Novel Antimicrobials from Computational Modelling and Drug Repositioning: Potential In Silico Strategies to Increase Therapeutic Arsenal Against Antimicrobial Resistance
Abstract
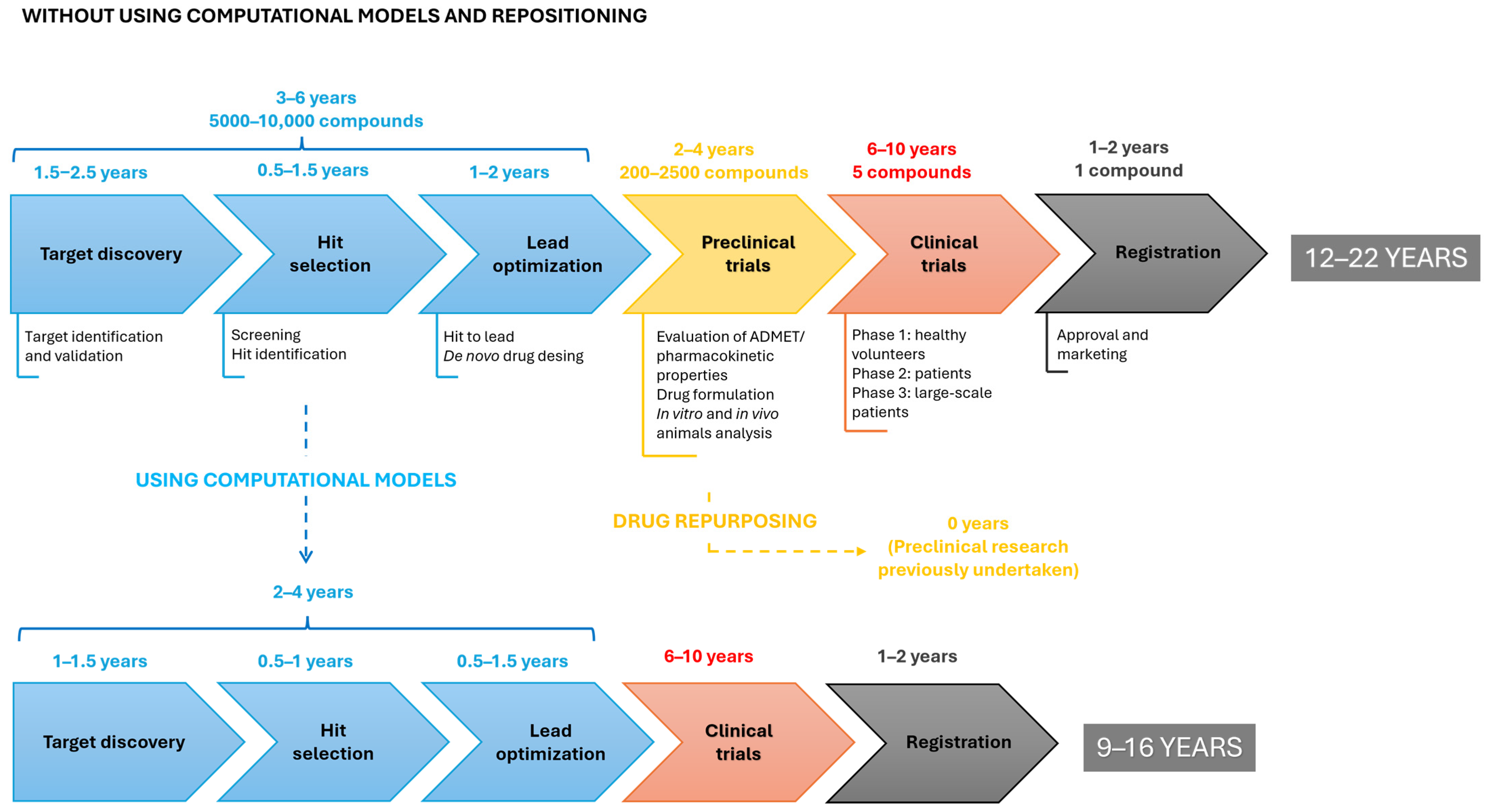
1. Introduction
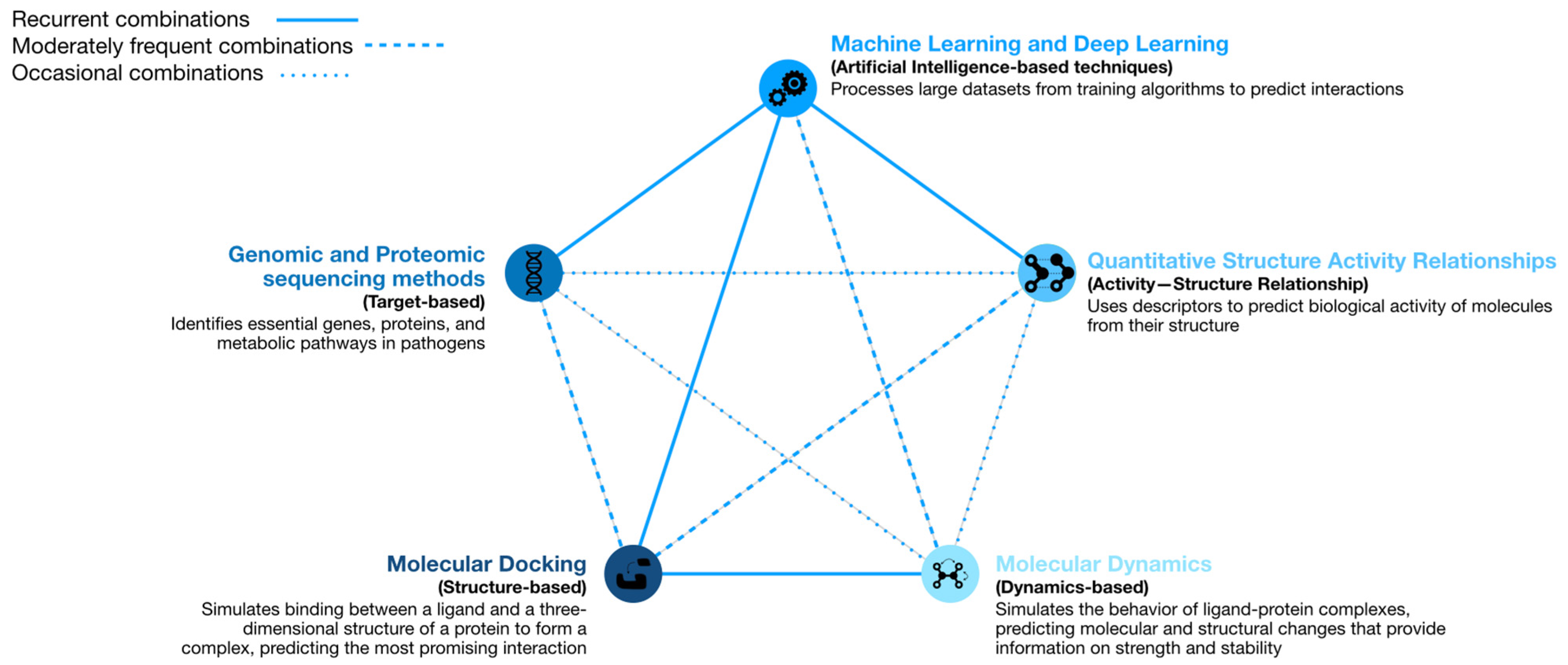
2. Computational Strategies with the Ability to Predict Repositioning of Known Drugs to Antimicrobials
2.1. Machine Learning
2.2. Molecular Docking
2.3. Molecular Dynamics
2.4. Genomic and Proteomic Sequencing Methods
2.5. Quantitative Structure–Activity Relationship Models
3. Future Directions
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ADME | Absorption, distribution, metabolism and excretion |
| ADMET | ADME + toxicity |
| AI | Artificial intelligence |
| AMR | Antimicrobial resistance |
| AUC | Area under the curve |
| AUROC | Area under the receiver operating curve |
| CARAMeL | Condition-specific Antibiotic Regimen Assessment using Mechanistic Learning |
| Cho1 | Fungal phosphatidylserine synthase |
| CYP51 | Sterol 14-demethylase |
| DFT | Density Functional Theory |
| DHFR | Dihydrofolate reductase |
| DL | Deep learning |
| DTI | Drug–target interactions |
| FAERS | FDA Adverse Event Reporting System |
| FDA | Food and Drug Administration |
| GEMs | Genome-scale metabolic models |
| LGA | Lamarckian genetic algorithm |
| MD | Molecular docking |
| ML | Machine learning |
| MRSA | Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus |
| NDM-1 | New Delhi metallo-β-lactamase |
| PASS | Prediction of activity spectra for substance |
| PBP3 | Penicillin-binding protein 3 |
| PDB | Protein Data Bank |
| QS | Quorum sensing |
| QSAR | Quantitative Structure–Activity Relationship |
| RND | Resistance nodulation division |
| TDA | Topological data analysis |
| TDL | Topological deep learning |
References
- GBD 2021 Antimicrobial Resistance Collaborators. Global burden of bacterial antimicrobial resistance 1990–2021: A systematic analysis with forecasts to 2050. Lancet 2024, 404, 1199–1226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tarín-Pelló, A.; Suay-García, B.; Pérez-Gracia, M.T. Antibiotic resistant bacteria: Current situation and treatment options to accelerate the development of a new antimicrobial arsenal. Expert Rev. Anti-Infect. Ther. 2022, 20, 1095–1108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lorente-Torres, B.; Llano-Verdeja, J.; Castañera, P.; Ferrero, H.Á.; Fernández-Martínez, S.; Javadimarand, F.; Mateos, L.M.; Letek, M.; Mourenza, Á. Innovative Strategies in Drug Repurposing to Tackle Intracellular Bacterial Pathogens. Antibiotics 2024, 13, 834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaur, H.; Kalia, M.; Chaudhary, N.; Singh, V.; Yadav, V.K.; Modgil, V.; Kant, V.; Mohan, B.; Bhatia, A.; Taneja, N. Repurposing of FDA approved drugs against uropathogenic Escherichia coli: In silico, in vitro, and in vivo analysis. Microb. Pathog. 2022, 169, 105665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, S.; Gu, Y.; Gu, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Li, L.; Wang, M.; Jiang, R.; Yu, X.; Chen, T.; Li, J. Machine learning-enabled virtual screening indicates the anti-tuberculosis activity of aldoxorubicin and quarfloxin with verification by molecular docking, molecular dynamics simulations, and biological evaluations. Brief. Bioinform. 2024, 26, 696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mongia, M.; Guler, M.; Mohimani, H. An interpretable machine learning approach to identify mechanism of action of antibiotics. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 10342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Rosa, T.F.; Foletto, V.S.; Serafin, M.B.; Bottega, A.; Hörner, R. Anti-infective properties of proton pump inhibitors: Perspectives. Int. Microbiol. 2022, 25, 217–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vieira, T.F.; Leitão, M.M.; Cerqueira, N.M.F.S.A.; Sousa, S.F.; Borges, A.; Simões, M. Montelukast and cefoperazone act as antiquorum sensing and antibiofilm agents against Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2024, 135, lxae088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarín-Pelló, A.; Suay-García, B.; Falcó, A.; Pérez-Gracia, M.T. Big Data to Expand the Antimicrobial Therapeutic Arsenal: De Novo Discovery and Drug Repurposing. In Encyclopedia of Information Science and Technology, 6th ed.; Mehdi Khosrow-Pour, D.B.A., Ed.; IGI Global: Hershey, PA, USA, 2025; advance online publication. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glajzner, P.; Bernat, A.; Jasińska-Stroschein, M. Improving the treatment of bacterial infections caused by multidrug-resistant bacteria through drug repositioning. Front. Pharmacol. 2024, 15, 1397602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cantrell, J.M.; Chung, C.H.; Chandrasekaran, S. Machine learning to design antimicrobial combination therapies: Promises and pitfalls. Drug Discov. Today 2022, 27, 1639–1651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shehadeh, F.; Felix, L.; Kalligeros, M.; Shehadeh, A.; Fuchs, B.B.; Ausubel, F.M.; Sotiriadis, P.P.; Mylonakis, E. Machine Learning-Assisted High-Throughput Screening for Anti-MRSA Compounds. IEEE/ACM Trans. Comput. Biol. Bioinform. 2024, 21, 1911–1921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chung, C.H.; Chandrasekaran, S. A flux-based machine learning model to simulate the impact of pathogen metabolic heterogeneity on drug interactions. PNAS Nexus 2022, 1, pgac132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morris, G.M.; Lim-Wilby, M. Molecular Docking. In Molecular Modeling of Proteins; Methods Molecular, Biology™; Kubol, A., Ed.; Humana Press: Totowa, NJ, USA, 2008; Volume 443, pp. 365–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gangopadhyay, A.; Chakraborty, H.J.; Datta, A. Protein Docking and Drug Design. In Applying Big Data Analytics in Bioinformatics and Medicine; Lytras, M.D., Papadopoulou, P., Eds.; IGI Global: Hershey, PA, USA, 2018; pp. 207–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Battah, B.; Chemi, G.; Butini, S.; Campiani, G.; Brogi, S.; Delogu, G.; Gemma, S. A Repurposing Approach for Uncovering the Anti-Tubercular Activity of FDA-Approved Drugs with Potential Multi-Targeting Profiles. Molecules 2019, 24, 4373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madugula, S.S.; Nagamani, S.; Jamir, E.; Priyadarsinee, L.; Sastry, G.N. Drug repositioning for anti-tuberculosis drugs: An in silico polypharmacology approach. Mol. Divers. 2022, 26, 1675–1695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tolba, M.S.; Hamed, M.M.; Sayed, M.; Kamal El-Dean, A.M.; Abdel-Mohsen, S.A.; Ibrahim, O.A.; Elgaher, A.A.M.; Hirsch, A.K.H.; Saddik, A.A. Design, Synthesis, Antimicrobial Activity, and Molecular Docking of Some New Diclofenac Derivatives. Polycycl. Aromat. Compd. 2022, 43, 5437–5452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Phelps, G.A.; Mangrum, M.M.; McLeish, J.; Phillips, E.K.; Lou, J.; Ancajas, C.F.; Rybak, J.M.; Oelkers, P.M.; Lee, R.E.; et al. The small molecule CBR-5884 inhibits the Candida albicans phosphatidylserine synthase. mBio 2024, 15, e0063324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mullarky, E.; Lucki, N.C.; Beheshti Zavareh, R.; Anglin, J.L.; Gomes, A.P.; Nicolay, B.N.; Wong, J.C.; Christen, S.; Takahashi, H.; Singh, P.K.; et al. Identification of a small molecule inhibitor of 3-phosphoglycerate dehydrogenase to target serine biosynthesis in cancers. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, 1778–1783, Erratum in Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, E1585. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1521548113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shaikh, S.A.; Patel, B.; Priyadarsini, I.K.; Vavilala, S.L. Combating planktonic and biofilm growth of Serratia marcescens by repurposing ebselen. Int. Microbiol. 2023, 26, 693–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbarossa, A.; Rosato, A.; Carrieri, A.; Fumarola, L.; Tardugno, R.; Corbo, F.; Fracchiolla, G.; Carocci, A. Exploring the Antibiofilm Effect of Sertraline in Synergy with Cinnamomum verum Essential Oil to Counteract Candida Species. Pharmaceuticals 2024, 17, 1109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cussotto, S.; Strain, C.R.; Fouhy, F.; Strain, R.G.; Peterson, V.L.; Clarke, G.; Stanton, C.; Dinan, T.G.; Cryan, J.F. Differential effects of psychotropic drugs on microbiome composition and gastrointestinal function. Psychopharmacology 2019, 236, 1671–1685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, P.; Lu, J.; Wang, Y.; Schembri, M.A.; Guo, J. Antidepressants promote the spread of antibiotic resistance via horizontally conjugative gene transfer. Environ. Microbiol. 2022, 24, 5261–5276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, D.; Hao, H.; Wei, Z.; Yang, D.; Yin, J.; Li, H.; Chen, Z.; Yang, Z.; Chen, T.; Zhou, S. Combined exposure to non-antibiotic pharmaceutics and antibiotics in the gut synergistically promote the development of multi-drug-resistance in Escherichia coli. Gut Microbes 2022, 14, 2018901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.; Xu, L.; Zhou, Y.; Cui, M.; Liu, D.; Wang, J.; Wang, Y.; Deng, X. Repurposing harmaline as a novel approach to reverse tmexCD1-toprJ1-mediated tigecycline resistance against Klebsiella pneumoniae infections. Microb. Cell Fact. 2024, 23, 152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, H.; Zhang, T.; Peng, K.; Peng, J.; Liu, X.; Xia, Z.; Chi, L.; Zhao, X.; Li, S.; Chen, S.; et al. Conjugative plasmids facilitate the transmission of tmexCD2-toprJ2 among carbapenem-resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 906, 167373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, K.Z.; You, C.; Wang, Y.J.; Dar, O.I.; Yin, L.J.; Xiang, S.L.; Jia, A.Q. Repurposing promethazine hydrochloride to inhibit biofilm formation against Burkholderia thailandensis. Med. Microbiol. Immunol. 2024, 213, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-Carlos, A.; Jacobo-Delgado, Y.; Santos-Mena, A.O.; García-Hernández, M.H.; De Jesus-Gonzalez, L.A.; Lara-Ramirez, E.E.; Rivas-Santiago, B. Histone deacetylase (HDAC) inhibitors-based drugs are effective to control Mycobacterium tuberculosis infection and promote the sensibility for rifampicin in MDR strain. Memórias Inst. Oswaldo Cruz 2023, 118, e230143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gracia, J.; Perumal, D.; Dhandapani, P.; Ragunathan, P. Systematic identification and repurposing of FDA-approved drugs as antibacterial agents against Streptococcus pyogenes: In silico and in vitro studies. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 257, 128667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Han, N.; Li, Y.; Zhao, F.; Xiong, W.; Zeng, Z. Evaluating the Antibacterial and Antivirulence Activities of Floxuridine against Streptococcus suis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 14211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, R.; Muthu, S.A.; Agarwal, M.; Mehto, N.K.; Pahuja, I.; Grover, A.; Dwivedi, V.P.; Ahmad, B.; Grover, S. Atosiban and Rutin exhibit anti-mycobacterial activity—An integrated computational and biophysical insight toward drug repurposing strategy against Mycobacterium tuberculosis targeting its essential enzyme HemD. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 253, 127208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, M.; Zhang, C.; Duan, Y.Y.; Liu, H.B.; Peng, X.Y.; Wei, Q.; Chen, Q.Y.; Sang, H.; Kong, Q.T. Antifungal activity of the repurposed drug disulfiram against Cryptococcus neoformans. Front. Pharmacol. 2024, 14, 1268649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tovar-Nieto, A.M.; Flores-Padilla, L.E.; Rivas-Santiago, B.; Trujillo-Paez, J.V.; Lara-Ramirez, E.E.; Jacobo-Delgado, Y.M.; López-Ramos, J.E.; Rodríguez-Carlos, A. The Repurposing of FDA-Approved Drugs as FtsZ Inhibitors Against Mycobacterium tuberculosis: An In silico and In vitro Study. Microorganisms 2024, 12, 1505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agarwal, S.M.; Nandekar, P.; Saini, R. Computational identification of natural product inhibitors against EGFR double mutant (T790M/L858R) by integrating ADMET, machine learning, molecular docking and a dynamics approach. RSC Adv. 2022, 12, 16779–16789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, A.P.; Agarwal, S.M. Recent advances in the area of plant-based anti-cancer drug discovery using computational approaches. Mol. Divers. 2024, 28, 901–925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ohra, S.; Sharma, R.; Kumar, A. Repurposing of drugs against bacterial infections: A pharmacovigilance-based data mining approach. Drug Dev. Res. 2024, 85, e22211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shailaja, S.; Harshitha, N.; Fasim, A.; More, S.S.; Das Mitra, S. Identification of a potential inhibitor for New Delhi metallo-β-lactamase 1 (NDM-1) from FDA approved chemical library-a drug repurposing approach to combat carbapenem resistance. J. Biomol. Struct. Dyn. 2023, 41, 7700–7711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medha; Joshi, H.; Sharma, S.; Sharma, M. Elucidating the function of hypothetical PE_PGRS45 protein of Mycobacterium tuberculosis as an oxido-reductase: A potential target for drug repurposing for the treatment of tuberculosis. J. Biomol. Struct. Dyn. 2023, 41, 10009–10025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ezquerra-Aznárez, J.M.; Degiacomi, G.; Gašparovič, H.; Stelitano, G.; Sammartino, J.C.; Korduláková, J.; Governa, P.; Manetti, F.; Pasca, M.R.; Chiarelli, L.R.; et al. The Veterinary Anti-Parasitic Selamectin Is a Novel Inhibitor of the Mycobacterium tuberculosis DprE1 Enzyme. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ngidi, N.T.P.; Machaba, K.E.; Mhlongo, N.N. In silico Drug Repurposing Approach: Investigation of Mycobacterium tuberculosis FadD32 Targeted by FDA-Approved Drugs. Molecules 2022, 27, 668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dwivedi, M.; Mukhopadhyay, S.; Yadav, S.; Dubey, K.D. A multidrug efflux protein in Mycobacterium tuberculosis; tap as a potential drug target for drug repurposing. Comput. Biol. Med. 2022, 146, 105607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borgio, J.F.; Almandil, N.B.; Selvaraj, P.; John, J.S.; Alquwaie, R.; AlHasani, E.; Alhur, N.F.; Aldahhan, R.; AlJindan, R.; Almohazey, D.; et al. The Potential of Dutasteride for Treating Multidrug-Resistant Candida auris Infection. Pharmaceutics. 2024, 16, 810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- David, H.; Vasudevan, S.; Solomon, A.P. Mitigating candidiasis with acarbose by targeting Candida albicans α-glucosidase: In-silico, in-vitro and transcriptomic approaches. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 11890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, A.; Kumar, S.; Gupta, V.K.; Singh, S.; Dwivedi, V.D.; Mina, U. Computational assessment of Withania somnifera phytomolecules as putative inhibitors of Mycobacterium tuberculosis CTP synthase PyrG. J. Biomol. Struct. Dyn. 2023, 41, 4903–4916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tarín-Pelló, A.; Suay-García, B.; Forés-Martos, J.; Falcó, A.; Pérez-Gracia, M.T. Computer-aided drug repurposing to tackle antibiotic resistance based on topological data analysis. Comput. Biol. Med. 2023, 166, 107496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Narimisa, N.; Razavi, S.; Khoshbayan, A.; Gharaghani, S.; Jazi, F.M. Targeting lon protease to inhibit persister cell formation in Salmonella typhimurium: A drug repositioning approach. Front. Cell Infect. Microbiol. 2024, 14, 1427312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossain, S.; Rafi, R.H.; Ripa, F.A.; Khan, M.R.I.; Hosen, M.E.; Molla, M.K.I.; Faruqe, M.O.; Al-Bari, M.A.A.; Das, S. Modulating the antibacterial effect of the existing antibiotics along with repurposing drug metformin. Arch. Microbiol. 2024, 206, 190, Erratum in Arch. Microbiol. 2024, 206, 274. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00203-024-03978-6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neves, B.J.; Braga, R.C.; Bezerra, J.C.B.; Cravo, P.V.L.; Andrade, C.H. In silico repositioning-chemogenomics strategy identifies new drugs with potential activity against multiple life stages of Schistosoma mansoni. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2015, 9, e3435, Erratum in PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2015, 9, e0003554. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pntd.0003554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- March-Vila, E.; Pinzi, L.; Sturm, N.; Tinivella, A.; Engkvist, O.; Chen, H.; Rastelli, G. On the integration of in silico drug design methods for drug repurposing. Front. Pharmacol. 2017, 8, 298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riaz, R.; Khan, K.; Aghayeva, S.; Uddin, R. Combatting antibiotic resistance in Gardnerella vaginalis: A comparative in silico investigation for drug target identification. PLoS ONE 2025, 20, e0314465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, M.H.; Khan, K.; Tauseef, S.; Jalal, K.; Haroon, U.; Uddin, R.; Abdellattif, M.H.; Khan, A.; Al-Harrasi, A. Identification of therapeutic drug target of Shigella Flexneri serotype X through subtractive genomic approach and in-silico screening based on drug repurposing. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2024, 122, 105611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borges, K.C.M.; Costa, V.A.F.; Neves, B.; Kipnis, A.; Junqueira-Kipnis, A.P. New antibacterial candidates against Acinetobacter baumannii discovered by in silico-driven chemogenomics repurposing. PLoS ONE 2024, 19, e0307913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, A.S.; Costa, V.A.F.; Freitas, V.A.Q.; Dos Anjos, L.R.B.; de Almeida Santos, E.S.; Arantes, T.D.; Costa, C.R.; de Sene Amâncio Zara, A.L.; Rodrigues Silva, M.R.; Neves, B.J. Drug to genome to drug: A computational large-scale chemogenomics screening for novel drug candidates against sporotrichosis. Braz. J. Microbiol. 2024, 55, 2655–2667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goswami, D.; Prajapati, J.; Dabhi, M.; Sharkey, L.K.R.; Pidot, S.J. MurG as a potential target of quercetin in Staphylococcus aureus supported by evidence from subtractive proteomics and molecular dynamics. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 7309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urra, G.; Valdés-Muñoz, E.; Suardiaz, R.; Hernández-Rodríguez, E.W.; Palma, J.M.; Ríos-Rozas, S.E.; Flores-Morales, C.A.; Alegría-Arcos, M.; Yáñez, O.; Morales-Quintana, L.; et al. From Proteome to Potential Drugs: Integration of Subtractive Proteomics and Ensemble Docking for Drug Repurposing against Pseudomonas aeruginosa RND Superfamily Proteins. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 8027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, S.; Gazara, R.K. Chapter 3—Next-generation sequencing: An expedition from workstation to clinical applications. In Translational Bioinformatics in Healthcare and Medicine; Raza, K., Dey, N., Eds.; Academic Press: San Diego, CA, USA, 2021; Volume 13, pp. 29–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, S.; Singh, S.; Satpathy, S.; Bhasin, M.; Kumar, A. Transcriptomics and systems biology identify non-antibiotic drugs for the treatment of ocular bacterial infection. IScience 2022, 25, 104862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Putra, G.S.; Putri, A.O.; Gunawan, S.N.F.; Anwari, F.; Sulistyowaty, M.I. The QSAR study of pyridothienopyrimidine derivatives as antimicrobial activities against pseudomonas aeruginosa. Pharm. Educ. 2024, 24, 363–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suay-García, B.; Bueso-Bordils, J.I.; Falcó, A.; Antón-Fos, G.M.; Alemán-López, P.A. Virtual Combinatorial Chemistry and Pharmacological Screening: A Short Guide to Drug Design. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 1620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nandi, S.; Kumar, M.; Kumari, R.; Saxena, A. Exploring the inhibitory mechanisms of indazole compounds against SAH/MTAN-mediated quorum sensing utilizing QSAR and docking. Drug Target Insights 2022, 16, 54–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, J.; Yang, X.; Ma, C. QSAR, Docking, and Molecular Dynamics Simulation Studies of Sigmacidins as Antimicrobials Against Streptococci. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 4085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bueso-Bordils, J.I.; Antón-Fos, G.M.; Falcó, A.; Duart, M.J.; Martín-Algarra, R.; Alemán-López, P.A. New Pharmacokinetic and Microbiological Prediction Equations to Be Used as Models for the Search of Antibacterial Drugs. Pharmaceuticals 2022, 15, 122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamble, S.; Singh, S.; Suresh, A.; Singothu, S.; Dandesena, D.; Bhandari, V.; Sharma, P. Epidrugs: Alternative chemotherapy targeting Theileria annulata schizont stage parasites. Microbiol. Spectr. 2024, 12, e0325823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bennett, R.L.; Licht, J.D. Targeting Epigenetics in Cancer. Annu. Rev. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2018, 58, 187–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murugan, N.; Malathi, J.; Therese, K.L.; Madhavan, H.N. Application of six multiplex PCR’s among 200 clinical isolates of Pseudomonas aeruginosa for the detection of 20 drug resistance encoding genes. Kaohsiung J. Med. Sci. 2018, 34, 79–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gohain, B.B.; Mazumder, B.; Rajkhowa, S.; Al-Hussain, S.A.; Zaki, M.E.A. Subtractive genomics and drug repurposing strategies for targeting Streptococcus pneumoniae: Insights from molecular docking and dynamics simulations. Front. Microbiol. 2025, 16, 1534659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, D.D.; Cang, Z.; Wei, G.W. A review of mathematical representations of biomolecular data. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2020, 22, 4343–4367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chazal, F.; Michel, B. An introduction to topological data analysis: Fundamental and practical aspects for data scientists. Front. Artif. Intell. 2021, 4, 667963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-Moraga, R.; Forés-Martos, J.; Suay-García, B.; Duval, J.L.; Falcó, A.; Climent, J. A COVID-19 drug repurposing strategy through quantitative homological similarities using a topological Data analysis-based framework. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suay-García, B.; Climent, J.; Pérez-Gracia, M.T.; Falcó, A. A comprehensive update on the use of molecular topology applications for anti-infective drug discovery. Expert Opin. Drug Discov. 2025, 20, 465–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Zhang, T.; Liu, Q.; Sutcharitchan, C.; Zhou, Z.; Zhang, D.; Li, S. Elucidating the role of artificial intelligence in drug development from the perspective of drug-target interactions. J. Pharm. Anal. 2025, 15, 101144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joshi, T.; Sharma, P.; Joshi, T.; Mathpal, S.; Pande, V.; Chandra, S. Repurposing of FDA approved drugs against Salmonella enteric serovar Typhi by targeting dihydrofolate reductase: An in silico study. J. Biomol. Struct. Dyn. 2022, 40, 3731–3744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Woldring, D.R.; Huang, F.; Huang, X.; Wei, G.W.l. Topological deep learning based deep mutational scanning. Comput. Biol. Med. 2023, 164, 107258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, O.; Wang, T.; Weng, G.; Jiang, D.; Wang, N.; Wang, X.; Zhao, H.; Wu, J.; Wang, E.; Chen, G.; et al. Learning on topological surface and geometric structure for 3D molecular generation. Nat. Comp. Sci. 2023, 3, 849–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Method | Predictions | ML Algorithm | Accurate Predictions | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mol2vec model (Morgan algorithm) | Machine learning-assisted high-throughput screening of low-molecular-weight molecules. | Balanced random forest classifier to predict molecules for anti-MRSA compounds. | AUC 2 of 0.795 with a sensitivity of 81% and a specificity of 70%. | [12] |
| CARAMeL | Simulating metabolic flux data using GEMs 1 and developing an ML model to predict combination therapy outcomes using flux from GEMs 1. Impact of pathogen metabolic heterogeneity on drug–target interactions predictions. | Random forest to predict combination therapy outcomes for E. coli and Mycobacterium tuberculosis. | AUROC 3 = 0.83 for synergy, AUROC 3 = 0.98 for antagonism. | [13] |
| Molecules | Class of Drug | Known Target | New Target | New Indication Predicted | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Promethazine | First-generation antihistamine | Histamine H1, H2, NMDA, muscarinic, alpha-adrenergic and dopamine receptors; purinoceptors; voltage-gated potassium or sodium channel; calmodulin | Quorum sensing (proteins btaR1, btaR2 and btaR3) of Burkholderia thailandensis | Biofilm formation inhibition and lipase activity by suppression of quorum sensing of B. thailandensis | [28] |
| Derivates of entinostat | Antitumorals | Human histone deacetylase | Histone deacetylase of M. tuberculosis | Metabolism inhibitors, antimicrobial peptides promoters and rifampicin adjuvants against M. tuberculosis | [29] |
| Nitrofural | Antibiotic, treatment of trypanosomiasis | Glutathione reductase | Proteins 1BVR, 1P9L, 1W66, 1XFC, 1U2Q, 1YLK, 1ZAU, 2FUM, 2CIN, 2WGE, 2A86,2JCV, 2A5V, 2QO1, 2QKX, 1E9X, 1W2G and 1EYE of M. tuberculosis | Antimicobacterial and antitubercular | [17] |
| Stavudine | Antiretroviral | Reverse transcriptase | 1BVR, 1P9L, 1XFC, 1U2Q, 1ZAU, 2FUM, 2CIN, 2WGE, 2A86, 2JCV, 2QO1, 2QKX, 1E9X and 1W2G of M. tuberculosis | ||
| Quinine | Antiparasitic | Protoporphyrin IX of Plasmodium falciparum | Proteins 1BVR, 1DF7, 1P9L, 1XFC, 1U2Q, 4FDO, 1ZAU, 2FUM, 2CIN, 2WGE, 2A86, 2JCV, 2A5V, 2QO1, 2QKX, 1E9X and 1W2G of M. tuberculosis | ||
| Quinidine | Antiparasitic Antiarrhythmic | Sodium channel | Proteins 1BVR, 1DF7, 1P9L, 1XFC, 1U2Q, 1ZAU, 2FUM, 2CIN, 2WGE, 2A86, 2JCV, 2A5V, 2QO1, 2QKX, 1E9X and 1W2G of M. tuberculosis | ||
| Amlodipine | Calcium channel blocker. Antihypertensive | Voltage-dependent calcium channel | RNA polymerase β’subunit (RpoC) of Streptococcus pyogenes | Inhibition of RpoC of S. pyogenes | [30] |
| Ranitidine | Histamine H2 antagonist | Histamine H2 receptors | |||
| Floxuridine | Antitumoral | Riboside phosphorylase, thymidylate synthetase | SLY gene, sly, fabps, gap and ef genes of Streptococcus suis | Hemolytic activity and expression levels of virulence-related genes of S. suis | [31] |
| Atovaquone | Antipaludic | Cytochrome bc1 complex and dihydroorotate dehydrogenase | FtsZ protein | Inhibition of FTsZ of M. tuberculosis | [34] |
| Paroxetine | Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor | 5-HT reuptake transporter | |||
| Nebivolol | Antihypertensive | Beta-1 adrenergic receptor | |||
| Atosiban | Inhibitor of oxytocin and vasopressin Delays preterm birth in pregnancy | Oxytocin receptors | Enzyme HemD | Inhibition of HemD of M. tuberculosis | [32] |
| Rutin | Flavonoid, vitamin supplement | Aldo-keto reductase and carbonyl reductase | |||
| Disulfiram | Treatment of alcohol dependence | Dopamine beta-hydroxylase and aldehyde dehydrogenase, mitochondrial | Aldehyde dehydrogenase of Cryptococcus neoformans | Inhibition of aldehyde dehydrogenase of C. neoformans | [33] |
| Molecules | Class of Drug | New Indication Predicted | Docking Score | Binding Score (Kcal/mol) | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lisinopril | Antihypertensive | Inhibition of: 3-deoxy-manno-octulosonate cytidylyltransferase UDP-2,3-diacylglucosamine hydrolase PBP3 1 of P. aeruginosa | −10.8 −9.2 −9.4 | −89.3 −50.7 −70.6 | [37] |
| Olmesartan | Antihypertensive | Inhibition of lipotheichoic acids flippase LtaA of S. aureus | −9.0 | −75.4 | |
| Atorvastatin | Lipid-lowering drug, statin | −8.6 | −96.9 | ||
| Inhibition of CDP-activated ribitol for teichoic acid precursors of S. pneumoniae | −7.4 | −74.6 | |||
| Rosiglitazone | Antidiabetic | Inhibition of d-alanine ligase of S. aureus | −7.3 | −70.4 | |
| Varenicline | Aid in smoking cessation | −7.1 | −48.7 | ||
| Valsartan | Antihypertensive | Inhibition of peptidoglycan deacetylase of S. pneumoniae | −7.4 | −62.6 | |
| Verapamil | Antihypertensive | Inhibition of protein PE_PGRS45 of M. tuberculosis | −6.2 to −5.9 | −58.8 | [39] |
| Entacapone Tolcapone | Treatment of Parkinson’s disease | −7.3 to −6.3 −7.9 to −6.3 | −40.0 −39.3 | ||
| Dutasteride | Antiandrogenic. Treatment of prostate cancer | Inhibition of 1,3-β-glucanosyltranferase from Candida auris | - | ≤−10 | [43] |
| Digoxin | Cardiac glycoside, treatment of heart failure | ||||
| Ergotamine | Vasoconstrictor, treatment of cluster headaches and migraines | ||||
| Paritaprevir | Antiviral, treatment of infections caused by the hepatitis C virus | ||||
| Acarbose | Hypoglycemic | Inhibition of alfa-glucosidase of C. albicans | −11.5 | - | [44] |
| Adapalene | Treatment of acne, retinoid | Inhibition of NDM-1 2 enzyme of E. coli and K. pneumoniae alone or in combination with meropenem | - | −9.2 | [38] |
| Selamectin | Parasiticide and antihelminthic in veterinary medicine | Inhibition of DprE1 enzyme of M. tuberculosis. Possible multitarget antibacterial compound | - | - | [40] |
| Accolate | Prophylaxis and treatment of asthma | Inhibition of FadD32 protein of M. tuberculosis | −9.3 | −45.1 | [41] |
| Sorafenib | Antitumoral | −10.0 | −32.7 | ||
| Mefloquine | Antimalarial | −8.0 | −26.8 | ||
| Loperamide | Antidiarrheal | −8.5 | −21.5 | ||
| Phytochemicals of Withania somnifera | Complement in anti-inflammatory, antidiabetic, antimicrobial, analgesic, antitumoral, anti-stress, neuroprotective, cardioprotective, rejuvenating and immunomodulatory treatments | Inhibition PyrG protein of M. tuberculosis | −12.6 to −10.8 | - | [45] |
| Glimepiride | Hypoglycemic | Inhibition of Tap protein of M. tuberculosis | −9.7 | −51.9 | [42] |
| Flecainide | Antiarrhythmic agent | −9.1 | −44.6 | ||
| Flupirtine | Investigated for treatment of fibromyalgia | −8.9 | −46.4 | ||
| Nimodipine | Calcium channel blocker, improvement in neurological outcomes | −7.0 | −46.1 | ||
| Amlodipine | Calcium channel blocker, antihypertensive | −7.2 | −42.6 |
| Molecules | Class of Drug | New Indication Predicted | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| Decitabine | Antitumoral, pyrimidine nucleoside analogue | Inhibition of phospho-2-dehydro-3-deoxyheptonate aldolase of Gardnerella vaginalis | [51] |
| Nitroglycerin | Nitrate vasodilator, preventive of different cardiac and circulatory problems | ||
| Phthalocyanine | Tetrapyrrole fundamental parent, under investigation in clinical trial for its antitumoral and antifungal effects and treatment of different skin diseases | Inhibition of serine acetyltransferase of S. flexneri serotype X | [52] |
| Fulacimstat | Chymase inhibitor, under investigation in clinical trial for treatment of heart diseases and diabetic kidney disease | ||
| Atogepant | Antimigraine, receptor for different molecules mediated by G proteins | ||
| Olverembatinib | Bcr-Abl inhibitor, under investigation in clinical trial for treatment of different leukemias and gastrointestinal stromal tumours | ||
| Olacaftor | Cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator, under investigation in clinical trial for treatment of cystic fibrosis | ||
| Tavaborole | Antifungal, treatment of onychomycosis caused by dermatophytes | Inhibition of LeuRS of A. baumannii | [53] |
| Ribavirin | Antiviral, treatment of infections caused by hepatitis C virus | Inhibition of inosine 5′-phosphate dehydrogenase of A. baumannii | |
| Leflunomide | Immunomodulator, treatment of rheumatoid arthritis | Interaction with dihydroorotate dehydrogenase of A. baumannii | |
| Atovaquone | Antiparasitic, treatment of malaria and AIDS-associated diseases | ||
| Homoharringtonine | Antitumoral, treatment of different leukemias | Inhibition of the 50S ribosomal subunit of A. baumannii | |
| Thiabendazole | Anthelmintic, tubulin inhibitor | Inhibition of succinate dehydrogenase of A. baumannii | |
| MKT-077 | Antitumoral, inhibitor of mitochondrial hsp 70 family member. | Inhibition of chaperone DnaK of A. baumanni | |
| Bifonazol | Antifungal, treatment of fungal skin infections, such as dermatomycosis | Interaction with sterol-14-alfa-demethylase of S. brasiliensis | [54] |
| Everolimus | Antitumoral, inhibition of mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) kinase, prevention of organ transplant rejection and treatment of various malignancies | Interaction with serine/threonine-protein kinase TOR of S. brasiliensis | |
| Quercetin | Flavonoid, antioxidant with specific inhibition of quinone reductase (QR2) | Inhibition of MurG of S. aureus. | [55] |
| MK-3207 | Antagonist of the calcitonin gene-related peptide type 1 receptor in humans, under investigation in clinical trial for migraine disorders | Inhibition of RND efflux pumps of P. aeruginosa | [56] |
| Bemcentinib (R-428) | Tyrosine-protein kinase receptor inhibitor, under investigation in clinical trial for myelodysplastic syndrome, melanoma, acute myeloid leukaemia, and mesothelioma | ||
| Suramin | MFP protein inhibitor, under investigation in clinical trial for non-small cell lung carcinoma, prostate adenocarcinoma, autism spectrum disorder and acute kidney injury | ||
| Glibenclamide | Hypoglycemic drugs in the treatment of non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus | Reverse the expression of the master regulators perturbed in S. aureus endophthalmitis | [58] |
| Clofilium tosylate | Benzene, under investigation in clinical trial for heart rhythm disorders | ||
| Dequalinium (fluomizin) | Antimicrobial, treatment of vaginosis and oral infections |
| Molecules | Class of Drug | Score | New Indication Predicted | References | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C19H14N6S, C19H14N6OS, C19H13FN6S, C18H14N6O2S, C18H14N6O3S. | Pyridothienopyrimidine derivatives, no previous known pharmacological activity | pMIC 1 −1.5 −1.2 −1.6 0.4 0.8 | Inhibition of P. aeruginosa growth, unknown mechanism of action | [59] | |
| C23H21N4Cl3O2S | Indazole compounds | pKi 2 2.8 | Inhibition of S-adenosyl homocysteine/methylthio-adenosine nucleosidase (SAH/MTAN) of E. coli mediated quorum sensing to produce AMR | [61] | |
| Sigmacidins (C21H13N2Cl3O4S) | Benzoic acid derivatives, no previous known pharmacological activity | Experimental pMIC 1: 5.7 2D QSAR pMIC 1: 4.9 3D QSAR pMIC 1: 5.2 | Inhibition of bacterial RNA polymerase-σ factor interaction of Streptococci/S. pneumoniae | [62] | |
| SAHA | Anti-cancer histone deacetylase inhibitor | ADME properties 3 within the margins | No Toxicity 3 | Inhibition of epigenetic pathways of T. annulata-infected cells | [64] |
| Trichostatin A | |||||
| BVT-948, | PRMT inhibitor | No Toxicity 3 | |||
| TCE-5003 | Hepatotoxicity 3 | ||||
| Methylstat | Histone demethylase inhibitor | Hepatotoxicity 3 | |||
| Plumbagin | ROS/apoptosis inducer inhibitor | AMES toxicity 3 | |||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tarín-Pelló, A.; Fernández-Álvarez, S.; Suay-García, B.; Pérez-Gracia, M.T. Novel Antimicrobials from Computational Modelling and Drug Repositioning: Potential In Silico Strategies to Increase Therapeutic Arsenal Against Antimicrobial Resistance. Molecules 2025, 30, 2303. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30112303
Tarín-Pelló A, Fernández-Álvarez S, Suay-García B, Pérez-Gracia MT. Novel Antimicrobials from Computational Modelling and Drug Repositioning: Potential In Silico Strategies to Increase Therapeutic Arsenal Against Antimicrobial Resistance. Molecules. 2025; 30(11):2303. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30112303
Chicago/Turabian StyleTarín-Pelló, Antonio, Sara Fernández-Álvarez, Beatriz Suay-García, and María Teresa Pérez-Gracia. 2025. "Novel Antimicrobials from Computational Modelling and Drug Repositioning: Potential In Silico Strategies to Increase Therapeutic Arsenal Against Antimicrobial Resistance" Molecules 30, no. 11: 2303. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30112303
APA StyleTarín-Pelló, A., Fernández-Álvarez, S., Suay-García, B., & Pérez-Gracia, M. T. (2025). Novel Antimicrobials from Computational Modelling and Drug Repositioning: Potential In Silico Strategies to Increase Therapeutic Arsenal Against Antimicrobial Resistance. Molecules, 30(11), 2303. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30112303












