Neuroprotective Evaluation of Murraya Carbazoles: In Vitro and Docking Insights into Their Anti-AChE and Anti-Aβ Activities
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Structural Physiognomies
2.2. Drug-Likeness, Toxicity Predictions, and ADME Properties of the Compounds
2.3. Molecular Docking
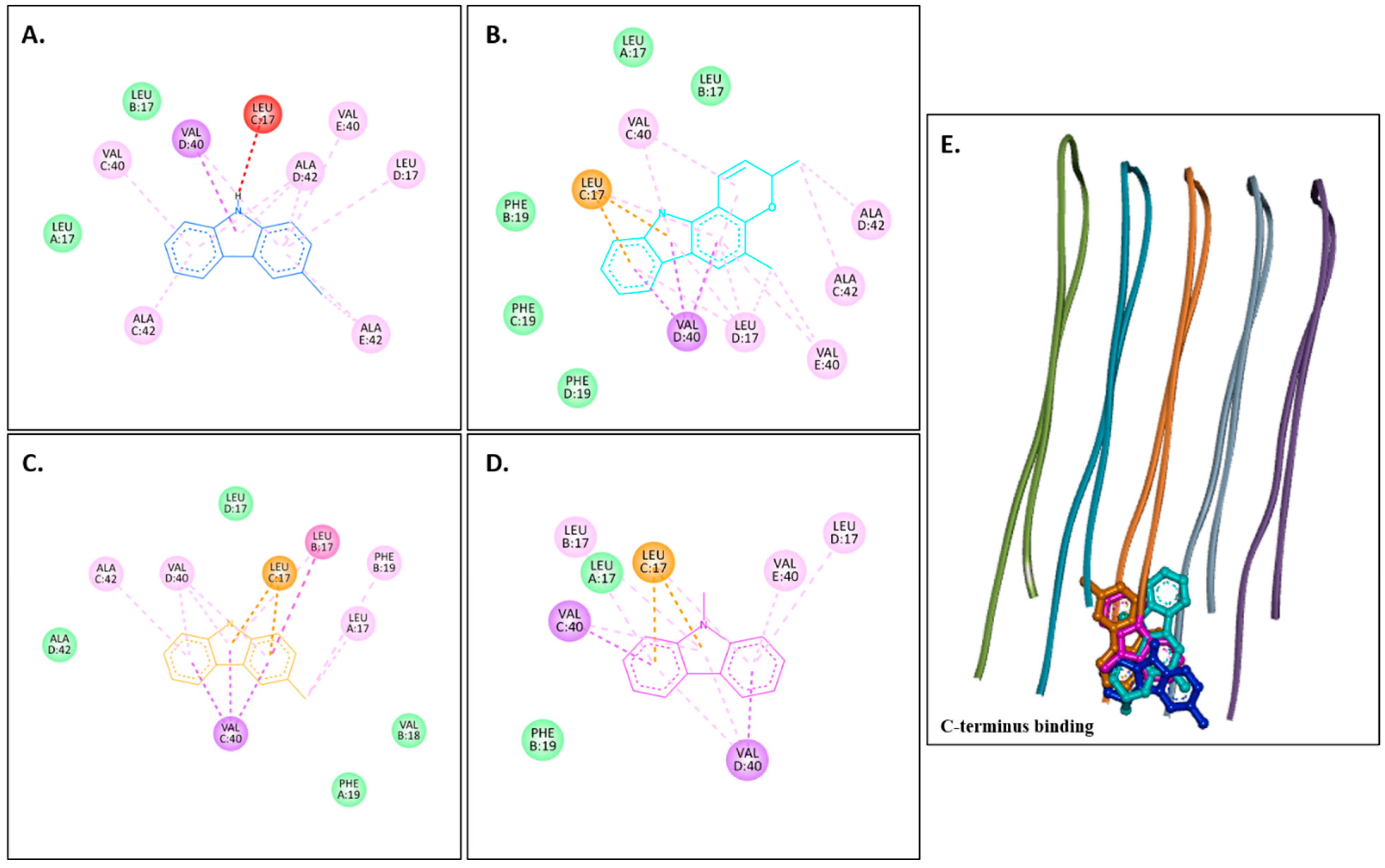
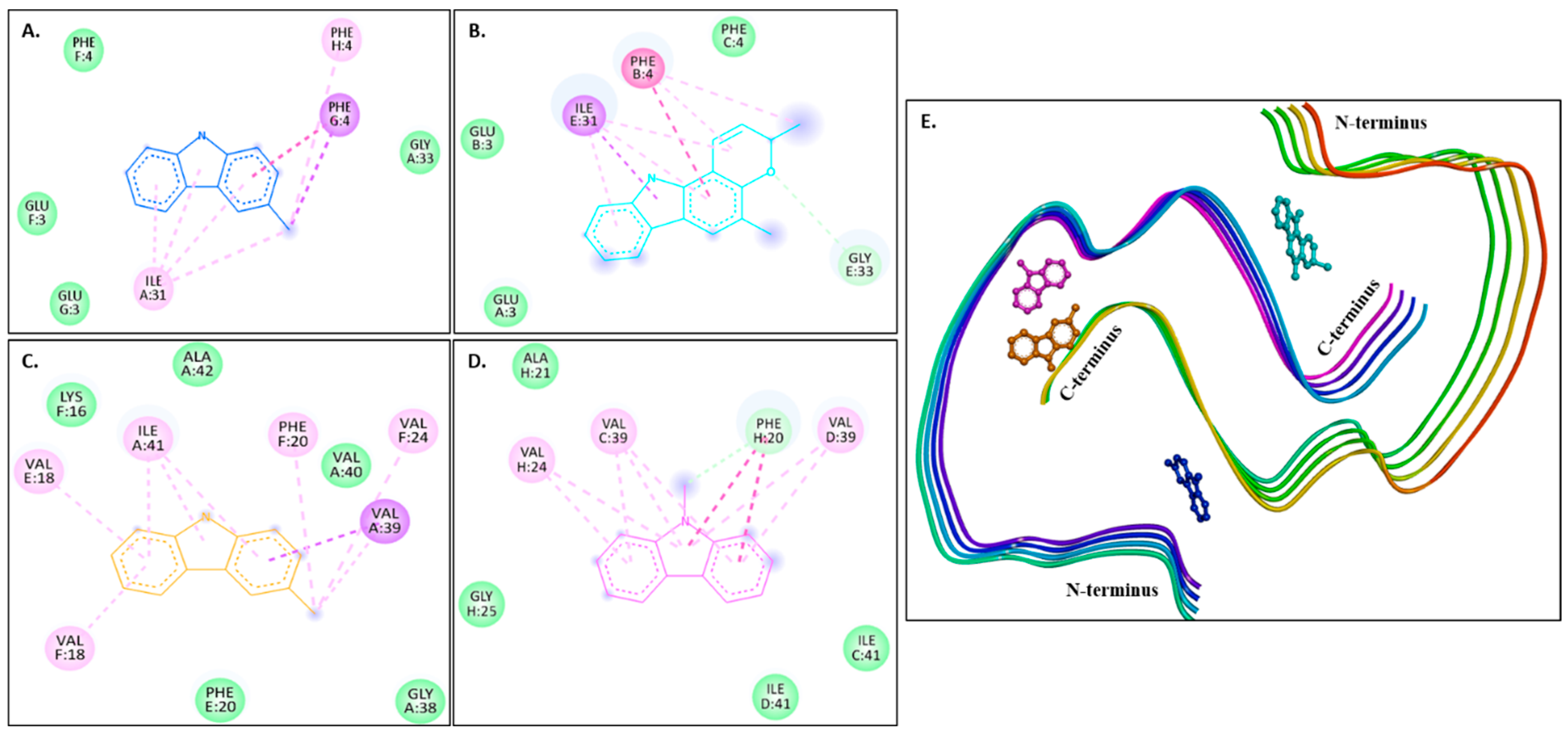
2.3.1. Docking with the AChE Receptor
2.3.2. Docking with Aβ Receptors
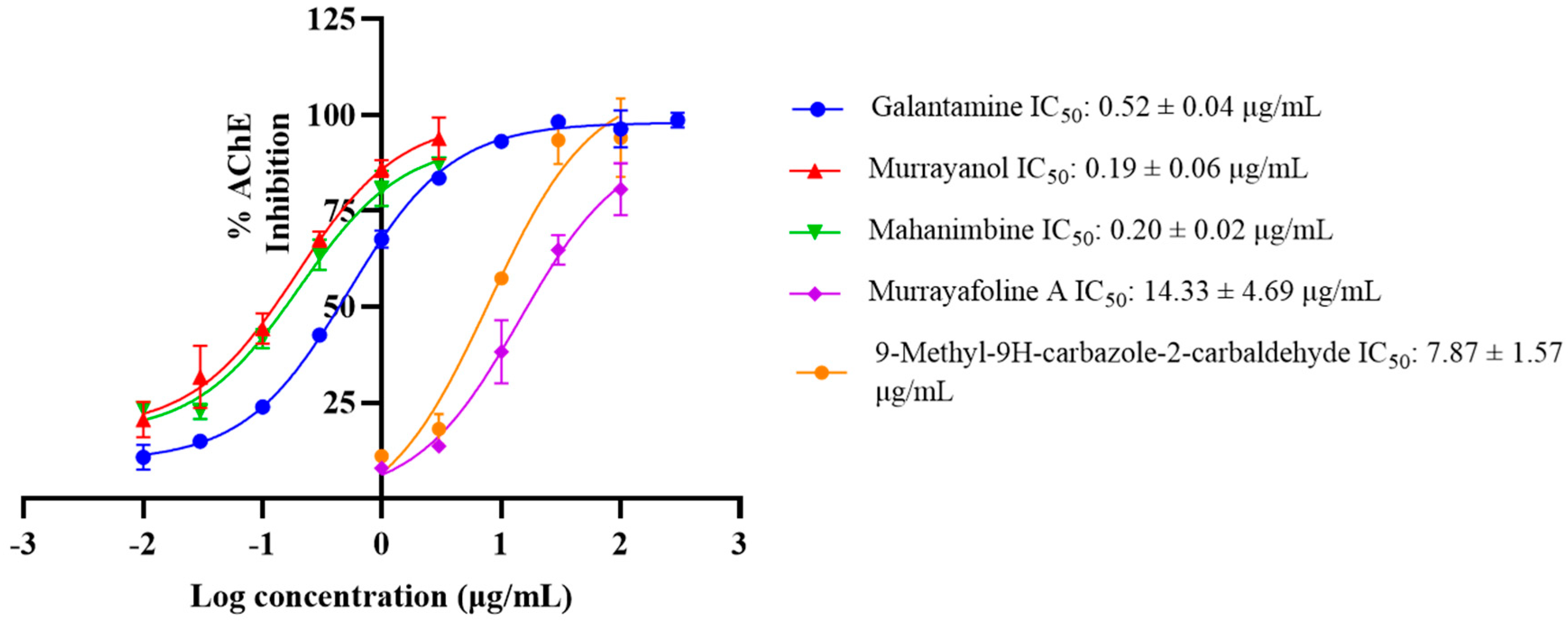
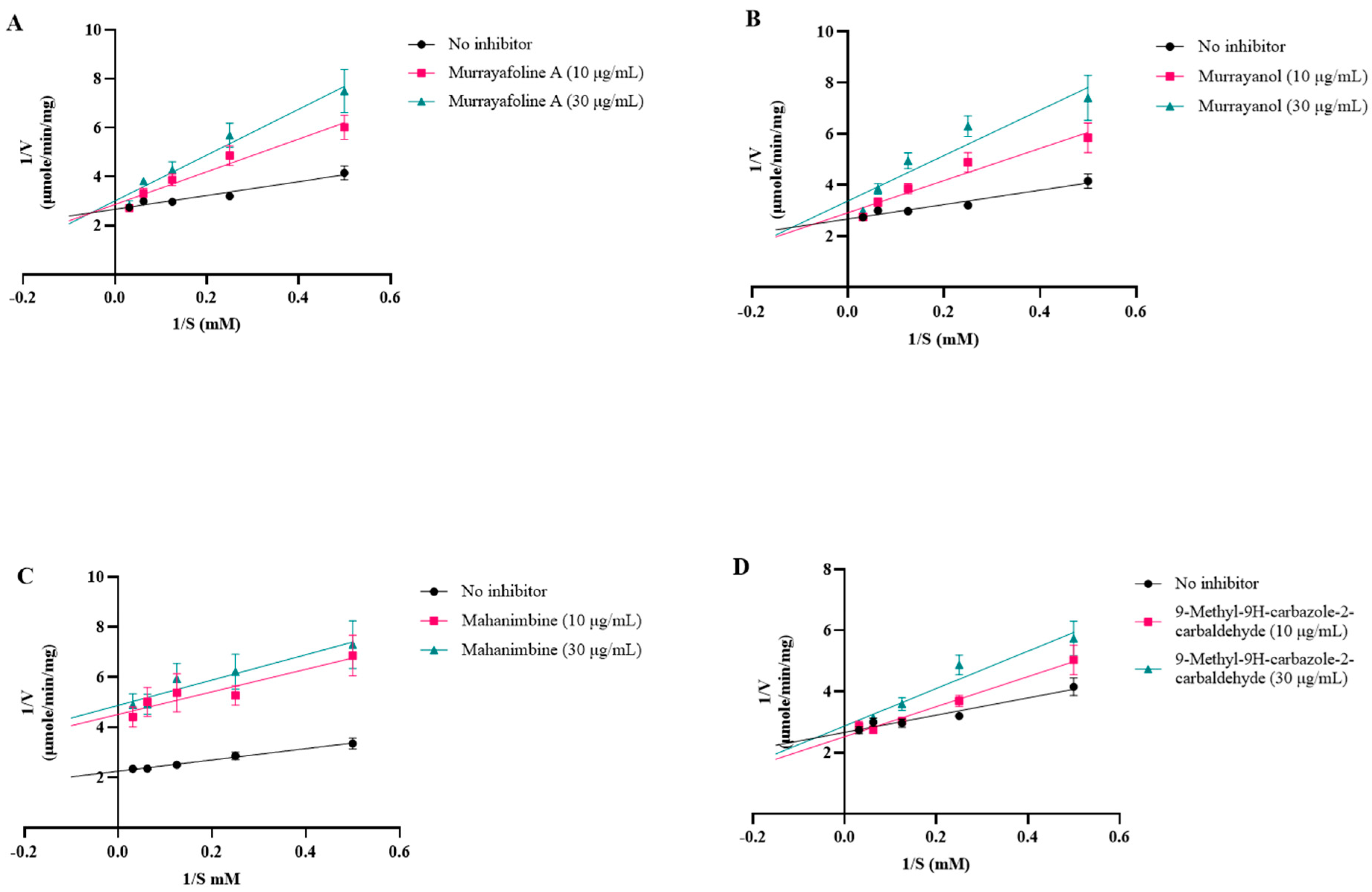
2.4. In Vitro Acetylcholinesterase (AChE) Inhibitory Activity
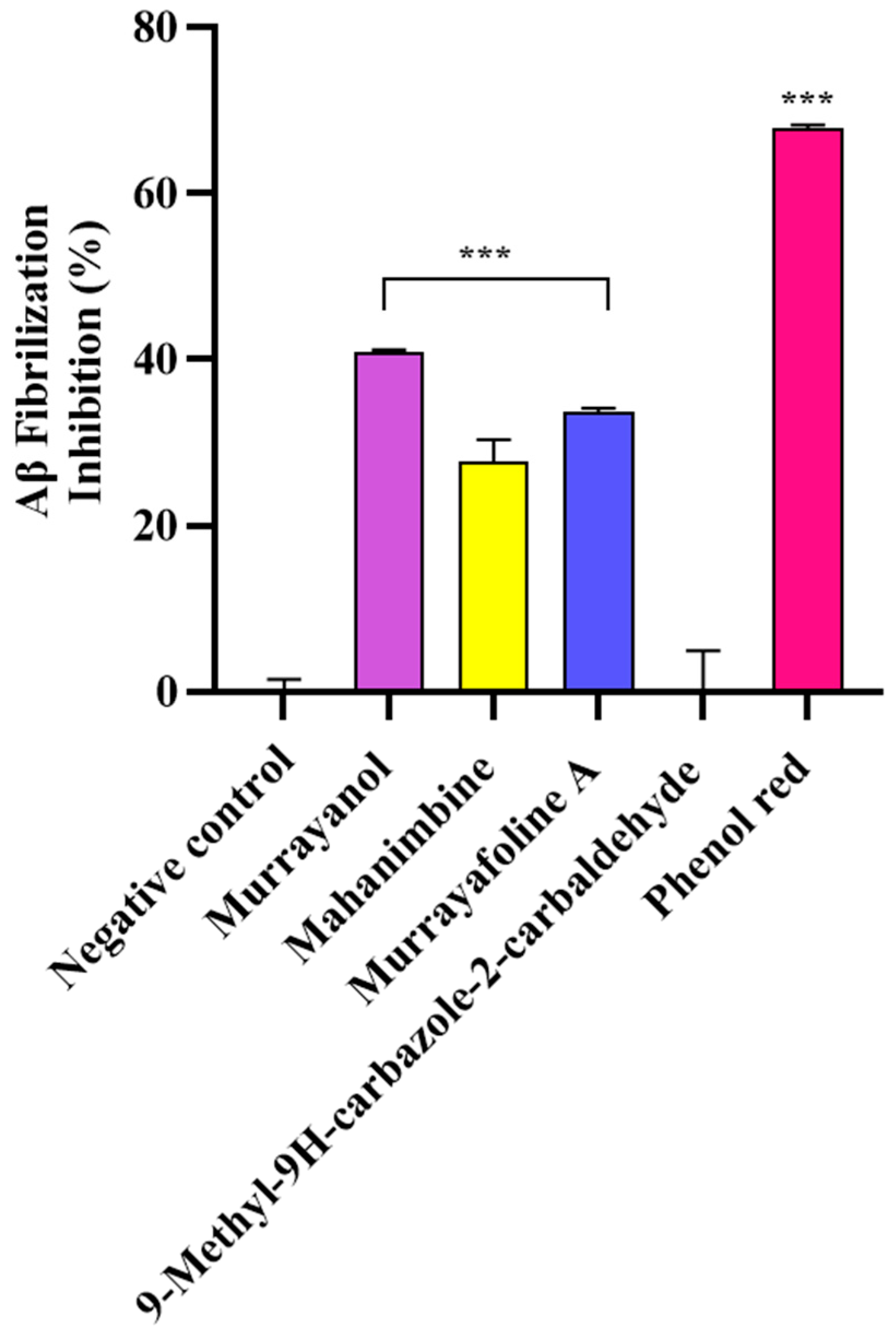
2.5. Anti-Aβ Fibrillization Activity
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Chemicals
4.2. In Silico Studies
4.2.1. Ligand Structure Selection
4.2.2. Protein Structure Selection and Preparation
4.2.3. Drug-Likeness, Toxicity Predictions, and ADME Properties of the Compounds
4.2.4. Molecular Docking
4.3. Anti-Acetylcholinesterase (AChE) Activity
- Inhibition percentage (I%) = [(A1 − A2) − (A3 − A4)]/(A1 − A2) × 100, where A1 = absorbance without inhibitor; A2 = negative control; A3 = absorbance of inhibitor; and A4 = negative control with inhibitor.
4.4. Thioflavin T (ThT) Assay
- where Fi = fluorescence intensity with inhibitor; Fc = fluorescence intensity without inhibitor.
4.5. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AChE | Acetylcholinesterase |
| ADMET | Absorption, distribution, metabolism, excretion and toxicity |
| Aβ | Amyloid β |
| BBB | Blood–brain barrier |
| CNS | Central nervous system |
| CYP | Cytochrome P450 |
| FLEX | Flexibility |
| Fsp3 | Fraction of sp3 carbon atoms |
| UNSATU | Unsaturation |
| INSOLU | Insolubility |
| LIPO | Lipophilicity |
| PAS | Peripheral anionic site |
| P-gp | P-glycoprotein |
| ROS | Reactive oxygen species |
| ThT | Thioflavin T |
| TPSA | Topological polar surface area |
References
- Suthar, P.; Kumar, S.; Kumar, V.; Vaidya, D.; Sharma, A.; Sharma, A. Murraya koenigii (L.) Spreng: Speculative ethnobotanical perspectives of ubiquitous herb with versatile nutra/functional properties. South Afr. J. Bot. 2022, 145, 111–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balakrishnan, R.; Vijayraja, D.; Jo, S.H.; Ganesan, P.; Su-Kim, I.; Choi, D.K. Medicinal Profile, Phytochemistry, and Pharmacological Activities of Murraya koenigii and its Primary Bioactive Compounds. Antioxidants 2020, 9, 101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramsewak, R.S.; Nair, M.G.; Strasburg, G.M.; DeWitt, D.L.; Nitiss, J.L. Biologically active carbazole alkaloids from Murraya k oenigii. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1999, 47, 444–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, M.A.; Sharma, N.; An, S.S.A. Phyto-Carbazole Alkaloids from the Rutaceae Family as Potential Protective Agents against Neurodegenerative Diseases. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhupatiraju, L.; Bethala, K.; Goh, K.W.; Dhaliwal, J.S.; Siang, T.C.; Menon, S.; Menon, B.; Anchu, K.B.; Chan, S.Y.; Ming, L.C.; et al. Influence of Murraya koenigii extract on diabetes induced rat brain aging. J. Med. Life 2023, 16, 307–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aina, O.S.; Rofiu, M.O.; Oloba-Whenu, O.A.; Olasupo, I.A.; Adams, L.A.; Familoni, O.B. Drug design and in-silico study of 2-alkoxylatedquinoline-3-carbaldehyde compounds: Inhibitors of Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Sci. Afr. 2023, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banerjee, P.; Kemmler, E.; Dunkel, M.; Preissner, R. ProTox 3.0: A webserver for the prediction of toxicity of chemicals. Nucleic Acids Res. 2024, 52, W513–W520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sudeep, H.V.; Amritha, R.; Gouthamchandra, K.; Chandrappa, S.; Shyamprasad, K. Kinetics and computational analysis of cholinesterase inhibition by REVERC3, a bisdemethoxycurcumin-rich Curcuma longa extract: Relevance to the treatment of Alzheimer’s disease. SAGE Open Med. 2020, 8, 2050312120973499. [Google Scholar]
- Burlingham, B.T.; Widlanski, T.S. An Intuitive Look at the Relationship of Ki and IC50: A More General Use for the Dixon Plot. J. Chem. Educ. 2003, 80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brandt, R.B.; Laux, J.E.; Yates, S.W. Calculation of inhibitor Ki and inhibitor type from the concentration of inhibitor for 50% inhibition for Michaelis-Menten enzymes. Biochem. Med. Metab. Biol. 1987, 37, 344–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hudson, S.A.; Ecroyd, H.; Kee, T.W.; Carver, J.A. The thioflavin T fluorescence assay for amyloid fibril detection can be biased by the presence of exogenous compounds. FEBS J. 2009, 276, 5960–5972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, H.; Yang, H.; Sharma, N.; An, S.S.A. Neuroprotection by Anethum graveolens (Dill) Seeds and Its Phytocompounds in SH-SY5Y Neuroblastoma Cell Lines and Acellular Assays. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 7104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilani, B.; Cassagnol, M. Biochemistry, Cytochrome P450. StatPearls. 2023. Available online: https://www.bio-conferences.org/articles/bioconf/ref/2023/20/bioconf_biomic2023_04002/bioconf_biomic2023_04002.html (accessed on 28 April 2025).
- Mittal, B.; Tulsyan, S.; Kumar, S.; Mittal, R.D.; Agarwal, G. Cytochrome P450 in cancer susceptibility and treatment. Adv. Clin. Chem. 2015, 71, 77–139. [Google Scholar]
- Krekels, E.H.J.; Rower, J.E.; Constance, J.E.; Knibbe, C.A.; Sherwin, C.M. Chapter 8—Hepatic Drug Metabolism in Pediatric Patients. In Drug Metabolism in Diseases; Xie, W., Ed.; Academic Press: Boston, MA, USA, 2017; pp. 181–206. [Google Scholar]
- Miners, J.O.; Birkett, D.J. Cytochrome P4502C9: An enzyme of major importance in human drug metabolism. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 1998, 45, 525–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, J.-M.; Li, H.-Y.; Liu, H.; Zhu, L.; Guo, Y.-B.; Pei, J.; An, H.; Li, Y.-S.; Li, S.-D.; Zhang, Z.-Y.; et al. N-terminal Domain of Amyloid-β Impacts Fibrillation and Neurotoxicity. ACS Omega 2022, 7, 38847–38855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lührs, T.; Ritter, C.; Adrian, M.; Riek-Loher, D.; Bohrmann, B.; Döbeli, H.; SchubertRiek, D.; Riek, R. 3D structure of Alzheimer’s amyloid-beta(1-42) fibrils. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 17342–17347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, C.; Murray, M.M.; Bernstein, S.L.; Condron, M.M.; Bitan, G.; Shea, J.-E.; Bowers, M.T. The Structure of Aβ42 C-Terminal Fragments Probed by a Combined Experimental and Theoretical Study. J. Mol. Biol. 2009, 387, 492–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Overk, C.R.; Felder, C.C.; Tu, Y.; Schober, D.A.; Bales, K.R.; Wuu, J.; Mufson, E.J. Cortical M1 receptor concentration increases without a concomitant change in function in Alzheimer’s disease. J. Chem. Neuroanat. 2010, 40, 63–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Çömlekçioğlu, N.; Korkmaz, N.; Yüzbaşıoğlu, M.A.; Uysal, İ.; Sevindik, M. Mistletoe (Loranthus europaeus Jacq.): Antioxidant, antimicrobial and anticholinesterase activities. Prospect. Pharm. Sci. 2024, 22, 164–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korkmaz, A.I.; Bal, C.; Krupodorova, T.; Yüzbaşıoğlu, M.A.; Sarıdoğan, B.G.Ö.; Sevindik, M. Some biological activities and element levels of Lycoperdon pratense. Prospect. Pharm. Sci. 2024, 22, 39–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasteel, E.E.J.; Nijmeijer, S.M.; Darney, K.; Lautz, L.S.; Dorne, J.L.C.M.; Kramer, N.I.; Westerink, R.H.S. Acetylcholinesterase inhibition in electric eel and human donor blood: An in vitro approach to investigate interspecies differences and human variability in toxicodynamics. Arch. Toxicol. 2020, 94, 4055–4065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, N.S.; Mukherjee, P.K.; Bhadra, S.; Saha, B.P.; Pal, B.C. Acetylcholinesterase inhibitory potential of a carbazole alkaloid, mahanimbine, from Murraya koenigii. Phytother. Res. 2009, 24, 629–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mani, V.; Azahan, N.S.M.; Ramasamy, K.; Lim, S.M.; James, R.M.J.; Alsharidah, M.; Alhowail, A.; Majeed, A.B.A. Mahanimbine-induced neuroprotection via cholinergic system and attenuated amyloidogenesis as well as neuroinflammation in lipopolysaccharides-induced mice. Pharmacogn. Mag. 2020, 16, 57–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biancalana, M.; Makabe, K.; Koide, A.; Koide, S. Molecular Mechanism of Thioflavin-T Binding to the Surface of β-Rich Peptide Self-Assemblies. J. Mol. Biol. 2009, 385, 1052–1063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, W.-R.; Wang, Y.; Cui, P.-F.; Xing, L.; Lee, J.; Kim, D.; Jiang, H.-L.; Oh, Y.-K. Applications of π-π stacking interactions in the design of drug-delivery systems. J. Control Release 2019, 294, 311–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brylinski, M. Aromatic interactions at the ligand–protein interface: Implications for the development of docking scoring functions. Chem. Biol. Drug Des. 2017, 91, 380–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.; Li, M.; Liu, J. π–π Stacking Interaction: A Nondestructive and Facile Means in Material Engineering for Bioapplications. Cryst. Growth Des. 2018, 18, 2765–2783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sedov, I.; Khaibrakhmanova, D. Molecular Mechanisms of Inhibition of Protein Amyloid Fibril Formation: Evidence and Perspectives Based on Kinetic Models. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 13428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, H.; Kim, D.Y.; Shim, K.H.; Sharma, N.; An, S.S.A. Multi-Targeting Neuroprotective Effects of Syzygium aromaticum Bud Extracts and Their Key Phytocompounds against Neurodegenerative Diseases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 8148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.J.C.; Nam, E.; Lee, H.J.; Savelieff, M.G.; Lim, M.H. Towards an understanding of amyloid-β oligomers: Characterization, toxicity mechanisms, and inhibitors. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2017, 46, 310–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, C.-H.; Zhou, Y.; Tu, P.-F.; Zeng, K.-W.; Jiang, Y. Natural carbazole alkaloid murrayafoline A displays potent anti-neuroinflammatory effect by directly targeting transcription factor Sp1 in LPS-induced microglial cells. Bioorganic Chem. 2022, 129, 106178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meng, E.C.; Goddard, T.D.; Pettersen, E.F.; Couch, G.S.; Pearson, Z.J.; Morris, J.H.; Ferrin, T.E. UCSF ChimeraX: Tools for structure building and analysis. Protein Sci. 2023, 32, e4792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ayodele, P.F.; Bamigbade, A.; Bamigbade, O.O.; Adeniyi, I.A.; Tachin, E.S.; Seweje, A.J.; Farohunbi, S.T. Illustrated Procedure to Perform Molecular Docking Using PyRx and Biovia Discovery Studio Visualizer: A Case Study of 10kt With Atropine. Prog. Drug Discov. Biomed. Sci. 2023, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellman, G.L.; Courtney, K.D.; Andres, V., Jr.; Featherstone, R.M. A new and rapid colorimetric determination of acetylcholinesterase activity. Biochem. Pharmacol. 1961, 7, 88–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
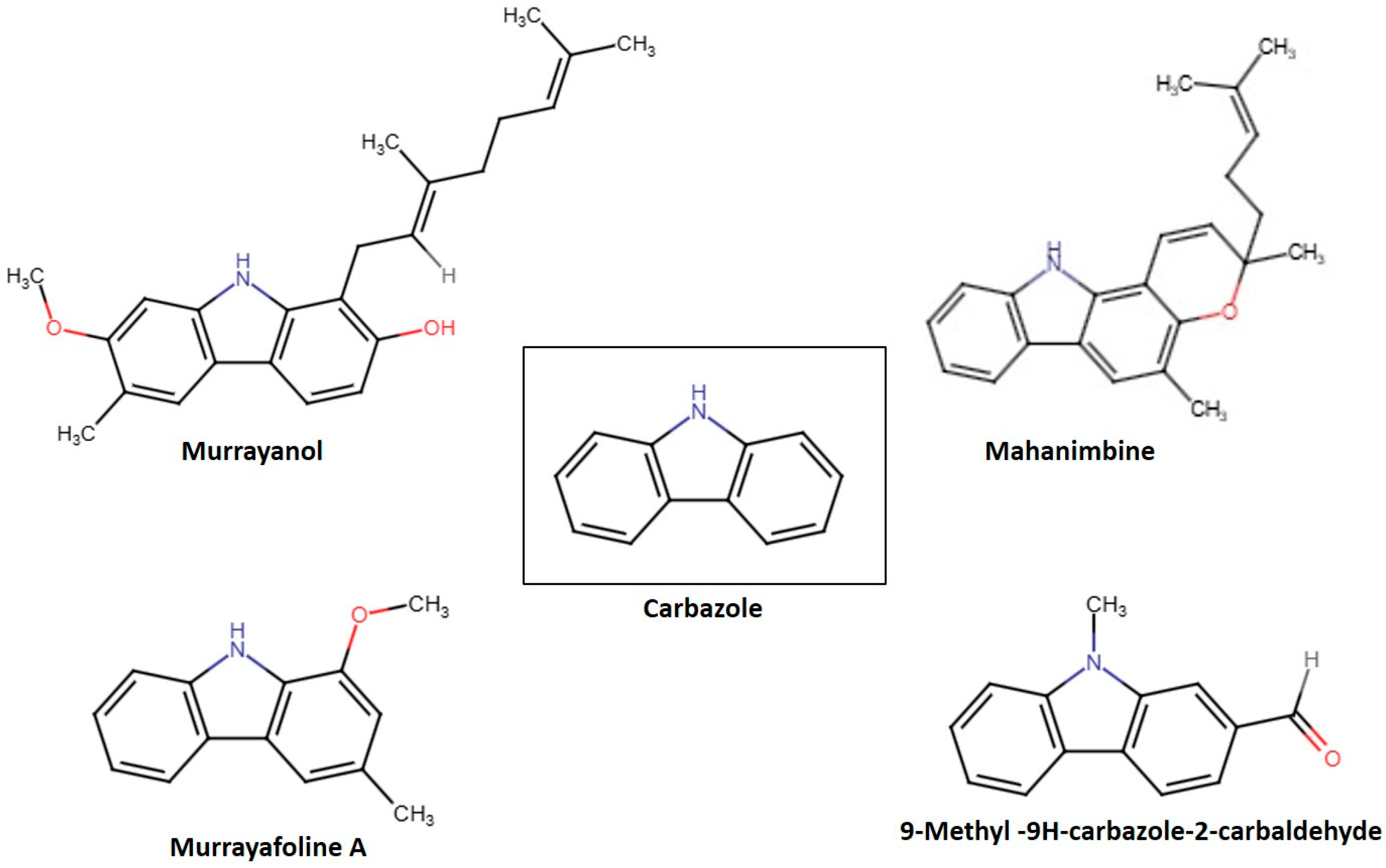
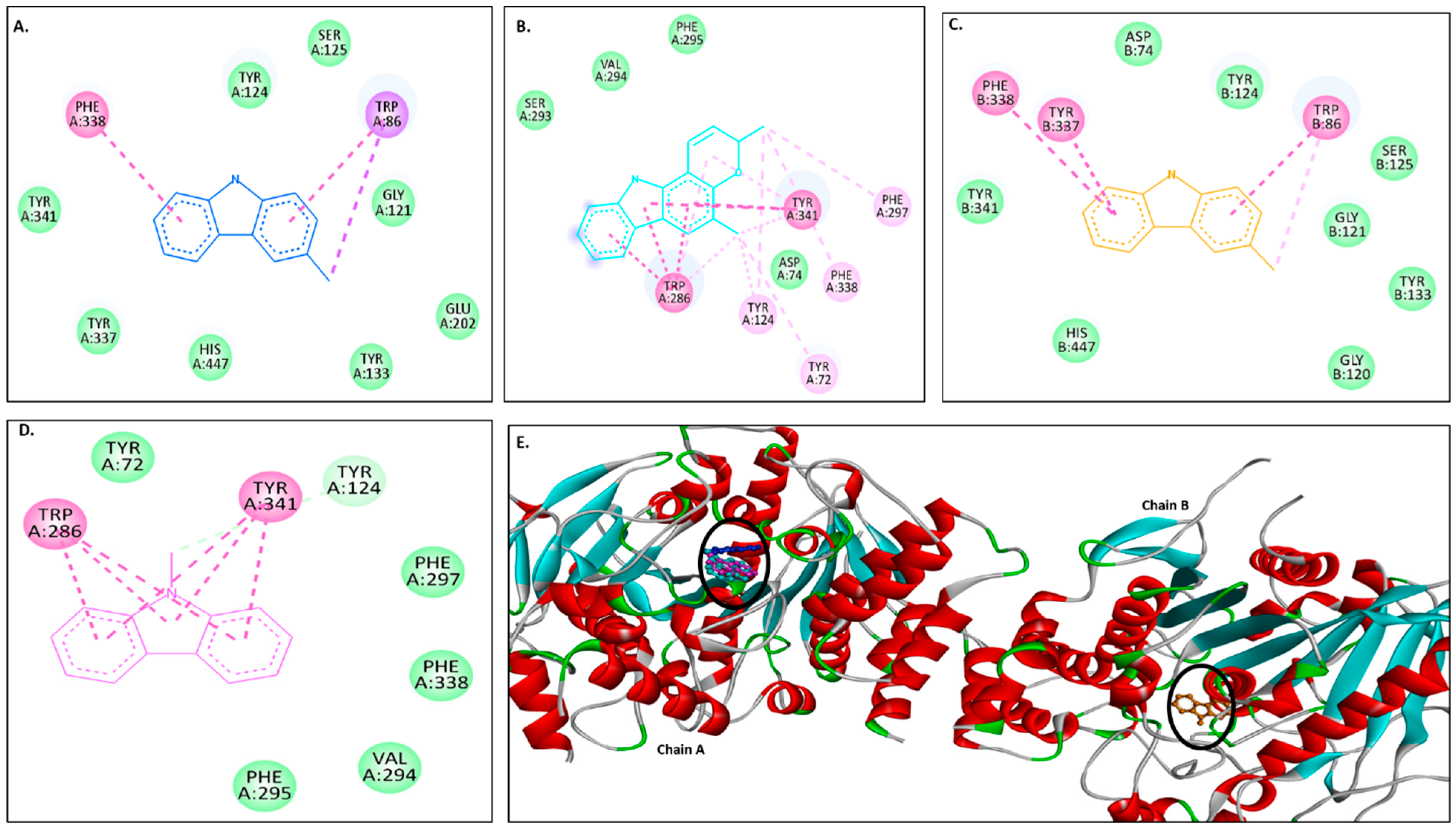
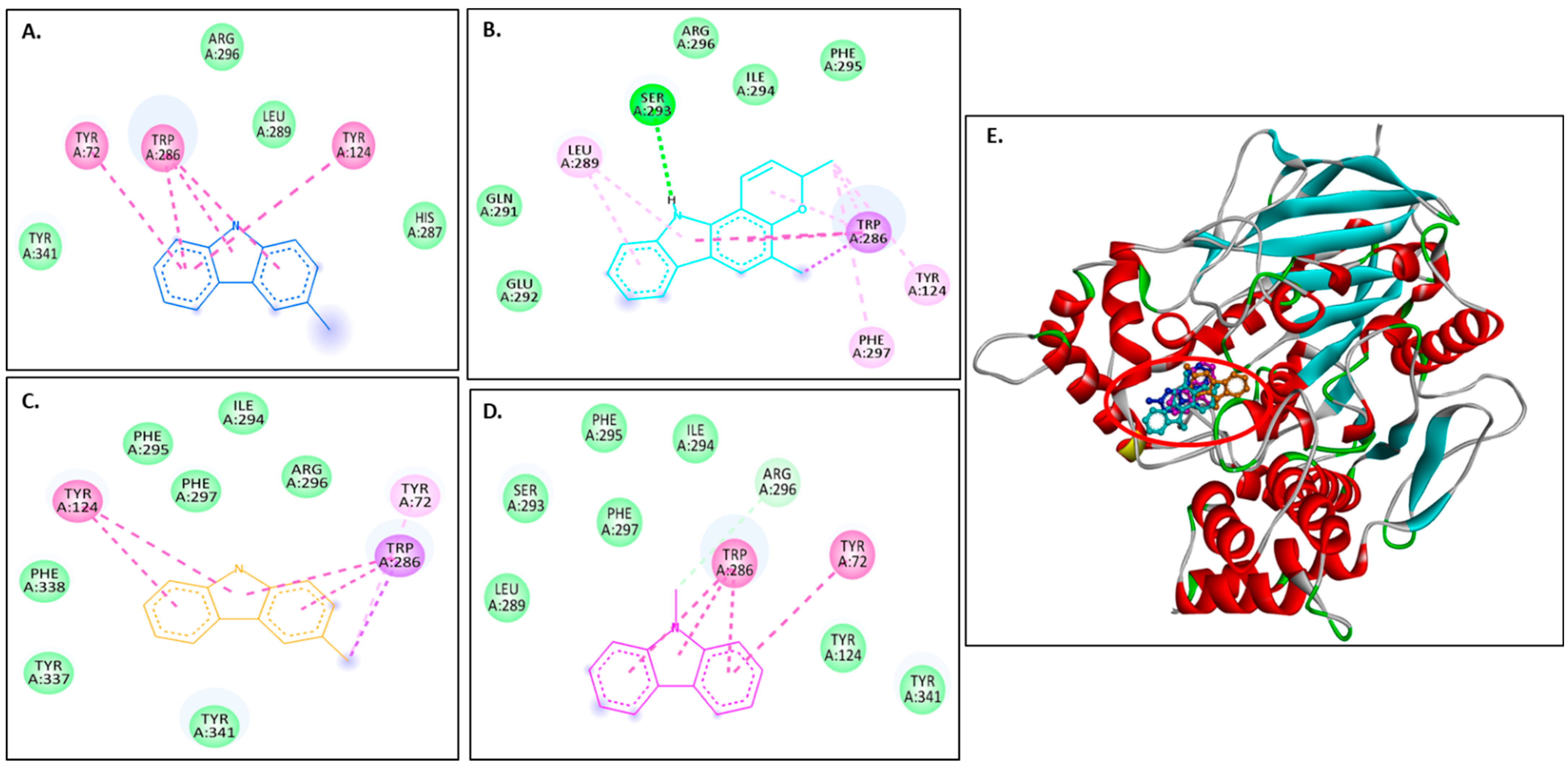
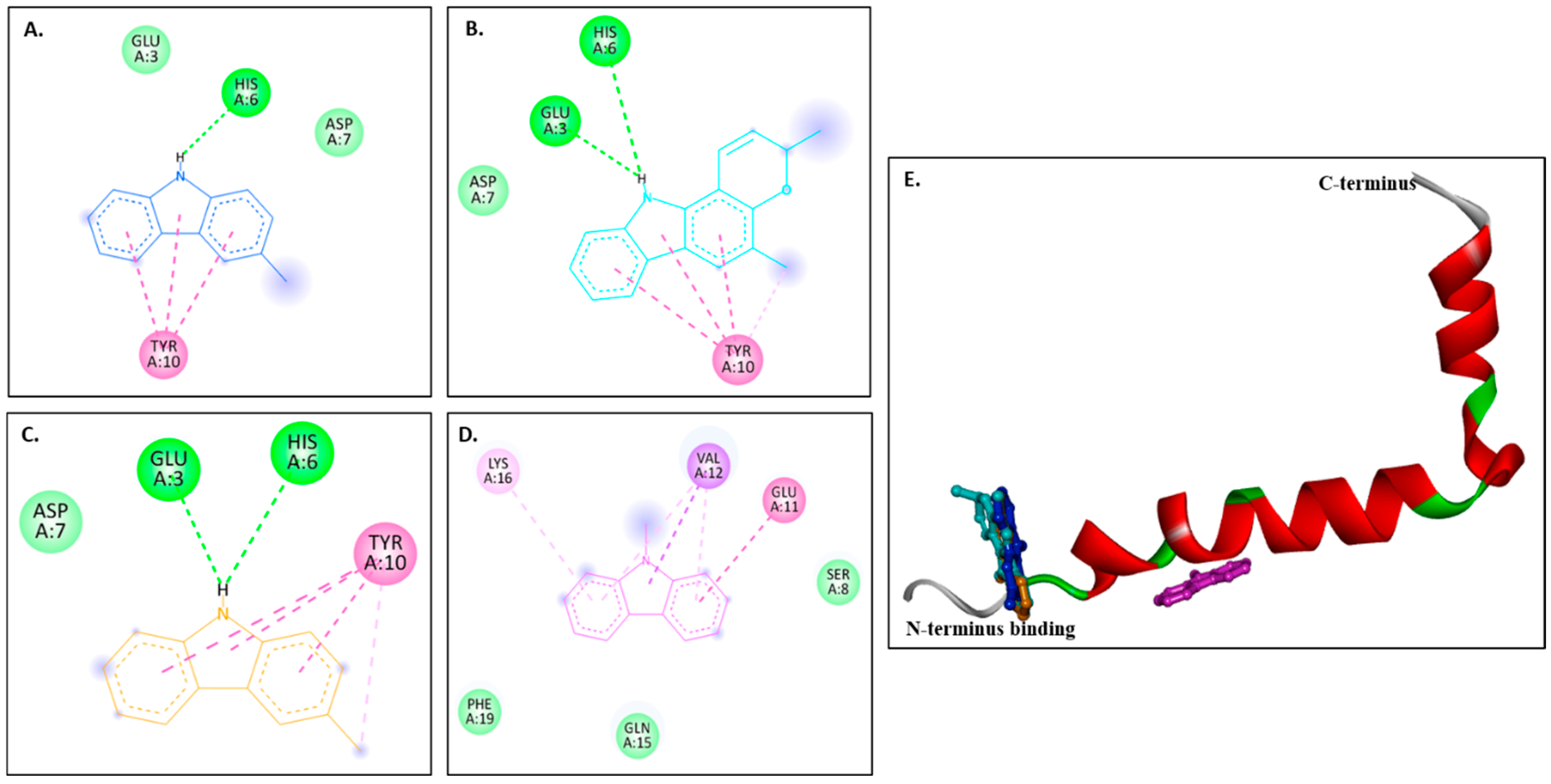
| Compounds | LIPO (CLogP) | Size (g/mol) | Polar (TPSA) | INSOLU LogS (Esol) | UNSATU (Fsp3) | Flex (RB) | Lipinski’s Rule | Bioavailability Score |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Murrayanol | 5.71 | 363.49 | 45.25 | −6.56 | 0.33 | 6 | 1 | 0.55 |
| Mahanimbine | 5.62 | 331.45 | 25.02 | −6.26 | 0.3 | 3 | 1 | 0.55 |
| Murrayafoline A | 3.31 | 211.26 | 25.02 | −4.03 | 0.14 | 1 | 0 | 0.55 |
| 9-Methyl-9H-carbazole-2-carbaldehyde | 2.71 | 209.24 | 22 | −3.44 | 0.07 | 1 | 0 | 0.55 |
| Compounds | CYP1A2 | CYP2C19 | CYP2C9 | CYP2D6 | CYP3A4 | GI Absorption | BBB Permeability | P-gp Substrate |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Murrayanol | No | Yes | No | Yes | No | High | No | No |
| Mahanimbine | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | High | No | Yes |
| Murrayafoline A | Yes | Yes | No | Yes | Yes | High | Yes | Yes |
| 9-Methyl-9H-carbazole-2-carbaldehyde | Yes | Yes | No | No | No | High | Yes | No |
| Compounds | Hepatotoxicity | Cytotoxicity | Neurotoxicity | LD50 (mg/kg) | Toxicity class |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Murrayanol | Inactive | Inactive | Inactive | 2300 | V |
| Mahanimbine | Inactive | Inactive | Inactive | 4000 | V |
| Murrayafoline A | Inactive | Inactive | Active | 1200 | III |
| 9-Methyl-9H-carbazole-2-carbaldehyde | Inactive | Inactive | Active | 1250 | IV |
| Compounds | Binding Affinities (kcal/mol) | |
|---|---|---|
| 4EY7 | 1C2B | |
| Murrayanol | −11 | −10.5 |
| Mahanimbine | −12.4 | −10.5 |
| Murrayafoline A | −9.1 | −7.7 |
| 9-Methyl-9H-carbazole-2-carbaldehyde | −8.8 | −8.2 |
| Compounds | Binding Affinities (kcal/mol) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| 1IYT | 2BEG | 8EZE | |
| Murrayanol | −6.2 | −8.0 | −7.4 |
| Mahanimbine | −6.6 | −7.6 | −8.0 |
| Murrayafoline A | −5.2 | −7.0 | −6.5 |
| 9-Methyl-9H-carbazole-2-carbaldehyde | −5.1 | −5.9 | −6.4 |
| Vmax (μmole/min/mg) | Km (mM) | Ki (µM) | Inhibition Type | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| No Inhibitor | 0.3710 | 0.9674 | ||
| Murrayanol 10 μg/mL Murrayanol 30 μg/mL | 0.3756 0.3613 | 3.011 4.894 | 0.444 0.470 | Competitive |
| Mahanimbine 10 μg/mL Mahanimbine 30 μg/mL | 0.2098 0.2231 | 1.150 0.9881 | 0.599 0.599 | Non-Competitive |
| Murrayafoline A 10 μg/mL Murrayafoline A 30 μg/mL | 0.3826 0.3753 | 3.227 4.505 | 58.71 61.04 | Competitive |
| 9-Methyl-9H-carbazole-2-carbaldehyde 10 μg/mL 9-Methyl-9H-carbazole-2-carbaldehyde 30 μg/mL | 0.3874 0.3634 | 1.733 2.509 | 29.18 31.35 | Competitive |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sharma, H.; Sharma, N.; An, S.S.A. Neuroprotective Evaluation of Murraya Carbazoles: In Vitro and Docking Insights into Their Anti-AChE and Anti-Aβ Activities. Molecules 2025, 30, 3138. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30153138
Sharma H, Sharma N, An SSA. Neuroprotective Evaluation of Murraya Carbazoles: In Vitro and Docking Insights into Their Anti-AChE and Anti-Aβ Activities. Molecules. 2025; 30(15):3138. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30153138
Chicago/Turabian StyleSharma, Himadri, Niti Sharma, and Seong Soo A. An. 2025. "Neuroprotective Evaluation of Murraya Carbazoles: In Vitro and Docking Insights into Their Anti-AChE and Anti-Aβ Activities" Molecules 30, no. 15: 3138. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30153138
APA StyleSharma, H., Sharma, N., & An, S. S. A. (2025). Neuroprotective Evaluation of Murraya Carbazoles: In Vitro and Docking Insights into Their Anti-AChE and Anti-Aβ Activities. Molecules, 30(15), 3138. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30153138








