Metabolomic Profiling of Iris palaestina via Molecular Networking and Its Anti-Diabetic Potential
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussions
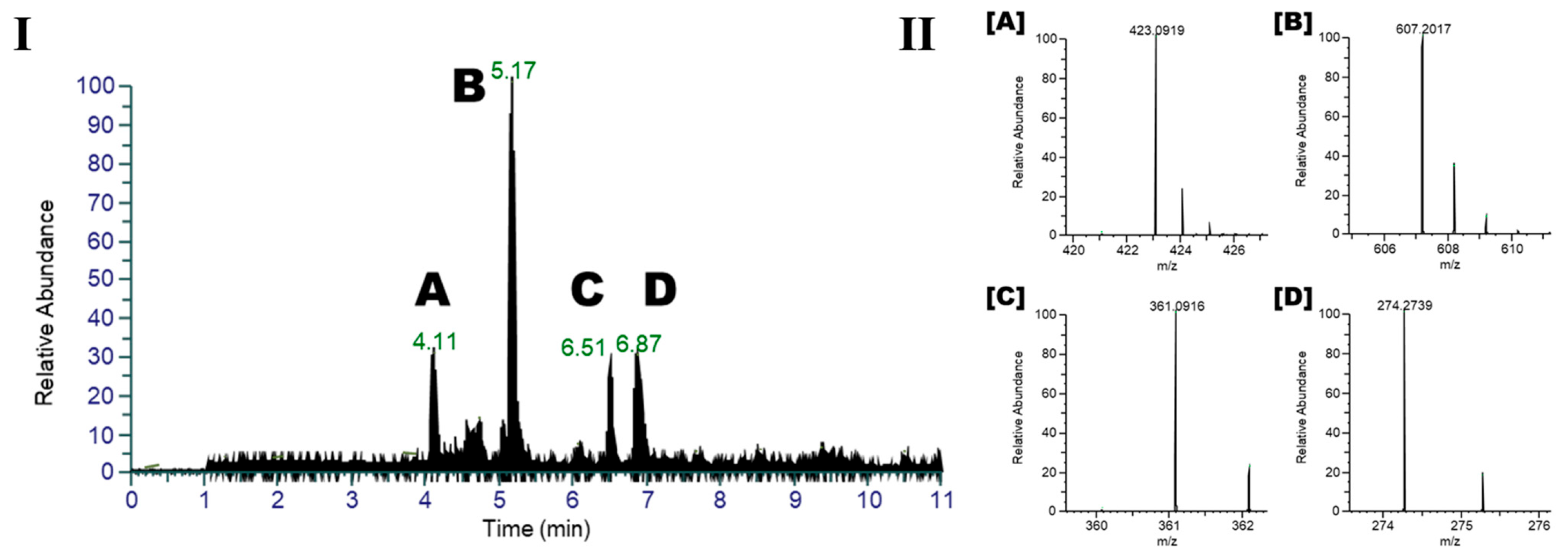
2.1. Metabolomic Profile of I. palaestina Flower Extract
2.2. Anti-Diabetic Potential of the Major Compounds
2.3. Chemotaxonomic Implications of the I. palaestina Flower Metabolite Profile
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Plant Material
3.2. Extraction and Isolation
3.3. Analysis of the Chemical Profile Using LC-HRMS/MS
3.4. General Experimental Procedure
3.5. Molecular Networking
3.6. Measurement of α-Glucosidase Activity
3.7. Statistical Analysis
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wilson, C.A. The complete plastid genome sequence of Iris gatesii (section Oncocyclus), a bearded species from southeastern Turkey. Aliso J. Syst. Florist. Bot. 2014, 32, 47–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Jaenicke, L.; Marner, F.-J. The irones and their origin. Pure Appl. Chem. 1990, 62, 1365–1368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kukula-Koch, W.; Sieniawska, E.; Widelski, J.; Urjin, O.; Głowniak, P.; Skalicka-Woźniak, K. Major secondary metabolites of Iris spp. Phytochem. Rev. 2015, 14, 51–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, U.; Breman, E.; Cossu, T.A.; Kenney, S. The conservation value of germplasm stored at the millennium seed bank, royal botanic gardens, Kew, UK. Biodivers. Conserv. 2018, 27, 1347–1386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saad, L.; Talhouk, S.N.; Mahy, G. Decline of endemic Oncocyclus irises (Iridaceae) of Lebanon: Survey and conservation needs. Oryx 2009, 43, 91–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldblatt, P.; Manning, J.; Gereau, R. Two new species of Babiana (Iridaceae: Crocoideae) from western South Africa, new names for B. longiflora and B. thunbergii, and comments on the original publication of the genus. Bothalia 2008, 38, 49–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Boltenkov, E.V.; Güner, A. Typification of some Oncocyclus (Iris, Iridaceae) names related to the Turkish flora. Phytotaxa 2020, 468, 045–061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mosihuzzman, M.; Naheed, S.; Hareem, S.; Talib, S.; Abbas, G.; Khan, S.N.; Choudhary, M.I.; Sener, B.; Tareen, R.B.; Israr, M. Studies on α-glucosidase inhibition and anti-glycation potential of Iris loczyi and Iris unguicularis. Life Sci. 2013, 92, 187–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choudhary, M.I.; Nur-e-Alam, M.; Baig, I.; Akhtar, F.; Khan, A.M.; Ndögnii, P.Ö.; Badarchiin, T.; Purevsuren, G.; Nahar, N.; Atta-ur-Rahman. Four new flavones and a new isoflavone from Iris bungei. J. Nat. Prod. 2001, 64, 857–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanawa, F.; Tahara, S.; Mizutani, J. Isoflavonoids produced by Iris pseudacorus leaves treated with cupric chloride. Phytochemistry 1991, 30, 157–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papendorf, O.; König, G.M.; Wright, A.D. Hierridin B and 2,4-dimethoxy-6-heptadecyl-phenol, secondary metabolites from the cyanobacterium Phormidium ectocarpi with antiplasmodial activity. Phytochemistry 1998, 49, 2383–2386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahdinezhad, M.R.; Hooshmand, S.; Soukhtanloo, M.; Jamshidi, S.T.; Ehtiati, S.; Ghorbani, A. Protective effects of a standardized extract of Iris germanica on pancreas and liver in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. Res. Pharm. Sci. 2021, 16, 71–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Royal Botanic Gardens. Iris palaestina (Baker) Barbey. Available online: https://powo.science.kew.org/taxon/urn:lsid:ipni.org:names:438937-1 (accessed on 12 May 2025).
- Abas, F.; Khatib, A.; Perumal, V.; Suppaiah, V.; Ismail, A.; Hamid, M.; Shaari, K.; Lajis, N. Metabolic alteration in obese diabetes rats upon treatment with Centella asiatica extract. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2016, 180, 60–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Silva, R.R.; Wang, M.; Nothias, L.-F.; van der Hooft, J.J.; Caraballo-Rodríguez, A.M.; Fox, E.; Balunas, M.J.; Klassen, J.L.; Lopes, N.P.; Dorrestein, P.C. Propagating annotations of molecular networks using in silico fragmentation. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2018, 14, e1006089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rogers, S.; Ong, C.W.; Wandy, J.; Ernst, M.; Ridder, L.; Van Der Hooft, J.J. Deciphering complex metabolite mixtures by unsupervised and supervised substructure discovery and semi-automated annotation from MS/MS spectra. Faraday Discuss. 2019, 218, 284–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quinn, R.A.; Nothias, L.-F.; Vining, O.; Meehan, M.; Esquenazi, E.; Dorrestein, P.C. Molecular networking as a drug discovery, drug metabolism, and precision medicine strategy. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2017, 38, 143–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramos, A.E.F.; Evanno, L.; Poupon, E.; Champy, P.; Beniddir, M.A. Natural products targeting strategies involving molecular networking: Different manners, one goal. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2019, 36, 960–980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beniddir, M.A.; Kang, K.B.; Genta-Jouve, G.; Huber, F.; Rogers, S.; Van Der Hooft, J.J. Advances in decomposing complex metabolite mixtures using substructure-and network-based computational metabolomics approaches. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2021, 38, 1967–1993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turk, A.; Lee, S.; Lee, H.H.; Yeon, S.W.; Ryu, S.H.; Seo, G.H.; Chang, H.Y.; Hwang, B.Y.; Lee, M.K. α-Glucosidase inhibitory fatty acids from Morchella fluvialis mushroom. Folia Hortic. 2023, 35, 369–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lephatsi, M.M.; Choene, M.S.; Kappo, A.P.; Madala, N.E.; Tugizimana, F. An Integrated Molecular Networking and Docking Approach to Characterize the Metabolome of Helichrysum splendidum and Its Pharmaceutical Potentials. Metabolites 2023, 13, 1104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amin, H.I.M.; Hussain, F.H.; Najmaldin, S.K.; Thu, Z.M.; Ibrahim, M.F.; Gilardoni, G.; Vidari, G. Phytochemistry and bio-logical activities of Iris species growing in Iraqi Kurdistan and phenolic constituents of the traditional plant Iris postii. Molecules 2021, 26, 264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, M.; Carver, J.J.; Phelan, V.V.; Sanchez, L.M.; Garg, N.; Peng, Y.; Nguyen, D.D.; Watrous, J.; Kapono, C.A.; Luzzatto-Knaan, T.; et al. Sharing and community curation of mass spectrometry data with Global Natural Products Social Molecular Networking. Nat. Biotechnol. 2016, 34, 828–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schymanski, E.L.; Jeon, J.; Gulde, R.; Fenner, K.; Ruff, M.; Singer, H.P.; Hollender, J. Identifying small molecules via high resolution mass spectrometry: Communicating confidence. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 48, 2097–2098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yi, X.; Dong, M.; Guo, N.; Tian, J.; Lei, P.; Wang, S.; Yang, Y.; Shi, Y. Flavonoids improve type 2 diabetes mellitus and its complications: A review. Front. Nutr. 2023, 10, 1192131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, T.; Tan, B.; Murtaza, G.; Liu, G.; Rahu, N.; Kalhoro, M.S.; Kalhoro, D.H.; Adebowale, T.O.; Mazhar, M.U.; ur Rehman, Z.; et al. Flavonoids and type 2 diabetes: Evidence of efficacy in clinical and animal studies and delivery strategies to enhance their therapeutic efficacy. Pharmacol. Res. 2020, 152, 104629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, C.M.; Freitas, M.; Fernandes, E. A comprehensive review on xanthone derivatives as α-glucosidase inhibitors. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2018, 157, 1460–1479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rohollahi, I.; Naji, A.M.; Stewart, J.R.; Kamrani, R. Morphological characterization of Iris hymenospatha and Iris histrio populations in Iran: Implications for conservation and breeding. Front. Plant Sci. 2024, 15, 1305240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khatib, S.; Faraloni, C.; Bouissane, L. Exploring the use of iris species: Antioxidant properties, phytochemistry, medicinal and industrial applications. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Y.; Shu, P.; Hong, J.; Qin, M. Qualitative and quantitative evaluation of phenolic compounds in Iris dichotoma Pall. Phytochem. Anal. 2012, 23, 197–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel-Baki, P.M.; El-Sherei, M.M.; Khaleel, A.E.; Abdel-Aziz, M.M.; Okba, M.M. Irigenin, a novel lead from Iris confusa for management of Helicobacter pylori infection with selective COX-2 and Hp IMPDH inhibitory potential. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 11457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwashina, T.; Mizuno, T. Flavonoids and xanthones from the genus Iris: Phytochemistry, relationships with flower colors and taxonomy, and activities and function. Nat. Prod. Commun. 2020, 15, 1934578X20937151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, S.; Al-Ahdal, A.; Khedr, A.; Mohamed, G. Antioxidant α-amylase inhibitors flavonoids from Iris germanica rhizomes. Rev. Bras. Farmacogn. 2017, 27, 170–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amin, H.I.M.; Hussain, F.H.; Maggiolini, M.; Vidari, G. Bioactive constituents from the traditional Kurdish plant Iris persica. Nat. Prod. Commun. 2018, 13, 1934578X1801300907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbaskhan, A.; Siddiqui, H.; Anjum, S.; Orhan, I.; Gurbuz, I.; Ayanoglud, F. New and known constituents from Iris unguicularis and their antioxidant activity. Heterocycles 2010, 82, 813–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pluskal, T.; Castillo, S.; Villar-Briones, A.; Orešič, M. MZmine 2: Modular framework for processing, visualizing, and analyzing mass spectrometry-based molecular profile data. BMC Bioinform. 2010, 11, 395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryu, S.H.; Ahn, J.H.; Turk, A.; Kim, S.B.; Hwang, B.Y.; Lee, M.K. Argutinic acid, A New Triterpenoid from the Fruits of Actinidia arguta. Nat. Prod. Sci. 2024, 30, 208–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

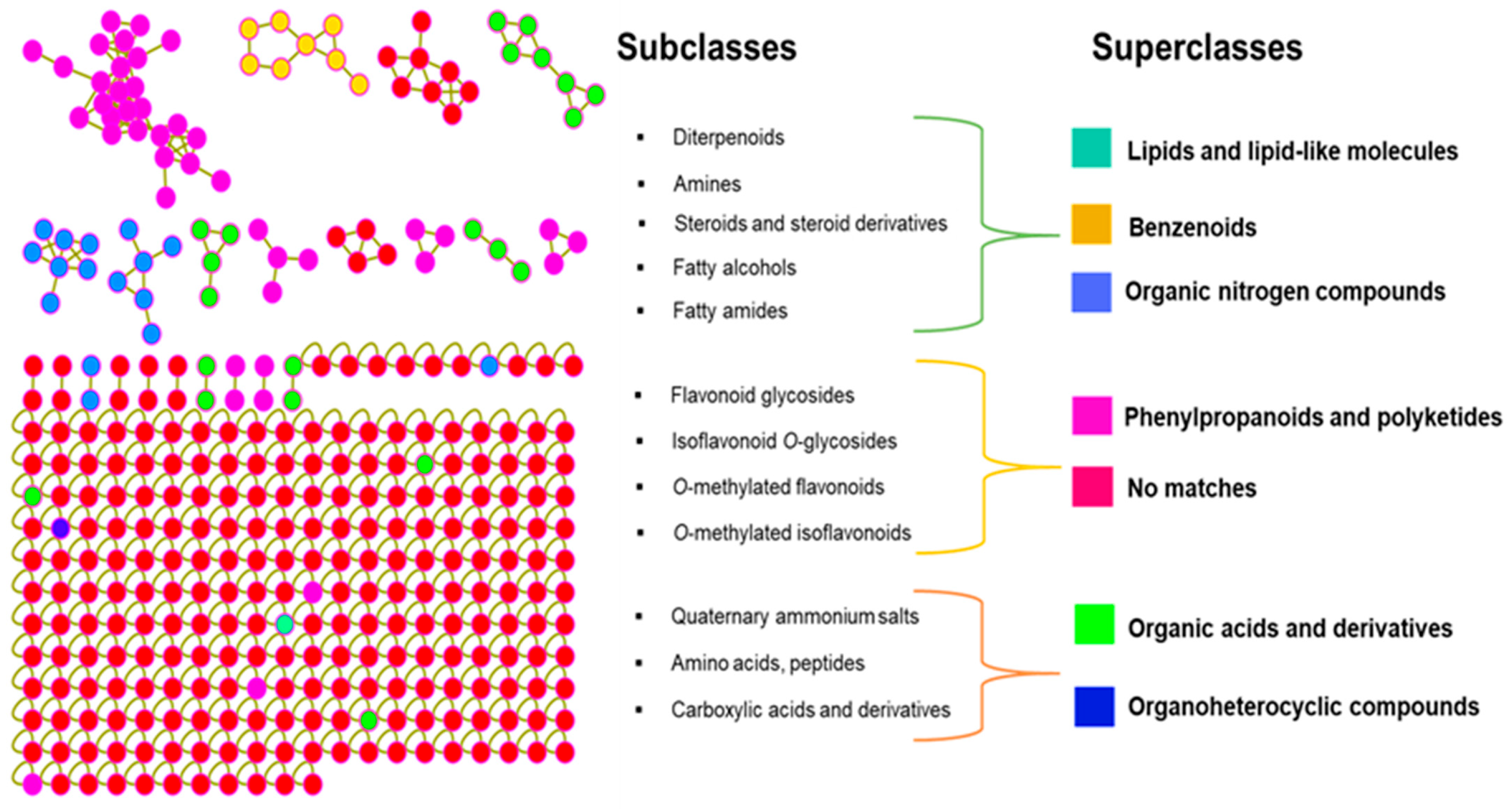
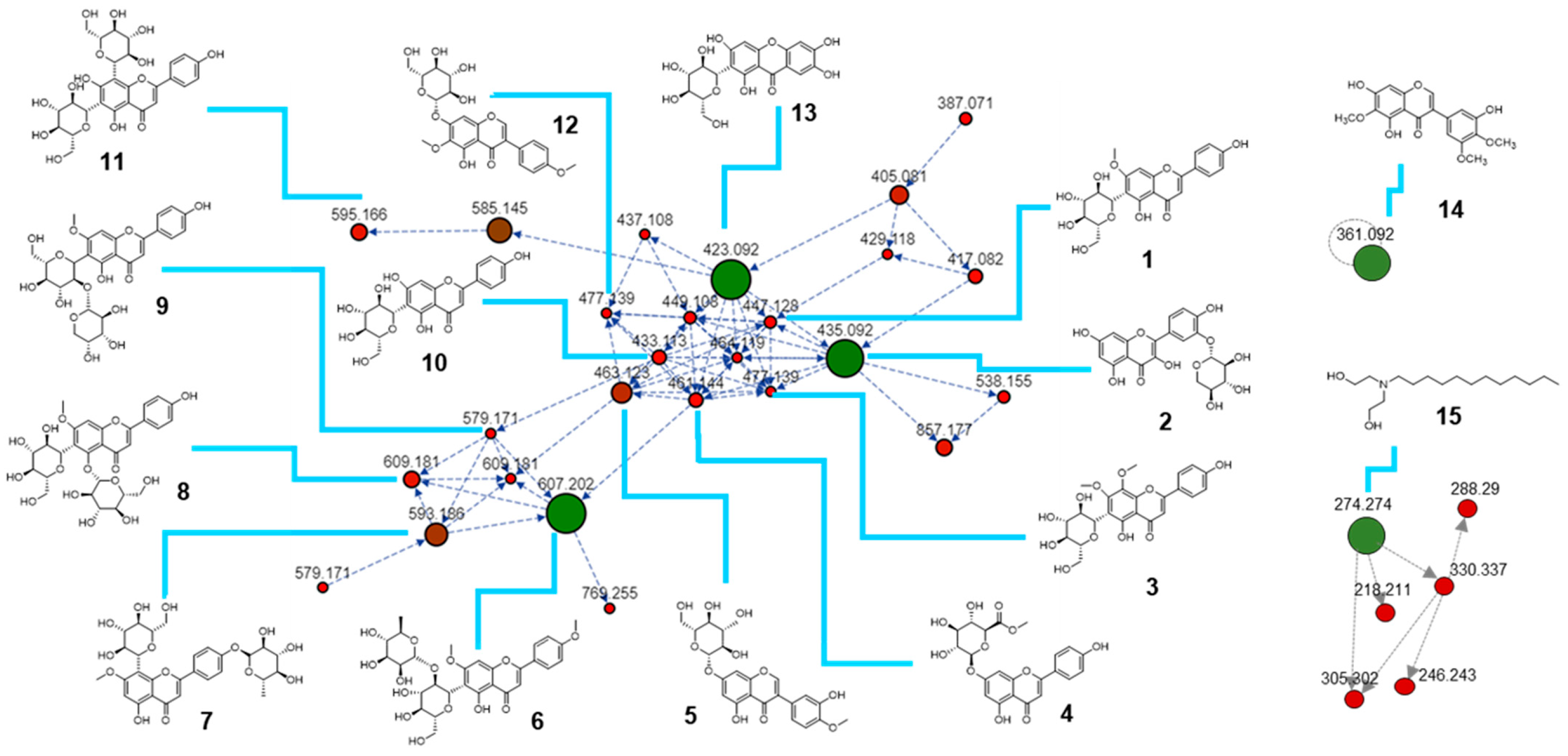
| Compound Number | [M + H]+ m/z | Molecular Formulas [M] | Adduct Types | Cosine Score | Compound Name |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 447.128 | C22H22O10 | [M + H]+ | 0.95 | Swertisin |
| 2 | 435.092 | C20H18O11 | [M + H]+ | 0.71 | Quercetin 3′-xyloside |
| 3 | 477.139 | C23H24O11 | [M + H]+ | 0.83 | Swertisin 8-methyl ether |
| 4 | 461.144 | C22H20O11 | [M + H]+ | 0.87 | Apigenin-7-O-glucuronide methyl ester |
| 5 | 463.123 | C22H22O11 | [M + H]+ | 0.92 | Pratensein-7-O-glucoside |
| 6 | 607.202 | C29H34O14 | [M + H]+ | 0.80 | Embinin |
| 7 | 593.186 | C28H32O14 | [M + H]+ | 0.94 | Isoswertisin 4′-O-rhamnoside |
| 8 | 609.181 | C28H32O15 | [M + H]+ | 0.86 | Swertisin 5-O-glucoside |
| 9 | 579.171 | C28H32O15 | [M + H]+ | 0.93 | Swertisin 2″-O-arabinoside |
| 10 | 433.113 | C22H22O10 | [M + H]+ | 0.92 | Isovitexin |
| 11 | 595.166 | C27H30O15 | [M + H]+ | 0.94 | Vicenin 2 |
| 12 | 477.139 | C23H24O11 | [M + H]+ | 0.83 | Irisolidone 7-O-glucoside |
| 13 | 423.092 | C19H18O11 | [M + H]+ | 0.93 | Mangiferin |
| 14 | 361.092 | C18H16O8 | [M + H]+ | 0.78 | Irigenin |
| 15 | 274.271 | C16H35NO2 | [M + H]+ | 0.89 | N-lauryldiethanolamine |
| Compounds | α-Glucosidase Inhibitory Activity (100 μM) | IC50 (μM) |
|---|---|---|
| Mangiferin (A) | 83.9 ± 3.4 | 36.1 ± 2.8 |
| Embinin (B) | 28.2 ± 6.3 | >100 |
| Irigenin (C) | 87.7 ± 6.6 | 32.1 ± 3.1 |
| N-lauryldiethanolamine (D) | NT a | NT a |
| Acarbose b | 74.6 ± 3.4 | 65.8 ± 2.3 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Turk, A.; Addam, K.; Hwang, B.Y.; Lee, M.K. Metabolomic Profiling of Iris palaestina via Molecular Networking and Its Anti-Diabetic Potential. Molecules 2025, 30, 2509. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30122509
Turk A, Addam K, Hwang BY, Lee MK. Metabolomic Profiling of Iris palaestina via Molecular Networking and Its Anti-Diabetic Potential. Molecules. 2025; 30(12):2509. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30122509
Chicago/Turabian StyleTurk, Ayman, Khodr Addam, Bang Yeon Hwang, and Mi Kyeong Lee. 2025. "Metabolomic Profiling of Iris palaestina via Molecular Networking and Its Anti-Diabetic Potential" Molecules 30, no. 12: 2509. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30122509
APA StyleTurk, A., Addam, K., Hwang, B. Y., & Lee, M. K. (2025). Metabolomic Profiling of Iris palaestina via Molecular Networking and Its Anti-Diabetic Potential. Molecules, 30(12), 2509. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30122509








