Physicochemical Characteristics of Phospholipid Vesicles for Spirulina-Based Dietary Supplement Delivery
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Standards and Reagents
3.2. Phospholipid Vesicles
3.2.1. Preparation
3.2.2. Physical Characterization
3.2.3. Long-Term Stability
3.2.4. PH Sensitivity of Phospholipid Vesicles
3.3. Biochemical Analysis
3.3.1. Chl a, Total Carot, and Polyphenol Quantification in Phospholipid Vesicles
3.3.2. Antioxidant Activity
3.4. In Vitro Release of Spirulina Extract
3.5. Cell Culture and Biocompatibility of Phospholipid Vesicles
3.6. Protective Effect of Phospholipid Vesicles Against Damage Induced in Cells by Hydrogen Peroxide (H2O2)
3.7. Statistical Analysis
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Najar-Almanzor, C.E.; Velasco-Iglesias, K.D.; Nunez-Ramos, R.; Uribe-Velázquez, T.; Solis-Bañuelos, M.; Fuentes-Carrasco, O.J.; Chairez, I.; García-Cayuela, T.; Carrillo-Nieves, D. Microalgae-assisted green bioremediation of food-processing wastewater: A sustainable approach toward a circular economy concept. J. Environ. Manag. 2023, 345, 118774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lafarga, T.; Sánchez-Zurano, A.; Villaró, S.; Morillas-España, A.; Acién, G. Industrial production of Spirulina as a protein source for bioactive peptide generation. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 116, 176–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, M.A.R.; Zhu, F.; Cui, Y.; Hu, X.; Chen, H.; Kayani, S.I.; Huo, S. Mechanistic insights into the nutritional and therapeutic potential of Spirulina (Arthrospira spp.): Challenges and opportunities. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2024, 151, 104648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spínola, M.P.; Mendes, A.R.; Prates, J.A. Chemical composition, bioactivities, and applications of Spirulina (Limnospira platensis) in food, feed, and medicine. Foods 2024, 13, 3656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anvar, A.A.; Nowruzi, B. Bioactive properties of Spirulina: A review. Microb. Bioact. 2021, 4, 134–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bortolini, D.G.; Maciel, G.M.; Fernandes, I.D.A.A.; Pedro, A.C.; Rubio, F.T.V.; Branco, I.G.; Haminiuk, C.W.I. Functional properties of bioactive compounds from Spirulina spp.: Current status and future trends. Food Chem. Mol. Sci. 2022, 5, 100134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calella, P.; Cerullo, G.; Di Dio, M.; Liguori, F.; Di Onofrio, V.; Galle, F.; Liguori, G. Antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and immunomodulatory effects of Spirulina in exercise and sport: A systematic review. Front. Nutr. 2022, 9, 1048258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Supriya, R.; Delfan, M.; Saeidi, A.; Samaie, S.S.; Al Kiyumi, M.H.; Escobar, K.A.; Zouhal, H. Spirulina supplementation with high-intensity interval training decreases adipokine levels and cardiovascular risk factors in men with obesity. Nutrients 2023, 15, 4891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishnan, H.; Kaushik, D.; Kumar, M.; Öz, E.; Brennan, C.; Proestos, C.; Kumar, V.; Ahmed, M.; Özç, F. Exploring the natural efficacy of spirulina powder for combating obesity, diabetes, and inflammation. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2024, 104, 9128–9136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gentscheva, G.; Nikolova, K.; Panayotova, V.; Peycheva, K.; Makedonski, L.; Slavov, P.; Yotkovska, I. Application of Arthrospira platensis for medicinal purposes and the food industry: A review of the literature. Life 2023, 13, 845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaouachi, M.; Vincent, S.; Groussard, C. A review of the health-promoting properties of Spirulina with a focus on athletes’ performance and recovery. J. Diet. Suppl. 2024, 21, 210–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaufman, M.W.; Roche, M.; Fredericson, M. The impact of supplements on sports performance for the trained athlete: A critical analysis. Curr. Sports Med. Rep. 2022, 21, 232–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McBurney, M.I.; Blumberg, J.B.; Costello, R.B.; Eggersdorfer, M.; Erdman, J.W.; Harris, W.S.; Schurgers, L.J. Beyond nutrient deficiency—Opportunities to improve nutritional status and promote health modernizing DRIs and supplementation recommendations. Nutrients 2021, 13, 1844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wegierska, A.E.; Charitos, I.A.; Topi, S.; Potenza, M.A.; Montagnani, M.; Santacroce, L. The connection between physical exercise and gut microbiota: Implications for competitive sports athletes. Sports Med. 2022, 52, 2355–2369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cataldi, S.; Bonavolontà, V.; Poli, L.; Clemente, F.M.; De Candia, M.; Carvutto, R.; Fischetti, F. The relationship between physical activity, physical exercise, and human gut microbiota in healthy and unhealthy subjects: A systematic review. Biology 2022, 11, 479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, F.; Fu, G.; Ma, Y.; Zhou, L.; Li, G.; Sun, C.; Zhang, T. Spirulina polysaccharide-based prebiotic foods preparations—A promising approach for modulating gut microbiota and improving health. J. Funct. Foods 2024, 116, 106158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trotta, T.; Porro, C.; Cianciulli, A.; Panaro, M.A. Beneficial effects of Spirulina consumption on brain health. Nutrients 2022, 14, 676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abd Elkader, H.T.A.E.; Essawy, A.E.; Al-Shami, A.S. Bioactive compounds of the genus Spirulina can prevent the progression of neurological diseases. Neurochem. J. 2024, 18, 47–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandes, F.A.; Carocho, M.; Prieto, M.A.; Barros, L.; Ferreira, I.C.F.R.; Heleno, S.A. Nutraceuticals and dietary supplements: Balancing out the pros and cons. Food Funct. 2024, 15, 6289–6303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aquino, R.P.; Auriemma, G.; Conte, G.M.; Esposito, T.; Sommella, E.; Campiglia, P.; Sansone, F. Development of chitosan/mannitol microparticles as a delivery system for the oral administration of a Spirulina bioactive peptide extract. Molecules 2020, 25, 2086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adjali, A.; Clarot, I.; Chen, Z.; Marchioni, E.; Boudier, A. Physicochemical degradation of phycocyanin and means to improve its stability: A short review. J. Pharm. Anal. 2022, 12, 406–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, L.; McClements, D.J.; Liu, X.; Liu, F. Overcoming biopotency barriers: Advanced oral delivery strategies for enhancing the efficacy of bioactive food ingredients. Adv. Sci. 2024, 11, 2401172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Li, Z.; Duan, Y.; Abbas, A.; Mundaca-Uribe, R.; Yin, L.; Wang, J. Gastrointestinal tract drug delivery using algae motors embedded in a degradable capsule. Sci. Robot. 2022, 7, eabo4160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Parliament and Council. Regulation (EC) No 178/2002 of the European Parliament and of the Council of 28 January 2002. Official Journal of the European Communities, L 31, 1–24. 2002. Available online: https://eur-lex.europa.eu/legal-content/EN/TXT/?uri=CELEX%3A32002R0178 (accessed on 10 June 2025).
- Coppens, P. The importance of food supplements for public health and well-being. In Hidden Hunger and the Transformation of Food Systems: How to Combat the Double Burden of Malnutrition? Biesalski, H.K., Koletzko, B., Eds.; World Review of Nutrition and Dietetic; S. Karger AG: Basel, Switzerland, 2020; Volume 121, pp. 66–72. [Google Scholar]
- 2024 CRN Consumer Survey on Dietary Supplements. Available online: https://www.nutritionaloutlook.com/view/council-for-responsible-nutrition-discloses-2024-consumer-survey-results-showcasing-increasing-of-specialty-product-usage (accessed on 6 May 2025).
- Djaoudene, O.; Romano, A.; Bradai, Y.D.; Zebiri, F.; Ouchene, A.; Yousfi, Y.; Madani, K. A global overview of dietary supplements: Regulation, market trends, usage during the COVID-19 pandemic, and health effects. Nutrients 2023, 15, 3320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barani, M.; Sangiovanni, E.; Angarano, M.; Rajizadeh, M.A.; Mehrabani, M.; Piazza, S.; Gangadharappa, H.V.; Pardakhty, A.; Mehrbani, M.; Dell’Agli, M.; et al. Phytosomes as Innovative Delivery Systems for Phytochemicals: A Comprehensive Review of Literature. Intern. J. Nanomed. 2021, 16, 6983–7022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Šturm, L.; Poklar Ulrih, N. Basic Methods for Preparation of Liposomes and Studying Their Interactions with Different Compounds, with the Emphasis on Polyphenols. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 6547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, H.; Lu, Y.; Qi, J.; Zhu, Q.; Chen, Z.; Wu, W. Adapting liposomes for oral drug delivery. Acta Pharm. Sin. B 2019, 9, 36–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mondal, D.; Mandal, R.P.; De, S. Addressing the superior drug delivery performance of bilosomes—A microscopy and fluorescence study. ACS Appl. Bio Mater. 2022, 5, 3896–3911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nayak, D.; Rathnanand, M.; Tippavajhala, V.K. Unlocking the potential of bilosomes and modified bilosomes: A comprehensive journey into advanced drug delivery trends. AAPS PharmSciTech 2023, 24, 238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Xue, A.; Zhang, C.; Yu, J.; Chen, W.; Sun, D. Bile salt liposomes for enhanced lymphatic transport and oral bioavailability of paclitaxel. Die Pharm. 2016, 71, 320–326. [Google Scholar]
- Jain, S.; Harde, H.; Indulkar, A.; Agrawal, A.K. Improved stability and immunological potential of tetanus toxoid containing surface engineered bilosomes following oral administration. Nanomedicine 2014, 10, 431–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milano, F.; Masi, A.; Madaghiele, M.; Sannino, A.; Salvatore, L.; Gallo, N. Current trends in gelatin-based drug delivery systems. Pharmaceutics 2023, 15, 1499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parashar, P.; Kumar, P.; Gautam, A.K.; Singh, N.; Bera, H.; Sarkar, S.; Saraf, S.A.; Saha, S. Gelatin-based nanomaterials in drug delivery and biomedical applications. In Biopolymer-Based Nanomaterials in Drug Delivery and Biomedical Applications; Grumezescu, A.M., Ed.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2021; pp. 407–426. [Google Scholar]
- Liang, C.; Du, J.; Hou, T.; Sui, L.; Li, J.; Zhao, Y.; Wu, D. Improvement of membrane stabilizer on the rehydrated reconstruction of spray-dried mannitol-based liposome powder. Colloid Polym. Sci. 2024, 302, 711–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, D.K.; Ahad, A.; Waheed, A.; Aqil, M.; Al-Jenoobi, F.I.; Al-Mohizea, A.M. Bilosomes: A Novel Platform for Drug Delivery. In Systems of Nanovesicular Drug Delivery; Iqbal, Z., Baboota, S., Eds.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2022; pp. 293–309. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, S.; Dash, A.K. Physical properties, their determination, and importance in pharmaceutics. In Pharmaceutics, Basic Principles and Application to Pharmacy Practice; Singh, S., Dash, A.K., Eds.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2024; pp. 67–113. [Google Scholar]
- Danaei, M.; Dehghankhold, M.; Ataei, S.; Hasanzadeh Davarani, F.; Javanmard, R.; Dokhani, A.; Mozafari, M.R. Impact of particle size and polydispersity index on the clinical applications of lipidic nanocarrier systems. Pharmaceutics 2018, 10, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lowry, G.V.; Hill, R.J.; Harper, S.; Rawle, A.F.; Hendren, C.O.; Klaessig, F.; Rumble, J. Guidance to improve the scientific value of zeta-potential measurements in nano EHS. Environ. Sci. Nano 2016, 3, 953–965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nsairat, H.; Khater, D.; Sayed, U.; Odeh, F.; Al Bawab, A.; Alshaer, W. Liposomes: Structure, composition, types, and clinical applications. Heliyon 2022, 8, e09394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ansari, I.; Shakeel, K. A review on bilosomes: Advanced drug delivery system. Int. J. Pharm. Sci. Med. 2023, 8, 48–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Machado, A.R.; Pinheiro, A.C.; Vicente, A.A.; Souza-Soares, L.A.; Cerqueira, M.A. Liposomes loaded with phenolic extracts of Spirulina LEB-18: Physicochemical characterization and behaviour under simulated gastrointestinal conditions. Food Res. Int. 2019, 120, 656–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zewail, M.; Gaafar, P.M.; Youssef, N.A.H.A.; Ali, M.E.; Ragab, M.F.; Kamal, M.F.; Abbas, H. Novel Spirulina platensis bilosomes for combating UVB-induced skin damage. Pharmaceuticals 2022, 16, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allaw, M.; Perra, M.; Parekh, P.; Serra, M.; Marongiu, J.; Castangia, I.; Fulgheri, F.; Caboni, P.; Tolle, G.; Corrias, F.; et al. Antioxidant and neuroprotective effects of nutriosomes and grape pomace phytochemicals in a cell model of oxidative stress and mouse model of Parkinson disease. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 11947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Păvăloiu, R.D.; Sha’at, F.; Neagu, G.; Deaconu, M.; Bubueanu, C.; Albulescu, A.; Sha’at, M.; Hlevca, C. Encapsulation of Polyphenols from Lycium barbarum Leaves into Liposomes as a Strategy to Improve Their Delivery. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 1938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agarry, I.E.; Wang, Z.; Cai, T.; Wu, Z.; Kan, J.; Chen, K. Utilization of different carrier agents for chlorophyll encapsulation: Characterization and kinetic stability study. Food Res. Int. 2022, 160, 111650. [Google Scholar]
- Hamadou, A.H.; Huang, W.C.; Xue, C.; Mao, X. Comparison of β-Carotene Loaded Marine and Egg Phospholipids Nanoliposomes. J. Food Eng. 2020, 283, 110055. [Google Scholar]
- Sonje, J.; Thakral, S.; Mayhugh, B.; Sacha, G.; Nail, S.; Srinivasan, J.; Suryanarayanan, R. Mannitol Hemihydrate in Lyophilized Protein Formulations: Impact of Its Dehydration during Storage on Sucrose Crystallinity and Protein Stability. Int. J. Pharm. 2022, 624, 121974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, S.; Wang, X.; Jin, Y.; Peng, N.; Wei, Z.; Lian, J.; Zhou, X. Dual Cryoprotection of Gelatin–Tea Polyphenol Microgels on Surimi by Targeting Ice Inhibition and Component Stabilization. Food Chem. 2025, 464, 141684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trenkenschuh, E.; Friess, W. Freeze-Thaw Stability of Aluminium Oxide Nanoparticles. Int. J. Pharm. 2021, 606, 120932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castangia, I.; Corrias, F.; Jiménez, F.J.L.; Aroffu, M.; Fulgheri, F.; Perra, M.; Manca, M.L. Formulation and testing of cutting-edge food supplements tailored for glucose and oxidation controlling, converting artichoke by-products in inulin-rich antioxidant phytocomplex loaded into zein liposomes. Food Biosci. 2024, 62, 105482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muhaimin, M.; Chaerunisaa, A.Y.; Bodmeier, R. Impact of dispersion time interval and particle size on release profiles of propranolol HCl and carbamazepines from microparticle blends system. Sci Rep. 2022, 12, 10360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Battogtokh, G.; Joo, Y.; Abuzar, S.M.; Park, H.; Hwang, S.J. Gelatin coating for the improvement of stability and cell uptake of hydrophobic drug-containing liposomes. Molecules 2022, 27, 1041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, X.; Fan, X.; Chen, C.; Lu, Q.; Zhou, H.; Zhao, Y.; Geng, H. Chemical and Structural Engineering of Gelatin-Based Delivery Systems for Therapeutic Applications: A Review. Biomacromolecules 2024, 25, 564–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ISO 10993-5:2009; Biological Evaluation of Medical Devices—Part 5: Tests for In Vitro Cytotoxicity. International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2009.
- United States Pharmacopeial Convention. USP 24–NF 19. In United States Pharmacopeia–National Formulary, 24th ed.; United States Pharmacopeial Convention: Rockville, MD, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Milia, M.; Pasquini, V.; Addis, P.; Angioni, A. Eco-Friendly Extraction to Enhance Antioxidants and Nutritional Value in Arthrospira platensis. Foods 2025, 14, 1510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castangia, I.; Manca, M.L.; Caddeo, C.; Maxia, A.; Murgia, S.; Pons, R.; Manconi, M. Faceted Phospholipid Vesicles Tailored for the Delivery of Santolina insularis Essential Oil to the Skin. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2015, 132, 185–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paseban, K.; Noroozi, S.; Gharehcheloo, R.; Haddadian, A.; Robattorki, F.F.; Dibah, H.; Gharaghie, T.P. Preparation and optimization of niosome encapsulated meropenem for significant antibacterial and anti-biofilm activity against methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus isolates. Heliyon 2024, 10, e35651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Milia, M.; Corrias, F.; Addis, P.; Chini Zitelli, G.; Cicchi, B.; Torzillo, G.; Andreotti, V.; Angioni, A. Influence of Different Light Sources on the Biochemical Composition of Arthrospira spp. Grown in Model Systems. Foods 2022, 11, 399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manconi, M.; Marongiu, F.; Castangia, I.; Manca, M.L.; Caddeo, C.; Tuberoso, C.I.G.; Fadda, A.M. Polymer-associated liposomes for the oral delivery of grape pomace extract. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2016, 146, 910–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manca, M.L.; Castangia, I.; Zaru, M.; Nácher, A.; Valenti, D.; Fernàndez-Busquets, X.; Manconi, M. Development of curcumin loaded sodium hyaluronate immobilized vesicles (hyalurosomes) and their potential on skin inflammation and wound restoring. Biomaterials 2015, 71, 100–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manca, M.L.; Zaru, M.; Manconi, M.; Lai, F.; Valenti, D.; Sinico, C.; Fadda, A.M. Glycerosomes: A new tool for effective dermal and transdermal drug delivery. Int. J. Pharma. 2013, 455, 66–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
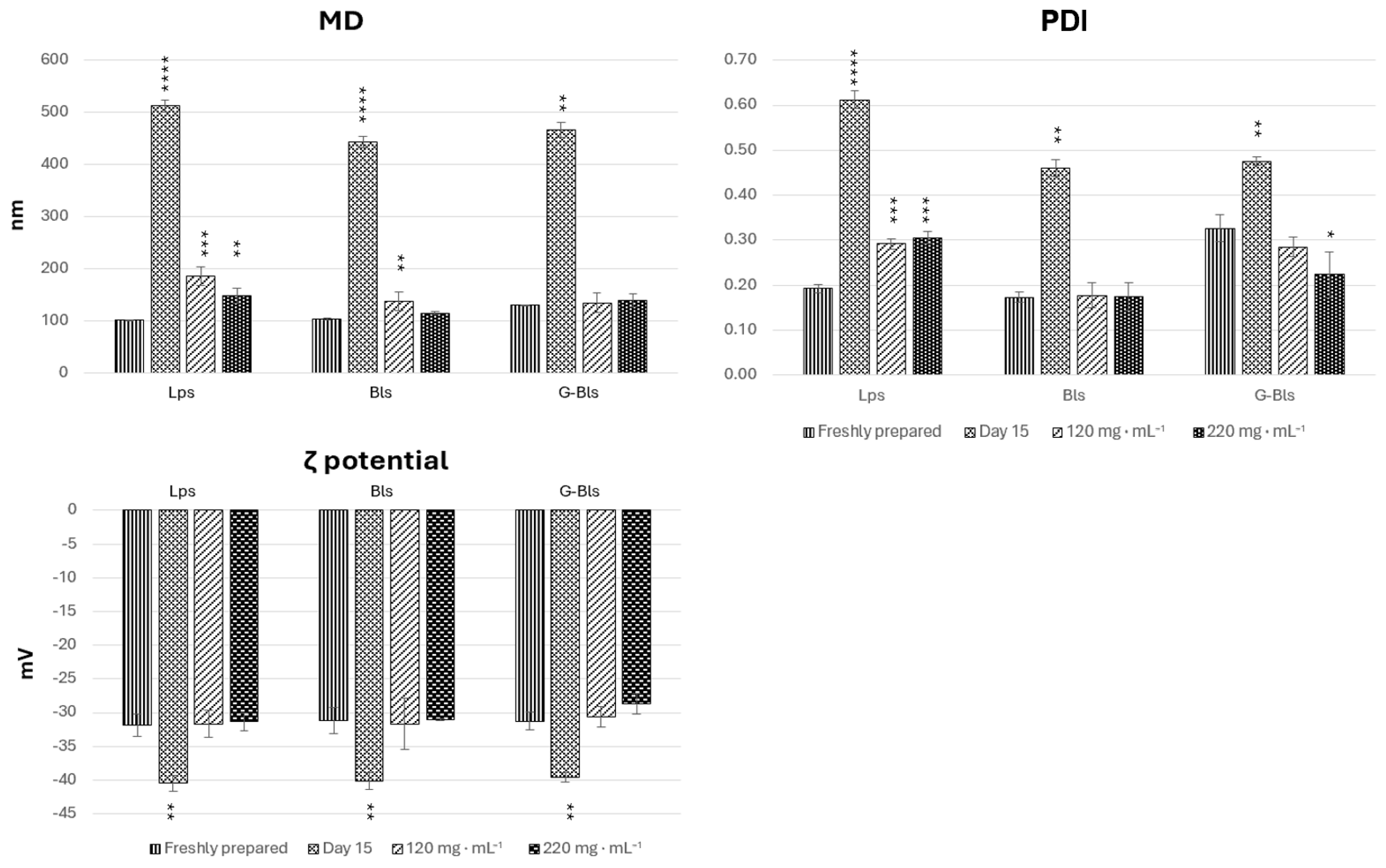
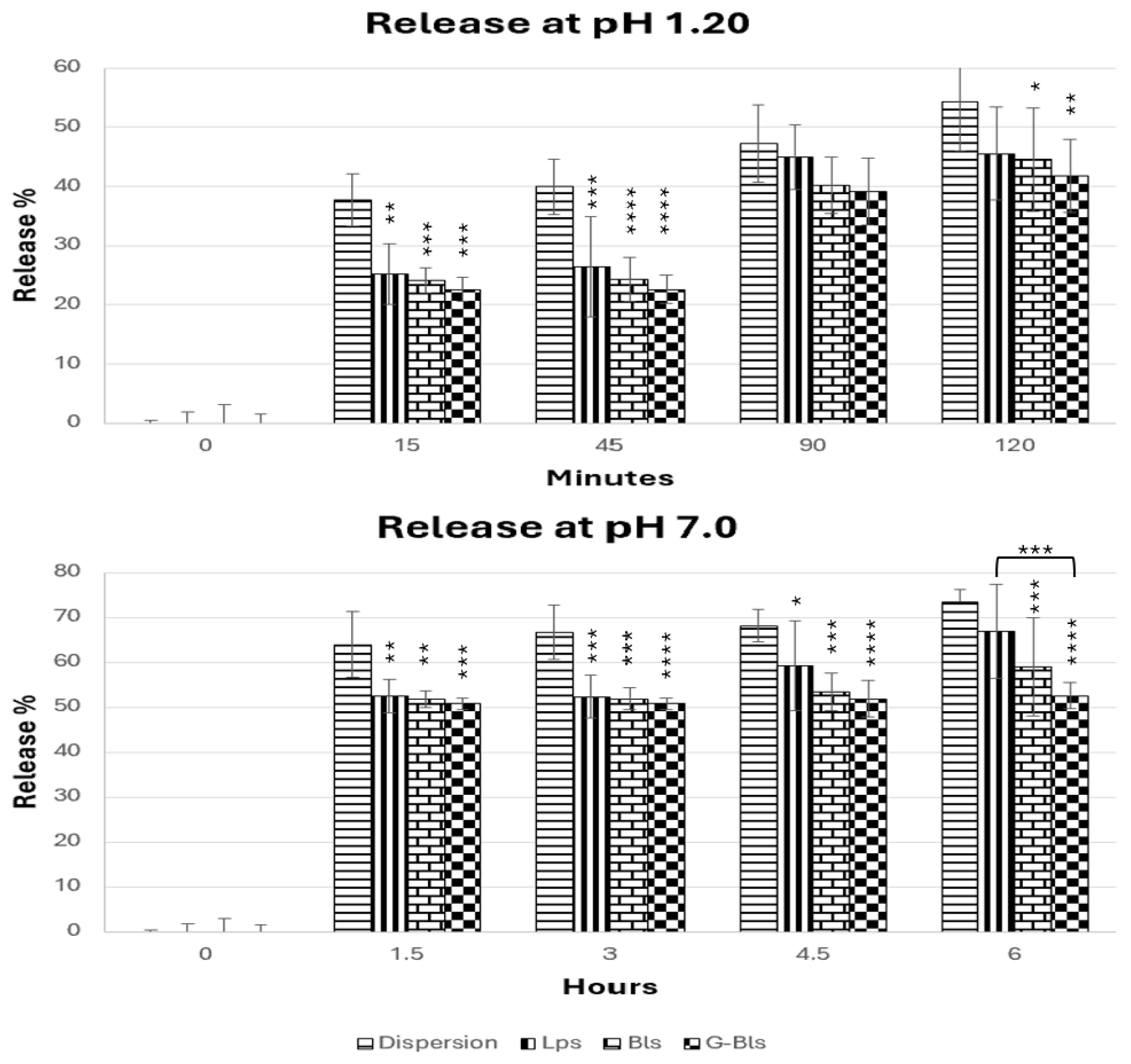
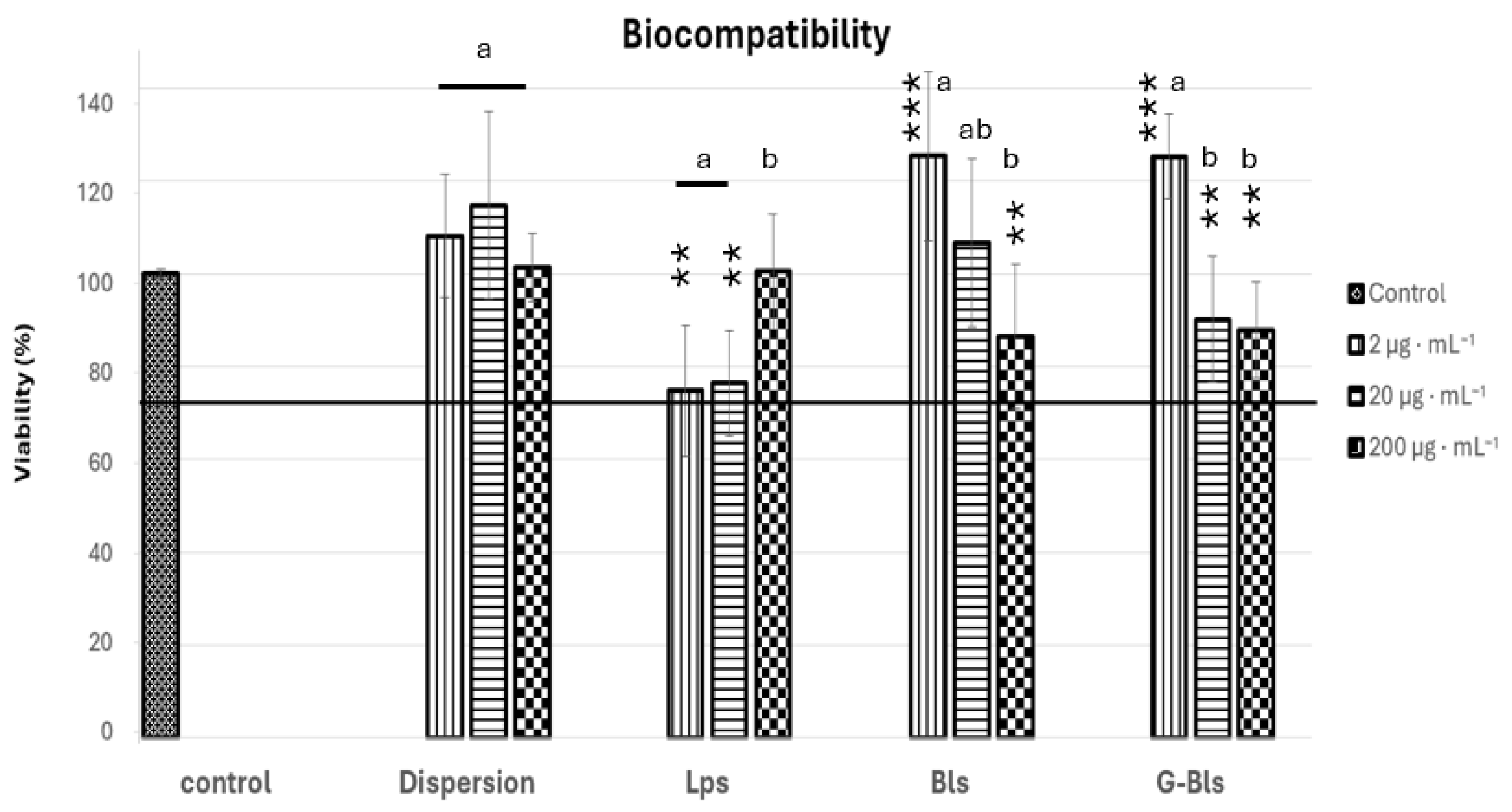
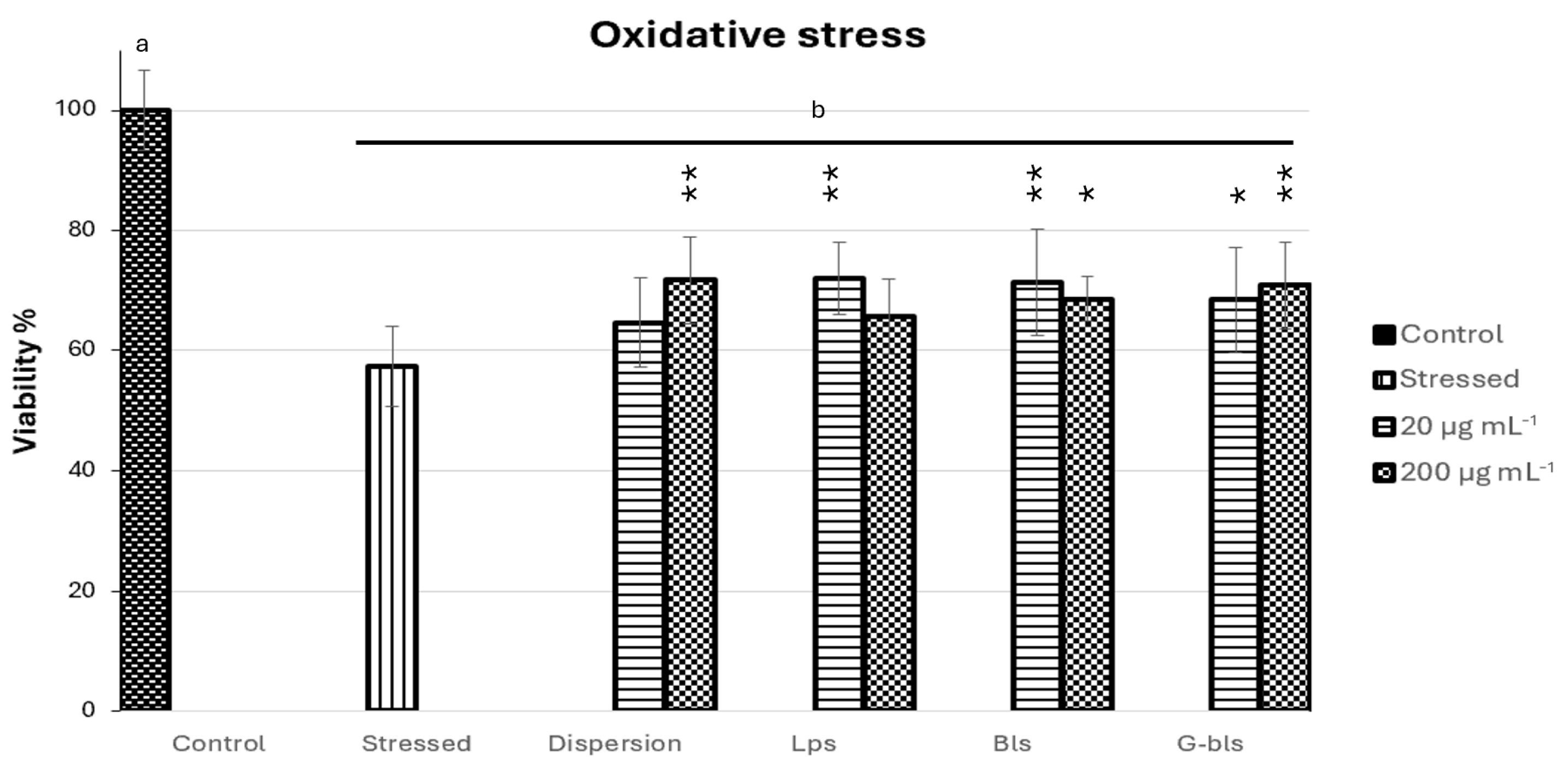
| Vesicle | MD (nm) | PDI | ζ Potential (mV) | EE (%) DPPH | EE (%) Tot. Polyphen | EE (%) Tot. Carot | EE (%) Chl a |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lps | 101.8 ± 0.5 a * | 0.2 a | −31.9 ± 5.2 a | 94.7 ± 6.0 a | 94.4 ± 11.2 a | 99.2 ± 11.5 a | 84.2 ±8.3 a |
| Bls | 103.2 ± 1.5 a | 0.2 a | −31.1 ± 6.4 a | 89.5 ± 5.3 a | 94.3 ± 10.3 a | 89.9 ± 4.6 a | 85.2 ± 11.0 a |
| G-Bls | 129.7 ± 1.2 b (e) | 0.3 b (c) | −31.3 ± 4.2 a | 95.4 ± 3.8 a | 82.1 ± 2.7 a | 91.1 ± 1.8 a | 86.6 ± 6.0 a |
| Phospholipid Vesicles | Mannitol (mg·mL−1) | Days | MD (nm) | PDI | ζ Potential (mV) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lps | 120 | 0 | 186.2 a * | 0.29 a | −31.7 a |
| 90 | 199.8 a (a) | 0.29 a (ab) | −29.3 a (ab) | ||
| 220 | 0 | 147.8 a | 0.31 a | −31.3 a | |
| 90 | 154.7 a (b) | 0.32 a (a) | −31.3 a (a) | ||
| Bls | 120 | 0 | 137.1 a | 0.18 a | −31.7 a |
| 90 | 137.1 a (c) | 0.18 a (c) | −31.7 a (a) | ||
| 220 | 0 | 115.0 a | 0.17 a | −31.3 a | |
| 90 | 121.0 a | 0.22 a (c) | −28.7 a (b) | ||
| G-Bls | 120 | 0 | 134.7 a | 0.29 a | −30.7 a |
| 90 | 139.5 a (c) | 0.31 a (a) | −31.3 a (a) | ||
| 220 | 0 | 131.8 a | 0.22 a | −28.7 a | |
| 90 | 131.6 a (c) | 0.22 a (bc) | −30.3 a (ab) |
| Vesicles | pH | Time | MD (nm) | PDI |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lps | Freshly prepared | - | 101.8 ± 0.5 c | 0.19 b |
| 1.2 | 2 h | 141.0 ± 1.9 b ** | 0.32 a * | |
| 7.0 | 6 h | 163.4 ± 1.6 ab ** | 0.39 a * | |
| Bls | Freshly prepared | - | 103.2 ± 1.6 c | 0.17 c |
| 1.2 | 2 h | 142.9 ± 3.2 b **** | 0.30 b * | |
| 7.0 | 6 h | 115.3 ± 1.2 a ** | 0.47 a *** | |
| G-Bls | Freshly prepared | - | 129.7 ± 1.2 b | 0.33 a |
| 1.2 | 2 h | 239.7 ± 2.9 a **** | 0.22 b ** | |
| 7.0 | 6 h | 221.2 ± 1.3 a **** | 0.20 b *** |
| Extract | S75 | Cholesterol | SDC | Gelatine | PBS | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| mg·mL−1 | mL | |||||
| Lps | 20 | 120 | 20 | - | - | 2 |
| Bls | 20 | 120 | 20 | 20 | - | 2 |
| G-Bls | 20 | 120 | 20 | 20 | 80 | 2 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Milia, M.; Castangia, I.; Corrias, F.; Aroffu, M.; Casula, M.; Manca, M.L.; Manconi, M.; Bouakline, H.; Angioni, A. Physicochemical Characteristics of Phospholipid Vesicles for Spirulina-Based Dietary Supplement Delivery. Molecules 2025, 30, 2581. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30122581
Milia M, Castangia I, Corrias F, Aroffu M, Casula M, Manca ML, Manconi M, Bouakline H, Angioni A. Physicochemical Characteristics of Phospholipid Vesicles for Spirulina-Based Dietary Supplement Delivery. Molecules. 2025; 30(12):2581. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30122581
Chicago/Turabian StyleMilia, Massimo, Ines Castangia, Francesco Corrias, Matteo Aroffu, Mattia Casula, Maria Letizia Manca, Maria Manconi, Hamza Bouakline, and Alberto Angioni. 2025. "Physicochemical Characteristics of Phospholipid Vesicles for Spirulina-Based Dietary Supplement Delivery" Molecules 30, no. 12: 2581. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30122581
APA StyleMilia, M., Castangia, I., Corrias, F., Aroffu, M., Casula, M., Manca, M. L., Manconi, M., Bouakline, H., & Angioni, A. (2025). Physicochemical Characteristics of Phospholipid Vesicles for Spirulina-Based Dietary Supplement Delivery. Molecules, 30(12), 2581. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30122581








