Nicotine Degradation by Trametes versicolor: Insights from Diverse Environmental Stressors and Wastewater Medium
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Nicotine Concentration and Determination
2.2. Mycelium Growth Inhibition, Fungal Resistance to Nicotine Concentrations
2.3. FT-IR Results
- Bands between 2966 and 2776 cm−1: C-H stretching.
- A slightly split band at 1577 cm−1: aromatic C=C and C=N double-bond stretching.
- Bands at 1458, 1428, and 1363 cm−1: C-H bending.
- Bands at 903, 806, and 716 cm−1: out-of-plane C-H bending of the monosubstituted pyridinic cycle.
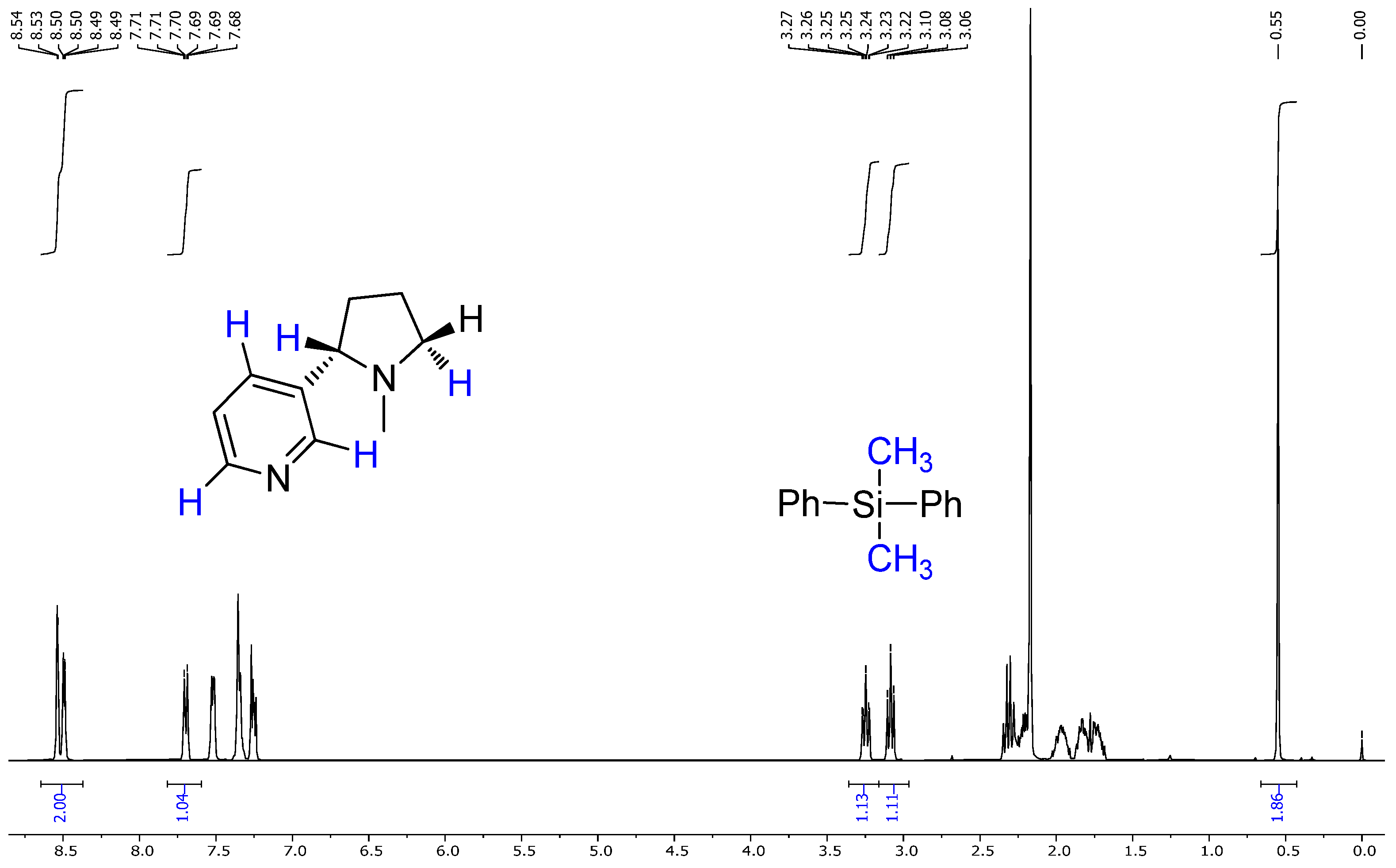
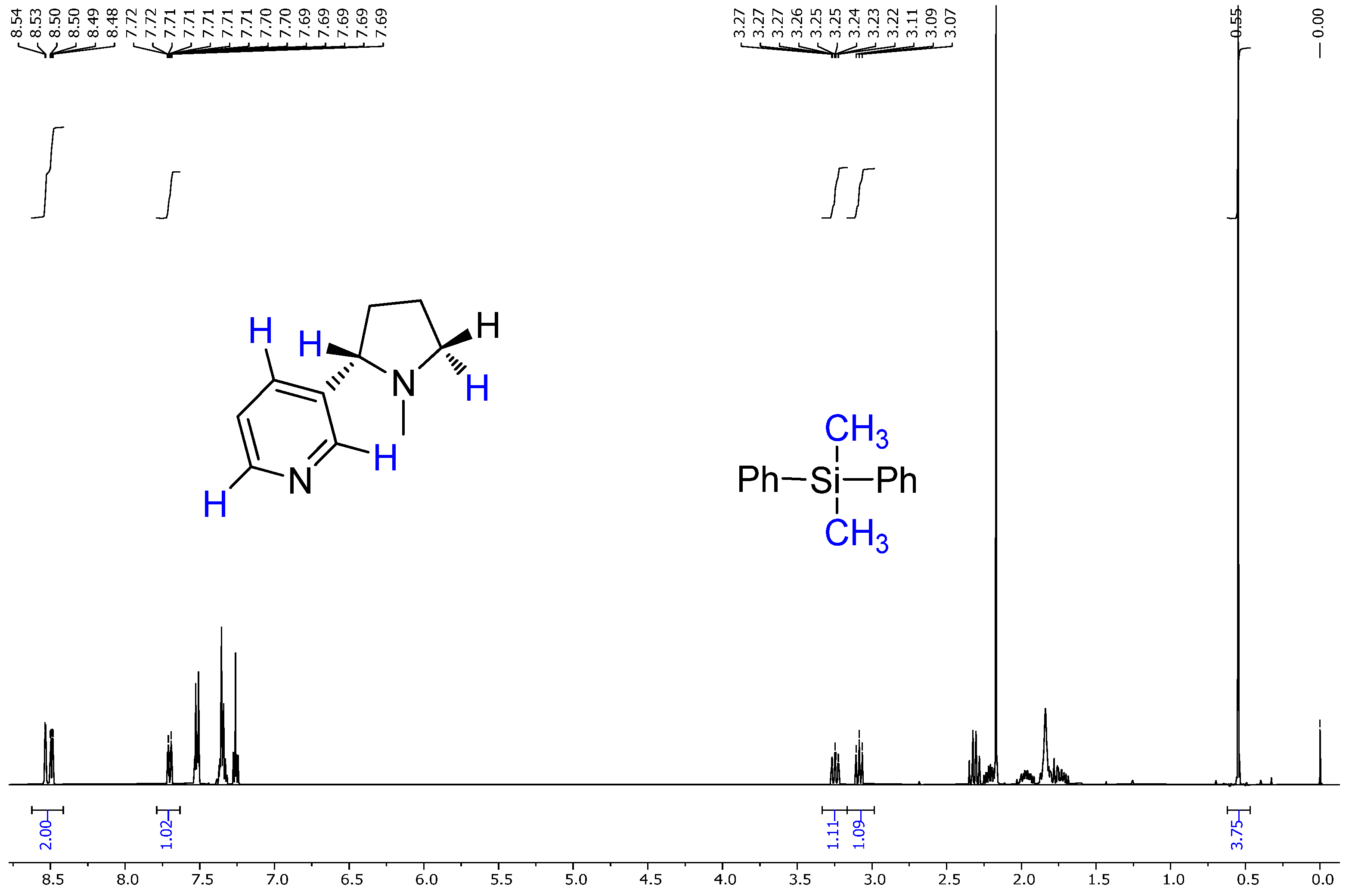
2.4. NMR Results
- Chemical shift values;
- Multiplicities;
- Coupling constants;
- Integration values.
- The extracted compound was indeed nicotine;
- It had high purity, as no major impurities or unexpected peaks were observed.
2.5. Discussion
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Chemicals and Materials
3.2. Nicotine Extraction
3.3. Nicotine Concentration and Determination
3.4. Cultural Condition of Trametes Versicolor
3.5. Mycelium Growth Inhibition by Different Nicotine Concentrations
3.6. Fungi Biomass Quantification
3.7. Biodegradation Experiments
3.8. Sample Extraction and Purification
3.9. FT-IR Analysis
3.10. NMR Analysis
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kondo, T.; Nakano, Y.; Adachi, S.; Murohara, T. Effects of Tobacco Smoking on Cardiovascular Disease. Circ. J. 2019, 83, 1980–1985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Percoco, G.; Patatian, A.; Eudier, F.; Grisel, M.; Bader, T.; Lati, E.; Savary, G.; Picard, C.; Benech, P. Impact of Cigarette Smoke on Physical-chemical and Molecular Proprieties of Human Skin in an Ex Vivo Model. Exp. Dermatol. 2021, 30, 1610–1618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohn, A.M.; Elmasry, H. First Use of Cannabis Compared to First Use of Alcohol and Tobacco: Associations with Single and Poly-Substance Use Behavior. Drug Alcohol Depend. 2023, 248, 109904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hossain, A.M.; Salehuddin, S.M. Analytical Determination of Nicotine in Tobacco Leaves by Gas Chromatography–Mass Spectrometry. Arab. J. Chem. 2013, 6, 275–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banožić, M.; Babić, J.; Jokić, S. Recent Advances in Extraction of Bioactive Compounds from Tobacco Industrial Waste—A Review. Ind. Crops Prod. 2020, 144, 112009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, J.; Shao, X. Determination of Tobacco Alkaloids by Gas Chromatography–Mass Spectrometry Using Cloud Point Extraction as a Preconcentration Step. Anal. Chim. Acta 2006, 561, 83–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harahap, A.F.P.; Fauzantoro, A.; Gozan, M. Bio-oil from Tobacco Plant. In Biorefinery of Oil Producing Plants for Value-Added Products; Abd-Aziz, S., Gozan, M., Ibrahim, M.F., Phang, L., Eds.; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2022; pp. 397–420. ISBN 978-3-527-34876-3. [Google Scholar]
- Švob Troje, Z.; Fröbe, Z.; Perović, Đ. Analysis of Selected Alkaloids and Sugars in Tobacco Extract. J. Chromatogr. A 1997, 775, 101–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Tamrah, S.A. Spectrophotometric Determination of Nicotine. Anal. Chim. Acta 1999, 379, 75–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bush, D.; Goniewicz, M.L. A Pilot Study on Nicotine Residues in Houses of Electronic Cigarette Users, Tobacco Smokers, and Non-Users of Nicotine-Containing Products. Int. J. Drug Policy 2015, 26, 609–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Civilini, M. Nicotine decontamination of tobacco agro-industrial waste and its degradation by micro-organisms. Waste Manag. Res. 1997, 15, 349–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stanisavljević, I.T.; Lazić, M.L.; Veljković, V.B. Ultrasonic Extraction of Oil from Tobacco (Nicotiana tabacum L.) Seeds. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2007, 14, 646–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Padhiary, S.; Samal, D.; Khandayataray, P.; Murthy, M.K. A Systematic Review Report on Tobacco Products and Its Health Issues in India. Rev. Environ. Health 2021, 36, 367–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boiangiu, R.S.; Brinza, I.; Honceriu, I.; Mihasan, M.; Hritcu, L. Insights into Pharmacological Activities of Nicotine and 6-Hydroxy-L-Nicotine, a Bacterial Nicotine Derivative: A Systematic Review. Biomolecules 2023, 14, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, R.; Tscharke, B.; O’Brien, J.; Mueller, J.F.; Wilkins, C.; Padhye, L.P. Assessment of Drugs of Abuse in a Wastewater Treatment Plant with Parallel Secondary Wastewater Treatment Train. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 658, 947–957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baker, D.R.; Kasprzyk-Hordern, B. Spatial and Temporal Occurrence of Pharmaceuticals and Illicit Drugs in the Aqueous Environment and during Wastewater Treatment: New Developments. Sci. Total Environ. 2013, 454–455, 442–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hedgespeth, M.L.; Sapozhnikova, Y.; Pennington, P.; Clum, A.; Fairey, A.; Wirth, E. Pharmaceuticals and Personal Care Products (PPCPs) in Treated Wastewater Discharges into Charleston Harbor, South Carolina. Sci. Total Environ. 2012, 437, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evgenidou, E.N.; Konstantinou, I.K.; Lambropoulou, D.A. Occurrence and Removal of Transformation Products of PPCPs and Illicit Drugs in Wastewaters: A Review. Sci. Total Environ. 2015, 505, 905–926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avagyan, R.; Spasova, M.; Lindholm, J. Determination of Nicotine-Related Impurities in Nicotine Pouches and Tobacco-Containing Products by Liquid Chromatography–Tandem Mass Spectrometry. Separations 2021, 8, 77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalčíková, G.; Alič, B.; Skalar, T.; Bundschuh, M.; Gotvajn, A.Ž. Wastewater Treatment Plant Effluents as Source of Cosmetic Polyethylene Microbeads to Freshwater. Chemosphere 2017, 188, 25–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kupper, T.; Plagellat, C.; Brändli, R.C.; De Alencastro, L.F.; Grandjean, D.; Tarradellas, J. Fate and Removal of Polycyclic Musks, UV Filters and Biocides during Wastewater Treatment. Water Res. 2006, 40, 2603–2612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.-Q.; Lam, J.C.W.; Li, W.-W.; Yu, H.-Q.; Lam, P.K.S. Spatial Distribution and Removal Performance of Pharmaceuticals in Municipal Wastewater Treatment Plants in China. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 586, 1162–1169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, N.; Shi, Y.; Li, W.; Xu, L.; Cai, Y. Concentrations and Distribution of Synthetic Musks and Siloxanes in Sewage Sludge of Wastewater Treatment Plants in China. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 476–477, 65–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aghaei, M.; Khoshnamvand, N.; Janjani, H.; Dehghani, M.H.; Karri, R.R. Exposure to Environmental Pollutants: A Mini-Review on the Application of Wastewater-Based Epidemiology Approach. J. Environ. Health Sci. Eng. 2024, 22, 65–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Essam, A.; Eldek, S.I.; Shehata, N. Management of Caffeine in Wastewater Using MOF and Perovskite Materials: Optimization, Kinetics, and Adsorption Isotherm Modelling. J. Environ. Health Sci. Eng. 2024, 22, 345–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peces, M.; Dottorini, G.; Nierychlo, M.; Andersen, K.S.; Dueholm, M.K.D.; Nielsen, P.H. Microbial Communities across Activated Sludge Plants Show Recurring Species-Level Seasonal Patterns. ISME Commun. 2022, 2, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagner, M.; Loy, A.; Nogueira, R.; Purkhold, U.; Lee, N.; Daims, H. Microbial community composition and function in wastewater treatment plants. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 2002, 81, 665–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, C.; Peces, M.; Andersen, M.H.; Kucheryavskiy, S.; Nierychlo, M.; Yashiro, E.; Andersen, K.S.; Kirkegaard, R.H.; Hao, L.; Høgh, J.; et al. Characterizing the Growing Microorganisms at Species Level in 46 Anaerobic Digesters at Danish Wastewater Treatment Plants: A Six-Year Survey on Microbial Community Structure and Key Drivers. Water Res. 2021, 193, 116871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, P.; Xu, W.; Sontag, P.; Li, X.; Xue, G.; Liu, T.; Sun, W. Correlating Microbial Community Compositions with Environmental Factors in Activated Sludge from Four Full-Scale Municipal Wastewater Treatment Plants in Shanghai, China. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2016, 100, 4663–4673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, A.; Senaidi, A.S.; Al-Rahbi, A.S.; Al-dawery, S.K. Biodegradation of Petroleum Wastewater for the Production of Bioelectricity Using Activated Sludge Biomass. J. Environ. Health Sci. Eng. 2022, 21, 133–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashemi, S.Y.; Shahmahmoodi, S.; Hadi, M.; Nodehi, R.N.; Alimohammadi, M.; Nejati, A.; Mesdaghinia, A. Quantitative Microbial Risk Assessment of Enteroviruses in Raw-Eatable Vegetables Irrigated by Wastewater: Examining Different Scenarios of Washing. J. Environ. Health Sci. Eng. 2022, 20, 629–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrando-Climent, L.; Cruz-Morató, C.; Marco-Urrea, E.; Vicent, T.; Sarrà, M.; Rodriguez-Mozaz, S.; Barceló, D. Non Conventional Biological Treatment Based on Trametes Versicolor for the Elimination of Recalcitrant Anticancer Drugs in Hospital Wastewater. Chemosphere 2015, 136, 9–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, Y.; Xian, H.; Shi, S.; Zhang, C.; Manik, S.M.N.; Mao, J.; Zhang, G.; Liao, W.; Wang, Q.; Liu, H. Biodegradation of Lignin and Nicotine with White Rot Fungi for the Delignification and Detoxification of Tobacco Stalk. BMC Biotechnol. 2016, 16, 81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meng, X.J.; Lu, L.L.; Gu, G.F.; Xiao, M. A Novel Pathway for Nicotine Degradation by Aspergillus Oryzae 112822 Isolated from Tobacco Leaves. Res. Microbiol. 2010, 161, 626–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; He, H.; Wang, M.; Wang, S.; Zhang, J.; Wei, W.; Xu, H.; Lv, Z.; Shen, D. Bioaugmentation of Activated Sludge with Acinetobacter sp. TW Enhances Nicotine Degradation in a Synthetic Tobacco Wastewater Treatment System. Bioresour. Technol. 2013, 142, 445–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Yang, G.; Min, H.; Lv, Z.; Jia, X. Bioaugmentation with the Nicotine-Degrading Bacterium Pseudomonas sp. HF-1 in a Sequencing Batch Reactor Treating Tobacco Wastewater: Degradation Study and Analysis of Its Mechanisms. Water Res. 2009, 43, 4187–4196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beškoski, V.P.; Gojgić-Cvijović, G.; Milić, J.; Ilić, M.; Miletić, S.; Šolević, T.; Vrvić, M.M. Ex Situ Bioremediation of a Soil Contaminated by Mazut (Heavy Residual Fuel Oil)—A Field Experiment. Chemosphere 2011, 83, 34–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brenner, K.; You, L.; Arnold, F.H. Engineering Microbial Consortia: A New Frontier in Synthetic Biology. Trends Biotechnol. 2008, 26, 483–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piotrowska-Cyplik, A.; Olejnik, A.; Cyplik, P.; Dach, J.; Czarnecki, Z. The Kinetics of Nicotine Degradation, Enzyme Activities and Genotoxic Potential in the Characterization of Tobacco Waste Composting. Bioresour. Technol. 2009, 100, 5037–5044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganas, P.; Sachelaru, P.; Mihasan, M.; Igloi, G.L.; Brandsch, R. Two Closely Related Pathways of Nicotine Catabolism in Arthrobacter nicotinovorans and Nocardioides sp. Strain JS614. Arch. Microbiol. 2008, 189, 511–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiribau, C.; Mihasan, M.; Ganas, P.; Igloi, G.L.; Artenie, V.; Brandsch, R. Final Steps in the Catabolism of Nicotine: Deamination versus Demethylation of Γ-N-methylaminobutyrate. FEBS J. 2006, 273, 1528–1536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cobzaru, C.; Ganas, P.; Mihasan, M.; Schleberger, P.; Brandsch, R. Homologous Gene Clusters of Nicotine Catabolism, Including a New ω-Amidase for α-Ketoglutaramate, in Species of Three Genera of Gram-Positive Bacteria. Res. Microbiol. 2011, 162, 285–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández-López, C.; González García, M.; Bueno-Crespo, A.; Martínez-España, R. Biodegradation Behaviour of Pharmaceutical Compounds and Selected Metabolites in Activated Sludge. A Forecasting Decision System Approach. J. Environ. Health Sci. Eng. 2024, 22, 229–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Ma, G.; Chen, T.; Hou, Y.; Yang, S.; Zhang, K.-Q.; Yang, J. Nicotine-Degrading Microorganisms and Their Potential Applications. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2015, 99, 3775–3785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sitaram, C.; Rupakula, R.; Reddy, B.N. Determination and Characterization of Degradation Products of Anastrozole by LC–MS/MS and NMR Spectroscopy. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2011, 56, 962–968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, C.R.; Burroughs, M.J.; Richards, L.A.; Dyer, L.A.; Urbano-Muñoz, F.; Lee, C.; Warner, M.; Dodson, C.D.; Wallace, I.S.; Jeffrey, C.S. 1H-NMR Guided Isolation of Bioactive Compounds from Species of the Genus Piper. Molecules 2025, 30, 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herrera-Jurado, E.A.; Terán-Sánchez, E.D.J.; Serrano-Contreras, J.I.; Zepeda-Vallejo, L.G. 1H Nuclear Magnetic Resonance-Based Targeted and Untargeted Metabolomics Profiling of Retail Samples of Cuachalalate (Amphipterygium adstringens). Molecules 2025, 30, 2185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iqbal, M.Y.; Rao, K.M.V.N.; Sridhar, G.; Raju, P.P.; Deshpande, G.R.; Babu, J.M. Characterization and Relative Response Factor Determination of Process Related Impurity in Naproxen by Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2011, 56, 484–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Görög, S.; Szántay, C. Spectroscopic Methods in Drug Quality Control and Development. In Encyclopedia of Spectroscopy and Spectrometry; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2010; pp. 2640–2650. ISBN 978-0-12-374413-5. [Google Scholar]
- Balayssac, S.; Assemat, G.; Danoun, S.; Malet-Martino, M.; Gilard, V. Quantitative 1H and 13C NMR and Chemometric Assessment of 13C NMR Data: Application to Anabolic Steroid Formulations. Molecules 2025, 30, 2060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, C.; Huang, Y.; Liu, P.; Wei, J.; Yang, Y.; Xu, L.; Xiao, M. Transcriptome Analysis of Genes and Metabolic Pathways Associated with Nicotine Degradation in Aspergillus oryzae 112822. BMC Genom. 2019, 20, 86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cogo, K.; Montan, M.F.; Bergamaschi, C.D.C.; Andrade, E.D.; Rosalen, P.L.; Groppo, F.C. In Vitro Evaluation of the Effect of Nicotine, Cotinine, and Caffeine on Oral Microorganisms. Can. J. Microbiol. 2008, 54, 501–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DuBois, A.E.; Bennett, Z.C.; Khalid, U.; Khalid, A.; Meece, R.A.; Difiore, G.J.; Gregory, R.L. Nicotine: Its Stimulating and Inhibitory Effects on Oral Microorganisms. Finefocus 2014, 1, 63–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, R.; Li, M.; Gregory, R.L. Effect of Nicotine on Growth and Metabolism of Streptococcus mutans. Eur. J. Oral Sci. 2012, 120, 319–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Del Sorbo, G.; Schoonbeek, H.; De Waard, M.A. Fungal Transporters Involved in Efflux of Natural Toxic Compounds and Fungicides. Fungal Genet. Biol. 2000, 30, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morrissey, J.P.; Osbourn, A.E. Fungal Resistance to Plant Antibiotics as a Mechanism of Pathogenesis. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 1999, 63, 708–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.-J.; Yang, D.-D.; Wei, Z.-Y.; Huang, J.; Chi, Y.-Q.; Lu, Y.-X.; Yin, F.-W. Reduction of Nicotine Content in Tobacco through Microbial Degradation: Research Progress and Potential Applications. Biotechnol. Biofuels 2024, 17, 144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, K.; Shi, M.; Pan, X.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, X.; Shen, T.; Tian, Y. Decolourization and Biodegradation of Methylene Blue Dye by a Ligninolytic Enzyme-Producing Bacillus thuringiensis: Degradation Products and Pathway. Enzym. Microb. Technol. 2022, 156, 109999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mali, H.; Shah, C.; Patel, D.H.; Trivedi, U.; Subramanian, R.B. Degradation Insight of Organophosphate Pesticide Chlorpyrifos through Novel Intermediate 2,6-Dihydroxypyridine by Arthrobacter sp. HM01. Bioresour. Bioprocess. 2022, 9, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeon, J.-M.; Park, S.-J.; Choi, T.-R.; Park, J.-H.; Yang, Y.-H.; Yoon, J.-J. Biodegradation of Polyethylene and Polypropylene by Lysinibacillus Species JJY0216 Isolated from Soil Grove. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2021, 191, 109662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meher, K.K.; Panchwagh, A.M.; Rangrass, S.; Gollakota, K.G. Biomethanation of Tobacco Waste. Environ. Pollut. 1995, 90, 199–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmit, C.G.; Jahan, K.; Schmit, K.H.; Debik, E.; Mahendraker, V. Activated Sludge and Other Aerobic Suspended Culture Processes. Water Environ. Res. 2009, 81, 1127–1193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mace, S.; Mata-Alvarez, J. Utilization of SBR Technology for Wastewater Treatment: An Overview. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2002, 41, 5539–5553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turner, A.J.; Hick, P.E. Inhibition of Aldehyde Reductase by Acidic Metabolites of the Biogenic Amines. Biochem. Pharmacol. 1975, 24, 1731–1733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Mu, X.; Li, W.; Xu, Q.; Xu, P.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, G. Structural, Mechanistic, and Functional Insights into an Arthrobacter nicotinovorans Molybdenum Hydroxylase Involved in Nicotine Degradation. Molecules 2021, 26, 4387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uchida, S.; Maeda, S.; Kisaki, T. Conversion of Nicotine into Nornicotine and N-Methylmyosmine by Fungi. Agric. Biol. Chem. 1983, 47, 1949–1953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dave, B.; Moysa, E.L.; Kuźnik, A. Comparative Analysis of Cosmetic Ingredient Degradation: Fungal vs. Bacterial Activity in Diverse Media as Potential Replacements. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 2024, 191, 105795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Long, Y.; Yu, G.; Wang, G.; Zhou, Z.; Li, P.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, K.; Wang, S. A Review on Microorganisms in Constructed Wetlands for Typical Pollutant Removal: Species, Function, and Diversity. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 845725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medici, A.; Luongo, G.; Previtera, L.; Naviglio, D.; Di Fabio, G.; Zarrelli, A. Degradation of Indomethacin in Wastewater: Removal with Sodium Hypochlorite and Analysis of Degradation Byproducts. Molecules 2025, 30, 2180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Briški, F.; Horgas, N.; Vuković, M.; Gomzi, Z. Aerobic Composting of Tobacco Industry Solid Waste—Simulation of the Process. Clean Technol. Environ. Policy 2003, 5, 295–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hooper, L.; Cassidy, A. A Review of the Health Care Potential of Bioactive Compounds. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2006, 86, 1805–1813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jureczko, M.; Przystaś, W.; Krawczyk, T.; Gonciarz, W.; Rudnicka, K. White-Rot Fungi-Mediated Biodegradation of Cytostatic Drugs—Bleomycin and Vincristine. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 407, 124632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodarte-Morales, A.I.; Feijoo, G.; Moreira, M.T.; Lema, J.M. Degradation of Selected Pharmaceutical and Personal Care Products (PPCPs) by White-Rot Fungi. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2011, 27, 1839–1846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Łobos-Moysa, E.; Bodzek, M. Application of Hybrid Biological Techniques to the Treatment of Municipal Wastewater Containing Oils and Fats. Desalination Water Treat. 2012, 46, 32–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, R.; Oliveira, M.B.P.P.; Alves, R.C. Chlorogenic Acids and Caffeine from Coffee By-Products: A Review on Skincare Applications. Cosmetics 2023, 10, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
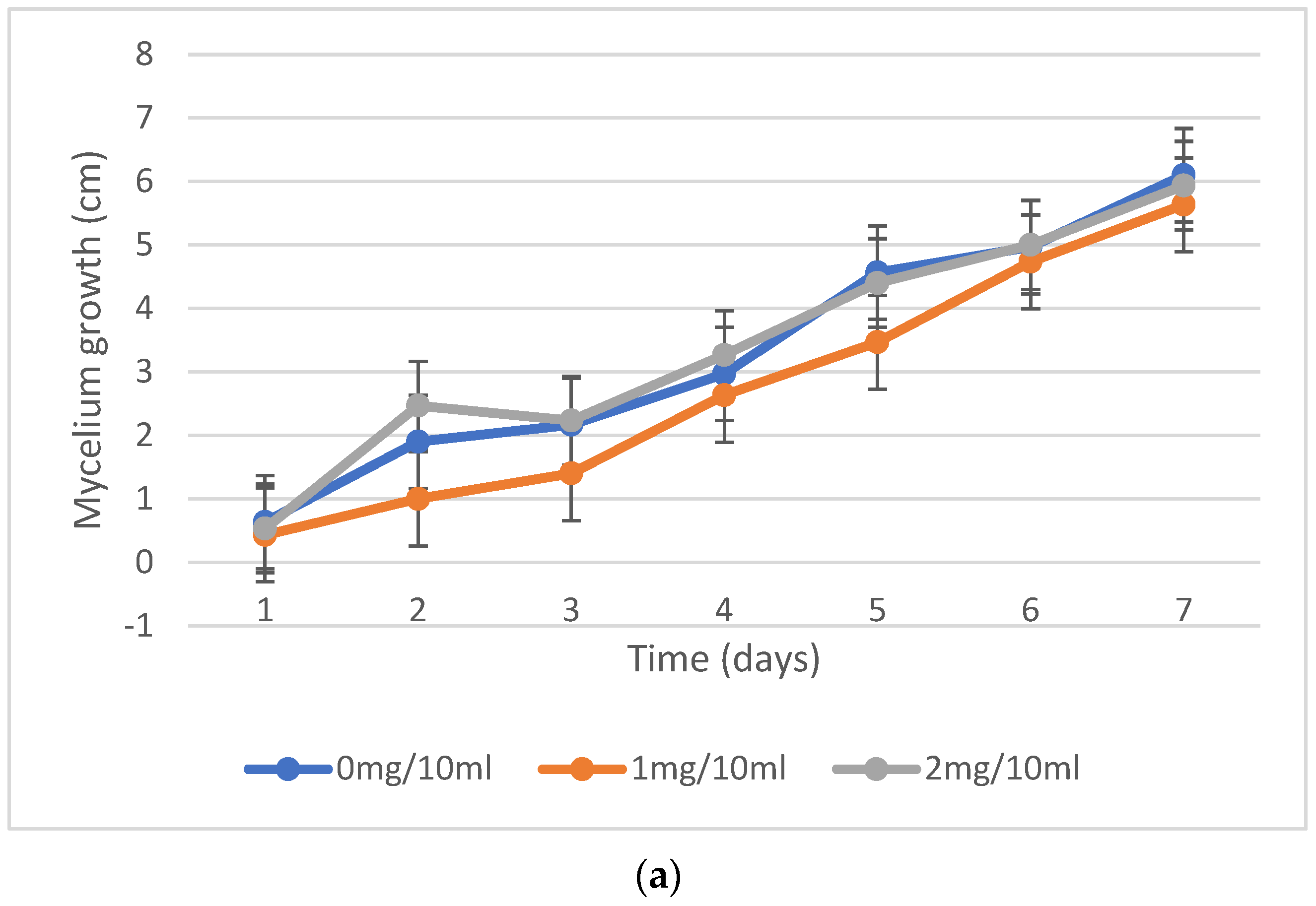
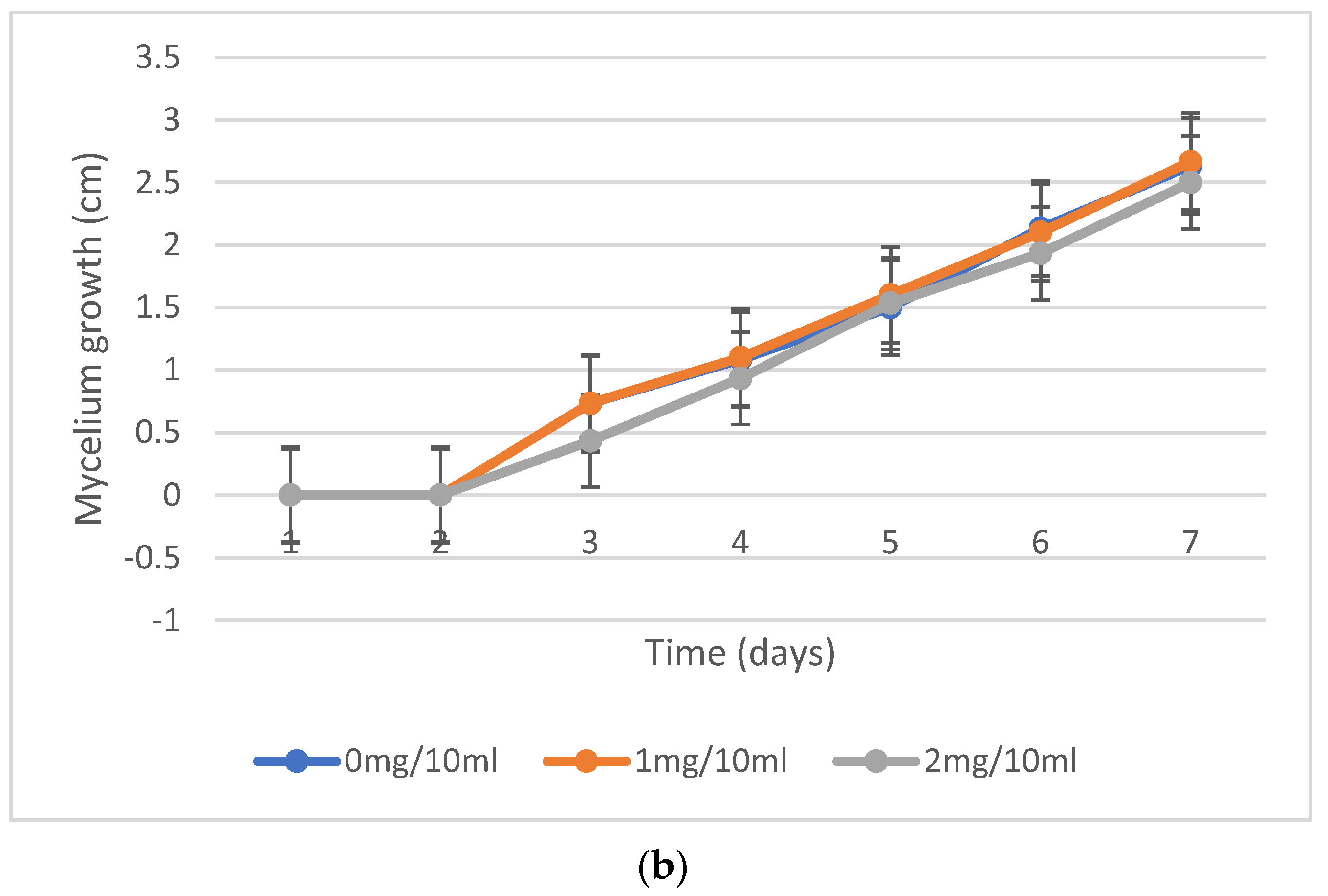
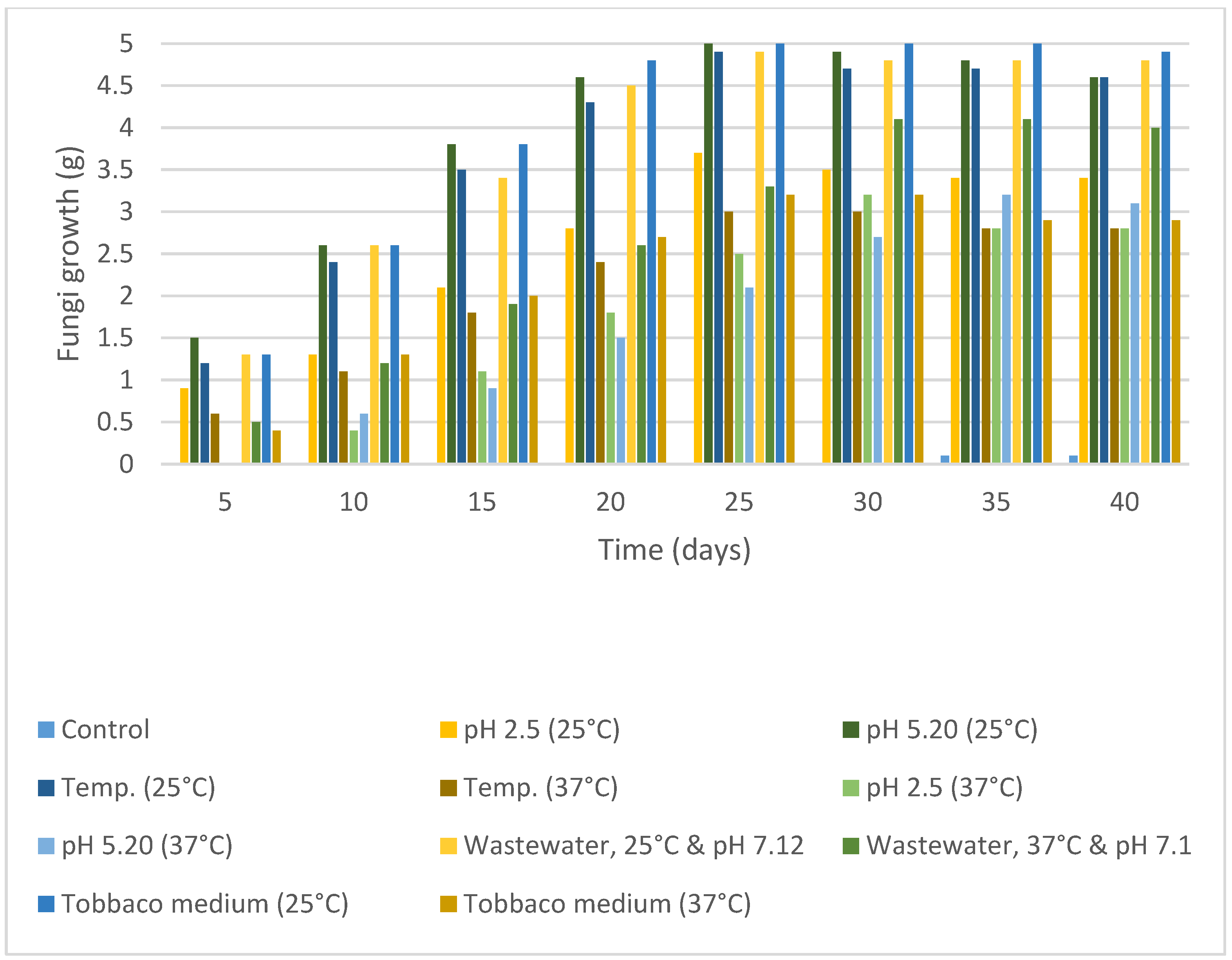
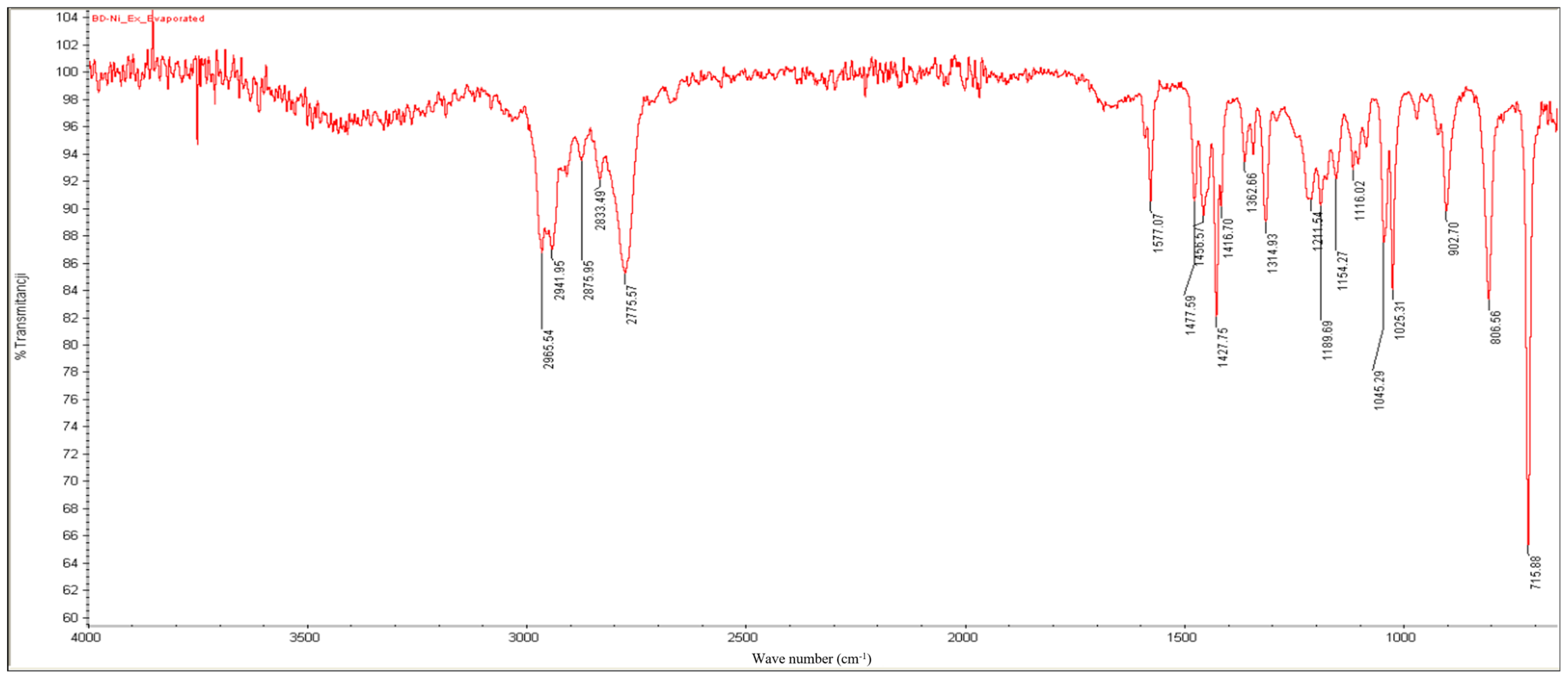

| No. | Fungi Inoculation | Concentration of Nicotine | Incubation |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Temperature at 25 °C (PDB) | 1 mg/10 mL | 25 °C |
| 2. | Temperature at 37 °C (PDB) | 1 mg/10 mL | 37 °C |
| 3. | pH 2.5 (25°) (PDB) | 1 mg/10 mL | 25 °C |
| 4. | pH 2.5 (37°) (PDB) | 1 mg/10 mL | 37 °C |
| 5. | pH 5.18 (25°) (PDB) | 1 mg/10 mL | 25 °C |
| 6. | pH 5.18 (37°) (PDB) | 1 mg/10 mL | 37 °C |
| 7. | pH 6.4 (25°) (SWW) | 1 mg/10 mL | 25 °C |
| 8. | pH 6.4 (37°) (SWW) | 1 mg/10 mL | 37 °C |
| 9. | 15 gm of tobacco (100 mL of SWW) | - | 25 °C |
| 9. | 15 gm of tobacco (100 mL of SWW) | - | 37 °C |
| 10. | Control sample (MilliQ water 25°) | 1 mg/10 mL | 25° C |
| 11. | Control sample (MilliQ water 37°) | 1 mg/10 mL | 37° C |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dave, B.; Moysa, E.L.; Kuźnik, A. Nicotine Degradation by Trametes versicolor: Insights from Diverse Environmental Stressors and Wastewater Medium. Molecules 2025, 30, 2658. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30122658
Dave B, Moysa EL, Kuźnik A. Nicotine Degradation by Trametes versicolor: Insights from Diverse Environmental Stressors and Wastewater Medium. Molecules. 2025; 30(12):2658. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30122658
Chicago/Turabian StyleDave, Bhautik, Ewa Lobos Moysa, and Anna Kuźnik. 2025. "Nicotine Degradation by Trametes versicolor: Insights from Diverse Environmental Stressors and Wastewater Medium" Molecules 30, no. 12: 2658. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30122658
APA StyleDave, B., Moysa, E. L., & Kuźnik, A. (2025). Nicotine Degradation by Trametes versicolor: Insights from Diverse Environmental Stressors and Wastewater Medium. Molecules, 30(12), 2658. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30122658







