Use of Naringinase to Modify the Sensory Quality of Foods and Increase the Bioavailability of Flavonoids: A Systematic Review
Abstract
1. Introduction
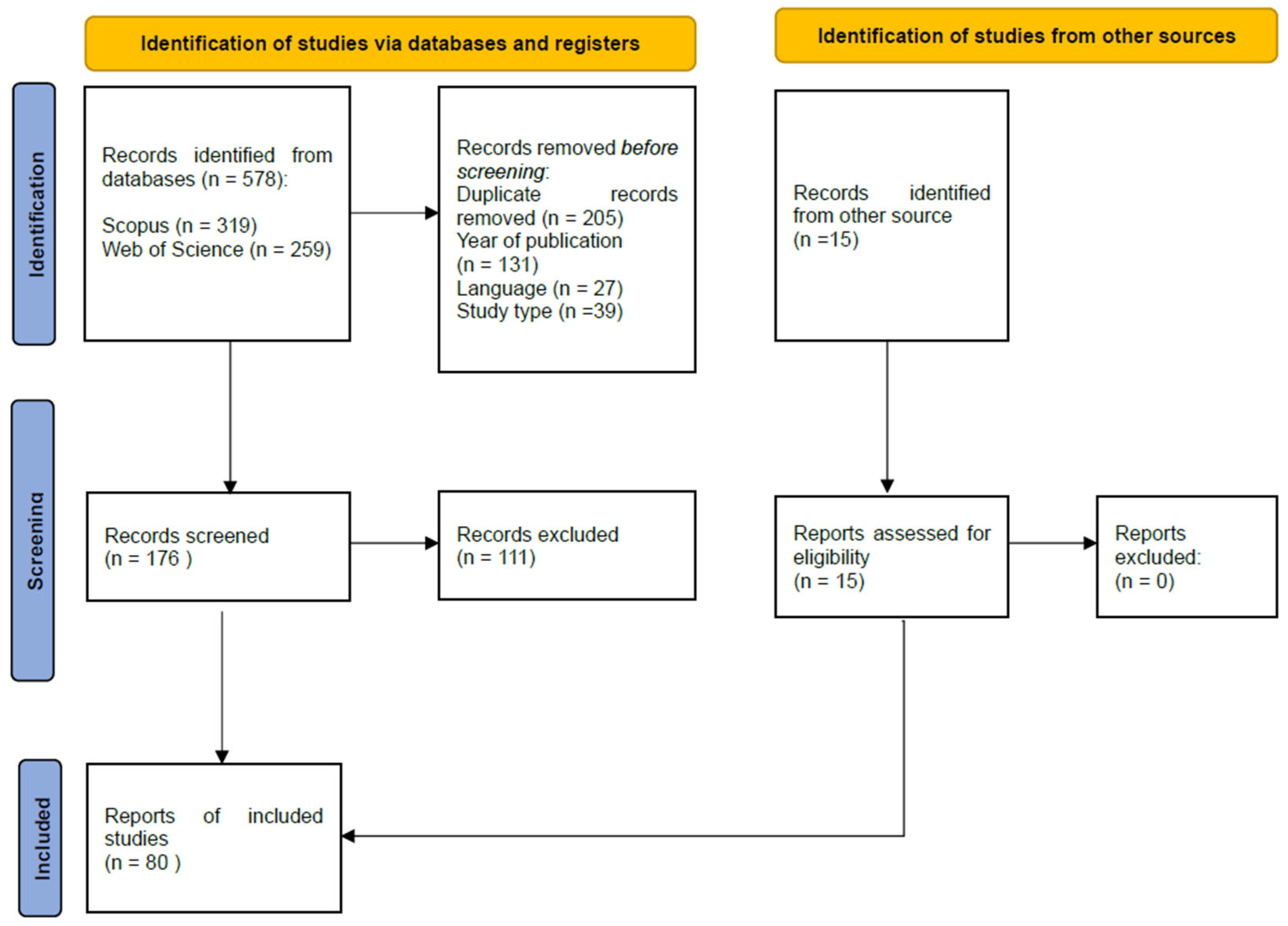
2. Methodology
3. Use of Naringinase
3.1. Removing the Bitter Taste of Citrus Juice
3.2. Flavor Enhancement of Fruit Juices and Wines
3.3. One-Time Clarification and Removal of the Bitter Taste of Beverages
3.4. Increasing the Bioavailability of Flavonoids
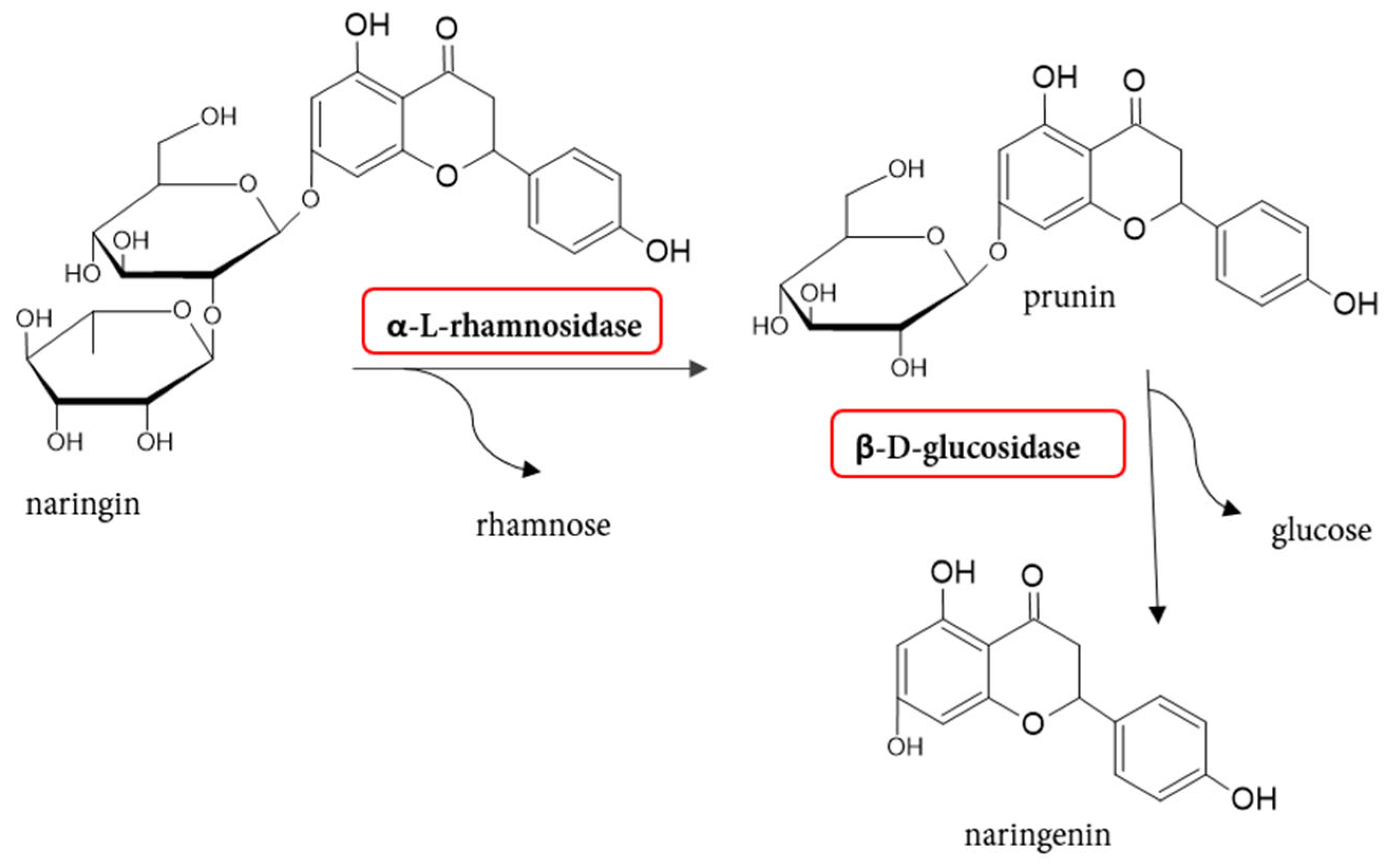
3.4.1. Hydrolysis of Naringin
3.4.2. Hydrolysis of Hesperidin
3.4.3. Hydrolysis of Rutin
3.5. Production of Functional Beverages with Enhanced Antioxidant Activity
3.6. Other Applications of Naringinase and Its Subunits
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviation
| Hes-7-G | hesperetin 7-O-glucoside |
References
- da Silva, C.M.G.; Contesini, F.J.; Sawaya, A.C.F.; Cabral, E.C.; da Silva Cunha, I.B.; Eberlin, M.N.; de Oliveira Carvalho, P. Enhancement of the antioxidant activity of orange and lime juices by flavonoid enzymatic de-glycosylation. Food Res. Int. 2013, 52, 308–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vila-Real, H.; Alfaia, A.J.; Bronze, M.R.; Calado, A.R.T.; Ribeiro, M.H.L. Enzymatic synthesis of the flavone glucosides prunin and isoquercetin, and the aglycones, naringenin and quercetin, with selective α-l-rhamnosidase and β-d-glucosidase activities of naringinase. Enzyme Res. 2011, 2011, 692618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Puri, M. Updates on naringinase: Structural and biotechnological aspects. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2012, 93, 49–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selim, M.S.; Abo Elsoud, M.M.; Sanad, M.N.M.E.; Elattal, N.A.; Rifaat, H.M.; Mohamed, S.S. Enzymatic debittering of citrus juices: Optimization, modeling, and characterization of naringinase production from marine Bacillus subtilis strain BSnari. Biocatal. Agric. Biotechnol. 2023, 53, 102853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, H.; Chen, F.; Cai, H.; Xiao, A.; You, Q.; Lu, Y. Characterization and preparation of Aspergillus niger naringinase for debittering citrus juice. J. Food Sci. 2012, 77, C1–C7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patil, M.B.; Dhake, A.B. Debittering of citrus fruit juice by naringinase of Penicillium purpurogenum. Int. J. Eng. Res. Sci. Technol. 2014, 3, 266–270. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, Y.; Jia, H.; Xi, M.; Xu, L.; Wu, S.; Li, X. Purification and characterization of a naringinase from a newly isolated strain of Bacillus amyloliquefaciens 11568 suitable for the transformation of flavonoids. Food Chem. 2017, 214, 39–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borzova, N.; Gudzenko, O.; Varbanets, L. Purification and characterization of a naringinase from Cryptococcus albidus. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2018, 184, 953–969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, A.M.; Nguyen, T.B.; Nguyen, V.D.; Bujna, E.; Dam, M.S.; Nguyen, Q.D. Changes in bitterness, antioxidant activity and total phenolic content of grapefruit juice fermented by Lactobacillus and Bifidobacterium strains. Acta Aliment. 2020, 49, 103–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balaraman, H.; Purushotaman, C.; Chandramouliswaran, K.; Rathnasamy, S. Simultaneous production and sustainable eutectic mixture based purification of naringinase with Bacillus amyloliquefaciens by valorization of tofu wastewater. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 14855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandove, G.; Sahota, P.; Gupta, N.; Singh, P. Production of low-alcoholic naturally carbonated fermented debittered beverage from W. Murcott mandarin (Citrus reticulata) by naringinase-producing yeast. J. Food Agric. Environ. 2016, 14, 30–34. [Google Scholar]
- Pegu, B.K.; Kardong, D.; Chutia, J.; Gogoi, D.K.; Buragohain, M. Microbial naringinase and its applications in debittering technology–A mini review. Biosci. Biotechnol. Res. Commun. 2021, 14, 493–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golgeri, M.D.B.; Mulla, S.I.; Bagewadi, Z.K.; Faniband, B.; Mishra, P.; Bankole, P.O.; Sharma, S.; Américo-Pinheiro, J.H.P.; Bharagava, R.N.; Romanholo Ferreira, L.F. Microbial naringinase: From microbial source to its current applications in various fields. Biologia 2025, 80, 977–991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, M.; Sehrawat, N.; Sharma, A.K.; Kumar, V.; Kumar, A. Naringinase: Microbial sources, production and applications in food processing industry. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. Food Sci. 2018, 8, 717–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Zhong, X.; Hu, X.; Tian, S.; Fan, G. Research progress on microbial naringinase. J. Henan Univ. Technol. (Nat. Sci. Ed.) 2024, 45, 19–30. [Google Scholar]
- Xia, X.K.; Zhang, Y.E.; Lei, S.J.; Hu, B.; Fu, C.X. Identification and iterative combinatorial mutagenesis of a new naringinase-producing strain, Aspergillus tubingensis MN589840. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 2021, 72, 141–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patil, S.V.; Koli, S.H.; Mohite, B.V.; Patil, R.P.; Patil, R.R.; Borase, H.P.; Patil, V.S. A novel screening method for potential naringinase-producing microorganisms. Biotechnol. Appl. Biochem. 2019, 66, 323–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadłek, J.; Sadłek, W. Biodostępna Kompozycja Flawonoidów Zawierających Ramnozę Oraz Jej Zastosowanie. PL Patent (11) 229133, 15 June 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Page, M.J.; McKenzie, J.E.; Bossuyt, P.M.; Boutron, I.; Hoffmann, T.C.; Mulrow, C.D.; Shamseer, L.; Tetzlaff, J.M.; Akl, E.A.; Brennan, S.E.; et al. The PRISMA 2020 statement: An updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. BMJ 2021, 372, n71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holt, S.; Miks, M.H.; Carvalho, B.T.; Thevelein, J.M.; Foulquié, M.R.; Thevelein, J.M. The molecular biology of fruity and floral aromas in beer and other alcoholic beverages. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2019, 43, 193–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bodakowska-Boczniewicz, J.; Garncarek, Z. Zastosowanie naringinazy w technologii soków i win. Pr. Nauk. UE Wroc. 2017, 494, 20–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, L.; Afonso, C.; Vila-Real, H.; Alfaia, A. Evaluation of the effect of high pressure on naringin hydrolysis in grapefruit juice with naringinase immobilised in calcium alginate beads. Food Technol. Biotechnol. 2008, 46, 146–150. [Google Scholar]
- Muñoz, M.; Holtheuer, J.; Wilson, L.; Urrutia, P. Grapefruit debittering by simultaneous naringin hydrolysis and limonin adsorption using naringinase immobilized in agarose supports. Molecules 2022, 27, 2687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cavia-Saiz, M.; Muñiz, P.; Ortega, N.; Busto, M.D. Effect of enzymatic debittering on antioxidant capacity and protective role against oxidative stress of grapefruit juice in comparison with adsorption on exchange resin. Food Chem. 2011, 125, 158–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribeiro, I.A.; Ribeiro, M.H.L. Naringin and naringenin determination and control in grapefruit juice by a validated HPLC method. Food Control 2008, 19, 432–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, S.; Xu, Y.; Fan, G.; Xiao, M.; Pan, S. Immobilization of naringinase on mesoporous molecular sieve MCM-41 and its application to debittering of white grapefruit. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2011, 257, 4096–4099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Silva, G.O.; Marapana, R.; Manawaduge, R. Effect of naringinase enzymatic treatment on the bitter compound naringin in fresh juice of “Bibila sweet” oranges. J. Pharmacogn. Phytochem. 2017, 6, 174–178. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, W.; Zhan, Y.; Shi, X.; Chen, J.; Deng, H.; Du, Y. Controllable immobilization of naringinase on electrospun cellulose acetate nanofibers and their application to juice debittering. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2017, 98, 630–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bodakowska-Boczniewicz, J.; Garncarek, Z. Immobilization of naringinase from Penicillium decumbens on chitosan microspheres for debittering grapefruit juice. Molecules 2019, 24, 4234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Housseiny, M.M.; Aboelmagd, H.I. Nano-encapsulation of naringinase produced by Trichoderma longibrachiatum ATCC18648 on thermally stable biopolymers for citrus juice debittering. J. Microbiol. 2019, 57, 521–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez-Temino, Y.; Ruíz, M.O.; Ortega, N.; Ramos, G.S. Immobilization of naringinase on asymmetric organic membranes: Application for debittering of grapefruit juice. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2021, 73, 102790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singla, G.; Panesar, P.S.; Sangwan, R.S.; Krishania, M. Enzymatic processing of Citrus reticulata (Kinnow) pomace using naringinase and its valorization through preparation of nutritionally enriched pasta. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 58, 3853–3860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, M.; Pareek, V. Minimization of limonin and naringin content in Kinnow juice using response surface methodology. Ann. Biol. 2022, 38, 88–95. [Google Scholar]
- Gupta, A.K.; Rather, M.A.; Mishra, P. Design and development of laboratory scale batch type device for debittering of bitter citrus juice. J. Food Process Eng. 2023, 46, e14265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sihmar, D.; Ray, A.B. Optimization of physical and enzymatic debittering methods for grapefruit juice. J. Appl. Hortic. 2023, 25, 211–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Zhu, S.; Chen, L.; Wang, Z.; Yu, M. Fermentation optimization of naringinase from a screened strain of Serratia marcescens C10 through response surface methodology. Biomass Convers. Biorefin. 2024, 14, 15621–15634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urrutia, P.; Arrieta, R.; Torres, C.; Guerrero, C.; Wilson, L. Amination of naringinase to improve citrus juice debittering using a catalyst immobilized on glyoxyl-agarose. Food Chem. 2024, 452, 139600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimmins, S.D.; Henríquez, A.; Torres, C.; Wilson, L.; Flores, M.; Pio, E.; Jullian, D.; Urbano, B.; Braun-Galleani, S.; Ottone, C.; et al. Immobilization of naringinase onto polydopamine-coated magnetic iron oxide nanoparticles for juice debittering applications. Polymers 2024, 16, 3279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devi, G.N.; Sangavi, G.; Chakravarthy, M.; Sweetlin, J.L. Isolation, production optimization, and purification of a debittering enzyme from Bacillus megaterium Auls 1. Chem. Biochem. Eng. Q. 2024, 38, 175–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del Nobile, M.A.; Piergiovanni, L.; Buonocore, G.G.; Fava, P.; Puglisi, M.L.; Nicolais, L. Naringinase immobilization in polymeric films intended for food packaging applications. J. Food Sci. 2003, 68, 4–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, H.; Rani, P.; Kim, H.; Eun, A.; Lee, B.; Yang, K.; Nam, S. A combination of commercial and traditional food-source-derived enzymatic treatment acts as a potential tool to produce functional yuzu (Citrus junos) powder. Food Chem. X 2023, 20, 100918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seong, H.-J.; Kim, H.; Cho, J.-Y.; Yang, K.-Y.; Nam, S.-H. Modulating flavanone compound for reducing the bitterness and improving dietary fiber, physicochemical properties, and anti-adipogenesis of green yuzu powder by enzymatic hydrolysis. Food Chem. X 2024, 22, 101329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Morais Souto, B.; Florentino Barbosa, M.; Marinsek Sales, R.M.; Conessa Moura, S.; de Rezende Bastos Araújo, A.; Ferraz Quirino, B. The potential of β-glucosidases for aroma and flavor improvement in the food industry. Microbe 2023, 1, 100004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Pombo, P.; Fariña, L.; Carrau, F.; Batista-Viera, F.; Brena, B.M. Aroma enhancement in wines using co-immobilized Aspergillus niger glycosidases. Food Chem. 2014, 143, 185–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, H.; Hong, P.; Ji, H.F.; Sun, H.; Chen, Y.H.; Xiao, A.F.; Chen, F. Comparative analyses of aromas of fresh, naringinase-treated and resin-absorbed juices of pummelo by GC-MS and sensory evaluation. Flavour Fragr. J. 2015, 30, 245–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, H.; Yang, Y.F.; Chen, F.; Ji, H.F.; Yang, H.; Ling, W.; Cai, H.N. Pectinase and naringinase help to improve juice production and quality from pummelo (Citrus grandis) fruit. Food Sci. Biotechnol. 2014, 23, 739–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michlmayr, H.; Brandes, W.; Eder, R.; Schümann, C.; del Hierro, A.M.; Kulbe, K.D. Characterization of two distinct glycosyl hydrolase family 78 α-l-rhamnosidases from Pediococcus acidilactici. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2011, 77, 6524–6530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, X.; Feng, T.; Liu, E.; Shan, P.; Zhang, Z.; Liao, L.; Ma, H. Ougan juice debittering using ultrasound-aided enzymatic hydrolysis: Impacts on aroma and taste. Food Chem. 2021, 345, 128767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, H.; Jiang, Q.; Lin, Q.; Ma, Q.; Wang, L.; Weng, S.; Huang, G.; Li, L.; Chen, F. Enzymatic hydrolysis and auto-isomerization during β-glucosidase treatment improve the aroma of instant white tea infusion. Food Chem. 2021, 342, 128565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, X.; Dong, Y.; Xie, Y.; Wang, L.; Wang, J.; Liu, Y.; Zhao, L.; Cao, F. Effects of β-glucosidase and α-rhamnosidase on the contents of flavonoids, ginkgolides, and aroma components in ginkgo tea drink. Molecules 2019, 24, 2009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ladole, M.R.; Pokale, P.B.; Varude, V.R.; Belokar, P.G.; Pandit, A.B. One-pot clarification and debittering of grapefruit juice using co-immobilized enzymes@chitosanMNPs. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 167, 1297–1307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Joshi, J.; Kumar, V.; Gautam, P.; Singh, S.; Kohli, D. Effect of immobilized enzymes naringinase and tannase produced from Aspergillus sp. isolate MK156394 isolated from rotten pomelo on quality characteristics of Citrus limetta juice and process optimization by using response surface methodology. Biointerface Res. Appl. Chem. 2021, 11, 9646–9657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, Y.; Xin, X.; Xu, H.; Yuan, H.; Li, X.; Yu, Y.; Zhao, G. Highly efficient bioconversion of flavonoid glycosides from citrus-processing wastes in solvent-buffer systems. Green Chem. 2020, 22, 3196–3207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slámová, K.; Kapešová, J.; Valentová, K. “Sweet flavonoids”: Glycosidase-catalyzed modifications. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 2126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Li, W.; Li, H.; Li, L.; Ni, H.; Chen, F.; Li, Q. Adding sorbitol improves the thermostability of α-l-rhamnosidase from. J. Food Biochem. 2021, 46, e14055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.S.; Huh, J.Y.; Nam, S.H.; Moon, S.K.; Lee, S.B. Enzymatic bioconversion of citrus hesperidin by Aspergillus sojae naringinase: Enhanced solubility of hesperetin-7-O-glucoside with in vitro inhibition of human intestinal maltase, HMG-CoA reductase, and growth of Helicobacter pylori. Food Chem. 2012, 135, 2253–2259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, A.; Huang, B.; Lei, L.; Lu, Y.-J.; Zhou, J.-L.; Wong, W.-L. Production of high antioxidant activity flavonoid monoglucosides from citrus flavanone with immobilised α-l-rhamnosidase in one step. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2019, 54, 2854–2862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moriwaki, M.; Kito, K.; Nakagawa, R.; Kapoor, M.P.; Matsumiya, Y.; Fukuhara, T.; Kobayashi, J.; Satomoto, K.; Yamagata, H.; Kuroiwa, Y. Increased bioavailability of diosmetin-7-glucoside-γ-cyclodextrin inclusion complex compared with diosmin in Sprague-Dawley rats. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2023, 87, 771–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moriwaki, M.; Tominaga, E.; Kito, K.; Nakagawa, R.; Kapoor, M.P.; Matsumiya, Y.; Fukuhara, T.; Kobayashi, J.; Satomoto, K.; Yamagata, H.; et al. Bioavailability of flavonoids in Ginkgo biloba extract-γ-cyclodextrin complex. Nat. Prod. Commun. 2023, 18, 1934578X231170221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Zheng, Z.; Ming, Y.; Lin, M.; Chen, L.; Huang, W.; Xiao, J.; Lin, H. Gynosaponin TN-1 producing from the enzymatic conversion of gypenoside XLVI by naringinase and its cytotoxicity on hepatoma cell lines. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2018, 119, 161–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Zheng, Z.; Ming, Y.; Bai, Y.; Chen, L.; Huang, W.; Lin, M.; Liu, S.; Xiao, J.; Lin, H. Compound K producing from the enzymatic conversion of gypenoside by naringinase. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2019, 130, 253–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Zhao, Y.; Lai, X.; Nong, J.; Zhao, G.; Xiao, X. One-pot biocatalytic synthesis and antioxidant activities of highly lipophilic naringin derivatives by using bi-functional whole-cells. Food Res. Int. 2020, 136, 109291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carceller, J.M.; Martínez Galán, J.P.; Monti, R.; Bassan, J.C.; Filice, M.; Yu, J.; Corma, A. Selective synthesis of citrus flavonoids prunin and naringenin using heterogeneized biocatalyst on graphene oxide. Green Chem. 2019, 21, 839–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seong, H.J.; Im, A.E.; Kim, H.; Park, N.; Yang, K.Y.; Kim, D.; Nam, S.H. Production of prunin and naringenin by using naringinase from Aspergillus oryzae NYO-2 and their neuroprotective properties and debitterization. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2023, 71, 1655–1666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, H.Y.; Lee, Y.B.; Bae, H.A.; Huh, J.Y.; Nam, S.H.; Sohn, H.S.; Lee, H.J.; Lee, S.B. Purification and characterisation of Aspergillus sojae naringinase: The production of prunin exhibiting markedly enhanced solubility with in vitro inhibition of HMG-CoA reductase. Food Chem. 2011, 124, 234–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Zhang, N.; Sun, X.; Zhan, H.; Tian, J.; Fei, X.; Liu, X.; Chen, G.; Wang, Y. Controllable biotransformation of naringin to prunin by naringinase immobilized on functionalized silica. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 2021, 96, 1218–1227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, A.; Singh, S.; Singh, R.S.; Schwarz, W.H.; Puri, M. Hydrolysis of citrus peel naringin by recombinant α-l-rhamnosidase from Clostridium stercorarium. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 2010, 85, 1419–1422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carceller, J.M.; Martínez Galán, J.P.; Monti, R.; Bassan, J.C.; Filice, M.; Yu, J.; Corma, A. Covalent immobilization of naringinase over two-dimensional 2D zeolites and its applications in a continuous process to produce citrus flavonoids and for debittering of juices. ChemCatChem 2020, 12, 4502–4511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salunkhe, J.D.; Mohite, B.V.; Patil, S.V. Naringenin biosynthesis and fabrication of naringenin mediated nano silver conjugate for antimicrobial potential. Nat. Prod. Res. 2023, 37, 3184–3190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Chen, P.-X.; Xiao, Q.; Chen, J.; Chen, F.-Q.; Yang, Q.-M.; Weng, H.-F.; Fang, B.-S.; Zhang, Y.-H.; Xiao, A.-F. Artificial naringinase system for cooperative enzymatic synthesis of naringenin. Biochem. Eng. J. 2022, 178, 108277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, C.M.; Zhang, W.T.; Xie, S.Y.; Zhuang, X.Y.; Guo, Z.W.; Xiao, Q.; Chen, J.; Chen, F.Q.; Yang, Q.M.; Ru, Y.; et al. Engineering artificial fusion naringinase for enhancing naringenin biosynthesis. Biochem. Eng. J. 2024, 205, 109253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazzaferro, L.S.; Breccia, J.D. Quantification of hesperidin in citrus-based foods using a fungal diglycosidase. Food Chem. 2012, 134, 2338–2344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shin, K.-C.; Nam, H.-K.; Oh, D.-K. Hydrolysis of flavanone glycosides by β-glucosidase from Pyrococcus furiosus and its application to the production of flavanone aglycones from citrus extracts. Agric. Food Chem. 2013, 61, 11532–11540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kapoor, M.P.; Moriwaki, M.; Minoura, K.; Timm, D.; Abe, A.; Kito, K. Structural investigation of hesperetin-7-O-glucoside inclusion complex with β-cyclodextrin: A spectroscopic assessment. Molecules 2022, 27, 5395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, D.; Gong, A.; Xu, Y.; Kinfack Tsabing, D.; Wu, F.; Wang, J. Isoquercitrin production from rutin catalyzed by naringinase under ultrasound irradiation. J. Mol. Catal. B Enzym. 2016, 134, 186–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, A.; Zhu, C.T.; Xu, Y.; Wang, F.Q.; Tsabing, D.K.; Wu, F.A.; Wang, J. Moving and unsinkable graphene sheets immobilized enzyme for microfluidic biocatalysis. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 4039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, Y.-S.; Huh, J.-Y.; Nam, S.-H.; Kim, D.; Lee, S.-B. Synthesis of Quercetin-3-O-Glucoside from Rutin by Penicillium decumbens Naringinase. J. Food Sci. 2013, 78, C411–C415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Ma, Y.; Wu, X.; Yu, L.; Xia, R.; Sun, G.; Wu, F. Selective hydrolysis by commercially available hesperidinase for isoquercitrin production. J. Mol. Catal. B Enzym. 2012, 81, 37–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerstorferová, D.; Fliedrová, B.; Halada, P.; Marhol, P.; Křen, V.; Weignerová, L. Recombinant α-l-rhamnosidase from Aspergillus terreus in selective trimming of rutin. Process Biochem. 2012, 47, 828–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, L.-L.; Zhu, C.-T.; Xiong, M.; Jin, C.-Q.; Sheng, S.; Wu, F.-A.; Wang, J. Enzyme immobilization on photopatterned temperature-response poly (N-isopropylacrylamide) for microfluidic biocatalysis. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 2019, 94, 1670–1678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weiz, G.; Breccia, J.D.; Mazzaferro, L.S. Screening and quantification of the enzymatic deglycosylation of the plant flavonoid rutin by UV–visible spectrometry. Food Chem. 2017, 229, 44–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Araujo, M.E.; Moreira Franco, Y.E.; Alberto, T.G.; Sobreiro, M.A.; Conrado, M.A.; Priolli, D.G.; Frankland Sawaya, A.C.H.; Ruiz, A.L.T.G.; de Carvalho, J.E.; Carvalho, P. de O. Enzymatic de-glycosylation of rutin improves its antioxidant and antiproliferative activities. Food Chem. 2013, 141, 266–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoo, J.M.; Kim, N.Y.; Seo, J.M.; Kim, S.J.; Lee, S.Y.; Kim, S.K.; Kim, H.D.; Lee, S.W.; Kim, M.R. Inhibitory effects of mulberry fruit extract in combination with naringinase on the allergic response in IgE-activated RBL-2H3 cells. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2014, 33, 469–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, C.; Li, R.; Ni, H.; Li, L.J.; Li, Q.B. The effects of α-l-rhamnosidase, β-d-glucosidase, and their combination on the quality of orange juice. J. Food Process. Preserv. 2021, 45, e15604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karabiber, E.B.; Yılmaz, E. Extraction and characterisation of lemon, orange and grapefruit seeds press cake proteins. Qual. Assur. Saf. Crops Foods 2017, 9, 357–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- İmece, A.; Şengül, M.; Çetin, B.; Aktaş, H. Effect of probiotic Lactiplantibacillus plantarum strains on some properties of grapefruit juice and naringin. J. Stored Prod. Res. 2024, 108, 102359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahota, P.P.; Kaur, N. Characterization of enzyme naringinase and the production of debittered low alcoholic kinnow (Citrus reticulata blanco). Int. J. Adv. Res. 2015, 3, 1220–1233. [Google Scholar]
- Ko, J.A.; Ryu, Y.B.; Kwon, H.J.; Jeong, H.J.; Park, S.J.; Kim, C.Y.; Wee, Y.J.; Kim, D.; Lee, W.S.; Kim, Y.M. Characterization of a novel steviol-producing β-glucosidase from Penicillium decumbens and optimal production of the steviol. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2013, 97, 8151–8161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, T.T.H.; Seo, C.; Kwak, S.H.; Kim, J.; Kang, H.K.; Kim, S.B.; Kim, D. Enzymatic production of steviol glucosides using β-glucosidase and their applications. In Enzymes in Food Biotechnology; Issue Chapter 23; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019; pp. 405–418. [Google Scholar]
- Nguyen, T.T.H.; Jung, S.; Kang, H.; Kim, Y.; Moon, Y.; Kim, M.; Kim, D. Production of rubusoside from stevioside by using a thermostable lactase from Thermus thermophilus and solubility enhancement of liquiritin and teniposide. Enzyme Microb. Technol. 2014, 64, 38–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, L.; Huang, B.; Liu, A.; Lu, Y.-J.; Zhou, J.-L.; Zhang, J.; Wong, W.-L. Enzymatic production of natural sweetener trilobatin from citrus flavanone naringin using immobilised α-l-rhamnosidase as the catalyst. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2018, 53, 2097–2103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walton, S.; Olcese, G. Sweet Taste Improving Compositions Including Naringenin. U.S. Patent No. 10,231,474, 12 November 2015. [Google Scholar]
- EFSA Panel on Food Additives and Flavourings; Castle, L.; Degen, G.; Engel, H.; Fowler, P.J.; José, M.; Fernandez, F.; Fürst, P.; Gürtler, R.R.; Husøy, T.; et al. Flavouring Group Evaluation 413 (FGE. 413): Naringenin. EFSA J. 2024, 22, e8747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, P.; Dou, T.Y.; Li, S.Y.; Lu, J.X.; Zou, L.W.; Wang, P.; Sun, Y.P.; Hao, D.C.; Ge, G.B. Highly selective and efficient biotransformation of linarin to produce tilianin by naringinase. Biotechnol. Lett. 2016, 38, 1367–1373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodiah, M.H.; Jamilah, B.; Norhayati, H.; Kharidah, M. Debittering of Borassus flabellifer mesocarp using naringinase: Impact on the composition, physicochemical characteristics, and functional properties. Malays. J. Sci. 2023, 42, 34–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rejane, A.; Ávila, A.; de Alves, G.; Juliana, M.; Macedo, A. Exploring in vitro effects of biotransformed isoflavones extracts: Antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and antilipogenic. J. Food Biochem. 2019, 43, e12850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Form of Enzyme Used | Source of Enzyme | Product | Condition of Juice Debittering | Reduction in Naringin | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Naringinase immobilized in calcium alginate bead | P. decumbens | Orange juice | 160 MPa, 37 °C, 20 min 500 enzyme mg·dm−3 juice) | 75% | [22] |
| Naringinase entrapped in k-carrageenan beads | P. decumbens | Grapefruit juice | 30 °C, 120 min, 4 (juice): 1 (k-carrageenan beads enzyme) | 70% | [25] |
| Free naringinase | P. decumbens | Grapefruit juice | 20 °C, 24 h, 25 cm3 juice, naringinase (0.4 U·cm−3), | 46.8% | [24] |
| Naringinase immobilized on mesoporous silica | - | White grapefruit juice | 60 °C, 30 min | 95.03% | [26] |
| Free naringinase | A. niger | Honey pomelo juice | 40 °C, 60 min | about 90% | [5] |
| Free naringinase | P. purpurogenum | Grapefruit juice | 40 °C, 4 h 100 U of enzyme/100 cm3 juice | 74% | [7] |
| Free naringinase | A. oryzae | Pomelo juice | 45 °C, 60 min | approximately 99% | [6] |
| Free naringinase | - | “Bibila sweet” oranges | 50 °C, 4 h 1.0 g of enzyme/dm3 juice | 86% | [27] |
| Naringinase immobilized on electrospun cellulose acetate nanofibers | - | Grapefruit juice | - | 22.72% | [28] |
| Free naringinase | C. albidus | Grapefruit juice | 40 °C and 60 °C, 60 min | 84% and 100% | [8] |
| Naringinase immobilized on chitosan microspheres activated with glutaraldehyde | A. niger | Grapefruit juice | 40 °C, 5 h | 75% | [29] |
| Naringinase encapsulated in nano-chitosan and nano-alginate | T. longibrachiatum | Grapefruit juice | 50 °C, 60 min | 50.5% and 44.15% | [30] |
| Naringinase immobilized on polyethersulfone ultrafiltration membrane | P. decumbens | Grapefruit juice | 45–50 °C 0.025 MPa | 50.1 ± 0.3% | [31] |
| Free naringinase | Thermomicrobia sp. | Kinnow juice pomace | 50 °C, pH 4.5, 4 h, | 65.95% | [32] |
| Free naringinase | A. niger | Kinnow juice | Room temperature, 12 h | 40.0% | [33] |
| Naringinase immobilized in agarose supports | A. aculeatus/A. niger | Grapefruit juice | 30 °C, 24 h | 74% | [23] |
| Free naringinase | B. amyloliquefaciens | Grape juice | 37 °C, 20 min | 23.4% | [10] |
| Free naringinase | B. subtilis | Lemon, grapefruit, orange, and mandarin | 4 h, 40–50 °C | 33–36% | [4] |
| Naringinase adsorbed onto a macroporous resin | A. niger | Pomelo juice | 60 °C, 160 min | 53.06% | [34] |
| Free naringinase | - | Grapefruit juice | 35 °C, 3 h 50 min | 55.77% | [35] |
| Free naringinase | Serratia marcescens | Grapefruit juice | 55 °C, 90 min | 85.93% | [36] |
| Naringinase chemically aminated prior to its immobilization on glyoxyl-agarose | A. aculeatus/A. niger | Grapefruit juice | 30 °C, 24 h | 74% | [37] |
| Naringinase immobilizes onto polydopamine-coated magnetic iron oxide nanoparticles | A. aculeatus/A. niger | Grapefruit juice | 50 °C, 24 h | 56% | [38] |
| Free naringinase | Bacillus megaterium | Lemon and tangerine juice | 37 °C | 45.78% (lemon juice) 42.71% (tangerine juice) | [39] |
| Form of Enzyme | Source of Enzyme | Product | Condition of Juice Debittering | Results | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Free naringinase | A. sojae | Orange juice/orange peel | 37 °C, 24 h, enzyme solution: 1.7–2 mg/mL | Production yield of Hes-7-G * was 71% for orange juice and 78% for orange peel | [56] |
| α-l-rhamnosidase and β-d-glucosidase | A. niger | Reaction mixture (20 mg of hesperidin and 40 mg of freeze-dried whole-cell catalysts was mixed with 2 cm3 of acetate buffer) | pH 5.0, 40 °C, 24 h | 93.9 ± 1.4% conversion of hesperidin; 73.3 ± 9.2% Hes-7-G; 26.7 ± 9.2% hesperetin | [53] |
| β-glucosidase | Pyrococcus furiosus | Orange peel extract | 95 °C for 12 h (pH 5.5) 100% citrus extract, 0.85 U cm−3 enzyme | 100% (w/v) conversion of hesperidin to 9.0 g·dm−3 hesperetin after 9 h, with a productivity of 1.00 g·dm−3·h−1 | [73] |
| α-l-rhamnosidase | A. niger | Reaction mixture (1 cm3 0.5 mM hesperidin, 0.98 cm3 phosphate citrate, and 20 mm−3 α-l-rhamnosidase) | 0.7 M sorbitol 60 °C, pH 4.5, 10 min | 63.26% hesperidin was hydrolyzed to Hes-7-G. completely hydrolyzed after 10 h reaction | [55] |
| Naringinase and β-cyclodextrin | β-cyclodextrin content 57.5%, hesperidinase, naringinase | 70 °C, pH 4.5 | 98% | [74] |
| Form of Enzyme | Source of Enzyme | Reaction Mixture | Condition of Reaction | Results | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Free naringinase (inactivation of β-d-glucosidase activity) | P. decumbens | 5 mM rutin, 50 mg·dm−3 enzyme | Residual activity of α-l-rhamnosidase (78%), pH 3.4, 60.0 °C, 6 h | Production yield of isoquercitrin, 61% | [2] |
| Free naringinase (inactivation of β-d-glucosidase activity) | P. decumbens | 5 mM rutin, 50 mg·dm−3 enzyme | pH 3.4, 60.0 °C, 6 h | Production yield of quercetin, 86% | [2] |
| Free naringinase (inactivate the unwanted β-d-glucosidase) | A. terreus | 100 g·dm−3 rutin, 20 cm3 enzyme | pH 8.0, 70 °C, 24 h | Production yield of isoquercitrin, 61%; volumetric productivity (up to 300 g·dm−3) | [79] |
| Hesperidinase (contains both α-l-rhamnosidase and β-d-glucosidase activities; inactivation of β-d-glucosidase activity) | A. niger | 20 cm3 saturated solution of rutin, 10 mg enzymes | pH 7.0, 40 °C, 30 h | Production yield of isoquercitrin 50.06% | [78] |
| Free naringinase (high α-l-rhamnosidase activity, very low β-d-glucosidase activity) | P. decumbens | 1.5 mM rutin, 0.1 mg·dcm−3 enzyme | pH 6, 37 °C, 12 h | Production yield of isoquercitrin, 92% | [77] |
| Free naringinase | P. decumbens | 0.8 g·dm−3, 3000 U·dm−3 enzyme | 40 °C, 20 min, ultrasound irradiation | Production yield of isoquercitrin, 95.20 ± 2.52% | [75] |
| Graphene-immobilized naringinase flowing in microchannels | P. decumbens | 0.05 g·dm−3 rutin, 8 μL, min−1 flow rate | 40 °C, 10 min | 92.24 ± 3.26% isoquercitrin | [76] |
| Photo pattern-immobilized naringinase on a microchip | P. decumbens | 0.03 g·dm−3 rutin, 5 µL, min−1 flow rate | 45 °C, 5 min | 93.28 ± 1.12% conversion of rutin, 87.98 ± 1.1% isoquercitrin yield | [80] |
| Free α-l-rhamnosidase and β-d-glucosidase | A. niger | 20 mg rutin, 40 mg of freeze-dried whole-cell catalysts | pH 5.0, 40 °C, 24 h | 97.2 ± 0.9% conversion of rutin; 94.2 ± 1.6% isoquercitrin; 5.86% ± 1.6% quercetin | [53] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bodakowska-Boczniewicz, J.; Garncarek, Z. Use of Naringinase to Modify the Sensory Quality of Foods and Increase the Bioavailability of Flavonoids: A Systematic Review. Molecules 2025, 30, 2376. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30112376
Bodakowska-Boczniewicz J, Garncarek Z. Use of Naringinase to Modify the Sensory Quality of Foods and Increase the Bioavailability of Flavonoids: A Systematic Review. Molecules. 2025; 30(11):2376. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30112376
Chicago/Turabian StyleBodakowska-Boczniewicz, Joanna, and Zbigniew Garncarek. 2025. "Use of Naringinase to Modify the Sensory Quality of Foods and Increase the Bioavailability of Flavonoids: A Systematic Review" Molecules 30, no. 11: 2376. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30112376
APA StyleBodakowska-Boczniewicz, J., & Garncarek, Z. (2025). Use of Naringinase to Modify the Sensory Quality of Foods and Increase the Bioavailability of Flavonoids: A Systematic Review. Molecules, 30(11), 2376. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30112376







