Abstract
The selective catalytic reduction of NOx with CH4 (CH4-SCR) holds the potential to simultaneously abate harmful NOx and CH4 greenhouse gases. In this study, a series of bimetallic M-In/H-SSZ-39 catalysts (where M represents Cr, Co, Ce, and Fe) were prepared via an ion exchange method and subsequently evaluated for their CH4-SCR activity. The influences of the preparation parameters, including the metal ion concentration and calcination temperature, as well as the operating conditions, such as the CH4/NO ratio, O2 concentration, water vapor content, and gas hourly space velocity (GHSV), on the catalytic activity of the optimal Cr-In/H-SSZ-39 catalyst were meticulously examined. The results revealed that the Cr-In/H-SSZ-39 catalyst exhibited peak CH4-SCR catalytic performance when the Cr(NO3)3 concentration was 0.0075 M, the In(NO3)3 concentration was 0.066 M, and the calcination temperature was 500 °C. Under optimal operating conditions, namely GHSV of 10,000 h−1, 400 ppm NO, 800 ppm CH4, 15 vol% O2, and 6 vol% H2O, the NOx conversion rate reached 93.4%. To shed light on the excellent performance of Cr-In/H-SSZ-39 under humid conditions, a comparative analysis of the crystalline phase, chemical composition, pore structure, surface chemical state, surface acidity, and redox properties of Cr-In/H-SSZ-39 and In/H-SSZ-39 was conducted. The characterization results indicated that the incorporation of Cr into In/H-SSZ-39 enhanced its acidity and also facilitated the generation of InO+ active species, which promoted the oxidation of NO and the activation of CH4, respectively. A synergistic effect was observed between Cr and In species, which significantly improved the redox properties of the catalyst. Consequently, the activated CH4 could further interact with InO+ to produce carbon-containing intermediates such as HCOO−, which ultimately reacted with nitrate-based intermediates to yield N2, CO2, and H2O.
1. Introduction
Climate change and atmospheric pollution constitute pressing global challenges confronting humanity in contemporary times [1]. As a consequence, increasingly stringent emission restrictions are driving improvements in both engine technology and fuel quality around the world. Compared to diesel, liquefied natural gas (LNG) has shown significant advantages in reducing emissions such as particulate matter (PM), sulfur oxides (SOx), and carbon dioxide (CO2). However, LNG engines may produce higher methane (CH4) emissions and also have nitrogen oxide (NOx) emission issues [2,3]. CH4 is a greenhouse gas with high global warming potential (GWP) that is approximately 25 times (100-year horizon) greater than that of CO2 [4]. NOx is a prominent constituent of atmospheric pollution, posing a substantial threat to the environment and human health [5,6,7]. Therefore, the advancement of technologies focused on the simultaneous removal of NOx and CH4 is crucial for future progress. The selective catalytic reduction of NOx using CH4 (CH4-SCR) as a reductant holds great promise for environmental protection and energy conservation [8,9,10].
Rational catalyst design is of great significance in ensuring an efficient and durable CH4-SCR reaction. For a considerable period of time, efforts have been devoted to metal-exchanged medium- or large-pore zeolites characterized by their ten-membered or twelve-membered rings (MR) [9,10,11,12,13,14,15,16,17,18]. However, these catalysts either had limited catalytic activity or were susceptible to framework collapse under high-temperature and high-humidity conditions [10]. In-exchanged zeolite beta (In/H-Beta) exhibited remarkable deNOx efficiency of ~97.6% under dry CH4-SCR conditions. Nonetheless, once water vapor was introduced, the catalytic activity of In/H-Beta was drastically diminished [19,20]. InO+ species tend to combine with H2O, forming species, which are unable to activate CH4 [18]. Moreover, prolonged exposure to H2O at elevated temperatures may induce the irreversible structural collapse of the zeolite framework, further compromising its catalytic performance [21]. Therefore, inhibiting the conversion of active centers and selecting a hydrothermally stable zeolite support are essential in mitigating catalyst deactivation caused by water vapor.
In the NH3-SCR field, the Cu-SSZ-39 zeolite (AEI topology), featuring cage-like channels with 8MR pore openings of 3.8 Å × 3.8 Å, has been highlighted for its exceptional hydrothermal stability and commendable catalytic activity [21,22,23,24,25]. Du et al. [21] conducted an in-depth investigation into the channel structure of a Cu-SSZ-39 catalyst, revealing its superior activity under humid conditions compared to its Cu-SSZ-13 counterpart. Even after undergoing high-temperature hydrothermal aging at 850 °C for 16 h, Cu-SSZ-39′s high deNOx activity was not significantly degraded. This stability was attributed to its more tortuous channel structure in comparison to SSZ-13, which effectively mitigated aluminum leaching and copper species aggregation under hydrothermal conditions. In some recent studies, SSZ-39 zeolites have also emerged as promising supports for CH4-SCR catalysts [26,27,28,29]. The Co-SSZ-39 catalyst synthesized by Li et al. [26] demonstrated a wider operating temperature window, higher peak NOx conversion, and more robust anti-poisoning performance compared to its Co-SSZ-13 counterpart in the CH4-SCR reaction. Detailed characterization of the catalyst revealed that Co2+ at the ion exchange sites served as the active species responsible for the catalytic activity in the CH4-SCR reaction. Typically, indium-exchanged zeolites are capable of catalyzing the CH4-SCR reaction more efficiently, making In species the preferred active components in many reported catalysts [10]. For instance, An et al. [27] reported that In/SSZ-39 exhibited superior catalytic activity compared to Cu-, Co-, and Fe/SSZ-39 catalysts. The low-temperature (400–450 °C) CH4-SCR activity of In/SSZ-39 was significantly enhanced with increasing indium loading within the studied range. The 3In/SSZ-39 catalyst demonstrated high NO removal efficiency of 90% and CH4 selectivity of 74.2% at a reaction temperature of 400 °C and a low CH4/NO ratio of 1. High-angle annular dark field scanning transmission electron microscopy (HAADF-STEM) images revealed that In species were highly dispersed on the SSZ-39 zeolite, which facilitated moderate CH4 activation and thereby enhanced the CH4-SCR activity at low temperatures. More importantly, the indium species loaded within the zeolite have been reported to synergize with various introduced second metals (or metal oxides), thereby significantly enhancing the activity and/or stability of the catalyst [18,28,30,31,32,33,34,35]. For instance, Chen et al. [28] constructed an In-Co3O4/H-SSZ-39(OA) catalyst through mild acid etching and ion exchange, which demonstrated improved stability under harsh operating conditions and achieved NO removal efficiency of ~80% at ~600 °C under a GHSV of 24,000 h−1. A small amount of Co3O4 nanoparticles on the zeolite surface greatly enhanced the catalytic activity by promoting CH4 conversion and enabling the greater storage of stable NxOy species at high temperatures.
In this study, a series of bimetallic M-In/H-SSZ-39 (M = Cr, Ce, Co, Fe) catalysts were prepared via a liquid-state ion exchange method, with the preparation conditions of Cr-In/H-SSZ-39—the catalyst exhibiting the highest catalytic activity—being optimized. The effects of various operating conditions on the catalytic activity of the Cr-In/H-SSZ-39 catalyst were systematically investigated. Furthermore, a comparative analysis of the crystalline phase, chemical composition, pore structure, surface chemical state, surface acidity, and redox properties of Cr-In/H-SSZ-39 and the monometallic In/H-SSZ-39 control was conducted to elucidate the underlying mechanisms responsible for the excellent catalytic activity.
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Screening of Bimetallic Catalysts
Various M-In/H-SSZ-39 catalysts were prepared by introducing Cr, Ce, Co, and Fe as the second metals, and their catalytic performance was assessed, as shown in Figure 1. It is evident from Figure 1a that the incorporation of Ce, Co, and Fe species failed to effectively enhance the CH4-SCR activity compared with the In/H-SSZ-39 catalyst. Conversely, the incorporation of Cr species significantly enhanced the catalytic performance, achieving NOx conversion of 55% at 575 °C, further escalating to 67.8% at 620 °C. Figure 1b shows that the CH4 conversion of all four catalysts increased as the temperature rose. Notably, the Cr-In/H-SSZ-39 catalyst exhibited superior CH4 conversion at >500 °C, achieving CH4 conversion of 60.1% at 600 °C. The CH4 conversion profiles of the other three catalysts were relatively similar. Methane had two possible conversion pathways: (1) partial oxidation, which further participated in NOx reduction reactions, and (2) direct catalytic combustion. The significantly different NOx conversion and similar CH4 conversion rates reflected the catalysts’ varying abilities to guide methane toward the desired NOx reduction pathway, as indicated by the CH4 selectivity (Figure 1c). It was apparent that the incorporation of Ce, Co, and Fe as secondary metals resulted in a decrease in CH4 selectivity under hydrothermal conditions compared to In/H-SSZ-39. However, incorporating Cr had a beneficial effect, with Cr-In/H-SSZ-39 demonstrating the highest CH4 selectivity of 61.4% at 550 °C.
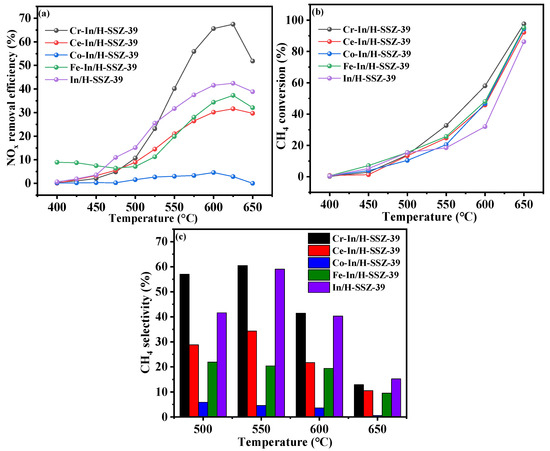
Figure 1.
Comparison of CH4-SCR activity of M-In/H-SSZ-39 and In/H-SSZ-39 catalysts: (a) NO removal efficiency, (b) CH4 conversion, (c) CH4 selectivity. Reaction reactions: [NO] = 400 ppm, [CH4] = 600 ppm, [O2] = 10 vol%, [H2O] = 6 vol%, Ar balance, GHSV = 21,000 h−1.
2.2. Effects of Preparation Conditions
2.2.1. Effects of Cr Concentration
Maintaining the In(NO3)3 concentration at 0.066 M, the catalytic performance of the xCr-In/H-SSZ-39 (x = 0, 0.0025, 0.005, 0.0075, and 0.01 M Cr(NO3)3) catalysts was compared, as shown in Figure 2. With the concentration of Cr(NO3)3 increased from 0 to 0.01 M, the catalytic activity roughly exhibited an initial enhancement, followed by a gradual decline (Figure 2a). When the Cr(NO3)3 concentration was 0.0075 M, the resulting catalyst exhibited the highest NOx conversion of 67.8% at 605 °C. Figure 2b shows the CH4 conversion profiles of the Cr-In/H-SSZ-39 catalysts. The Cr-containing samples all exhibited enhanced CH4 conversion compared to the monometallic In/H-SSZ-39. Figure 2c shows that the introduction of Cr ions at varying concentrations enhanced the CH4 selectivity of the catalyst. Notably, the CH4 selectivity of 0.0075Cr-In/H-SSZ-39 was the highest at 600 °C, corresponding to its highest deNOx activity. A mixed solution of 0.0075 M Cr(NO3)3 and 0.066 M In(NO3)3 was therefore used for ion exchange in subsequent experiments.
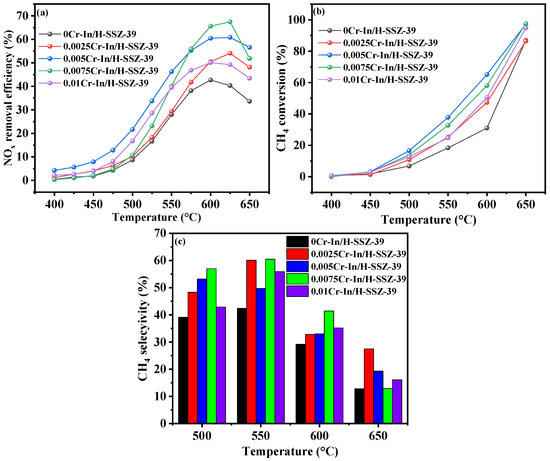
Figure 2.
CH4-SCR activity of Cr-In/H-SSZ-39 catalysts prepared with different Cr(NO3)3 concentrations. (a) NO removal efficiency, (b) CH4 conversion, (c) CH4 selectivity. Reaction reactions: [NO] = 400 ppm, [CH4] = 600 ppm, [O2] = 10 vol%, [H2O] = 6 vol%, Ar balance, GHSV = 21,000 h−1.
2.2.2. Effects of Calcination Temperature
The calcination temperature exerts a significant influence on the specific surface area of a catalyst and the chemical state of the active species [20]. To investigate the effects of the calcination temperature on the deNOx activity of the catalysts, Cr-In/H-SSZ-39 samples were calcined at different temperatures (400 °C, 450 °C, 500 °C, 550 °C, and 600 °C) and designated as Cr-In/H-SSZ-39-x, where x represents the calcination temperature. As shown in Figure 3a, the catalytic activity of the Cr-In/H-SSZ-39 catalysts initially increased and then declined with the rise in the calcination temperature. The catalysts calcined at 500 °C demonstrated the optimal CH4-SCR deNOx performance, high CH4 conversion (Figure 3b), and high CH4 selectivity (Figure 3c), indicating that 500 °C was the optimal calcination temperature for the Cr-In/H-SSZ-39 catalyst.
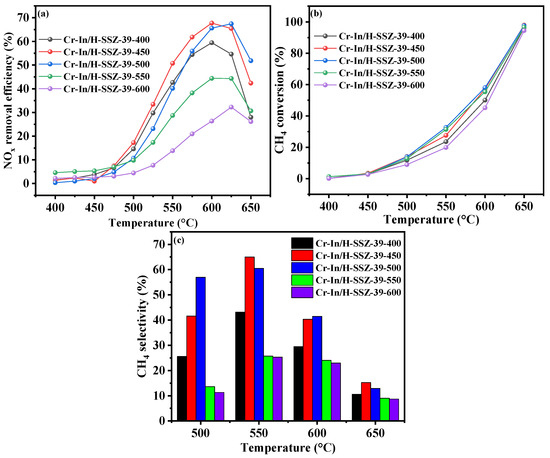
Figure 3.
CH4-SCR activity of Cr-In/H-SSZ-39 catalysts calcined at different temperatures. (a) NO removal efficiency, (b) CH4 conversion, (c) CH4 selectivity. Reaction reactions: [NO] = 400 ppm, [CH4] = 600 ppm, [O2] = 10 vol%, [H2O] = 6 vol%, Ar balance, GHSV = 21,000 h−1.
2.3. Effects of Reaction Conditions
2.3.1. CH4/NO Ratio
The CH4-SCR process removes NO through the reaction of methane, nitric oxide, and oxygen, generating harmless nitrogen, water, and low-GWP carbon dioxide. The CH4/NO ratio is a key indicator in assessing the effectiveness of the reaction. Figure 4a illustrates the catalytic activity of the Cr-In/H-SSZ-39 catalysts under various CH4/NO ratios. At a CH4/NO ratio of 1.0, Cr-In/H-SSZ-39 exhibited excellent catalytic activity in the high-temperature range, achieving a peak NOx conversion of 59.6% at 600 °C. By progressively elevating the CH4 concentration in the feed gas, the catalyst’s activity at <600 °C was continuously enhanced. A reasonable explanation is that the higher CH4 initial concentration at a fixed NOx concentration allowed more CH4 to be involved in NOx reduction at low temperatures, where CH4 activation was relatively difficult. At a CH4/NO ratio of 1.5, the Cr-In/H-SSZ-39 catalyst demonstrated its peak NOx conversion of 67.8% at 600 °C. When the CH4/NO ratio was further increased to 2, the catalyst’s peak NOx conversion reached 76.1% at 600 °C. However, an excessively high concentration of CH4 could not be fully converted over the catalyst, leading to the direct emission of high-GWP CH4. It is evident from Figure 4b that the CH4 conversion decreased as the CH4/NO ratio increased. Moreover, as shown in Figure 4c, a decrease in the CH4 selectivity at >600 °C was observed as the CH4/NO ratio increased, which might be attributed to the fact that a major portion of CH4 was catalytically combusted at high temperatures. At CH4/NO ratios of 1.5 and 2, the CH4 selectivity at 500 and 550 °C was similar, with a higher supply of CH4 naturally leading to enhanced deNOx activity.
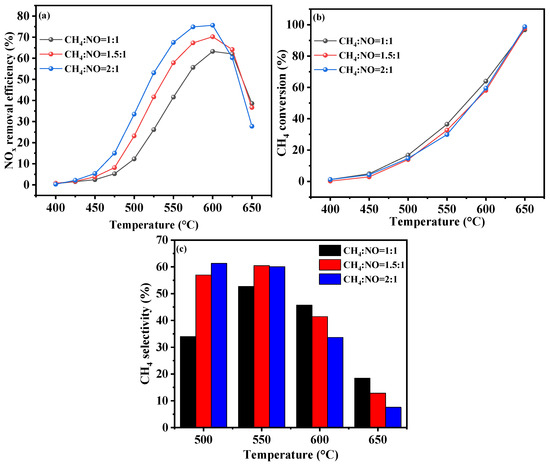
Figure 4.
CH4-SCR activity of Cr-In/H-SSZ-39 catalysts under different CH4/NO ratios. (a) NO removal efficiency, (b) CH4 conversion, and (c) CH4 selectivity. Reaction conditions: [NO] = 400 ppm, [CH4] = 400/600/800 ppm, [O2] = 10 vol%, [H2O] = 6 vol%, Ar balance, GHSV = 21,000 h−1.
2.3.2. O2 Concentration
In CH4-SCR, inadequate O2 concentrations might result in incomplete reactions between CH4 and NOx, whereas excessive ones might prompt the overcombustion of CH4. Figure 5a depicts the NOx conversion profile of the Cr-In/H-SSZ-39 catalyst under different O2 concentrations. The catalyst exhibited optimal deNOx performance at an O2 concentration of 10 vol%, with stable catalytic performance exceeding 60% above 550 °C. Specifically, at 600 °C, the deNOx performance remained stable above 60%, achieving peak catalytic performance of 80.6%. However, as the O2 concentration was further increased to 20 vol%, the catalytic performance of the catalyst declined. As observed in Figure 5b, CH4 conversion increased with the rise in the O2 concentration, primarily due to the enhanced oxidation kinetics of CH4 under oxygen-rich conditions. Specifically, the highest CH4 conversion occurred at 20 vol% O2, followed by comparable CH4 conversion at 15 vol% and 10 vol% O2. As shown in Figure 5c, the CH4 selectivity exhibited a trend similar to that of the NOx removal efficiency with respect to the O2 concentration. This correlation can be attributed to the fact that, at an O2 concentration of 20 vol%, CH4 more readily reacts with oxygen, thereby reducing its selectivity toward NOx.
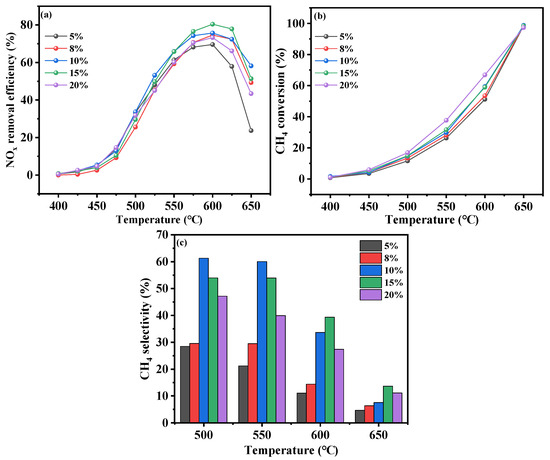
Figure 5.
CH4-SCR activity of Cr-In/H-SSZ-39 catalysts under different O2 concentrations. (a) NO removal efficiency, (b) CH4 conversion, and (c) CH4 selectivity. Reaction conditions: [NO] = 400 ppm, [CH4] = 600 ppm, [O2] = 5/8/10/15/20 vol%, [H2O] = 6 vol%, Ar balance, GHSV = 21,000 h−1.
2.3.3. Gaseous Hourly Space Velocity
The influence of the GHSV on the deNOx performance of the Cr-In/H-SSZ-39 catalyst was also investigated, as shown in Figure 6. It could be found that the NOx conversion gradually increased with the reduction in GHSV from 30,000 h−1 to 10,000 h−1 (Figure 6a). At a GHSV of 16,000 h−1, the catalyst achieved the peak catalytic activity at 600 °C, with an NOx conversion rate of 86.1%. When the GHSV was further decreased to 10,000 h−1, the catalyst demonstrated its highest deNOx activity at a slightly lower temperature of 590 °C, with remarkable NOx conversion of 93.4%. A decreasing GHSV led to an increase in CH4 conversion (Figure 6b). CH4 was more effectively reacted within the temperature range of 400–650 °C at a lower GHSV. Furthermore, Figure 6c reveals that the CH4 selectivity remained high at a GHSV of 10,000 h−1, indicating that CH4 predominantly participated in NOx reduction.
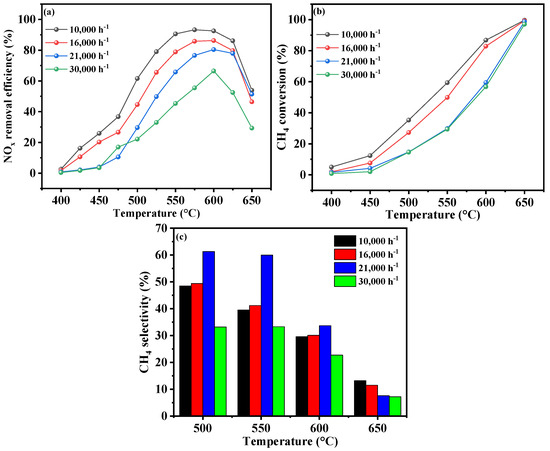
Figure 6.
CH4-SCR activity of Cr-In/H-SSZ-39 catalyst under different GHSVs. (a) NOx removal efficiency, (b) CH4 conversion, and (c) CH4 selectivity. Reaction conditions: [NO] = 400 ppm, [CH4] = 600 ppm, [O2] = 10 vol%, [H2O] = 6 vol%, Ar balance, GHSV = 10,000/16,000/21,000/30,000 h−1.
2.3.4. Water Vapor Content
The tolerance of the Cr-In/H-SSZ-39 catalyst to water vapor was examined (Figure 7). In the absence of water vapor, the catalyst achieved high NOx conversion of 86% at 580 °C (Figure 7a). Peak NOx conversion of 80.6% was observed at 600 °C when 6 vol% water vapor was introduced. As the water content was further increased to 10 vol% and 15 vol%, the peak NOx conversion declined to 70.6% and 52%, respectively. These findings underscore the robust hydrothermal stability of the Cr-In/H-SSZ-39 catalyst. Figure 7b shows that CH4 conversion declined with increasing water content, indicating that water vapor inhibited CH4 conversion. At water vapor content of 10 vol%, the CH4 conversion of the catalyst was 51.3% at 600 °C, a value between those observed at 6 vol% and 15 vol% water vapor content. Figure 7c shows the direct correlation between the CH4 selectivity and catalytic performance at temperatures below 550 °C. When the water vapor content was 6 vol%, the CH4 selectivity at 600 °C exceeded that observed without water vapor, indicating that water vapor might exert a stronger inhibitory effect on CH4 combustion.
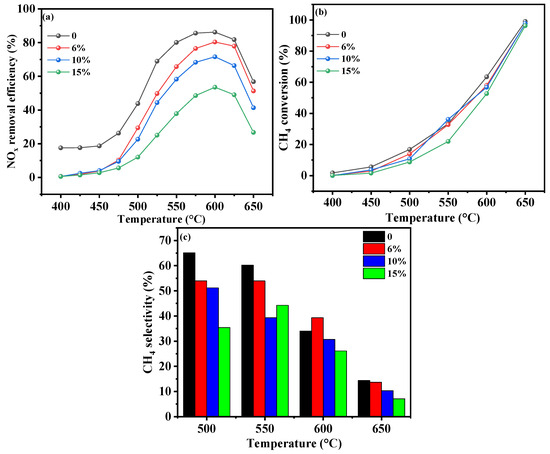
Figure 7.
CH4-SCR activity of Cr-In/H-SSZ-39 catalyst under different H2O concentrations. (a) NOx removal efficiency, (b) CH4 conversion, and (c) CH4 selectivity. Reaction conditions: [NO] = 400 ppm, [CH4] = 600 ppm, [O2] = 10 vol%, [H2O] = 0/6/10/15 vol%, Ar balance, GHSV = 21,000 h−1.
2.4. Cyclic and Stability Testing
The results of the long-term operation test and three consecutive TPSR tests of the Cr-In/H-SSZ-39 catalyst are presented in Figure 8. At a constant temperature of 600 °C, the NOx conversion of the catalyst decreased from 70% to 59% after 1 h of exposure to hydrothermal conditions (Figure 8a). Following this initial decline, the conversion exhibited a gradual and steady decrease over time. In the presence of 10 vol% H2O, the catalytic activity remained above 50% for up to 5 h and above 40% for up to 12 h. These results demonstrate the robust stability of the Cr-In/H-SSZ-39 catalyst under high-temperature hydrothermal conditions. As shown in Figure 8b, the Cr-In/H-SSZ-39 catalyst retained a high level of catalytic activity, achieving NO removal efficiency of 58% and 51% in the second and third cycles, respectively. Compared with the In/H-Beta catalyst [20], the Cr-In/H-SSZ-39 catalyst exhibited higher stability after multiple cycles. The N2 selectivity, as an essential indictor, was assessed, and the results are presented in Figure 8c. It can be seen that the N2 selectivity exceeds 99%, with almost no N2O being produced.
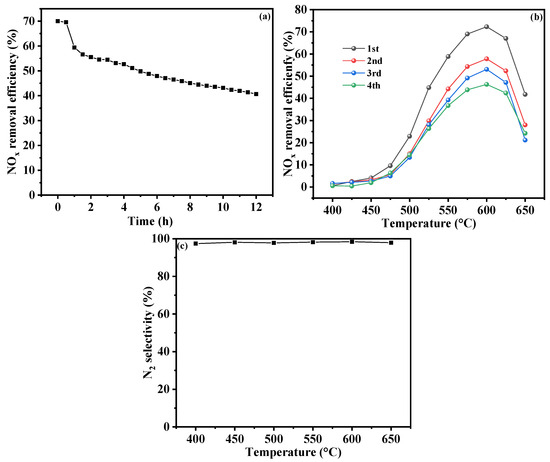
Figure 8.
(a) Long-term operation test for Cr-In/H-SSZ-39, (b) catalytic activity of Cr-In/H-SSZ-39 in three consecutive TPSR cycles, and (c) N2 selectivity test. Reaction conditions: [NO] = 400 ppm, [CH4] = 800 ppm, [O2] = 15 vol%, [H2O] = 10 vol%, Ar balance, GHSV = 21,000 h−1.
2.5. Characterization and Analysis of the Cr-In/H-SSZ-39 Catalyst
2.5.1. Analysis of Composition and Texture Properties
Figure 9 shows the PXRD patterns of the H-SSZ-39, In/H-SSZ-39, and Cr-In/H-SSZ-39 samples. The characteristic diffraction peaks (9.5°, 10.7°, 13.0°, 16.2°, 17.0°, 17.3°, 20.8°, and 24.1°) of each sample aligned well with the simulated AEI structure, indicating that the SSZ-39 zeolite remained intact after incorporating In and Cr species. For zeolite-based deNOx catalysts, maintaining a stable crystalline structure is crucial to ensure the distribution of metal species in their exchangeable sites. The micromorphologies of the In/H-SSZ-39 and Cr-In/H-SSZ-39 catalysts were observed by SEM, as shown in Figure 10. There was no discernible difference in the micromorphologies of the two samples, both consisting of aggregated cuboid crystals with smooth surfaces. The surface area and pore structure of the catalyst influence the dispersion and accessibility of the active species. As shown in Figure 11 and Table 1, the Cr-In/H-SSZ-39 and In/H-SSZ-39 catalysts presented micropore-dominant pore structure, evidenced by the type I N2 adsorption–desorption isotherms (Figure 11) and steep N2 adsorption behavior at P/P0 < 0.01. The preserved intrinsic microporosity characteristics demonstrated that the introduction of Cr/In species did not cause significant disruption to the ordered framework structure of the SSZ-39 zeolite, in line with the PXRD patterns and SEM observations.
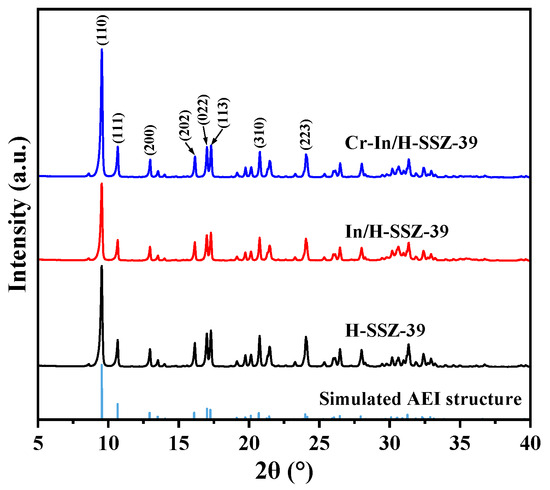
Figure 9.
PXRD patterns of H-SSZ-39, In/H-SSZ-39, and Cr-In/H-SSZ-39. The data of the simulated AEI structure are from the Database of Zeolite Structures.
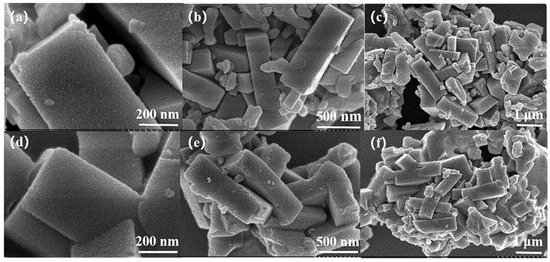
Figure 10.
SEM images of (a–c) In/H-SSZ-39 and (d–f) Cr-In/H-SSZ-39 catalysts.
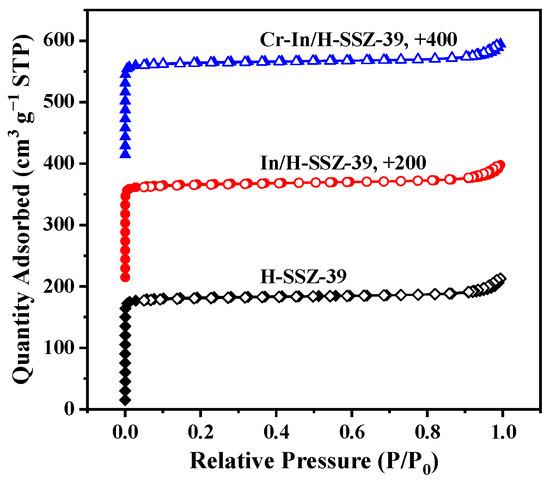
Figure 11.
N2 adsorption–desorption isotherms of H-SSZ-39, In/H-SSZ-39, and Cr-In/H-SSZ-39 samples.

Table 1.
Textural properties of In/H-SSZ-39 and Cr-In/H-SSZ-39 samples.
To determine the elemental compositions of the catalysts, the ICP-OES technique was employed, as summarized in Table 2. The Cr content in Cr-In/H-SSZ-39 was 0.075 wt%, indicating that the Cr ions (0.0075 M) in the ion exchange solution migrated into the zeolites. In/H-SSZ-39 exhibited In content of 5.5 wt%, whereas the In content of Cr-In/H-SSZ-39 slightly decreased to 4.7 wt%, suggesting that In and Cr ions might compete for zeolites’ finite exchangeable sites during the ion exchange process.

Table 2.
Compositional analysis of H-SSZ-39, In/H-SSZ-39, and Cr-In/H-SSZ-39 samples.
2.5.2. Analysis of Chemical States and Redox Properties
Figure 12a presents the In 3d5/2 XPS spectra of the In/H-SSZ-39 and Cr-In/H-SSZ-39 catalysts, and the according calculations are summarized in Table 3. Spectral deconvolution allowed for the identification of three indium species: (~445.6 eV), InO+ (~444.5 eV), and In2O3 (~443.9 eV) [29]. Furthermore, a discernible shift in the In 3d5/2 spectra toward higher binding energies was observed for Cr-In/H-SSZ-39 compared to In/H-SSZ-39, which could be explained by the interaction between Cr and In species. Higher binding energy is indicative of more oxidative surface chemistry, which promotes stronger interactions with SCR reactant species and, consequently, enhances NOx conversion. Table 3 shows that the Cr-In/H-SSZ-39 catalyst demonstrated a larger proportion of InO+ species (InO+/( + InO+ + In2O3) = 0.54) compared to In/H-SSZ-39 (0.49). Given that InO+ is widely recognized as the primary active site in In-exchanged zeolite CH4-SCR catalysts [18,30,33,34], more InO+ species might also contribute to the exceptional deNOx activity of Cr-In/H-SSZ-39. Figure 12b shows the O 1s XPS spectra of the two catalysts, which were deconvoluted into three distinct peaks, i.e., oxygen adsorbed on hydroxyl groups (Oγ, 532.4–533.1 eV), surface oxygen species (Oβ, 532.1–532.6 eV), and lattice oxygen (Oα, 531.0–531.5 eV) [20,36,37,38]. Notably, the Oβ content of Cr-In/H-SSZ-39 reached 40.4%, representing a 3.9% increase compared to that of In/H-SSZ-39 (36.5%). Introducing Cr species into the In/H-SSZ-39 catalyst led to an increase in the Oβ content. Considering that surface oxygen is more involved in complete oxidation reactions, the higher surface oxygen content of Cr-In/H-SSZ-39 promotes CH4 activation [19], thereby enhancing its catalytic activity.
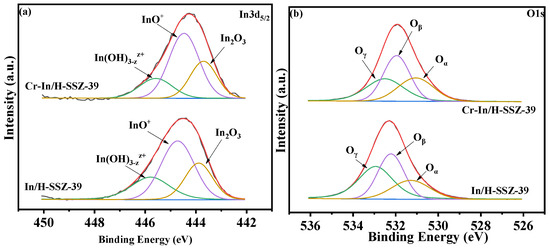
Figure 12.
XPS spectra of (a) In 3d5/2 and (b) O 1s spectra of In/H-SSZ-39 and Cr-In/H-SSZ-39 catalysts.

Table 3.
Surface element compositions of In/H-SSZ-39 and Cr-In/H-SSZ-39 samples.
The redox properties of the two catalysts were investigated by the H2-TPR method, as depicted in Figure 13. Cr-In/H-SSZ-39 exhibited a reduction peak at 222 °C, attributable to the reduction of Cr6+ to Cr3+ [39]. Additionally, a prominent reduction peak was observed at 310 °C/329 °C, which corresponded to the reduction of In3+ [30]. Notably, the reduction peak of InO+ in the Cr-In/H-SSZ-39 catalyst shifted to a higher temperature in comparison to that of the In/H-SSZ-39 catalyst. This finding suggests a synergistic interaction between Cr and In species [40].
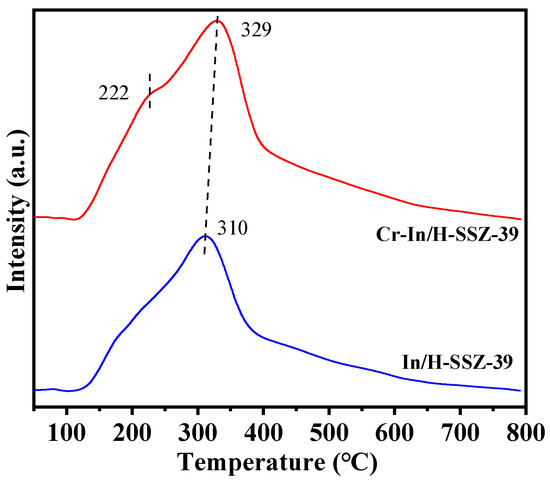
Figure 13.
H2-TPR profiles of In/H-SSZ-39 and Cr-In/H-SSZ-39 catalysts.
The acidity of the two catalysts was investigated by NH3-TPD, and the results are shown in Figure 14 and Table 4. The NH3-TPD profiles were deconvoluted into three distinct peaks: peak I at ~180 °C, attributed to surface hydroxyl groups and weak Lewis acid sites (LAS); peak II at ~470 °C, associated with strong LAS; and peak III at ~540 °C, linked to strong Brønsted acids. Notably, Cr-In/H-SSZ-39 demonstrated 11.3% higher total acidity (2.018 mmol g−1 vs. 1.813 mmol g−1) than its In/H-SSZ-39 counterpart. This observation aligns well with the trend observed in the CH4-SCR performance, thereby reinforcing the pivotal role of acidic sites in enhancing catalytic activity [29].
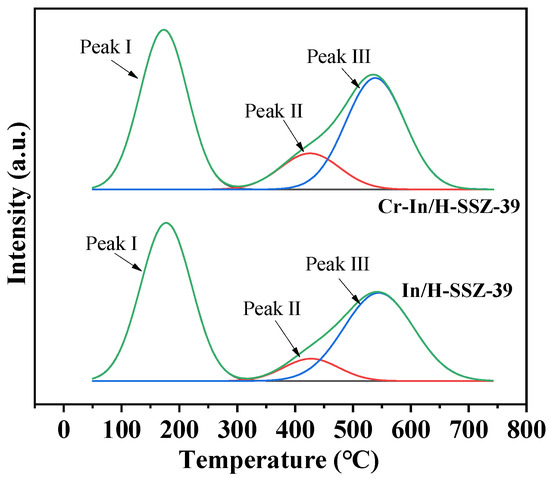
Figure 14.
NH3-TPD profiles of In/H-SSZ-39 and Cr-In/H-SSZ-39 catalysts.

Table 4.
The strength and quantity of surface acid sites of In/H-SSZ-39 and Cr-In/H-SSZ-39 samples based on NH3-TPD measurements.
2.6. Characterization of the Cr-In/H-SSZ-39 Catalyst After Reaction
2.6.1. Analysis of Chemical States
Figure 15a and Table 4 present a comparison of the Cr 2p spectra for the Cr-In/H-SSZ-39 catalyst before and after the reaction. XPS spectral deconvolution resolved characteristic Cr3+ (2p3/2 at 571.8 eV, 2p1/2 at 588.1 eV) and Cr6+ (2p3/2 at 577.5 eV, 2p1/2 at 586.8 eV) oxidation states. Cr3+ played a pivotal role in generating oxygen vacancies on the catalyst surface. Oxygen vacancies serve as active sites that promote reactant activation via interacting with NO2 to generate surface-adsorbed nitrite () and nitrate () intermediates, ultimately contributing to the enhanced catalytic performance [41]. The Cr3+/Cr6+ ratios of the fresh and used Cr-In/H-SSZ-39 catalysts were 0.58 and 0.57, respectively, indicating that the catalyst retained a considerable number of Cr3+ active sites, which were essential for its effective catalytic performance. Figure 15b shows the In 3d5/2 spectra of the fresh and used Cr-In/H-SSZ-39 catalysts, which could be deconvoluted into three distinct indium species: , InO+, and In2O3. The calculated InO+/(InO+ + In2O3 + ) ratio of the used Cr-In/H-SSZ-39 catalyst remained stable at 0.53, almost identical to the value of the fresh one (0.54). Additionally, as shown in Figure 15c, the content of Oβ was almost unchanged after the reaction under humid conditions, decreasing slightly from 40.4% to 40.2%. The consistent Cr3+/Cr6+, InO+/(InO+ + In2O3 + ), and Oβ ratios explain the excellent cyclability and hydrothermal stability of the Cr-In/H-SSZ-39 catalyst.
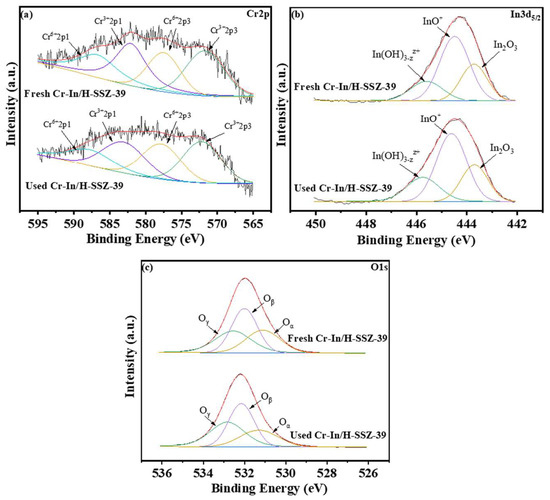
Figure 15.
XPS (a) Cr 2p, (b) In 3d5/2, and (c) O 1s spectra of the fresh and used Cr-In/H-SSZ-39 catalysts.
2.6.2. Analysis of Acidity
Figure 16 shows the NH3-TPD profiles of the fresh and used Cr-In/H-SSZ-39 catalysts, which could be deconvoluted into three NH3 desorption peaks. The NH3 desorption from the used Cr-In/H-SSZ-39 catalyst at the three temperature ranges was slightly lower than that of the fresh catalyst, indicating the reduced acidity of the catalyst after the reaction (Table 4). The minor loss of acidity after the reaction might also have contributed to the retention of its strong deNOx performance.
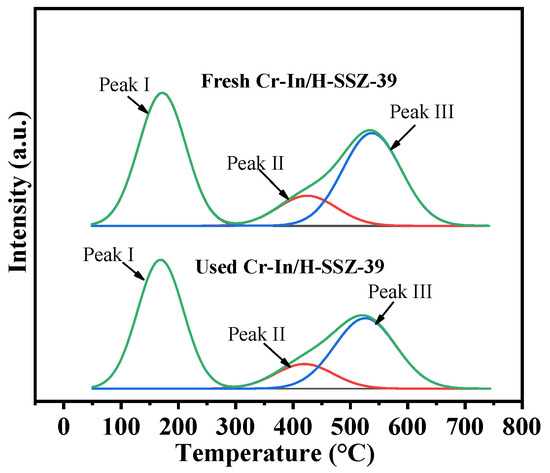
Figure 16.
NH3-TPD profiles of fresh and used Cr-In/H-SSZ-39 catalysts.
2.7. Analysis of Water Resistance Mechanism
Based on our previous study of the CH4-SCR deNOx mechanism over In/H-Beta [38], BAS could induce a small amount of In2O3 on the zeolite surface to generate InO+ active sites; CH4 is mainly adsorbed on InO+ sites, which provide the activated oxygen (O*) necessary for CH4 activation. Combining this with the present research results, the CH4-SCR deNOx mechanism over the Cr-In/H-SSZ-39 catalyst is as follows:
- It could be seen from PXRD that the catalyst maintained its crystalline properties to a great extent after introducing Cr and In species;
- The NH3-TPD and XPS results showed that the incorporation of Cr into In/H-SSZ-39 increased the number of BAS and generated more InO+ species, thus promoting NO oxidation and CH4 activation;
- A strong interaction between Cr and In species was found from the XPS and H2-TPR results; introducing Cr species increased the redox properties of the catalyst, thus promoting NO oxidation.
3. Experimental Section
3.1. Catalyst Preparation
3.1.1. Chemicals
H-SSZ-39 zeolite with an Si/Al ratio of 16 was provided by China Catalyst Holding Co., Ltd. (Zibo, China). Indium(III) nitrate hydrate (In(NO3)3·xH2O, 99.9% metal basis, indium content of 28–37%) was acquired from Shanghai Aladdin Biochemical Technology Co., Ltd. (Shanghai, China). Chromium(III) nitrate nonahydrate (Cr(NO3)3·9H2O, 99.95% metal basis), cerium(III) nitrate hexahydrate (Ce(NO3)3·6H2O, 99.5% metal basis), cobalt(II) nitrate hexahydrate (Co(NO3)2·6H2O, 99.99% metal basis), and iron(III) nitrate nonahydrate (Fe(NO3)3·9H2O, 99.9% metal basis) were bought from Shanghai Macklin Biochemical Technology Co., Ltd. (Shanghai, China). All reagents were used as received, without further purification. Home-made ultrapure water (18.25 MΩ·cm) was used throughout the entire experiment.
3.1.2. Preparation of Monometallic In/H-SSZ-39 Catalyst
The In/H-SSZ-39 catalyst was prepared via a liquid-state ion exchange method. First, 100 mL of 0.066 M In(NO3)3 aqueous solution was prepared by dissolving In(NO3)3·xH2O in ultrapure water. Subsequently, 3 g of H-SSZ-39 zeolite was dispersed into the In(NO3)3 solution. The resultant mixture was uniformly agitated at a constant temperature of 85 °C for 8 h using a magnetic stirrer. The solid was recovered by centrifugation, thoroughly washed five times with deionized water, and then dried in an oven at 80 °C for 12 h. Lastly, the dried sample was calcined in a muffle furnace at 500 °C for 3 h, after which it was sealed and stored for future use.
3.1.3. Preparation of Bimetallic M-In/H-SSZ-39 Catalyst
The preparation process of the M-In/H-SSZ-39 catalyst was similar to that of In/H-SSZ-39, except that a mixed aqueous solution of In(NO3)3 and the second metal M precursor (Cr(NO3)3·9H2O, Ce(NO3)3·6H2O, Co(NO3)2·6H2O, and Fe(NO3)3·9H2O) was used. Variations were introduced into the synthesis process to optimize the properties of the Cr-In/H-SSZ-39 catalyst. For Cr content optimization, different amounts of Cr(NO3)3·9H2O (0.11 g, 0.21 g, 0.32 g, and 0.43 g) were dissolved in 100 mL of 0.066 M In(NO3)3 aqueous solution during the initial step. To determine the optimal calcination temperature, the materials were calcined at 450 °C, 500 °C, 550 °C, and 600 °C in the final step.
3.2. Catalytic Activity Measurement
The activity evaluation experiments were conducted at atmospheric pressure using the temperature-programmed surface reaction (TPSR) method. A certain mass of catalyst particles (40–60 mesh) was first loaded in a fixed-bed quartz reactor. The reaction gas mixture composed of 400 ppm NO, 600 ppm CH4, 10 vol% O2, and 6 vol% H2O with an Ar balance at a total flow rate of 100 mL min−1 was introduced into the reactor, corresponding to a GHSV of ~21,000 h−1 for 0.1 g of catalyst particles. After establishing NOx adsorption–desorption equilibrium at 100 °C, a programmed temperature ramp was initiated, gradually raising the reactor temperature from 100 °C to 675 °C at a heating rate of 5 °C min−1. The concentrations of NOx were monitored by a nitrogen oxide analyzer (Teledyne Model T200H, Teledyne Monitor Labs, Inc., Centennial, CO, USA), while the CH4, CO, and CO2 concentrations were analyzed by a gas chromatograph (Fuli GC9790II, China) equipped with a Porapak-Q column (Agilent, Santa Clara, CA, USA) and a flame ionization detector (FID). A gas chromatograph (Agilent 7890B) was used to detect the N2 content; the detectors were TCD and ECD detectors; a 5A molecular sieve column was used; and the carrier gases were N2 and He. The CH4-SCR activity of the catalyst was assessed using the following parameters: NOx removal efficiency (η), CH4 conversion (γ), CH4 selectivity (α), and N2 selectivity (SN2). These were calculated using Equations (1), (2), (3), and (4), respectively:
where c(NOx)in is the input concentration of NOx, c(NOx)out is the output concentration of NOx, c(CH4)in is the input concentration of CH4, c(CH4)out is the output concentration of CH4, and c(N2)out is the concentration of N2 formed, respectively.
3.3. Catalyst Characterization
Scanning electron microscopy (SEM) observation was conducted using a Thermo Scientific Apreo 2S HiVac (Waltham, MA, USA). To understand the crystalline phases and structures of the catalysts, powder X-ray diffraction (PXRD) patterns were recorded by a Bruker D8 Venture diffractometer (Germany) in the diffraction angle range of 2θ = 5–40° (2° min−1) with Cu Kα radiation (λ = 1.5418 Å) at 40 kV and 40 mA. Inductively coupled plasma optical emission spectrometry (ICP-OES, Agilent 720ES, USA) was used to determine the elemental content of Cr, In, Si, and Al in the bulk catalyst. The specific surface area and pore structure of the catalyst samples were calculated from N2 adsorption–desorption isotherms measured at 77 K on a Micromeritics ASAP 2460 instrument (Micromeritics, GA, USA). Prior to measurement, the samples were degassed at 300 °C for 6 h to eliminate adsorbed impurities. The surface elemental composition and chemical state of the catalyst were analyzed using X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) on an ESCALAB MK-II electron spectrometer (Thermo Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA) with a monochromatic Al Kα radiation source (1486.6 eV). The binding energy values were calibrated using the C 1s peak at 284.8 eV for adventitious carbon. The reducibility of the catalysts was evaluated by temperature-programmed reduction with hydrogen (H2-TPR) using an AutoChem Ⅱ 2920 instrument (Micromeritics, Norcross, GA, USA). Before the measurement, 50 mg samples (40–60 mesh) were loaded into a U-shaped quartz tube and pretreated at 500 °C in an He gas flow of 30 mL/min for 2 h. After being cooled to 50 °C under the same atmosphere, the samples were exposed to a 10 vol% H2/Ar mixture at a flow rate of 30 mL/min and heated from 50 °C to 650 °C at a ramp rate of 10 °C/min. Temperature-programmed desorption of ammonia (NH3-TPD) was conducted using a 5 vol% NH3/N2 gas mixture under a similar temperature program to investigate the acidic properties of the samples.
4. Conclusions
In summary, a Cr-In/H-SSZ-39 catalyst with high CH4-SCR deNOx performance was successfully prepared, and its preparation conditions were systematically optimized. The effects of the operating conditions were investigated, and the CH4-SCR deNOx mechanism over Cr-In/H-SSZ-39 was elucidated. The main findings of this study are as follows:
(1) The Cr-In/H-SSZ-39 catalyst exhibited optimal NOx conversion of 80% when exchanged with a mixed solution of 0.0075 M Cr(NO3)3 and 0.066 M In(NO3)3, calcined at 500 °C, and tested under conditions of 400 ppm NO, 600 ppm CH4, 10 vol% O2, 6 vol% H2O, and a GHSV of 21,000 h−1. The catalytic activity of Cr-In/H-SSZ-39 under humid conditions was significantly superior to that of the monometallic In/H-SSZ-39.
(2) Under the optimized operating conditions, the Cr-In/H-SSZ-39 catalyst demonstrated excellent regeneration ability and long-term stability. Specifically, under 10 vol% H2O content and at 600 °C, the NOx conversion in four consecutive cycles were 71%, 58%, 51%, and 43%, respectively. The long-term operation test further demonstrated that the NOx removal efficiency was kept at over 50% for up to 5 h and above 40% for up to 12 h.
(3) The incorporation of Cr into the In/H-SSZ-39 catalyst resulted in an increase in BAS and the production of more InO+ active species, which were responsible to the oxidation of NO and the activation of CH4. A potent synergistic interaction was observed between Cr and In species. The additional Cr3+ species significantly enhanced the redox properties of the catalyst, further promoting the oxidation of NO and the activation of CH4, ultimately leading to an improvement in catalytic activity. This approach holds promise as a feasible strategy to enhance the catalytic performance of In/H-SSZ-39 under harsh high-temperature hydrothermal conditions commonly encountered in practical applications.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, J.Z.; Methodology, J.J., M.W., G.C. and R.Z.; Software, J.Z., J.J., M.W., G.C. and R.Z.; Validation, J.Z.; Formal analysis, J.Z., M.W., G.C., Y.B. and R.Z.; Investigation, J.Z., J.J., M.W., X.Z. and R.Z.; Resources, J.Z., J.J., G.C., X.Z., Y.B. and R.Z.; Data curation, M.W., X.Z. and Y.B.; Writing—original draft, J.Z., M.W. and G.C.; Writing—review & editing, J.J., G.C. and R.Z.; Funding acquisition, J.J. and R.Z. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the Special Project for Sustainable Development Science Technology in Shenzhen grant number [KCXFZ20201221173000001, KCXFZ20240903094201002], the Natural Science Foundation of Guangdong grant number [No. 2022A1515011075], and the Special Foundation for Sustainable Development Research of Shenzhen grant number [No. KCXST20221021111405012].
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Informed consent was obtained from all subjects involved in the study.
Data Availability Statement
The original contributions presented in this study are included in the article. Further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Conflicts of Interest
Author Xiaoyuan Zuo was employed by the company Shandong Pallet Environmental Technology Co., Ltd. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
References
- Wang, Q.-J.; Feng, G.-F.; Wang, H.-J.; Chang, C.-P. The Influence of Political Ideology on Greenhouse Gas Emissions. Glob. Environ. Change 2022, 74, 102496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomson, H.; Corbett, J.J.; Winebrake, J.J. Natural Gas as a Marine Fuel. Energy Policy 2015, 87, 153–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, N.; Hong, Y.; Cai, Y.; Dong, F.; Song, J. The Removal of CH4 and NOx from Marine LNG Engine Exhaust by NTP Combined with Catalyst: A Review. Materials 2023, 16, 4969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Cui, K.; Lv, J.; Zhang, J.; Peng, C.; Li, Y.; Gu, Z.; Song, X. Biochar Amendments Increase Soil Organic Carbon Storage and Decrease Global Warming Potentials of Soil CH4 and N2O under N Addition in a Subtropical Moso Bamboo Plantation. For. Ecosyst. 2022, 9, 100054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boningari, T.; Smirniotis, P.G. Impact of Nitrogen Oxides on the Environment and Human Health: Mn-Based Materials for the NOx Abatement. Curr. Opin. Chem. Eng. 2016, 13, 133–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ricciardolo, F.L.M.; Sterk, P.J.; Gaston, B.; Folkerts, G. Nitric Oxide in Health and Disease of the Respiratory System. Physiol. Rev. 2004, 84, 731–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Vries, W. Impacts of Nitrogen Emissions on Ecosystems and Human Health: A Mini Review. Curr. Opin. Environ. Sci. 2021, 21, 100249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellmann, A.; Atia, H.; Bentrup, U.; Brückner, A. Mechanism of the Selective Reduction of NOx by Methane over Co-ZSM-5. Appl. Catal. B 2018, 230, 184–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Armor, J.N. Selective Catalytic Reduction of NOx with Methane over Metal Exchange Zeolites. Appl. Catal. B 1993, 2, 239–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Wang, X.; Qin, M.; Li, Q. Selective Catalytic Reduction of NOx with CH4 over Zeolite Catalysts: Research Progress, Challenges and Perspectives. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2022, 10, 107270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaucký, D.; Vondrová, A.; Dědeček, J.; Wichterlová, B. Activity of Co Ion Sites in ZSM-5, Ferrierite, and Mordenite in Selective Catalytic Reduction of NO with Methane. J. Catal. 2000, 194, 318–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, F.; Hu, W.; Chen, J.; Wu, Y.; Qu, P.; Yuan, S.; Zhong, L.; Chen, Y. Insight into Enhancement of NO Reduction with Methane by Multifunctional Catalysis over a Mixture of Ce/HZSM-5 and CoOx in Excess of Oxygen. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2018, 57, 13312–13317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bustamante, F.; Córdoba, F.; Yates, M.; Montes de Correa, C. The Promotion of Cobalt Mordenite by Palladium for the Lean CH4-SCR of NOx in Moist Streams. Appl. Catal. A 2002, 234, 127–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutierrez, L.; Lombardo, E.A. Steam Resistant CoLa-Mordenite Catalysts for the SCR of NOx with CH4. Appl. Catal. A 2009, 360, 107–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costilla, I.O.; Sanchez, M.D.; Volpe, M.A.; Gigola, C.E. Ce Effect on the Selective Catalytic Reduction of NO with CH4 on Pd-Mordenite in the Presence of O2 and H2O. Catal. Today 2011, 172, 84–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anunziata, O.A.; Beltramone, A.R.; Requejo, F.G. In-Containing BEA Zeolite for Selective Catalytic Reduction of NOx: Part I: Synthesis, Characterization and Catalytic Activity. J. Mol. Catal. A Chem. 2007, 267, 194–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, H.; Jian, Y.; Yu, Y.; Chen, N.; He, C.; He, C. Promotional Mechanism of Propane on Selective Catalytic Reduction of NOx by Methane over In/H-BEA at Low Temperature. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2016, 390, 608–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, B.; Zhao, T.; Du, J.; Hu, J.; Shi, Y.; Zhao, J.; Chen, J. Reaction and Deactivation Mechanisms of a CeIn/HBEA Catalyst with Dual Active Sites for Selective Catalytic Reduction of NOx by CH4. Appl. Catal. B 2024, 358, 124343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Chen, Y.; Wang, Y.; Li, Z.; Nkinahamira, F.; Zhu, R.; Zhang, J.; Sun, S.; Zhu, Y.; Li, H.; et al. The Poisoning Mechanism of H2O/SO2 to In/H-Beta for Selective Catalytic Reduction of NOx with Methane. Appl. Catal. A 2023, 649, 118973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Dong, L.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Zhu, R.; Li, C.; Hong, M. Amino-Acid Modulated Hierarchical In/H-Beta Zeolites for Selective Catalytic Reduction of NO with CH4 in the Presence of H2O and SO2. Nanoscale 2022, 14, 5915–5928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shan, Y.; Shan, W.; Shi, X.; Du, J.; Yu, Y.; He, H. A Comparative Study of the Activity and Hydrothermal Stability of Al-Rich Cu-SSZ-39 and Cu-SSZ-13. Appl. Catal. B 2020, 264, 118511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, J.; Tang, X.; Huang, C.; Liu, J.; Shan, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Ren, M.; Wang, Y.; Shan, W.; Yu, Y.; et al. Facile One-Pot Synthesis of Cu-SSZ-39 Catalysts with Excellent Catalytic Performance in NH3-SCR Reaction. Appl. Catal. B 2024, 356, 124258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fickel, D.W.; D’Addio, E.; Lauterbach, J.A.; Lobo, R.F. The Ammonia Selective Catalytic Reduction Activity of Copper-Exchanged Small-Pore Zeolites. Appl. Catal. B 2011, 102, 441–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Y.; Sun, Y.; Shan, Y.; Chen, J.; Du, J.; He, G.; He, H. Unexpected Promotion Effect of H2O on the Selective Catalytic Reduction of NOx with NH3 over Cu-SSZ-39 Catalysts. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2024, 58, 3520–3529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, J.; Han, S.; Huang, C.; Shan, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Shan, W.; He, H. Comparison of Precursors for the Synthesis of Cu-SSZ-39 Zeolite Catalysts for NH3-SCR Reaction. Appl. Catal. B 2023, 338, 123072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Zhang, L.; Ma, Y.; Fan, K.; Zhang, J.; Wu, J.; Yan, W.; Meng, X.; Wu, Q.; Yang, F.; et al. Selective Catalytic Reduction of NOx with Methane over Cobalt-Exchanged SSZ-39 Zeolite. Chem. Eng. J. 2024, 496, 153191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, S.; Wang, P.; Wang, K.; Wang, X.; Li, B.; Guo, X. Efficient in/SSZ-39 Catalysts for the Selective Catalytic Reduction of NO with CH4. Front. Chem. 2024, 12, 1439581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, G.; Zhang, W.; Zhu, R.; Chen, Y.; Zhao, M.; Hong, M. Engineering In-Co3O4/H-SSZ-39(OA) Catalyst for CH4-SCR of NOx: Mild Oxalic Acid (OA) Leaching and Co3O4 Modification. Molecules 2024, 29, 3747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Jiang, J.; Wang, M.; Chen, J.; Li, J.; Wang, X.; Zhu, R. Innovative in/H-SSZ-39 Catalysts: An Exploration in NOx Reduction via CH4-SCR. Catalysts 2024, 14, 582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Chang, Y.; Dai, W.; Wu, G.; Guan, N.; Li, L. Bimetallic Cr-In/H-SSZ-13 for Selective Catalytic Reduction of Nitric Oxide by Methane. Chin. J. Catal. 2018, 39, 1004–1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Chang, Y.; Dai, W.; Wu, G.; Guan, N.; Li, L. Ru-In/H-SSZ-13 for the Selective Reduction of Nitric Oxide by Methane: Insights from Temperature-Programmed Desorption Studies. Appl. Catal. B 2018, 236, 404–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Wen, Z.; Zhu, R.; Li, Z.; Ding, R.; Zhu, Y.; Gu, T.; Yang, R.; Zhu, Z. In/H-Beta Modified by Co3O4 and Its Superior Performance in the Presence of H2O and SO2 for Selective Catalytic Reduction of NOx with CH4. Chem. Eng. J. Adv. 2020, 3, 100029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Xu, G.; Zhang, Y.; Chang, C.; Jiang, M.; Ruan, L.; Xiao, M.; Yan, Z.; Yu, Y.; He, H. Designing a Ce/In-CHA OXZEO Catalyst for High-Efficient Selective Catalytic Reduction of Nitrogen Oxide with Methane. Appl. Catal. B 2024, 348, 123820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, W.; Wang, X.; Liu, Y.; Miao, B.; Li, Q. Enhanced Activity and Water Resistance of SiO2-Coated Co/In-SSZ-13 Catalysts in the Selective Catalytic Reduction of NOx with CH4. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2024, 12, 113746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Lv, G.; Li, Y.; Liu, Y.; Song, C. Selective Catalytic Reduction of NOX with CH4 over in/SSZ-13 Zeolites: The Enhancement of High-Temperature Catalytic Activity by Ce Modification. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2024, 12, 111830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Pu, J.; Gao, L.; Shan, S. Selective Catalytic Reduction of NOx with NH3 and CH4 over Zeolite Supported Indium-Cerium Bimetallic Catalysts for Lean-Burn Natural Gas Engines. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 403, 126394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, M.; Zhao, J.; Ding, R.; Zhu, R.; Li, H.; Li, Z.; Zhang, J.; Zhu, Y.; Li, H. Insights into the Superior Resistance of In-Co3O4-Ga2O3/H-Beta to SO2 and H2O in the Selective Catalytic Reduction of NOx by CH4. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2022, 626, 89–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Zhang, G.; He, J.; Wen, Z.; Li, Z.; Gu, T.; Ding, R.; Zhu, Y.; Zhu, R. Effect of Preparation and Reaction Conditions on the Performance of In/H-Beta for Selective Catalytic Reduction of NOx with CH4. Chemosphere 2020, 252, 126458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, W.; Tang, Q.; Huang, S.; Zhang, L.; Jia, Z.; Guo, L. Low Temperature Catalytic Combustion of Chlorobenzene over Cobalt Based Mixed Oxides Derived from Layered Double Hydroxides. Appl. Catal. B 2020, 278, 119336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoo, J.S.; Khan, T.S.; Abild-Pedersen, F.; Nørskov, J.K.; Studt, F. On the Role of the Surface Oxygen Species during A–H (A = C, N, O) Bond Activation: A Density Functional Theory Study. Chem. Commun. 2015, 51, 2621–2624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, M.; Liu, N.; Dai, C.; Chen, B. CO2 Oxidative Dehydrogenation of Propane to Olefin over Cr-M (M = Zr, La, Fe) Based Zeolite Catalyst. Catalysts 2024, 14, 370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).