Discovery of Novel Imidazothiazole-Based Hydroxamic Acid Derivatives as Potent Indoleamine 2,3-Dioxygenase 1 and Histone Deacetylase 6 Dual Inhibitors
Abstract
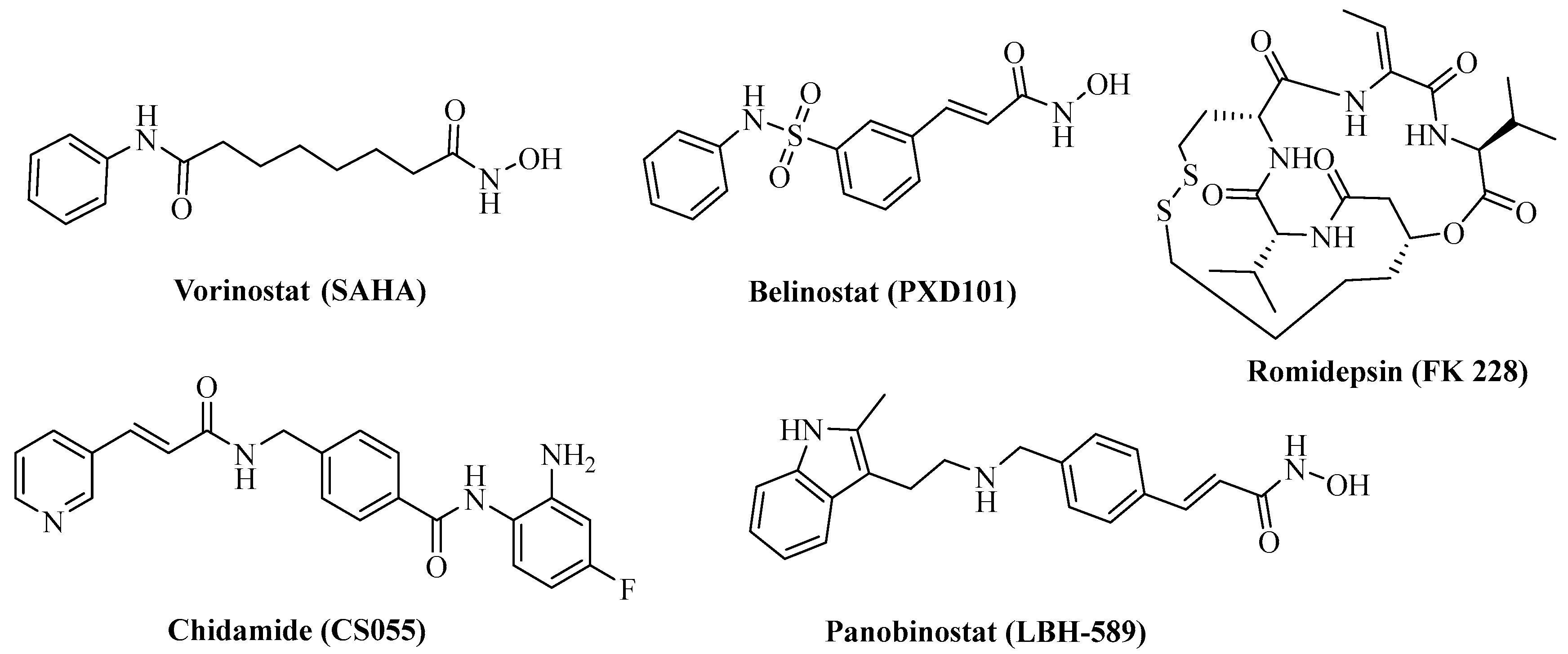
1. Introduction
2. Results
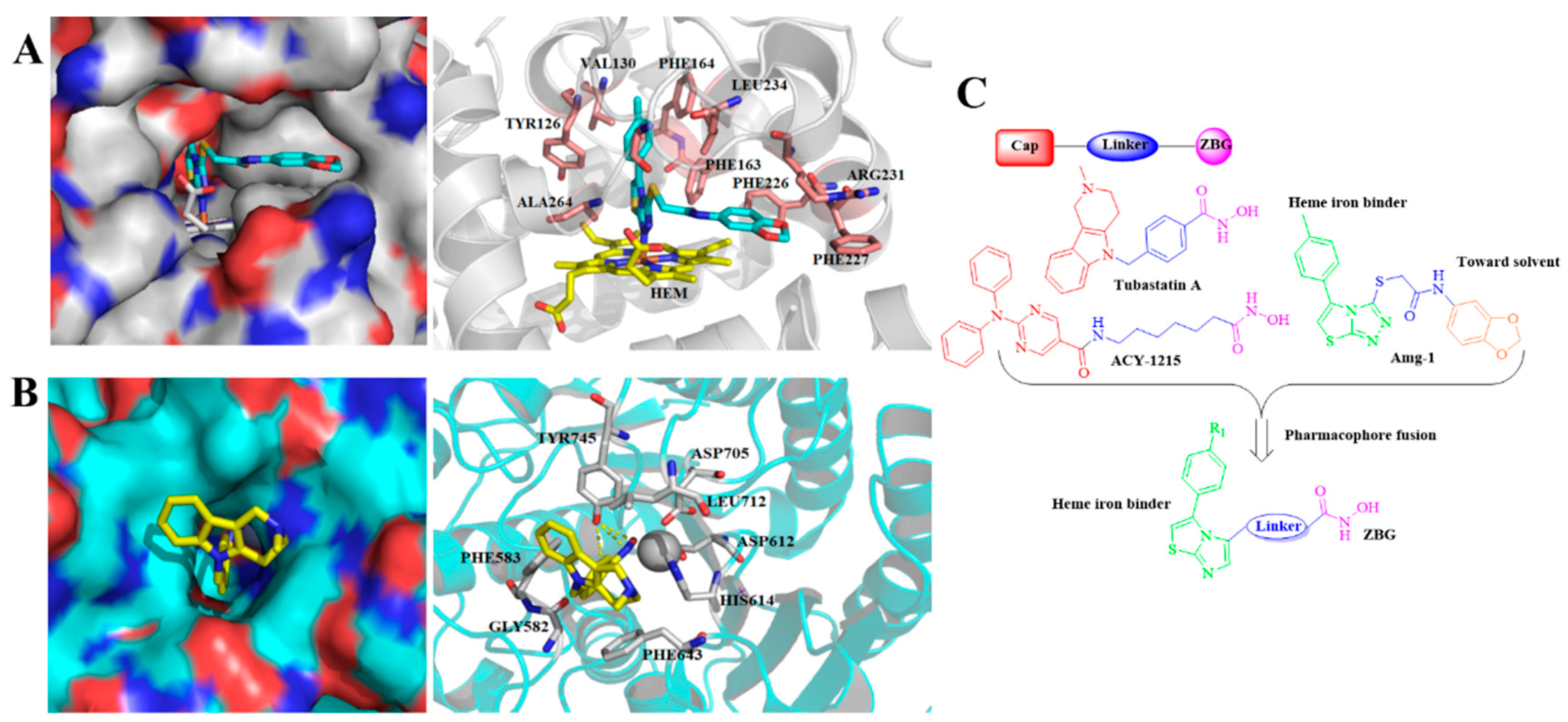
2.1. Rational Design of Novel IDO1 and HDAC6 Dual Inhibitors
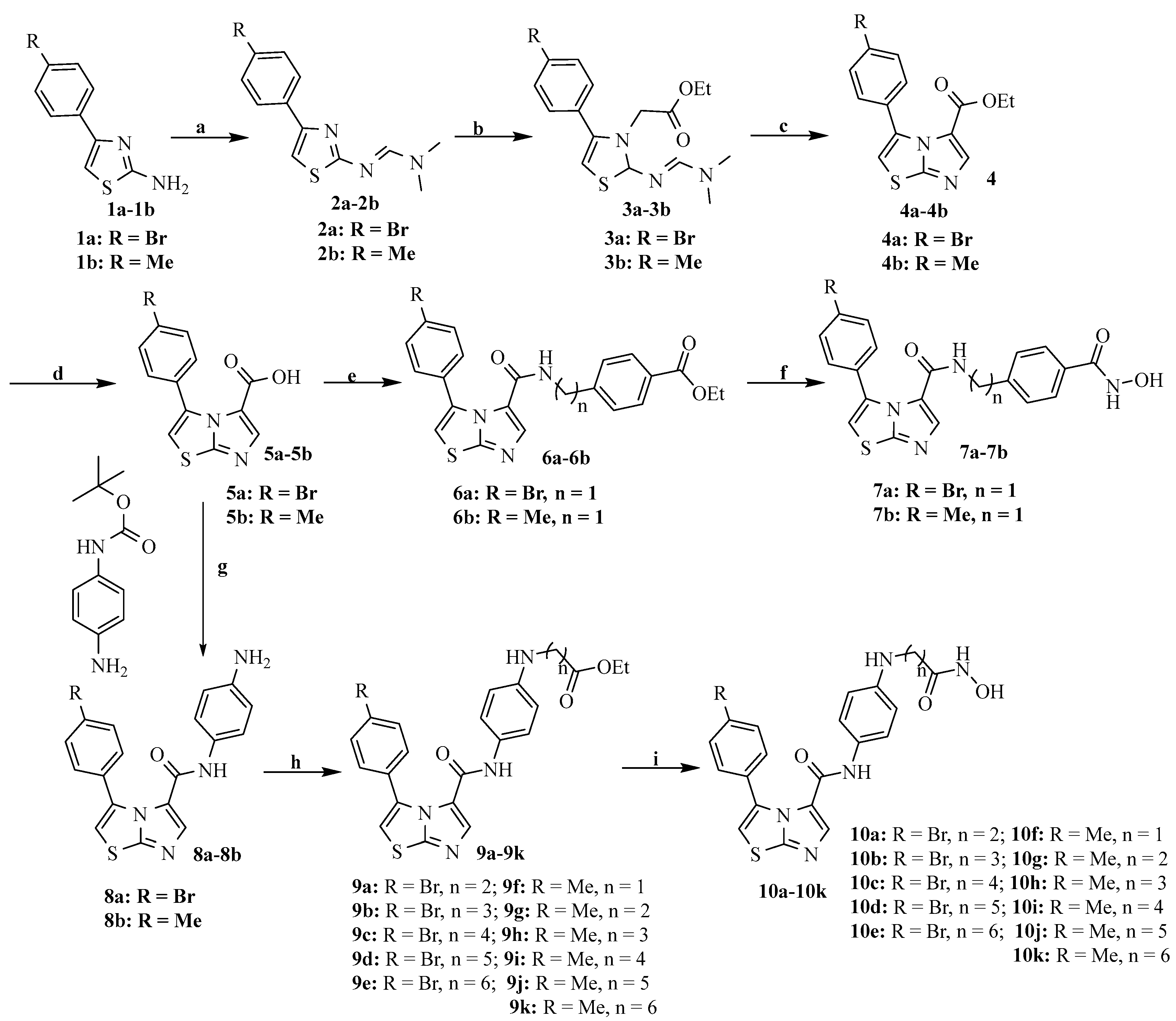
2.2. Chemistry
2.3. In Vitro IDO1/HDAC6 Enzyme Inhibition
2.4. HDAC Isoform Selectivity of Compounds 7a, 10e, and 10k
2.5. Binding Modes of Compound 10e with IDO1 and HDAC6
2.6. In Vitro Antiproliferative Activity of Selected Compounds
2.7. Inhibition of HDAC in HCT-116 Cells by Compound 10e
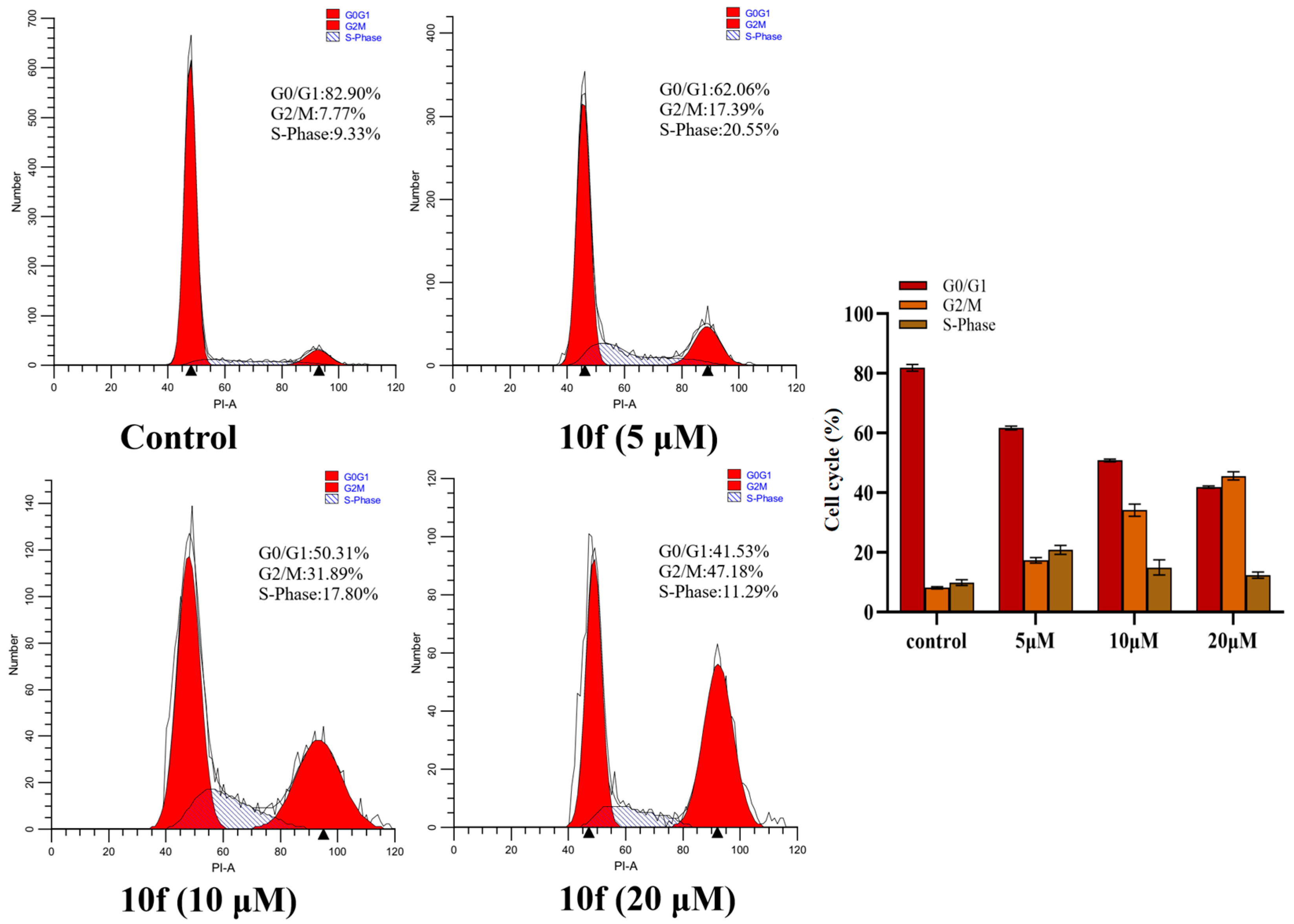
2.8. Cell Cycle Arrest
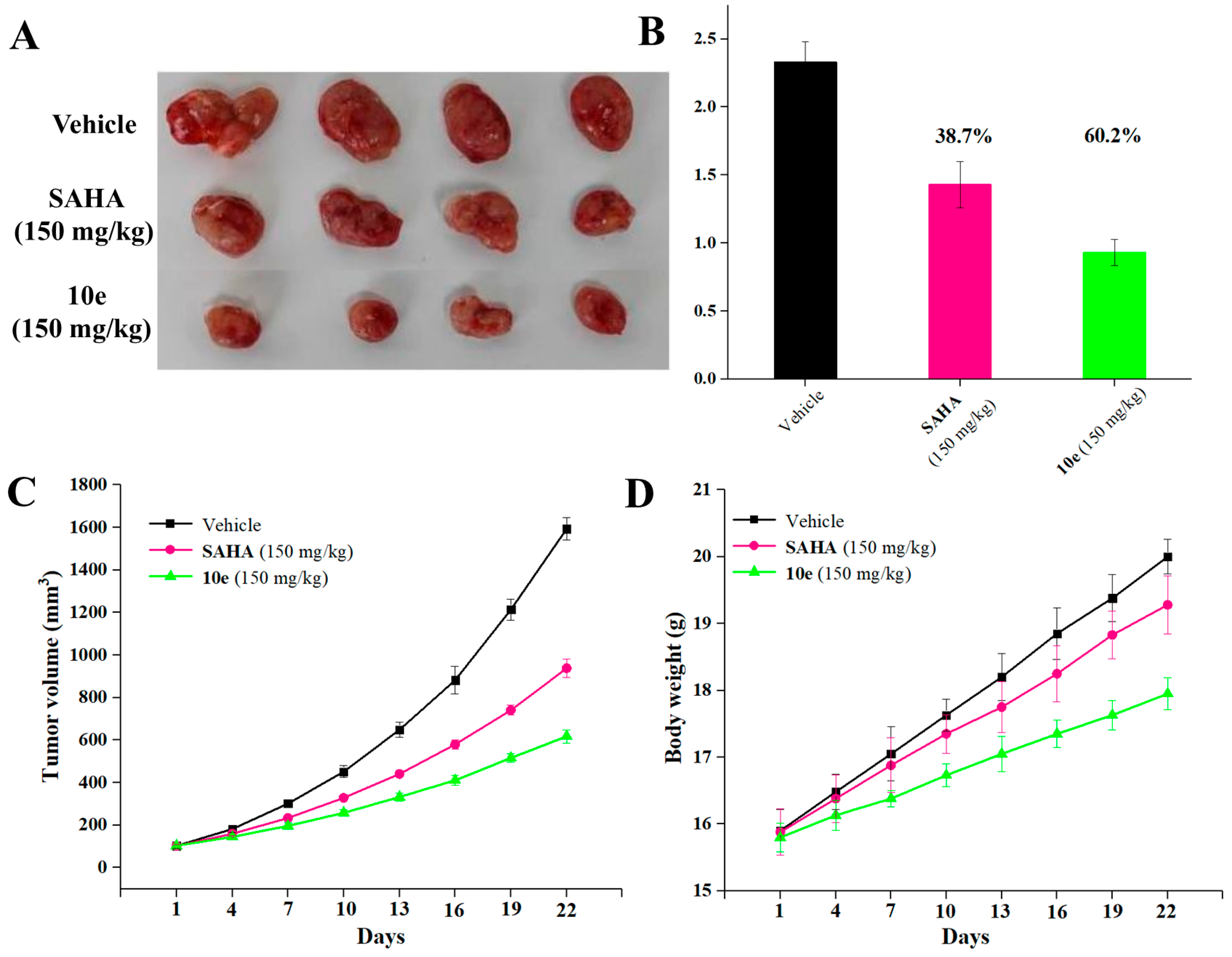
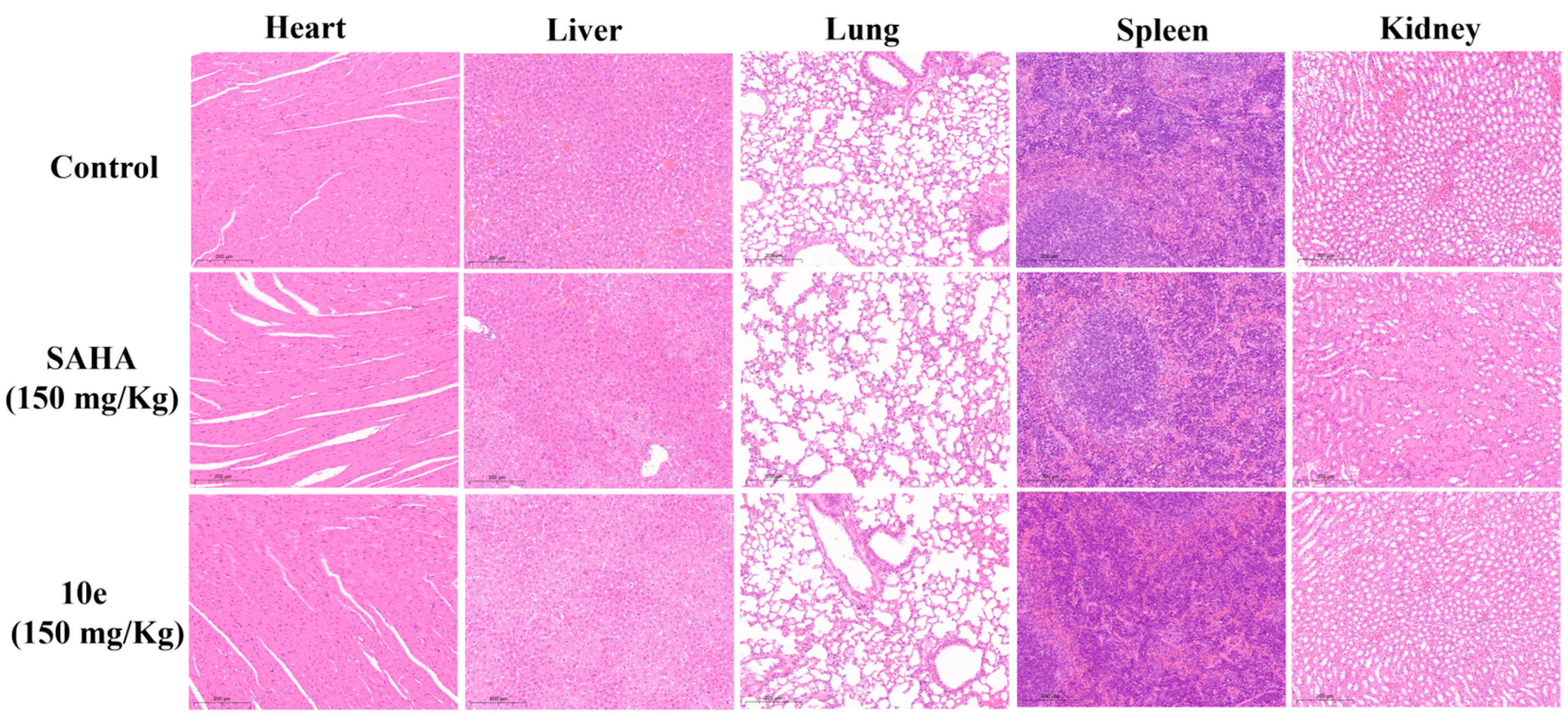
2.9. In Vivo Antitumor Effects
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. General Information
3.2. General Procedure for Preparation of Compounds 7a, 7b, and 10a–10k
3.3. Biological Assays
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sharma, P.; Allison, J.P. The future of immune checkpoint therapy. Science 2015, 348, 56–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Binnewies, M.; Roberts, E.W.; Kersten, K.; Chan, V.; Fearon, D.F.; Merad, M.; Coussens, L.M.; Gabrilovich, D.I.; Ostrand-Rosenberg, S.; Hedrick, C.C.; et al. Understanding the tumor immune microenvironment (TIME) for effective therapy. Nat. Med. 2018, 24, 541–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalbasi, A.; Ribas, A. Tumour-intrinsic resistance to immune checkpoint blockade. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2020, 20, 25–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kirchhammer, N.; Trefny, M.P.; der Maur, P.A.; Läubli, H.; Zippelius, A. Combination cancer immunotherapies: Emerging treatment strategies adapted to the tumor microenvironment. Sci. Transl. Med. 2022, 14, eabo3605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hughes, P.E.; Caenepee, S.; Wu, L.C. Targeted Therapy and Checkpoint Immunotherapy Combinations for the Treatment of Cancer. Trends Immunol. 2016, 37, 462–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Li, X.; Liu, F.; Li, S.; Shi, D. Rational Multitargeted Drug Design Strategy from the Perspective of a Medicinal Chemist. J. Med. Chem. 2021, 64, 10581–10605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ricciuti, B.; Leonardi, G.C.; Puccetti, P.; Fallarino, F.; Bianconi, V.; Sahebkar, A.; Baglivo, S.; Chiari, R.; Pirro, M. Targeting indoleamine-2,3-dioxygenase in cancer: Scientific rationale and clinical evidence. Pharmacol. Therapeut. 2019, 196, 105–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Zhang, R.; Li, S.; Liu, J. IDO1: An important immunotherapy target in cancer treatment. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2017, 47, 70–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weng, T.; Qiu, X.; Wang, J.; Li, Z.; Bian, J. Recent discovery of indoleamine-2,3-dioxygenase 1 inhibitors targeting cancer immunotherapy. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2018, 143, 656–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Opitz, C.A.; Litzenburger, U.M.; Sahm, F.; Ott, M.; Tritschler, I.; Trump, S.; Schumacher, T.; Jestaedt, L.; Schrenk, D.; Weller, M.; et al. An endogenous tumour-promoting ligand of the human aryl hydrocarbon receptor. Nature 2011, 478, 197–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prendergast, G.C.; Mondal, A.; Dey, S.; Laury-Kleintop, L.D.; Muller, A.J. Inflammatory Reprogramming with IDO1 Inhibitors: Turning Immunologically Unresponsive ‘Cold’ Tumors ‘Hot’. Trends. Cancer 2018, 4, 38–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- NayakKapoor, A.; Hao, Z.; Sadek, R.; Dobbins, R.; Marshall, L.; Vahanian, N.N.; Ramsey, W.J.; Kennedy, E.; Mautino, M.R.; Link, C.J.; et al. Phase Ia study of the indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase 1 (IDO1) inhibitor navoximod (GDC-0919) in patients with recurrent advanced solid tumors. Cancer Immunol. 2018, 6, 1–12. [Google Scholar]
- Feng, X.; Liao, D.; Liu, D.; Ping, A.; Li, Z.; Bian, J. Development of Indoleamine 2,3-Dioxygenase 1 Inhibitors for Cancer Therapy and Beyond: A Recent Perspective. J. Med. Chem. 2020, 63, 15115–15139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, Y.-H.; Liao, F.-Y.; Tseng, C.-T.; Kuppusamy, R.; Li, A.-S.; Chen, C.-H.; Fan, Y.-S.; Wang, S.-Y.; Wu, M.-H.; Hsueh, C.-C.; et al. Unique sulfur–aromatic interactions contribute to the binding of potent imidazothiazole indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase inhibitors. J. Med. Chem. 2020, 63, 1642–1659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tojo, S.; Kohno, T.; Tanaka, T.; Kamioka, S.; Ota, Y.; Ishii, T.; Kamimoto, K.; Asano, S.; Isobe, Y. Crystal Structures and Structure–Activity Relationships of Imidazothiazole Derivatives as IDO1 Inhibitors. ACS Med. Chem. Lett. 2014, 5, 1119–1123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Hu, Z.; Zhang, J.; Ren, C.; Wang, Y. Dual-target inhibitors of indoleamine 2, 3 dioxygenase 1 (Ido1): A promising direction in cancer immunotherapy. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2022, 238, 114524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ru, J.; Wang, Y.; Li, Z.; Wang, J.; Ren, C.; Zhang, J. Technologies of targeting histone deacetylase in drug discovery: Current progress and emerging prospects. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2023, 261, 115800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Y.; Hou, H.; Zhou, B.; Gao, J.; Gao, F. Hydroxamic acid hybrids: Histone deacetylase inhibitors with anticancer therapeutic potency. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2023, 262, 115879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, T.; Wang, F.; Elhassan, R.M.; Cheng, Y.; Tang, X.; Chen, W.; Fang, H.; Hou, X. Targeting histone deacetylases for cancer therapy: Trends and challenges. Acta Pharm. Sin. B 2023, 13, 2425–2463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zang, J.; Liang, X.; Huang, Y.; Jia, Y.; Li, X.; Xu, W.; Chou, C.J.; Zhang, Y. Discovery of Novel Pazopanib-Based HDAC and VEGFR Dual Inhibitors Targeting Cancer Epigenetics and Angiogenesis Simultaneously. J. Med. Chem. 2018, 61, 5304–5322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suraweera, A.; O’Byrne, K.J.; Richard, D.J. Combination Therapy with Histone Deacetylase Inhibitors (HDACi) for the Treatment of Cancer: Achieving the Full Therapeutic Potential of HDACi. Front. Oncol. 2018, 8, 92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Wang, F.; Chen, X.; Wang, J.; Zhao, Y.; Li, Y.; He, B. Zinc-dependent deacetylase (HDAC) inhibitors with different zinc binding groups. Curr. Top. Med. Chem. 2019, 19, 223–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, T.; Wan, Y.; Xiao, Y.; Xia, C.; Duan, G. Dual-Target Inhibitors Based on HDACs: Novel Antitumor Agents for Cancer Therapy. J. Med. Chem. 2020, 63, 8977–9002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, X.; Sun, Z.; Kuang, P.; Chen, J. Recent progress on HDAC inhibitors with dual targeting capabilities for cancer treatment. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2020, 208, 112831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.-H.; Ma, Q.; Wu, H.-P.; Khamis, M.Y.; Li, Y.-H.; Ma, L.-Y.; Liu, H.-M. A Review of Progress in Histone Deacetylase 6 Inhibitors Research: Structural Specificity and Functional Diversity. J. Med. Chem. 2021, 64, 1362–1391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Wang, J.; Zhao, P.; Dang, B.; Liang, T.; Steimbach, R.R.; Miller, A.K.; Liu, J.; Wang, X.; Zhang, T.; et al. Tetrahydro-β-carboline derivatives as potent histone deacetylase 6 inhibitors with broad-spectrum antiproliferative activity. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2023, 260, 115776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Yang, K.; Zhang, Z.; Leisten, E.D.; Li, Z.; Xie, H.; Liu, J.; Smith, K.A.; Novakova, Z.; Barinka, C.; et al. Development of Multifunctional Histone Deacetylase 6 Degraders with Potent Antimyeloma Activity. J. Med. Chem. 2019, 62, 7042–7057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, H.; Qu, J.; Jin, N.; Xu, J.; Lin, C.; Chen, Y.; Yang, X.; He, X.; Tang, S.; Lan, X.; et al. Feedback Activation of Leukemia Inhibitory Factor Receptor Limits Response to Histone Deacetylase Inhibitors in Breast Cancer. Cancer Cell 2016, 30, 459–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Pan, X.; Zhang, W.; Guo, H.; Cheng, S.; He, Q.; Yang, B.; Ding, L. Epigenetic strategies synergize with PD-L1/PD-1 targeted cancer immunotherapies to enhance antitumor responses. Acta Pharm. Sin. B 2020, 10, 723–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noonepalle, S.; Shen, S.; Ptáček, J.; Tavares, M.T.; Zhang, G.; Stránský, J.; Pavlíček, J.; Ferreira, G.M.; Hadley, M.; Pelaez, G.; et al. Rational Design of Suprastat: A Novel Selective Histone Deacetylase 6 Inhibitor with the Ability to Potentiate Immunotherapy in Melanoma Models. J. Med. Chem. 2020, 63, 10246–10262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, X.; Li, L.; Chen, J.; Ren, Y.; Liu, J.; Yu, Z.; Cao, H.; Chen, J. Discovery of Novel Histone Deacetylase 6 (HDAC6) Inhibitors with Enhanced Antitumor Immunity of Anti-PD-L1 Immunotherapy in Melanoma. J. Med. Chem. 2022, 65, 2434–2457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miyake, Y.; Keusch, J.J.; Wang, L.; Saito, M.; Hess, D.; Wang, X.; Melancon, B.J.; Helquist, P.; Gut, H.; Matthias, P. Structural insights into HDAC6 tubulin deacetylation and its selective inhibition. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2016, 12, 748–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, Q.; Tang, Y.; Hu, Q.; Wang, B.; Ruan, X.; Zhou, Q. Discovery of novel itaconimide-based derivatives as potent HDAC inhibitors for the efficient treatment of prostate cancer. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2024, 269, 116315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, K.; Song, L.-H.; Liang, Q.-L.; Zhang, Y.; Ma, X.-L.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, H.-Y.; Jiang, C.-N.; Wei, J.-H.; Huang, R.-Z. Discovery of novel sulfonamide chromone-oxime derivatives as potent indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase 1 inhibitors. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2023, 254, 115349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, S.; Svoboda, M.; Zhang, G.; Cavasin, M.A.; Motlova, L.; McKinsey, T.A.; Eubanks, J.H.; Barinka, C.; Kozikowski, A.P. Structural and in Vivo Characterization of Tubastatin A, a Widely Used Histone Deacetylase 6 Inhibitor. ACS Med. Chem. Lett. 2020, 11, 706–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yee, A.J.; Bensinger, W.I.; Supko, J.G.; Voorhees, P.M.; Berdeja, J.G.; Richardson, P.G.; Libby, E.N.; Wallace, E.E.; Birrer, N.E.; Burke, J.N.; et al. Ricolinostat plus lenalidomide, and dexamethasone in relapsed or refractory multiple myeloma: A multicentre phase Ib trial. Lancet Oncol. 2016, 17, 1569–1578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vögerl, K.; Ong, N.; Senger, J.; Herp, D.; Schmidtkunz, K.; Marek, M.; Müller, M.; Bartel, K.; Shaik, T.B.; Porter, N.J.; et al. Synthesis and Biological Investigation of Phenothiazine-Based Benzhydroxamic Acids as Selective Histone Deacetylase 6 Inhibitors. J. Med. Chem. 2019, 62, 1138–1166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Wang, T.; Wang, F.; Niu, T.; Liu, Z.; Chen, X.; Long, C.; Tang, M.; Cao, D.; Wang, X.; et al. Discovery of selective histone deacetylase 6 inhibitors using the quinazoline as the cap for the treatment of cancer. J. Med. Chem. 2016, 59, 1455–1470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, S.-M.; Liang, G.-B.; Wang, H.-L.; Jiang, H.; Ma, X.-L.; Wei, J.-H.; Huang, R.-Z.; Zhang, Y. Discovery of 4-(N-dithiobenzyl piperazine)-1,8-naphthalimide as a potent multi-target antitumor agent with good efficacy, limited toxicity, and low resistance. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2024, 263, 115937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Q.; Zhang, S.; Liu, J.; Zhou, X.; Ariffin, N.S.; Wei, J.; Shi, C.; Ma, X.; Zhang, Y.; Huang, R. Discovery of novel 1,8-naphthalimide piperazinamide based benzenesulfonamides derivatives as potent carbonic anhydrase IX inhibitors and ferroptosis inducers for the treatment of triple-negative breast cancer. Bioorg. Chem. 2024, 150, 107596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.-Q.; Mao, Z.-C.; Xu, Y.-L.; Chen, X.-M.; Wang, H.-L.; Wang, Q.; Wei, J.-H.; Huang, R.-Z.; Zhang, Y. Discovery of two biotin-PEG4-diarylidenyl piperidone prodrugs as potent antitumor agents with good efficacy, limited toxicity, and low resistance. Bioorg. Chem. 2023, 131, 106323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, R.; Jing, X.; Huang, X.; Pan, Y.; Fang, Y.; Liang, G.; Liao, Z.; Wang, H.; Chen, Z.; Zhang, Y. Bifunctional naphthoquinone aromatic amide-oxime derivatives exert combined immunotherapeutic and antitumor effects through simultaneous targeting of indoleamine-2,3-dioxygenase and signal transducer and activator of transcription 3. J. Med. Chem. 2020, 63, 1544–1563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, X.; Wang, M.; You, Q.; Kong, J.; Zhang, H.; Yu, C.; Wang, Y.; Wang, H.; Huang, R. Synthesis, mechanisms of action, and toxicity of novel aminophosphonates derivatives conjugated irinotecan in vitro and in vivo as potent antitumor agents. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2020, 189, 112067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, G.-B.; Wei, J.-H.; Jiang, H.; Huang, R.-Z.; Qin, J.-T.; Wang, H.-L.; Wang, H.-S.; Zhang, Y. Design, synthesis and antitumor evaluation of new 1,8-naphthalimide derivatives targeting nuclear DNA. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2021, 210, 112951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



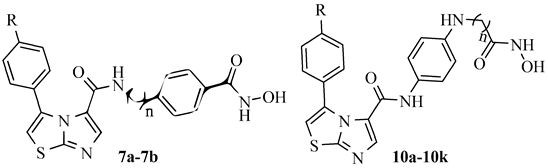 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Compd. | R | n | IDO1 IC50 (μM) a | HDAC6 Inhibition Rate at 1 μM |
| 7a | Br | 1 | 0.53 ± 0.11 | 85.64% |
| 7b | Me | 1 | 0.96 ± 0.13 | 47.95% |
| 10a | Br | 2 | 1.87 ± 0.06 | 22.44% |
| 10b | Br | 3 | 1.06 ± 0.02 | 25.24% |
| 10c | Br | 4 | 0.34 ± 0.09 | 19.37% |
| 10d | Br | 5 | 0.12 ± 0.01 | 46.16% |
| 10e | Br | 6 | 0.086 ± 0.02 | 90.45% |
| 10f | Me | 1 | 6.16 ± 0.83 | 28.83% |
| 10g | Me | 2 | 2.07 ± 0.29 | 31.25% |
| 10h | Me | 3 | 1.78 ± 0.47 | 33.66% |
| 10i | Me | 4 | 0.59 ± 0.11 | 35.49% |
| 10j | Me | 5 | 0.38 ± 0.05 | 40.23% |
| 10k | Me | 6 | 0.16 ± 0.03 | 70.69% |
| Epacadostat | - | - | 0.064 ± 0.01 | - |
| SAHA | - | - | - | 91.66% |
| 5a | - | - | 6.52 ± 0.45 | - |
| IC50 (nM) a | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Compd. | HDAC1 | HDAC4 | HDAC6 | HDAC11 | SI c |
| 7a | 2449 | 31.53% b | 84.44 | 6064.00 | 29.00 |
| 10e | 1078 | 9.58% | 58.23 | 24.37% | 18.51 |
| 10k | 1188 | 9.68% | 390.70 | 29.77% | 3.04 |
| SAHA | 90.87 | 33,911 | 37.17 | 52,903.00 | 2.44 |
| IC50 (μM) a | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Compd. | HCT-116 | SW480 | MDA-MB-231 | MCF-7 | HK2 |
| 7a | >80 | >80 | >80 | >80 | - |
| 10d | 24.43 ± 4.78 | >80 | >80 | 52.94 ± 6.95 | - |
| 10e | 16.42 ± 3.76 | 23.43 ± 3.86 | 43.74 ± 1.89 | 36.46 ± 5.45 | >80 |
| 10j | >80 | >80 | >80 | >80 | - |
| 10k | >80 | >80 | >80 | >80 | - |
| SAHA | 2.64 ± 4.26 | 4.32 ± 2.26 | 18.32 ± 5.61 | 6.32 ± 0.88 | 26.60 ± 4.31 |
| Epacadostat | >80 | >80 | >80 | >80 | - |
| 5a | >80 | >80 | >80 | >80 | >80 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, S.; Wang, Y.-F.; Lu, H.-R.; Yang, X.-Q.; Zhang, Y.; Ma, X.-L.; Huang, R.-Z. Discovery of Novel Imidazothiazole-Based Hydroxamic Acid Derivatives as Potent Indoleamine 2,3-Dioxygenase 1 and Histone Deacetylase 6 Dual Inhibitors. Molecules 2025, 30, 2508. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30122508
Zhang S, Wang Y-F, Lu H-R, Yang X-Q, Zhang Y, Ma X-L, Huang R-Z. Discovery of Novel Imidazothiazole-Based Hydroxamic Acid Derivatives as Potent Indoleamine 2,3-Dioxygenase 1 and Histone Deacetylase 6 Dual Inhibitors. Molecules. 2025; 30(12):2508. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30122508
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Shi, Yan-Fei Wang, Hai-Rui Lu, Xue-Qin Yang, Ye Zhang, Xian-Li Ma, and Ri-Zhen Huang. 2025. "Discovery of Novel Imidazothiazole-Based Hydroxamic Acid Derivatives as Potent Indoleamine 2,3-Dioxygenase 1 and Histone Deacetylase 6 Dual Inhibitors" Molecules 30, no. 12: 2508. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30122508
APA StyleZhang, S., Wang, Y.-F., Lu, H.-R., Yang, X.-Q., Zhang, Y., Ma, X.-L., & Huang, R.-Z. (2025). Discovery of Novel Imidazothiazole-Based Hydroxamic Acid Derivatives as Potent Indoleamine 2,3-Dioxygenase 1 and Histone Deacetylase 6 Dual Inhibitors. Molecules, 30(12), 2508. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30122508






