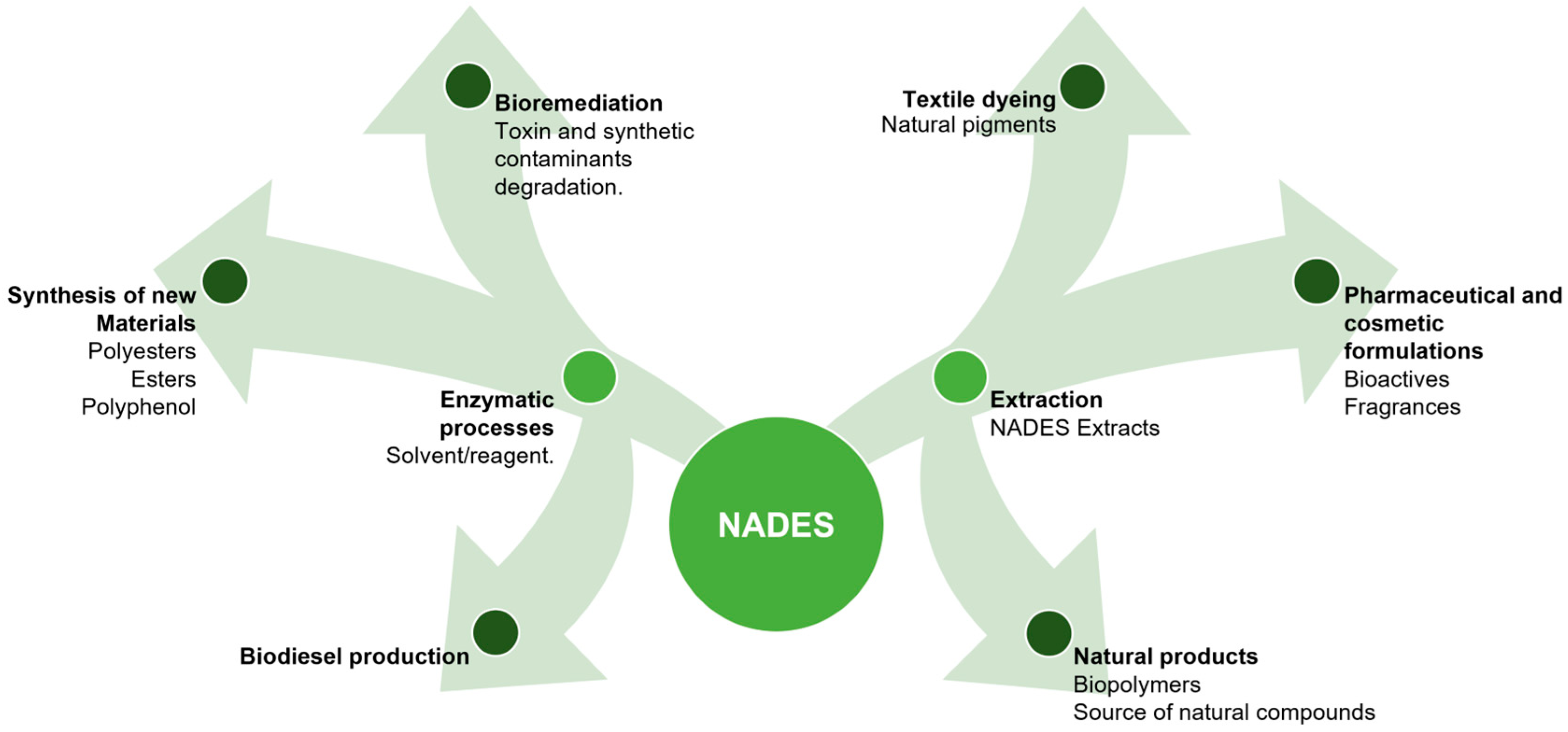
The Versatility of NADES Across Applications
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. The Use of NADES on Enzymatic Processes
2.1. The Role of NADES on Lipase Stability and Reactivity
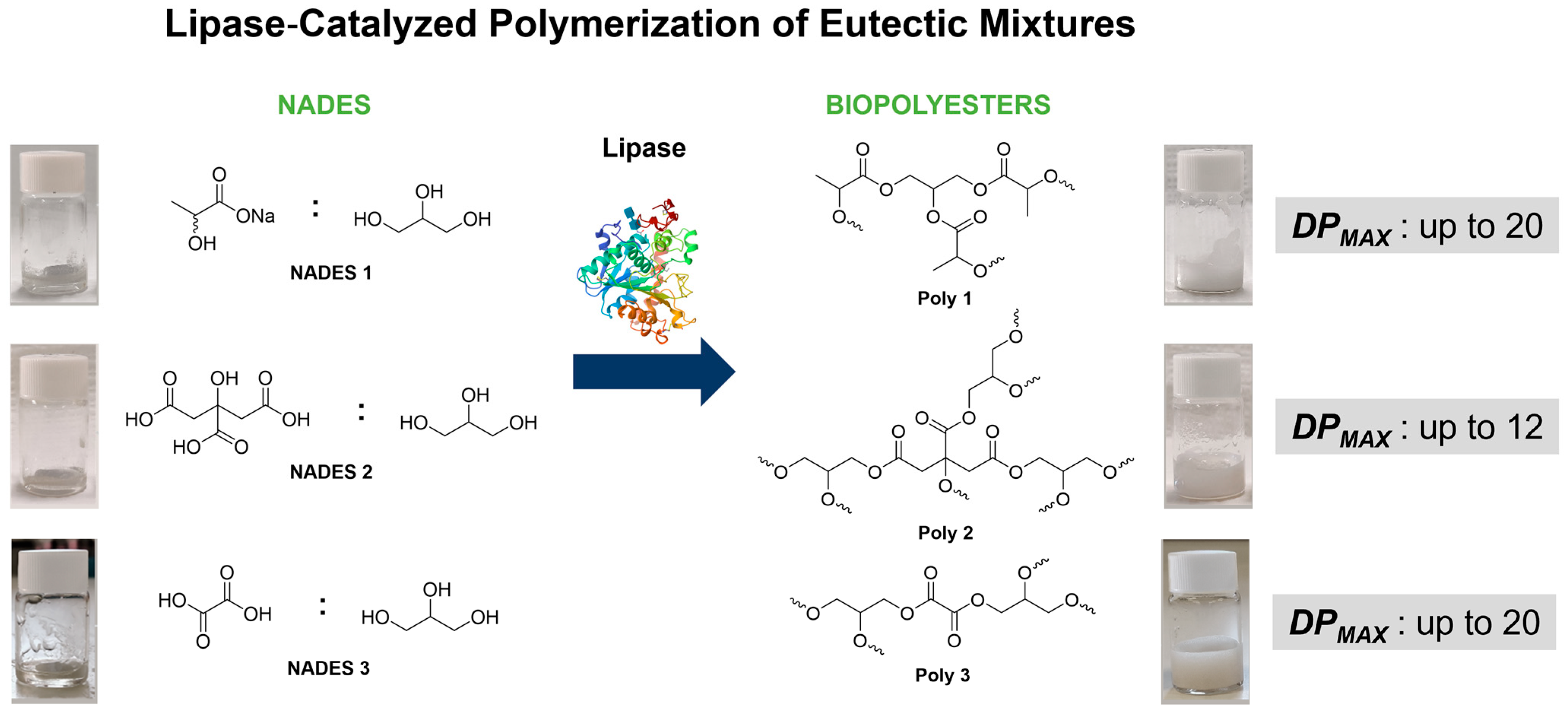
Lipase–NADES Systems for the Synthesis of Biopolyesters: A Case Study
2.2. The Role of NADES on Laccase Stability and Reactivity
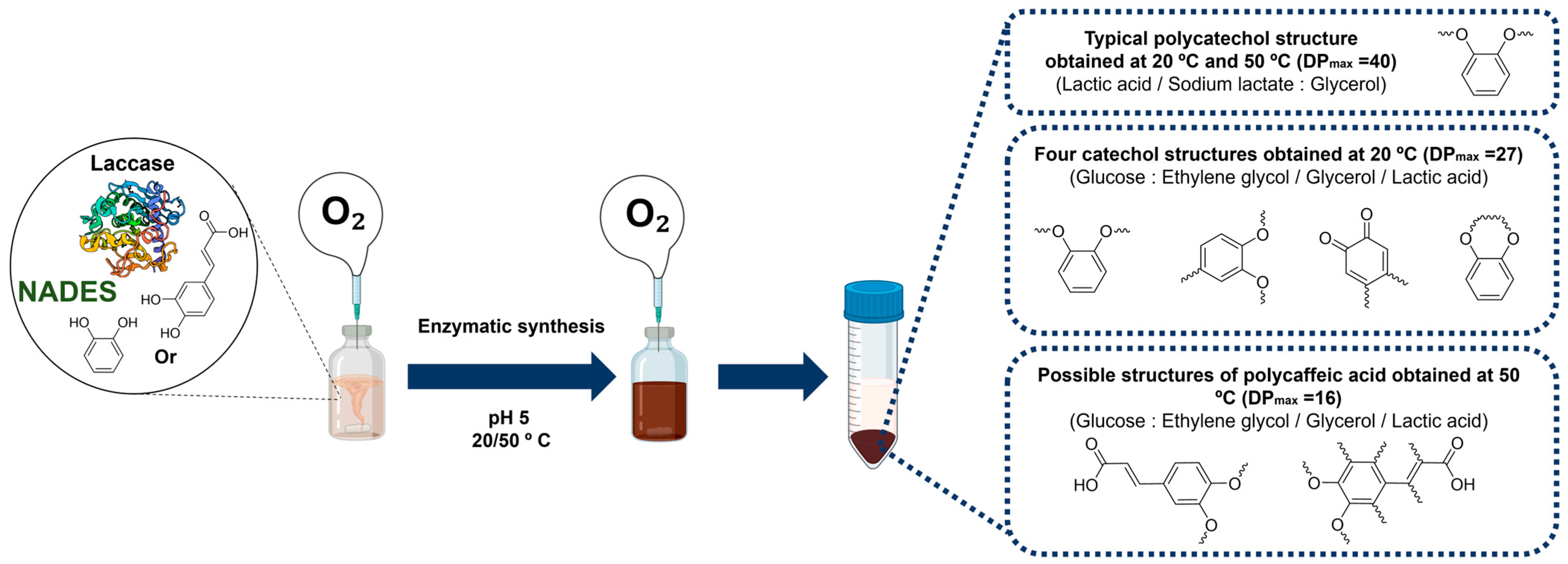
Laccase–NADES Systems for the Synthesis of New Polymers: A Case Study
3. The Use of NADES in the Extraction Processes
Extraction of Bioactive Compounds Using NADES as Solvents: A Case Study
4. The Use of NADES in Cosmetics
NADES Extracts and Their Application in Cosmetics: A Case Study
5. Conclusions and Future Perspectives
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dai, Y.; van Spronsen, J.; Witkamp, G.-J.; Verpoorte, R.; Choi, Y.H. Natural deep eutectic solvents as new potential media for green technology. Anal. Chim. Acta 2013, 766, 61–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zdanowicz, M.; Wilpiszewska, K.; Spychaj, T. Deep eutectic solvents for polysaccharides processing. A review. Carbohydr. Polym. 2018, 200, 361–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruesgas-Ramón, M.; Figueroa-Espinoza, M.C.; Durand, E. Application of Deep Eutectic Solvents (DES) for Phenolic Compounds Extraction: Overview, Challenges, and Opportunities. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2017, 65, 3591–3601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, Y.; Witkamp, G.-J.; Verpoorte, R.; Choi, Y.H. Tailoring properties of natural deep eutectic solvents with water to facilitate their applications. Food Chem. 2015, 187, 14–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, E.L.; Abbott, A.P.; Ryder, K.S. Deep Eutectic Solvents (DES) and Their Applications. Chem. Rev. 2014, 114, 11060–11082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbott, A.P.; Boothby, D.; Capper, G.; Davies, D.L.; Rasheed, R.K. Deep eutectic solvents formed between choline chloride and carboxylic acids: Versatile alternatives to ionic liquids. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2004, 126, 9142–9147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abbott, A.P.; Capper, G.; Davies, D.L.; Rasheed, R.K.; Tambyrajah, V. Novel solvent properties of choline chloride/urea mixtures. Chem. Commun. 2003, 70–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodriguez Rodriguez, N.; van den Bruinhorst, A.; Kollau, L.J.B.M.; Kroon, M.C.; Binnemans, K. Degradation of Deep-Eutectic Solvents Based on Choline Chloride and Carboxylic Acids. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2019, 7, 11521–11528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Florindo, C.; Oliveira, F.S.; Rebelo, L.P.N.; Fernandes, A.M.; Marrucho, I.M. Insights into the Synthesis and Properties of Deep Eutectic Solvents Based on Cholinium Chloride and Carboxylic Acids. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2014, 2, 2416–2425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santana, A.P.R.; Mora-Vargas, J.A.; Guimarães, T.G.S.; Amaral, C.D.B.; Oliveira, A.; Gonzalez, M.H. Sustainable synthesis of natural deep eutectic solvents (NADES) by different methods. J. Mol. Liq. 2019, 293, 111452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altunay, N.; Elik, A.; Gürkan, R. Preparation and application of alcohol based deep eutectic solvents for extraction of curcumin in food samples prior to its spectrophotometric determination. Food Chem. 2020, 310, 125933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cunha, S.C.; Fernandes, J.O. Extraction techniques with deep eutectic solvents. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2018, 105, 225–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freitas, D.S.; Rocha, D.; Castro, T.G.; Noro, J.; Castro, V.I.B.; Teixeira, M.A.; Reis, R.L.; Cavaco-Paulo, A.; Silva, C. Green Extraction of Cork Bioactive Compounds Using Natural Deep Eutectic Mixtures. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2022, 10, 7974–7989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noro, J.; Castro, T.G.; Cavaco-Paulo, A.; Silva, C. Substrate hydrophobicity and enzyme modifiers play a major role in the activity of lipase from Thermomyces lanuginosus. Catal. Sci. Technol. 2020, 10, 5913–5924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, J.C.; Zhang, B.; Martinez, M.; Kuruba, B.; Brozik, J.; Kang, C.; Zhang, X. Structural studies of Myceliophthora Thermophila Laccase in the presence of deep eutectic solvents. Enzym. Microb. Technol. 2021, 150, 109890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freitas, D.S.; Rocha, D.; Noro, J.; Castro, T.G.; Cavaco-Paulo, A.; Silva, C. Eutectic Mixtures as Green Solvents for Laccase-Catalyzed Reactions. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2023, 11, 16594–16607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freitas, D.S.; Quesado, V.; Rocha, D.; Noro, J.; Martins, M.; Cavaco-Paulo, A.; Silva, C. Lipase-Catalysed Polymerization of Eutectic Mixtures. ChemSusChem 2023, 16, e202202374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freitas, D.S.; Rocha, D.; Santos, J.; Noro, J.; Tavares, T.D.; Teixeira, M.O.; Araújo, D.; Castro, J.; Silva, S.; Felgueiras, H.P.; et al. Developing translucent emulsions using sustainable NADES-based extracts. J. Mol. Liq. 2024, 415, 126413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Othman, A.M.; Sanromán, Á.; Moldes, D. Laccase multi-point covalent immobilization: Characterization, kinetics, and its hydrophobicity applications. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2023, 107, 719–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hatimuria, M.; Das, J.; Gavvala, K.; Bag, S.; Pabbathi, A. Recent advances in the use of laccase enzyme in deep eutectic solvents. Sustain. Chem. Pharm. 2023, 33, 101148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gotor-Fernández, V.; Paul, C.E. Deep eutectic solvents for redox biocatalysis. J. Biotechnol. 2019, 293, 24–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khodaverdian, S.; Dabirmanesh, B.; Heydari, A.; Dashtban-Moghadam, E.; Khajeh, K.; Ghazi, F. Activity, stability and structure of laccase in betaine based natural deep eutectic solvents. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 107, 2574–2579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buzatu, A.R.; Todea, A.; Pop, R.; Dreavă, D.M.; Paul, C.; Bîtcan, I.; Motoc, M.; Peter, F.; Boeriu, C.G. Designed Reactive Natural Deep Eutectic Solvents for Lipase-Catalyzed Esterification. Molecules 2025, 30, 778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Li, Y.; Ali, S.; Li, P.; Zhang, W.; Rauch, M.C.R.; Willot, S.J.P.; Ribitsch, D.; Choi, Y.H.; Alcalde, M.; et al. Natural Deep Eutectic Solvents as Performance Additives for Peroxygenase Catalysis. ChemCatChem 2020, 12, 989–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.; Tong, S.; Sun, L.; Gu, X. Cellulase immobilization to enhance enzymatic hydrolysis of lignocellulosic biomass: An all-inclusive review. Carbohydr. Polym. 2023, 321, 121319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.; Wang, H.; Nie, Y.; Zhang, X.; Ji, X. Natural Deep Eutectic Solvents Enhanced Electro-Enzymatic Conversion of CO2 to Methanol. Front. Chem. 2022, 10, 894106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Song, Y.; Yan, Y.; Chen, W.; Ren, T.; Ma, A.; Li, S.; Jia, Y. Characterization of an epilactose-producing cellobiose 2-epimerase from Clostridium sp. TW13 and reutilization of waste milk. Food Chem. 2025, 480, 143948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Z.; Yan, Y.; Wu, Z.; Song, Y.; Xu, J. Expression and Characterization of L-Arabinose Isomerase and Its Enzymatic Recycling of the Expired Milk. Foods 2025, 14, 1873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Z.; Song, Y.; Yan, Y.; Wu, Z.; Xu, J. Simulative Fabrication of Milk Fortified with Sialyloligosaccharides and Its Prospective Applications. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2025, 73, 15835–15846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castillo, E.; Torres-Gavilán, A.; Sandoval, G.; Marty, A. Thermodynamical methods for the optimization of lipase-catalyzed reactions. In Methods in Molecular Biology; Humana Press: Totowa, NJ, USA, 2012; Volume 861, pp. 383–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durand, E.; Lecomte, J.; Baréa, B.; Piombo, G.; Dubreucq, E.; Villeneuve, P. Evaluation of deep eutectic solvents as new media for Candida antarctica B lipase catalyzed reactions. Process Biochem. 2012, 47, 2081–2089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Li, K.; Wang, J.; Xu, L.; Yan, J.; Yang, M.; Yan, Y. A novel strategy for biodiesel production by combination of liquid lipase, deep eutectic solvent and ultrasonic-assistance in scaled-up reactor: Optimization and kinetics. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 372, 133740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehta, A.; Guleria, S.; Sharma, R.; Gupta, R. 6—The lipases and their applications with emphasis on food industry. In Microbial Biotechnology in Food and Health; Ray, R.C., Ed.; Academic Press: Burlington, NJ, USA, 2021; pp. 143–164. [Google Scholar]
- Alcántara, A.R.; Hernaiz, M.J.; Sinisterra, J.V. 3.28—Biocatalyzed Production of Fine Chemicals. In Comprehensive Biotechnology, 2nd ed.; Moo-Young, M., Ed.; Academic Press: Burlington, NJ, USA, 2011; pp. 309–331. [Google Scholar]
- Annapure, U.S.; Gaur, S.S. Chapter 16—Commercial enzymes in dairy processing. In Value-Addition in Food Products and Processing Through Enzyme Technology; Kuddus, M., Aguilar, C.N., Eds.; Academic Press: Burlington, NJ, USA, 2022; pp. 205–219. [Google Scholar]
- Buzatu, A.R.; Soler, M.A.; Fortuna, S.; Ozkilinc, O.; Dreavă, D.M.; Bîtcan, I.; Badea, V.; Giannozzi, P.; Fogolari, F.; Gardossi, L.; et al. Reactive natural deep eutectic solvents increase selectivity and efficiency of lipase catalyzed esterification of carbohydrate polyols. Catal. Today 2024, 426, 114373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nian, B.; Cao, C.; Liu, Y. Activation and stabilization of Candida antarctica lipase B in choline chloride-glycerol-water binary system via tailoring the hydrogen-bonding interaction. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 136, 1086–1095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Semproli, R.; Chanquia, S.N.; Bittner, J.P.; Müller, S.; Domínguez de María, P.; Kara, S.; Ubiali, D. Deep Eutectic Solvents for the Enzymatic Synthesis of Sugar Esters: A Generalizable Strategy? ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2023, 11, 5926–5936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Putra, S.S.S.; Chew, C.Y.; Hayyan, A.; Elgharbawy, A.A.M.; Taskin-Tok, T.; Hayyan, M.; Ngoh, G.C.; Saleh, J.; Al Abdulmonem, W.; Alghsham, R.S.; et al. Nanodiamonds and natural deep eutectic solvents as potential carriers for lipase. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 270, 132245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buzatu, A.R.; Todea, A.; Peter, F.; Boeriu, C.G. The Role of Reactive Natural Deep Eutectic Solvents in Sustainable Biocatalysis. ChemCatChem 2024, 16, e202301597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Jin, T.; Nian, B.; Cheng, W. Solvent Tolerance Improvement of Lipases Enhanced Their Applications: State of the Art. Molecules 2024, 29, 2444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, J.-N.; Dou, Y. Deep eutectic solvents for biocatalytic transformations: Focused lipase-catalyzed organic reactions. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2020, 104, 1481–1496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berthet, S.; Thevenin, J.; Baratiny, D.; Demont-Caulet, N.; Debeaujon, I.; Bidzinski, P.; Leple, J.-C.; Huis, R.; Hawkins, S.; Gomez, L.-D.; et al. Chapter 5—Role of Plant Laccases in Lignin Polymerization. In Advances in Botanical Research; Jouanin, L., Lapierre, C., Eds.; Academic Press: Burlington, NJ, USA, 2012; Volume 61, pp. 145–172. [Google Scholar]
- Toledo, M.L.; Pereira, M.M.; Freire, M.G.; Silva, J.P.A.; Coutinho, J.A.P.; Tavares, A.P.M. Laccase Activation in Deep Eutectic Solvents. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2019, 7, 11806–11814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, J.; Fu, J.; Silva, C.; Cavaco-Paulo, A. Can Laccase-Assisted Processing Conditions Influence the Structure of the Reaction Products? Trends Biotechnol. 2019, 37, 683–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varriale, S.; Delorme, A.E.; Andanson, J.-M.; Devemy, J.; Malfreyt, P.; Verney, V.; Pezzella, C. Enhancing the Thermostability of Engineered Laccases in Aqueous Betaine-Based Natural Deep Eutectic Solvents. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2022, 10, 572–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bassanini, I.; Ferrandi, E.E.; Riva, S.; Monti, D. Biocatalysis with Laccases: An Updated Overview. Catalysts 2021, 11, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khlupova, M.E.; Morozova, O.V.; Vasil’eva, I.S.; Shumakovich, G.P.; Zaitseva, E.A.; Chertkov, V.A.; Shestakova, A.K.; Yaropolov, A.I. Polymerization of (+)-Catechin in a Deep Eutectic Solvent Using a Fungal Laccase: Physicochemical Properties of the Products and Inhibition of α-Glucosidase. Appl. Biochem. Microbiol. 2021, 57, 712–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ezgi Ünlü, A.; Prasad, B.; Anavekar, K.; Bubenheim, P.; Liese, A. Investigation of a green process for the polymerization of catechin. Prep. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2017, 47, 918–924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bisht, A.; Sahu, S.C.; Kumar, A.; Maqsood, S.; Barwant, M.M.; Jaiswal, S.G. Recent advances in conventional and innovative extraction techniques for recovery of high-added value compounds for food additives and nutraceuticals. Food Phys. 2025, 2, 100047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhadange, Y.A.; Carpenter, J.; Saharan, V.K. A Comprehensive Review on Advanced Extraction Techniques for Retrieving Bioactive Components from Natural Sources. ACS Omega 2024, 9, 31274–31297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qader, I.B.; Laguerre, M.; Lavaud, A.; Tenon, M.; Prasad, K.; Abbott, A.P. Selective Extraction of Antioxidants by Formation of a Deep Eutectic Mixture through Mechanical Mixing. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2023, 11, 4168–4176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soltanmohammadi, F.; Jouyban, A.; Shayanfar, A. New aspects of deep eutectic solvents: Extraction, pharmaceutical applications, as catalyst and gas capture. Chem. Pap. 2021, 75, 439–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaul, M.J.; Qadah, D.; Mandella, V.; Dietz, M.L. Systematic evaluation of hydrophobic deep-melting eutectics as alternative solvents for the extraction of organic solutes from aqueous solution. RSC Adv. 2019, 9, 15798–15804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Espino, M.; de los Ángeles Fernández, M.; Gomez, F.J.V.; Silva, M.F. Natural designer solvents for greening analytical chemistry. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2016, 76, 126–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koh, Q.Q.; Kua, Y.L.; Gan, S.; Tan, K.W.; Lee, T.Z.E.; Cheng, W.K.; Lau, H.L.N. Sugar-based natural deep eutectic solvent (NADES): Physicochemical properties, antimicrobial activity, toxicity, biodegradability and potential use as green extraction media for phytonutrients. Sustain. Chem. Pharm. 2023, 35, 101218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bajkacz, S.; Rusin, K.; Wolny, A.; Adamek, J.; Erfurt, K.; Chrobok, A. Highly Efficient Extraction Procedures Based on Natural Deep Eutectic Solvents or Ionic Liquids for Determination of 20-Hydroxyecdysone in Spinach. Molecules 2020, 25, 4736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, M.M.; Yiin, C.L.; Lock, S.S.M.; Chin, B.L.F.; Othman, I.; binti Ahmad Zauzi, N.S.; Chan, Y.H. Natural deep eutectic solvents (NADES) for sustainable extraction of bioactive compounds from medicinal plants: Recent advances, challenges, and future directions. J. Mol. Liq. 2025, 425, 127202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macário, I.P.E.; Oliveira, H.; Menezes, A.C.; Ventura, S.P.M.; Pereira, J.L.; Gonçalves, A.M.M.; Coutinho, J.A.P.; Gonçalves, F.J.M. Cytotoxicity profiling of deep eutectic solvents to human skin cells. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 3932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayyan, M.; Mbous, Y.P.; Looi, C.Y.; Wong, W.F.; Hayyan, A.; Salleh, Z.; Mohd-Ali, O. Natural deep eutectic solvents: Cytotoxic profile. SpringerPlus 2016, 5, 913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rocha, D.; Freitas, D.S.; Magalhães, J.; Fernandes, M.; Silva, S.; Noro, J.; Ribeiro, A.; Cavaco-Paulo, A.; Martins, M.; Silva, C. NADES-Based Cork Extractives as Green Ingredients for Cosmetics and Textiles. Processes 2023, 11, 309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villa, C.; Caviglia, D.; Robustelli della Cuna, F.S.; Zuccari, G.; Russo, E. NaDES Application in Cosmetic and Pharmaceutical Fields: An Overview. Gels 2024, 10, 107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freitas, D.S.; Cavaco-Paulo, A.; Silva, C. Enhancing insights into the phenomena of deep eutectic solvents. Sustain. Mater. Technol. 2024, 41, e01039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freitas, D.S.; Rocha, D.; Santos, J.; Noro, J.; Tavares, T.D.; Teixeira, M.O.; Araújo, D.; Castro, J.; Almeida, C.; Silva, S.; et al. NADES-in-Oil Emulsions Enriched with Essential OIL for Cosmetic Application. Processes 2025, 13, 374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasyliev, G.; Lyudmyla, K.; Hladun, K.; Skiba, M.; Vorobyova, V. Valorization of tomato pomace: Extraction of value-added components by deep eutectic solvents and their application in the formulation of cosmetic emulsions. Biomass Convers. Biorefinery 2022, 12, 95–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marijan, M.; Jablan, J.; Jakupović, L.; Jug, M.; Marguí, E.; Dalipi, R.; Sangiorgi, E.; Zovko Končić, M. Plants from Urban Parks as Valuable Cosmetic Ingredients: Green Extraction, Chemical Composition and Activity. Agronomy 2022, 12, 204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, K.M.; Ko, J.; Zhao, J.; Jin, Y.; Yoo, D.E.; Han, S.Y.; Lee, J. Multi-functioning deep eutectic solvents as extraction and storage media for bioactive natural products that are readily applicable to cosmetic products. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 151, 87–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernández-Corroto, E.; Plaza, M.; Marina, M.L.; García, M.C. Sustainable extraction of proteins and bioactive substances from pomegranate peel (Punica granatum L.) using pressurized liquids and deep eutectic solvents. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2020, 60, 102314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Y.; Jung, D.; Li, K.; Park, K.; Ko, J.; Yang, M.; Lee, J. Application of Deep Eutectic Solvents to Prepare Mixture Extracts of Three Long-Lived Trees with Maximized Skin-Related Bioactivities. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 2581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oktaviyanti, N.D.; Kartini; Mun’im, A. Application and optimization of ultrasound-assisted deep eutectic solvent for the extraction of new skin-lightening cosmetic materials from Ixora javanica flower. Heliyon 2019, 5, e02950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alishlah, T.; Mun’im, A.; Jufri, M. Optimization of Urea-Glycerin Based NADES-UAE for Oxyresveratrol Extraction from Morus alba Roots for Preparation of Skin Whitening Lotion. J. Young Pharm. 2019, 11, 155–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buarque, F.S.; Monteiro e Silva, S.A.; Ribeiro, B.D. Choline chloride-based deep eutectic solvent as an inhibitor of metalloproteases (collagenase and elastase) in cosmetic formulation. 3 Biotech 2023, 13, 219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| NADES | Components | Molar Ratio | Abbr. | Lipase-Assisted Catalysis | Laccase-Assisted Catalysis | Extraction Processes | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 |  Glycerol | 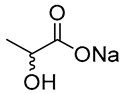 Sodium DL-lactate | 1:1 | GLY:SL [13,16,17] | Solvent and substrate | Solvent | Solvent |
| 2 | 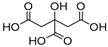 Citric acid |  Glycerol | 1:1 | CA:GLY [16,17] | Solvent and substrate | Solvent | |
| 3 | 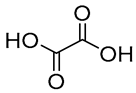 Oxalic acid | 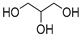 Glycerol | 1:1 | OA:GLY [17] | Solvent and substrate | ||
| 4 | 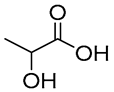 DL-Lactic acid | 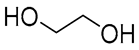 Ethylene glycol | 1:1 | LA:EG [16] | Solvent | ||
| 5 |  DL-Lactic acid | 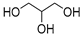 Glycerol | 1:1; 1:4 | LA:GLY [13,16,18] | Solvent | Solvent | |
| 6 | 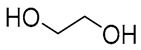 Ethylene glycol | 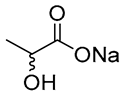 Sodium DL-lactate | 1:1 | EG:SL [13,16] | Solvent | Solvent | |
| 7 | 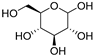 Glucose | 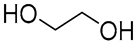 Ethylene glycol | 1:1 | GLU:EG [16] | Solvent | ||
| 8 |  Glucose |  Glycerol | 1:1 | GLU:GLY [16] | Solvent | ||
| 9 | 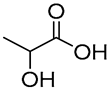 DL-Lactic acid | 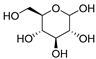 Glucose | 1:1 | LA:GLU [16] | Solvent | ||
| 10 |  Citric acid |  Ethylene glycol | 1:1 | CA:EG [16,17] | Solvent | ||
| 11 | 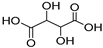 Tartaric acid | 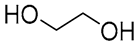 Ethylene glycol | 1:1 | TA:EG [16] | Solvent | ||
| 12 |  Tartaric acid |  Glycerol | 1:1 | TA:GLY [16] | Solvent | ||
| 13 | 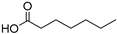 Enanthic acid | 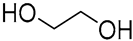 Ethylene glycol | 1:1 | EA:EG [16] | Solvent | ||
| 14 | 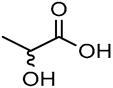 DL-Lactic acid (LA) | 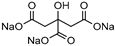 Sodium citrate (tribasic) (SC) | 4:1 | LA:SC [13] | Solvent | ||
| Application Area | NADES System (Examples) | Target or Substrate | Key Outcomes | Role | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Enzymes—Lipase | Choline Chloride:Glycerol, Choline Chloride:Sugar, Betaine:Urea, Sodium lactate:Glycerol, … | Fatty acids + polyols (esterification, biodiesel, biosurfactants), … | ↑ Activity; ↑ Thermal/operational stability; ↑ Selectivity; | H-bonding stabilizes catalytic triad; tuned polarity improves substrate solubility; controlled water activity reduces hydrolysis; enables reusability. | [17,23,31,33,34,35,36,37,38,39,42] |
| Enzymes—Laccase | Betaine:Glycerol, Choline Chloride:Glycerol, Betaine:Mannose, Lactic acid:Glycerol, … | Phenolics, flavonoids, catechols (polymerization, oxidation), … | ↑ Activity; ↑ Stability; ↑ Catalytic efficiency; | NADES stabilize tertiary folds and copper centers; polarity favors substrate access; water addition reduces viscosity while maintaining H-bond protection. | [16,20,22,43,44,45,48,49] |
| Extraction | Choline Chloride:Malic Acid, Choline Chloride:Glycerol/Urea, Lactic acid:Glycerol, Sugar-based NADES, … | Flavonoids, phenolics, polyphenols, alkaloids, fatty acids, terpenoids, … | ↑ Yield; ↑ Selectivity; ↓ Toxic solvent use; | Strong H-bonding enhances solubility of polar compounds; tunable polarity allows selective extraction; biodegradable and safer than VOCs. | [3,4,5,11,12,13,50,51,52,53,54,55,56,57,58,59,60,61] |
| Cosmetics | Choline Chloride:Sorbitol, Choline Chloride:Glycerol, Urea:Glycerol, Lactic acid:Glycerol, … | Flavonoids, phenolics, polyphenols, alkaloids, fatty acids, terpenoids, … | ↑ Solubility; ↑ Stability; ↑ Skin penetration, enzyme inhibition (anti-aging); | Biocompatible and eco-friendly; H-bonding stabilizes actives; enhances dermal delivery; NADES act as both extractants and formulation carriers. | [18,62,63,64,65,66,67,68,69,70,71,72] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Freitas, D.S.; Ribeiro, A.; Cavaco-Paulo, A.; Silva, C. The Versatility of NADES Across Applications. Molecules 2025, 30, 3862. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30193862
Freitas DS, Ribeiro A, Cavaco-Paulo A, Silva C. The Versatility of NADES Across Applications. Molecules. 2025; 30(19):3862. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30193862
Chicago/Turabian StyleFreitas, David S., Artur Ribeiro, Artur Cavaco-Paulo, and Carla Silva. 2025. "The Versatility of NADES Across Applications" Molecules 30, no. 19: 3862. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30193862
APA StyleFreitas, D. S., Ribeiro, A., Cavaco-Paulo, A., & Silva, C. (2025). The Versatility of NADES Across Applications. Molecules, 30(19), 3862. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30193862










