatocellular carcinoma Colon cancer | In vitro; HepG2, Caco-2, Vero cell lines Nano delivery of BV by chitosan coating | Cytotoxicity Anti-microbial |
| (H. N. Lim et al., 2019) [306] | Melittin from BV | Melanoma cancer | In vitro; B16F10, A375SM, SK-MEL-28 cell line | Gene Expression-Pathway, Cell invasion inhibition |
| (Mansour et al., 2021) [314] | BV (Apis m.) and melittin | Hepatocellular carcinoma | In vitro; HepG2, THLE-2 cell lines In silico; Molecular docking | Cytotoxicity, Gene Expression-Pathway |
| (Małek et al., 2022) [315] | BV (Apis m.) | Glioblastoma | In vitro; 8-MG-BA, GAMG, HT22 cell lines | Neurological, cytotoxicity, MMP-2 and MMP-9 |
| (Tetikoğlu & Çelik-Uzuner, 2023) [316] | BV (Apis m.) | Breast cancer, Hepatocellular carcinoma | In vitro; MDA-MB-231, HepG2, NIH3T3 cell line | Genotoxicity, Gene Expression-Pathway |
| (Saghi et al., 2022) [309] | BV (Apis m.) | Colorectal cancer | In vitro; HT-29, NIH3T3 cell lines | Apoptosis Gene Expression-Pathway, ROS, anti-tumor |
| (D.-H. Kim et al., 2020) [256] | BV (Apis m.) | Cervical cancer | In vitro; C33A, HeLa, Caski cell line | Apoptosis, Gene Expression-Pathway |
| (J. Zhao et al., 2022) [310] | BV | Pancreatic cancer | In vitro; PANC-1 cell line | Apoptosis, Cytotoxicity, anti-metastatic |
| (J. E. Yu et al., 2022) [311] | BV | Lung cancer Glioblastoma, Hepatocellular carcinoma Breast cancer | In vitro; A549, A172, NCI-H460, MDA-MB-231, Hep3B cell lines | Apoptosis, Gene Expression-Pathway, autophagy |
| (Pinto et al., 2024) [32] | BV (Apis m.) | Hepatocellular carcinoma, Colon cancer, Breast cancer, Cervical cancer, Gastric adenocarcinoma | In vitro; HeLa, Caco-2, Vero, MCF-7, NCI-H460, AGS, PLP2, RAW 264.7, cell lines Nanoparticle delivery of BV | Anti-inflammatory, Therapeutic, Cytotoxicity |
| (Małek et al., 2025) [317] | BV (Apis m.), Melittin | Glioblastoma | In vitro: MO3.1, LN229 and LN18 cell line | Cytotoxicity |
| (Jeong et al., 2019) [318] | BV (Apis m.) | Lung cancer | In vitro: A549, H793, H23 lung cancer cell lines | Anti-metastatic, cytotoxicity, cell invasion inhibition, Gene expression pathway |
| (İlhan et al., 2025) [319] | BV | Thyroid medullary carcinoma | In vitro: Thyroid cancer cell line Nanoparticle delivery of BV: ZIF-8 | Cytotoxicity, gene expression-pathway |
| (Amer et al., 2025) [320] | BV (Apis m.) | Lung cancer | In vitro: Vero, A549 cell line; bacteria: Mycobacterium smegmatis Nanoparticle delivery by chitosan | Anti-bacterial Anti-tumor Antibiotic resistance |
| (Halici et al., 2025) [321] | BV | Chronic myeloid leukemia (CML) | In vitro: K562 cell line | Cell viability |
| (Qanash et al., 2025) [322] | BV (Apis m.) | Hepatocellular Carcinoma | In vitro: HEPG2 cell line; Bacteria: S. aureus, Bacillus subtilis, E. coli, Salmonella Typhimurium; Fungi: Aspergillus niger, C. albicans Nanoparticle delivery by zinc oxide and polyvinyl alcohol nanofilm | Anti-inflammatory, Anti-microbial, cytotoxicity Anti-oxidant activity hemolytic activity |
| (Gülmez et al., 2017) [213] | BV (Apis m.) | Colon adenocarcinoma Cervical cancer, Glioblastoma | In vitro; HT-29, HeLa, C6, Vero | Anti-microbial, apoptosis, apitherapy, cytotoxicity |
| (Abdel-Monsef et al., 2023) [215] | Superoxide dismutase from BV (Apis m.) | Breast cancer Hepatocellular carcinoma | In vitro; HepG-2, MCF-7 cell lines | Anti-microbial, Characterization of BV, anti-tumor |
| (Sobral et al., 2016) [323] | BV (Apis m.) | Lung cancer Breast cancer Cervical cancer Leukemia Hepatocellular carcinoma | In vitro; HeLa, NCI-H460, RAW264.7, HepG2, MCF-7 cell lines | Anti-inflammatory, cytotoxicity, Anti-oxidant activity, Characterization of BV |
| (El Mehdi et al., 2021) [324] | BV (Apis m. intermissa) | Lung cancer Hepatocellular carcinoma Cervical cancer Melanoma Breast cancer | In vitro; HeLa, NCI-H460, RAW264.7, MM127, HepG2, MCF-7 cell lines | Anti-inflammatory, chemical profiling of BV, Cytotoxicity |
| (Borojeni et al., 2020) [325] | BV (Apis m.) | Lung cancer Cervical cancer breast cancer | In vitro; A549, HeLa, MDA-MB-231 cell lines | Apoptosis, cytotoxicity |
| (Kabakci et al., 2023) [158] | BV | breast cancer | In vitro; MCF-10A, MCF-7 cell lines | Apoptosis, cell cycle arrest, cytotoxicity |
| (Hwang et al., 2022) [36] | BV (Apis m.) | Lung cancer | In vitro; A549 cell line | Anti-inflammatory, cytotoxicity |
| (Chahla et al., 2024) [326] | BV (Apis m. syriaca) | Glioblastoma | In vitro; U87 cell line In vivo; Animal: mice | Cytotoxicity, anti-tumor, brain multiform |
| (Abass et al., 2025) [37] | BV (Apis m.) | Ehrlich ascites carcinoma | In vitro: EAC cell line In vivo; Animal: mice Xenograft | Anti-inflammatory Liver |
| (El-Bassion et al., 2016) [327] | BV (honeybee) | Lung Cancer Colon Cancer Cervical Cancer Prostate Cancer Larynx Cancer Rhabdomyosarcoma Hepatocellular Carcinoma Breast Cancer | In vitro; HeLa, A549, HCT116, PC3, HEP-2C, RDA, MCF-7, HepG2 cell lines In vivo; Animal: rats | Cytotoxicity |
| (Soukhtanloo et al., 2019) [328] | BV (Apis m.) | Colon Cancer | In vitro; HT-29, L929 cell lines | Apoptosis, Gene Expression-Pathway |
| (Alalawy et al., 2020) [329] | BV (Apis m.) | Cervical Cancer | In vitro; HeLa cell line Nanoparticle delivery of BV by chitosan coating | Apoptosis, cytotoxicity |
| (Frangieh et al., 2019) [174] | BV (Apis m.) | Breast Cancer | In vitro; 3T3, MCF-7 cell lines | Anti-bacterial, chemical profiling of BV, Anti-oxidant activity, |
| (El-Didamony, Amer et al., 2022) [330] | BV | Prostate cancer | In vitro; OEC, PC3 cell lines Delivery of BV | Apoptosis, cytotoxicity, cellular toxicity |
| (Duffy et al., 2020) [331] | BV (Apis m.) and melittin | Breast cancer | In vitro; MDA-MB-231, MCF-7, HDFa, HEK293FT, MCF-10A, MCF-12A, SKBR3 breast cancer, SUM149, SUM159, T-47D, ZR-75-1 cell lines | Membrane interactions of melittin, Gene Expression-Pathway |
| (Duarte et al., 2022) [332] | BV (Apis m.) | Breast cancer Colon Cancer | In vitro; HT-29, MCF-7 cell lines | Chemical profiling of BV, Synergy with 5-FU, cytotoxicity |
| (Sengul et al., 2024) [333] | BV | Lung cancer | In vitro; A549 cell line | Synergy with stem cells |
| (Lebel et al., 2021) [334] | BV and melittin | Glioblastoma | In vitro; Hs683, T98G, U737 cell lines | Apoptosis, Cytotoxicity, Characterization of BV, anti-tumor |
| (M. Sarhan et al., 2020) [268] | BV (Apis m.) | Liver cancer | In vitro; HUh7it-1 cell line | Anti-viral, gene expression |
| (A. G. Kamel et al., 2024) [335] | BV | Breast cancer Hepatocellular Carcinoma | In vitro; HepG2, MCF-7, HSF cell lines Nano delivery by chitosan | Gene Expression-Pathway, anti-tumor |
| (Amar et al., 2021) [336] | BV (Apis m.) | Tongue squamous cell carcinoma Melanoma | In vitro; TSCC, SCC25 cell lines | Synergy with cisplatin, Gene Expression-Pathway, cytotoxicity |
| (Shaimaa H. Shadeed, 2022) [337] | BV | Colon cancer | In vitro; Caco-2, HCT116 cell lines | Synergy with cetuximab, apoptosis, Gene Expression-Pathway, cytotoxicity |
| (Drigla et al., 2016) [338] | BV | Breast cancer | In vitro; MCF-7, HS578T cell lines | Synergy with propolis, Cytotoxicity |
| (Khamis et al., 2024) [339] | Not just BV, but also hesperidin and piperin | Breast cancer | In vitro; MCF-7 cell line In vivo; Animal: rats | Synergy with tamoxifen, Apoptosis, Gene Expression-Pathway, anti-angiogenesis |
| (Badivi et al., 2024) [340] | BV | Lung cancer | In vitro; A549 cell line Delivery of BV by PEGylate | Apoptosis, Gene Expression-Pathway, cytotoxicity |
| (Mirzavi et al., 2024) [56] | BV | Colon cancer | In vitro; C26 cell line In vivo; Animal: mice, Xenograft | Anti-inflammatory, Gene Expression-Pathway, Anti-oxidant activity, anti-tumor |
| (Babayeva et al., 2024) [341] | BV (Apis m.) | Hepatocellular Carcinoma Colon cancer Ewing sarcoma Prostate cancer | In vitro; HUH7, HT-29, Caco-2, A-673, SW-48, CARM-L12 TG3, PC-3 cell lines | Cytotoxicity |
| (Orman et al., 2025) [342] | BV (Apis m.) | Prostate cancer Breast cancer | In vitro; CCD34-Lu, HEK293 MDA-MB-231, PC3 | Apoptosis, Delivery with mesoporous silica |
Despite the increasing interest in BV as a possible anti-cancer treatment, there are still significant research gaps. Most investigations are confined to in vitro studies, with only a handful of in vivo models and no clinical trials so far, which impedes clinical application. There is a scarcity of detailed studies examining less prevalent cancers, mechanisms of drug resistance, long-term toxicity, and the comparative effects on healthy cells. Moreover, most research does not adequately address molecular mechanisms, immune modulation, or interactions within the tumor microenvironment. Although some advancements have been made with nanoparticle delivery systems, targeted and advanced delivery technologies still require further exploration. Inconsistencies regarding the source of the venom, its purification, and dosing also emphasize the need for standardization. The limited use of systems biology, bioinformatics, and personalized medicine underscores the need for stronger interdisciplinary research to fully realize bee venom’s therapeutic potential in cancer.
4.3.2. Melittin in Cancer Research
In vitro cell culture has been widely implemented in cancer research regarding melittin as well as bee venom (Table 10). Preclinical studies using animal models, in particular mouse models, are also common regarding the anti-cancer effects of melittin (Table 11). Targeting various types of cancer, many studies involve xenografts (Table 11) and the inoculation of human cancer cell lines. Xenograft is the transplantation of living tissue from a different species or species to another. In cancer research, xenograft models are powerful preclinical tools created by transplanting human tumor cells into immunocompromised animals, typically mice. These models allow researchers to observe the growth, invasion, and metastasis of human cancer cells within a living organism. They are widely used to evaluate the efficacy and toxicity of newly developed anti-cancer agents, including chemotherapy, targeted therapies, and immunotherapies. Xenograft models employing aggressive human cancer cell lines such as MDA-MB-231 are particularly valuable for studying metastatic processes [113,117]. As a result, they provide critical insights during the preclinical stage, offering a more reliable foundation for the transition to human clinical trials (Table 10).
In many of the studies, a prominent experimental design choice is melittin analogs. These peptides are engineered—through design, hybridization, synthesis, and conjugation—to reduce melittin’s drawbacks, such as cytotoxicity and hemolysis, while enhancing stability against environmental degradation and improving therapeutic efficiency. Additionally, peptide design to target specific molecular interactions is a popular research topic [155,298,343,344] (Table 10). Components of these largely chemical interactions can be other peptides, therapeutic molecules, nanoparticles such as metal ions, or other biocompatible delivery elements [301,345,346]. For melittin synthesis, plasmid-based E. coli design is a noticeable method, alongside fungi. Not just as a stand-alone, melittin can be used as an enhancer for chemotherapy agents like cisplatin. In this case, membrane disruption potential plays a major role, and melittin may have synergistic effects or may behave like a delivery tool [200,331,347,348].

Table 10.
In vitro cancer models for Melittin.
Table 10.
In vitro cancer models for Melittin.
| Article Name | Cancer Type | Cell Lines | Experimental Design | Additional Information |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| (Ebrahimdoust et al., 2023) [298] | Leukemia | Jurkat T, Raji cell lines | Melittin-derived cecropin-A-(CM11), Melittin hybrid | Apoptosis, Anti-tumor |
| (Sattayawat et al., 2025) [299] | lung cancer | Vero, A549, NCI-H460, NCI-H1975 cell lines | Apis florea, Apis m. Synergy with gefitinib | Apoptosis, Cytotoxicity Gene expression-pathway |
| (Alibeigi et al., 2025) [300] | Breast cancer | MCF-10A, SKBR3, and MCF-7 cell lines | Apis cerana cerana Melittin synthesis via E. coli Melittin-loaded pectin | Cytotoxicity, Gene expression-pathway, Hemolytic activity, Wound healing |
| (S. Liu et al., 2025) [346] | Cervical cancer | HeLa cell line | Apis m. Mel-7 Nanoparticle delivery by black phosphorous, Nanosheet | AMP, Anti-bacterial, Wound dressing/healing Cell viability |
| (Y. Li et al., 2025) [349] | Cervical cancer | HeLa cell line | Melittin analog design Melp5 analog Melittin-derived: d-m159 | Apoptosis Gene expression-pathway Oxidative stress |
| (Zheng et al., 2024) [301] | Hepatocellular carcinoma, breast cancer | HepG2, 4T1, CT26cell line | Nanoparticle delivery of melittin: polydopamine | |
| (Hamze Mostafavi et al., 2025) [122] | Breast cancer | BT-474 NIH3T3 | Delivery Synergy with Trastuzumab Melittin synthesis via E. coli | Immunomodulation |
| (Lischer et al., 2021) [350] | Breast cancer | MCF-7 cell line | Melittin purification | Apis cerana, Anti-tumor Cytotoxicity |
| (Sevin et al., 2023) [88] | Brain cancer | U87MG glioblastoma cell line | BV (Apis m.) Apamin PLA2 | Cytotoxicity, Gene expression-pathway, Immunomodulation |
| (Yaacoub et al., 2022) [297] | Cervical Cancer | HeLa cell line | Apis m. PLA2 | Anti-coagulation, Proteolytic activity, Cytotoxicity |
| (Zarrinnahad et al., 2018) [302] | Cervical Cancer | HeLa cell line | Apis mellifera Melittin purification | Apoptosis, Honey bee venom, Hemolytic activity Cytotoxicity |
| (Moghaddam et al., 2020) [351] | Breast cancer | 4T1 cell line | Cisplatin Doxorubicin | Cytotoxicity Gene Expression-Pathway Hemolytic activity |
| (Bayat et al., 2022) [345] | Breast cancer | MCF-7 cell line | Delivery of melittin with nanoparticles Synergy | Cytotoxicity |
| (H. N. Lim et al., 2019) [306] | Melanoma | A375SM, SK-MEL-28, B16F10 cell lines | Not just melittin | Cell migration inhibition, Cell invasion, Gene expression-pathway |
| (Do et al., 2014) [247] | Skin cancer | SCC12, SCC25, NHK cell lines | C. albicans | AMP, Anti-fungal, Cytotoxicity, Skin diseases |
| (Y. Xiao et al., 2024) [343] | Breast cancer | MCF-7, SKBR3, MDA-MB-231 cell lines | Melittin derived; Mel-22, Mel-23a, Mel-23b Delivery of melittin | Stabilization of melittin Serum stability |
| (Daniluk et al., 2022) [352] | Breast cancer | MDA-MB-231, HFFF2, MCF-7 cell lines | Delivery of melittin with nanoparticles | Gene expression-pathway |
| (Dabbagh Moghaddam et al., 2021) [353] | Breast cancer | 4T1 and SKBR3 cell lines | Delivery of melittin with nanoparticles: Niosomes | Gene expression-pathway Hemolytic activity Wound dressing/healing |
| (Jiang et al., 2019) [155] | Liver cancer | SMMC-7721 cell line | Melittin hybrid design Synergy with thanatin | AMP, Anti-bacterial, Hemolytic activity |
| (Y. Wu et al., 2017) [344] | Liver cancer | SMMC-7721 and HepG2 cell lines | Melittin derived; Mel-S4, Mel-S3, Mel-S1, Mel-S2 | Hemolytic activity |
| (Sahsuvar et al., 2023) [159] | Cervical cancer Breast cancer | HeLa, 3T3, C33A, NSF, MCF-7 cell lines | Synergy Melittin hybrid Conjugate | Anti-bacterial, Anti-oxidant activity, Cytotoxicity, Folic acid, Hemolytic activity |
| (E. Han et al., 2023) [354] | Breast cancer | MCF-7 cell line | Delivery of melittin Not just melittin Doxorubicin | Gene expression-pathway Drug resistance Chemotherapy |
| (Jamasbi et al., 2018) [162] | Gastric cancer | MKN-7, MKN-74, NUGC-3 cell lines | Melittin synthesis via E. coli | Anti-bacterial, Cytotoxicity ROS, Hemolytic activity |
| (Kyung et al., 2018) [347] | Lung, Breast and Cervical cancer | A549, NCI-1299, MCF-7, HeLa cell lines | Delivery of melittin | Apoptosis Membrane interactions Cell penetrating Cytotoxicity |
| (M. Su et al., 2016) [355] | Ovarian cancer | SKOV3 cell line | Melittin-derived; atf-melittin Melittin synthesis via fungi | Anti-tumor Honey bee venom |
| (Qi et al., 2020) [356] | Cervical cancer | HeLa cell line | Delivery of melittin with nanoparticles | Apoptosis Cytotoxicity |
| (Honari et al., 2024) [357] | Non-small cell lung cancer | A549, Calu-3, MRC-5 cell lines | Delivery of melittin with nanoparticles: niosomes | Apoptosis Cytotoxicity Wound dressing/healing |
| (Ertilav & Nazıroğlu, 2023) [305] | Glioblastoma | DBTRG-05MG cell line | Cisplatin Synergy | Apoptosis Anti-tumor Cytotoxicity Gene Expression-Pathway Honey bee venom Oxidant activity |
| (Duffy et al., 2020) [331] | Triple negative breast cancer | SKBR3, MDA-MB-231, MCF-10A, HEK293FT, SUM149, SUM159, MCF-12A, HDFa, T-47D, ZR-75-1, MCF-7 cell lines | Delivery BV Bombus terrestris | Apis m. Membrane interactions of melittin Gene Expression-Pathway |
| (El-Didamony et al., 2024) [187] | Colon cancer Liver cancer | HCT116, Wi-38, Huh7 cell lines | Melittin-derived: melittin alcalase-hydrolusate Melittin hybrid Characterization of BV | Anti-bacterial Anti-biofilm Anti-tumor Apis m. Cell migration inhibition Cytotoxicity Multifunctional bioagent |
| (Zamani et al., 2024) [304] | Colorectal cancer | HCT116 cell line | Cytotoxicity Gene Expression-Pathway Autophagy | |
| (Z. Jin et al., 2018) [358] | Bladder cancer | T24 and 5637 cell line | Gene expression-pathway | |
| (Sangboonruang et al., 2020) [359] | Melanoma | NIH3T3 and A375 cell lines | Apis florea Apoptosis Gene Expression-Pathway Cytotoxicity | |
| (H. Li, 2024) [360] | Lung cancer | H1299 and A549 cell lines | Gene expression-pathway Anti-angiogenesis Anti-tumor | |
| (Kreinest et al., 2020) [361] | Hodgkin lymphoma | KM-H2 and L-428 cell lines | Cisplatin Synergy | Cytotoxicity Chemotherapy resistance |
| (Tipgomut et al., 2018) [362] | Human Bronchogenic Carcinoma Lung cancer | ChaGo-K1, THP-1 Wi-38 cell lines | Apoptosis Cell cycle arrest Cytotoxicity Apis m. | |
| (X. Li et al., 2022) [363] | Lung cancer | A549 cell line | Apoptosis Ferroptosis Wound dressing/healing ROS | |
| (Kong et al., 2016) [364] | Gastric cancer | SGC-7901 Cell line | Apoptosis ROS Gene Expression-Pathway | |
| (Zorilă et al., 2020) [348] | Colon cancer Osteosarcoma Liver cancer | HT-29, MG-63, HepG2, L929 cell lines | Liposome In silico analysis | AMP Membrane interactions |
| (Q. Chen et al., 2019) [365] | Liver cancer | Huh7, SMMC-7721 and HepG2 cell lines | Gene expression-pathway | |
| (J. Yao et al., 2020) [366] | Bladder cancer | 5637 and UM-UC-3 cell lines | Anti-metastatic Cell migration inhibition Gene Expression-Pathway | |
| (Mir Hassani et al., 2021) [367] | Breast cancer | MDA-MB-231 cell line | Anti-angiogenesis Anti-tumor Gene Expression-Pathway | |
| (X. Wang et al., 2017) [303] | Pancreatic cancer | SW1990, Capan1, AsPC-1, BXPC-3 and HEK293T cell lines | Gemcitabine Synergy | Chemotherapy resistance Anti-tumor Gene Expression-Pathway |
| (X. Li et al., 2023) [368] | Lung cancer | A549 cell line | Anti-tumor, Autophagy Apoptosis, Gene Expression-Pathway | |
| (Salimian et al., 2022) [369] | Breast cancer | MDA-MB-231 cell line | Anti-metastatic, Cell migration inhibition, Cytotoxicity, Gene Expression-Pathway | |
| (Z. Zhang et al., 2016) [370] | Human hepatocellular carcinoma | Bel-7402, Hep3b, Huh7, HUVEC, HepG2, LO2, SMMC-7721, MHCC97-H cell lines | Anti-angiogenesis Anti-metastatic Apis m. Gene Expression-Pathway | |
| (Jeong et al., 2014) [371] | Breast cancer | MDA-MB-231 and MCF-7 cell lines | Apis m. | Cell invasion Gene Expression-Pathway |
| (J.-Y. Huang et al., 2021) [372] | Gastric adenocarcinoma | AGS cell line | Anti-metastatic Gene Expression-Pathway Wound dressing/healing | |
| (Y. Lv et al., 2022) [373] | Breast cancer Hepatocellular carcinoma | MCF-7, Hepa1-6 cell lines | Melittin analog Melittin synthesis In silico analysis Apis m. | Anti-tumor Cytotoxicity Hemolytic activity Molecular dynamics |
| (H. Jung et al., 2022) [312] | Cervical cancer | BEAS-2B, RAW264.7, RBL-2H3, HeLa cell lines | Melittin derived | Anti-inflammatory Allergy Anti-oxidant activity Cytotoxicity |
| (Plasay et al., 2022) [374] | Breast cancer | MCF-7 cell line | Apoptosis Gene Expression-Pathway | |
| (Ceremuga et al., 2020) [375] | ALL, CML | CCRF-CEM, K-562 cell lines | Apis m. | Apoptosis |
| (Plasay & Muslimin, 2024) [376] | Colorectal cancer | WiDr cell line | Gene expression-pathway Cytotoxicity Honey bee venom | |
| (Obeidat et al., 2023) [377] | Leukemia | K-562 cell line | BV Melittin purification | Apoptosis Cell cycle arrest Apis m. Cytotoxicity |
| (Alonezi et al., 2017) [378] | Ovarian cancer | A2780, A2780CR cell lines | Synergy with cisplatin Delivery of melittin | Activity/mechanism Cytotoxicity |
| (Lebel et al., 2021) [334] | Glioblastoma | Hs683, U737, T98G cell lines | Characterization of BV BV | Apoptosis Anti-tumor Cytotoxicity |
| Li et al., 2018 [307] | Lung cancer Cervical cancer | A549 and HeLa cell lines | Delivery by nanoparticles: zeolitic imidazolate | Gene expression-pathway |
| (Wattanakul et al., 2019) [379] | Colon cancer | Caco-2 cell line | Delivery of melittin with nanoparticles: alginate | Chemotherapy enhancement |
| (H. Lai et al., 2017) [380] | Breast cancer | MCF-7 Cell line | Delivery of melittin with nanoparticles: nanodiamonds | Cytotoxicity |
| (Nikodijević et al., 2024) [381] | Colon cancer | HT-29 and MRC-5 cell lines | Apoptosis Drug resistance Cytotoxicity | |
| (M. C. Shin et al., 2016) [382] | Glioblastoma Cervical cancer | U87MG, LS174T, MDCK, CT26 and HeLa cell lines | Gelonin synergy Characterization Melittin Genetic design | Anti-tumor Cytotoxicity Ribosome inhibition |
| (Maani et al., 2023) [383] | In silico analysis | Melittin hybrid design In silico analysis | Molecular dynamics of melittin | |
| (Keykanlu et al., 2016) [384] | Breast cancer | MCF-7 cell line | Delivery of melittin with nanoparticles: Perfluorooctyl Bromide Synergy with lactoferrin | Hemolytic activity |
| (S.-K. Zhang et al., 2016) [200] | Glioblastoma Cervical cancer | HeLa cell line | Apis m. Melittin-derived peptide: AR-23, RV-23 | AMP Anti-bacterial Hemolytic activity Membrane interactions |
| (Keil et al., 2020) [55] | Lung cancer | Jurkat T lymphocytes, A549 cell lines | Melittin is only reference molecule | Anti-inflammatory Immunomodulation Asthma disease Endosomal escape |
| (Rajabnejad et al., 2018) [385] | Lung cancer | L929 and A549 cell lines | Apis m. Delivery of melittin with AS1411 | Alpha helical peptide Cytotoxicity Hemolytic activity |
| (C. Zhou et al., 2020) [386] | Esophageal carcinoma | TE1 and Het-1a cell lines | Synergy | Apoptosis Anti-tumor Cell migration inhibition Cell cycle arrest Gene Expression-Pathway ROS |
| (Soliman et al., 2019) [387] | Gastric adenocarcinoma | COLO205, HCT-15, AGS cell lines | Melittin | Membrane Interactions Cytotoxicity |
| (Nakagawa et al., 2020) [388] | Melanoma | A375, A2058 cell lines | Allium sativum Melittin is the only reference Cytotoxicity Hemolytic activity | |
| (Gao et al., 2024) [389] | Lung cancer | A549 cell line | Melittin hybrid: melittin-mil-2 | Anti-tumor Gene Expression-Pathway |
| (Erkoc et al., 2022) [57] | Breast cancer | HUVEC, MDA-MB-231, HEK293T, RAW264.7 and HMEC-1 cell lines | BV BV elements melittin derived | Anti-inflammatory Honeybee Gene Expression-Pathway Apis m. Anti-tumor |
| (Delvaux & Rice, 2022) [390] | Liver cancer | HepG2 cell line | Melittin derived; melP5 Melittin synthesis Conjugate Delivery of melittin | Endosomal escape with melittin |
| (Yan et al., 2022) [391] | Bladder cancer | T24, EJ, BIU87 SV-HUC-1 cell lines | Delivery of melittin RNA | Apoptosis Gene Expression-Pathway Anti-tumor |
| (Daniluk et al., 2019) [392] | Breast cancer | MDA-MB-231 and MCF-7 cell lines | Delivery of melittin with nanoparticles: graphene | Apoptosis, ROS, Cytotoxicity, Membrane interactions |
| (R. Wang et al., 2022) [393] | Cancer | In silico analysis | AMP Melittin derived | Membrane interactions |
| (Hussein et al., 2023) [394] | Breast cancer | MDA-MB-231, MCF-7 cell lines | Delivery of melittin | Carnosine Synergy with olaparib |
| (Gasanoff et al., 2021) [124] | T cell leukemia | Jurkat T cell line | Docking | Membrane interactions Immunomodulation |
| (Q. Liu et al., 2025) [395] | Hepatocelular carcinoma | 293T, A20, COC1, Hepa1-6, Hepg2, Huvec, U937 | Melittin | Membrane interactions Peptide design Hemolytic activity |
| (Raveendran et al., 2020) [396] | Breast Cancer | MDA-MB-231 and MCF-7 cell lines | Delivery of melittin | Cytotoxicity |
| (R. Wu et al., 2025) [397] | Ovarian cancer | SKOV3 cell line | Melittin | Apoptosis Gene Expression-Pathway Cell cycle arrest |
| (Feng et al., 2020) [398] | Colon Cancer | CT26 cell line | Delivery of melittin Hydrogel | Membrane interactions |
| (Motiei et al., 2021) [399] | Breast Cancer | MDA-MB-231 cell line | Delivery of melittin with nanoparticles: chitosan | Apoptosis Nano peptide: LTX-315 Synergy with miRNA34a |
| (Ibrahim et al., 2025) [400] | Lung cancer | A549 cell line | Gene Expression-Pathway Synergy | |
| (Bahreyni et al., 2023) [110] | Breast and cervical cancer, melanoma | 4T1, B16F10, HeLa, MDA-MB-231 cell lines | Synergy Delivery | Anti-tumor Melittin derived Immunomodulation |

Table 11.
In vivo animal model cancer research with melittin (cell lines used for induction of in vivo cancer models).
Table 11.
In vivo animal model cancer research with melittin (cell lines used for induction of in vivo cancer models).
| Article Name | Cancer Type | Cell Lines | Experimental Design | Additional Information |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| (H. Wang et al., 2025) [111] | Breast cancer | 4T1 cell line | Delivery of melittin Conjugate Melittin synthesis Xenograft | Cytotoxicity Anti-tumor Immunomodulation Promelittin |
| (Song et al., 2023) [112] | Cervical cancer Melanoma | HeLa, B16F10-OVA, DC2.4-Gal8-GFP cell lines | Vaccine D-melittin Drug delivery | Immunogenicity Immunomodulation Cell viability |
| (Rocha et al., 2022) [401] | Bone cancer Colorectal cancer | HT-29 cell line | Xenograft | Apis m. Anti-metastatic Cell viability |
| (S. Jia et al., 2025) [402] | Osteosarcoma | K7M2 cells and BMDCs | Animal: mice Melittin-derived peptide | AMP Hemolytic activity |
| (H. Zhang et al., 2025) [403] | Glioblastoma | Hs683 and T98G cell lines | Delivery of melittin with nanoparticles: liposome Xenograft Synergy with Resveratrol | Anti-tumor Hemolytic activity Gene Expression-Pathway Hemolytic activity |
| (F. Jia et al., 2021) [404] | Non-small cell lung carcinoma, Ovarian cancer | NCI-H358 and SKOV3 cell lines | Delivery of melittin Xenograft | Anti-tumor Cytotoxicity Hemolytic activity |
| (S. Lv et al., 2021) [405] | Breast cancer Lung cancer Colon carcinoma | A549, CT26, 3T3, MDA-MB-231 cell lines | Delivery of melittin with nanoparticles D-melittin | Anti-tumor Hemolytic activity |
| (Shir et al., 2011) [113] | Glioblastoma, Breast cancer, Vulval epidermoid carcinoma | A431, U138MG, U87MG, MDA-MB-231 cell lines | Delivery of melittin Xenograft | Gene Expression-Pathway Interactions Hemolytic activity Immunomodulation |
| (S. Kim et al., 2022) [406] | Breast cancer Acute Monocytic Leukemia | 4T1 and THP-1 cell lines | Delivery of melittin Hybrid design Xenograft | Anti-metastatic Honeybee Hemolytic activity |
| (X. Kang et al., 2024) [169] | Hepatocellular carcinoma | HepG2 cell line | E. coli, K. pneumoniae, S. aureus Not just melittin | Anti-bacterial AMP Bacterial vaginosis disease Cytotoxicity |
| (Y. Wang et al., 2025) [407] | Lung cancer | A549 lung cancer cell line (A549/DDP) | Xenograft | Gene Expression-Pathway Chemotherapy resistance Honeybee |
| (J. Zhang et al., 2023) [408] | Hepatocellular carcinoma | BHK-21, L02, epG2 cell lines | Delivery of melittin with nanoparticles Xenograft | Cytotoxicity Membrane interactions Hemolytic activity |
| (X. Yu et al., 2019) [114] | Liver cancer, Colon carcinoma, Melanoma, Breast cancer | 4T1, B16F10, CT26 cell lines | Delivery of melittin with nanoparticles Xenograft | Gene Expression-Pathway Anti-metastatic Anti-tumor Immunomodulation |
| (Chang et al., 2022) [409] | Breast cancer | MCF-7 and 4T1 cell lines | Melittin synergy with radiation Xenograft | Apoptosis Apis m. Anti-tumor |
| (P. Wu et al., 2022) [115] | Breast cancer, Hepatocellular carcinoma | 4T1 and HEP1-6 cell lines | Not just melittin Delivery of melittin with siRNA nanoparticles Synergy Xenograft | Anti-metastatic Anti-tumor Cold tumor Immunomodulation Apoptosis Pathway interactions |
| (P. Xu et al., 2024) [410] | Glioblastoma | U251 cell line | Xenograft | Gene Expression-Pathway Cell cycle arrest Anti-metastatic Anti-tumor |
| (Meng et al., 2024) [411] | Hepatocellular carcinoma, Cervical cancer, Leukemia, | HeLa, Huh7, HEK293T, K-562, HEK293, HepG2, Hepa1-6 cell lines | Delivery of vector Melittin analog design: p5RHH | Transduction Transfection |
| (S.-F. Zhang & Chen, 2017) [412] | Lung cancer | A549 cell line | Xenograft | Gene Expression-Pathway Cell migration inhibition Apis m. Wound dressing/healing Anti-angiogenesis Anti-tumor |
| (S. Zhang et al., 2021) [413] | Lung cancer | A549 cell line | Xenograft | Apoptosis Gene Expression-Pathway Chemotherapy resistance Anti-tumor Glycolysis inhibition |
| (H. Zhu et al., 2021) [414] | Bone cancer | 143 B cell line | Xenograft | Gene Expression-Pathway Anti-metastatic |
| (Qin et al., 2016) [415] | Bone cancer | UMR-106 cell line | Xenograft | Anti-tumor Anti-angiogenesis Gene Expression-Pathway |
| (Yan et al., 2023) [416] | Prostate Cancer | DU145, PC3 cell lines | Synergy with cisplatin Xenograft | Wound dressing/healing Gene Expression-Pathway Cell migration inhibition Anti-tumor Cisplatin sensitivity |
| (R. Yu et al., 2021) [417] | Lung cancer | A549 and H358 cell lines | Xenograft | Apoptosis Gene Expression-Pathway Cytotoxicity Cell migration inhibition |
| (C. Lee et al., 2017) [116] | Lung cancer Papillary adenocarcinoma | LCC, MLE12, and H441 cell lines | Xenograft | Gene Expression-Pathway Anti-tumor ROS Immunomodulation |
| (Luo et al., 2023) [418] | Colorectal cancer | HCT116, HT-29, SW-480, CCD 841 cell lines | Xenograft | Apoptosis Anti-tumor |
| (X. Wang et al., 2018) [419] | Pancreatic cancer | PANC-1, SW1990, HPDE, PATU8988, HS766T and BCPC3 cell lines | RNA Xenograft | Gene Expression-Pathway |
| (X. Yu et al., 2020) [420] | Melanoma | B16F10 and E0771 cell lines | Delivery of melittin with nanoparticles Xenograft | Anti-tumor |
| (M. Liu et al., 2016) [117] | Lung cancer Liver cancer Breast cancer Ovarian cancer | A549, SMMC-7721, MDA-MB-231, SKOV3 and CTLL-2 cell lines | Melittin fusion design Xenograft | Anti-tumor Cytotoxicity Immunomodulation |
| (Guo et al., 2023) [118] | Breast cancer | 4T1 cell line | Delivery of melittin with nanoparticles: metal-phenol Xenograft | Anti-tumor Hemolytic activity |
| (Cheng & Xu, 2020) [421] | Breast cancer Colon cancer | MCF-7, HCT116 cell lines | Delivery of melittin with nanoparticles: Melittin synthesis design Xenograft | Redox sensitivity |
| (Q. Zhao et al., 2022) [422] | Anaplastic thyroid carcinoma | CAL-62 and C-643 cell lines | Synergy with apatinib Xenograft | Gene Expression-Pathway Pyroptosis Anti-tumor |
| (Y. Xie et al., 2023) [423] | Liver cancer | Huh7 and HEK293 cell lines | Delivery of melittin-derived peptide | |
| (I.-H. Han et al., 2022) [121] | Melanoma | B16F10 and THP-1 cell lines | Xenograft | Anti-tumor Gene Expression-Pathway Immunomodulation Wound dressing/healing |
| (Khorsand-Dehkordi & Doosti, 2024) [313] | Breast cancer | MCF-7, MCF-10A, RAW264.7 and 4T1 cell lines | Melittin synthesis via E. coli Xenograft | Anti-tumor apoptosis Gene Expression-Pathway Hemolytic activity |
| (Rahman et al., 2025) [424] | Ovarian cancer | HEK293, KGN, OVCAR-3, SKOV3 cell lines | Animal: mice Xenograft | Gene Expression-Pathway |
| (Sun et al., 2025) [425] | Ovarian cancer | SKOV3 cell lines | Animal: mice İnjection Xenograft | Gene Expression-Pathway |
| (Pedro et al., 2025) [426] | Osteosarcoma | MG-63, UMR-106, D-17 cell lines | 3D cell culture | Cytotoxicity Cell migration inhibition |
| (X. Xie et al., 2022) [427] | Osteosarcoma | 143 B cell line | Animal: mice Xenograft | Apoptosis Gene Expression-Pathway |
| (Y. Li et al., 2018) [307] | Cervical cancer Lung cancer | A549, HeLa, U14 cell lines | Animal: mice Xenograft | Gene Expression-Pathway Anti-tumor Hemolytic activity Nanodelivery with zeolitic imidazole |
| (D. Zhang et al., 2025) [126] | Breast cancer | 4T1 | Animal: mice Injection Delivery of melittin with nanoparticles: hyaluronic acid (HA) and metal (Fe) | Anti-tumor ROS Anti-oxidant activity |
| (Dai et al., 2025) [125] | Breast Cancer | Animal: mice Delivery of melittin | Gene Expression-Pathway | |
| (Tang et al., 2022) [119] | Melittin | B16F10, B16, MB-49, MC38, MC38-OVA | Animal: mice Delivery with MnO2 Vaccine | Anti-tumor Cytotoxicity Immunomodulation |
| (K. Yang et al., 2023) [120] | Melittin | B16-luc, B16F10 | Animal: mice Vaccine Delivery with hydrogel | Anti-tumor Cytotoxicity Hemolytic activity Immunomodulation |
| (Shen et al., 2024) [123] | Melittin | CT26, NIH3T3, HUVEC, CAF | Animal: mice Delivery Synergy | Hemolytic activity Immunomodulation |
Although melittin has been more extensively studied in vivo than bee venom, several notable limitations on melittin research become apparent. Most in vitro studies focus on common cancers like breast, cervical, and lung, while aggressive types such as pancreatic, esophageal, and blood cancers remain underexplored. Research often relies on a few standard cell lines (e.g., HeLa, MCF-7, A549, 4T1), limiting model diversity. Although nanoparticle delivery systems and melittin analogs are being developed, variability in venom sources, delivery methods, and design strategies hinders standardization. In vivo studies are few, mainly in mouse xenografts, with little progress toward clinical trials. Moreover, while cytotoxicity and apoptosis are well studied, interactions with the tumor microenvironment, immune response, metastasis, and chemotherapy resistance are less understood. Additionally, multi-omics or systems are deficient biology approaches that could illuminate the comprehensive biological effects. Lastly, long-term animal studies inadequately address the toxicity and off-target consequences—particularly hemolytic activity. Closing these gaps is vital for advancing melittin from experimental treatment to clinical use in cancer care.
In light of the identified research gaps in both in vitro and in vivo investigations, future studies exploring melittin and bee venom for cancer treatment should focus on several important areas. To enhance the therapeutic significance of melittin, it is crucial to broaden the range of cancer models, particularly by including rare, treatment-resistant, and metastatic forms. Additionally, future research should aim to diversify the cell lines used and implement 3D cultures or organoid systems that more accurately represent the tumor microenvironment. In vivo investigations should advance beyond simplistic xenograft models to encompass metastatic and immunocompetent systems, allowing for a more accurate assessment of effectiveness, toxicity, and immune reactions. Standardized melittin analogs and delivery systems are needed to reduce hemolysis and improve tumor selectivity. Applying multi-omics and systems biology approaches may uncover mechanisms, resistance pathways, and biomarkers for therapy monitoring. Studies exploring the combination of melittin with current chemotherapeutics, immunotherapies, or radiotherapies should be expanded through well-planned synergy assessments, along with thorough long-term safety investigations. Ultimately, it will be essential to address the translational gap with comprehensive preclinical toxicology, pharmacokinetics, and clinical trial frameworks to propel melittin-based therapies toward practical oncology use.
5. Anti-Oxidant Activity
Anti-oxidant activity refers to the capacity of a substance to neutralize free radicals (harmful molecules such as Reactive Oxygen Species, ROS). Free radicals can cause oxidative stress in cells, damaging DNA, proteins, and lipids [162]. This contributes to the development of many diseases, such as aging, cancer, cardiovascular disease, and neurodegenerative disorders.
Bee venom and its main component, melittin, are not only notable for their anti-inflammatory, anti-microbial and anti-cancer effects, but also for their anti-oxidant activity (Table 12). Melittin has the potential to neutralize free radicals and reduce cellular damage associated with oxidative stress. Therefore, bee venom and melittin are considered protective or supportive agents in diseases where oxidative stress plays a key role.

Table 12.
Research on the anti-oxidant activity of bee venom and melittin.
6. Conclusions
This scoping review aims to comprehensively update the current research on the therapeutic potential and bioactivity of bee venom (BV) and its major protein melittin (MEL), which could be systematically (meta)analyzed in future work. It highlights the research fields where BV, MEL and other compounds were predominantly studied while at the same time identifying research gaps and fields that have received comparatively less attention. Figure 3 shows the growing publication numbers on bee venom (BV) and melittin (M), particularly regarding their anti-microbial (overall 179 studies) and anti-cancer (overall 170 studies) effects, followed by anti-inflammatory (overall 85), immunomodulatory (overall 37), and anti-oxidant (overall 32) properties (Figure 3A). Publication trends reveal a sharp increase since 2020, peaking in 2022 (68 studies) and remaining high through 2025 (62 studies so far) (Figure 3B), highlighting sustained scientific attention to their therapeutic potential.
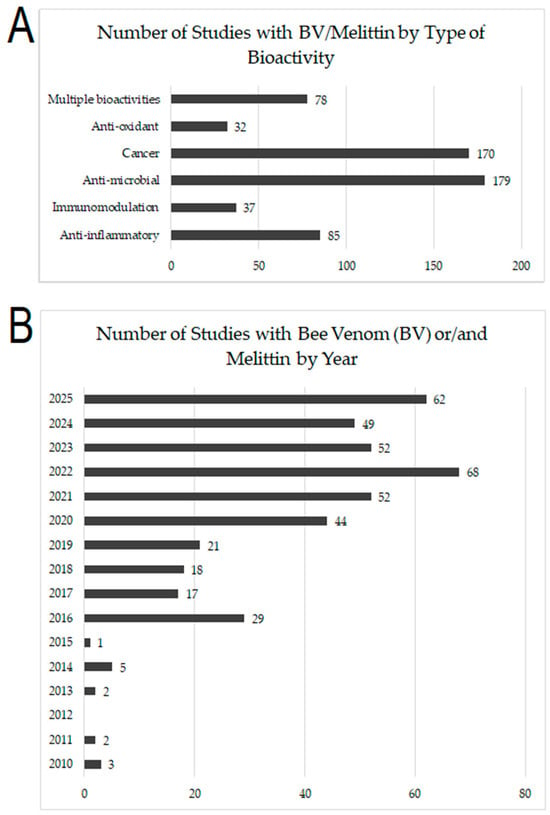
Figure 3.
(A) The number of studies related to specific bee venom (BV)/melittin (M) bioactivity; (B) The overall number of relevant studies published between 2010–2025.
The literature is largely relevant to anti-cancer and anti-microbial activities. The main reason for that is that cancer and infectious diseases are among the major public health issues worldwide. Another reason is the availability of numerous in vitro protocols, thus making it relatively easy to conduct anti-cancer and anti-microbial studies. Anti-cancer research commonly emphasizes the detection of apoptosis-related markers in vitro, anti-metastatic effects, and synergy with conventional chemotherapeutic agents (Table 9 and Table 10). In vivo studies are less frequent and are predominantly conducted using pure melittin rather than bee venom (Table 11). E. coli, S. aureus, and C. albicans are the most studied micro-organisms, and drug/antibiotic resistance is the most popular area for BV/melittin anti-microbial research (Table 8). After the COVID-19 pandemic in 2020, not surprisingly, studies on the effects of BV/melittin against SARS-CoV-2 and MERS viruses have increased.
The anti-inflammatory effects of BV and MEL on rheumatoid arthritis have been extensively studied using animal models (Table 3, Table 4 and Table 5). However, research on their effects on Parkinson’s and Alzheimer’s diseases remains limited. Although these neurodegenerative disorders are associated with inflammation, the required experimental models are technically challenging and relatively costly. Inflammatory conditions are closely linked to immunological deficiencies, which need to be addressed through immunomodulatory approaches. The immunomodulatory activity of BV/MEL has been relatively less studied (Table 6), and most of the existing research focuses on the effects of MEL in cancer models (Table 7). This suggests that anti-cancer studies involving BV/MEL extend beyond cancer treatment alone, also contributing to our understanding of their immunomodulatory potential.
Studies on anti-oxidant activity of BV and/or melittin include a broad spectrum of in vivo (ducks, mice, rats, fish, quail) and in vitro (cell lines such as MCF-7, HeLa, Raw264.7, HT22, and others) models, targeting diseases including neurodegenerative and inflammatory diseases, cancer, diabetes, and colitis. Many studies report anti-oxidant effects alongside anti-inflammatory, cytotoxic, and immunomodulatory, often through gene expression analysis, DPPH assays, or in synergy with other agents (e.g., L-DOPA, cordycepin, propolis, Cu2+) (Table 12). BV is delivered through various systems, including injection, microneedles, nanoparticles, and acupuncture, reflecting growing interest in targeted or alternative therapies. Additionally, multiple studies investigated the chemical profile and hemolytic activity of BV, underlining its complex bioactivity and potential for both therapeutic interventions and toxicity.
Clinically, BV and MEL show promise as adjunctive or alternative therapeutic agents, particularly in conditions where conventional treatments are limited. Their strong anti-bacterial and anti-inflammatory activities point to possible applications in wound healing, drug-resistant infections, and chronic inflammatory diseases. In oncology, MEL pro-apoptotic and cytotoxic properties can be used in targeted delivery systems to minimize systemic toxicity while treating aggressive or resistant tumors. Melittin appears more advantageous in clinical trials than bee venom, as it is a peptide, suggesting that it can be produced synthetically under strict laboratory conditions without the need for beekeeping. On the other hand, bee venom is a mixture of numerous compounds that might act synergistically.
In the current body of research, in vivo studies are predominantly related to investigations of anti-inflammatory, anti-oxidant, and immunomodulatory effects implementing organism-level models necessary to reveal systemic immune interactions across multiple tissues and organs (Table 13). In contrast, cancer research relies largely on in vitro approaches, implementing well-characterized cell lines, the relative simplicity of modeling single-tissue pathologies, and reduced infrastructure requirements. Nevertheless, clinical studies remain limited due to ethical, logistical, and technical constraints. Anti-microbial investigations may be conducted either in vitro or in vivo, because microorganisms are simple unicellular organisms (Table 13). Furthermore, melittin is more frequently investigated in cancer-related studies than bee venom (BV), given that BV composition varies depending on species and collection methods, whereas melittin, as its principal component, is commercially available in standardized form of a well-defined chemical structure.

Table 13.
Experimental design of articles.
Conclusively, bee venom and its major compound, melittin, are among the most promising natural compounds due to their diverse biological activities. Their well-documented anti-inflammatory, anti-microbial, immunomodulatory, anti-cancer, and anti-oxidant properties suggest potential applications in the prevention and treatment of various diseases. Melittin’s ability to modulate cellular signaling pathways to suppress inflammation, regulate immune responses, combat microbial agents, reduce oxidative stress, and inhibit the proliferation and spread of cancer cells highlights its significant pharmacological value. These multifaceted effects underscore the need for continued research on bee venom and melittin, as well as further evaluation in clinical trials.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, D.M.; Methodology, P.M.E. and D.M.; Resources, P.M.E. and D.M.; Writing—Original Draft Preparation, P.M.E., F.B.-T. and S.Ç.-U.; Writing—Review & Editing, P.M.E., F.B.-T., S.Ç.-U., S.K., O.Y. and D.M.; Supervision, D.M., S.K. and O.Y. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Acknowledgments
P.M.E. is a student at Karadeniz Technical University and received an ERASMUS+ internship at the University of Thessaly, Department of Biochemistry & Biotechnology (Larissa, Greece).
Conflicts of Interest
Author Oktay Yıldız was employed by Okta R&D Eng Services Industry Trade Limited Company. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
References
- Housecroft, C.E. The Sting’s the Thing: Chemical Education. Chimia 2019, 73, 1037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isidorov, V.; Zalewski, A.; Zambrowski, G.; Swiecicka, I. Chemical Composition and Antimicrobial Properties of Honey Bee Venom. Molecules 2023, 28, 4135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nader, R.A.; Mackieh, R.; Wehbe, R.; El Obeid, D.; Sabatier, J.M.; Fajloun, Z. Beehive Products as Antibacterial Agents: A Review. Antibiotics 2021, 10, 717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarez-Suarez, J.M. (Ed.) Bee Products—Chemical and Biological Properties; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Germany, 2017; ISBN 978-3-319-59688-4. [Google Scholar]
- Khalil, A.; Elesawy, B.H.; Ali, T.M.; Ahmed, O.M. Bee Venom: From Venom to Drug. Molecules 2021, 26, 4941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ullah, A.; Aldakheel, F.M.; Anjum, S.I.; Raza, G.; Khan, S.A.; Tlak Gajger, I. Pharmacological Properties and Therapeutic Potential of Honey Bee Venom. Saudi Pharm. J. 2023, 31, 96–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yaacoub, C.; Wehbe, R.; Roufayel, R.; Fajloun, Z.; Coutard, B. Bee Venom and its Two Main Components—Melittin and Phospholipase A2—As Promising Antiviral Drug Candidates. Pathogens 2023, 12, 1354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abd-El-Samie, E.M.; Seyam, H.; El-Deeb, A.; El-Mohandes, S.; Badr, M.S.; Surano, A.; Abou Kubaa, R. The Antiviral Activities of Egyptian Ethanolic Propolis Extract and Honey Bee Venom against Honey Bees Infected with Multiple Viruses in Vitro. J. Apic. Res. 2024, 64, 848–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samanci, T.; Kekeçoğlu, M. Comparison of Commercial and Anatolian Bee Venom in Terms of Chemical Composition. Uludag Bee J. 2019, 19, 61–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sonmez, E.; Kekecoglu, M.; Bozdeveci, A.; Karaoglu, S.A. Chemical Profiling and Antimicrobial Effect of Anatolian Honey Bee Venom. Toxicon 2022, 213, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carpena, M.; Nuñez-Estevez, B.; Soria-Lopez, A.; Simal-Gandara, J. Bee Venom: An Updating Review of its Bioactive Molecules and its Health Applications. Nutrients 2020, 12, 3360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cornara, L.; Biagi, M.; Xiao, J.; Burlando, B. Therapeutic Properties of Bioactive Compounds from Different Honeybee Products. Front. Pharmacol. 2017, 8, 412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.H.; Gang, J.; Yang, E.; Kim, W.; Jin, Y.-H. Bee Venom Acupuncture Attenuates Oxaliplatin-Induced Neuropathic Pain by Modulating Action Potential Threshold in A-Fiber Dorsal Root Ganglia Neurons. Toxins 2020, 12, 737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sung, S.-H.; Lee, G. Bee Venom Acupuncture Effects on Pain and its Mechanisms: An Updated Review. Toxins 2021, 13, 608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.S.; Kim, B.Y.; Yoon, H.J.; Choi, Y.S.; Jin, B.R. Secapin, a Bee Venom Peptide, Exhibits Anti-Fibrinolytic, Anti-Elastolytic, and Anti-Microbial Activities. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2016, 63, 27–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Page, M.J.; McKenzie, J.E.; Bossuyt, P.M.; Boutron, I.; Hoffmann, T.C.; Mulrow, C.D.; Shamseer, L.; Tetzlaff, J.M.; Akl, E.A.; Brennan, S.E.; et al. The PRISMA 2020 Statement: An Updated Guideline for Reporting Systematic Reviews. BMJ 2021, 372, n71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmedy, O.A.; Ibrahim, S.M.; Salem, H.H.; Kandil, E.A. Antiulcerogenic Effect of Melittin via Mitigating TLR4/TRAF6 Mediated NF-κB and p38MAPK Pathways in Acetic Acid-Induced Ulcerative Colitis in Mice. Chem. Biol. Interact. 2020, 331, 109276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.M.; Cho, S.-N.; Son, E.; Song, C.-H.; Kim, D.-S. Apamin from Bee Venom Suppresses Inflammation in a Murine Model of Gouty Arthritis. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2020, 257, 112860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Qin, F.; Liu, C.; Zhao, Z.; Wu, H.; Li, J.; Zhang, Z.; Qin, Q. Alleviating Heat Stress-Induced Immune Organ Damage in Ducks: Role of Melittin. Trop. Anim. Health Prod. 2025, 57, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abd El-Hameed, A.M.; Abuelsaad, A.S.A.; Khalil, A. Bee Venom Acupuncture Therapy Ameliorates Neuroinflammatory Alterations in a Pilocarpine-Induced Epilepticus Model. Metab. Brain Dis. 2021, 36, 2047–2058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zahran, F.; Mohamad, A.; Zein, N. Bee Venom Ameliorates Cardiac Dysfunction in Diabetic Hyperlipidemic Rats. Exp. Biol. Med. 2021, 246, 2630–2644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdelrahaman, D.; Shanab, O.; Abdeen, A.; Abdelkader, A.; Elazab, K.M.; Kouriem, H.; Maher, Z.M.; Abu-Almakarem, A.S.; Mohamed, M.E.; Elbastawisy, Y.M.; et al. Bee Venom Ameliorates Gentamicin-Induced Kidney Injury by Restoring Renal Aquaporins and Enhancing Anti-oxidant and Anti-Inflammatory Activities in Rats. Front. Pharmacol. 2025, 16, 1525529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aly, E.K.; Mahmoud, H.S.; Alkhalifah, D.H.M.; Shehab, G.M.G.; Abuelsaad, A.S.A.; Abdel-Rehiem, E.S.; Abdul-Hamid, M. Bee Venom Ameliorates Oxidative Stress and Histopathological Changes of Hippocampus, Liver and Testis during Status Epileptics. Neuropeptides 2023, 101, 102368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gu, H.; An, H.-J.; Gwon, M.-G.; Bae, S.; Leem, J.; Lee, S.-J.; Han, S.-M.; Zouboulis, C.C.; Park, K.-K. Bee Venom and its Major Component Melittin Attenuated Cutibacterium Acnes- and IGF-1-Induced Acne Vulgaris via Inactivation of Akt/mTOR/SREBP Signaling Pathway. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 3152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goo, B.; Lee, J.; Park, C.; Yune, T.; Park, Y. Bee Venom Alleviated Edema and Pain in Monosodium Urate Crystals-Induced Gouty Arthritis in Rat by Inhibiting Inflammation. Toxins 2021, 13, 661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badawi, H.; Abdel-Salam, R.; Abdel-Salam, O.; Youness, E.; Shaffie, N.; Eldenshary, E.D. Bee Venom Attenuates Neurodegeneration and Motor Impairment and Modulates the Response to L-Dopa or Rasagiline in a Mice Model of Parkinson’s Disease. Iran. J. Basic Med. Sci. 2020, 23, 1628–1638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.; Hong, J.Y.; Jeon, W.-J.; Baek, S.H.; Ha, I.-H. Bee Venom Melittin Protects against Cisplatin-Induced Acute Kidney Injury in Mice via the Regulation of M2 Macrophage Activation. Toxins 2020, 12, 574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, D.; Choi, W.; Bae, H. Bee Venom Phospholipase A2 Alleviate House Dust Mite-Induced Atopic Dermatitis-Like Skin Lesions by the CD206 Mannose Receptor. Toxins 2018, 10, 146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, G.-H.; Lee, S.; Choi, D.B.; Shin, D.; Kim, J.; Yang, H.; Bae, H. Bee Venom Phospholipase A2 Ameliorates Atherosclerosis by Modulating Regulatory T Cells. Toxins 2020, 12, 609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baek, H.; Park, S.-Y.; Ku, S.J.; Ryu, K.; Kim, Y.; Bae, H.; Lee, Y.-S. Bee Venom Phospholipase A2 Induces Regulatory T Cell Populations by Suppressing Apoptotic Signaling Pathway. Toxins 2020, 12, 198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, D.-W.; Choi, J.-G.; Kim, J.; Park, J.B.; Lee, J.-H.; Kim, H.-W. Bee Venom Reduces Burn-Induced Pain via the Suppression of Peripheral and Central Substance P Expression in Mice. J. Veter Sci. 2021, 22, e9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinto, M.B.; Pires, P.C.; Calhelha, R.C.; Silva, A.R.; Sousa, M.J.; Vilas-Boas, M.; Falcão, S.I.; Veiga, F.; Makvandi, P.; Paiva-Santos, A.C. Bee Venom-Loaded Niosomes as Innovative Platforms for Cancer Treatment: Development and Therapeutical Efficacy and Safety Evaluation. Pharmaceuticals 2024, 17, 572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Danesh-Seta, T.; Emami, F.; Nasr-Esfahani, M.H.; Ghaedi, K.; Aliomrani, M. Bee Venom–Derived BBB Shuttle and its Correlation with Oligodendrocyte Proliferation Markers in Mice Model of Multiple Sclerosis. Neurotox. Res. 2021, 39, 1181–1188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, W.-H.; An, H.-J.; Kim, J.-Y.; Gwon, M.-G.; Gu, H.; Jeon, M.; Sung, W.J.; Han, S.M.; Pak, S.C.; Kim, M.-K.; et al. Beneficial Effects of Melittin on Ovalbumin-Induced Atopic Dermatitis in Mouse. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 17679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaik, R.A.; Alotaibi, M.F.; Nasrullah, M.Z.; Alrabia, M.W.; Asfour, H.Z.; Abdel-Naim, A.B. Cordycepin- Melittin Nanoconjugate Intensifies Wound Healing Efficacy in Diabetic Rats. Saudi Pharm. J. 2023, 31, 736–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, Y.-N.; Kwon, I.-S.; Na, H.-H.; Park, J.-S.; Kim, K.-C. Dual Cytotoxic Responses Induced by Treatment of A549 Human Lung Cancer Cells with Sweet Bee Venom in a Dose-Dependent Manner. J. Pharmacopunct. 2022, 25, 390–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abass, S.F.; Hussein, M.S.; Hasan, A.F.; Al-Dulimi, A.G.; El-Wahsh, H.M. Effect of Bee Venom (Apis mellifera) on Liver Damage in Mice with Ehrlich Ascites Carcinoma. Regul. Mech. Biosyst. 2025, 33, e25040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hegazi, A.G.; Ibrahim, F.; Ganem, M.; Abdel-Rahman, E.H.; Aziz, S.W.; Medhat, A.; Monir, R.; El Gendy, A. Evaluation of the Apiacupuncture against the Damages and Erythrocyte Osmotic Fragility Induced by Oxidative Stress in Egyptian Patients with Chronic Neck Pain. Egypt. J. Chem. 2023, 67, 467–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yaghoubi, A.; Amel Jamehdar, S.; Reza Akbari Eidgahi, M.; Ghazvini, K. Evaluation of the Therapeutic Effect of Melittin Peptide on the Ulcerative Colitis Mouse Model. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2022, 108, 108810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghorbani, Z.; Abdollahifar, M.A.; Vakili, K.; Moghaddam, M.H.; Mehdizadeh, M.; Marzban, H.; Rasoolijazi, H.; Aliaghaei, A. Melittin Administration Ameliorates Motor Function, Prevents Apoptotic Cell Death and Protects Purkinje Neurons in the Rat Model of Cerebellar Ataxia Induced by 3-Acetylpyridine. Toxicon 2022, 205, 57–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zan, H.; Liu, J.; Yang, M.; Zhao, H.; Gao, C.; Dai, Y.; Wang, Z.; Liu, H.; Zhang, Y. Melittin Alleviates Sepsis-Induced Acute Kidney Injury by Promoting GPX4 Expression to Inhibit Ferroptosis. Redox Rep. 2024, 29, 2290864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, T.; Zhang, J.; Xiao, A.; Liu, W.; Shang, Y.; An, J. Melittin Ameliorates CVB3-Induced Myocarditis via Activation of the HDAC2-Mediated GSK-3β/Nrf2/ARE Signaling Pathway. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2016, 480, 126–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.-Y.; Leem, J.; Hong, H.-L. Melittin Ameliorates Endotoxin-Induced Acute Kidney Injury by Inhibiting Inflammation, Oxidative Stress, and Cell Death in Mice. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2021, 2021, 8843051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, X.; Pei, S.; Zhou, D.; Zhou, P.; Huang, Y.; Hu, X.; Li, T.; Wang, Y.; Huang, Z.; Li, N. Melittin Ameliorates Inflammation in Mouse Acute Liver Failure via Inhibition of PKM2-Mediated Warburg Effect. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2021, 42, 1256–1266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aghighi, Z.; Ghorbani, Z.; Moghaddam, M.H.; Fathi, M.; Abdollahifar, M.-A.; Soleimani, M.; Karimzadeh, F.; Rasoolijazi, H.; Aliaghaei, A. Melittin Ameliorates Motor Function and Prevents Autophagy-Induced Cell Death and Astrogliosis in Rat Models of Cerebellar Ataxia Induced by 3-Acetylpyridine. Neuropeptides 2022, 96, 102295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vu, H.D.; Huynh, P.T.; Ryu, J.; Kang, U.R.; Youn, S.W.; Kim, H.; Ahn, H.J.; Park, K.; Hwang, S.-K.; Chang, Y.-C.; et al. Melittin-Loaded Iron Oxide Nanoparticles Prevent Intracranial Arterial Dolichoectasia Development through Inhibition of Macrophage-Mediated Inflammation. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2021, 17, 3818–3836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, X.; Kang, J.; Li, Y.; Zhang, H.; Yang, Z.; Chen, E. Melittin Protects against Neural Cell Damage in Rats Following Ischemic Stroke. Neuropeptides 2024, 107, 102462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.; Hong, J.Y.; Jeon, W.-J.; Lee, J.; Lee, Y.J.; Ha, I.-H. Melittin Regulates Iron Homeostasis and Mediates Macrophage Polarization in Rats with Lumbar Spinal Stenosis. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2022, 156, 113776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Z.; Fan, Z.; Liu, J.; Wang, J.; Xu, M.; Li, X.; Xu, Y.; Lu, Y.; Han, C.; Zhang, Z. Melittin-Carrying Nanoparticle Suppress T Cell-Driven Immunity in a Murine Allergic Dermatitis Model. Adv. Sci. 2023, 10, 2204184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, X.; Zhang, X.; Fan, J.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, L.; Duan, R.; Hao, H. Neuroprotective Effects of Melittin Against Cerebral Ischemia and Inflammatory Injury via Upregulation of MCPIP1 to Suppress NF-κB Activation In Vivo and In Vitro. Neurochem. Res. 2024, 49, 348–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, C.D.; Yoo, J.; An, E.J.; Sung, C.Y.; Jeong, D.H.; Park, S.-Y.; Kim, J.-H.; Lee, G. Pharmacokinetic Improvement Provided by Microneedle Patch in Delivering Bee Venom, a Case Study in Combating Scopolamine-Induced Neurodegeneration in Mouse Model. Drug Deliv. 2022, 29, 2855–2867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.-Y.; Lee, S.-J.; Maeng, Y.-I.; Leem, J.; Park, K.-K. Protective Effects of Bee Venom against Endotoxemia-Related Acute Kidney Injury in Mice. Biology 2020, 9, 154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.-Y.; Jang, H.-J.; Leem, J.; Kim, G.-M. Protective Effects of Bee Venom-Derived Phospholipase A2 against Cholestatic Liver Disease in Mice. Biomedicines 2021, 9, 992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shin, D.; Lee, G.; Sohn, S.-H.; Park, S.; Jung, K.-H.; Lee, J.; Yang, J.; Cho, J.; Bae, H. Regulatory T Cells Contribute to the Inhibition of Radiation-Induced Acute Lung Inflammation via Bee Venom Phospholipase A2 in Mice. Toxins 2016, 8, 131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keil, T.W.M.; Baldassi, D.; Merkel, O.M. T-cell targeted pulmonary siRNA delivery for the treatment of asthma. WIREs Nanomed. Nanobiotechnol. 2020, 12, e1634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirzavi, F.; Saghi, H.; Ebrahimi, S.; Mahdinezhad, M.R.; Hosseini, H.; Soukhtanloo, M. The Anti-Tumor, Anti-Oxidative, and Anti-Inflammatory Effects of Bee Venom in C26 Colon Carcinoma-Bearing Mice Model. Iran. J. Sci. 2024, 48, 69–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erkoc, P.; Von Reumont, B.M.; Lüddecke, T.; Henke, M.; Ulshöfer, T.; Vilcinskas, A.; Fürst, R.; Schiffmann, S. The Pharmacological Potential of Novel Melittin Variants from the Honeybee and Solitary Bees against Inflammation and Cancer. Toxins 2022, 14, 818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, H.-J.; Kim, J.-Y.; Kim, W.-H.; Han, S.-M.; Park, K.-K. The Protective Effect of Melittin on Renal Fibrosis in an Animal Model of Unilateral Ureteral Obstruction. Molecules 2016, 21, 1137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, W.-R.; Kim, K.-H.; An, H.-J.; Kim, J.; Chang, Y.-C.; Chung, H.; Park, Y.-Y.; Lee, M.-L.; Park, K. The Protective Effects of Melittin on Propionibacterium Acnes –Induced Inflammatory Responses In Vitro and In Vivo. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2014, 134, 1922–1930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bae, S.; Gu, H.; Gwon, M.-G.; An, H.-J.; Han, S.-M.; Lee, S.-J.; Leem, J.; Park, K.-K. Therapeutic Effect of Bee Venom and Melittin on Skin Infection Caused by Streptococcus Pyogenes. Toxins 2022, 14, 663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, H.; Kim, J.; Kim, W.; Gwon, M.; Gu, H.M.; Jeon, M.J.; Han, S.; Pak, S.C.; Lee, C.; Park, I.S.; et al. Therapeutic Effects of Bee Venom and its Major Component, Melittin, on Atopic Dermatitis in Vivo and in Vitro. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2018, 175, 4310–4324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, M.; Ryu, J.; Vu, H.D.; Kim, D.; Youn, Y.-J.; Park, M.H.; Huynh, P.T.; Hwang, G.-B.; Youn, S.W.; Jeong, Y.H. Transferrin-Conjugated Melittin-Loaded L-Arginine-Coated Iron Oxide Nanoparticles for Mitigating Beta-Amyloid Pathology of the 5XFAD Mouse Brain. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 14954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Wang, Z.-X.; Xu, K.-F.; An, Y.; Cui, M.; Zhang, X.; Tian, L.; Li, C.; Wu, F.-G. A Metal–Polyphenol-Based Antidepressant for Alleviating Colitis-Associated Mental Disorders. Adv. Mater. 2025, 37, e2410993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, J.; Chen, S.; Zhu, Z.; Chen, J.; Xia, J.; Fang, B.; Guo, J.; Wu, B.; Ma, G. Construction of Naturally Derived Hydrogels Containing Anti-Inflammatory Melittin for Sustained Drug Delivery to Treat Osteoarthritis Disease. Biomed. Mater. 2025, 20, 035019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nam, Y.-W.; Im, D.; Garcia, A.S.C.; Tringides, M.L.; Nguyen, H.M.; Liu, Y.; Orfali, R.; Ramanishka, A.; Pintilie, G.; Su, C.-C.; et al. Cryo-EM Structures of the Small-Conductance Ca2+-Activated KCa2.2 Channel. Nat. Commun. 2025, 16, 3690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romanenko, I.G.; Chepurova, N.I.; Kriventsov, M.A. Histopathological Changes in Periodontal Tissue during Experimental Apical Periodontitis and its Correction with Hydroxyapathite and Lysozyme. Clin. Dent. 2025, 28, 58–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayoub, M.; Fayjaloun, S.; Roufayel, R.; El Obeid, D.; Fajloun, Z.; Rima, M.; Karam, M. Influence of Apis mellifera Syriaca Bee Venom on Nociception and Inflammatory Cytokine Profiles in Experimental Hyperalgesia. Toxins 2025, 17, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, J.-W.; Lu, W.-H. Melittin Alleviates Bleomycin-Induced Pulmonary Fibrosis in Vivo through Regulating TGF-Β1/Smad2/3 and AMPK/SIRT1/PGC-1α Signaling Pathways. Iran. J. Basic Med. Sci. 2025, 28, 426–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, T.; Yuan, Z.; Yu, J.; Chen, L.; Hao, W.; Xu, X. Melittin Inhibits MPP+-Induced HT22 Cell Death by Suppressing Bax Activation and Improving Mitochondrial Function. Korean J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 2025, 29, 487–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Izbicka, E.; Streeper, R.T. Mixtures of Diethyl Azelate as Novel Nonopioid Modalities for Pain Management. Cureus 2025, 17, e79960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, M.; Wang, X.; Bao, S.; Wang, D.; Zhao, J.; Wang, Q.; Liu, C.; Zhao, H.; Zhang, C. Orchestrating AMPK/mTOR Signaling to Initiate Melittin-Induced Mitophagy: A Neuroprotective Strategy against Parkinson’s Disease. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 281, 136119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, D.-Y.; Kang, Y.-M.; Seol, S. Suppression of Skin Lesions and SLE Nephritis by Increasing Treg in MRL/FASlpr Mice by Administration of Bee Venom Apitoxin®. Adv. Rheumatol. 2025, 65, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, M.; Deng, P.; Li, Q.; Tang, Q.; Li, J.; Zhang, L. The H2S-Releasing Multifunctional Composite Ionic Liquid Facilitates Topical Melittin Delivery for Psoriasis Treatment through RONS Scavenging and Inflammation Inhibition. Chem. Eng. J. 2025, 508, 160972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, J.; Bi, F.; Tian, Q.; Tian, K. Melittin Treats Periprosthetic Osteolysis in a Rat Model by Inhibiting the NF-kB Pathway and Regulating the Ratio of Receptor Activator of Nuclear Factor Kappa B Ligand/Osteoprotegerin. J. Arthroplast. 2024, 39, 1845–1855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Zhao, W.; Gong, X.; Yue, D.; Liu, Y.; Tian, Y.; Dong, K. Exploring Potential Network Pharmacology-and Molecular Docking-Based Mechanism of Melittin in Treating Rheumatoid Arthritis. Medicine 2023, 102, e34728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yousefpoor, Y.; Amani, A.; Divsalar, A.; Mousavi, S.E.; Shakeri, A.; Sabzevari, J.T. Anti-Rheumatic Activity of Topical Nanoemulsion Containing Bee Venom in Rats. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2022, 172, 168–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, G.-M.; Lee, B.; Hong, R.; Park, S.-Y.; Cho, D.-E.; Yeom, M.; Park, H.-J.; Bae, H.; Hahm, D.-H. Bee Venom Phospholipase A2 Alleviates Collagen-Induced Polyarthritis by Inducing Foxp3+ Regulatory T Cell Polarization in Mice. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 3511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharaf, S.E.; Alsanosi, S.; Alzahrani, A.R.; Al-Ghamdi, S.S.; Sharaf, S.E.; Ayoub, N. Knowledge, Attitude, and Practice of Bee Venom Acupuncture Therapy on Rheumatoid Arthritis Among Patients in Saudi Arabia. Int. J. Gen. Med. 2022, 15, 1171–1183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Chen, F.; Yang, L.; Qiu, F.; Zhong, G.; Gao, S.; Xi, W.; Lai, M.; He, Q.; Chen, Y.; et al. Melittin Acupoint Injection in Attenuating Bone Erosion in Collagen-Induced Arthritis Mice via Inhibition of the RANKL/NF-κB Signaling Pathway. Quant. Imaging Med. Surg. 2023, 13, 5996–6013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choe, J.-Y.; Kim, S.-K. Melittin Inhibits Osteoclast Formation through the Downregulation of the RANKL-RANK Signaling Pathway and the Inhibition of Interleukin-1β in Murine Macrophages. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2017, 39, 539–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, G.; He, P.; Zhao, J.; He, C.; Jiang, M.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Sun, X. Polymeric Microneedle-Mediated Transdermal Delivery of Melittin for Rheumatoid Arthritis Treatment. J. Control. Release 2021, 336, 537–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, L.; Wang, Z.; Peng, C.; He, M.; Wang, F.; He, H.; Liu, C. Microneedle Assisted Melittin-Chondroitin Sulfate Administration for the Transdermal Therapy of Rheumatoid Arthritis. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2025, 14, e2400543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, T.; Li, D.; Ren, J.; Chen, C.; Li, S.; Song, Z.; Xu, N.; Liu, T.; Liu, S. Soluble Microneedle Acupuncture Patches Containing Melittin Liposomes for the Percutaneous Treatment of Rheumatoid Arthritis. Nanomed. Nanotechnol. Biol. Med. 2025, 64, 102806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Praphawilai, P.; Kaewkod, T.; Suriyaprom, S.; Panya, A.; Disayathanoowat, T.; Tragoolpua, Y. Anti-Herpes Simplex Virus and Anti-Inflammatory Activities of the Melittin Peptides Derived from Apis mellifera and Apis florea Venom. Insects 2024, 15, 109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, W.-H.; An, H.-J.; Kim, J.-Y.; Gwon, M.-G.; Gu, H.; Jeon, M.; Kim, M.-K.; Han, S.-M.; Park, K.-K. Anti-Inflammatory Effect of Melittin on Porphyromonas Gingivalis LPS-Stimulated Human Keratinocytes. Molecules 2018, 23, 332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Im, E.J.; Kim, S.J.; Hong, S.B.; Park, J.-K.; Rhee, M.H. Anti-Inflammatory Activity of Bee Venom in BV2 Microglial Cells: Mediation of MyD88-Dependent NF-κ B Signaling Pathway. Evid. Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2016, 2016, 3704764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malan, M.; Serem, J.C.; Bester, M.J.; Neitz, A.W.H.; Gaspar, A.R.M. Anti-inflammatory and Anti-endotoxin Properties of Peptides Derived from the Carboxy-terminal Region of a Defensin from the Tick Ornithodoros savignyi. J. Pept. Sci. 2016, 22, 43–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sevin, S.; Kivrak, İ.; Tutun, H.; Uyar, R.; Ayaz, F. Apis mellifera Anatoliaca Venom Exerted Anti-Inflammatory Activity on LPS-Stimulated Mammalian Macrophages by Reducing the Production of the Inflammatory Cytokines. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2023, 195, 3194–3205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abu-Zeid, E.H.; Khalifa, B.A.; Elewa, Y.H.A.; Arisha, A.H.; Ismail, T.A.; Hendam, B.M.; Abdel-Hamid, S.E. Bee Venom Apis mellifera Lamarckii Rescues Blood Brain Barrier Damage and Neurobehavioral Changes Induced by Methyl Mercury via Regulating Tight Junction Proteins Expression in Rat Cerebellum. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2021, 154, 112309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, H.-S.; Kim, Y.S.; Lee, K.-S.; Seo, H.-S.; Lee, C.-Y.; Kim, K.K. Detoxification of Bee Venom Increases its Anti-Inflammatory Activity and Decreases its Cytotoxicity and Allergenic Activity. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2021, 193, 4068–4082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Streeper, R.T.; Izbicka, E. Diethyl Azelate for the Treatment of Brown Recluse Spider Bite, a Neglected Orphan Indication. In Vivo 2022, 36, 86–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbasi, F.; Shawrang, P.; Motamedi-Sedeh, F.; Sadeghi, M. Effect of Gamma-Irradiated Honey Bee Venom on Gene Expression of Inflammatory and Anti-Inflammatory Cytokines in Mice. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2023, 118, 110084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alqarni, A.M.; Ferro, V.A.; Parkinson, J.A.; Dufton, M.J.; Watson, D.G. Effect of Melittin on Metabolomic Profile and Cytokine Production in PMA-Differentiated THP-1 Cells. Vaccines 2018, 6, 72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eid, B.G.; Alhakamy, N.A.; Fahmy, U.A.; Ahmed, O.A.A.; Md, S.; Abdel-Naim, A.B.; Caruso, G.; Caraci, F. Melittin and Diclofenac Synergistically Promote Wound Healing in a Pathway Involving TGF-Β1. Pharmacol. Res. 2022, 175, 105993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senturk, A.; Dalkiran, B.; Acikgoz, B.; Aksu, I.; Acikgoz, O.; Kiray, M. The Effects of Bee Venom on Liver and Skeletal Muscle in Exhaustive Swimming Rats. Biol. Futur. 2022, 73, 237–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jo, H.; Baek, H.; Park, S.-Y.; Goo, B.; Jung, W.-S.; Bae, H.; Nam, S.-S. The Responsiveness of Bee Venom Phospholipase A2 on Regulatory T Cells Correlates with the CD11c+CD206+Population in Human Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cells. Toxins 2021, 13, 717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tseng, Y.-K.; Lu, Y.-H.; Liu, Y.; Weng, Z.-W.; Lin, Y.-T.; Tsai, C.-H.; Wu, Y.-L.; Huang, R.-N. A Novel Chitin-Based Purification System Using GAL1 Fusion Tags: Enhancing Recombinant Protein Production While Retaining Biological Activity. Microb. Biotechnol. 2025, 18, e70157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rășinar, A.D.; Radulov, I.; Berbecea, A.; Floares, D.; Vicar, N.; Simiz, E.; Dragomirescu, M.; Pătruică, S. Assessing the Influence of Stimulatory Feeding of Bee Colonies on Mineral Composition and Anti-oxidant Activity of Bee Venom. Insects 2025, 16, 423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Chen, Y.; Huang, W.; Zhou, J.; Yang, D. Melittin Promotes the Proliferation of Schwann Cells in Hyperglycemic Environment by Up-Regulating the Crabp2/Wnt/β-Catenin Signaling Pathway. Mol. Med. Rep. 2025, 31, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Liu, M.; Chen, L.; Gong, Y.; Ma, W.; Jiang, Y. Study on the Effect of Bee Venom and its Main Component Melittin in Delaying Skin Aging in Mice. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lomeli-Lepe, A.K.; Castañeda-Cabral, J.L.; Ureña-Guerrero, M.E.; Cabrera, G.G.; López-Pérez, S.J. Bee Venom Reduces Early Inflammation and Oxidative Stress Associated with Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Alpha-Synuclein in the Substantia Nigra-Striatum Axis. Cell Biochem. Biophys. 2025, 83, 1185–1196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basuini, M.F.E. Bee Venom Enhances Performance and Immune Function in Thinlip Mullet: A Promising Approach for Sustainable Aquaculture. Fish Shellfish. Immunol. 2024, 151, 109713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karimi, G.; Fatemi, S.; Memar, B.; Khorrami, M.-B.; Amali, A.; Sadeghi, M.; Esmaeili, S.-A.; Riahi-Zanjani, B. Melittin as a Safe Compound to BALB/c Mice Immune System; a Tiered Approach Immunotoxicity Screening. BMC Complement. Med. Ther. 2023, 23, 377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eweis, A.; Hassan, K.; Shoman, S.; Taha, H.; Mohamed, E. Investigation of Honey Bee Venom Effect on the Immunogenicity of Foot-and-Mouth Disease Vaccine in Sheep. Open Vet. J. 2022, 12, 919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; Kim, H.-W.; Chang, S.-H.; Leem, K.-H.; Park, H.-J. Bee Venom Prevents Mucin 5AC Production through Inhibition of AKT and SPDEF Activation in Airway Epithelia Cells. Toxins 2021, 13, 773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, M.; Lee, M.-H.; Seo, Y.-J.; Kim, J.; Oh, J.; Kim, J.; Cho, Y.; Chang, J.; Kim, H. Development of Melittin-Conjugated Lipid Nanoparticle (LNP-MEL) for mRNA-Based Respiratory Syncytial Virus (RSV) Vaccination. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2025, 149, 604–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sylvestre, M.; Lv, S.; Yang, L.F.; Luera, N.; Peeler, D.J.; Chen, B.-M.; Roffler, S.R.; Pun, S.H. Replacement of L-Amino Acid Peptides with D-Amino Acid Peptides Mitigates Anti-PEG Antibody Generation against Polymer-Peptide Conjugates in Mice. J. Control. Release 2021, 331, 142–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fontana, F.; Figueiredo, P.; Bauleth-Ramos, T.; Correia, A.; Santos, H.A. Immunostimulation and Immunosuppression: Nanotechnology on the Brink. Small Methods 2018, 2, 1700347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernitsa, S.; Dayan, R.; Stephanou, A.; Tzvetanova, I.D.; Patrikios, I.S. Natural Biomolecules and Derivatives as Anticancer Immunomodulatory Agents. Front. Immunol. 2023, 13, 1070367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bahreyni, A.; Liu, H.; Mohamud, Y.; Xue, Y.C.; Fan, Y.M.; Zhang, Y.L.; Luo, H. A Combination of Genetically Engineered Oncolytic Virus and Melittin-CpG for Cancer Viro-Chemo-Immunotherapy. BMC Med. 2023, 21, 193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Yang, C.; Wu, T.; Fan, J.; Zhu, H.; Liu, J.; Ding, B. A Highly Tumor-Permeating DNA Nanoplatform for Efficient Remodeling of Immunosuppressive Tumor Microenvironments. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2025, 64, e202412804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, K.; Nguyen, D.C.; Luu, T.; Yazdani, O.; Roy, D.; Stayton, P.S.; Pun, S.H. A Mannosylated Polymer with Endosomal Release Properties for Peptide Antigen Delivery. J. Control. Release 2023, 356, 232–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shir, A.; Ogris, M.; Roedl, W.; Wagner, E.; Levitzki, A. EGFR-Homing dsRNA Activates Cancer-Targeted Immune Response and Eliminates Disseminated EGFR-Overexpressing Tumors in Mice. Clin. Cancer Res. 2011, 17, 1033–1043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.; Chen, L.; Liu, J.; Dai, B.; Xu, G.; Shen, G.; Luo, Q.; Zhang, Z. Immune Modulation of Liver Sinusoidal Endothelial Cells by Melittin Nanoparticles Suppresses Liver Metastasis. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, P.; Zhang, H.; Sun, M.; Mao, S.; He, Q.; Shi, Y.; Deng, Y.; Dong, Z.; Xu, Q.; Zhao, C.; et al. Manipulating Offense and Defense Signaling to Fight Cold Tumors with Carrier-Free Nanoassembly of Fluorinated Prodrug and siRNA. Adv. Mater. 2022, 34, 2203019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, C.; Bae, S.-J.S.; Joo, H.; Bae, H. Melittin Suppresses Tumor Progression by Regulating Tumor-Associated Macrophages in a Lewis Lung Carcinoma Mouse Model. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 54951–54965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, M.; Wang, H.; Liu, L.; Wang, B.; Sun, G. Melittin-MIL-2 Fusion Protein as a Candidate for Cancer Immunotherapy. J. Transl. Med. 2016, 14, 155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Zhang, X.; Wang, S.-Z.; Feng, H.-H.; Wu, S.-Y.; Wu, F.-G. Metal–Phenolic Network-Facilitated “Foe-to-Friend” Conversion of Melittin for Cancer Immunotherapy with Boosted Abscopal Effect. Research 2023, 6, 0052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, S.; Zhou, L.; He, H.; Cui, L.; Ren, Z.; Tai, Y.; Xie, Z.; Cao, Y.; Meng, D.; Liu, Q.; et al. MnO2-Melittin Nanoparticles Serve as an Effective Anti-Tumor Immunotherapy by Enhancing Systemic Immune Response. Biomaterials 2022, 288, 121706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, K.; Zhou, Y.; Huang, B.; Zhao, G.; Geng, Y.; Wan, C.; Jiang, F.; Jin, H.; Ye, C.; Chen, J. Sustained Release of Tumor Cell Lysate and CpG from an Injectable, Cytotoxic Hydrogel for Melanoma Immunotherapy. Nanoscale Adv. 2023, 5, 2071–2084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, I.-H.; Jeong, C.; Yang, J.; Park, S.-H.; Hwang, D.-S.; Bae, H. Therapeutic Effect of Melittin–dKLA Targeting Tumor-Associated Macrophages in Melanoma. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 3094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamze Mostafavi, S.; Mohammadi, S.; Mousavi Alborzi, F.S.; Hajiahmadi, F.; Ahmadvand, D.; Gheibi, N.; Naderi-Manesh, H.; Shariatifar, H.; Farasat, A. TRA/MEL Immunoliposomes Act as a Targeted Medicine in BT-474 Breast Cancer Cells. J. Liposome Res. 2025, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, W.; Li, Y.; Yang, Z.; Li, W.; Cao, Y.; Liu, Y.; Wang, Z.; Pei, R.; Xing, C. Tumor Microenvironment Reprogramming Combined with Immunogenic Enhancement by Nanoemulsions Potentiates Immunotherapy. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2024, 22, 154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gasanoff, E.; Liu, Y.; Li, F.; Hanlon, P.; Garab, G. Bee Venom Melittin Disintegrates the Respiration of Mitochondria in Healthy Cells and Lymphoblasts, and Induces the Formation of Non-Bilayer Structures in Model Inner Mitochondrial Membranes. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 11122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, Y.; Yu, X.; Zhao, Y.; Wei, J.; Lin, D.; Wang, J.; Zhang, R.; Yuan, X.; Li, S.; Huang, S.; et al. Targeted Modulation of the Meningeal Lymphatic Reverse Pathway for Immunotherapy of Breast Cancer Brain Metastases. ACS Nano 2025, 19, 4830–4844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, D.; Wang, T.; Zhang, X.; Xu, Y.; Ming, J.; Wang, X.; Liu, Z.; Li, J.; Su, X. Synchronously Delivering Melittin and Evoking Ferroptosis via Tumor Microenvironment-Triggered Self-Destructive Metal–Organic Frameworks to Boost Cancer Immunotherapy. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2025, 14, e2500003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, W.J.; Matejczuk, K.; Ee, K.Y.; Boutrou, I.; Hew, P.S.; Szweda, P.; Mossialos, D. Honey Bee and Stingless Bee Products: Effects on Microbial Virulence Factors and Pathogenicity Mechanisms. J. Funct. Foods 2025, 132, 106967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, W.; Hu, L.; Wang, Y.; Lv, L.; Wang, H.; Shi, W.; Zhu, J.; Lu, H. A Hemolysin Secretion Pathway-Based Novel Secretory Expression Platform for Efficient Manufacturing of Tag Peptides and Anti-Microbial Peptides in Escherichia coli. Bioresour. Bioprocess. 2021, 8, 115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akbari, R.; Hakemi Vala, M.; Hashemi, A.; Aghazadeh, H.; Sabatier, J.-M.; Pooshang Bagheri, K. Action Mechanism of Melittin-Derived Antimicrobial Peptides, MDP1 and MDP2, de Novo Designed against Multidrug Resistant Bacteria. Amino Acids 2018, 50, 1231–1243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, X.; Feng, Y.; Shi, H.; Wang, F.; Wang, Z.; Hou, S.; Song, X.; Yang, J.; Liu, L. A Hydrogel Dressing with Tunable Critical Temperature and Photothermal Modulating Melittin Release for Multiply Antibacterial Treatment. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 239, 124272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ludwig, T.; Volke, D.; Krizsan, A. Analysis of Engineered T7 Bacteriophages Containing Genetic Sequences Encoding Antimicrobial Peptides. Front. Antibiot. 2025, 3, 1515874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Enigk, K.; Jentsch, H.; Rodloff, A.C.; Eschrich, K.; Stingu, C.-S. Activity of Five Antimicrobial Peptides against Periodontal as Well as Non-Periodontal Pathogenic Strains. J. Oral Microbiol. 2020, 12, 1829405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanuğur-Samanc, A.E.; Kekeçoğlu, M. An Evaluation of the Chemical Content and Microbiological Contamination of Anatolian Bee Venom. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0255161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Lee, K.S.; Kim, B.Y.; Choi, Y.S.; Yoon, H.J.; Jia, J.; Jin, B.R. Anti-Fibrinolytic and Anti-Microbial Activities of a Serine Protease Inhibitor from Honeybee (Apis cerana) Venom. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part C Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2017, 201, 11–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-Delgado, O.; Espinoza-Culupú, A.O.; López-López, E. Antimicrobial Activity of Apis mellifera Bee Venom Collected in Northern Peru. Antibiotics 2023, 12, 779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arteaga, V.; Lamas, A.; Regal, P.; Vázquez, B.; Miranda, J.M.; Cepeda, A.; Franco, C.M. Antimicrobial Activity of Apitoxin from Apis mellifera in Salmonella Enterica Strains Isolated from Poultry and its Effects on Motility, Biofilm Formation and Gene Expression. Microb. Pathog. 2019, 137, 103771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Socarras, K.; Theophilus, P.; Torres, J.; Gupta, K.; Sapi, E. Antimicrobial Activity of Bee Venom and Melittin against Borrelia Burgdorferi. Antibiotics 2017, 6, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Zhang, X.; Meng, C.; Ji, S.; Guo, K. Antimicrobial Activity of the Recombinant Peptide Melittin-Thanatin with Three Glycine to Tryptophan Mutations. Prep. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2023, 53, 849–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gourkhede, D.P.; Bhoomika, S.; Pathak, R.; Yadav, J.P.; Nishanth, D.; Vergis, J.; Malik, S.V.S.; Barbuddhe, S.B.; Rawool, D.B. Antimicrobial Efficacy of Cecropin A (1–7)-Melittin and Lactoferricin (17–30) against Multi-Drug Resistant Salmonella Enteritidis. Microb. Pathog. 2020, 147, 104405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, W.; Li, C.; Li, M.; Zong, X.; Han, D.; Chen, Y. Antimicrobial Peptide Melittin against Xanthomonas Oryzae Pv. Oryzae, the Bacterial Leaf Blight Pathogen in Rice. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2016, 100, 5059–5067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huan, Y.; Kong, Q.; Tang, Q.; Wang, Y.; Mou, H.; Ying, R.; Li, C. Antimicrobial Peptides/Ciprofloxacin-Loaded O-Carboxymethyl Chitosan/Self-Assembling Peptides Hydrogel Dressing with Sustained-Release Effect for Enhanced Anti-Bacterial Infection and Wound Healing. Carbohydr. Polym. 2022, 280, 119033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakhiet, E.K.; Hussi, H.A.; Elshehaby, M. Apis mellifera Venom Inhibits Bacterial and Fungal Pathogens in Vitro. Pak. J. Biol. Sci. 2022, 25, 875–884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, S.; Kim, J.; Hong, I.; Woo, S.; Kim, S.; Jang, H.; Pak, S. Antibacterial Activity and Antibiotic-Enhancing Effects of Honeybee Venom against Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Molecules 2016, 21, 79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dosler, S.; Karaaslan, E.; Alev Gerceker, A. Antibacterial and Anti-Biofilm Activities of Melittin and Colistin, Alone and in Combination with Antibiotics against Gram-Negative Bacteria. J. Chemother. 2016, 28, 95–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, F.; Liu, H.; Wei, Y.; Xue, R.; Liu, Z.; Chu, X.; Tian, X.; Yin, L.; Tang, H. Antibacterial Brush Polypeptide Coatings with Anionic Backbones. Acta Biomater. 2023, 155, 359–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chudinova, Y.V.; Shagdarova, B.T.; Il’iNa, A.V.; Varlamov, V.P. Antibacterial Effect of Peptide Conjugates with a Quaternized Chitosan Derivative and its Estimation by the Method of Atomic Force Microscopy. Appl. Biochem. Microbiol. 2016, 52, 496–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lima, W.G.; Batista Filho, F.L.; Lima, I.P.; Simião, D.C.; Brito, J.C.M.; Da Cruz Nizer, W.S.; Cardoso, V.N.; Fernandes, S.O.A. Antibacterial, Anti-Biofilm, and Anti-Adhesive Activities of Melittin, a Honeybee Venom-Derived Peptide, against Quinolone-Resistant Uropathogenic Escherichia coli (UPEC). Nat. Prod. Res. 2022, 36, 6381–6388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirzaei, R.; Ghaleh, H.E.G.; Ranjbar, R. Anti-biofilm Effect of Melittin Alone and in Combination with Conventional Antibiotics toward Strong Biofilm of MDR-MRSA and -Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 14, 1030401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuzmenkov, A.I.; Peigneur, S.; Nasburg, J.A.; Mineev, K.S.; Nikolaev, M.V.; Pinheiro-Junior, E.L.; Arseniev, A.S.; Wulff, H.; Tytgat, J.; Vassilevski, A.A. Apamin Structure and Pharmacology Revisited. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 977440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarhan, W.A.; Azzazy, H.M. Apitherapeutics and Phage-Loaded Nanofibers As Wound Dressings With Enhanced Wound Healing and Antibacterial Activity. Nanomedicine 2017, 12, 2055–2067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strömstedt, A.A.; Park, S.; Burman, R.; Göransson, U. Bactericidal Activity of Cyclotides Where Phosphatidylethanolamine-Lipid Selectivity Determines Antimicrobial Spectra. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Biomembr. 2017, 1859, 1986–2000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zolfagharian, H.; Mohajeri, M.; Babaie, M. Bee Venom (Apis mellifera) an Effective Potential Alternative to Gentamicin for Specific Bacteria Strains: Bee Venom an Effective Potential for Bacteria. J. Pharmacopunct. 2016, 19, 225–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gökmen, T.G.; Yazgan, H.; Özdemir, Y.; Sevin, S.; Turut, N.; Karahan, Ş.; Eşki, F.; Kıvrak, İ.; Sezer, O.; Ütük, A.E. Chemical Composition and Antibacterial Activity of Bee Venom against Multi-Drug Resistant Pathogens. Onderstepoort J. Vet. Res. 2023, 90, 2097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moridi, K.; Hemmaty, M.; Akbari Eidgahi, M.R.; Fathi Najafi, M.; Zare, H.; Ghazvini, K.; Neshani, A. Construction, Cloning, and Expression of Melittin Antimicrobial Peptide Using Pichia Pastoris Expression System. Gene Rep. 2020, 21, 100900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, X.; Qian, K.; Liu, G.; Sun, L.; Zhou, G.; Li, J.; Fang, X.; Ge, H.; Lv, Z. Design and Activity Study of a Melittin–Thanatin Hybrid Peptide. AMB Express 2019, 9, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.; Liu, J.; Gou, L.; Li, J.; Yuan, B.; Yang, K.; Ma, Y. Designing Melittin-Graphene Hybrid Complexes for Enhanced Antibacterial Activity. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2019, 8, 1801521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akhzari, S.; Nabian, S.; Shayan, P.; Mazaheri Nezhad Fard, R.; Soltani, M.; Taheri, M. Designing of RNA Molecule Translating for Activitable Melittin as Selective Targeting of Leishmania Infected Cells. Iran. J. Parasitol. 2021, 16, 443–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kabakci, D.; Ürkü, Ç.; Önalan, Ş. Determination of the Antibacterial Effect of Bee Venom against Rainbow Trout Pathogens and Antibiotic Resistance Gene Expression. Acta Vet. 2023, 73, 374–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahsuvar, S.; Guner, R.; Gok, O.; Can, O. Development and Pharmaceutical Investigation of Novel Cervical Cancer-Targeting and Redox-Responsive Melittin Conjugates. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 18225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaiwala, R.; Sharma, P.; Ganapathy Ayappa, K. Differentiating Interactions of Antimicrobials with Gram-Negative and Gram-Positive Bacterial Cell Walls Using Molecular Dynamics Simulations. Biointerphases 2022, 17, 061008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Ma, R.; Chen, J.; Xie, Q.; Luo, W.; Sun, P.; Liu, Z.; Guo, J. Discovery of Melittin as Triple-Action Agent: Broad-Spectrum Antibacterial, Anti-Biofilm, and Potential Anti-Quorum Sensing Activities. Molecules 2024, 29, 558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamasbi, E.; Lucky, S.S.; Li, W.; Hossain, M.A.; Gopalakrishnakone, P.; Separovic, F. Effect of Dimerized Melittin on Gastric Cancer Cells and Antibacterial Activity. Amino Acids 2018, 50, 1101–1110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Liu, R.; Wang, X.; Wu, H.; Yi, X.; Huang, L.; Qin, Q. Effects of Melittin on Laying Performance and Intestinal Barrier Function of Quails. Poult. Sci. 2023, 102, 102355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravensdale, J.; Wong, Z.; O’Brien, F.; Gregg, K. Efficacy of Antibacterial Peptides Against Peptide-Resistant MRSA Is Restored by Permeabilization of Bacteria Membranes. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 1745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeon, E.; Kim, M.K.; Park, Y. Efficacy of the Bee-Venom Antimicrobial Peptide Osmin against Sensitive and Carbapenem-Resistant Klebsiella Pneumoniae Strains. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2024, 63, 107054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, S.; Li, W.; Baloch, A.R.; Wang, M.; Li, H.; Cao, B.; Zhang, H. Efficient Biosynthesis of a Cecropin A-Melittin Mutant in Bacillus subtilis WB700. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 40587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Xia, W.; Zhang, M.; Wu, R.; Song, X.; Hao, Y.; Feng, Y.; Zhang, L.; Li, D.; Kang, W.; et al. Engineering of Antimicrobial Peptide Fibrils with Feedback Degradation of Bacterial-Secreted Enzymes. Chem. Sci. 2023, 14, 10914–10924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bevalian, P.; Pashaei, F.; Akbari, R.; Bagheri, K.P. Eradication of Vancomycin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus on a Mouse Model of Third-Degree Burn Infection by Melittin: An Antimicrobial Peptide from Bee Venom. Toxicon 2021, 199, 49–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, X.; Zhao, T.; Song, Y.; Zhang, J.; Yuan, T.; Han, Q. Evaluation of the Activity of Antimicrobial Peptides against Bacterial Vaginosis. Open Life Sci. 2024, 19, 20220927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ali, S.E.-S.; El-Ghannam, G.; Hashish, M.E.-S.; Elsayed, H.; Ali, A.K.; Marzouk, W.M.; Khattaby, A.M.; El-Wahab, A.M.A.; Abdel-Hafez, S.H.; Attia, Y.A. Exploring Bee Venom and Silver Nanoparticles for Controlling Foulbrood Pathogen and Enhancing Lifespan of Honeybees. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 19013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vergis, J.; Malik, S.V.S.; Pathak, R.; Kumar, M.; Kurkure, N.V.; Barbuddhe, S.B.; Rawool, D.B. Exploring Galleria mellonella Larval Model to Evaluate Antibacterial Efficacy of Cecropin A (1-7)-Melittin against Multi-Drug Resistant Enteroaggregative Escherichia coli. Pathog. Dis. 2021, 79, ftab010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Liu, Z.; Xu, G.; Li, L.; Xuan, K.; Xu, Y.; Zhang, R. Expression of Melittin in Fusion with GST in Escherichia coli and its Purification as a Pure Peptide with Good Bacteriostatic Efficacy. ACS Omega 2020, 5, 9251–9258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abou Zekry, S.S.; Abdellatif, A.; Azzazy, H.M.E. Fabrication of Pomegranate/Honey Nanofibers for Use as Antibacterial Wound Dressings. Wound Med. 2020, 28, 100181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frangieh, J.; Salma, Y.; Haddad, K.; Mattei, C.; Legros, C.; Fajloun, Z.; El Obeid, D. First Characterization of The Venom from Apis mellifera Syriaca, A Honeybee from The Middle East Region. Toxins 2019, 11, 191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, S.; Lu, X.; Gou, L.; Li, J.; Ma, Y.; Liu, J.; Yang, K.; Yuan, B. Graphene Oxide as Antibacterial Sensitizer: Mechanically Disturbed Cell Membrane for Enhanced Poration Efficiency of Melittin. Carbon 2019, 149, 248–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bardbari, A.M.; Arabestani, M.R.; Karami, M.; Keramat, F.; Aghazadeh, H.; Alikhani, M.Y.; Bagheri, K.P. Highly Synergistic Activity of Melittin with Imipenem and Colistin in Biofilm Inhibition against Multidrug-Resistant Strong Biofilm Producer Strains of Acinetobacter Baumannii. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2018, 37, 443–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirzaei, R.; Alikhani, M.Y.; Arciola, C.R.; Sedighi, I.; Irajian, G.; Jamasbi, E.; Yousefimashouf, R.; Bagheri, K.P. Highly Synergistic Effects of Melittin With Vancomycin and Rifampin Against Vancomycin and Rifampin Resistant Staphylococcus Epidermidis. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 869650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, H.; Hu, X.; Zhang, L.; Fa, K.; Liao, M.; Liu, H.; Fragneto, G.; Campana, M.; Lu, J.R. How Do Antimicrobial Peptides Disrupt the Lipopolysaccharide Membrane Leaflet of Gram-Negative Bacteria? J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2023, 637, 182–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stephani, J.C.; Gerhards, L.; Khairalla, B.; Solov’yov, I.A.; Brand, I. How Do Antimicrobial Peptides Interact with the Outer Membrane of Gram-Negative Bacteria? Role of Lipopolysaccharides in Peptide Binding, Anchoring, and Penetration. ACS Infect. Dis. 2024, 10, 763–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maiden, M.M.; Zachos, M.P.; Waters, C.M. Hydrogels Embedded With Melittin and Tobramycin Are Effective Against Pseudomonas aeruginosa Biofilms in an Animal Wound Model. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 1348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zarghami, V.; Ghorbani, M.; Bagheri, K.P.; Shokrgozar, M.A. Improving Bactericidal Performance of Implant Composite Coatings by Synergism between Melittin and Tetracycline. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 2022, 33, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Birteksoz-Tan, A.S.; Zeybek, Z.; Hacioglu, M.; Savage, P.B.; Bozkurt-Guzel, C. In Vitro Activities of Antimicrobial Peptides and Ceragenins against Legionella Pneumophila. J. Antibiot. 2019, 72, 291–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marques Pereira, A.F.; Albano, M.; Bérgamo Alves, F.C.; Murbach Teles Andrade, B.F.; Furlanetto, A.; Mores Rall, V.L.; Delazari Dos Santos, L.; De Oliveira Orsi, R.; Fernandes Júnior, A. Influence of Apitoxin and Melittin from Apis mellifera Bee on Staphylococcus aureus Strains. Microb. Pathog. 2020, 141, 104011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, M.; Gong, H.; Quan, X.; Wang, Z.; Hu, X.; Chen, Z.; Li, Z.; Liu, H.; Zhang, L.; McBain, A.J.; et al. Intramembrane Nanoaggregates of Antimicrobial Peptides Play a Vital Role in Bacterial Killing. Small 2023, 19, 2204428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rouhi, A.; Falah, F.; Azghandi, M.; Alizadeh Behbahani, B.; Tabatabaei-Yazdi, F.; Ibrahim, S.A.; Dertli, E.; Vasiee, A. Investigating the Effect of Melittin Peptide in Preventing Biofilm Formation, Adhesion and Expression of Virulence Genes in Listeria Monocytogenes. Probiotics Antimicro. Prot. 2024. Available online: https://link.springer.com/journal/12602/online-first?filterOpenAccess=false&page=8 (accessed on 11 September 2025). [CrossRef]
- Shams Khozani, R.; Shahbazzadeh, D.; Harzandi, N.; Feizabadi, M.M.; Pooshang Bagheri, K. Kinetics Study of Antimicrobial Peptide, Melittin, in Simultaneous Biofilm Degradation and Eradication of Potent Biofilm Producing MDR Pseudomonas aeruginosa Isolates. Int. J. Pept. Res. Ther. 2019, 25, 329–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Didamony, S.E.; Kalaba, M.H.; Sharaf, M.H.; El-Fakharany, E.M.; Osman, A.; Sitohy, M.; Sitohy, B. Melittin Alcalase-Hydrolysate: A Novel Chemically Characterized Multifunctional Bioagent; Antibacterial, Anti-Biofilm and Anticancer. Front. Microbiol. 2024, 15, 1419917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zarghami, V.; Ghorbani, M.; Bagheri, K.P.; Shokrgozar, M.A. Prevention the Formation of Biofilm on Orthopedic Implants by Melittin Thin Layer on Chitosan/Bioactive Glass/Vancomycin Coatings. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 2021, 32, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galdiero, E.; Siciliano, A.; Gesuele, R.; Di Onofrio, V.; Falanga, A.; Maione, A.; Liguori, R.; Libralato, G.; Guida, M. Melittin Inhibition and Eradication Activity for Resistant Polymicrobial Biofilm Isolated from a Dairy Industry after Disinfection. Int. J. Microbiol. 2019, 2019, 4012394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alajmi, R.A.; Barakat, I.A.H.; Alfozan, L.; Mahmoud, A.; Layqah, L.; Yehia, H.M.; Metwally, D.M. Microbiological Investigation Study for Apis mellifera Yemenitica and Apis mellifera Carnica Bee Venoms on Selected Bacterial Strains. Braz. J. Microbiol. 2022, 53, 709–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mandal, M.; Mandal, S. MM-GBSA and QM/MM Simulation-Based in Silico Approaches for the Inhibition of Acinetobacter Baumannii Class D OXA-24 β-Lactamase Using Antimicrobial Peptides Melittin and RP-1. Chem. Phys. Impact 2024, 8, 100401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saraswat, J.; Wani, F.A.; Dar, K.I.; Rizvi, M.M.A.; Patel, R. Noncovalent Conjugates of Ionic Liquid with Antibacterial Peptide Melittin: An Efficient Combination against Bacterial Cells. ACS Omega 2020, 5, 6376–6388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chetty, T.; Mhlongo, J.T.; Waddad, A.Y.; Albericio, F.; De La Torre, B.G. Novel CA(1–7)M(2–9) Analogs: Synthesis, Characterization, and Antibacterial Evaluation. ACS Med. Chem. Lett. 2022, 13, 1370–1377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, L.; Deng, Z.; Zhang, W.; Liu, S.; Zhang, F.; Zhou, J.; Ma, C.; Wang, C. Opposite Regulatory Effects of Immobilized Cations on the Folding vs. Assembly of Melittin. Front. Chem. 2021, 9, 685947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rangel, K.; Curty Lechuga, G.; Almeida Souza, A.L.; Rangel Da Silva Carvalho, J.P.; Simões Villas Bôas, M.H.; De Simone, S.G. Pan-Drug Resistant Acinetobacter Baumannii, but Not Other Strains, Are Resistant to the Bee Venom Peptide Melittin. Antibiotics 2020, 9, 178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- AL-Ani, I.; Zimmermann, S.; Reichling, J.; Wink, M. Pharmacological Synergism of Bee Venom and Melittin with Antibiotics and Plant Secondary Metabolites against Multi-Drug Resistant Microbial Pathogens. Phytomedicine 2015, 22, 245–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babaeekhou, L.; Ghane, M.; Mohammad Rafiee, M. Photodynamic Therapy and its Synergism with Melittin Against Drug-Resistant Acinetobacter Baumannii Isolates with High Biofilm Formation Ability. Curr. Microbiol. 2023, 80, 324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nehme, H.; Ayde, H.; El Obeid, D.; Sabatier, J.M.; Fajloun, Z. Potential Inhibitory Effect of Apis mellifera’s Venom and of its Two Main Components—Melittin and PLA2—On Escherichia coli F1F0-ATPase. Antibiotics 2020, 9, 824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zarghami, V.; Ghorbani, M.; Pooshang Bagheri, K.; Shokrgozar, M.A. Melittin Antimicrobial Peptide Thin Layer on Bone Implant Chitosan-Antibiotic Coatings and Their Bactericidal Properties. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2021, 263, 124432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.-K.; Ma, Q.; Li, S.-B.; Gao, H.-W.; Tan, Y.-X.; Gong, F.; Ji, S.-P. RV-23, a Melittin-Related Peptide with Cell-Selective Antibacterial Activity and High Hemocompatibility. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2016, 26, 1046–1056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pashaei, F.; Bevalian, P.; Akbari, R.; Pooshang Bagheri, K. Single Dose Eradication of Extensively Drug Resistant Acinetobacter spp. In a Mouse Model of Burn Infection by Melittin Antimicrobial Peptide. Microb. Pathog. 2019, 127, 60–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brand, I.; Khairalla, B. Structural Changes in the Model of the Outer Cell Membrane of Gram-Negative Bacteria Interacting with Melittin: An in Situ Spectroelectrochemical Study. Faraday Discuss. 2021, 232, 68–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hakimi Alni, R.; Tavasoli, F.; Barati, A.; Shahrokhi Badarbani, S.; Salimi, Z.; Babaeekhou, L. Synergistic Activity of Melittin with Mupirocin: A Study against Methicillin-Resistant S. aureus (MRSA) and Methicillin-Susceptible S. aureus (MSSA) Isolates. Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 2020, 27, 2580–2585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pereira, A.F.M.; Sani, A.A.; Zapata, T.B.; Sousa, D.S.M.D.; Rossini, B.C.; Santos, L.D.D.; Rall, V.L.M.; Riccardi, C.D.S.; Fernandes Júnior, A. Synergistic Antibacterial Efficacy of Melittin in Combination with Oxacillin against Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA). Microorganisms 2023, 11, 2868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmoudi, H.; Alikhani, M.Y.; Imani Fooladi, A.A. Synergistic Antimicrobial Activity of Melittin with Clindamycin on the Expression of Encoding Exfoliative Toxin in Staphylococcus aureus. Toxicon 2020, 183, 11–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Güven Gökmen, T.; Yazgan, H.; Sevin, S.; Turut, N.; Karahan, Ş.; Eşki, F.; Kıvrak, İ.; Sezer, O.; Erdem Ütük, A. The Antibacterial Effect of Bee Venom on Subclinical Mastitis Agents: An Alternative for Local Treatment. J. Appl. Anim. Res. 2023, 51, 323–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rad, P.M.; Rahbarnia, L.; Safary, A.; ShadiDizaji, A.; Maani, Z. The Synthetic Antimicrobial Peptide Derived From Melittin Displays Low Toxicity and Anti-Infectious Properties. Probiotics Antimicro. Prot. 2024, 16, 490–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oehler, M.A.; Hayes, D.G.; D’Souza, D.H.; Senanayake, M.; Gurumoorthy, V.; Pingali, S.V.; O’Neill, H.M.; Bras, W.; Urban, V.S. Assessment of Antimicrobial Activity of Melittin Encapsulated in Bicontinuous Microemulsions Prepared Using Renewable Oils. J. Surfactants Deterg. 2023, 26, 387–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharaf, M.; Zahra, A.A.; Alharbi, M.; Mekky, A.E.; Shehata, A.M.; Alkhudhayri, A.; Ali, A.M.; Al Suhaimi, E.A.; Zakai, S.A.; Al Harthi, N.; et al. Bee Chitosan Nanoparticles Loaded with Apitoxin as a Novel Approach to Eradication of Common Human Bacterial, Fungal Pathogens and Treating Cancer. Front. Microbiol. 2024, 15, 1345478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, M.B.M.; El-Ssayad, M.F.; Yousef, S.Y.A.; Salem, S.H. Bee Venom: A Potential Natural Alternative to Conventional Preservatives for Prolonging the Shelf-Life of Soft Cheese ‘Talaga’. Heliyon 2024, 10, e28968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharaf, M.; Mohammed, E.J.; Farahat, E.M.; Alrehaili, A.A.; Alkhudhayri, A.; Ali, A.M.; Zahra, A.A.; Zakai, S.A.; Elkelish, A.; AlHarbi, M.; et al. Biocide Syntheses Bee Venom-Conjugated ZnO@αFe2O3 Nanoflowers as an Advanced Platform Targeting Multidrug-Resistant Fecal Coliform Bacteria Biofilm Isolated from Treated Wastewater. Microbiol. Res. 2023, 14, 1489–1510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, S.; Li, W.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, Y.; Cao, B. Cecropin A–Melittin Mutant with Improved Proteolytic Stability and Enhanced Antimicrobial Activity against Bacteria and Fungi Associated with Gastroenteritis in Vitro. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2014, 451, 650–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gülmez, Y.; Aydın, A.; Can, İ.; Tekin, Ş.; Cacan, E. Cellular Toxicity and Biological Activities of Honey Bee (Apis mellifera L.) Venom. Marmara Pharm. J. 2017, 21, 251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamel, A.; Suleiman, W.; Elfeky, A.; El-Sherbiny, G.; Elhaw, M. Characterization of Bee Venom and Its Synergistic Effect Combating Antibiotic Resistance of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Egypt. J. Chem. 2021, 65, 297–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel-Monsef, M.M.; Darwish, D.A.; Zidan, H.A.; Hamed, A.A.; Ibrahim, M.A. Characterization, Antimicrobial and Antitumor Activity of Superoxide Dismutase Extracted from Egyptian Honeybee Venom (Apis mellifera Lamarckii). J. Genet. Eng. Biotechnol. 2023, 21, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sullivan, R.; Santarpia, P.; Lavender, S.; Gittins, E.; Liu, Z.; Anderson, M.H.; He, J.; Shi, W.; Eckert, R. Clinical Efficacy of a Specifically Targeted Antimicrobial Peptide Mouth Rinse: Targeted Elimination of Streptococcus Mutans and Prevention of Demineralization. Caries Res. 2011, 45, 415–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maitip, J.; Mookhploy, W.; Khorndork, S.; Chantawannakul, P. Comparative Study of Antimicrobial Properties of Bee Venom Extracts and Melittins of Honey Bees. Antibiotics 2021, 10, 1503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanuğur Samancı, A.E.; Kekeçoğlu, M. Development of a Cream Formulation Containing Bee Venom and Other Bee Products. J. Cosmet. Dermatol. 2022, 21, 4913–4920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radhakrishnan, N.; Kumar, S.D.; Shin, S.-Y.; Yang, S. Enhancing Selective Antimicrobial and Anti-biofilm Activities of Melittin through 6-Aminohexanoic Acid Substitution. Biomolecules 2024, 14, 699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Celebi, D.; Celebi, O.; Baser, S.; Taghizadehghalehjoughi, A. Escherichia coli K99 Suşuna Karşı Arı Zehiri ve Arı Zehrinden İzole Edilen Eksozomun Antimikrobiyal ve Antibiyofilm Etkinliğinin Değerlendirilmesi. Kafkas Univ. Vet. Fak. Derg. 2023, 29, 239–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akbari, R.; Hakemi Vala, M.; Sabatier, J.-M.; Pooshang Bagheri, K. Fast Killing Kinetics, Significant Therapeutic Index, and High Stability of Melittin-Derived Antimicrobial Peptide. Amino Acids 2022, 54, 1275–1285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harries, E.; Carmona, L.; Muñoz, A.; Ibeas, J.I.; Read, N.D.; Gandía, M.; Marcos, J.F. Genes Involved in Protein Glycosylation Determine the Activity and Cell Internalization of the Antifungal Peptide PAF26 in Saccharomyces Cerevisiae. Fungal Genet. Biol. 2013, 58–59, 105–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Liu, L.; Yu, T.-Y.; Tang, L.; Yin, M.; Zhu, W.; Jiang, X.; Wang, H. High-Level Expression and Purification of Melittin in Escherichia coli Using SUMO Fusion Partner. Int. J. Pept. Res. Ther. 2021, 27, 9–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, A.R.; Teixeira, C.; Sousa, C.F.; Bessa, L.J.; Gomes, P.; Gameiro, P. How Insertion of a Single Tryptophan in the N-Terminus of a Cecropin A-Melittin Hybrid Peptide Changes Its Antimicrobial and Biophysical Profile. Membranes 2021, 11, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thankappan, B.; Thomas, A.; Sakthivadivel, A.; Shanmuganathan, N.; Angayarkanni, J. In Vitro and in Vivo Antimicrobial Activity of Self-Assembled Melittin Nanoparticles: A Comparative Study with Melittin Peptide. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2023, 226, 113331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Askari, P.; Namaei, M.H.; Ghazvini, K.; Hosseini, M. In Vitro and in Vivo Toxicity and Antibacterial Efficacy of Melittin against Clinical Extensively Drug-Resistant Bacteria. BMC Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2021, 22, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elswaby, S.; Sadik, M.; Azouz, A.; Emam, N.; Ali, M. In Vitro Evaluation of Antimicrobial and Anti-oxidant Activities of Honeybee Venom and Propolis Collected from Various Regions in Egypt. Egypt. Pharm. J. 2022, 21, 207–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Picoli, T.; Peter, C.M.; Zani, J.L.; Waller, S.B.; Lopes, M.G.; Boesche, K.N.; Vargas, G.D.; Hübner, S.D.O.; Fischer, G. Melittin and Its Potential in the Destruction and Inhibition of the Biofilm Formation by Staphylococcus aureus, Escherichia coli and Pseudomonas aeruginosa Isolated from Bovine Milk. Microb. Pathog. 2017, 112, 57–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aburayan, W.S.; Alajmi, A.M.; Alfahad, A.J.; Alsharif, W.K.; Alshehri, A.A.; Booq, R.Y.; Alsudir, S.A.; Alsulaihem, F.M.; Bukhary, H.A.; Badr, M.Y.; et al. Melittin from Bee Venom Encapsulating Electrospun Fibers as a Potential Antimicrobial Wound Dressing Patches for Skin Infections. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarez, A.B.; Caruso, B.; Petersen, S.B.; Rodríguez, P.E.A.; Fidelio, G.D. Melittin-Solid Phospholipid Mixed Films Trigger Amyloid-like Nano-Fibril Arrangements at Air-Water Interface. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Biomembr. 2022, 1864, 184048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hejníková, M.; Tomčala, A.; Černý, J.; Kodrík, D. Melittin—The Principal Toxin of Honeybee Venom—Is Also Produced in the Honeybee Fat Body. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part C Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2024, 281, 109928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.; Su, G.; Jiang, S.; Chen, L.; Huang, J.; Yang, F. New N-Terminal Fatty-Acid-Modified Melittin Analogs with Potent Biological Activity. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babaie, M.; Panah, A.G.; Mehrabi, Z.; Mollaei, A. Partial Purification and Characterization of Antimicrobial Effects from Snake (Echis carinatus), Scorpion (Mesosobuthus epues) and Bee (Apis mellifera) Venoms. Iran. J. Med. Microbiol. 2020, 14, 460–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pola, R.; Vícha, M.; Trousil, J.; Grosmanová, E.; Pechar, M.; Rumlerová, A.; Studenovský, M.; Kučerová, E.; Ulbrich, P.; Vokatá, B.; et al. Polymer-Antimicrobial Peptide Constructs with Tailored Drug-Release Behavior. Pharmaceutics 2023, 15, 406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nabizadeh, S.; Rahbarnia, L.; Nowrozi, J.; Farajnia, S.; Hosseini, F. Rational Design of Hybrid Peptide with High Antimicrobial Property Derived from Melittin and Lasioglossin. J. Biomol. Struct. Dyn. 2023, 42, 13091–13099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chou, S.; Li, Q.; Wu, H.; Li, J.; Chang, Y.-F.; Shang, L.; Li, J.; Wang, Z.; Shan, A. Selective Antifungal Activity and Fungal Biofilm Inhibition of Tryptophan Center Symmetrical Short Peptide. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 8231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pourahmadi, M.; Pourahmadi, K.; Modaresi, F.; Atashpoor, S.; Azad, A.; Ranjbaran, A.; Ghasemian, A. The Antibacterial and Anti-Biofilm Traits of the Novel BMAP-27-Melittin Conjugated Peptide Nanoparticle Against Streptococcus Mutans: Clinical Isolates from Oral Cavity. Iran. J. Pathol. 2022, 17, 294–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-García, B.; Gandía, M.; Muñoz, A.; Carmona, L.; Marcos, J.F. A Genomic Approach Highlights Common and Diverse Effects and Determinants of Susceptibility on the Yeast Saccharomyces Cerevisiae Exposed to Distinct Antimicrobial Peptides. BMC Microbiol. 2010, 10, 289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Wang, C.; Gao, N.; Lyu, Y.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, S.; Wang, J.; Shan, A. A Novel Dual-Targeted α-Helical Peptide With Potent Antifungal Activity Against Fluconazole-Resistant Candida Albicans Clinical Isolates. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 548620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kočendová, J.; Vaňková, E.; Volejníková, A.; Nešuta, O.; Buděšínský, M.; Socha, O.; Hájek, M.; Hadravová, R.; Čeřovský, V. Antifungal Activity of Analogues of Antimicrobial Peptides Isolated from Bee Venoms against Vulvovaginal candida spp. FEMS Yeast Res. 2019, 19, foz013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.-B. Antifungal Activity of Bee Venom and Sweet Bee Venom against Clinically Isolated Candida Albicans. J. Pharmacopunct. 2016, 19, 45–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Didamony, S.E.; Kalaba, M.H.; El-Fakharany, E.M.; Sultan, M.H.; Sharaf, M.H. Antifungal and Anti-biofilm Activities of Bee Venom Loaded on Chitosan Nanoparticles: A Novel Approach for Combating Fungal Human Pathogens. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2022, 38, 244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.-Y.; Park, S.-C.; Noh, G.; Kim, H.; Yoo, S.-H.; Kim, I.R.; Lee, J.R.; Jang, M.-K. Antifungal Effect of A Chimeric Peptide Hn-Mc against Pathogenic Fungal Strains. Antibiotics 2020, 9, 454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.; Kwon, O.; An, H.-J.; Park, K.K. Antifungal Effects of Bee Venom Components on Trichophyton Rubrum: A Novel Approach of Bee Venom Study for Possible Emerging Antifungal Agent. Ann. Dermatol. 2018, 30, 202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Todorova, T.; Boyadzhiev, K.; Dimitrov, M.; Parvanova, P. Bee Venom Genotoxicity on Saccharomyces Cerevisiae Cells—The Role of Mitochondria and YAP1 Transcription Factor. Toxicology 2024, 503, 153768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hilpert, K.; Rumancev, C.; Gani, J.; Collis, D.W.P.; Lopez-Perez, P.M.; Garamus, V.M.; Mikut, R.; Rosenhahn, A. Can BioSAXS Detect Ultrastructural Changes of Antifungal Compounds in Candida Albicans?—An Exploratory Study. Front. Pharmacol. 2023, 14, 1141785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Do, N.; Weindl, G.; Grohmann, L.; Salwiczek, M.; Koksch, B.; Korting, H.C.; Schäfer-Korting, M. Cationic Membrane-active Peptides—Anticancer and Antifungal Activity as Well as Penetration into Human Skin. Exp. Dermatol. 2014, 23, 326–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.-M.; Park, S.-C.; Yoon, Y.; Jang, M.-K.; Lee, J.R. Effect of Tryptophan Position and Lysine/Arginine Substitution in Antimicrobial Peptides on Antifungal Action. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2024, 704, 149700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmoud, S.H.; Kandel, M.; El-Seedi, H.; Al Naggar, Y. Honey Bee Venom Promotes the Immune System and Reduces Vairimorpha (Nosema) Ceranae Infection in Honey Bees (Apis mellifera L.). Apidologie 2024, 55, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, C.; Lee, D.G. Melittin Induces Apoptotic Features in Candida Albicans. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2010, 394, 170–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, E.J.; Leng, E.G.T.; Tram, N.D.T.; Periayah, M.H.; Ee, P.L.R.; Barkham, T.M.S.; Poh, Z.S.; Verma, N.K.; Lakshminarayanan, R. Rationalisation of Antifungal Properties of α-Helical Pore-Forming Peptide, Mastoparan B. Molecules 2022, 27, 1438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, D.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Yu, Q.; Liu, S.; Li, M. Synthesis of the Ternary Nanocomposites Composed of Zinc 2-Methylimidazolate Frameworks, Lactoferrin and Melittin for Antifungal Therapy. J. Mater. Sci. 2022, 57, 16809–16819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, S.-H.; Ye, M.-K.; Choi, S.-Y.; Park, K.-K. The Effects of Melittin and Apamin on Airborne Fungi-Induced Chemical Mediator and Extracellular Matrix Production from Nasal Polyp Fibroblasts. Toxins 2017, 9, 348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, G.N.; Choi, J.; Wu, K.; Saeedian, N.; Yang, E.; Park, H.; Woo, S.-J.; Lim, G.; Kim, S.-G.; Eo, S.-K.; et al. A Vesicular Stomatitis Virus-Based Prime-Boost Vaccination Strategy Induces Potent and Protective Neutralizing Antibodies against SARS-CoV-2. PLoS Pathog. 2021, 17, e1010092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peskova, M.; Heger, Z.; Janda, P.; Adam, V.; Pekarik, V. An Enzymatic Assay Based on Luciferase Ebola Virus-like Particles for Evaluation of Virolytic Activity of Antimicrobial Peptides. Peptides 2017, 88, 87–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.-H.; Lee, H.-W.; Park, H.-W.; Lee, H.-W.; Chun, K.-H. Bee Venom Inhibits the Proliferation and Migration of Cervical-Cancer Cells in an HPV E6/E7-Dependent Manner. BMB Rep. 2020, 53, 419–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Männle, H.; Hübner, J.; Münstedt, K. Beekeepers Who Tolerate Bee Stings Are Not Protected against SARS-CoV-2 Infections. Toxicon 2020, 187, 279–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hood, J.L.; Jallouk, A.P.; Campbell, N.; Ratner, L.; Wickline, S.A. Cytolytic Nanoparticles Attenuate HIV-1 Infectivity. Antivir. Ther. 2013, 18, 95–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, E.; Michalski, C.J.; Choo, S.H.; Kim, G.N.; Banasikowska, E.; Lee, S.; Wu, K.; An, H.-Y.; Mills, A.; Schneider, S.; et al. First Phase I Human Clinical Trial of a Killed Whole-HIV-1 Vaccine: Demonstration of Its Safety and Enhancement of Anti-HIV Antibody Responses. Retrovirology 2016, 13, 82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enayathullah, M.G.; Parekh, Y.; Banu, S.; Ram, S.; Nagaraj, R.; Kumar, B.K.; Idris, M.M. Gramicidin S and Melittin: Potential Anti-Viral Therapeutic Peptides to Treat SARS-CoV-2 Infection. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 3446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dehghani, B.; Hasanshahi, Z.; Hashempour, T. HIV Capsid and Protease, New Targets of Melittin. Int. J. Pept. Res. Ther. 2020, 26, 2057–2065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mustafa, G.; Mahrosh, H.S.; Salman, M.; Ali, M.; Arif, R.; Ahmed, S.; Ebaid, H. In Silico Analysis of Honey Bee Peptides as Potential Inhibitors of Capripoxvirus DNA-Directed RNA Polymerase. Animals 2023, 13, 2281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muzammal, M.; Khan, M.; Mohaini, M.; Alsalman, A.; Hawaj, M.; Farid, A. In Silico Analysis of Honeybee Venom Protein Interaction with Wild Type and Mutant (A82V + P375S) Ebola Virus Spike Protein. Biologics 2022, 2, 45–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baldassi, D.; Ambike, S.; Feuerherd, M.; Cheng, C.-C.; Peeler, D.J.; Feldmann, D.P.; Porras-Gonzalez, D.L.; Wei, X.; Keller, L.-A.; Kneidinger, N.; et al. Inhibition of SARS-CoV-2 Replication in the Lung with siRNA/VIPER Polyplexes. J. Control. Release 2022, 345, 661–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uddin, M.B.; Lee, B.-H.; Nikapitiya, C.; Kim, J.-H.; Kim, T.-H.; Lee, H.-C.; Kim, C.G.; Lee, J.-S.; Kim, C.-J. Inhibitory Effects of Bee Venom and Its Components against Viruses in Vitro and in Vivo. J. Microbiol. 2016, 54, 853–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chianese, A.; Zannella, C.; Palma, F.; Di Clemente, L.; Monti, A.; Doti, N.; De Filippis, A.; Galdiero, M. Melittin-Related Peptides Interfere with Sandfly Fever Naples Virus Infection by Interacting with Heparan Sulphate. Microorganisms 2023, 11, 2446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das Neves, J.; Nunes, R.; Rodrigues, F.; Sarmento, B. Nanomedicine in the Development of Anti-HIV Microbicides. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2016, 103, 57–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarhan, M.; El-Bitar, A.M.H.; Hotta, H. Potent Virucidal Activity of Honeybee “Apis mellifera” Venom against Hepatitis C Virus. Toxicon 2020, 188, 55–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Maksoud, E.A.A.; Rady, M.H.; Mahmoud, A.G.T.; Hamza, D.; Seadawy, M.G.; Essa, E.E. Potential Therapeutic Biomolecules of Hymenopteran Venom against SARS-CoV-2 from Egyptian Patients. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 15363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farhoudi, R.; Taheri, M.; Soltani, M.; Nezhad Fard, R.M.; Shahedin, G.J.; Nabian, S. Rational Design of a Hybrid Peptide against Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 Using Melittin and Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme 2 as Pharmaceutical Agents. Adv. Biomed. Res. 2022, 11, 88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Rabia, M.; Alhakamy, N.; Ahmed, O.; Eljaaly, K.; Alaofi, A.; Mostafa, A.; Asfour, H.; Aldarmahi, A.; Darwish, K.; Ibrahim, T.; et al. Repurposing of Sitagliptin- Melittin Optimized Nanoformula against SARS-CoV-2; Antiviral Screening and Molecular Docking Studies. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elnosary, M.E.; Aboelmagd, H.A.; Habaka, M.A.; Salem, S.R.; El-Naggar, M.E. Synthesis of Bee Venom Loaded Chitosan Nanoparticles for Anti-MERS-COV and Multi-Drug Resistance Bacteria. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 224, 871–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartmann, A.D.; Wilhelm, N.; Erfle, V.; Hartmann, K. Wirksamkeit von Melittin Bei Der Behandlung von Katzen Mit Feliner Immunschwächevirusinfektion. Tieraerztliche Prax. Ausg. Kleintiere Heimtiere 2016, 44, 417–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, Z.; Yuan, X.; Chen, W.; Chen, H.; Li, B.; Bi, Z.; Lyu, Y.; Shan, A. Design of Proteolytic-Resistant Antifungal Peptides by Utilizing Minimum d-Amino Acid Ratios. J. Med. Chem. 2024, 67, 10891–10905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, M.; Li, Y.; Cha, S.; Zhao, L.; Liu, C.; Sui, M.; Xue, C.; Dong, N. Development of Targeted Antimicrobial Peptides for Escherichia coli: Combining Phage Display and Rational Design for Food Safety Application. Food Chem. 2025, 470, 142685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teiba, I.I.; Mazrou, Y.S.A.; Makhlouf, A.H.; Elsheery, N.I.; Hekal, S.H.A.; Abu-Elala, N.M.; Bakry, M.K.; El-Bilawy, E.H.; Shehata, A.I. Effects of Liposomal Vitamin C, Coenzyme Q10, and Bee Venom Supplementation on Bacterial Communities and Performance in Nile Tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus). Biology 2025, 14, 309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Bilawy, E.H.; Mamdouh, I.; Behiry, S.; Teiba, I.I. Evaluating the Antibacterial Efficacy of Bee Venom against Multidrug-Resistant Pathogenic Bacteria: Escherichia coli, Salmonella Typhimurium, and Enterococcus Faecalis. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2025, 41, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.H.; Park, J.; Park, K.-K.; An, H.-J.; Lee, Y.W. Evaluation of Antifungal Activities of Bee Venom Components Against Malassezia Strains. Korean J. Med. Mycol. 2019, 91–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.-Y.; Li, X.; Zhao, T.; Liu, Y.; Xia, X.-S.; Wu, X.-M. Functional Analysis of the Escherichia coli mrdA Gene in Melittin Resistance. Front. Microbiol. 2025, 15, 1516808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sonmez, E.; Kekecoglu, M.; Bozdeveci, A.; Alapy Karaoglu, S. In Vitro Research on Antimicrobial Activity of Native Anatolian Honey Bee Products against Paenibacillus Larvae Strains. J. Agric. Sci. Technol. 2025, 27, 189–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lima, W.G.; De Brito, J.C.M.; Cardoso, V.N.; Fernandes, S.O.A. In-Depth Characterization of Antibacterial Activity of Melittin against Staphylococcus aureus and Use in a Model of Non-Surgical MRSA-Infected Skin Wounds. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2021, 156, 105592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fahad Alharbi, L.N.; Rehman, S.; Azmi, S.; Alamri, A.; Alnimr, A.; Ansari, M.A. Novel Circular Antimicrobial Peptides to Combat a Critical Listed Bacterial Pathogen Multi Drug Resistant Acinetobacter Baumannii. Microb. Pathog. 2025, 203, 107448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.D.; Park, J.; Radhakrishnan, N.K.; Aryal, Y.P.; Jeong, G.-H.; Pyo, I.-H.; Ganbaatar, B.; Lee, C.W.; Yang, S.; Shin, Y.; et al. Novel Leech Antimicrobial Peptides, Hirunipins: Real-Time 3D Monitoring of Antimicrobial and Anti-biofilm Mechanisms Using Optical Diffraction Tomography. Adv. Sci. 2025, 12, e2409803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramos-Alcántara, S.; Napan, M.A.C.; Campana, G.L.; Ortiz, J.T. Potential Inhibitory Effect of the Peptide Melittin Purified from Apis mellifera Venom on CTX-M-Type Extended-Spectrum β-Lactamases of Escherichia coli. Antibiotics 2025, 14, 403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reyad, A.M.; Ali, S.F.; Al Kalamawy, I.A.; Radwan, T.E.E. Synergistic Effect of the Bee Venom with Traditional Antibiotics on Multi-Drug Resistant Bacteria. Egypt. J. Med. Microbiol. 2025, 34, 237–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Fu, H.; Wu, W.; Zong, L.; Li, D.; Zhuang, B.; Qi, Y.; Qi, X.; Liang, T. Synthesis and Evaluation of Melittin-Modified Peptides for Antibacterial Activity. Toxins 2025, 17, 98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Li, L.; Li, R.; Li, X.; Li, S.; Su, C.; Liao, H. Arginine N-Glycosylation of Melittin Enhances Its Bacteriostatic Activity and Antiproliferative Therapeutic Index. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2025, 23, 4471–4479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, J.; Li, X.; Lin, M.; Han, Z.; Wang, X.; Guo, J.; Wu, B.; Xia, J. Bifunctional Copper Ion/Melittin Incorporated Hydrogel with Antimicrobial and Anti-oxidant Capabilities for Infected Skin Wound Healing. Mater. Des. 2025, 250, 113631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Singh, A.K.; Wu, X.; Lyu, Y.; Bhunia, A.K.; Narsimhan, G. Characterization of Antimicrobial Activity against Listeria and Cytotoxicity of Native Melittin and Its Mutant Variants. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2016, 143, 194–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, L.; Zhang, X.; Gao, J.; Yue, J.; Zhang, L.; Pan, G. Dual Peptide-Coordinated Dynamic Hydrogel with Antibacterial and Proangiogenic Activities for Infected Skin Wounds. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2025, 285, 138349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maleki, H.; Rai, A.; Pinto, S.; Evangelista, M.; Cardoso, R.M.S.; Paulo, C.; Carvalheiro, T.; Paiva, A.; Imani, M.; Simchi, A.; et al. High Antimicrobial Activity and Low Human Cell Cytotoxicity of Core–Shell Magnetic Nanoparticles Functionalized with an Antimicrobial Peptide. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 11366–11378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Li, T.; Xing, J.; He, S.; Wu, W.; Shan, A.; Wang, J. The Novel Peptide Adjuvants Potentiate Antimicrobial Properties of Melittin against Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus and Their Efficacy as Potential Food Preservatives. Food Control 2025, 170, 111037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awad, E.H.; Arafa, W.; Ali, H.R.; Barakat, O.S.; Ahmed, M.N. Unveiling the Anti-Biofilm Potential of Bee Venom against Multi-Drug Resistant Human Pathogenic Bacteria and Fungi: Perspectives into the Efficacy and Possible Mechanisms. Microb. Pathog. 2025, 200, 107358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Yang, S.; Li, S.; Lang, J.C.; Mao, C.; Kroll, P.; Tang, L.; Dong, H. Self-Assembled Peptide Nanofibers Display Natural Antimicrobial Peptides to Selectively Kill Bacteria without Compromising Cytocompatibility. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 11, 28681–28689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, G.B.; Huh, J.-E.; Lee, H.-J.; Kim, D.; Lee, G.-J.; Park, H.-K.; Lee, J.-D. Anti-Cancer Effect of Bee Venom on Human MDA-MB-231 Breast Cancer Cells Using Raman Spectroscopy. Biomed. Opt. Express 2018, 9, 5703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagy, R.A.A.; Mohamed, M.H.; Elhakim, H.K.; El-Maksoud, M.D.A.; Afify, M.; Mohamed, A.E.R.F.; Eid, M.M.; Khafaga, D.S.R. Anticancer effect of Sorafenib-loaded iron oxide nanoparticles and bee venom on some genes expression in hepatocellular carcinoma. Egypt. J. Chem. 2022, 65, 1477–1487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yaacoub, C.; Wehbe, R.; Salma, Y.; El-Obeid, D.; El Bersaoui, R.; Coutard, B.; Fajloun, Z. Apis mellifera Syriaca Venom: Evaluation of Its Anticoagulant Effect, Proteolytic Activity, and Cytotoxicity along with Its Two Main Compounds—MEL and PLA2—On HeLa Cancer Cells. Molecules 2022, 27, 1653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebrahimdoust, M.; Hayati, H.M.; Moghaddam, M.M.; Bahreini, M. A Short Cationic Peptide Derived from Cecropin and Melittin Peptides Induce Apoptosis in Jurkat and Raji Leukemia Cell Lines. Protein Pept. Lett. 2023, 30, 477–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sattayawat, P.; Kaewkod, T.; Thongyim, S.; Chiawpanit, C.; Wutti-In, Y.; Thepmalee, C.; Tragoolpua, Y.; Disayathanoowat, T.; Panya, A. A Comparative Study of Melittins from Apis florea and Apis mellifera as Cytotoxic Agents Against Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer (NSCLC) Cells and Their Combination with Gefitinib. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 2498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alibeigi, E.; Dehkordi, A.A.; Asadian, M.; Doosti, A.; Piri-Gharaghie, T. Administration of Apis Cerana Cerana Melittin Gene-Encapsulated Pectin for Breast Cancer Therapy: An Investigation of a New Anti-Cancer Agent. Cancer Nanotechnol. 2025, 16, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Wei, Q.; Han, X.; Tao, X.; Cao, T.; Chen, T.; Cao, P.; Zhan, Q. Homologous Polydopamine Ameliorates Haemolysis of Melittin for Enhancing Its Anticancer Efficacy. J. Mater. Chem. B 2024, 12, 5431–5438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zarrinnahad, H.; Mahmoodzadeh, A.; Hamidi, M.P.; Mahdavi, M.; Moradi, A.; Bagheri, K.P.; Shahbazzadeh, D. Apoptotic Effect of Melittin Purified from Iranian Honey Bee Venom on Human Cervical Cancer HeLa Cell Line. Int. J. Pept. Res. Ther. 2018, 24, 563–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Xie, J.; Lu, X.; Li, H.; Wen, C.; Huo, Z.; Xie, J.; Shi, M.; Tang, X.; Chen, H.; et al. Melittin Inhibits Tumor Growth and Decreases Resistance to Gemcitabine by Downregulating Cholesterol Pathway Gene CLU in Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma. Cancer Lett. 2017, 399, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zamani, M.; Bozorg-Ghalati, F.; Mokarram, P. Melittin as an Activator of the Autophagy and Unfolded Protein Response Pathways in Colorectal HCT116 Cell Line. Iran. Biomed. J. 2024, 28, 46–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ertilav, K.; Nazıroğlu, M. Honey Bee Venom Melittin Increases the Oxidant Activity of Cisplatin and Kills Human Glioblastoma Cells by Stimulating the TRPM2 Channel. Toxicon 2023, 222, 106993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lim, H.N.; Baek, S.B.; Jung, H.J. Bee Venom and Its Peptide Component Melittin Suppress Growth and Migration of Melanoma Cells via Inhibition of PI3K/AKT/mTOR and MAPK Pathways. Molecules 2019, 24, 929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Xu, N.; Zhu, W.; Wang, L.; Liu, B.; Zhang, J.; Xie, Z.; Liu, W. Nanoscale Melittin@Zeolitic Imidazolate Frameworks for Enhanced Anticancer Activity and Mechanism Analysis. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 22974–22984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, C.D.; Yoo, J.; Hwang, S.-Y.; Cho, S.-Y.; Kim, M.; Jang, H.; No, K.O.; Shin, J.C.; Kim, J.-H.; Lee, G. Bee Venom Activates the Nrf2/HO-1 and TrkB/CREB/BDNF Pathways in Neuronal Cell Responses against Oxidative Stress Induced by Aβ1–42. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 1193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saghi, H.; Mirzavi, F.; Afshari, A.R.; Jalili-Nik, M.; Mashkani, B.; Soukhtanloo, M. Bee Venom Induces Anti-Tumor Effects in HT-29 Colon Cancer Cells through Regulation of Cell Proliferation and Apoptosis. Biologia 2022, 77, 3595–3602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Hu, W.; Zhang, Z.; Zhou, Z.; Duan, J.; Dong, Z.; Liu, H.; Yan, C. Bee Venom Protects against Pancreatic Cancer via Inducing Cell Cycle Arrest and Apoptosis with Suppression of Cell Migration. J. Gastrointest. Oncol. 2022, 13, 847–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.E.; Kim, Y.; Hong, D.E.; Lee, D.W.; Chang, J.Y.; Yoo, S.S.; Kim, M.J.; Son, D.J.; Yun, J.; Han, S.-B.; et al. Bee Venom Triggers Autophagy-Induced Apoptosis in Human Lung Cancer Cells via the mTOR Signaling Pathway. J. Oncol. 2022, 2022, 8916464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, H.; Kim, Y.S.; Jung, D.-M.; Lee, K.-S.; Lee, J.-M.; Kim, K.K. Melittin-Derived Peptides Exhibit Variations in Cytotoxicity and Anti-oxidant, Anti-Inflammatory and Allergenic Activities. Anim. Cells Syst. 2022, 26, 158–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khorsand-Dehkordi, S.; Doosti, A. Upregulation of EPSTI1/Drp1/AKT1 Signaling Pathways Using pDNA/Melittin Against Breast Cancer. Biochem. Genet. 2024, 63, 2276–2298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mansour, G.H.; El-Magd, M.A.; Mahfouz, D.H.; Abdelhamid, I.A.; Mohamed, M.F.; Ibrahim, N.S.; Wahab, A.H.A.A.; Elzayat, E.M. Bee Venom and Its Active Component Melittin Synergistically Potentiate the Anticancer Effect of Sorafenib against HepG2 Cells. Bioorg. Chem. 2021, 116, 105329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Małek, A.; Kocot, J.; Mitrowska, K.; Posyniak, A.; Kurzepa, J. Bee Venom Effect on Glioblastoma Cells Viability and Gelatinase Secretion. Front. Neurosci. 2022, 16, 792970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tetikoğlu, S.; Çelik-Uzuner, S. Bee Venom Induces the Interaction between Phosphorylated Histone Variant, H2AX, and the Intracellular Site of beta-Actin in Liver and Breast Cancer Cells. Chem. Biodivers. 2023, 20, e202300401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Małek, A.; Strzemski, M.; Kapka-Skrzypczak, L.; Kurzepa, J. Anticancer Activity of Melittin-Containing Bee Venom Fraction Against Glioblastoma Cells In Vitro. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 2376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, Y.-J.; Park, Y.-Y.; Park, K.-K.; Choi, Y.H.; Kim, C.-H.; Chang, Y.-C. Bee Venom Suppresses EGF-Induced Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition and Tumor Invasion in Lung Cancer Cells. Am. J. Chin. Med. 2019, 47, 1869–1883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- İlhan, H.; Kabakcı, D.; Seçme, M. Cytotoxic Effects of Bee Venom-Loaded ZIF-8 Nanoparticles on Thyroid Cancer Cells: A Promising Strategy for Targeted Therapy. Med. Oncol. 2025, 42, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amer, A.E.; Eldin, Z.E.; Elnemr, S.S.; Amin, B.H. In Vitro Antibacterial and Anticancer Applications of Chitosan Nanoparticles Loaded with Apis mellifera Venom. Egypt. J. Chem. 2025, 68, 63–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halici, H.; Un, H.; Celik, S.; Karakoy, Z.; Bayraktutan, Z.; Ozlu, C.; Cadirci, E.; Halici, Z.; Atila, A.; Mercantepe, F. Low-Dose Bee Venom as a Potential Therapeutic Agent Against Human Chronic Myeloid Leukaemia Cells. Protein J. 2025, 44, 297–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qanash, H.; Bazaid, A.S.; Alharbi, S.F.; Binsaleh, N.K.; Barnawi, H.; Alharbi, B.; Alsolami, A.; Almashjary, M.N. Therapeutic Effects of Nanocoating of Apitoxin (Bee venom) and Polyvinyl Alcohol Supplemented with Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles. Pharmaceutics 2025, 17, 172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sobral, F.; Sampaio, A.; Falcão, S.; Queiroz, M.J.R.P.; Calhelha, R.C.; Vilas-Boas, M.; Ferreira, I.C.F.R. Chemical Characterization, Anti-oxidant, Anti-Inflammatory and Cytotoxic Properties of Bee Venom Collected in Northeast Portugal. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2016, 94, 172–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Mehdi, I.; Falcão, S.I.; Harandou, M.; Boujraf, S.; Calhelha, R.C.; Ferreira, I.C.F.R.; Anjos, O.; Campos, M.G.; Vilas-Boas, M. Chemical, Cytotoxic, and Anti-Inflammatory Assessment of Honey Bee Venom from Apis mellifera Intermissa. Antibiotics 2021, 10, 1514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borojeni, S.K.; Zolfagharian, H.; Babaie, M.; Javadi, I. Cytotoxic Effect of Bee (A. Mellifera) Venom on Cancer Cell Lines. J. Pharmacopunct. 2020, 23, 212–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chahla, C.; Rima, M.; Mouawad, C.; Roufayel, R.; Kovacic, H.; El Obeid, D.; Sabatier, J.-M.; Luis, J.; Fajloun, Z.; El-Waly, B. Effect of Apis mellifera Syriaca Bee Venom on Glioblastoma Cancer: In Vitro and In Vivo Studies. Molecules 2024, 29, 3950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Bassion, M.N.; Mahfouz, H.M.; Hussein, A.S.; El-Hamamy, M.M.; Daim, M.M.A.; Bufo, S.A. Effect of Honey Bee Venom on Cancer in Rats Model. J. Entomol. 2016, 13, 72–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soukhtanloo, M.; Zare, M.; Khayatzadeh, J.; Sadegh Nia, H.; Mojarad, M.; Baghbani, F.; Sargolzaei, J.; Sadeghian, H.; Sisakhti, M. Effects of Bee Venom on Activity and Expression of 15-Lipoxygenase-1 in Human HT29 Colon Cancer. Acta Pol. Pharm. Drug Res. 2019, 76, 75–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alalawy, A.I.; El Rabey, H.A.; Almutairi, F.M.; Tayel, A.A.; Al-Duais, M.A.; Zidan, N.S.; Sakran, M.I. Effectual Anticancer Potentiality of Loaded Bee Venom onto Fungal Chitosan Nanoparticles. Int. J. Polym. Sci. 2020, 2020, 2785304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Didamony, S.E.; Amer, R.I.; El-Osaily, G.H. Formulation, Characterization and Cellular Toxicity Assessment of a Novel Bee-Venom Microsphere in Prostate Cancer Treatment. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 13213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duffy, C.; Sorolla, A.; Wang, E.; Golden, E.; Woodward, E.; Davern, K.; Ho, D.; Johnstone, E.; Pfleger, K.; Redfern, A.; et al. Honeybee Venom and Melittin Suppress Growth Factor Receptor Activation in HER2-Enriched and Triple-Negative Breast Cancer. NPJ Precis. Oncol. 2020, 4, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duarte, D.; Falcão, S.I.; El Mehdi, I.; Vilas-Boas, M.; Vale, N. Honeybee Venom Synergistically Enhances the Cytotoxic Effect of CNS Drugs in HT-29 Colon and MCF-7 Breast Cancer Cell Lines. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sengul, F.; Vatansev, H.; Ozturk, B. Investigation the Effects of Bee Venom and H-Dental-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells on Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Cells (A549). Mol. Biol. Rep. 2024, 51, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lebel, A.A.; Kisembo, M.V.; Soucy, M.-F.N.; Hébert, M.P.A.; Morin, P.J.; Boudreau, L.H. Molecular Characterization of the Anticancer Properties Associated with Bee Venom and Its Components in Glioblastoma Multiforme. Chem. Biol. Interact. 2021, 347, 109622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamel, A.G.; Sabet, S.; El-Shibiny, A. Potential Mitochondrial ROS-Mediated Damage Induced by Chitosan Nanoparticles Bee Venom-Loaded on Cancer Cell Lines. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 279, 135362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amar, S.; El-Bolok, A.H.M.; El-Gayar, S.F.; Sholkamy, M.I. Synergistic Cytotoxic Effect of Honey Bee Venom and Cisplatin on Tongue Squamous Cell Carcinoma Cell Line. Open Access Maced. J. Med. Sci. 2021, 9, 1739–1744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaimaa, H. Shadeed Synergistic Effect of Cetuximab in Combination with Bee Venom: A Novel Approach for the Treatment of Colon Cancer. Biointerface Res. Appl. Chem. 2022, 13, 178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drigla, F.; Balacescu, O.; Visan, S.; Bisboaca, S.E.; Berindan-Neagoe, I.; Marghitas, L.A. Synergistic Effects Induced by Combined Treatments of Aqueous Extract of Propolis and Venom. Med. Pharm. Rep. 2016, 89, 104–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khamis, A.A.; Ali, E.M.M.; Salim, E.I.; El-Moneim, M.A.A. Synergistic Effects of Bee Venom, Hesperidin, and Piperine with Tamoxifen on Apoptotic and Angiogenesis Biomarker Molecules against Xerographic MCF-7 Injected Rats. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 1510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Badivi, S.; Kazemi, S.; Eskandarisani, M.; Moghaddam, N.A.; Mesbahian, G.; Karimifard, S.; Afzali, E. Targeted Delivery of Bee Venom to A549 Lung Cancer Cells by PEGylate Liposomal Formulation: An Apoptotic Investigation. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 17302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babayeva, A.; Dibek, E.; Kıvrak, İ.; Çöl, B. The Cytotoxic Effects of Turkish Bee Venom (Apis mellifera) on Selected Cancer Cell Lines. Int. J. Pept. Res. Ther. 2024, 30, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orman, B.; Koç, A.; Şen Karaman, D.; Nalbantsoy, A. Intrinsic Apoptotic Effect of Anatolian Honeybee (Apis mellifera anatoliaca) Venom Promoted with Mesoporous Silica Nanocarriers. Turk. J. Biol. 2025, 49, 185–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Y.; Zhou, H.; Shi, P.; Zhao, X.; Liu, H.; Li, X. Clickable Tryptophan Modification for Late-Stage Diversification of Native Peptides. Sci. Adv. 2024, 10, eadp9958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Y.; Han, M.; Liu, C.; Liu, T.; Feng, Y.; Zou, Y.; Li, B.; Liao, H. Design, Synthesis, and Antiproliferative Activities of Stapled Melittin Peptides. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 17514–17518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayat, P.; Abnous, K.; Balarastaghi, S.; Taghdisi, S.M.; Saeedi, M.; Yazdian-Robati, R.; Mahmoudi, M. Aptamer AS1411-Functionalized Gold Nanoparticle-Melittin Complex for Targeting MCF-7 Breast Cancer Cell Line. Nanomed. J. 2022, 9, 164–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Shi, Z.; Teng, L.; Nie, J.; Zhang, L. Biocompatible Black Phosphorus Nanosheets-Antimicrobial Peptide Nanocomposites for Enhanced Anti-Infection Therapy. Molecules 2025, 30, 872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kyung, H.; Kim, H.; Lee, H.; Lee, S.J. Enhanced Intracellular Delivery of Macromolecules by Melittin Derivatives Mediated Cellular Uptake. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2018, 58, 290–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zorilă, B.; Necula, G.; Radu, M.; Bacalum, M. Melittin Induces Local Order Changes in Artificial and Biological Membranes as Revealed by Spectral Analysis of Laurdan Fluorescence. Toxins 2020, 12, 705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Li, D.; Jiang, Z.; Yuan, Z.; Sun, Z.; Sun, L. D-M159 Synergistically Induces Apoptosis in HeLa Cells Through Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress and Mitochondrial Dysfunction. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 3172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lischer, K.; Sitorus, S.; Guslianto, B.; Avila, F.; Khayrani, A.; Sahlan, M. Anti-Breast Cancer Activity on MCF-7 Cells of Melittin from Indonesia’s Apis Cerana: An In Vitro Study. Asian Pac. J. Cancer Prev. 2021, 22, 3913–3920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moghaddam, F.D.; Mortazavi, P.; Hamedi, S.; Nabiuni, M.; Roodbari, N.H. Apoptotic Effects of Melittin on 4T1 Breast Cancer Cell Line is Associated with Up Regulation of Mfn1 and Drp1 mRNA Expression. Anti-Cancer Agents Med. Chem. 2020, 20, 790–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daniluk, K.; Lange, A.; Pruchniewski, M.; Małolepszy, A.; Sawosz, E.; Jaworski, S. Delivery of Melittin as a Lytic Agent via Graphene Nanoparticles as Carriers to Breast Cancer Cells. J. Funct. Biomater. 2022, 13, 278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dabbagh Moghaddam, F.; Akbarzadeh, I.; Marzbankia, E.; Farid, M.; Khaledi, L.; Reihani, A.H.; Javidfar, M.; Mortazavi, P. Delivery of Melittin-Loaded Niosomes for Breast Cancer Treatment: An in Vitro and in Vivo Evaluation of Anti-Cancer Effect. Cancer Nano 2021, 12, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, E.; Kim, D.; Cho, Y.; Lee, S.; Kim, J.; Kim, H. Development of Polymersomes Co-Delivering Doxorubicin and Melittin to Overcome Multidrug Resistance. Molecules 2023, 28, 1087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, M.; Chang, W.; Zhang, K.; Cui, M.; Wu, S.; Xu, T. Expression and Purification of Recombinant ATF-Mellitin, a New Type Fusion Protein Targeting Ovarian Cancer Cells, in P. pastoris. Oncol. Rep. 2016, 35, 1179–1185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qi, J.; Chen, Y.; Xue, T.; Lin, Y.; Huang, S.; Cao, S.; Wang, X.; Su, Y.; Lin, Z. Graphene Oxide-Based Magnetic Nanocomposites for the Delivery of Melittin to Cervical Cancer HeLa Cells. Nanotechnology 2020, 31, 065102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Honari, P.; Shahbazzadeh, D.; Behdani, M.; Pooshang Bagheri, K. Highly in Vitro Anti-Cancer Activity of Melittin-Loaded Niosomes on Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Cells. Toxicon 2024, 241, 107673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, Z.; Yao, J.; Xie, N.; Cai, L.; Qi, S.; Zhang, Z.; Li, B. Melittin Constrains the Expression of Identified Key Genes Associated with Bladder Cancer. J. Immunol. Res. 2018, 2018, 5038172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sangboonruang, S.; Kitidee, K.; Chantawannakul, P.; Tragoolpua, K.; Tragoolpua, Y. Melittin from Apis florea Venom as a Promising Therapeutic Agent for Skin Cancer Treatment. Antibiotics 2020, 9, 517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H. Melittin Inactivates YAP/HIF-1α Pathway via up-Regulation of LATS2 to Inhibit Hypoxia-Induced Proliferation, Glycolysis and Angiogenesis in NSCLC. Clinics 2024, 79, 100407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kreinest, T.; Volkmer, I.; Staege, M.S. Melittin Increases Cisplatin Sensitivity and Kills KM-H2 and L-428 Hodgkin Lymphoma Cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 22, 343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tipgomut, C.; Wongprommoon, A.; Takeo, E.; Ittiudomrak, T.; Puthong, S.; Chanchao, C. Melittin Induced G1 Cell Cycle Arrest and Apoptosis in Chago-K1 Human Bronchogenic Carcinoma Cells and Inhibited the Differentiation of THP-1 Cells into Tumour- Associated Macrophages. Asian Pac. J. Cancer Prev. 2018, 19, 3427–3434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Zhu, S.; Li, Z.; Meng, Y.-Q.; Huang, S.-J.; Yu, Q.-Y.; Li, B. Melittin Induces Ferroptosis and ER Stress-CHOP-Mediated Apoptosis in A549 Cells. Free Radic. Res. 2022, 56, 398–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kong, G.-M.; Tao, W.-H.; Diao, Y.-L.; Fang, P.-H.; Wang, J.-J.; Bo, P.; Qian, F. Melittin Induces Human Gastric Cancer Cell Apoptosis via Activation of Mitochondrial Pathway. World J. Gastroenterol. 2016, 22, 3186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Lin, W.; Yin, Z.; Zou, Y.; Liang, S.; Ruan, S.; Chen, P.; Li, S.; Shu, Q.; Cheng, B.; et al. Melittin Inhibits Hypoxia-Induced Vasculogenic Mimicry Formation and Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition through Suppression of HIF-1 α /Akt Pathway in Liver Cancer. Evid. Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2019, 2019, 9602935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, J.; Zhang, Z.; Li, S.; Li, B.; Wang, X. Melittin Inhibits Proliferation, Migration and Invasion of Bladder Cancer Cells by Regulating Key Genes Based on Bioinformatics and Experimental Assays. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2020, 24, 655–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mir Hassani, Z.; Nabiuni, M.; Parivar, K.; Abdirad, S.; Karimzadeh, L. Melittin Inhibits the Expression of Key Genes Involved in Tumor Microenvironment Formation by Suppressing HIF-1α Signaling in Breast Cancer Cells. Med. Oncol. 2021, 38, 77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Li, Z.; Meng, Y.-Q.; Qiao, H.; Zhai, K.-R.; Li, Z.-Q.; Wei, S.-L.; Li, B. Melittin Kills A549 Cells by Targeting Mitochondria and Blocking Mitophagy Flux. Redox Rep. 2023, 28, 2284517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salimian, F.; Nabiuni, M.; Salehghamar, E. Melittin Prevents Metastasis Of Epidermal Growth Factor-Induced MDA-MB-231 Cells Through The Inhibition Of The SDF-1α/CXCR4 Signaling Pathway. Cell J. 2022, 24, 85–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.; Zhang, H.; Peng, T.; Li, D.; Xu, J. Melittin Suppresses Cathepsin S-Induced Invasion and Angiogenesis via Blocking of the VEGF-A/VEGFR-2/MEK1/ERK1/2 Pathway in Human Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Oncol. Lett. 2016, 11, 610–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Jeong, Y.-J.; Choi, Y.; Shin, J.-M.; Cho, H.-J.; Kang, J.-H.; Park, K.-K.; Choe, J.-Y.; Bae, Y.-S.; Han, S.-M.; Kim, C.-H.; et al. Melittin Suppresses EGF-Induced Cell Motility and Invasion by Inhibiting PI3K/Akt/mTOR Signaling Pathway in Breast Cancer Cells. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2014, 68, 218–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.-Y.; Peng, S.-F.; Chueh, F.-S.; Chen, P.-Y.; Huang, Y.-P.; Huang, W.-W.; Chung, J.-G. Melittin Suppresses Epithelial–Mesenchymal Transition and Metastasis in Human Gastric Cancer AGS Cells via Regulating Wnt/BMP Associated Pathway. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2021, 85, 2250–2262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lv, Y.; Chen, X.; Chen, Z.; Shang, Z.; Li, Y.; Xu, W.; Mo, Y.; Wang, X.; Xu, D.; Li, S.; et al. Melittin Tryptophan Substitution with a Fluorescent Amino Acid Reveals the Structural Basis of Selective Antitumor Effect and Subcellular Localization in Tumor Cells. Toxins 2022, 14, 428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Plasay, M.; Natzir, R.; Cangara, M.H.; Hardjo, M.; Syahrijuita, S.; Soraya, G.V. Melittin-Induced Cell Death Through P53 and 8-OHdG in Breast Cell Cancer MCF-7. Biomed. Pharmacol. J. 2022, 15, 979–983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ceremuga, M.; Stela, M.; Janik, E.; Gorniak, L.; Synowiec, E.; Sliwinski, T.; Sitarek, P.; Saluk-Bijak, J.; Bijak, M. Melittin—A Natural Peptide from Bee Venom Which Induces Apoptosis in Human Leukaemia Cells. Biomolecules 2020, 10, 247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plasay, M.; Muslimin, L. Melittin, A Potential Natural Toxin with Anticancer Properties: Regulating IL-1β, COX-2 and TNF-α in Human Colorectal Cancer Cells WiDr. Trends Sci. 2024, 21, 7424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obeidat, M.; Al-khraisat, I.F.; Jaradat, D.M.M.; Ghanim, B.Y.; Abdallah, Q.M.; Arqoub, D.A.; Sabbah, D.; Al-Sanabra, O.M.; Arafat, T.; Qinna, N.A. Mellitin Peptide Quantification in Seasonally Collected Crude Bee Venom and Its Anticancer Effects on Myelogenous K562 Human Leukaemia Cell Line. BMC Complement. Med. Ther. 2023, 23, 132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alonezi, S.; Tusiimire, J.; Wallace, J.; Dufton, M.; Parkinson, J.; Young, L.; Clements, C.; Park, J.-K.; Jeon, J.-W.; Ferro, V.; et al. Metabolomic Profiling of the Synergistic Effects of Melittin in Combination with Cisplatin on Ovarian Cancer Cells. Metabolites 2017, 7, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wattanakul, K.; Imae, T.; Chang, W.-W.; Chu, C.-C.; Nakahata, R.; Yusa, S. Oligopeptide-Side Chained Alginate Nanocarrier for Melittin-Targeted Chemotherapy. Polym. J. 2019, 51, 771–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, H.; Chen, F.; Lu, M.; Stenzel, M.H.; Xiao, P. Polypeptide-Grafted Nanodiamonds for Controlled Release of Melittin to Treat Breast Cancer. ACS Macro Lett. 2017, 6, 796–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikodijević, D.D.; Jovankić, J.V.; Radenković, N.M.; Cvetković, D.M.; Podolski-Renić, A.M.; Milutinović, M.G. Potential of Melittin to Induce Apoptosis and Overcome Multidrug Resistance in Human Colon Cancer Cell Line. Toxin Rev. 2024, 43, 224–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, M.C.; Min, K.A.; Cheong, H.; Moon, C.; Huang, Y.; He, H.; Yang, V.C. Preparation and Characterization of Gelonin-Melittin Fusion Biotoxin for Synergistically Enhanced Anti-Tumor Activity. Pharm. Res. 2016, 33, 2218–2228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maani, Z.; Farajnia, S.; Rahbarnia, L.; Hosseingholi, E.Z.; Khajehnasiri, N.; Mansouri, P. Rational Design of an Anti-Cancer Peptide Inhibiting CD147 / Cyp A Interaction. J. Mol. Struct. 2023, 1272, 134160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keykanlu, H.; Zibaei, S.; Ardjmand, M.; Safekordi, A. Reload Purified Melittin and Lactoferrin on Perfluorooctyl Bromide Nanoparticles (PFOB-Nps) and Examine the Distribution of Particle Size, Zeta Potential and Confirmation of Their Accession on the Nanoparticles Via Tryptophan Fluorescence and Circular Dichroism (CD) and Its Anti-Cancer Effects on Human Breast Cancer Cell Line MCF7. Orient. J. Chem. 2016, 32, 3099–3111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Rajabnejad, S.H.; Mokhtarzadeh, A.; Abnous, K.; Taghdisi, S.M.; Ramezani, M.; Razavi, B.M. Targeted Delivery of Melittin to Cancer Cells by AS1411 Anti-Nucleolin Aptamer. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 2018, 44, 982–987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, C.; Ma, J.; Lu, Y.; Zhao, W.; Xu, B.; Lin, J.; Ma, Y.; Tian, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, W.; et al. TERT Promoter Regulating Melittin Expression Induces Apoptosis and G0/G1 Cell Cycle Arrest in Esophageal Carcinoma Cells. Oncol. Lett. 2020, 21, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soliman, C.; Eastwood, S.; Truong, V.K.; Ramsland, P.A.; Elbourne, A. The Membrane Effects of Melittin on Gastric and Colorectal Cancer. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0224028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakagawa, C.; Suzuki-Karasaki, M.; Suzuki-Karasaki, M.; Ochiai, T.; Suzuki-Karasaki, Y. The Mitochondrial Ca2+ Overload via Voltage-Gated Ca2+ Entry Contributes to an Anti-Melanoma Effect of Diallyl Trisulfide. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, W.; Li, W.; Wang, Z.; Li, Y.; Liu, M. The Novel Fusion Protein Melittin-MIL-2 Exhibits Strong Antitumor Immune Effect in Lung Adenocarcinoma Cell A549. Clin. Respir. J. 2024, 18, e13805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Delvaux, N.A.; Rice, K.G. The Reduced-charge Melittin Analogue MelP5 Improves the Transfection of Non-viral DNA Nanoparticles. J. Pept. Sci. 2022, 28, e3404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, R.; Dai, W.; Wu, R.; Huang, H.; Shu, M. Therapeutic Targeting m6A-Guided miR-146a-5p Signaling Contributes to the Melittin-Induced Selective Suppression of Bladder Cancer. Cancer Lett. 2022, 534, 215615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daniluk, K.; Kutwin, M.; Grodzik, M.; Wierzbicki, M.; Strojny, B.; Szczepaniak, J.; Bałaban, J.; Sosnowska, M.; Chwalibog, A.; Sawosz, E.; et al. Use of Selected Carbon Nanoparticles as Melittin Carriers for MCF-7 and MDA-MB-231 Human Breast Cancer Cells. Materials 2019, 13, 90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Shi, M.-Y.; Ma, B.-B.; Sheng, J. Mechanism of Leakage in Phosphatidylserine-Containing Membranes by Melittin. Mol. Biol. 2022, 56, 1012–1019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussein, M.M.A.; Abdelfattah-Hassan, A.; Eldoumani, H.; Essawi, W.M.; Alsahli, T.G.; Alharbi, K.S.; Alzarea, S.I.; Al-Hejaili, H.Y.; Gaafar, S.F. Evaluation of Anti-Cancer Effects of Carnosine and Melittin-Loaded Niosomes in MCF-7 and MDA-MB-231 Breast Cancer Cells. Front. Pharmacol. 2023, 14, 1258387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Jia, S.-X.; Chi, Q.-N.; Jin, L.; Chen, X.-Q.; Li, J.; Qi, Y.-K.; Du, S.-S. Efficient Synthesis, Stability-Guided Optimization and Anticancer Evaluation of Bee Venom Peptide Melittin. Bioorgan. Chem. 2025, 159, 108344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raveendran, R.; Chen, F.; Kent, B.; Stenzel, M.H. Estrone-Decorated Polyion Complex Micelles for Targeted Melittin Delivery to Hormone-Responsive Breast Cancer Cells. Biomacromolecules 2020, 21, 1222–1233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, R.; Li, N.; Huang, W.; Yang, Y.; Zang, R.; Song, H.; Shi, J.; Zhu, S.; Liu, Q. Melittin Suppresses Ovarian Cancer Growth by Regulating SREBP1-Mediated Lipid Metabolism. Phytomedicine 2025, 137, 156367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, J.-P.; Zhu, R.; Jiang, F.; Xie, J.; Gao, C.; Li, M.; Jin, H.; Fu, D. Melittin-Encapsulating Peptide Hydrogels for Enhanced Delivery of Impermeable Anticancer Peptides. Biomater. Sci. 2020, 8, 4559–4569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Motiei, M.; Aboutalebi, F.; Forouzanfar, M.; Dormiani, K.; Nasr-Esfahani, M.H.; Mirahmadi-Zare, S.Z. Smart Co-Delivery of miR-34a and Cytotoxic Peptides (LTX-315 and Melittin) by Chitosan Based Polyelectrolyte Nanocarriers for Specific Cancer Cell Death Induction. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2021, 128, 112258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, H.M.; Alessa, J.; Khalil, H.B.; Bekhet, G.A.; Khalifa, A. Synergistic Anti-Cancer Activity of Melittin and Erlotinib in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 2903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rocha, M.M.; Dariva, I.; Zornoff, G.C.; De Laurentis, G.S.; Mendes, G.C.; Santana, M.G.; Miguel, G.C.D.G.C.D.; Ferreira Junior, R.S.; Sciani, J.M.; Priolli, D.G. A New Therapeutic Approach for Bone Metastasis in Colorectal Cancer: Intratumoral Melittin. J. Venom. Anim. Toxins Incl. Trop. Dis. 2022, 28, e20210067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, S.; Chen, Y.; Zhuo, C.; Hu, M.; Zhang, C.; Cai, H.; Li, X.; Chen, H.; Yu, X. Aptamer-Modified Melittin Micelles Efficiently Inhibit Osteosarcoma Deterioration by Inducing Immunogenic Cell Death. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2025, 249, 114512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Wang, Y.; Geng, X.; Dong, M.; Liu, Z.; Sun, C.; Yu, K.; Xin, W.; Xu, Y.; Xu, N.; et al. ANG-Modified Liposomes Coloaded with α-Melittin and Resveratrol Induce Apoptosis and Pyroptosis in Glioblastoma Cells by Impeding Wnt/β-Catenin Signaling. CNS Neurosci. Ther. 2025, 31, e70437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, F.; Chen, P.; Wang, D.; Sun, Y.; Ren, M.; Wang, Y.; Cao, X.; Zhang, L.; Fang, Y.; Tan, X.; et al. Bottlebrush Polymer-Conjugated Melittin Exhibits Enhanced Antitumor Activity and Better Safety Profile. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2021, 13, 42533–42542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, S.; Sylvestre, M.; Song, K.; Pun, S.H. Development of D-Melittin Polymeric Nanoparticles for Anti-Cancer Treatment. Biomaterials 2021, 277, 121076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.; Choi, I.; Han, I.-H.; Bae, H. Enhanced Therapeutic Effect of Optimized Melittin-dKLA, a Peptide Agent Targeting M2-like Tumor-Associated Macrophages in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 15751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Yuan, J.; Liu, J.; Li, X.; Zhou, C.; Qian, M.; Zou, Z.; Lu, C.; Huang, G.; Jin, M. Melittin Suppresses Aerobic Glycolysis by Regulating HSF1/PDK3 to Increase Chemosensitivity of NSCLC. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2025, 986, 177084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Liu, X.; Xia, Y.; Xu, S.; Liu, X.; Xiao, H.; Wang, X.; Liu, C.; Liu, G. Genetically Engineered Nano-melittin Vesicles for Multimodal Synergetic Cancer Therapy. Bioeng. Transl. Med. 2023, 8, e10482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, S.-N.; Kim, S.-H.; Kim, H.J.; Jeong, Y.J.; Lee, K.C. In Vitro and In Vivo Investigation of the Radiation-Sensitizing Effects of Melittin in Breast Cancer Cells. Int. J. Pept. Res. Ther. 2022, 28, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, P.; Zhou, J.; Xing, X.; Hao, Y.; Gao, M.; Li, Z.; Li, X.; Li, M.; Xiao, Y. Melitoxin Inhibits Proliferation, Metastasis, and Invasion of Glioma U251 Cells by Down-Regulating F2RL1. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2024, 196, 6234–6252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meng, J.; He, Y.; Yang, H.; Zhou, L.; Wang, S.; Feng, X.; Yahya Al-shargi, O.; Yu, X.; Zhu, L.; Ling, C. Melittin Analog p5RHH Enhances Recombinant Adeno-Associated Virus Transduction Efficiency. J. Integr. Med. 2024, 22, 72–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, S.-F.; Chen, Z. Melittin Exerts an Antitumor Effect on Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Cells. Mol. Med. Rep. 2017, 16, 3581–3586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, S.; Lv, X.; Li, L.; Luo, Y.; Xiang, H.; Wang, L.; Li, Y. Melittin Inhibited Glycolysis and Induced Cell Apoptosis in Cisplatinresistant Lung Adenocarcinoma Cells via TRIM8. Biocell 2021, 45, 167–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, H.; Chen, D.; Xie, X.; Li, Y.; Fan, T. Melittin Inhibits Lung Metastasis of Human Osteosarcoma: Evidence of Wnt/β-Catenin Signaling Pathway Participation. Toxicon 2021, 198, 132–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, G.; Chen, Y.; Li, H.; Xu, S.; Li, Y.; Sun, J.; Rao, W.; Chen, C.; Du, M.; He, K.; et al. Melittin Inhibits Tumor Angiogenesis Modulated by Endothelial Progenitor Cells Associated with the SDF-1α/CXCR4 Signaling Pathway in a UMR-106 Osteosarcoma Xenograft Mouse Model. Mol. Med. Rep. 2016, 14, 57–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, R.; Dai, W.; Mao, Y.; Yu, G.; Li, W.; Shu, M.; Xu, B. Melittin Inhibits Tumor Cell Migration and Enhances Cisplatin Sensitivity by Suppressing IL-17 Signaling Pathway Gene LCN2 in Castration-resistant Prostate Cancer. Prostate 2023, 83, 1430–1445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, R.; Wang, M.; Wang, M.; Han, L. Melittin Suppresses Growth and Induces Apoptosis of Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer Cells via down-Regulation of TGF-β-Mediated ERK Signal Pathway. Braz. J. Med. Biol. Res. 2021, 54, e9017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y.; Xu, C.; Luo, B.; Liang, G.; Zhang, Q. Melittin Treatment Prevents Colorectal Cancer from Progressing in Mice through ER Stress-Mediated Apoptosis. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2023, 75, 645–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Li, H.; Lu, X.; Wen, C.; Huo, Z.; Shi, M.; Tang, X.; Chen, H.; Peng, C.; Fang, Y.; et al. Melittin-Induced Long Non-Coding RNA NONHSAT105177 Inhibits Proliferation and Migration of Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma. Cell Death Dis. 2018, 9, 940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, X.; Dai, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Qi, S.; Liu, L.; Lu, L.; Luo, Q.; Zhang, Z. Melittin-Lipid Nanoparticles Target to Lymph Nodes and Elicit a Systemic Anti-Tumor Immune Response. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 1110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, B.; Xu, P. Redox-Sensitive Nanocomplex for Targeted Delivery of Melittin. Toxins 2020, 12, 582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Q.; Feng, H.; Yang, Z.; Liang, J.; Jin, Z.; Chen, L.; Zhan, L.; Xuan, M.; Yan, J.; Kuang, J.; et al. The Central Role of a Two-way Positive Feedback Pathway in Molecular Targeted Therapies-mediated Pyroptosis in Anaplastic Thyroid Cancer. Clin. Transl. Med. 2022, 12, e727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y.; Wang, J.; He, Y.; Yu, X.; Zheng, Q.; Ling, C.; Feng, X.; Zhu, L. The Use of Melittin to Enhance Transgene Expression Mediated by Recombinant Adeno-Associated Virus Serotype 2 Vectors Both in Vitro and in Vivo. J. Integr. Med. 2023, 21, 106–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, N.A.; Chrusciel, M.; Ponikwicka-Tyszko, D.; Pulawska-Moon, K.; Stelmaszewska, J.; Doroszko, M.; Kreuzer, O.J.; Rivero-Muller, A.; Li, X.; Ziecik, A.J.; et al. Hecate-FSHβ33-53C/S Lytic Peptide Conjugate Selectively Kills Targeted Follicle Stimulating Hormone Receptor (FSHR)-Positive Cancer Cells. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2025, 186, 118022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.; Ding, J.; Jiang, Y.; Zhang, D.; Yu, J.; Sun, S.; Zhou, J.; Yu, C. Melittin Inhibits Ovarian Cancer Cell Growth by Downregulating MMP9 Expression via the JAK2-STAT3 Signaling Pathway. Curr. Med. Chem. 2025, 32, e20240053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedro, G.; da Silva Brasileiro, F.C.; Ferreira, R.S.; Marques Bráz, A.M.; Laufer-Amorim, R. Melittin Inhibits Proliferation, Migration, and Invasion in Osteosarcoma Cell Lines Using 2D and 3D Models. J. Venom. Anim. Toxins Incl. Trop. Dis. 2025, 31, e20240053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, X.; Li, Y.; Zhu, H.; Chen, L.; Chen, D.; Lin, S.; Fan, T. Melittin Inhibits Growth of Human Osteosarcoma 143B Cells through Induction of Apoptosis via Suppressing the Wnt/β-Catenin Signaling Pathway. Anti-Cancer Agents Med. Chem. 2022, 22, 3172–3181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, H.G.; Lee, K.S.; Kim, B.Y.; Yoon, H.J.; Choi, Y.S.; Lee, K.Y.; Wan, H.; Li, J.; Jin, B.R. Honeybee (Apis cerana) Vitellogenin Acts as an Antimicrobial and Anti-oxidant Agent in the Body and Venom. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2018, 85, 51–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alhage, J.; Elbitar, H.; Taha, S.; Benvegnu, T. In Vitro Assessment of Anti-oxidant, Antimicrobial, Cytotoxic, Anti-Inflammatory, and Antidiabetic Activities of Campanula Retrorsa Crude Extracts. Pharmacogn. Res. 2018, 10, 397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sani, A.A.; Pereira, A.F.M.; Furlanetto, A.; Sousa, D.S.M.D.; Zapata, T.B.; Rall, V.L.M.; Fernandes Júnior, A. Inhibitory Activities of Propolis, Nisin, Melittin and Essential Oil Compounds on Paenibacillus alvei and Bacillus subtilis. J. Venom. Anim. Toxins Incl. Trop. Dis. 2022, 28, 20220025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orrù, A.; Pittau, B.; Pettinau, F. Shedding Light on the Anti-oxidant Activity of Bee Venom Using a 2,2-Diphenyl-1-Picrylhydrazyl Assay in a Detergent-Based Buffer. Molecules 2025, 30, 640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).