Abstract
A series of eleven new N-alkyl 3-(3-benzyloxyquinoxalin-2-yl) propanamides were prepared based on the azide coupling of 3-(3-benzyloxyquinoxalin-2-yl) propanhydrazide with a variety of primary and secondary amines and the consequent conjunction of a broad spectrum of lipophile and hydrophile characters to a quinoxaline ring system. 3-(3-benzyloxyquinoxalin-2-yl) propanhydrazide was produced in a two-step reaction of methyl 3-(3-oxo-3,4-dihydroquinoxalin-2-yl) propanoate with benzyl chloride followed by the hydrazinolysis of the corresponding ester. The antiproliferative activity of the compounds was tested in various cancer cell lines, including PC-3, Hela, HCT-116, and MCF-7; they showed a wide spectrum of activity for most of the tested compounds. Compound 6k exhibited the highest activity, which was comparable to that of doxorubicin, with IC50 (µM) values of 12.17 ± 0.9, 9.46 ± 0.7, 10.88 ± 0.8, and 6.93 ± 0.4 µM compared to 8.87 ± 0.6, 5.57 ± 0.4, 5.23 ± 0.3, and 4.17 ± 0.2 µM for doxorubicin against Hela, HCT-116, and MCF-7, respectively. The in silico mechanistic study revealed the inhibition of HDAC-6 through the binding of the unique zinc finger ubiquitin-binding domain (HDAC6 Zf-UBD). The docking results showed a specific binding pattern that emphasized the crucial role of the quinoxaline ring and its substituents. The newly developed derivatives were evaluated for antitumor effects against four cancer cell lines PC-3, HeLa, HCT-116, and MCF-7. This research led to the identification of a quinoxaline-based scaffold exhibiting broad-spectrum antiproliferative activity and a distinct mechanism involving binding to HDAC6 Zf-UBD. The findings highlight its potential for further optimization and preclinical studies to support future anticancer drug development.
1. Introduction
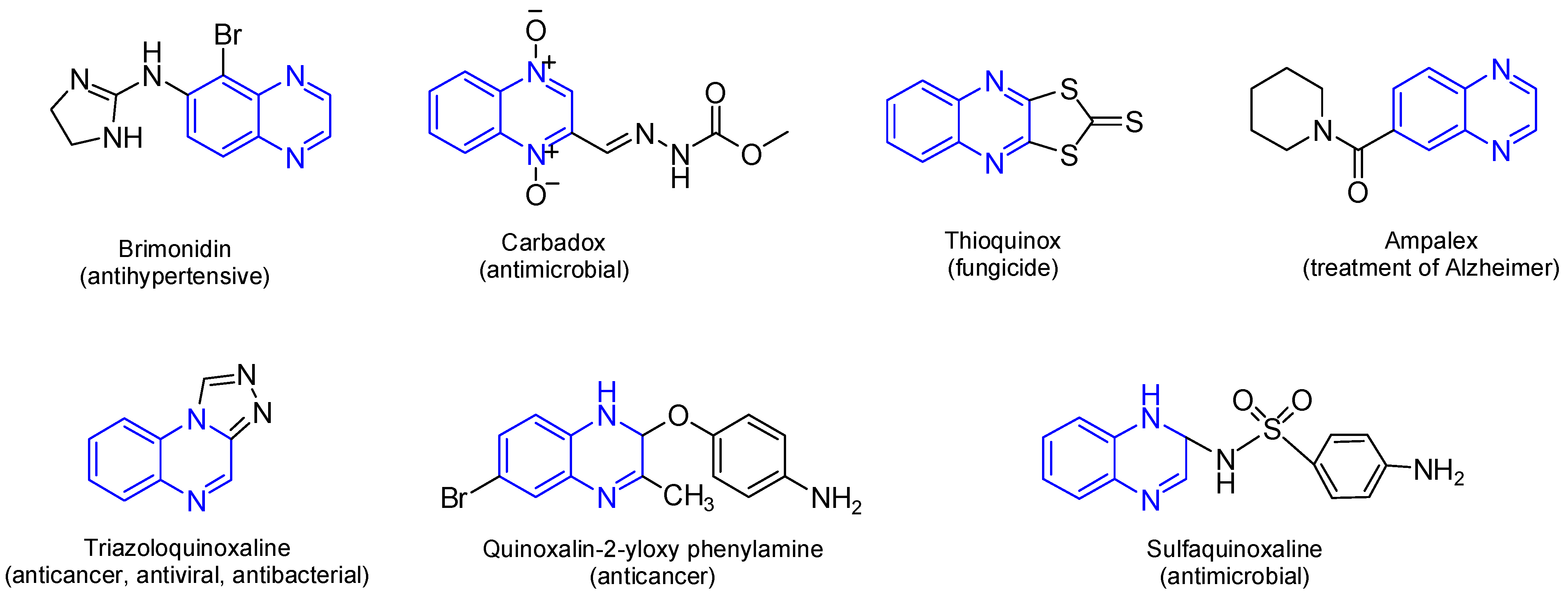
Quinoxaline is a fused heterocyclic compound consisting of a benzene ring fused to a pyrazine ring. This privileged scaffold has attracted significant attention in medicinal chemistry due to its remarkable biological and pharmacological properties. Quinoxaline and its derivatives have been widely recognized for their diverse therapeutic applications, including anticancer [1,2,3], antitumor [4], antimicrobial, antiparasitic, antiviral, antioxidant [2,5], anti-inflammatory, anticonvulsant [6], and antidiabetic activities [5,7]. The structural rigidity and electron-rich nitrogen atoms of the quinoxaline ring contribute to its ability to interact with various biological targets, including enzymes, DNA, and receptor proteins, enhancing its therapeutic potential [8]. The pharmacological relevance of quinoxaline lies in its broad-spectrum activity and structural adaptability. Quinoxaline’s fused heterocyclic core can be readily modified at various positions to improve its pharmacological properties, enabling the development of potent and selective drug candidates [9]. The aromatic system of quinoxaline provides planarity, facilitating intercalation with nucleic acids or interaction with hydrophobic pockets in enzymes and receptors [10,11]. Moreover, the nitrogen atoms in the ring system play a critical role in forming hydrogen bonds and coordination complexes, which are essential for biological activity, further allowing it to intercalate into nucleic acids or engage with hydrophobic pockets in enzymes and receptors [7,12,13]. Additionally, several studies have shown a wide range of pharmacological activities for quinoxaline derivatives (Figure 1) [2,3,4,7,14,15,16,17]. There are many commercially available quinoxalines that play an essential role in the pharmaceutical and industrial market [18]. Several clinically approved drugs and therapeutic agents incorporate the quinoxaline moiety, for instance, Carbadox, a veterinary antimicrobial [14], and Echinomycin, a quinoxaline-based cyclic peptide antibiotic with antitumor activity [15,16]. Erdafitinib (Balversa), a quinoxaline containing pan-FGFR inhibitor, received full FDA approval for FGFR-altered advanced urothelial carcinoma [13].
Figure 1.
Bioactive and pharmaceutical of quinoxaline derivatives. Quinoxaline rings are highlighted in blue color.
Quinoxaline can be easily synthesized and structurally modified through various methods for pharmacokinetic improvement [10,19,20]. The quinoxaline scaffold is significant in anticancer drug development showing inhibition of topoisomerase enzymes [21,22,23,24], and, specific kinase inhibitors, especially those involved in cancer cell signaling path [25,26,27], antiproliferative effects against various cancer cell lines, and the induction of apoptosis [28,29,30,31,32]. Chemoselective reaction of amides with electrophiles is a well-known simple procedure for structure modification of biologically active compounds to produce either pure N, O-substituted products or a mixture of both [33,34,35,36,37]. We now report the synthesis of N-alkyl 3-(3-benzyloxyquinoxalin-2-yl) propanamides based on azide coupling of 3-(3-benzyloxyquinoxalin-2-yl) propanhydrazide with a variety of amines with a broad range of lipophilicity for biological evaluation.
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Chemistry
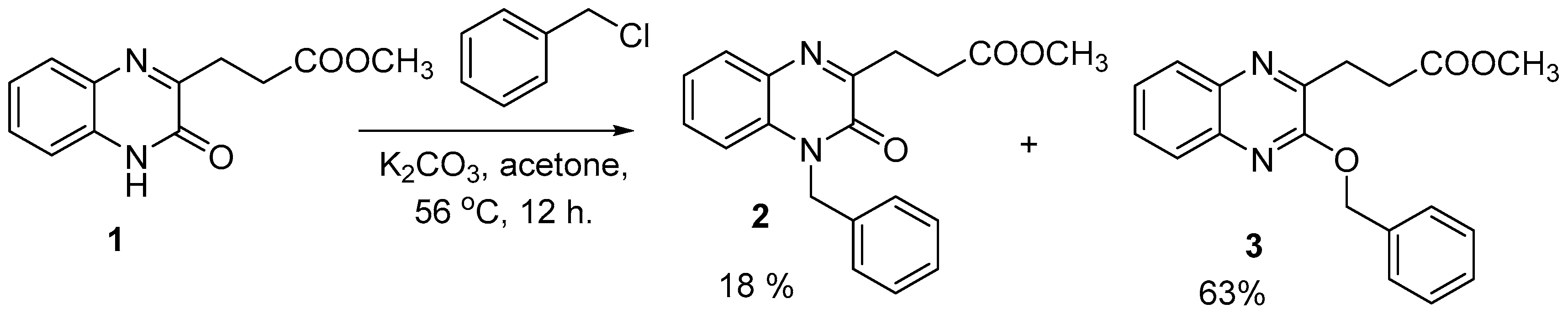
Methyl 3-(3-oxo-3,4-dihydroquinoxalin-2-yl) propanoate (1) is considered as an excellent model for examining the chemoselctive reactions of amides with electrophiles and the structure modification of the quinoxaline ring for the biological evaluation. The chemoselective reactions of amides with electrophiles are governed by a number of factors. The structure of the parent amide and electrophiles in use, ruled by Hard-Soft Acid-Base Principle (HSAB Principle), other factors is related to solvent and bases [33,34,35,36,37]. This behavior directed the reaction of amides with electrophiles to produce one of the following three categories: N-substituted, O-substituted and a mixture of both N- and O-. Some researchers tend to block the harder nucleophile using very polar solvents and consequently directed the reaction to give selective softer alkylated product [38,39]. Another factor is the strong bases as NaH might affect the tautomerization equilibrium of the ambident amide and make the oxygen more available for the reaction with hard electrophiles [40,41]. After a number of attempts using a variety of solvents; quinoxaline 1 reacted benzyl chloride in the presence of potassium carbonate in DMF, acetonitrile and ethanol for 12 h. and gave a mixture of methyl 3-(4-benzyl-3-oxo-3,4-dihydroquinoxalin-2-yl) propanoate (2) and methyl 3-(3-benzyloxyquinoxalin-2-yl) propanoate (3) in a variety of yields, Table 1.

Table 1.
Comparison of O- and N-substituted yields in different solvents.
Targeting the selective formation of O-substituted methyl 3-(3-benzyloxyquinoxalin-2-yl) propanoate (3) or in best cases with higher yields. quinoxaline 1 reacted with benzyl chloride in the presence of dry potassium carbonate in acetone under reflux condition for 12 h. and gave a mixture of N- (2) and the desired O-benzylquinoxaline (3) in 18% and 63%, respectively, Scheme 1.
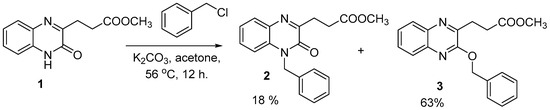
Scheme 1.
Reaction of quinoxaline (1) with benzyl chloride in acetone under reflux, yielding a mixture of compounds (2) (18%) and (3) (63%).
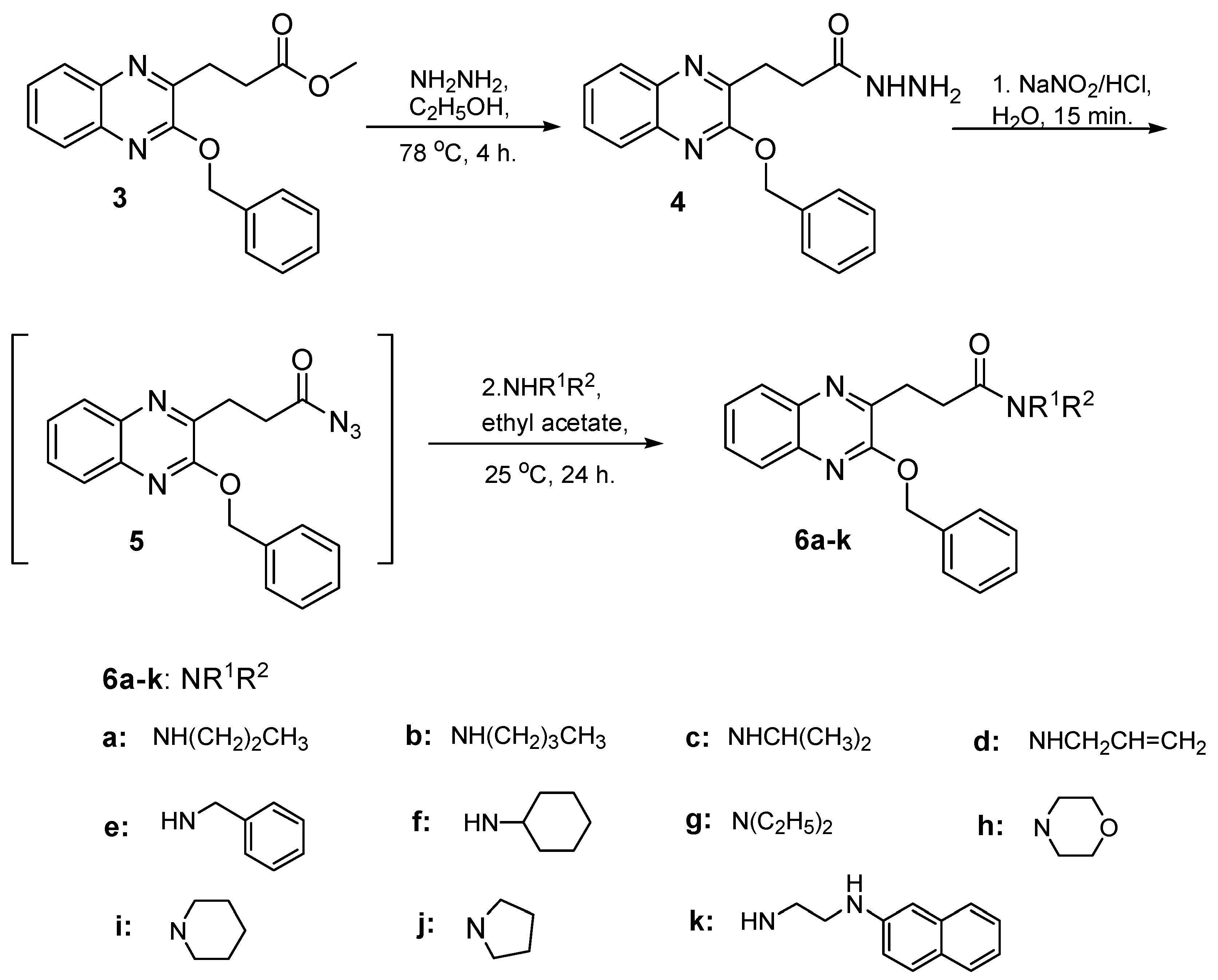
O-Benzylquinoxaline 3 reacted with hydrazine hydrate in ethanol 95% for 4 h. gave 3-(3-benzyloxyquinoxalin-2-yl) propanhydrazide (4) in 87% yield, Scheme 2. Hydrazide 4 is a useful precursor for the structure modification of quinoxaline ring via azide coupling method to introduce a number of residues having lipophile and hydrophile characters useful for biological application. Thus, the reaction of hydrazide 4 with NaNO2 and HCl mixture at 0 °C presumably gave the azide 5 and was directly extracted with cold ethyl acetate, dried and used insitu without further purification. The in situ generated ethyl acetate azide 5 solution reacted with a variety of primary and secondary amines to afford N-alkyl 3-(3-benzyloxyquinoxalin-2-yl) propanamide 6a–k in excellent yield, Scheme 2.
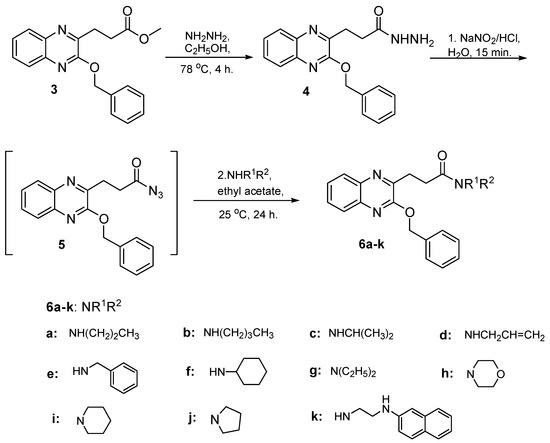
Scheme 2.
Preparation of N-alkyl 3-(3-benzyloxyquinoxalin-2-yl) propanamides 6a–k.
The structure assignment of methyl 3-(3-benzyloxyquinoxalin-2-yl) propanoate (3), 3-(3-benzyloxyquinoxalin-2-yl) propanhydrazide (4) and N-alkyl 3-(3-benzyloxyquinoxalin-2-yl) propanamides 6a–k was based on 1H, 13C NMR as well as physicochemical analysis. Thus, the 1H NMR spectrum of N-allyl-3-(3-benzyloxyquinoxalin-2-yl)propanamide (6d) exhibits signals at δ 3.78, 4.96–5.09 and 5.67–5.74 ppm corresponding to NCH2, CH2=CH and CH2=CH, respectively of the allyl residue. The 1H NMR spectrum of (6d) also shows signals at δ 2.73, 3.25 and 5.45 ppm corresponding to CH2, CH2CO and OCH2, respectively. the 13C NMR spectrum of N-allyl-3-(3-benzyloxyquinoxalin-2-yl)propanamide (6d) showed signals at δ 45.0, 115.8 and 135.4 (CH) ppm due to NHCH2, CH2=CH and CH2=CH, respectively of the allyl residue, while gave signals at δ 27.9, 30.3, and 68.1 ppm due to CH2, CH2CO and OCH2, respectively, typically associated with O-substitution.
2.2. Cytotoxicity Assay
The compounds were tested in various cancer cell lines to explore their potential antiproliferative activity and their suitability for further testing and development. Four cancer types were initially selected including prostate (PC-3), ovarian (Hela), Colon (HCT-116), and breast (MCF-7). The results showed an interesting inhibition profile with a noticed relative activity against the tested cell lines. Compounds showed the highest activity against MCF-7, and Hela the relative lower activity against PC-3, and HCT-116. The IC50 ranged from 6.93 ± 0.4–85.20 ± 4.2 µM for MCF-7, 10.88 ± 0.8–81.65 ± 4.0 µM for HCT-116, 9.46 ± 0.7–91.38 ± 4.8 µM for Hela, and 12.17 ± 0.9–94.14 ± 4.9 µM for PC-3 (Table 2). Compound 6k exhibited the highest activity against the four cancer cell lines with IC50 of 6.93 ± 0.4, 10.88 ± 0.8, 9.46 ± 0.7, and 12.17 ± 0.9 µM for MCF-7, HCT-116, Hela, and PC-3 respectively. In general, compounds that showed good activity (IC [42] < 50 µM) included compounds 2, 4, 6f, 6g, and 6i Compounds with moderate to weak activity (IC50 50–100 µM) included compounds 3, 6a, 6b, 6c, 6d, 6e, 6h, and 6j. In conclusion, the synthesized quinoxaline compounds showed good antiproliferative activity and wide spectrum of activity against the tested cell lines and deserve further investigations and development.

Table 2.
Cytotoxic activity of some compounds against tumor cell line.
2.3. Docking Study
The synthesized quinoxaline derivatives exhibited a wide range of antiproliferative activity against various cancer types including prostate cancer (PC-3), ovarian cancer (Hela), colon cancer (HCT-116), and breast cancer (MCF-7). The initial structure activity elucidation revealed that the lead compounds 2 and 4 showed good activity compared to some of the substituted amide derivatives (6k, 6i) while other derivatives exhibited lower activity (6b, 6e). The compounds 6f, 6h, 6i, and 6j although bearing similar substituents, showed variable activity with 6i being the most active followed by 6f. Therefore, a more specific binding requirements should be investigated based on the stereochemical conformations and target interactions. Searching for similar structures of the lead compounds 3, and 4 on PubChem revealed an experimentally validated target of structurally similar compounds. This target was identified as HDAC-6 bound to an inhibitor interestingly which binds the unique zinc finger ubiquitin-binding domain (HDAC6 Zf-UBD) and not the catalytic domain [42]. HDAC6 is localized in the cytoplasm has multifaceted functions in cell migration and reprogramming, and is associated with several diseases, including cancer and viral infections. Indeed, this was the first small molecule known to bind the HDAC6 Zf-UBD therefore, the development of other HDAC6 Zf-UBD inhibitors signifies an innovative strategy for elucidating the in vivo functions of HDAC-6 and the subsequent development of therapeutically active molecules to treat diseases such as cancer.
All compounds were docked in the HDAC6 Zf-UBD binding site using Glide in Maestro applying the extra precision (XP) module. The docking was initially validated by redocking the crystal ligand and computing the RMSD of the anticipated conformation relative to the crystal structure. The computed RMSD was determined to be 1.98, indicating good accuracy in the software’s prediction of docking poses of similar structures on the HDAC6 Zf-UBD binding site.
The XP docking scores were found to perfectly align with the experimental activity range of most of the tested compounds, categorizing the compounds into active, moderately active, weakly active, and inactive (Table 3). MM-GBSA enhances docking outcomes by integrating solvation and ligand flexibility, yielding more accurate binding free energy estimations. The results of the binding free energy calculations showed negative values for all compounds ranging from −44.99 to −29.60, which reflected favorable binding for the whole series. The calculations also stratified the compounds well relative to their experimental IC50. Compound 2 had the highest free energy of binding (−44.99 Kcal/mol) followed by compound 6k (−42.76 Kcal/mol) and, compound 6g (−37.05 Kcal/mol), while compound 3 showed the lowest free energy of binding (−29.60 Kcal/mol). Interestingly, the crystal ligand had a calculated binding free energy of −22.80 Kcal/mol which is even lower than the least active compounds (3, 6b) and almost half of the predicted activity of the most active compounds (2, 6k).

Table 3.
Calculated XP scores, and experimental IC50 (µM) for compounds 2, 3, 4, 6b, 6g, and 6k.
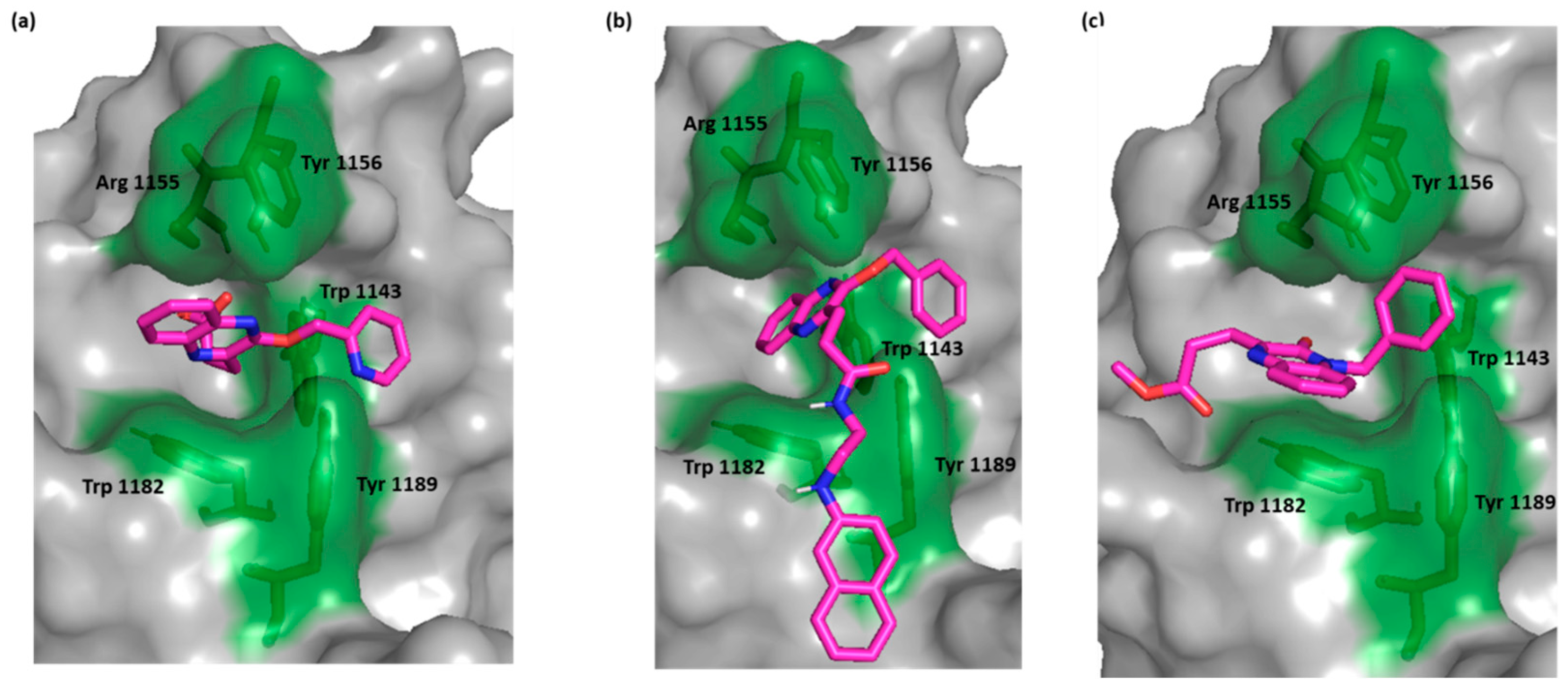
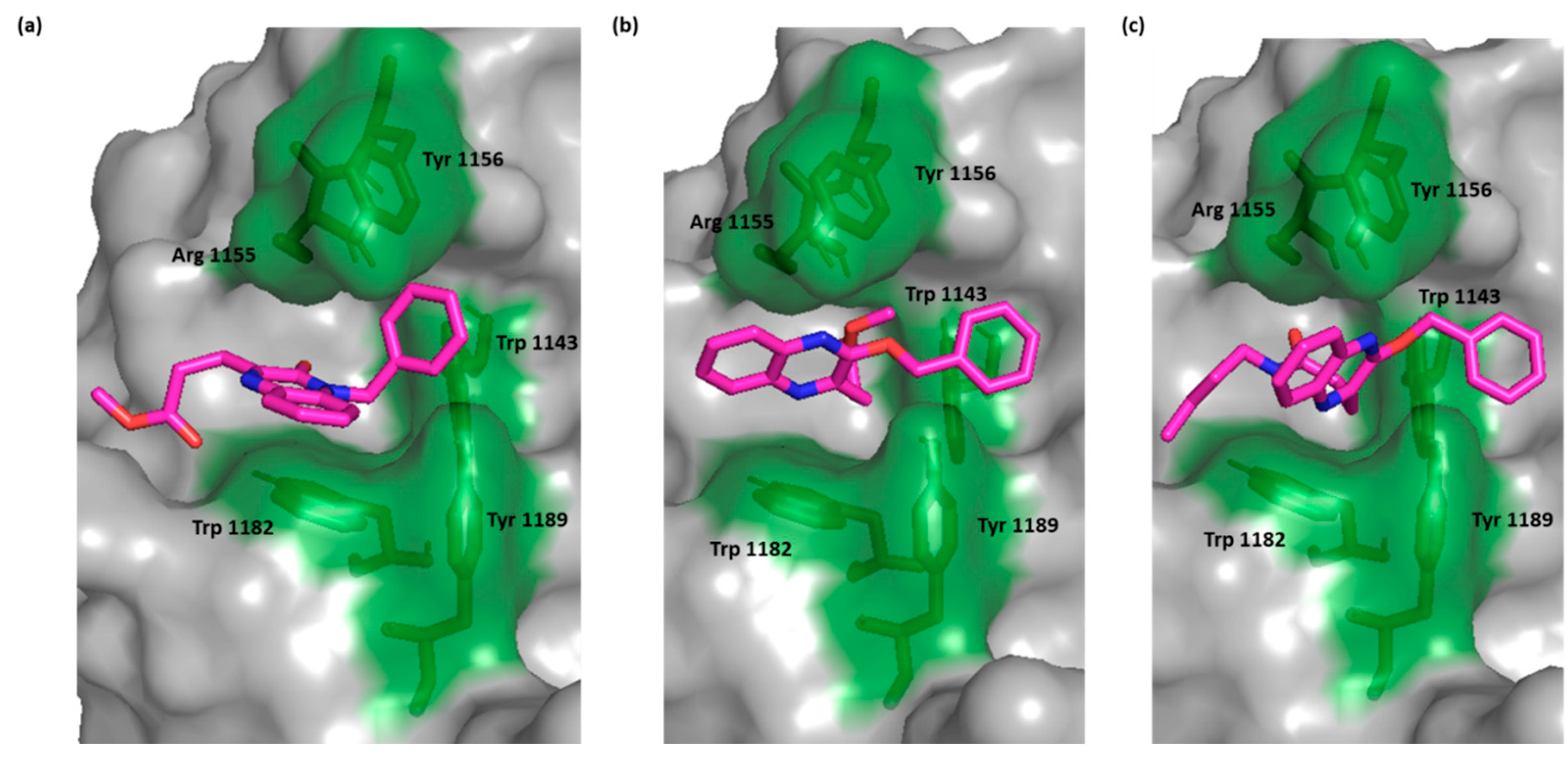
For the most active compounds, 4 and 6k, and similar to the crystal ligand, the compounds docked in the deep cavity pocket which normally accommodates the C-terminal residues of the C-terminal end of ubiquitin. For these compounds, the quinoxaline ring lay between Arg 1155 and Trp 1182 and established π-π stacking with Trp 1182. In the crystal ligand, a carboxylate group moved deeper into the cavity and formed a H bond with Arg 1155. This interaction was lacking in both compounds 6k and 4 suggesting that the π-π stacking with Trp 1182 is more important than binding Arg 1155. The most active compound, as with the crystal ligand, was able to extend its benzyloxy group into the adjacent juxtaposed pocket and binds Trp 1143 (Figure 2).
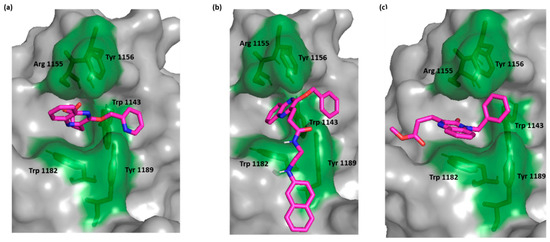
Figure 2.
Surface representation of HDAC-6 (PDB IDs: 5WPB) binding site, showing key interacting residues in green sticks and bound to (a) crystal ligand, (b) compound 6k, and (c) compound 4.
Compound 2, a moderately active compound performed π-π stacking with Trp 1182 while, the low active compounds, 3 and 6b, lacked this interaction while maintaining interaction with Trp 1143. This finding emphasized the importance of Trp 1182 as a crucial residue in binding the HDAC6 Zf-UBD binding site and through π interaction (Figure 3).
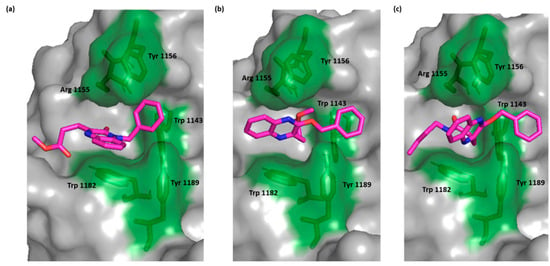
Figure 3.
Surface representation of HDAC-6 (PDB IDs: 5WPB) binding site showing key interacting residues in green sticks and bound to (a) compound 2, (b) compound 3, (c) compound 6b (green).
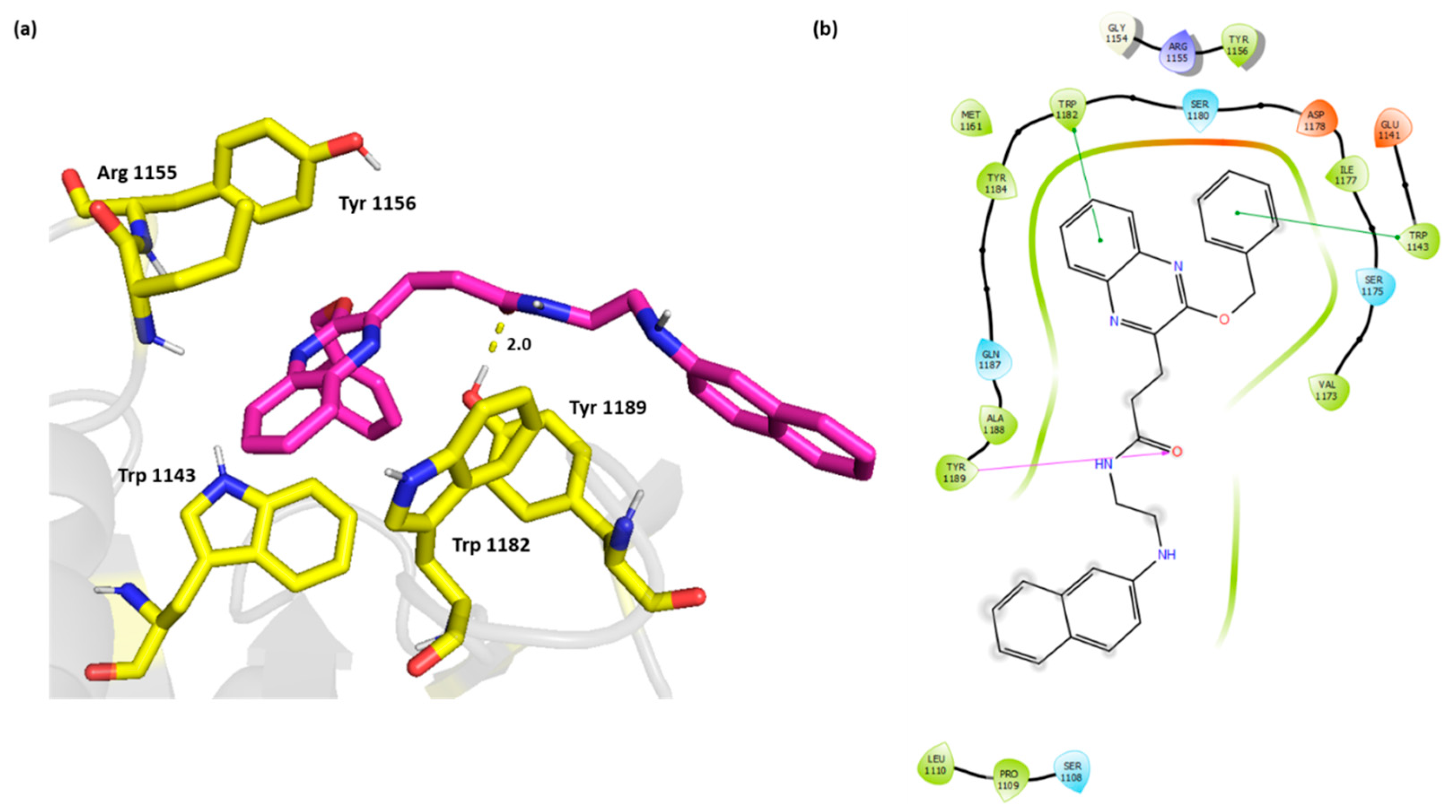
The 2D and 3D overlay of compound 6k is represented in Figure 4 On top of the π-π stacking with Trp 1182, and Trp 1143, the compound was able to bind Tyr 1189 through H bond. The naphthyl aminoethyl chain protruded outside the cavity and formed van der Waals interactions with Ser 1108, Pro 1109, and Leu 1110.
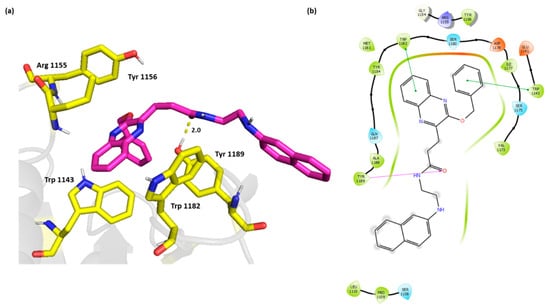
Figure 4.
(a) Three-dimensional representation of the binding interactions between compound 6k as sticks (carbon atoms in magenta), and HDAC-6 (PDB IDs: 5WPB) binding site shown as sticks (carbon atom in yellow). Potential electrostatic interactions are represented as yellow dotted lines and are measured in Angstrom. (b) Two-dimensional ligand–protein binding interactions between compound 6k and HDAC-6 (PDB IDs: 5WPB) binding site. H bonds are represented as purple lines and π-π stacking as green lines.
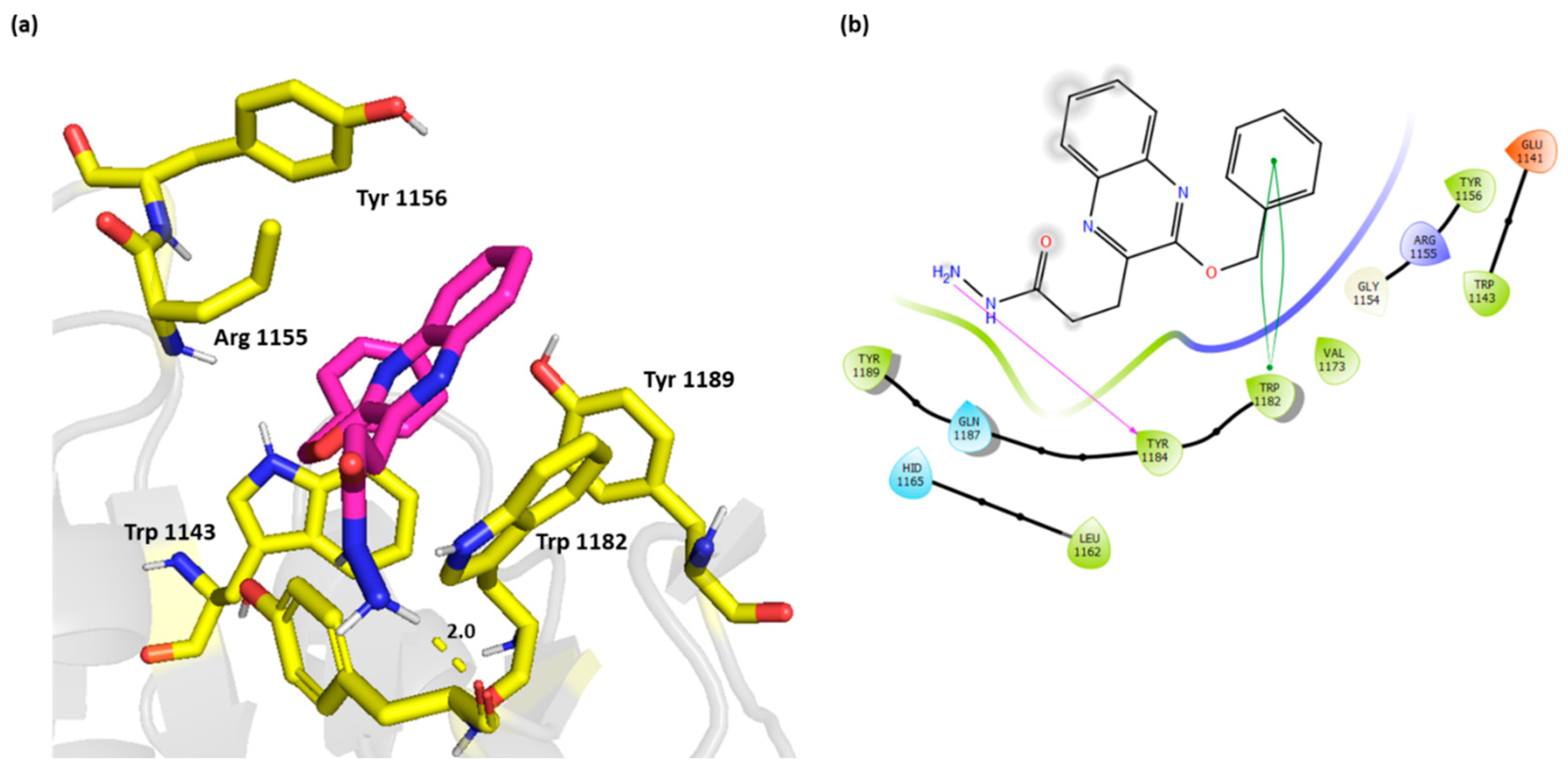
Compound 4 on the other hand did not exhibit the π-π stacking with Trp 1143, however, it interacted with Tyr 1184 through H bond. This active compound showed a strong π-π interaction with Trp 1182 (Figure 5).
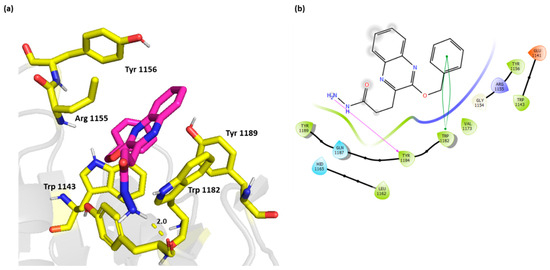
Figure 5.
(a) Three-dimensional representation of the binding interactions between compound 4 as sticks (carbon atoms in magenta), and HDAC-6 (PDB IDs: 5WPB) binding site shown as sticks (carbon atom in yellow). Potential electrostatic interactions are represented as yellow dotted lines and are measured in Angstrom. (b) Two-dimensional ligand–protein binding interactions between compound 4 and HDAC-6 (PDB IDs: 5WPB) binding site. H bonds are represented as purple lines and π-π stacking as green lines.
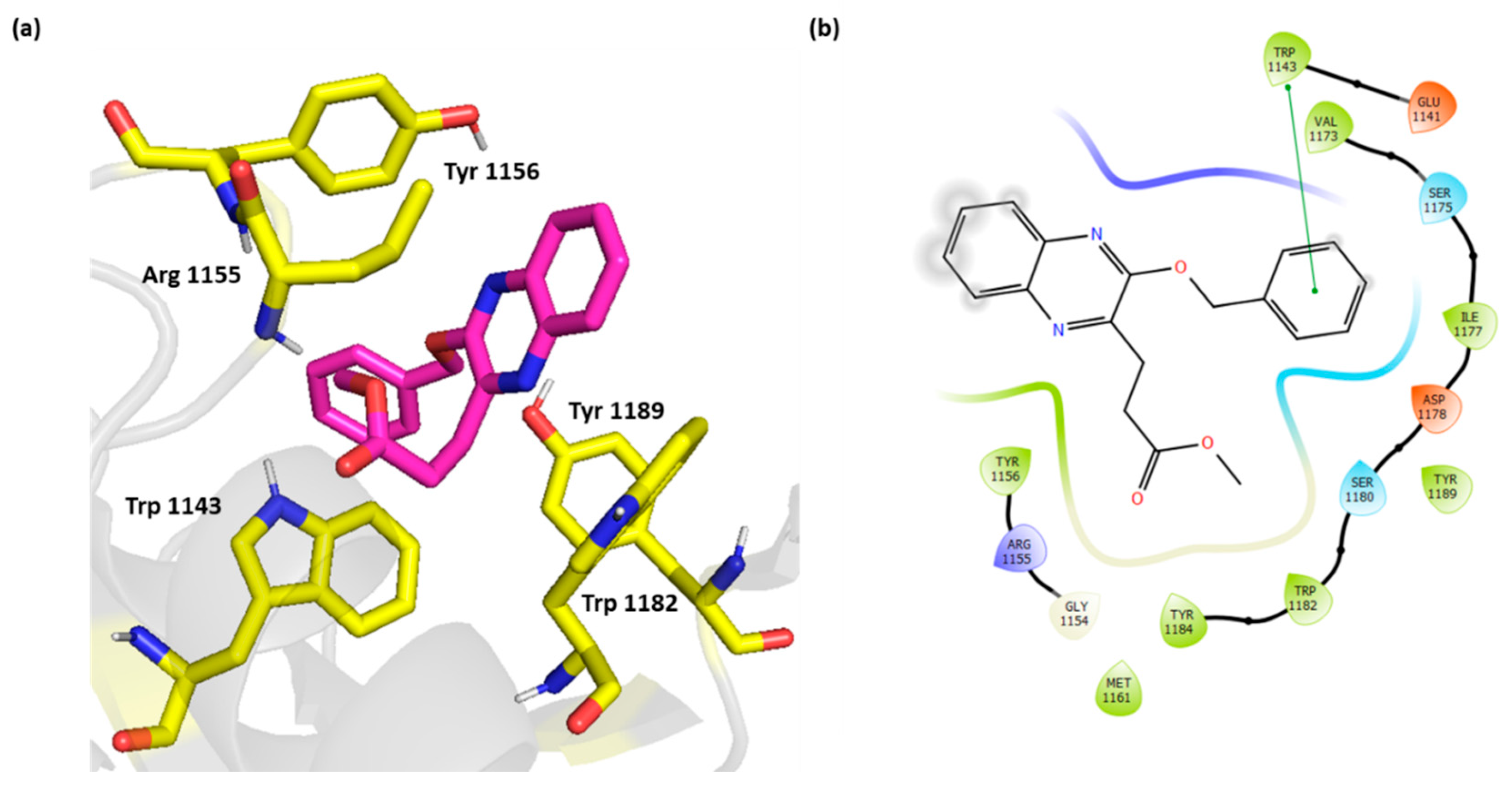
The weakly active compound 3 showed only π-π stacking with its benzyloxy group and Trp 1143 with no additional electrostatic interactions (Figure 6).
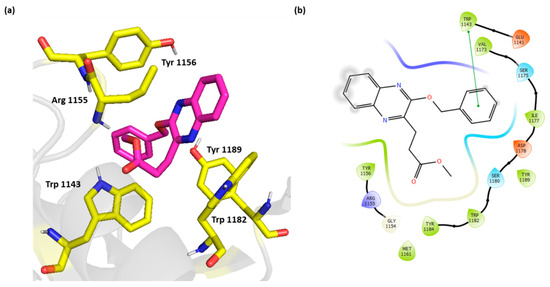
Figure 6.
(a) Three-dimensional representation of the binding interactions between compound 3 as sticks (carbon atoms in magenta), and HDAC-6 (PDB IDs: 5WPB) binding site shown as sticks (carbon atom in yellow). Potential electrostatic interactions are represented as yellow dotted lines and are measured in Angstrom. (b) Two-dimensional ligand–protein binding interactions between compound 3 and HDAC-6 (PDB IDs: 5WPB) binding site. π-π stacking are represented as green lines.
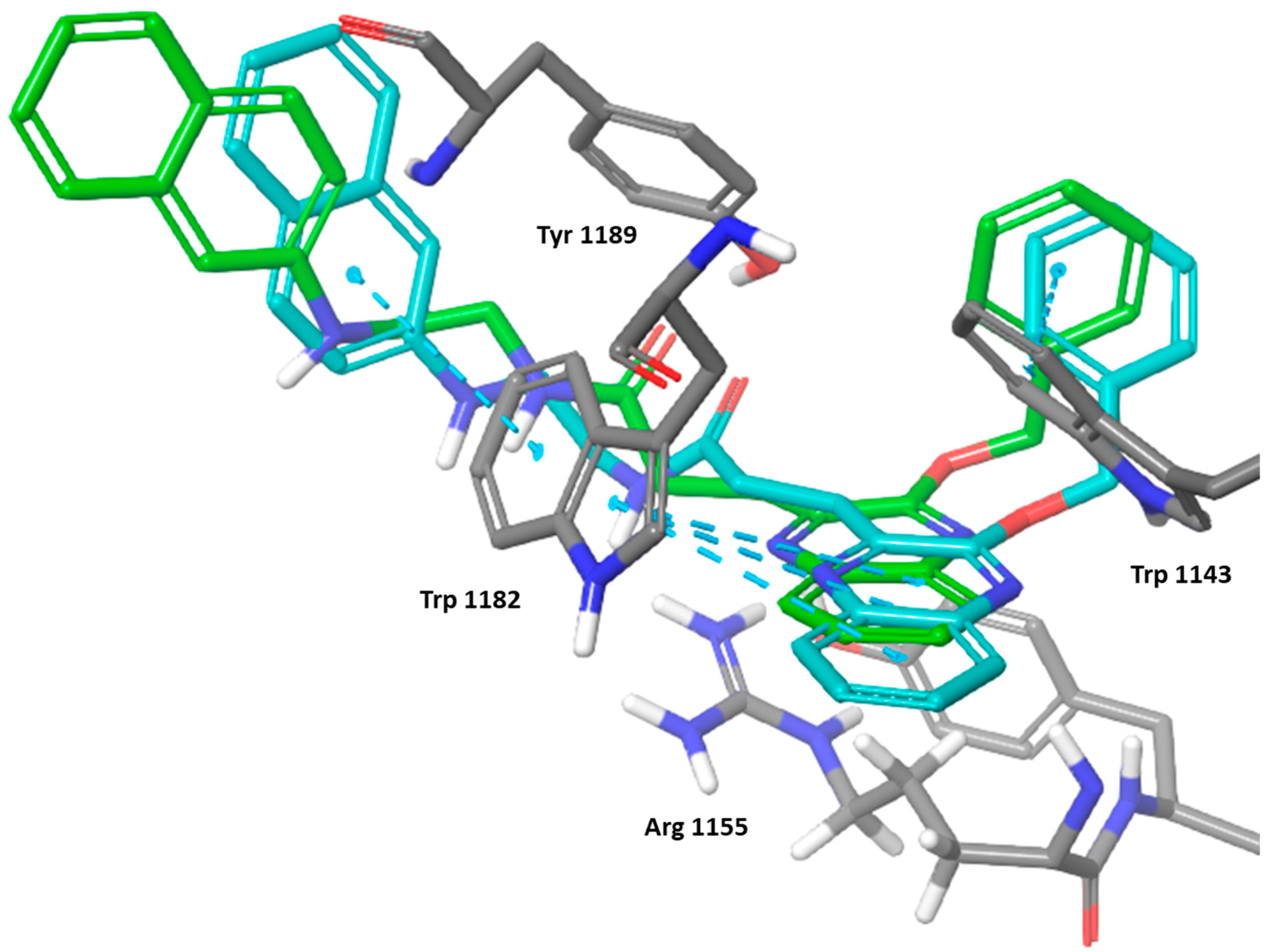
The induced fit docking for the most active compound 6k showed an induced fit that strengthened the π-π stacking with Trp 1182 and Trp 1143 as well as potental hydrogen bonding with Arg 1155 (Figure 7). The IDF score was found to be −192.83 indicating a highly favorable binding interaction.
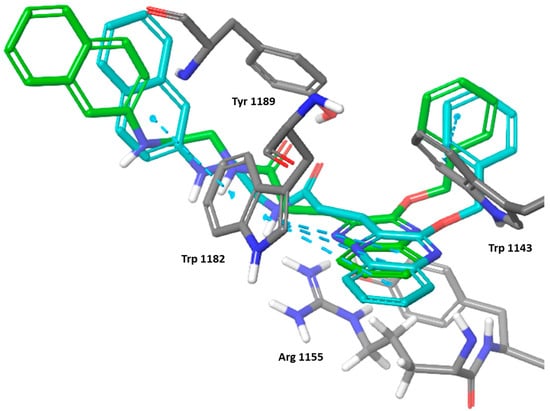
Figure 7.
Three-dimensional representation of the binding interactions between compound 6k; induced fit pose as sticks (carbon atoms in cyan), XP docking pose as sticks (carbon atoms in green), and HDAC-6 (PDB IDs: 5WPB) binding site shown as sticks (carbon atom in gray). π-π stacking are represented as dashed lines.
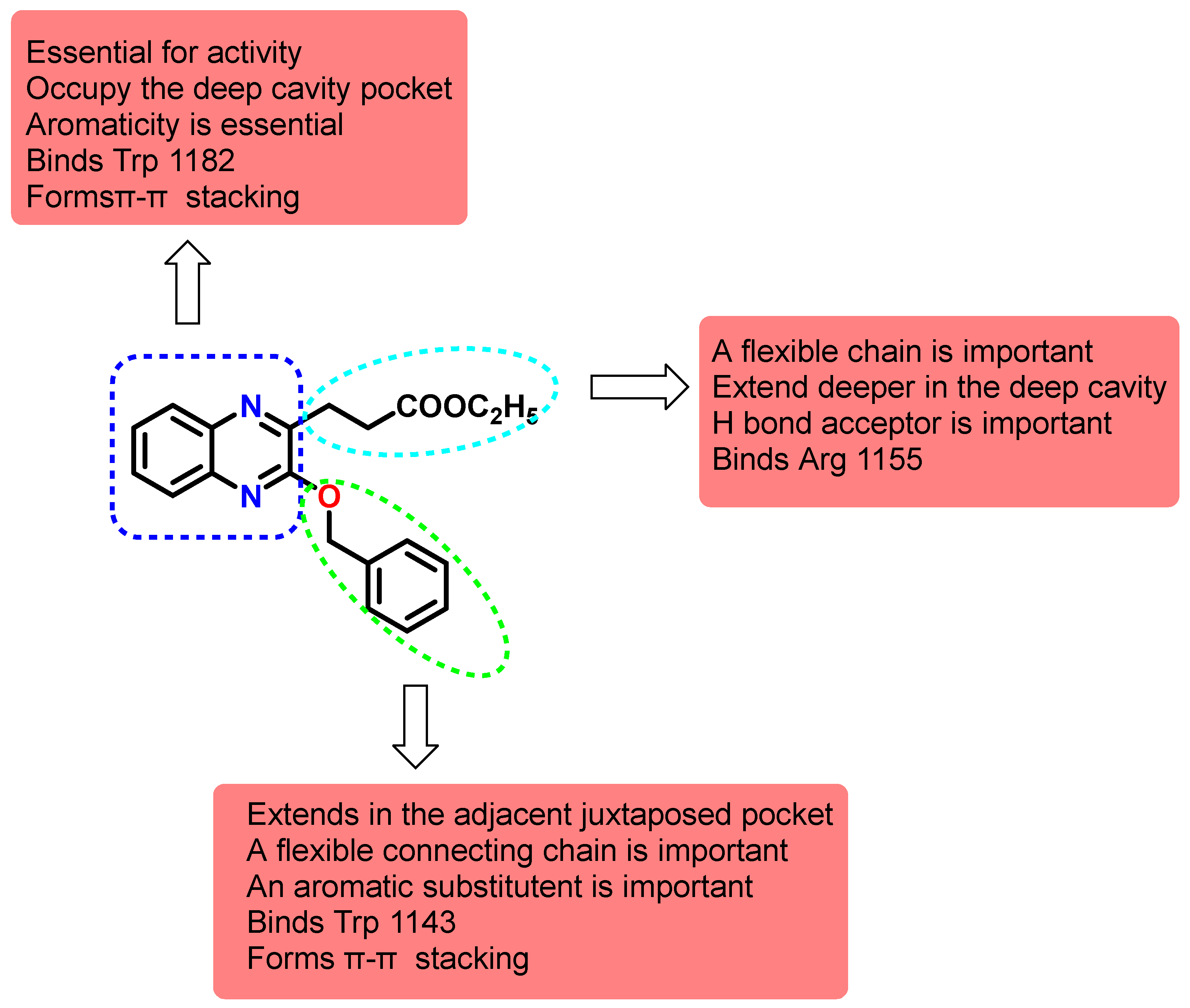
A more conclusive structure activity relationship was depicted after the docking studies. The quinoxaline ring with its aromaticity is essential for activity to bind the key residues Trp 1182 through π-π stacking. Nevertheless, the importance of the heterocyclic nitrogen was not concluded which provided the potential for other heterocycles and benzoheterocycles. The substitution in the 2 and 3 positions are important to fulfil the other binding requirements that confer potency and selectivity for the compounds. Although the benzyloxy did not seem to be crucial since the oxygen is not involved in binding, importantly, the arylalkyl substituent should extend into the adjacent cavity and bind Trp 1143 through π-π stacking. The second substituent should bear a flexible chain to extend deeply into the cavity and H bond acceptor preferably a carboxylate that binds Arg 1155 through the H bonds or more strongly with a salt bridge (Figure 8).
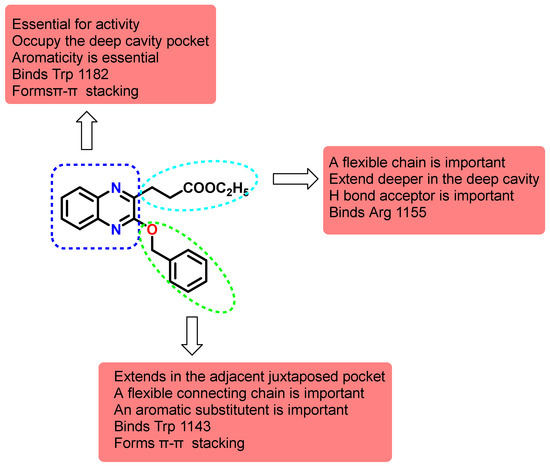
Figure 8.
Structure activity relationship map of synthesized quinoxalines on HDAC6 Zf-UBD binding site.
In conclusion, the synthesized quinoxaline derivatives showed good in silico inhibitory activity to HDAC-6 through binding to the HDAC6 Zf-UBD binding site. The compounds represent initial leads that could be further optimized for binding and preclinical development. Future optimization should rely on design molecules that are tailored to occupy the ubiquitin cavity with the quinoxaline ring that binds to Trp 1182 and that bears two substituents one that would extend deeper into the cavity to bind Arg 1155 and another one with an aromatic system that would extend into the adjacent pocket and binds Trp 1143.
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Chemistry
3.1.1. General Procedures
All chemicals were obtained from Sigma-Aldrich., solvent were purified and dried in the usual way. Thin layer chromatography (TLC): silica gel 60 F254 plastic plates (E. Merck, layer thickness 0.2 mm) detected by UV absorption. Elemental analyses were performed on a Carlo Erba analyzer model 110 (Carlo Erba Instruments, Milan, Italy). Melting points were measured using a Stuart SMP10 digital melting point apparatus (Cole-Parmer Ltd., Stone, UK) and are reported without correction. 1H and 13C NMR spectra were recorded at 400 MHz, respectively (JEOL RESONANCE) in CDCl3 and DMSO solution with tetramethylsilane as an internal standard. The mass spectra were measured with a KRATOS analytical compact; on MALDI-MS the spectrometer was using 2,5-dihydroxybenzoic acid (DHB) as matrix. Methyl 3-(3-oxo-3,4-dihydroquinoxalin-2-yl) propanoate (1) was prepared according to reported literature [31,32].
3.1.2. General Procedure for Alkylation of Methyl 3-(3-Oxo-3,4-dihydroquinoxalin-2-yl)propanoate (1)
Potassium carbonate (3.1 g, 22.5 mmol) and benzyl chloride (3.7 mL, 30 mmol) were added subsequently to a solution of methyl 3-(3-oxo-3,4-dihydroquinoxalin-2-yl) propanoate (1) (3.1 g, 22.5 mmol) in acetone (30 mL). For 12 h, the reaction mixture was heated to 56 °C. After the reaction mixture was filtered out, the filtrate was evaporated under reduced pressure, and the oily residue was column chromatographed using ethyl acetate: petroleum ether (3:1) as an eluent. This allowed for the eventual excellent yields of N- and O-allyl quinoxaline 2 and 3, respectively.
Methyl 3-(4-Benzyl-3-oxo-3,4-dihydroquinoxalin-2-yl)propanoate (2)
White crystals (76%), M.p.: 132–133 °C. 1H NMR spectrum, (400 MHz, CDCl3), δ, ppm (J, Hz): 2.74 (t, J = 7.2 Hz, 2H, CH2), 3.36 (t, J = 7.2 Hz, 2H, CH2CO), 3.73 (s, 3H, OCH3), 5.50 (s, 2H, NCH2), 7.23–7.33 (m, 7H, Ar-H), 7.38–7.42 (m, 1H, Ar-H), 7.79 (d, J = 8.0 Hz, 1H, Ar-H). 13C NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3), δ, ppm: 27.9 (CH2), 30.3 (CH2CO), 45.9 (NHCH2), 53.8 (OCH3), 126.5 (C-Ar), 126.8, 127.0, 128.1, 128.5, 128.6, 128.7, 129.1, 136.6, 138.6, 139.8 (C-Ar), 148.8 (C=N), 155.5 (C=O), 173.4 (C=O). MS (MALDI, positive mode, matrix DHB): m/z = 345.3 (M + Na)+. Anal. Calcd. For C19H18N2O3 (322.37): C, 70.79; H, 5.63; N, 8.69. Found: C, 71.05; H, 5.41; N, 8.98.
Methyl 3-(3-Benzyloxyquinoxalin-2-yl)propanoate (3)
White crystals (63%), M.p.: 85–86 °C. 1H NMR spectrum, (400 MHz, CDCl3), δ, ppm (J, Hz): 2.98 (t, J = 7.2 Hz, 2 H, CH2), 3.38 (t, J = 7.2 Hz, 2 H, CH2CO), 3.75 (s, 3 H, OCH3), 5.61 (s, 2 H, OCH2), 7.36–7.47 (m, 3 H, Ar-H), 7.53–7.59 (m, 3 H, Ar-H), 7.65 (t, J = 8.0 Hz, 1 H, Ar-H), 7.83 (d, J = 8.0 Hz, 1 H, Ar-H), 7.98 (d, J = 8.0 Hz, 1 H, Ar-H). 13C NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3), δ, ppm: 27.1 (CH2), 30.7 (CH2CO), 51.3 (OCH3), 68.9 (OCH2), 126.5, 126.8, 126.9, 128.1, 128.5, 128.6, 128.7, 129.1, 136.6, 138.6, 139.8 (C-Ar), 148.2 (C=N), 155.6 (C=N), 173.7 (C=O). MS (MALDI, positive mode, matrix DHB): m/z = 345.3 (M + Na)+. Anal. Calcd. For C19H18N2O3 (322.1): C, 70.79; H, 5.63; N, 8.69. Found: C, 70.53; H, 5.83; N, 8.61.
3.1.3. Preparation of 3-(3-Benzyloxyquinoxalin-2-yl)propanhydrazide (4)
After adding hydrazine hydrate (60%) (0.2 mL, 2.0 mmol) to a solution of methyl 3-(3-benzyloxyquinoxalin-2-yl) propanoate (3) (1.0 mmol) in ethyl alcohol 95% (15 mL), the reaction mixture was refluxed for 4 h, refrigerated for 12 h, and the resulting crystals were filtered and crystallized from ethanol 95% to yield 4.
White crystals (87%), M.p.: 171–173 °C. 1H NMR spectrum, (400 MHz, DMSO), δ, ppm (J, Hz): 2.99 (t, J = 7.2 Hz, 2 H, CH2), 3.37 (t, J = 7.2 Hz, 2 H, CH2CO), 4.22 (bs, 2 H, NH2), 5.61 (s, 2 H, OCH2), 7.39–7.49 (m, 3 H, Ar-H), 7.55–7.59 (m, 3 H, Ar-H), 7.65 (t, J = 8.0 Hz, 1 H, Ar-H), 7.89 (d, J = 8.0 Hz, 1 H, Ar-H), 8.00 (d, J = 8.0 Hz, 1 H, Ar-H), 9.18 (bs, 1 H, NH). 13C NMR (400 MHz, DMSO), δ, ppm: 27.9 (CH2), 30.8 (CH2CO), 68.1 (OCH2), 126.5, 126.8, 126.9, 128.1, 128.6, 128.8, 128.9, 129.1, 136.6, 138.8, 139.7 (C-Ar), 148.7 (C=N), 155.6 (C=N), 170.5 (C=O). MS (MALDI, positive mode, matrix DHB): m/z = 345.3 (M + Na)+. Anal. Calcd. For C18H18N4O2 (322.37): C, 67.07; H, 5.63; N, 17.38. Found: C, 66.85; H, 5.43; N, 17.71.
3.1.4. Preparation of N-Alkyl 3-(3-Benzyloxyquinoxalin-2-yl)propanamide 6a–k
AcOH (6 mL), 1 N HCl (3 mL), and water (3 mL) were added to 3-(3-benzyloxyquinoxalin-2-yl) propanhydrazide (4) (1.0 g, 10.0 mmol) to create a slurry, which was then cooled to −5 °C for 15 min. A cold solution of NaNO2 (1.0 g, 15 mmol) in water (2.0 mL) was added to the slurry portion-wise for 20 min, resulting in a yellow syrup that was extracted multiple times using cold ethyl acetate (30 mL). The combined extracts were then rinsed with cold 3% NaHCO3, H2O, and finally dried (Na2SO4) to produce the in-situ generated ethyl acetate solution of azide 5. Propyl amine, butyl amine, isopropyl amine, allyl amine, benzyl amine, cyclohexyl amine, diethyl amine, morpholine, piperidine, pyrrolidine and N1-(naphthalen-2-yl)ethane-1,2-diamine (10.0 mmol) were added to cold ethyl acetate solution of azide 5 and the reaction mixture was kept at −5 °C for 24 h. The reaction mixture was then washed with 1 N HCl, followed by a 3% solution of NaHCO3, H2O, and finally dried over (Na2SO4). The reaction mixture was evaporated under reduced pressure until it was completely dry, and the residue was crystallized with petroleum ether/ethyl acetate to yield the desired products 6a–k in high yields.
3-(3-Benzyloxyquinoxalin-2-yl)-N-propyl-propanamide (6a)
From n-propyl amine with 3-(3-benzyloxyquinoxalin-2-yl)propanoyl azide (5). White crystals (76%), M.p.: 101–103 °C. 1H NMR spectrum, (400 MHz, CDCl3), δ, ppm (J, Hz): 0.87–0.93 (m, 3 H, CH3), 1.45–1.54 (m, 2 H, CH2), 2.81 (t, J = 7.2 Hz, 2 H, CH2), 3.21 (q, J = 7.2 Hz, 2 H, NHCH2), 3.35 (t, J = 7.2 Hz, 2 H, CH2CO), 5.57 (s, 2 H, OCH2), 6.30 (bs, 1 H, NH), 7.33–7.42 (m, 3 H, Ar-H), 7.50–7.59 (m, 3 H, Ar-H), 7.63 (t, J = 8.0 Hz, 1 H, Ar-H), 7.85 (d, J = 8.0 Hz, 1 H, Ar-H), 7.93 (d, J = 8.0 Hz, 1 H, Ar-H). 13C NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3), δ, ppm: 14.2 (CH3), 23.1 (CH2), 27.9 (CH2), 27.9 (CH2), 30.7 (CH2CO), 40.2 (NHCH2), 68.1 (OCH2), 126.4, 126.8, 126.9, 128.1, 128.4, 128.6, 128.7, 129.1, 136.6, 138.6, 139.8 (C-Ar), 148.3 (C=N), 155.6 (C=N), 173.7 (C=O). MS (MALDI, positive mode, matrix DHB): m/z = 372.4 (M + Na)+. Anal. Calcd. For C21H23N3O2 (349.43): C, 72.18; H, 6.63; N, 12.03. Found: C, 72.11; H, 6.84; N, 11.86.
3-(3-Benzyloxyquinoxalin-2-yl)-N-butyl-propanamide (6b)
From butyl amine with 3-(3-(benzyloxyquinoxalin-2-yl)propanoyl azide (5). White crystals (91%), M.p.: 85–86 °C. 1H NMR spectrum, (400 MHz, CDCl3), δ, ppm (J, Hz): 0.89 (t, J = 7.2 Hz, 3 H, CH3), 1.09–1.13 (m, 2 H, CH2), 1.31–1.36 (m, 2 H, CH2), 2.65 (t, J = 7.2 Hz, 2H, CH2), 3.15–3.22 (m, 4 H, NHCH2, CH2CO), 5.40 (s, 2 H, OCH2), 6.30 (bs, 1 H, NH), 7.14–7.24 (m, 3 H, Ar-H), 7.34–7.37 (m, 3 H, Ar-H), 7.49 (t, J = 8.0 Hz, 1H, Ar-H), 7.67 (d, J = 8.0 Hz, 1H, Ar-H), 7.74 (d, J = 8.0 Hz, 1H, Ar-H). 13C NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3), δ, ppm: 14.2 (CH3), 19.9 (CH2), 27.9 (CH2), 30.3 (CH2CO), 34.9 (CH2), 43.4 (NHCH2), 68.1 (OCH2), 126.5, 126.8, 126.9, 128.1, 128.5, 128.6, 128.7, 129.1, 136.6, 138.6, 139.7 (C-Ar), 148.8 (C=N), 155.6 (C=N), 171.3 (C=O). MS (MALDI, positive mode, matrix DHB): m/z = 386.4 (M + Na)+. Anal. Calcd. For C22H25N3O2 (363.46): C, 72.70; H, 6.93; N, 11.56. Found: C, 73.03; H, 7.21; N, 11.76.
3-(3-Benzyloxyquinoxalin-2-yl)-N-isopropylpropanamide (6c)
From isopropyl amine with 3-(3-benzyloxyquinoxalin-2-yl)propanoyl azide (5). White crystals (67%), M.p.: 170–171 °C. 1H NMR spectrum, (400 MHz, CDCl3), δ, ppm (J, Hz): 1.02 (d, J = 6.0 Hz, 6 H, 2CH3), 2.68 (t, J = 7.2 Hz, 2 H, CH2), 3.27 (t, J = 7.2 Hz, 2 H, CH2CO), 3.92–4.00 (m, 1 H, NHCH), 5.48 (s, 2 H, OCH2), 6.00 (bs, 1 H, NH), 7.24–7.35 (m, 3 H, Ar-H), 7.44–7.48 (m, 3 H, Ar-H), 7.52–7.56 (m, 1 H, Ar-H), 7.78 (d, J = 8.0 Hz, 1 H, Ar-H), 7.86 (d, J = 8.0 Hz, 1 H, Ar-H). 13C NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3), δ, ppm: 23.1 (CH3), 27.9 (CH2), 30.3 (CH2CO), 48.7 (NHCH), 68.1 (OCH2), 126.5, 126.8, 126.9, 128.1, 128.5, 128.6, 128.7, 129.1, 136.7, 138.9, 139.7 (C-Ar), 148.8 (C=N), 155.6 (C=N), 172.5 (C=O). MS (MALDI, positive mode, matrix DHB): m/z = 372.4 (M + Na)+. Anal. Calcd. For C21H23N3O2 (349.43): C, 72.18; H, 6.63; N, 12.03. Found: C, 71.86; H, 6.85; N, 11.74.
N-Allyl-3-(3-(Benzyloxyquinoxalin-2-yl)propanamide (6d)
From allyl amine with 3-(3-benzyloxyquinoxalin-2-yl)propanoyl azide (5). White crystals (71%), M.p.: 67–68 °C. 1H NMR spectrum, (400 MHz, CDCl3), δ, ppm (J, Hz): 2.73 (t, J = 7.2 Hz, 2 H, CH2), 3.25 (t, J = 7.2 Hz, 2 H, CH2CO), 3.78 (t, J = 7.2 Hz, 2 H, NHCH2), 4.96–5.09 (m, 2 H, CH2=CH), 5.45 (s, 2 H, OCH2), 5.67–5.74 (m, 1 H, CH2=CH), 6.27 (bs, 1 H, NH), 7.23–7.32 (m, 3 H, Ar-H), 7.40–7.45 (m, 3 H, Ar-H), 7.53 (t, J = 8.0 Hz, 1 H, Ar-H), 7.76 (d, J = 8.0 Hz, 1 H, Ar-H), 7.89 (d, J = 8.0 Hz, 1 H, Ar-H). 13C NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3), δ, ppm: 27.9 (CH2), 30.3 (CH2CO), 45.0 (NHCH2), 68.1 (OCH2), 115.8 (CH2), 126.5, 126.8, 126.9, 128.1, 128.5, 128.6, 128.7, 129.1 (C-Ar), 135.4 (CH), 136.6, 138.7, 139.8 (C-Ar), 148.8 (C=N), 155.6 (C=N), 172.3 (C=O). MS (MALDI, positive mode, matrix DHB): m/z = 370.4 (M + Na)+. Anal. Calcd. For C21H21N3O2 (347.42): C, 72.60; H, 6.09; N, 12.10. Found: C, 72.87; H, 5.85; N, 11.92.
N-Benzyl-3-(3-Benzyloxyquinoxalin-2-yl)propanamide (6e)
From benzyl amine with 3-(3-benzyloxyquinoxalin-2-yl)propanoyl azide (5). White crystals (82%), M.p.: 122–123 °C. 1H NMR spectrum, (400 MHz, CDCl3), δ, ppm (J, Hz): 2.76 (t, J = 7.2 Hz, 2 H, CH2), 3.28 (t, J = 7.2 Hz, 2 H, CH2CO), 4.34 (d, J = 7.2 Hz, 2 H, NHCH2), 5.48 (s, 2 H, OCH2), 6.39 (bs, 1 H, NH), 7.21–7.35 (m, 4 H, Ar-H), 7.42–7.47 (m, 4 H, Ar-H), 7.52 (t, J = 8.0 Hz, 2 H, Ar-H), 7.74 (d, J = 8.0 Hz, 2 H, Ar-H), 7.86 (d, J = 8.0 Hz, 2 H, Ar-H). 13C NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3), δ, ppm: 27.9 (CH2), 30.3 (CH2CO), 45.9 (NHCH2), 68.1 (OCH2), 126.5, 126.8, 126.9, 127.4, 128.1, 128.5, 128.6, 128.7, 129.1, 129.4, 136.6, 137.1, 138.6, 139.8 (C-Ar), 148.9 (C=N), 155.6 (C=N), 172.9 (C=O). MS (MALDI, positive mode, matrix DHB): m/z = 420.4 (M + Na)+. Anal. Calcd. For C25H23N3O2 (397.48): C, 75.55; H, 5.83; N, 10.57. Found: C, 75.32; H, 6.03; N, 10.74.
3-(3-Benzyloxyquinoxalin-2-yl)-N-cyclohexylpropanamide (6f)
From cyclohexyl amine with 3-(3-benzyloxyquinoxalin-2-yl)propanoyl azide (5). White crystals (66%), M.p.: 81–83 °C. 1H NMR spectrum, (400 MHz, CDCl3), δ, ppm (J, Hz): 1.18–1.30 (m, 2 H, CH2), 1.59–1.64 (m, 4 H, 2CH2), 1.79–1.85 (m, 4 H, 2CH2), 2.70 (t, J = 7.2 Hz, 2 H, CH2), 3.27 (t, J = 7.2 Hz, 2 H, CH2CO), 3.56–3.67 (m, 1 H, NHCH), 5.49 (s, 2 H, OCH2), 6.22 (bs, 1 H, NH), 7.24–7.35 (m, 3 H, Ar-H), 7.39–7.49 (m, 3 H, Ar-H), 7.53 (t, J = 8.0 Hz, 1 H, Ar-H), 7.76 (d, J = 8.0 Hz, 1 H, Ar-H), 7.84 (d, J = 8.0 Hz, 1 H, Ar-H). 13C NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3), δ, ppm: 23.1 (CH2), 25.3 (CH2), 27.8 (CH2), 30.3 (CH2CO), 32.8 (CH2), 53.8 (NHCH), 68.1 (OCH2), 126.5, 126.8, 126.9, 128.1, 128.5, 128.6, 128.7, 129.1 (C-Ar), 136.6, 138.6, 139.8 (C-Ar), 148.9 (C=N), 155.7 (C=N), 172.8 (C=O). MS (MALDI, positive mode, matrix DHB): m/z = 412.5 (M + Na)+. Anal. Calcd. For C24H27N3O2 (389.2): C, 74.01; H, 6.99; N, 10.79. Found: C, 73.79; H, 7.21; N, 10.98.
3-(3-Benzyloxyquinoxalin-2-yl)-N,N-diethylpropanamide (6g)
From diethyl amine with 3-(3-benzyloxyquinoxalin-2-yl)propanoyl azide (5). White crystals (77%), M.p.: 96–97 °C. 1H NMR spectrum, (400 MHz, CDCl3), δ, ppm (J, Hz): 1.13 (t, J = 7.2 Hz, 3 H, CH3), 1.25 (t, J = 7.2 Hz, 3 H, CH3), 2.92 (t, J = 7.2 Hz, 2 H, CH2), 3.39–3.43 (m, 6 H, CH2CO, 2NCH2), 5.59 (s, 2 H, OCH2), 7.23–7.38 (m, 3 H, Ar-H), 7.49–7.56 (m, 4 H, Ar-H), 7.83 (d, J = 8.0 Hz, 1 H, Ar-H), 7.97 (d, J = 8.0 Hz, 1 H, Ar-H). 13C NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3), δ, ppm: 14.2 (2CH3), 27.9 (CH2), 30.3 (CH2CO), 45.0 (2NCH2), 68.1 (OCH2), 126.5, 126.8, 126.9, 128.1, 128.5, 128.6, 128.7, 129.1, 136.6, 138.7, 139.7 (C-Ar), 148.8 (C=N), 155.7 (C=N), 172.6 (C=O). MS (MALDI, positive mode, matrix DHB): m/z = 386.4 (M + Na)+. Anal. Calcd. For C22H25N3O2 (363.46): C, 72.70; H, 6.93; N, 11.56. Found: C, 72.43; H,7.23; N, 11.69.
3-(3-Benzyloxyquinoxalin-2-yl)-1-morpholin-4-yl-propan-1-one (6h)
From morpholine with 3-(3-benzyloxyquinoxalin-2-yl)propanoyl azide (5). White crystals (64%), M.p.: 86–87 °C. 1H NMR spectrum, (400 MHz, CDCl3), δ, ppm (J, Hz): 2.89 (t, J = 7.2 Hz, 2 H, CH2), 3.36 (t, J = 7.2 Hz, 2 H, CH2CO), 3.47–3.72 (m, 8 H, 2OCH2, 2NCH2), 5.58 (s, 2 H, OCH2), 7.24–7.41 (m, 3 H, Ar-H), 7.50–7.58 (m, 3 H, Ar-H), 7.61 (t, J = 8.0 Hz, 1H, Ar-H), 7.83 (d, J = 8.0 Hz, 1H, Ar-H), 7.97 (d, J = 8.0 Hz, 1H, Ar-H). 13C NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3), δ, ppm: 27.9 (CH2), 30.8 (CH2CO), 46.3 (2NCH2), 65.1 (2OCH2), 68.1 (OCH2), 126.5, 126.6, 126.9, 128.1, 128.5, 128.6, 128.9, 129.1, 136.6, 138.7, 139.8 (C-Ar), 148.8 (C=N), 155.5 (C=N), 172.6 (C=O). MS (MALDI, positive mode, matrix DHB): m/z = 400.4 (M + Na)+. Anal. Calcd. For C22H23N3O3 (377.44): C, 70.01; H, 6.14; N, 11.13. Found: C, 69.81; H, 6.43; N, 10.88.
3-(3-Benzyloxyquinoxalin-2-yl)-1-piperidin-1-yl-propan-1-one (6i)
From piperidine with 3-(3-benzyloxyquinoxalin-2-yl)propanoyl azide (5). White crystals (56%), M.p.: 74–75 °C. 1H NMR spectrum, (400 MHz, CDCl3), δ, ppm (J, Hz): 1.23–1.30 (m, 2 H, CH2), 1.52–1.67 (m, 4 H, 2CH2), 2.91 (t, J = 7.2 Hz, 2 H, CH2), 3.36 (t, J = 7.2 Hz, 2 H, CH2CO), 3.47–3.58 (m, 4 H, 2NCH2), 5.58 (s, 2 H, OCH2), 7.21–7.41 (m, 3 H, Ar-H), 7.50–7.56 (m, 3 H, Ar-H), 7.61 (t, J = 8.0 Hz, 1 H, Ar-H), 7.84 (d, J = 8.0 Hz, 1 H, Ar-H), 7.96 (d, J = 8.0 Hz, 1 H, Ar-H). 13C NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3), δ, ppm: 21.4 (CH2), 25.4 (CH2), 27.9 (CH2), 30.3 (CH2CO), 46.3 (2NCH2), 68.1 (OCH2), 126.5, 126.8, 126.9, 128.1, 128.5, 128.6, 128.7, 129.1, 136.6, 138.7, 139.8 (C-Ar), 148.8 (C=N), 155.9 (C=N), 172.4 (C=O). MS (MALDI, positive mode, matrix DHB): m/z = 398.4 (M + Na)+. Anal. Calcd. For C23H25N3O2 (375.47): C, 73.57; H, 6.71; N, 11.19. Found: C, 73.22; H, 6.43; N, 10.78.
3-(3-Benzyloxyquinoxalin-2-yl)-1-(pyrrolidin-1-yl)propan-1-one (6j)
From pyrrolidine with 3-(3-benzyloxyquinoxalin-2-yl)propanoyl azide (5). White crystals (74%), M.p.: 67–68 °C. 1H NMR spectrum, (400 MHz, CDCl3), δ, ppm (J, Hz): 1.74 (t, J = 7.2 Hz, 2 H, CH2), 1.84 (t, J = 7.2 Hz, 2 H, CH2), 2.75 (t, J = 7.2 Hz, 2 H, CH2), 3.28 (t, J = 7.2 Hz, 2 H, NCH2), 3.36 (t, J = 7.2 Hz, 2 H, CH2CO), 3.42 (t, J = 7.2 Hz, 2 H, NCH2), 5.45 (s, 2 H, OCH2), 7.20–7.39 (m, 3 H, Ar-H), 7.40–7.51 (m, 4 H, Ar-H), 7.75 (d, J = 8.0 Hz, 1 H, Ar-H), 7.87 (d, J = 8.0 Hz, 1 H, Ar-H). 13C NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3), δ, ppm: 26.2 (2CH2), 27.9 (CH2), 30.3 (CH2CO), 48.7 (2NCH2), 68.1 (OCH2), 126.5, 126.8, 126.9, 128.1, 128.5, 128.6, 128.7, 129.1, 136.7, 138.7, 139.8 (C-Ar), 148.8 (C=N), 155.9 (C=N), 171.3 (C=O). MS (MALDI, positive mode, matrix DHB): m/z = 384.4 (M + Na)+. Anal. Calcd. For C22H23N3O2 (361.44): C, 73.11; H, 6.41; N, 11.63. Found: C, 73.53; H, 6.21; N, 11.82.
3-(3-Benzyloxyquinoxalin-2-yl)-N-(2-(naphthalen-2-ylamino)ethyl)propanamide (6k)
From N1-(naphthalen-2-yl)ethane-1,2-diamine with 3-(3-benzyloxyquinoxalin-2-yl)-propanoyl azide (5). White crystals (71%), M.p.: 148–149 °C. 1H NMR spectrum, (400 MHz, CDCl3), δ, ppm (J, Hz): 2.76–3.79 (m, 2 H, CH2), 3.25–3.29 (m, 2 H, CH2CO), 3.57–3.65 (m, 4 H, 2 NHCH2), 5.49 (s, 2 H, OCH2), 6.32 (bs, 1 H, NH), 6.62 (bs, 1 H, NH), 7.08–7.32 (m, 9 H, Ar-H), 7.41–7.69 (m, 7 H, Ar-H). 13C NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3), δ, ppm: 27.9 (CH2), 30.3 (CH2CO), 40.2 (NHCH2), 43.4 (NHCH2), 68.1 (OCH2), 122.5, 123.7, 125.7, 126.5, 126.8, 126.9, 127.4, 127.7, 128.1, 128.5, 128.6, 128.7, 129.1, 129.4, 130.2, 131.6, 136.7, 138.6, 139.8, 142.9 (C-Ar), 148.8 (C=N), 155.5 (C=N), 170.8 (C=O). MS (MALDI, positive mode, matrix DHB): m/z = 499.5 (M + Na)+. Anal. Calcd. For C30H28N4O2 (476.58): C, 75.61; H, 5.92; N, 11.76. Found: C, 75.32; H, 6.22; N, 11.54.
3.2. Biological Studies
3.2.1. Cell Line
Human prostate cancer (PC3), Epitheliod Carcinoma Cervix cancer (Hela), Mammary gland breast cancer (MCF-7) and Colorectal carcinoma Colon cancer (HCT-116). The cell line was obtained from ATCC via Holding company for biological products and vaccines (VACSERA).
3.2.2. Reagents and Cell Viability Assay
The experimental materials included RPMI-1640 culture medium, MTT reagent, and dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO), all sourced from Sigma-Aldrich (St. Louis, MO, USA), along with fetal bovine serum (FBS) obtained from GIBCO (UK Paisley, UK). Doxorubicin was employed as the standard reference drug for evaluating anticancer activity. To assess the cytotoxic effects of the synthesized compounds, an MTT assay was performed on the previously described cell lines. This colorimetric technique depends on the enzymatic reduction of the yellow tetrazolium bromide (MTT) to a purple formazan product by mitochondrial dehydrogenase enzymes in viable cells. Cells were cultured in RPMI-1640 medium supplemented with 10% FBS, 100 U/mL of penicillin, and 100 µg/mL of streptomycin. They were incubated at 37 °C in a humidified environment containing 5% carbon dioxide. For the assay, cells were seeded into 96-well plates at a density of 1 × 104 cells per well and allowed to adhere for 48 h. Subsequently, they were treated with various concentrations of the test compounds and incubated for 24 h. Following treatment, 20 µL of MTT solution (5 mg/mL) was added to each well and the plates were incubated for an additional 4 h to allow for formazan crystal formation. After incubation, 100 µL of DMSO was added to each well to dissolve the formazan. The absorbance was measured at 570 nm using a microplate reader (EXL 800, BioTek Instruments, Winooski, VT, USA). Cell viability was the percentage of relative cell viability was determined by the equation: (A570 of treated cells/A570 of untreated control) × 100 [43,44].
3.3. Molecular Modeling and Docking
3.3.1. Software
The molecular modelling software Maestro by Schrödinger (Version 2024-4 software release) was used for computational studies [45].
3.3.2. Crystal Structures
The X-ray coordinates of HDAC-6 in complex with inhibitor in the zinc finger domain and Ubiquitin (PDB IDs: 5WPB) was obtained from the Research Collaboratory for Structural Bioinformatics (RCSB) Protein Data Bank (PDB) [46,47].
3.3.3. Protein Preparation
The PDB structures were optimized for docking via the Protein Preparation Workflow. The preparation and minimizing process occurred at a pH of 7.4, with adjustments made to the ionization states. Polar hydrogens were included, while non-essential water molecules were eliminated from the structures. The structures of the targets were ultimately minimized using the OPLS3 force field, with a preset rmsd value of 0.30 Å for non-hydrogen atoms [48].
3.3.4. Receptor Grid Generation
A grid box of 20 Å3 was generated at the centre of the bound ligand without any constraints and with a 1.00 van der Waals radius along with a cutoff of 0.25 for partial charges using default parameters.
3.3.5. Ligand Preparation
The ligands were prepared using LigPrep, by generating the most likely ionization states at a pH of 7 ± 1 and then structures’ optimization with the OPLS3 force field.
3.3.6. Validation of the Molecular Docking
The validation of the molecular docking was performed by calculating the accuracy of the predicted conformations’ match with the experimental conformations [49,50,51]. The crystallographic ligand was docked into the protein target using the same docking criteria used for the prepared ligands. The docked position with the lowest binding energy was then aligned with the conformation of the crystallographic structure using Maestro’s structure superimposition tool and the root mean square deviation (RMSD) of the alignment was then calculated.
3.3.7. Molecular Docking
The extra precision mode (XP) on Glide was employed for all docking operations, utilizing a van der Waals (vdw) radius scaling factor of 0.80, a partial charge cut-off of 0.15, and no constraints. The XP score was employed to rank ligands and ascertain the best docked conformation for each ligand. The molecular mechanics–generalized Born surface area (MM-GBSA) binding free energy was computed for the top ranked poses using the Prime MM-GBSA module and set in context with the experimental binding affinities. Figures were produced with PyMol 3.1.3.1 Graphical Software (Schrödinger®, New York, NY, USA).
3.3.8. Induced Fit Docking
Flexible docking was performed using the Induced-fit docking (IFD) tool in Maestro. Each ligand underwent an initial docking and then, side-chain prediction within 5 Å around every ligand pose [52]. This was accompanied by an energy minimization of each protein/ligand complex and a final prediction of the most favorable binding pose based on the IFD score [53].
4. Conclusions
A series of 11 new N-alkyl 3-(3-benzyloxyquinoxalin-2-yl) propanamides were prepared, based on the azide coupling of 3-(3-benzyloxyquinoxalin-2-yl) propanhydrazide with a variety of primary and secondary amines. This work targeted the chemoselective preparation of methyl 3-(3-benzyloxyquinoxalin-2-yl) propanoate and, in the best cases with higher yields, achieved this by the reaction of methyl 3-(3-oxo-3,4-dihydroquinoxalin-2-yl) propanoate with benzyl chloride in the presence of dry potassium carbonate in acetone under reflux condition for 12 h. The O-substituted benzyl derivative was hydrazinolyzed to provide the corresponding hydrazide. The compounds showed an interesting cytotoxic profile against a set of cancer cell lines including PC-3, Hela, HCT-116, and MCF-7. Compound 6k had the highest activity an IC50 of values 12.17 ± 0.9, 9.46 ± 0.7, 10.88 ± 0.8, and 6.93 ± 0.4 µM compared to 8.87 ± 0.6, 5.57 ± 0.4, 5.23 ± 0.3, and 4.17 ± 0.2 µM for Doxorubicin against Hela, HCT-116, and MCF-7, respectively. The docking studies revealed the inhibition of HDAC-6 through binding the ubiquitin-binding domain and not the catalytic domain. This study produced a quinoxaline-based scaffold with a broad spectrum of antiproliferative activity and a unique mode of action through binding HDAC6 Zf-UBD that should be subjected to further optimization and preclinical testing and that can assist in future anticancer drug development.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Data are contained within the article.
Acknowledgments
I would like to thank the Basic and Applied Scientific Research Centre at Imam Abdulrahman Bin Faisal University, for the co-workers and making the all analyses.
Conflicts of Interest
The author declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Kaushal, T.; Srivastava, G.; Sharma, A.; Singh Negi, A. An Insight into Medicinal Chemistry of Anticancer Quinoxalines. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2019, 27, 16–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patinote, C.; Raevens, S.; Baumann, A.; Pellegrin, E.; Bonnet, P.-A.; Deleuze-Masquéfa, C. [1,2,4]Triazolo[4,3-a]Quinoxaline as Novel Scaffold in the Imiqualines Family: Candidates with Cytotoxic Activities on Melanoma Cell Lines. Molecules 2023, 28, 5478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, A.; Singh, A.K.; Singh, H.; Vijayan, V.; Kumar, D.; Naik, J.; Thareja, S.; Yadav, J.P.; Pathak, P.; Grishina, M.; et al. Nitrogen Containing Heterocycles as Anticancer Agents: A Medicinal Chemistry Perspective. Pharmaceuticals 2023, 16, 299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, D.; Liu, P.; Jiang, Y.; He, X.; Zhang, L.; Wang, L.; Yang, T. Discovery and SAR Study of Quinoxaline-Arylfuran Derivatives as a New Class of Antitumor Agents. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 2420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bouali, N.; Hammouda, M.B.; Ahmad, I.; Ghannay, S.; Thouri, A.; Dbeibia, A.; Patel, H.; Hamadou, W.S.; Hosni, K.; Snoussi, M.; et al. Multifunctional Derivatives of Spiropyrrolidine Tethered Indeno-Quinoxaline Heterocyclic Hybrids as Potent Antimicrobial, Antioxidant and Antidiabetic Agents: Design, Synthesis, In Vitro and In Silico Approaches. Molecules 2022, 27, 7248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chawla, G.; Gupta, O.; Pradhan, T. A Review on Multipurpose Potential of Bioactive Heterocycle Quinoxaline. ChemistrySelect 2023, 8, e202301401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alasmary, F.A.S.; Abdullah, D.A.; Masand, V.H.; Ben Bacha, A.; Omar Ebeid, A.M.; El-Araby, M.E.; Alafeefy, A.M. Synthesis, Molecular Modelling, and Biological Evaluation of Novel Quinoxaline Derivatives for Treating Type II Diabetes. J. Enzyme Inhib. Med. Chem. 2024, 39, 2395985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elwan, A.; Sakr, H.; El-Helby, A.-G.A.; El-morsy, A.; Abdelgawad, M.A.; Ghoneim, M.M.; El-Sherbiny, M.; El-Adl, K. Triazoloquinoxalines-Based DNA Intercalators-Topo II Inhibitors: Design, Synthesis, Docking, ADMET and Anti-Proliferative Evaluations. J. Enzyme Inhib. Med. Chem. 2022, 37, 1556–1567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Waseem, A.M.; Elmagzoub, R.M.; Abdelgadir, M.M.M.; Bahir, A.A.; EL-Gawaad, N.S.A.; Abdel-Samea, A.S.; Rao, D.P.; Kossenas, K.; Bräse, S.; Hashem, H. An Insight into the Therapeutic Impact of Quinoxaline Derivatives: Recent Advances in Biological Activities (2020–2024). Results Chem. 2025, 13, 101989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mamedov, V.A. Quinoxalines (Synthesis, Reactions, Mechanisms and Structure); Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2016; ISBN 978-3-319-29771-2. [Google Scholar]
- Waring, M.J.; Ben-Hadda, T.; Kotchevar, A.T.; Ramdani, A.; Touzani, R.; Elkadiri, S.; Hakkou, A.; Bouakka, M.; Ellis, T. 2,3-Bifunctionalized Quinoxalines: Synthesis, DNA Interactions and Evaluation of Anticancer, Anti-Tuberculosis and Antifungal Activity. Molecules 2002, 7, 641–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shivani; Mahajan, A.T.; Chaudhary, S. Emerging Trends in Quinoxaline-Based Analogs as Protein Kinase Inhibitors: Structural Developments and SAR Insights. ChemMedChem 2025, 20, e202400592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dehnavi, F.; Akhavan, M.; Bekhradnia, A. Advances in Quinoxaline Derivatives: Synthetic Routes and Antiviral Efficacy against Respiratory Pathogens. RSC Adv. 2024, 14, 35400–35423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buravchenko, G.I.; Shchekotikhin, A.E. Quinoxaline 1,4-Dioxides: Advances in Chemistry and Chemotherapeutic Drug Development. Pharmaceuticals 2023, 16, 1174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cuesta-Seijo, J.A.; Sheldrick, G.M. Structures of Complexes between Echinomycin and Duplex DNA. Acta Crystallogr. D Biol. Crystallogr. 2005, 61, 442–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kong, D.; Park, E.J.; Stephen, A.G.; Calvani, M.; Cardellina, J.H.; Monks, A.; Fisher, R.J.; Shoemaker, R.H.; Melillo, G. Echinomycin, a Small-Molecule Inhibitor of Hypoxia-Inducible Factor-1 DNA-Binding Activity. Cancer Res. 2005, 65, 9047–9055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zayed, M.F. Chemistry, Synthesis, and Structure Activity Relationship of Anticancer Quinoxalines. Chemistry 2023, 5, 2566–2587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suwanhom, P.; Saetang, J.; Khongkow, P.; Nualnoi, T.; Tipmanee, V.; Lomlim, L. Synthesis, Biological Evaluation, and In Silico Studies of New Acetylcholinesterase Inhibitors Based on Quinoxaline Scaffold. Molecules 2021, 26, 4895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yashwantrao, G.; Saha, S. Recent Advances in the Synthesis and Reactivity of Quinoxaline. Org. Chem. Front. 2021, 8, 2820–2862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, J.A.; Pessoa, A.M.; Cordeiro, M.N.D.S.; Fernandes, R.; Prudêncio, C.; Noronha, J.P.; Vieira, M. Quinoxaline, Its Derivatives and Applications: A State of the Art Review. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2015, 97, 664–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eissa, I.H.; El-Naggar, A.M.; El-Sattar, N.E.A.A.; Youssef, A.S.A. Design and Discovery of Novel Quinoxaline Derivatives as Dual DNA Intercalators and Topoisomerase II Inhibitors. Anticancer Agents Med. Chem. 2018, 18, 195–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Adl, K.; El-Helby, A.-G.A.; Sakr, H.; Elwan, A. Design, Synthesis, Molecular Docking and Anti-Proliferative Evaluations of [1,2,4]Triazolo[4,3-a]Quinoxaline Derivatives as DNA Intercalators and Topoisomerase II Inhibitors. Bioorg. Chem. 2020, 105, 104399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ibrahim, M.K.; Taghour, M.S.; Metwaly, A.M.; Belal, A.; Mehany, A.B.M.; Elhendawy, M.A.; Radwan, M.M.; Yassin, A.M.; El-Deeb, N.M.; Hafez, E.E.; et al. Design, Synthesis, Molecular Modeling and Anti-Proliferative Evaluation of Novel Quinoxaline Derivatives as Potential DNA Intercalators and Topoisomerase II Inhibitors. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2018, 155, 117–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Montero, V.; Montana, M.; Carré, M.; Vanelle, P. Quinoxaline Derivatives: Recent Discoveries and Development Strategies towards Anticancer Agents. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2024, 271, 116360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oyallon, B.; Brachet-Botineau, M.; Logé, C.; Robert, T.; Bach, S.; Ibrahim, S.; Raoul, W.; Croix, C.; Berthelot, P.; Guillon, J.; et al. New Quinoxaline Derivatives as Dual Pim-1/2 Kinase Inhibitors: Design, Synthesis and Biological Evaluation. Molecules 2021, 26, 867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.C.; Boggu, P.R.; Yu, H.N.; Ki, S.Y.; Jung, J.M.; Kim, Y.S.; Park, G.M.; Ma, S.H.; Kim, I.S.; Jung, Y.H. Synthesis and Biological Evaluation of Quinoxaline Derivatives as Specific C-Met Kinase Inhibitors. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2020, 30, 127189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, X.; Lan, P.; Chen, Q.; Liu, H.; Chen, Z.; Wang, T.; Wang, Z. Synthesis and Biological Evaluation of Quinoxaline Derivatives as ASK1 Inhibitors. J. Enzyme Inhib. Med. Chem. 2024, 39, 2414382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qi, J.; Huang, J.; Zhou, X.; Luo, W.; Xie, J.; Niu, L.; Yan, Z.; Luo, Y.; Men, Y.; Chen, Y.; et al. Synthesis and Biological Evaluation of Quinoxaline Derivatives as Tubulin Polymerization Inhibitors That Elevate Intracellular ROS and Triggers Apoptosis via Mitochondrial Pathway. Chem. Biol. Drug Des. 2019, 93, 617–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El Newahie, A.M.S.; Nissan, Y.M.; Ismail, N.S.M.; Abou El Ella, D.A.; Khojah, S.M.; Abouzid, K.A.M. Design and Synthesis of New Quinoxaline Derivatives as Anticancer Agents and Apoptotic Inducers. Molecules 2019, 24, 1175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Montero, V.; Montana, M.; Khoumeri, O.; Correard, F.; Estève, M.-A.; Vanelle, P. Synthesis, In Vitro Antiproliferative Activity, and In Silico Evaluation of Novel Oxiranyl-Quinoxaline Derivatives. Pharmaceuticals 2022, 15, 781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aboelmagd, A.; Alotaibi, S.H.; El Rayes, S.M.; Elsayed, G.M.; Ali, I.A.I.; Fathalla, W.; Pottoo, F.H.; Khan, F.A. Synthesis and Anti Proliferative Activity of New N-Pentylquinoxaline Carboxamides and Their O-Regioisomer. ChemistrySelect 2020, 5, 13439–13453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aboelmagd, A.; Rayes, S.M.E.; Gomaa, M.S.; Ali, I.A.I.; Fathalla, W.; Pottoo, F.H.; Khan, F.A.; Khalifa, M.E. The Synthesis and Antiproliferative Activity of New N-Allyl Quinoxalinecarboxamides and Their O-Regioisomers. New J. Chem. 2021, 45, 831–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Megahed, M.; Fathalla, W.; Alsheikh, A.A. Synthesis and Antimicrobial Activity of Methyl 2-(2-(2-Arylquinazolin-4-Yl)Oxy) Acetylamino Alkanoates. J. Heterocycl. Chem. 2018, 55, 2799–2808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fathalla, W. Chemoselective Synthesis of 3,6,7-Trisubstituted 2-(2,3:5,6-Di-O-Isopropylidene-β-D-Mannofuranosyloxy]- and 2-(2-Acetamido-3,4,6-Tri-O-Acetyl-2-Deoxy-β-D-Glucopyranosyloxy)Quinoxaline Derivatives. Chem. Heterocycl. Comp. 2015, 51, 67–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ismail, E.F.; Ali, I.A.I.; Fathalla, W.; Alsheikh, A.A.; Tamneya, E.S.E. Synthesis of Methyl [3-Alkyl-2-(2,4-Dioxo-3,4-Dihydro-2H-Quinazolin-1-Yl)-Acetamido] Alkanoate. Arkivoc 2017, 2017, 104–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, I.A.I.; Fathalla, W. N1-Allyl-3-Substituted-6,7-Dimethyl-1,2-Dihydro-2-Quinoxalinone as Key Intermediate for New Acyclonucleosides and Their Regioisomer O-Analogues. Heteroat. Chem. 2006, 17, 280–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, I.A.I.; Fathalla, W.; Rayes, S.M.E. Convenient Syntheses of Methyl 2-[2-(3-Acetyl-4-Methyl-2-Oxo-1,2-Dihydroquinolin-1-Yl)Acetamido] Alkanoates and Their O-Regioisomers. Arkivoc 2008, 2008, 179–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abad, N.; Al-Ostoot, F.H.; Ashraf, S.; Chkirate, K.; Aljohani, M.S.; Alharbi, H.Y.; Buhlak, S.; El Hafi, M.; Van Meervelt, L.; Al-Maswari, B.M.; et al. Synthesis, Crystal Structure, DFT Calculations, Hirshfeld Surface Analysis, Energy Frameworks, Molecular Dynamics and Docking Studies of Novel Isoxazolequinoxaline Derivative (IZQ) as Anti-Cancer Drug. J. Mol. Struct. 2021, 1232, 130004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Son, J.-H.; Zhu, J.S.; Phuan, P.-W.; Cil, O.; Teuthorn, A.P.; Ku, C.K.; Lee, S.; Verkman, A.S.; Kurth, M.J. High-Potency Phenylquinoxalinone Cystic Fibrosis Transmembrane Conductance Regulator (CFTR) Activators. J. Med. Chem. 2017, 60, 2401–2410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Z.; Wei, C.; Wu, S.; Zhang, W.; Song, R.; Hu, D. Synthesis, Anti-Potato Virus Y Activities, and Interaction Mechanisms of Novel Quinoxaline Derivatives Bearing Dithioacetal Moiety. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2022, 70, 7029–7038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ali, I.A.I.; El Rayes, S.M. Synthesis of Quinoxaline Reverse Ribofuranosides and Their O-Regioisomers. Monatsh. Chem. 2014, 145, 1371–1380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harding, R.J.; Ferreira de Freitas, R.; Collins, P.; Franzoni, I.; Ravichandran, M.; Ouyang, H.; Juarez-Ornelas, K.A.; Lautens, M.; Schapira, M.; von Delft, F.; et al. Small Molecule Antagonists of the Interaction between the Histone Deacetylase 6 Zinc-Finger Domain and Ubiquitin. J. Med. Chem. 2017, 60, 9090–9096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mosmann, T. Rapid Colorimetric Assay for Cellular Growth and Survival: Application to Proliferation and Cytotoxicity Assays. J. Immunol. Methods 1983, 65, 55–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Denizot, F.; Lang, R. Rapid Colorimetric Assay for Cell Growth and Survival. Modifications to the Tetrazolium Dye Procedure Giving Improved Sensitivity and Reliability. J. Immunol. Methods 1986, 89, 271–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sherje, A.P.; Kulkarni, V.; Murahari, M.; Nayak, U.Y.; Bhat, P.; Suvarna, V.; Dravyakar, B. Inclusion Complexation of Etodolac with Hydroxypropyl-Beta-Cyclodextrin and Auxiliary Agents: Formulation Characterization and Molecular Modeling Studies. Mol. Pharm. 2017, 14, 1231–1242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rose, P.W.; Prlić, A.; Altunkaya, A.; Bi, C.; Bradley, A.R.; Christie, C.H.; Costanzo, L.D.; Duarte, J.M.; Dutta, S.; Feng, Z.; et al. The RCSB Protein Data Bank: Integrative View of Protein, Gene and 3D Structural Information. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017, 45, D271–D281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burley, S.K.; Bhikadiya, C.; Bi, C.; Bittrich, S.; Chen, L.; Crichlow, G.V.; Christie, C.H.; Dalenberg, K.; Di Costanzo, L.; Duarte, J.M.; et al. RCSB Protein Data Bank: Powerful New Tools for Exploring 3D Structures of Biological Macromolecules for Basic and Applied Research and Education in Fundamental Biology, Biomedicine, Biotechnology, Bioengineering and Energy Sciences. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021, 49, D437–D451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, C.; Wu, C.; Ghoreishi, D.; Chen, W.; Wang, L.; Damm, W.; Ross, G.A.; Dahlgren, M.K.; Russell, E.; Von Bargen, C.D.; et al. OPLS4: Improving Force Field Accuracy on Challenging Regimes of Chemical Space. J. Chem. Theory Comput. 2021, 17, 4291–4300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gomaa, M.S.; Alturki, M.S.; Tawfeeq, N.; Hussein, D.A.; Pottoo, F.H.; Al Khzem, A.H.; Sarafroz, M.; Abubshait, S. Discovery of Non-Peptide GLP-1 Positive Allosteric Modulators from Natural Products: Virtual Screening, Molecular Dynamics, ADMET Profiling, Repurposing, and Chemical Scaffolds Identification. Pharmaceutics 2024, 16, 1607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gomaa, M.S.; Ahmed, A.H.A.; El Rayes, S.M.; Ali, I.A.I.; Fathalla, W.; Alturki, M.S.; Alkhzem, A.H.; Almalki, A.H.; Aldawsari, M.F.; Pottoo, F.H.; et al. Design, Synthesis and Antiproliferative Activity against Colorectal Cancer Cells of Methyl 2-(3-(2-Oxo-3-Phenylquinoxalin-1(2H)-Yl)Propanamido)Alkanoates and Related Compounds. J. Mol. Struct. 2025, 1330, 141456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaundoo, R.; Bohmann, J.; Gutierrez, G.E.; Klimas, N.; Broderick, G.; Craddock, T.J.A. Using a Consensus Docking Approach to Predict Adverse Drug Reactions in Combination Drug Therapies for Gulf War Illness. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 3355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salam, M.A.; Al-Amin, M.Y.; Salam, M.T.; Pawar, J.S.; Akhter, N.; Rabaan, A.A.; Alqumber, M.A.A. Antimicrobial Resistance: A Growing Serious Threat for Global Public Health. Healthcare 2023, 11, 1946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Z.; Chen, Y.; Fang, Y.; Wang, X.; Chen, Y.; Qi, Q.; Huang, F.; Xiao, X. Meta-Analysis of Colistin for the Treatment of Acinetobacter Baumannii Infection. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 17091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).