Capparis L. (Capparaceae): A Scoping Review of Phytochemistry, Ethnopharmacology and Pharmacological Activities
Abstract
1. Introduction
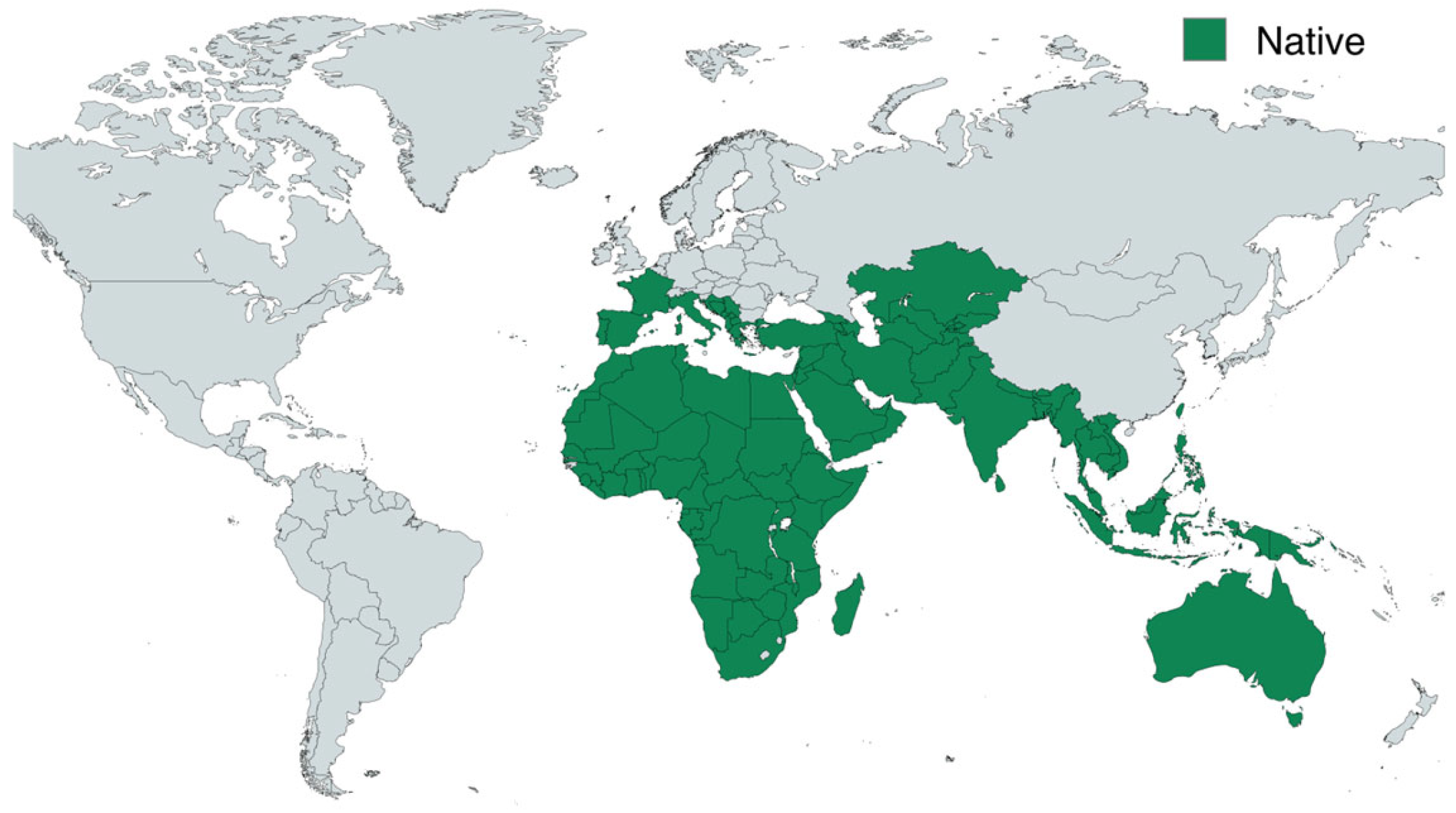
2. Botanical Classification, Morphology, and Geographical Distribution
3. Ethnopharmacology
4. Phytochemistry
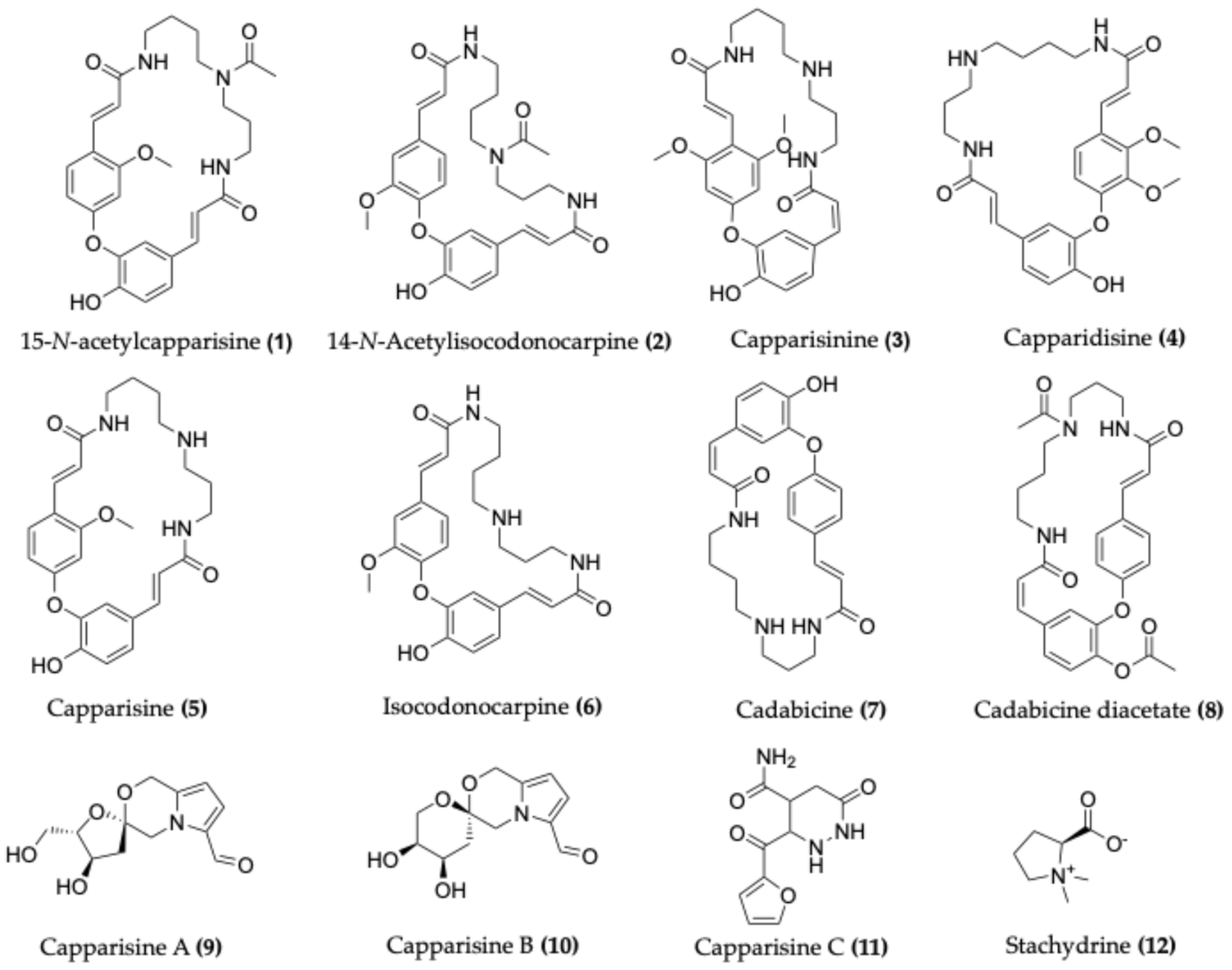
4.1. Alkaloids
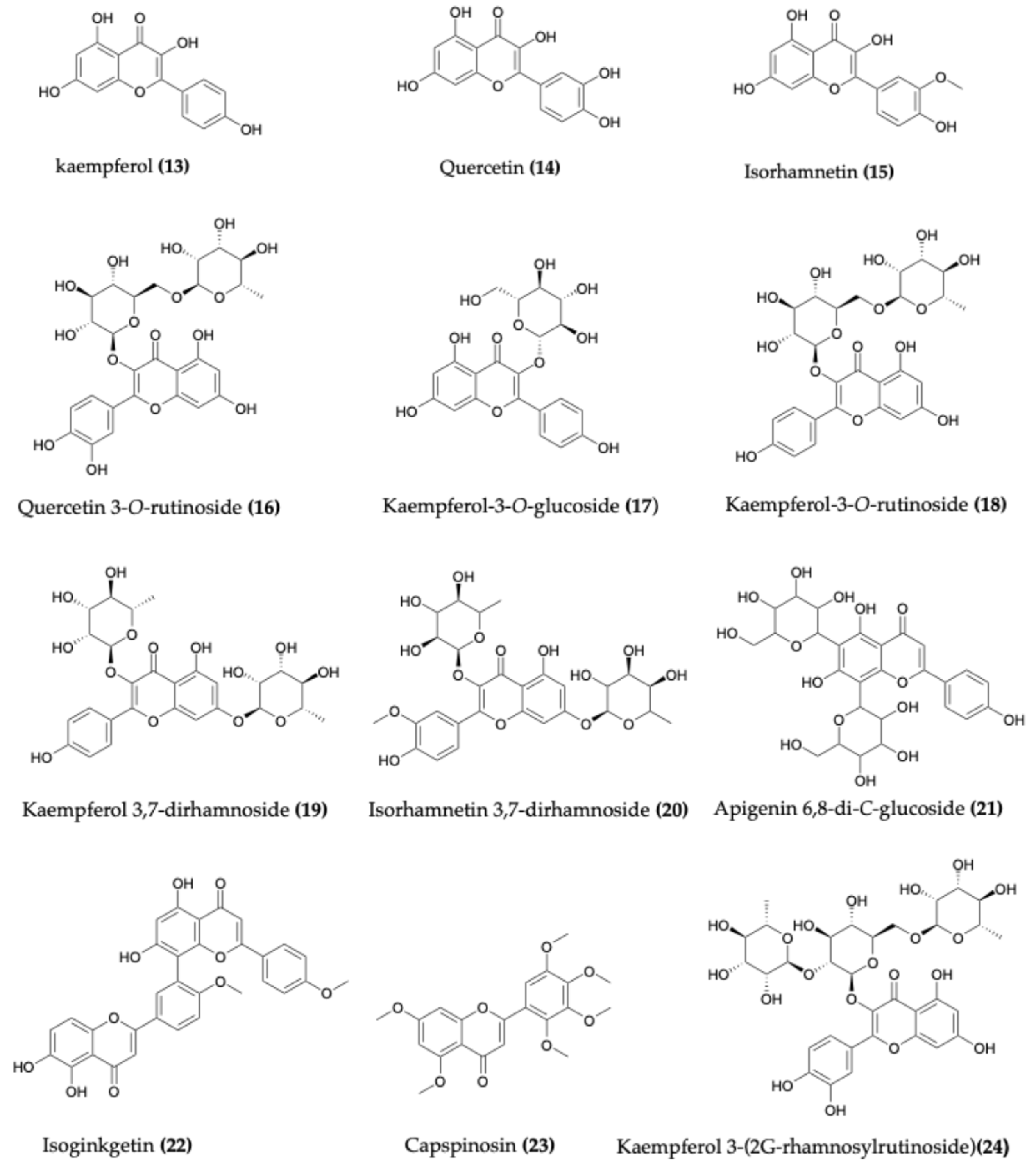
4.2. Flavonoids
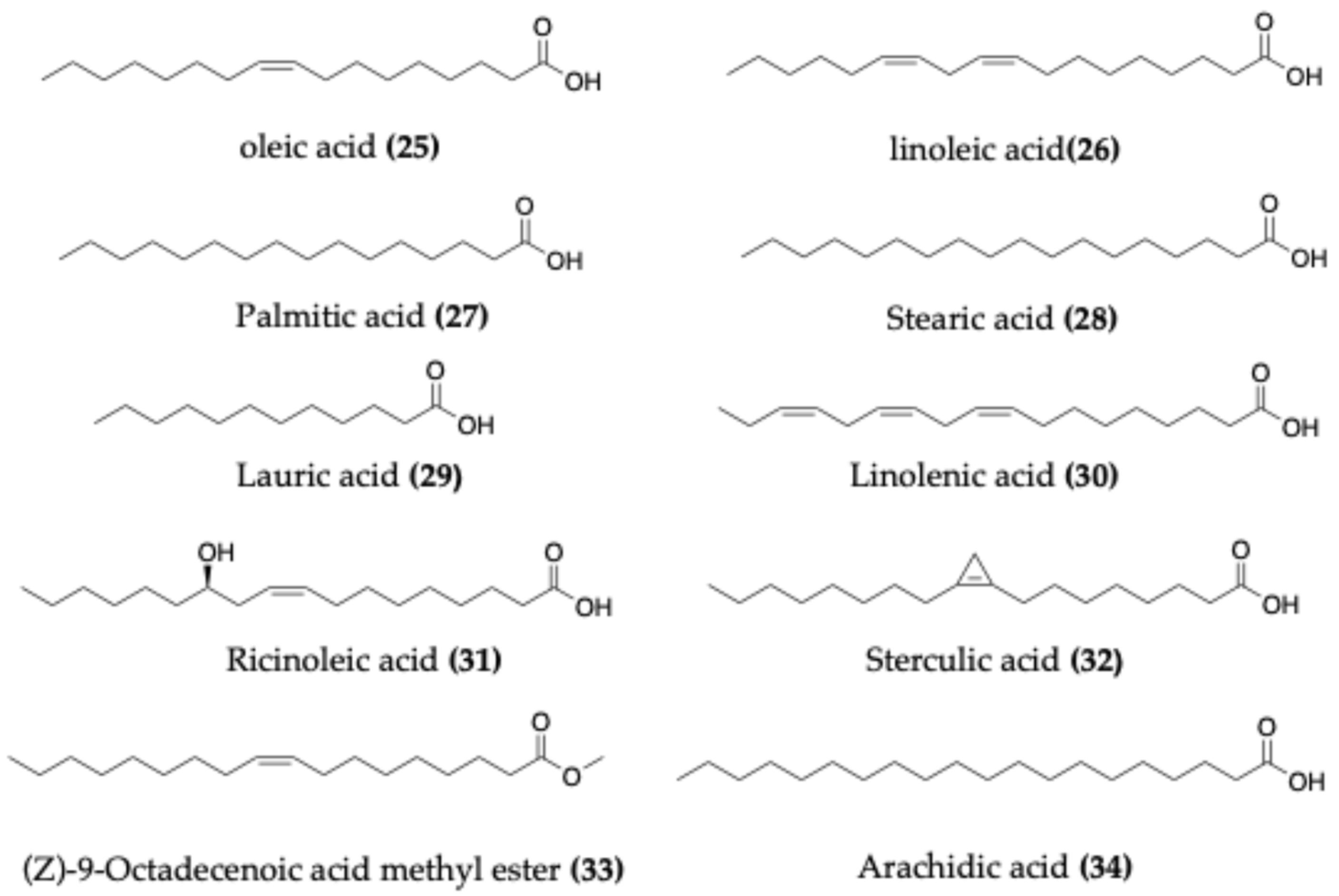
4.3. Fatty Acids
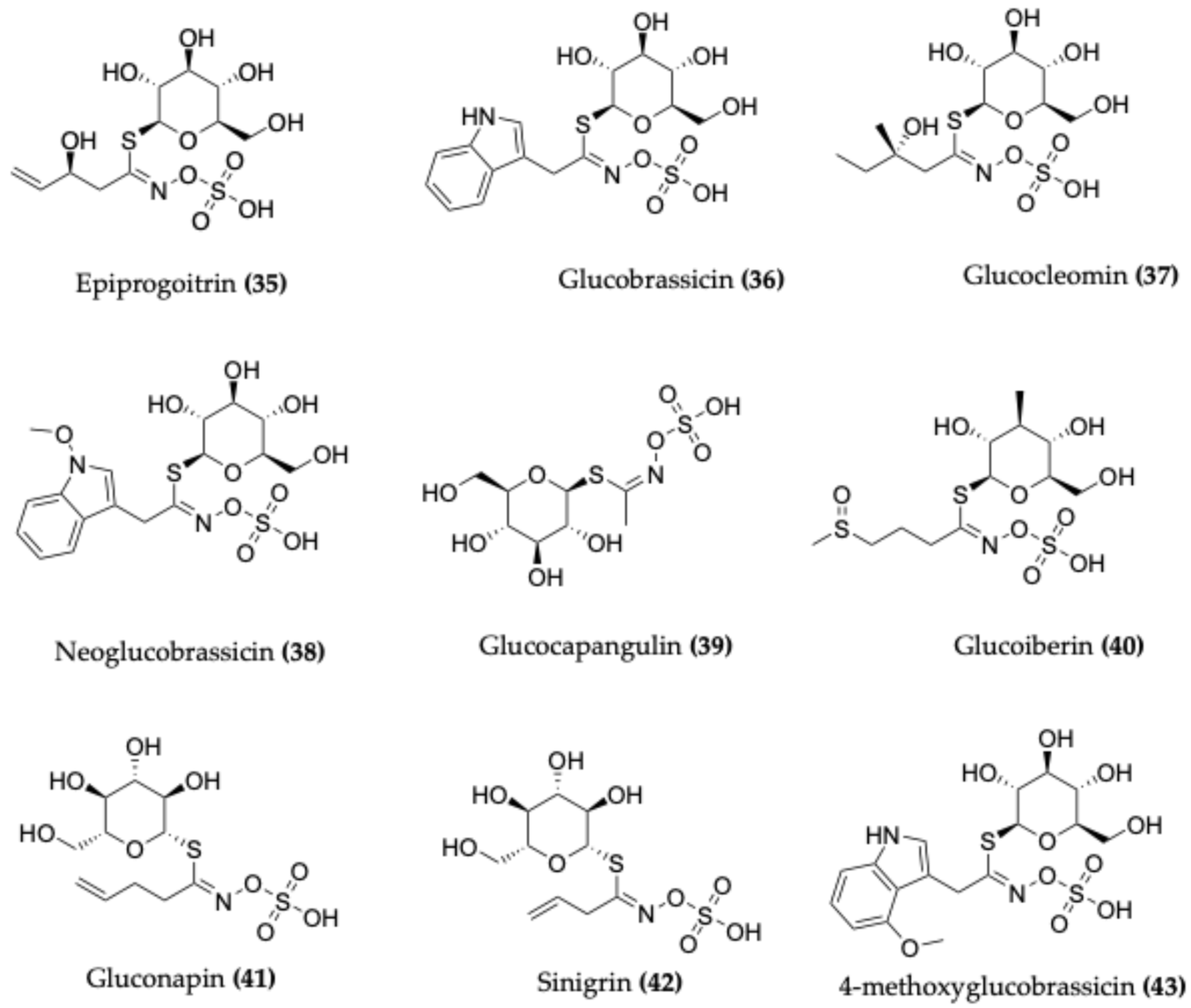
4.4. Glucosinolates
4.5. Sterols
4.6. Essential Oil Constituents
5. Pharmacological Activities
5.1. Effect on Cardiovascular System
5.2. Anti-Cancer/Cytotoxic Activity
5.3. Anti-Diabetic Activity
5.4. Anti-Inflammatory and Pain-Relief Activities
5.5. Anti-Infective Activities
5.6. Antioxidant Activity
5.7. Anti-Hyperlipidemia
5.8. Other Pharmacological Activities
6. Materials and Methods
7. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rivera, D.; Friis, I.; Inocencio, C.; Obón, C.; Alcaraz, F.; Reales, A. The typification of Capparis inermis Forssk., C. sinaica Veill. and C. cartilaginea Decne. (Capparaceae). Taxon 2003, 52, 307–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inocencio, C.; Rivera, D.; Obón, M.C.; Alcaraz, F.; Barreña, J.-A. A systematic revision of Capparis section Capparis (Capparaceae) 1, 2. Ann. Mo. Bot. Gard. 2006, 93, 122–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mercado-Gómez, J.D.; González, M.A.; Morales-Puentes, M.E. Synopsis of Capparaceae to the flora of Colombia. Rodriguésia 2019, 70, e0023201X. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brevard, H.; Brambilla, M.; Chaintreau, A.; Marion, J.P.; Diserens, H. Occurrence of elemental sulphur in capers (Capparis spinosa L.) and first investigation of the flavour profile. Flavour Fragr. J. 1992, 7, 313–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lansky, E.P.; Paavilainen, H.M. Caper: The Genus Capparis, 1st ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2013; pp. 7–10+35+119. [Google Scholar]
- Rivera, D.; Inocencio, C.; Obón, C.; Alcaraz, F. Review of food and medicinal uses of Capparis L. Subgenus Capparis (Capparidaceae). Econ. Bot. 2003, 57, 515–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chedraoui, S.; Abi-Rizk, A.; El-Beyrouthy, M.; Chalak, L.; Ouaini, N.; Rajjou, L. Capparis spinosa L. in A Systematic Review: A Xerophilous Species of Multi Values and Promising Potentialities for Agrosystems under the Threat of Global Warming. Front. Plant Sci. 2017, 8, 1845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tlili, N.; Elfalleh, W.; Saadaoui, E.; Khaldi, A.; Triki, S.; Nasri, N. The caper (Capparis L.): Ethnopharmacology, phytochemical and pharmacological properties. Fitoterapia 2011, 82, 93–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Annaz, H.; Sane, Y.; Bitchagno, G.T.M.; Ben Bakrim, W.; Drissi, B.; Mahdi, I.; El Bouhssini, M.; Sobeh, M. Caper (Capparis spinosa L.): An Updated Review on Its Phytochemistry, Nutritional Value, Traditional Uses, and Therapeutic Potential. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 878749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inocencio, C.; Rivera, D.; Alcaraz, F.; Tomás-Barberán, F.A. Flavonoid content of commercial capers (Capparis spinosa, C. sicula and C. orientalis) produced in mediterranean countries. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2000, 212, 70–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Royal Botanic Gardens Kew. Capparis Tourn. Ex L. Available online: https://powo.science.kew.org/taxon/urn:lsid:ipni.org:names:30001561-2 (accessed on 21 August 2025).
- Fici, S. The genus Capparis L. (Capparaceae) in Laos and Cambodia. Kew Bull. 2023, 78, 1–41. [Google Scholar]
- Han, Y.-X.; Kuai, S.-Q.; Sun, H.-L.; Wang, H.-G. Two novel spermidine alkaloids from the roots of Capparis acutifolia. Nat. Prod. Res. 2025, 39, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subramanian, S.K.; Ramani, P. Antioxidant and cytotoxic activities of Indian caper (Capparis brevispina DC (Capparaceae)) leaf extracts. Eur. J. Integr. Med. 2020, 33, 101038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moharram, B.A.; AL-Mahbashi, H.M.; Al-Maqtari, T.; Saif-Ali, R.; Al-Hakami, I.A.; Alhaj, W.T. Leaves of Capparis cartilaginea Exhibit a Promising Antidiabetic Activity in Alloxan-Induced Diabetic Rats. Int. J. Pharm. Res. Allied Sci. 2023, 12, 65–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamed, A.R.; Abdel-Shafeek, K.A.; Abdel-Azim, N.S.; Ismail, S.I.; Hammouda, F.M. Chemical investigation of some Capparis species growing in Egypt and their antioxidant activity. Evid.-Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2007, 4, 25–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Youssef, R.S. Medicinal and non-medicinal uses of some plants found in the middle region of Saudi Arabia. J. Med. Plants Res. 2013, 7, 2501–2513. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, D.; Singh, R. Kair (Capparis decidua): A potential ethnobotanical weather predictor and livelihood security shrub of the arid zone of Rajasthan and Gujarat. Indian J. Tradit. Knowl. 2011, 10, 146–155. [Google Scholar]
- Jini, D.; Joseph, B. A Medicinal Potency of Capparis decidua—A Harsh Terrain Plant. Res. J. Phytochem. 2011, 5, 1–13. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, P.; Mishra, G.; Sangeeta; Srivastava, S.; Jha, K.; Khosa, R. Traditional uses, phytochemistry and pharmacological properties of Capparis decidua: An Overview. Der Pharm. Lett. 2010, 3, 71–82. [Google Scholar]
- Kondawar, M.S.; Kamble, K.G.; Khandare, M.M.; Maharshi, K.H.; Awale, V.B. Evaluation of the Locomotor and Diuretic Activities of Ethanolic Extract of Leaves of Capparis divaricata Lam. Int. J. Pharm. Pharm. Sci. 2011, 3, 265–267. [Google Scholar]
- Reddy, A.M.; Babu, M.V.S.; Rao, R.R. Ethnobotanical study of traditional herbal plants used by local people of Seshachalam Biosphere Reserve in Eastern Ghats, India. Herba Pol. 2019, 65, 40–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luecha, P.; Umehara, K.; Miyase, T.; Noguchi, H. Antiestrogenic constituents of the Thai medicinal plants Capparis flavicans and Vitex glabrata. J. Nat. Prod. 2009, 72, 1954–1959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khandare, N. HPLC Analysis of Ethnomedicinal important Plant Capparis grandis L.f. from Western Melghat Region (MS) India. Int. J. Multidiscip. Res. 2023, 5, 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Virmani, P.; Shamim, N.; Ramdas; Thorat, V.A.; Tiwari, N.; Shanker, K.; Chandra Kaushik, A.; Singh, K.; Chanda, D. Anti-asthmatic potential of Rudanti (Capparis moonii Wight): Integrated metabolomics and network pharmacology approach for identifying lead molecule, associated pharmacological mechanisms, and ex-vivo experimental studies. Food Biosci. 2025, 71, 107350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, P.; Malpathak, N. Estimation of Antioxidant Activity and Total Phenol, Flavonoid Content among Natural Populations of Caper (Capparis moonii, Wight) from Western Ghats Region. Indian J. Pharm. Educ. Res. 2016, 50, 495–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maurya, S.; Datar, M.N.; Choudhary, R.K. The Genus Capparis L. in India: Capers; MACS-Agharkar Research Institute: Pune, India, 2020; Volume 1, p. 70. [Google Scholar]
- Selvamani, P.; Latha, S.; Elayaraja, K.; Babu, P.S.; Gupta, J.K.; Pal, T.K.; Ghosh, L.K.; Sen, D.J. Antidiabetic Activity of the Ethanol Extract of Capparis sepiaria L Leaves. Indian J. Pharm. Sci. 2008, 70, 378–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tomar, J.; Mishra, A.K.; Singh, H.; Yadav, C.; Mudgal, P.; Bajaj, S.; Mishra, A. Assessment of anxiolytic potential of Capparis sepiaria L. extract, Triterpenoid fraction and its constituent in zebrafish (Danio rerio) larvae model. S. Afr. J. Bot. 2025, 184, 50–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahrajabian, M.H.; Sun, W.; Cheng, Q. Plant of the Millennium, Caper (Capparis spinosa L.), chemical composition and medicinal uses. Bull. Natl. Res. Cent. 2021, 45, 131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Yang, T.; Wang, C. Capparis spinosa L. as a potential source of nutrition and its health benefits in foods: A comprehensive review of its phytochemistry, bioactivities, safety, and application. Food Chem. 2023, 409, 135258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakr, R.O.; El Bishbishy, M.H. Profile of bioactive compounds of Capparis spinosa var. aegyptiaca growing in Egypt. Rev. Bras. Farmacogn. 2016, 26, 514–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, X.-X.; Feng, Y.-L.; Yang, S.-L.; Xu, L.-Z.; Li, Y.-Q. A New Anthraquinone from Capparis himalayensis. Chem. Nat. Compd. 2015, 51, 40–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.-Q.; Yang, S.-L.; Li, H.-R.; Xu, L.-Z. Two New Alkaloids from Capparis himalayensis. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 2008, 56, 189–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Celepli, S.; Çolak, B.; Aydemir Sezer, Ü.; Celepli, P.; Bigat, I.; Duymuş, M.E.; Körez, M.K.; Hücümenoğlu, S.; Kismet, K.; Şahin, M. The effects of Capparis ovata seed oil on the healing of traumatic skin wounds. Ulus. Travma Acil Cerrahi Derg. 2022, 28, 1205–1213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gazioglu, I.; Semen, S.; Acar, O.O.; Kolak, U.; Sen, A.; Topcu, G. Triterpenoids and steroids isolated from Anatolian Capparis ovata and their activity on the expression of inflammatory cytokines. Pharm. Biol. 2020, 58, 925–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taskin, T.; Taşkın, D.; Cam, M.; Emre, G. Phenolic compounds, biological activities and trace elements of Capparis ovata var. canescens. Rev. Biol. Trop. 2020, 68, 590–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gebrehiwot, S.; Karri, K. Traditional uses, phytochemistry, and pharmacological properties of Capparis tomentosa Lam.: A review. Drug Invent. Today 2020, 13, 1006. [Google Scholar]
- Tekulu, G.H.; Hiluf, T.; Brhanu, H.; Araya, E.M.; Bitew, H.; Haile, T. Anti-inflammatory and anti-nociceptive property of Capparis tomentosa Lam. root extracts. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2020, 253, 112654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sama, W.; Ajaiyeoba, E. Phytochemical and Antimicrobial Studies Of Capparis thonningii And Capparis tomemtosa. Pharmacogn. Mag. 2006, 2, 119–122. [Google Scholar]
- Venkataswamy, M.; Karunakaran, R.S.; Islam, M.S.; Meriga, B. Capparis zeylanica L. root extract promotes apoptosis and cell cycle arrest, inhibits epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition and triggers E-cadherin expression in breast cancer cell lines. 3 Biotech 2023, 13, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghule, B.V.; Murugananthan, G.; Nakhat, P.D.; Yeole, P.G. Immunostimulant effects of Capparis zeylanica Linn. leaves. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2006, 108, 311–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, V.U.; Arif, S.; Amber, A.U.R.; Fizza, K. Capparisinine, a new alkaloid from Capparis decidua. Liebigs Ann. Der Chem. 1987, 1987, 161–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, V.U.; Ismail, N.; Amber, A.-U.-R. Isocodonocarpine from Capparis decidua. Phytochemistry 1989, 28, 2493–2495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, X.P.; Wu, T.; Abdurahim, M.; Su, Z.; Hou, X.L.; Aisa, H.A.; Wu, H. New spermidine alkaloids from Capparis spinosa roots. Phytochem. Lett. 2008, 1, 59–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, J.; Zhang, Z.-W.; Yu, W.-J.; Liao, J.-Y.; Luo, X.-G.; Shen, Y.-J. Stachydrine, a major constituent of the Chinese herb leonurus heterophyllus sweet, ameliorates human umbilical vein endothelial cells injury induced by anoxia-reoxygenation. Am. J. Chin. Med. 2010, 38, 157–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, T.; Wang, C.-h.; Chou, G.-x.; Wu, T.; Cheng, X.-m.; Wang, Z.-t. New alkaloids from Capparis spinosa: Structure and X-ray crystallographic analysis. Food Chem. 2010, 123, 705–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, X.J.; Meng, Q.Y.; Yu, M.X.; Bai, H.J. Determination of stachydrine hydrochloride in different parts of Capparis spinosa L. by dual wavelength TLC scanning. Guangpu Shiyanshi 2010, 27, 1959–1963. [Google Scholar]
- Manzoor-i-Khuda, M.; Habermehl, G. Chemical Constituents of Corchorus capsuJaris and C. olitorius (Jute Plant), III. Structure of Corosin. Z. Für Naturforschung C 1974, 29, 209–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaind, K.; Gandhi, K.; Junega, T.; Kjær, A.; Nielsen, B.J. 4, 5, 6, 7-tetrahydroxydecyl isothiocyanate derived from a glucosinolate in Capparis grandis. Phytochemistry 1975, 14, 1415–1418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rathee, P.; Rathee, D.; Rathee, D.; Rathee, S. In vitro anticancer activity of stachydrine isolated from Capparis decidua on prostate cancer cell lines. Nat. Prod. Res. 2012, 26, 1737–1740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ba, M.; Jiang, S.; He, Z.; Chen, W.; Huang, D.; Sun, L. New alkaloids isolated from the fruits of Capparis spinosa L. and their xanthine oxidase inhibitory activity. Phytochem. Lett. 2025, 68, 103002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, H.; Zhao, J.; Turak, A. New Alkaloid from Capparis spinosa. Chem. Nat. Compd. 2024, 60, 908–911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.F.; Xie, C.; Jian, R.; Kang, J.; Li, Y.; Zhuang, C.L.; Yang, F.; Zhang, L.L.; Lai, L.; Wu, T.; et al. Biflavonoids from Caper (Capparis spinosa L.) fruits and their effects in inhibiting NF-kappa B activation. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2011, 59, 3060–3065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pelotto, J.P.; Martínez, M.A.D.P. Flavonoid aglycones from Argentinian Capparis species (Capparaceae). Biochem. Syst. Ecol. 1998, 26, 577–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharaf, M.; El-Ansari, M.A.; Saleh, N.A. Flavonoids of four Cleome and three Capparis species. Biochem. Syst. Ecol. 1997, 25, 161–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kapoor, B.; Mishra, R. Flavonoid contents from some capparidaceous medicinal plants of north-west Rajasthan. Indian J. Pharm. Biol. Res. 2013, 1, 09–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saxena, V.; Goutam, A. Isolation and study of the flavone glycoside; luteolin-7-O-β-D-glucopyranoside from the seeds of the Capparis decidua (Forsk.). Int. J. Chem. Sci. 2008, 6, 7–10. [Google Scholar]
- Su, D.-M.; Tang, W.-Z.; Yu, S.-S.; Liu, Y.-B.; Qu, J.; Yu, D.-Q. Water-soluble constituents from roots of Capparis tenera. China J. Chin. Mater. Medica 2008, 33, 1021–1023. [Google Scholar]
- Alsharif, B.; Hante, N.; Govoni, B.; Verli, H.; Kukula-Koch, W.; Jose Santos-Martinez, M.; Boylan, F. Capparis cartilaginea decne (Capparaceae): Isolation of flavonoids by high-speed countercurrent chromatography and their anti-inflammatory evaluation. Front. Pharmacol. 2023, 14, 1285243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vieira, C.; Fetzer, S.; Sauer, S.K.; Evangelista, S.; Averbeck, B.; Kress, M.; Reeh, P.W.; Cirillo, R.; Lippi, A.; Maggi, C.A. Pro-and anti-inflammatory actions of ricinoleic acid: Similarities and differences with capsaicin. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg’s Arch. Pharmacol. 2001, 364, 87–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daulatabad, C.M.J.D.; Desai, V.A.; Hosamani, K.M. New source of oil with novel fatty acids for industrial utilization. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 1991, 30, 2596–2598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel-Mogib, M.; Ezmirly, S.; Basaif, S. Phytochemistry of Dipterygium glaucum and Capparis decidua. J. Saudi Chem. Soc. 2000, 4, 103–108. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, W.-j.; Bai, H.-j.; Pang, X.-a.; Sun, H.-z. GC/MS analysis of fatty acid in Capparis spinosa seed oil. Chin. J. Anal. Lab. 2008, 27, 42. [Google Scholar]
- Tlili, N.; Munne-Bosch, S.; Nasri, N.; Saadaoui, E.; Khaldi, A.; Triki, S. Fatty acids, tocopherols and carotenoids from seeds of Tunisian caper “Capparis spinosa”. J. Food Lipids 2009, 16, 452–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sen Gupta, A.; Chakrabarty, M. Composition of the seed fats of the Capparidaceae family. J. Sci. Food Agric. 1964, 15, 69–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haque, M.; Haque, K. Sub-acute toxicity study of a novel compound E-Octadec-7-en-5-ynoic acid from Capparis zeylanica Linn roots. Agric Biol JN Am 2011, 2, 708–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kittur, M.; Mahajanshetti, C.; Lakshminarayana, G. Characteristics and composition of Trichosanthes bracteata, Urena sinuata and Capparis divaricata seeds and oils. J. Oil Technol. Assoc. India 1993, 25, 39. [Google Scholar]
- Matthäus, B.; Özcan, M. Glucosinolates and fatty acid, sterol, and tocopherol composition of seed oils from Capparis spinosa Var. spinosa and Capparis ovata Desf. Var. canescens (Coss.) Heywood. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2005, 53, 7136–7141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, J.C.; Sytsma, K.J.; Iltis, H.H. Phylogeny of Capparaceae and Brassicaceae based on chloroplast sequence data. Am. J. Bot. 2002, 89, 1826–1842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bor, M.; Ozkur, O.; Ozdemir, F.; Turkan, I. Identification and Characterization of the glucosinolate–myrosinase System in Caper (Capparis ovata Desf.). Plant Mol. Biol. Rep. 2009, 27, 518–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, Z.; Rizk, A.; Hammouda, F.; El-Nasr, M.S. Glucosinolates of egyptian Capparis species. Phytochemistry 1972, 11, 251–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schraudolf, H. Indole glucosinolates of Capparis spinosa. Phytochemistry 1989, 28, 259–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, I.; Stuart, K. Glucosinolates in two Jamaican Capparis species. Phytochemistry 1968, 7, 1409–1410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Đulović, A.; Manase, M.J.; Čulić, V.; Burčul, F.; Rollin, P.; Blažević, I. Glucosinolate Profiles of Capparis spp. and Maerua baillonii (Capparaceae) and Cytotoxicity of Methyl Isothiocyanate-Rich Isolates From Capparis spinosa subsp. rupestris. Chem. Biodivers 2025, 22, e202402573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tlili, N.; Nasri, N.; Saadaoui, E.; Khaldi, A.; Triki, S. Sterol composition of caper (Capparis spinosa) seeds. Afr. J. Biotechnol. 2010, 9, 3328–3333. [Google Scholar]
- Sawadogo, M.; Tessier, A.; Delaveau, P. Chemical study of Capparis corymbosa roots. Plantes Med. Phytother. 1981, 15, 234–239. [Google Scholar]
- Perianayagam, J.; Sharma, S.; Pillai, K. Anti-inflammatory potential of β-Sitosterol on acute and chronic inflammation models. Phytopharm. Ther. Values IV 2008, 22, 25–35. [Google Scholar]
- Gupta, J.; Ali, M. Phytoconsitituents of Capparis decidua root barks. J. Med. Aromat. Plant Sci. 1998, 20, 683–689. [Google Scholar]
- Ramachandram, R.; Ali, M.; Mir, S.R. Phytoconstituents from Capparis moonii fruits. Indian J. Nat. Prod. 2004, 20, 40–42. [Google Scholar]
- Özcan, M.; Akgül, A. Influence of species, harvest date and size on composition of capers (Capparis spp.) flower buds. Food/Nahr. 1998, 42, 102–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, K.; Chou, C.; Pan, W. Studies on the constituents of the stems of Capparis formosana Hemsl. Taiwan Yaoxue Zazhi 1977, 28, 2–5. [Google Scholar]
- Zia-Ul-Haq, M.; Cavar, S.; Qayum, M.; Imran, I.; de Feo, V. Compositional studies: Antioxidant and antidiabetic activities of Capparis decidua (Forsk.) Edgew. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2011, 12, 8846–8861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaudhury, N.A.; Ghosh, D. Taraxasterol and other triterpenoids in Capparis sepiaria leaves. Phytochemistry 1970, 9, 1885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khanfar, M.A.; Sabri, S.S.; Abu Zarga, M.H.; Zeller, K.-P. The chemical constituents of Capparis spinosa of Jordanian origin. Nat. Prod. Res. 2003, 17, 9–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, W.; Li, N.; Li, X. Isolation and identification of organic acids from pericarp of Capparis spinosa L. Shenyang Yaoke Daxue Xuebao 2008, 25, 790–792. [Google Scholar]
- Merlino, M.; Condurso, C.; Cincotta, F.; Nalbone, L.; Ziino, G.; Verzera, A. Essential Oil Emulsion from Caper (Capparis spinosa L.) Leaves: Exploration of Its Antibacterial and Antioxidant Properties for Possible Application as a Natural Food Preservative. Antioxidants 2024, 13, 718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grimalt, M.; Sánchez-Rodríguez, L.; Hernández, F.; Legua, P.; Carbonell-Barrachina, Á.A.; Almansa, M.S.; Amorós, A. Volatile Profile in Different Aerial Parts of Two Caper Cultivars (Capparis spinosa L.). J. Food Qual. 2021, 2021, 6620776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gramosa, N.V.; Lemos, T.L.G.; Braz-Filho, R. Volatile Constituents Isolated from Capparis flexuosa of Brazil. J. Essent. Oil Res. 1997, 9, 709–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Ghorab, A.; Shibamoto, T.; ÖZCAN, M.M. Chemical composition and antioxidant activities of buds and leaves of capers (Capparis ovata Desf. var. canescens) cultivated in Turkey. J. Essent. Oil Res. 2007, 19, 72–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alsharif, B.; Babington, G.A.; Radulović, N.; Boylan, F. Volatiles of Capparis cartilaginea Decne. from Saudi Arabia. Plants 2022, 11, 2518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, A.J.; Gilani, A.H. Blood pressure lowering effect of the extract of aerial parts of Capparis aphylla is mediated through endothelium-dependent and independent mechanisms. Clin. Exp. Hypertens. 2011, 33, 470–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilani, A.U.H.; Aftab, K. Hypotensive and spasmolytic activities of ethanolic extract of Capparis cartilaginea. Phytother. Res. 1994, 8, 145–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, Z.N.; Eddouks, M.; Michel, J.B.; Sulpice, T.; Hajji, L. Cardiovascular Effect of Capparis spinosa Aqueous Extract. Part III: Antihypertensive Effect in Spontaneously Hypertensive Rats. Am. J. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2007, 2, 111–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saka, P.; Osafo, K.; Antwi, S.; Martey, O.; Quasie, O.; Antwi-Adjei, M.; Asiedu-Larbi, J.; Takyi, N.; Donkor, K.; Okine, L. The anti-dyslipidemic effects of milled root bark Ethanolic extract of Capparis erythrocarpus in Sprague-Dawley Rats: Implications for obesity and cardiovascular diseases. J. Appl. Pharm. Sci. 2018, 8, 001–008. [Google Scholar]
- Kunwar, B.; Jain, V.; Verma, S.K. Qualitative phytochemical screening and in vitro thrombolytic activity of Capparis decidua Edgew. Fruit. GSC Biol. Pharm. Sci. 2022, 19, 160–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, L.; Xie, L.q.; Ji, Y.b. Preliminary Study on Apoptotic Effect Induced by N-Butanol Extract in Capparis spinosa L. on SGC-7901. In Proceedings of the 2010 4th International Conference on Bioinformatics and Biomedical Engineering, Chengdu, China, 18–20 June 2010; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Sheikh, M.; Eshraghi, H.; Khoshnia, M.; Mazandarani, M.; Moradi, A. Cytotoxicity effect of Capparis spinosa L. On the HepG2 human hepatocellular carcinoma cell line. Med. Lab. J. 2017, 16, 73–77. [Google Scholar]
- Moghadamnia, Y.; Mousavi Kani, S.N.; Ghasemi-Kasman, M.; Kazemi Kani, M.T.; Kazemi, S. The Anti-cancer Effects of Capparis spinosa Hydroalcoholic Extract. Avicenna J. Med. Biotechnol. 2019, 11, 43–47. [Google Scholar]
- Alghamdi, A.H.; Ahmed, A.A.E.; Abdalgadir, H.; Bashir, M.; Khalid, A.; Abdalla, A.N.; Elzubier, M.E.; Adnan Almaimani, R.; Refaat, B.; Alzahrani, K.; et al. In-vitro Cytotoxicity Investigations for Phytoconstituents of Saudi Medicinal Plants With Putative Ocular Effects. Integr. Cancer Ther. 2024, 23, 15347354241256649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eddouks, M.; Lemhadri, A.; Hebi, M.; El Hidani, A.; Zeggwagh, N.A.; El Bouhali, B.; Hajji, L.; Burcelin, R. Capparis spinosa L. aqueous extract evokes antidiabetic effect in streptozotocin-induced diabetic mice. Avicenna J. Phytomed. 2017, 7, 191–198. [Google Scholar]
- Kazemian, M.; Abad, M.; Haeri, M.R.; Ebrahimi, M.; Heidari, R. Anti-diabetic effect of Capparis spinosa L. root extract in diabetic rats. Avicenna J. Phytomed. 2015, 5, 325–332. [Google Scholar]
- Sekrani, I.; Souad, A.; Benrebaia, M.; Bouaroudge, A.; Erenler, R.; Benkiniouar, R.; Cacan, E.; Menad, A. Algerian Capparis spinosa n-BuOH Extract Alleviates Diabetic Neuropathy Induced with Streptozotocin in Rats. Egypt. J. Chem. 2022, 65, 519–538. [Google Scholar]
- Ramzani Ghara, A.; Ezzati Ghadi, F.; Hosseini, S.H.; Piacente, S.; Cerulli, A.; Alizadeh, A.; Mirmahmoudi, R. Antioxidant and antidiabetic effect of Capparis decidua edgew (Forssk.) extract on liver and pancreas of streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. J. Appl. Biotechnol. Rep. 2021, 8, 76–82. [Google Scholar]
- Balekari, U.; Veeresham, C. In Vivo and in Vitro Evaluation of Anti Diabetic and Insulin Secretagogue Activities of Capparis zeylanica. Pharmacol. Pharm. 2015, 6, 311–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huseini, H.F.; Hasani-Rnjbar, S.; Nayebi, N.; Heshmat, R.; Sigaroodi, F.K.; Ahvazi, M.; Alaei, B.A.; Kianbakht, S. Capparis spinosa L. (Caper) fruit extract in treatment of type 2 diabetic patients: A randomized double-blind placebo-controlled clinical trial. Complement. Ther. Med. 2013, 21, 447–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vahid, H.; Bonakdaran, S.; Khorasani, Z.M.; Jarahi, L.; Rakhshandeh, H.; Ghorbani, A.; Zarghi, N.; Yousefi, M. Effect of Capparis spinosa Extract on Metabolic Parameters in Patients with Type-2 Diabetes: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Endocr. Metab. Immune Disord. Drug Targets 2019, 19, 100–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ageel, A.; Parmar, N.; Mossa, J.; Al-Yahya, M.; Al-Said, M.; Tariq, M. Anti-inflammatory activity of some Saudi Arabian medicinal plants. Agents Actions 1986, 17, 383–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sini, K.R.; Sinha, B.N.; Rajasekaran, A. Protective effects of Capparis zeylanica Linn. Leaf extract on gastric lesions in experimental animals. Avicenna J. Med. Biotechnol. 2011, 3, 31. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhang, H.; Han, B.; Chen, W. Research on the extraction of polysaccharides in Capparis spinosa L. and antiinflammatory and analgesic effects. Shihezi Daxue Xuebao (Ziran Kexue Ban) 2011, 29, 205–209. [Google Scholar]
- El Azhary, K.; Tahiri Jouti, N.; El Khachibi, M.; Moutia, M.; Tabyaoui, I.; El Hou, A.; Achtak, H.; Nadifi, S.; Habti, N.; Badou, A. Anti-inflammatory potential of Capparis spinosa L. in vivo in mice through inhibition of cell infiltration and cytokine gene expression. BMC Complement. Altern. Med. 2017, 17, 81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, X.X.; Lou, F.F.; Sun, F.Y.; Zhao, N.; Sun, J.; Shen, A.J.; Liu, C.L. Capparis spinosa inhibits proliferation and fibrosis of myofibroblasts in systemic sclerosis through modulation of MAPK signaling. Mol. Cell. Toxicol. 2025, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hajimehdipoor, H.; Jafari, F.; Keramatian, B. The effect of Capparis spinosa on inflammatory responses in a mouse model of allergic asthma. Res. J. Pharmacogn. 2024, 11, 77–86. [Google Scholar]
- Dehnavi, S.; Shariati-Sarabi, Z.; Rakhshandeh, H.; Ghoryani, M.; Tavakol Afshari, J.; Mobasheri, L.; Mohammadi, M. Capparis spinosa significantly improves Th17/Treg imbalance in patients with rheumatoid arthritis: A randomized double blind, placebo-controlled clinical trial in Iran. J. Funct. Foods 2025, 130, 106926. [Google Scholar]
- Bektas, N.; Arslan, R.; Goger, F.; Kirimer, N.; Ozturk, Y. Investigation for anti-inflammatory and anti-thrombotic activities of methanol extract of Capparis ovata buds and fruits. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2012, 142, 48–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thamer, F.H.; Al-opari, A.M.; Al-Gani, A.M.S.; Al-jaberi, E.A.; Allugam, F.A.; Almahboub, H.H.; Mosik, H.M.; Khalil, H.H.; Abduljalil, M.M.; Alpogosh, M.Y.; et al. Capparis cartilaginea Decne. as a natural source of antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and anti-cancer herbal drug. Phytomed. Plus 2024, 4, 100502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arslan, R.; Bektas, N. Antinociceptive effect of methanol extract of Capparis ovata in mice. Pharm. Biol. 2010, 48, 1185–1190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaudhari, S.; Chavan, M.; Gaud, R. Phytochemical and pharmacological studies on the roots of Capparis sepiaria. Indian J. Pharm. Sci. 2004, 66, 454–457. [Google Scholar]
- Ghule, B.; Murugananthan, G.; Yeole, P. Analgesic and antipyretic effects of Capparis zeylanica leaves. Fitoterapia 2007, 78, 365–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Upadhyay, R.K.; Ahmad, S.; Tripathi, R.; Rohtagi, L.; Jain, S.C. Screening of antimicrobial potential of extracts and pure compounds isolated from Capparis decidua. J. Med. Plants Res. 2010, 4, 439–445. [Google Scholar]
- Upadhyay, R.K.; Rohatgi, L.; Chaubey, M.K.; Jain, S.C. Ovipositional responses of the pulse beetle, Bruchus chinensis (Coleoptera: Bruchidae) to extracts and compounds of Capparis decidua. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2006, 54, 9747–9751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Latha, S.; Selvamani, P.; Pal, T.; Gupta, J. Anthelmintic Activity of Heliotropium zeylanicum and Capparis sepiaria L. Asian J. Chem. 2009, 21, 5780–5782. [Google Scholar]
- Soltan, M.M.; Zaki, A.K. Antiviral screening of forty-two Egyptian medicinal plants. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2009, 126, 102–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arena, A.; Bisignano, G.; Pavone, B.; Tomaino, A.; Bonina, F.; Saija, A.; Cristani, M.; D’Arrigo, M.; Trombetta, D. Antiviral and immunomodulatory effect of a lyophilized extract of Capparis spinosa L. buds. Phytother. Res. Int. J. Devoted Pharmacol. Toxicol. Eval. Nat. Prod. Deriv. 2008, 22, 313–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali-Shtayeh, M.S.; Abu Ghdeib, S.I. Antifungal activity of plant extracts against dermatophytes. Mycoses 1999, 42, 665–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boga, C.; Forlani, L.; Calienni, R.; Hindley, T.; Hochkoeppler, A.; Tozzi, S.; Zanna, N. On the antibacterial activity of roots of Capparis spinosa L. Nat. Prod. Res. 2011, 25, 417–421. [Google Scholar]
- Abdel-Sattar, E.; Maes, L.; Salama, M.M. In vitro activities of plant extracts from Saudi Arabia against malaria, leishmaniasis, sleeping sickness and Chagas disease. Phytother. Res. 2010, 24, 1322–1328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lam, S.K.; Ng, T.B. A protein with antiproliferative, antifungal and HIV-1 reverse transcriptase inhibitory activities from caper (Capparis spinosa) seeds. Phytomedicine 2009, 16, 444–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darwish, R.M.; Aburjai, T.A. Effect of ethnomedicinal plants used in folklore medicine in Jordan as antibiotic resistant inhibitors on Escherichia coli. BMC Complement. Altern. Med. 2010, 10, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacobson, R.L.; Schlein, Y. Lectins and toxins in the plant diet of Phlebotomus papatasi (Diptera: Psychodidae) can kill Leishmania major promastigotes in the sandfly and in culture. Ann. Trop. Med. Parasitol. 1999, 93, 351–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mantawy, M.M.; Hamed, M.A.; Sammour, E.M.; Sanad, M. Influence of Capparis spinosa and Acacia arabica on certain biochemical haemolymph parameters of Biomphalaria alexandrina. J. Egypt. Soc. Parasitol. 2004, 34, 659–677. [Google Scholar]
- Ambedkar, G.; Muniyan, M. Piscicidal activity of methanolic extract of Capparis stylosa on the freshwater fish Channa punctatus (Bloch.). Internet J. Toxicol. 2009, 6, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohan, R.; Suganthi, A. Antibacterial activity of the root extracts of Capparis stylosa. Orient. J. Chem. 1998, 14, 137–138. [Google Scholar]
- Mahdi, S.A.A. Antibacterial and Antivirulence Activities of Capparis spinosa L. against Acinetobacter baumannii and Streptococcus mutans. Eur. J. Ecol. Biol. Agric. 2025, 2, 95–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gull, T.; Sultana, B.; Bhatti, I.A.; Jamil, A. Antibacterial potential of Capparis spinosa and Capparis decidua extracts. Int. J. Agric. Biol. 2015, 17, 727–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, P.; Wu, J.; Chang, Z.; Yang, F.; Zhang, X.; Hou, K.; Ping, D.; Li, S. Sodium alginate hydrogel loaded with Capparis spinosa L. extract for antimicrobial and antioxidant wound dressing applications. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2025, 289, 138883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mirza, A.S.; Baig, M.T.; Huma, A.; Ibrahim, S.; Shahid, U.; Jabeen, A.; Ali, M.M.; Sheikh, S.; Syed, N.; Fatima, R.; et al. Antibacterial Activity of Methanol Extract of Capparis Decidua Edgew (Forssk.) Against Staphylococcus Aureus, Bacillus Cereus, Salmonella Typhi, And Escherichia Coli. Pharmacophore 2020, 11, 46–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Khafagi, M.F.J.; Mohammed, D.Y. Study antibacterial activity of crude Capparis spinosa L. extracts against Helicobacter pylori infection and determine their bioactive compounds. Iraqi J. Sci. 2023, 64, 503–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alkhaibari, A.M.; Alanazi, A.D. Chemical Composition and Insecticidal, Antiplasmodial, and Anti-Leishmanial Activity of Capparis spinosa Essential Oil and Its Main Constituents. Evid.-Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2022, 2022, 6371274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dangi, K.; Mishra, S. Antioxidative and β cell regeneration effect of Capparis aphylla stem extract in streptozotocin induced diabetic rat. Biol. Med. 2011, 3, 82–91. [Google Scholar]
- Yadav, P.; Sarkar, S.; Bhatnagar, D. Lipid peroxidation and antioxidant enzymes in erythrocytes and tissues in aged diabetic rats. Indian J. Exp. Biol. 1997, 35, 389–392. [Google Scholar]
- Ali, S.; Al-Amin, T.; Mohamed, A.; Gameel, A. Hepatoprotective activity of aqueous and methanolic extracts of Capparis decidua stems against carbon tetrachloride induced liver damage in rats. J. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2009, 4, 167–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akay, F.; Yildiz, F. Estimation of total antioxidant capacity of pomegranate, apricot, caper, eggplant and oils. In Proceedings of the Eurofoodchem XI Meeting, Norwich, UK, 26–28 September 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Bonina, F.; Puglia, C.; Ventura, D.; Aquino, R.; Tortora, S.; Sacchi, A.; Saija, A.; Tomaino, A.; Pellegrino, M.; de Capariis, P. In vitro antioxidant and in vivo photoprotective effects of a lyophilized extract of Capparis spinosa L. buds. J. Cosmet. Sci. 2002, 53, 321–336. [Google Scholar]
- Germano, M.P.; De Pasquale, R.; D’angelo, V.; Catania, S.; Silvari, V.; Costa, C. Evaluation of extracts and isolated fraction from Capparis spinosa L. buds as an antioxidant source. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2002, 50, 1168–1171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tesoriere, L.; Butera, D.; Gentile, C.; Livrea, M. Bioactive components of caper (Capparis spinosa L.) from Sicily and antioxidant effects in a red meat simulated gastric digestion. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2007, 55, 8465–8471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, T.; Wang, C.; Liu, H.; Chou, G.; Cheng, X.; Wang, Z. A new antioxidant compound from Capparis spinosa. Pharm. Biol. 2010, 48, 589–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nadaroglu, H.; Demir, N.; Demir, Y. Antioxidant and radical scavenging activities of capsules of caper (Capparis spinosa). Asian J. Chem. 2009, 21, 5123. [Google Scholar]
- Bhoyar, M.S.; Mishra, G.P.; Naik, P.K.; Srivastava, R. Estimation of antioxidant activity and total phenolics among natural populations of Caper (‘Capparis spinosa’) leaves collected from cold arid desert of Trans-Himalayas. Aust. J. Crop Sci. 2011, 5, 912–919. [Google Scholar]
- Gadgoli, C.; Mishra, S. Antihepatotoxic activity of p-methoxy benzoic acid from Capparis spinosa. J. Ethnopharmacol. 1999, 66, 187–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Haci, I.A.; Didi, A.; Atik-Bekkara, F.; Didi, M.A. Total phenolic contents and antioxidant activity of organic fractions from Capparis spinosa and Limonastrium feei. Nat. Prod. Indian J. 2010, 6, 118–124. [Google Scholar]
- Eddouks, M.; Lemhadri, A.; Michel, J.-B. Hypolipidemic activity of aqueous extract of Capparis spinosa L. in normal and diabetic rats. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2005, 98, 345–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chahlia, N. Evaluation of Hypolipidaemic Activity of Capparis decidua. Int. J. Biomed. Sci. 2009, 5, 70–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitada, K.; Shibuya, K.; Ishikawa, M.; Nakasugi, T.; Oho, T. Enhancement of oral moisture using tablets containing extract of Capparis masaikai Levl. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2009, 122, 363–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sonbol, H.; Al-Balwi, Z. Effect of ethanol extract of Capparis Cartilaginea on osteoporosis-induced rats. Int. J. Pharm. Phytopharmacol. Res. 2018, 8, 59–67. [Google Scholar]
- Nabavi, S.F.; Maggi, F.; Daglia, M.; Habtemariam, S.; Rastrelli, L.; Nabavi, S.M. Pharmacological effects of Capparis spinosa L. Phytother. Res. 2016, 30, 1733–1744. [Google Scholar]
- Matsuyama, K.; Villareal, M.O.; El Omri, A.; Han, J.; Kchouk, M.E.; Isoda, H. Effect of Tunisian Capparis spinosa L. extract on melanogenesis in B16 murine melanoma cells. J. Nat. Med. 2009, 63, 468–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goyal, M.; Nagori, B.; Sasmal, D. Sedative and anticonvulsant effects of an alcoholic extract of Capparis decidua. J. Nat. Med. 2009, 63, 375–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trombetta, D.; Occhiuto, F.; Perri, D.; Puglia, C.; Santagati, N.A.; Pasquale, A.D.; Saija, A.; Bonina, F. Antiallergic and antihistaminic effect of two extracts of Capparis spinosa L. flowering buds. Phytother. Res. Int. J. Devoted Pharmacol. Toxicol. Eval. Nat. Prod. Deriv. 2005, 19, 29–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
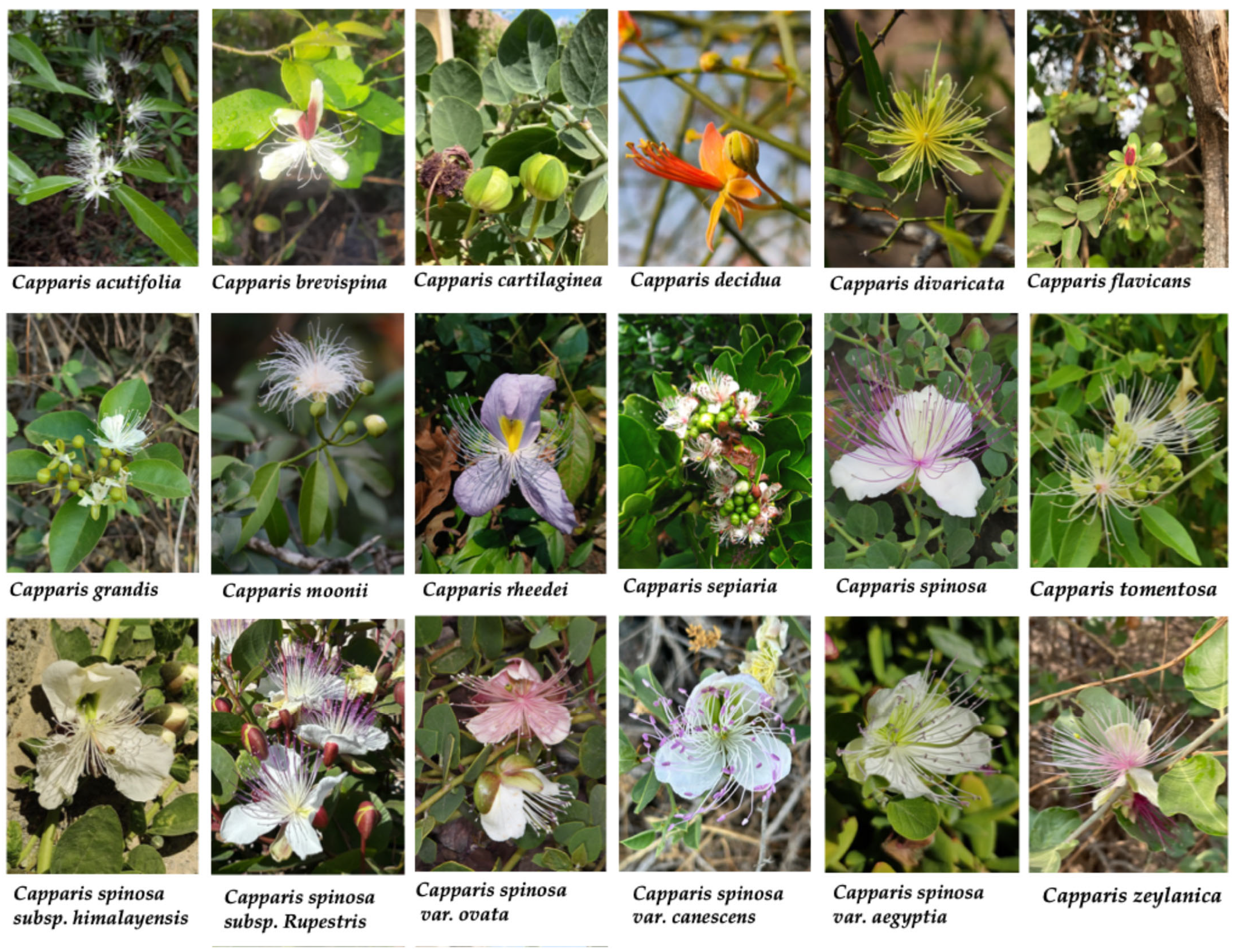


| Species | Common Name | Region | Part Used | Traditional Uses | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Capparis acutifolia Sweet | Chinese caper | China, Taiwan, Bhutan, India, Thailand, Vietnam | Roots | Rheumatic arthralgia; abdominal pain | [12,13] |
| Capparis brevispina DC. | Indian caper | South India, Sri Lanka | Not specified | Stomachic; tonic; wound healing; fever; hepatoprotective | [14] |
| Capparis cartilaginea Decne. | Cartilage caper; | NE and E Africa, Arabian Peninsula, W. Asia, Indian Subcontinent | Fruit; Leaf; Stem/Shoots; Root | Rheumatism, arthritis, skin inflammation, wounds, bruises, childbirth, earache, diabetes, antiseptic | [15,16,17] |
| Capparis decidua (Forssk.) Edgew. | Bare caper | N and Tropical Africa, W. Asia, Indian Subcontinent | Fruit; Bark; Root; Stem; Leaf; Flower buds | Rheumatism, arthritis, asthma, cough, toothache, GI disorders, diabetes, cardiac issues, skin problems, antidiabetic, antioxidant | [18,19,20] |
| Capparis divaricata Lam. | Spreading caper. | India, Sri Lanka | Bark; Leaf | Analgesic, diuretic, antiulcer, aphrodisiac, skin eruptions, insect bites, infertility | [21,22] |
| Capparis flavicans Kurz | Hedge caper or wild caperbush | India, Cambodia, Myanmar, Thailand | Leaf | Galactagogue | [23] |
| Capparis grandis L.f. | Grand caper or tree caper | India, Sri Lanka, Myanmar, Thailand | Leaf; Bark; Root; Flower | Asthma, skin eruptions, wounds, insect bites, blood tonic, sterility, paralysis | [24] |
| Capparis moonii Wight. | Large caper and moon’s caper. | South India, Sri Lanka | Fruit; Seed | Asthma, cough, pulmonary tuberculosis, weakness | [25,26] |
| Capparis rheedei DC. | Rheed’s wild caper | Central and South America, Caribbean | Not specified | Diuretic, sedative, skin problems, spasms, emmenagogue | [27] |
| Capparis sepiaria L. | Wild caper bus | Africa, China, Indian Subcontinent, Indochina, Malesia, Australia | Seed; Leaf; Root; Stem; Root bark; Flower | Digestive disorders, diabetes, respiratory issues, skin diseases, blood purifier, tonic, antipyretic, anti-inflammatory, gout | [28,29] |
| Capparis spinosa L. | Caper bush | Mediterranean, Africa, Europe, Middle East, Asia, Pacific | Flower buds, Fruits, Leaf, Branch tips, Shoots, Root, Root bark | Pickled condiment; GI disorders; rheumatism; gout; haemorrhoids; fever; liver and kidney issues; headache; toothache | [30,31] |
| Capparis spinosa var. aegyptia (Lam.) Boiss. | Egyptian caper | N. Africa, Middle East, E. Mediterranean | Root bark; stem bark; fruit | Anti-inflammatory; diuretic; rheumatism; arthritis; gout; hypertension; malaria; GI problems | [8,32] |
| Capparis spinosa subsp. himalayensis (Jafri) Fici | - | Himalayan region, Central Asia, Caucasus, China | Leaf, Fruits, Root, Root bark, Part not specified | Rheumatism; gout; palsy; joint pain; sores; paralysis; toothache; intestinal worms | [33,34] |
| Capparis spinosa subsp. Rupestris (Sm.) Nyman | Rock caper | Mediterranean, S. Europe, N. Africa, W. Asia, N. S. America | Plant | Stomach ailments | [6,34] |
| Capparis spinosa var. ovata (Desf.) Sm. | - | Algeria, Libya, Morocco, Italy, Tunisia | Root; Part not specified | Digestive disorders; respiratory problems; anti-inflammatory; headache; snakebite | [6,35,36] |
| Capparis spinosa var. canescens Coss. | - | W. Asia, Arabian Peninsula | Root; Root bark; Part not specified | Rheumatism; respiratory issues; diuretic; expectorant; snakebite antidote | [37] |
| Capparis tomentosa Lam. | Woolly caper bush or African caper | Tropical Africa, Arabian Peninsula | Fruit, Leaf, Stem, Bark, Root, Root ashes, Root bark | Rheumatism; reproductive health; respiratory and GI disorders; malaria; diabetes; psychiatric conditions; skin infections; snakebite | [38,39,40] |
| Capparis zeylanica L. | Ceylon caper | Tropical Asia, Malesia, Indochina | Leaf, Root bark, Part not specified | Anti-inflammatory; analgesic; febrifuge; helminthic infections; GI issues; immune disorders; paralysis; rheumatism | [41,42] |
| Class | Species | Part Used | Compounds | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Isothiocyanates | C. spinosa | Leaves | Methyl isothiocyanate, Ethyl isothiocyanate, Isopropyl isothiocyanate, Butyl isothiocyanate, Isobutyl isothiocyanate | [87] |
| Leaves and flower buds | Methyl isothiocyanate, Butyl isothiocyanate, Isobutyl isothiocyanate, Benzyl isothiocyanate, Benzyl isocyanide | [88] | ||
| C. zeylanica (syn. flexuosa) | Trunk bark, leaves, and pod peel | 3-Methyl-3-buteneisothiocyanate, Butyl isothiocyanate | [89] | |
| C. ovata Desf. var. canescens | Buds and leaves | Methyl isothiocyanate, Isopropyl isothiocyanate, butyl isothiocyanate, isobutyl isothiocyanate | [90] | |
| C. grandis | Roots | 4,5,6,7-Tetrahydroxydecyl isothiocyanate | [50] | |
| C. cartilaginea | Leaves | Isopropyl isothiocyanate, (E)-1-Isothiocyanato-2-butene, 2-Butyl isothiocyanate, Isobutyl isothiocyanate | [91] | |
| Terpenoids | C. sepiaria | Leaves | α-Amyrin, Erythrodiol, Taxasterol | [84] |
| C. spinosa | Leaves | Eucalyptol, Linalool, Sabinol, (E)-p-Mentha-2,8-dien-1-ol, (Z)-p-Mentha-2,8-dien-1-ol, Camphor, Karahanaenone, Menthone, Pinocarvone, Isomenthone, Neomenthol, Terpinen-4-ol, p-Cymen-8-ol, α-Terpineol, Nerol, (Z)-Carveol, Pulegone, Carvone, Geraniol, Perilla alcohol, Caryophyllene oxide, α-Bisabolol oxide B | [87] | |
| C. cartilaginea | Leaves | Myrcene, p-Cymene, Limonene, Eucalyptol, γ-Terpinene, Linalool, Camphor, 4-Terpineol, p-Cymen-9-ol, α-Terpineol, O-Methylthymol, Cumin aldehyde, Piperitone, Thymol, α-Terpinyl acetate | [91] | |
| Volatile Acids | C. spinosa | Flower buds | Octanoic acid, Nonanoic acid, Decanoic acid. | [88] |
| C. cartilaginea | Leaves | Dodecanoic acid | [91] | |
| Volatile Esters | C. spinosa | Leaves | 2-Propenyl hexanoate, Methyl 2,6-cresote (methyl 2,6-dimethylbenzoate), Massoia lactone, (Z)-3-Hexenyl benzoate, Isopropyl tetradecanoate, 2-Phenylethyl benzoate | [87] |
| Leaves and flower buds | Butyl 2-propenoate, Methyl benzoate, Methyl octanoate, Linalyl acetate, Isoamyl benzoate, Methyl laurate, Ethyl benzoate | [88] | ||
| C. cartilaginea | Leaves | (Z)-3-Hexen-1-yl benzoate | [91] | |
| C. ovata Desf. var. canescens | Buds and leaves | Ethyl 2-hydroxypropionate, Hexyl acetate, 2-Phenylethyl acetate, Benzyl isovalerate, Methyl hexadecanoate | [90] | |
| Volatile Ketones | C. spinosa | Leaves | 3-Heptanone, 2-Heptanone, 3-Methyl-2-cyclohexen-1-one, 1-Octen-3-one, 6-Methyl-5-hepten-2-one, 2-Octanone, Acetophenone, 2-Nonanone, (E,E)-3,5-Octadien-2-one, 6-Methyl-3,5-heptadien-2-one, 2-Nonen-4-one, 3-Nonen-2-one, Benzophenone | [87] |
| Leaves, aerial parts | 6-Methyl-5-hepten-2-one, 3,5-Octadien-2-one, Neryl acetone. | [88] | ||
| C. ovata Desf. var. canescens | Buds and leaves | Cyclohexanone, 2-Heptanone, 6-Methyl-5-hepten-2-one, (E,E)-3,5-Octadien-2-one, Isophorone (3,5,5-trimethyl-2-cyclohexen-1-one), Karahanaenone (2,2,5-trimethyl-4-cycloheptene-1-one), Frambinone [4-(4-hydroxyphenyl)-2-butanone], Zingerone [4-(4-hydroxy-3-methoxyphenyl)-2-butanone], 4-(3-hydroxy-2-methoxyphenyl)-2-butanone | [90] | |
| Volatile aldehydes | C. spinosa | Leaves | (E)-2-Hexenal, Octanal, Nonanal, Decanal, 2-Phenyl-2-butenal, 4-Methyl-2-phenyl-2-pentenal, 5-Methyl-2-phenyl-2-hexenal | [87] |
| C. ovata Desf. var. canescens | Buds and leaves | Hexanal, Furfural, (E)-2-Hexenal, Heptanal, Benzaldehyde, Phenylacetaldehyde, 2,4-Dimethylbenzaldehyde, Cinnamic aldehyde (3-phenyl-2-propenal), Vanillin (4-hydroxy-3-methoxybenzaldehyde) | [90] | |
| Volatile Alcohols | C. spinosa | Leaves | (Z)-3-Hexen-1-ol, 1-Hexanol, 2,4-Dimethyl-3-heptanol, 1-Heptanol, 1-Octen-3-ol, 6-Methyl-5-hepten-2-ol, 3-Ethyl-hexanol, 2-Octen-1-ol, 1-Nonen-4-ol, 1-Octanol, 1-Nonanol, 1-Decanol, 1-Dodecanol, 1-Tetradecanol, 1-Hexadecanol (Z)-3-Hexen-1-ol, 1-Hexanol, 2,4-Dimethyl-3-heptanol, 1-Heptanol, 1-Octen-3-ol, 6-Methyl-5-hepten-2-ol, 3-Ethyl-hexanol, 2-Octen-1-ol, 1-Nonen-4-ol, 1-Octanol, 1-Nonanol, 1-Decanol, 1-Dodecanol, 1-Tetradecanol, 1-Hexadecanol | [87] |
| Sulphur-Containing Compounds | C. spinosa | Leaves | Dimethyl disulfide, Dimethyl trisulfide, Dimethyl tetrasulfide, Dimethyl pentasulfide, Cyclic octatonic sulphur | [87] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Alsharif, B.; Boylan, F. Capparis L. (Capparaceae): A Scoping Review of Phytochemistry, Ethnopharmacology and Pharmacological Activities. Molecules 2025, 30, 3705. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30183705
Alsharif B, Boylan F. Capparis L. (Capparaceae): A Scoping Review of Phytochemistry, Ethnopharmacology and Pharmacological Activities. Molecules. 2025; 30(18):3705. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30183705
Chicago/Turabian StyleAlsharif, Bashaer, and Fabio Boylan. 2025. "Capparis L. (Capparaceae): A Scoping Review of Phytochemistry, Ethnopharmacology and Pharmacological Activities" Molecules 30, no. 18: 3705. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30183705
APA StyleAlsharif, B., & Boylan, F. (2025). Capparis L. (Capparaceae): A Scoping Review of Phytochemistry, Ethnopharmacology and Pharmacological Activities. Molecules, 30(18), 3705. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30183705








