Computational Design and Evaluation of Peptides to Target SARS-CoV-2 Spike–ACE2 Interaction
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Selection of Peptides from PepI-Covid19 Database
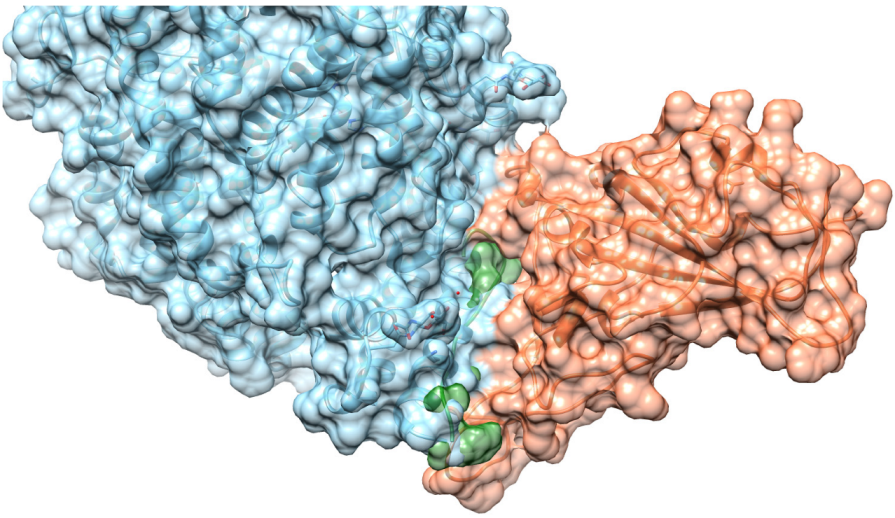
2.2. Assessment of Peptide/RBD Interactions Using MD
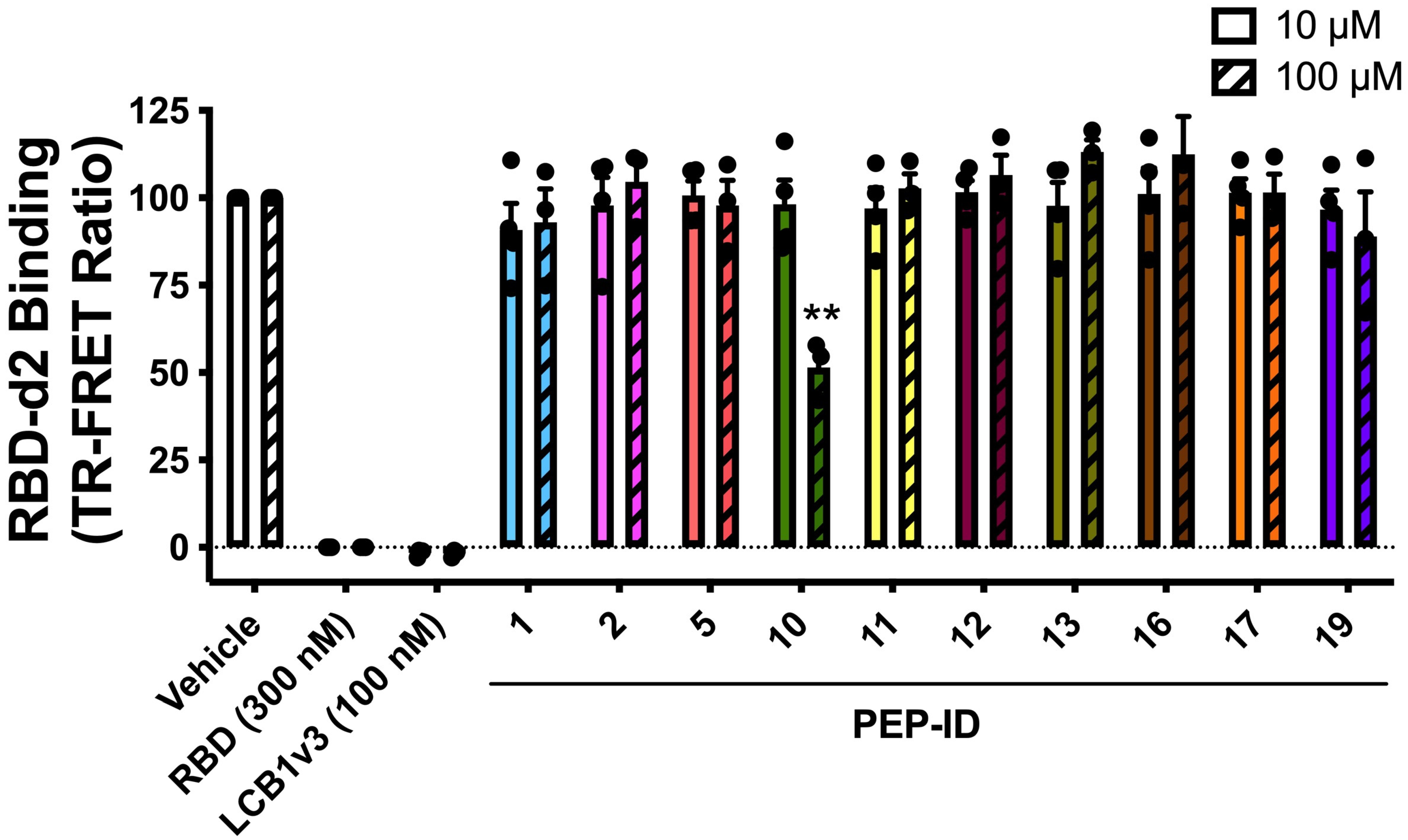
2.3. Experimental Validation Using TR-FRET
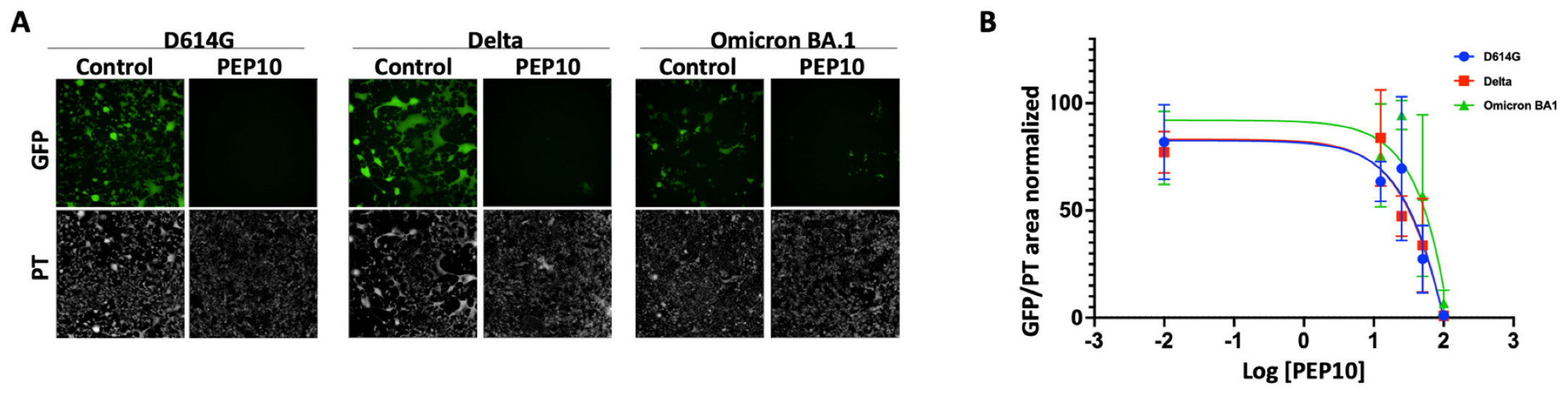
2.4. Effect of PEP10 on SARS-CoV-2 Spike-Mediated Viral Infection
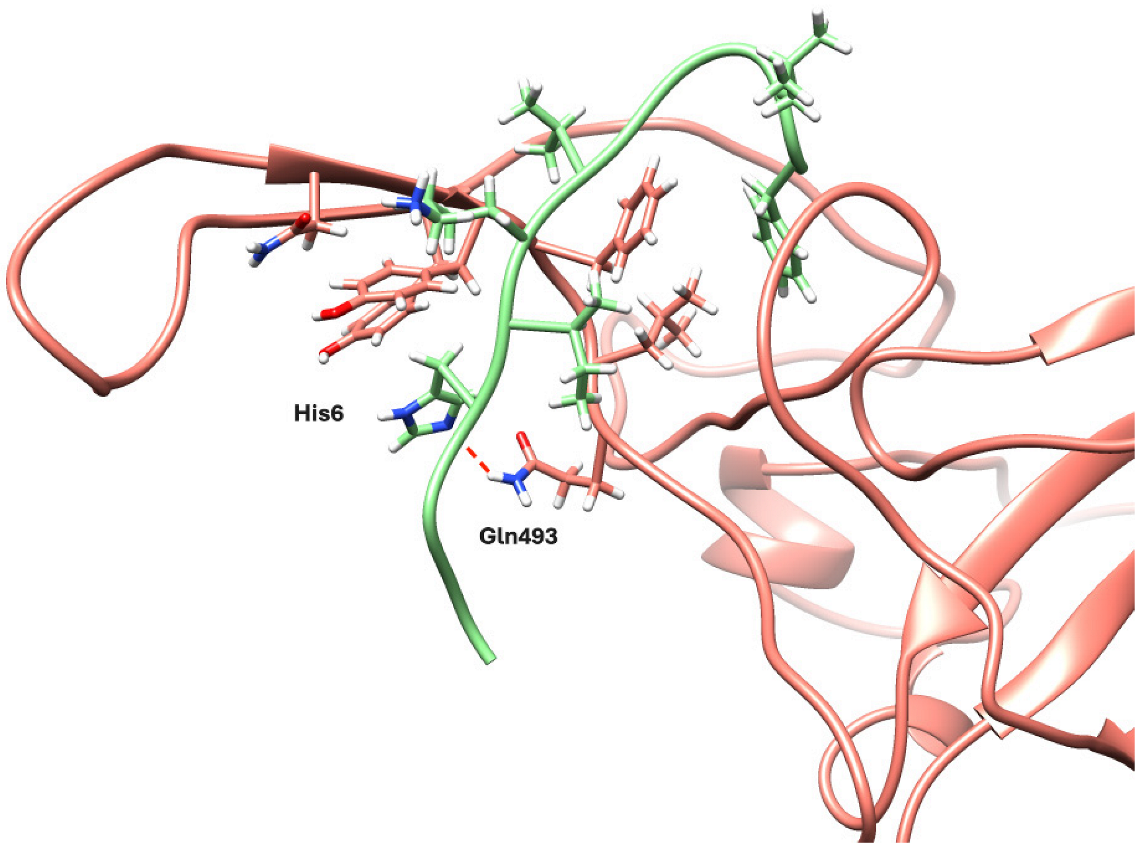
2.5. Structural Analyses of PEP10
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Selection of Peptides from PepI-Covid19 Database
3.2. Molecular Dynamics Simulations
3.2.1. System Preparation and Equilibration
3.2.2. Production Runs
3.3. Time-Resolved Fluorescence Energy Transfer Analyses
3.3.1. Peptides
3.3.2. TR-FRET
3.4. Infection by SARS-CoV-2 Spike Pseudotyped Viruses
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yan, R.; Zhang, Y.; Li, Y.; Xia, L.; Guo, Y.; Zhou, Q. Structural Basis for the Recognition of SARS-CoV-2 by Full-Length Human ACE2. Science 2020, 367, 1444–1448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Gan, H.; Liang, Z.; Liu, L.; Liu, Q.; Mai, Y.; Chen, H.; Lei, B.; Yu, S.; Chen, H.; et al. Review of Therapeutic Mechanisms and Applications Based on SARS-CoV-2 Neutralizing Antibodies. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 14, 1122868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Li, F.; Du, L. Therapeutic Nanobodies against SARS-CoV-2 and Other Pathogenic Human Coronaviruses. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2024, 22, 304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pomplun, S.; Jbara, M.; Quartararo, A.J.; Zhang, G.; Brown, J.S.; Lee, Y.-C.; Ye, X.; Hanna, S.; Pentelute, B.L. De Novo Discovery of High-Affinity Peptide Binders for the SARS-CoV-2 Spike Protein. ACS Cent. Sci. 2021, 7, 156–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Markov, P.V.; Ghafari, M.; Beer, M.; Lythgoe, K.; Simmonds, P.; Stilianakis, N.I.; Katzourakis, A. The evolution of SARS-CoV-2. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2023, 21, 361–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duarte, C.M.; Ketcheson, D.I.; Eguíluz, V.M.; Agustí, S.; Fernández-Gracia, J.; Jamil, T.; Laiolo, E.; Gojobori, T.; Alam, I. Rapid evolution of SARS-CoV-2 challenges human defenses. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 6457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Beltran, W.F.; Lam, E.C.; St. Denis, K.; Nitido, A.D.; Garcia, Z.H.; Hauser, B.M.; Feldman, J.; Pavlovic, M.N.; Gregory, D.J.; Poznansky, M.C.; et al. Multiple SARS-CoV-2 Variants Escape Neutralization by Vaccine-Induced Humoral Immunity. Cell 2021, 184, 2372–2383.e9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffmann, M.; Krüger, N.; Schulz, S.; Cossmann, A.; Rocha, C.; Kempf, A.; Nehlmeier, I.; Graichen, L.; Moldenhauer, A.-S.; Winkler, M.S.; et al. The Omicron Variant Is Highly Resistant against Antibody-Mediated Neutralization: Implications for Control of the COVID-19 Pandemic. Cell 2022, 185, 447–456.e11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, F.; Zai, X.; Zhang, Z.; Xu, J.; Chen, W. Challenges and Developments in Universal Vaccine Design against SARS-CoV-2 Variants. NPJ Vaccines 2022, 7, 167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wójcik, P.; Berlicki, Ł. Peptide-Based Inhibitors of Protein-Protein Interactions. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2016, 26, 707–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burley, S.K.; Bhikadiya, C.; Bi, C.; Bittrich, S.; Chao, H.; Chen, L.; Craig, P.A.; Crichlow, G.V.; Dalenberg, K.; Duarte, J.M.; et al. RCSB Protein Data Bank (RCSB.org): Delivery of experimentally-determined PDB structures alongside one million computed structure models of proteins from artificial intelligence/machine learning. Nucleic Acids Res. 2023, 51, D488–D508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernandez-Fuentes, N.; Molina, R.; Oliva, B. A Collection of Designed Peptides to Target SARS-CoV-2 Spike RBD-ACE2 Interaction. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 11627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leaver-Fay, A.; Tyka, M.; Lewis, S.M.; Lange, O.F.; Thompson, J.; Jacak, R.; Kaufman, K.W.; Renfrew, P.D.; Smith, C.A.; Sheffler, W.; et al. Rosetta3. In Methods in Enzymology; Johnson, M.L., Brand, L., Eds.; Computer Methods, Part C; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2011; Volume 487, pp. 545–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raveh, B.; London, N.; Schueler-Furman, O. Sub-Angstrom Modeling of Complexes Between Flexible Peptides and Globular Proteins. Proteins Struct. Funct. Bioinform. 2010, 78, 2029–2040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sheffler, W.; Baker, D. RosettaHoles2: A Volumetric Packing Measure for Protein Structure Refinement and Validation. Protein Sci. 2010, 19, 1991–1995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, J.; Ge, J.; Yu, J.; Shan, S.; Zhou, H.; Fan, S.; Zhang, Q.; Shi, X.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, L.; et al. Structure of the SARS-CoV-2 Spike Receptor-Binding Domain Bound to the ACE2 Receptor. Nature 2020, 581, 215–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Petitjean, S.J.L.; Koehler, M.; Zhang, Q.; Dumitru, A.C.; Chen, W.; Derclaye, S.; Vincent, S.P.; Soumillion, P.; Alsteens, D. Molecular Interaction and Inhibition of SARS-CoV-2 Binding to the ACE2 Receptor. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 4541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarma, S.; Herrera, S.M.; Xiao, X.; Hudalla, G.A.; Hall, C.K. Computational Design and Experimental Validation of ACE2-Derived Peptides as SARS-CoV-2 Receptor Binding Domain Inhibitors. J. Phys. Chem. B 2022, 126, 8129–8139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, H.; Ma, Y.; Bi, J.; Li, Z.; Wang, Y.; Su, Z.; Gerstweiler, L.; Ren, Y.; Zhang, S. Experimental and molecular dynamics simulation studies on the physical properties of three HBc-VLP derivatives as nanoparticle protein vaccine candidates. Vaccine 2024, 42, 125992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chieochansin, T.; Sanachai, K.; Darai, N.; Chiraphapphaiboon, W.; Choomee, K.; Yenchitsomanus, P.T.; Thuwajit, C.; Rungrotmongkol, T. In silico advancements in Peptide-MHC interaction: A molecular dynamics study of predicted glypican-3 peptides and HLA-A*11:01. Heliyon 2024, 10, e36654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cecon, E.; Burridge, M.; Cao, L.; Carter, L.; Ravichandran, R.; Dam, J.; Jockers, R. SARS-CoV-2 Spike Binding to ACE2 in Living Cells Monitored by TR-FRET. Cell Chem. Biol. 2022, 29, 74–83.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chauhan, J.; Cecon, E.; Labani, N.; Gbahou, F.; Real, F.; Bomsel, M.; Dubey, K.D.; Das, R.; Dam, J.; Jockers, R.; et al. Development of indolealkylamine derivatives as potential multi-target agents for COVID-19 treatment. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2023, 249, 115152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Cecon, E.; Fernandois, D.; Renault, N.; Coelho, C.F.F.; Wenzel, J.; Bedart, C.; Izabelle, C.; Gallet, S.; Le Poder, S.; Klonjkowski, B.; et al. Melatonin drugs inhibit SARS-CoV-2 entry into the brain and virus-induced damage of cerebral small vessels. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2022, 79, 361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Cecon, E.; Dam, J.; Jockers, R. Detection of SARS-CoV-2 spike protein binding to ACE2 in living cells by TR-FRET. STAR Protoc. 2022, 3, 101024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Cao, L.; Goreshnik, I.; Coventry, B.; Case, J.B.; Miller, L.; Kozodoy, L.; Chen, R.E.; Carter, L.; Walls, A.C.; Park, Y.-J.; et al. De Novo Design of Picomolar SARS-CoV-2 Miniprotein Inhibitors. Science 2020, 370, 426–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lan, Q.; Chan, J.F.; Xu, W.; Wang, L.; Jiao, F.; Zhang, G.; Pu, J.; Zhou, J.; Xia, S.; Lu, L.; et al. A Palmitic Acid-Conjugated, Peptide-Based pan-CoV Fusion Inhibitor Potently Inhibits Infection of SARS-CoV-2 Omicron and Other Variants of Concern. Viruses 2022, 14, 549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valiente, P.A.; Wen, H.; Nim, S.; Lee, J.; Kim, H.J.; Kim, J.; Perez-Riba, A.; Paudel, Y.P.; Hwang, I.; Kim, K.D.; et al. Computational Design of Potent D-Peptide Inhibitors of SARS-CoV-2. J. Med. Chem. 2021, 64, 14955–14967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badia-Villanueva, M.; Defaus, S.; Foj, R.; Andreu, D.; Oliva, B.; Sierra, A.; Fernandez-Fuentes, N. Evaluation of Computationally Designed Peptides against TWEAK, a Cytokine of the Tumour Necrosis Factor Ligand Family. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 1066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Segura, J.; Fernandez-Fuentes, N. PCRPi—DB: A Database of Computationally Annotated Hot Spots in Protein Interfaces. Nucleic Acids Res. 2011, 39, D755–D760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jo, S.; Kim, T.; Iyer, V.G.; Im, W. CHARMM-GUI: A Web-Based Graphical User Interface for CHARMM. J. Comput. Chem. 2008, 29, 1859–1865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brooks, B.R.; Brooks, C.L.; Mackerell, A.D.; Nilsson, L.; Petrella, R.J.; Roux, B.; Won, Y.; Archontis, G.; Bartels, C.; Boresch, S.; et al. CHARMM: The Biomolecular Simulation Program. J. Comput. Chem. 2009, 30, 1545–1614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Cheng, X.; Swails, J.M.; Yeom, M.S.; Eastman, P.K.; Lemkul, J.A.; Wei, S.; Buckner, J.; Jeong, J.C.; Qi, Y.; et al. CHARMM-GUI Input Generator for NAMD, GROMACS, AMBER, OpenMM, and CHARMM/OpenMM Simulations Using the CHARMM36 Additive Force Field. J. Chem. Theory Comput. 2016, 12, 405–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Phillips, J.C.; Hardy, D.J.; Maia, J.D.C.; Stone, J.E.; Ribeiro, J.V.; Bernardi, R.C.; Buch, R.; Fiorin, G.; Hénin, J.; Jiang, W.; et al. Scalable Molecular Dynamics on CPU and GPU Architectures with NAMD. J. Chem. Phys. 2020, 153, 044130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, J.; Rauscher, S.; Nawrocki, G.; Ran, T.; Feig, M.; de Groot, B.L.; Grubmüller, H.; MacKerell, A.D. CHARMM36m: An Improved Force Field for Folded and Intrinsically Disordered Proteins. Nat. Methods 2017, 14, 71–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Darden, T.; York, D.; Pedersen, L. Particle mesh Ewald: An N⋅log(N) method for Ewald sums in large systems. J. Chem. Phys. 1993, 98, 10089–10092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hess, B.; Bekker, H.; Berendsen, H.J.C.; Fraaije, J.G.E.M. LINCS: A linear constraint solver for molecular simulations. J. Comput. Chem. 1997, 18, 1463–1472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harvey, M.J.; Giupponi, G.; Fabritiis, G.D. ACEMD: Accelerating Biomolecular Dynamics in the Microsecond Time Scale. J. Chem. Theory Comput. 2009, 5, 1632–1639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| ID | Sequence | Secondary Structure 1 | Size 2 |
|---|---|---|---|
| PEP1 * | QDGRDDETKHED | CCHHHHHHTTCC | 12 |
| PEP2 * | QASSLDSAHWRDLYGEYY | CCGGGGGSCHHHHSCSCC | 18 |
| PEP3 | TLNRGLDESSREHHRE | CCCSSCCHHHHHHHHC | 16 |
| PEP4 | DEDKERHEKEDYDNQK | CHHHHHHHHTTSTTTC | 16 |
| PEP5 * | TRDKYRFGESEYED | CTTTTCTTSHHHHC | 14 |
| PEP6 | DKADGANTGGGGTK | CCCCCCSSCCCCCC | 14 |
| PEP7 | DKYWHQWEDERHSGGQ | CHHHHHHHHTTSSTTC | 16 |
| PEP8 | GKGHTSTGTTQ | CCSCCCCCCCC | 11 |
| PEP9 | GGGQSSTGRGKD | CCCCCEECTTCC | 12 |
| PEP10 * | EWHGAHIKVTQLF | CCSSCCCCCCCCC | 13 |
| PEP11 * | QDDTQEDKDRHLKDEIYK | CHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHC | 18 |
| PEP12 * | QRFSEERYRAWVSHEND | CCCCHHHHHHHHHHHTC | 17 |
| PEP13 * | QLGDLHRDRKGEENNRQ | CCCCCCHHHHHHHHHHC | 17 |
| PEP14 | QEQTERDKRQHEKDSDWYQ | CHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHSCC | 19 |
| PEP15 | TDEDKKYH | CHHHHHHC | 8 |
| PEP16 * | TDAGKDGWADHIYHRQY | CGGGGGGHHHHHHHHHC | 17 |
| PEP17 * | TSDDFAEEHWKAHAGAYKL | CHHHHHHHHHHHTHHHHHC | 19 |
| PEP18 | NEDKNRHGEASYGNQYG | CHHHHHHHHHTTCCCCC | 17 |
| PEP19 * | DAERRREEEKGRDQ | CHHHHHHHHHTTCC | 14 |
| PEP20 | AAEEQRKRDEWWRKGTS | CHHHHHHHHHHHHTTCC | 17 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Almabhouh, S.; Cecon, E.; Basubas, F.; Molina-Fernandez, R.; Maciej Stepniewski, T.; Selent, J.; Jockers, R.; Rahmeh, A.; Oliva, B.; Fernandez-Fuentes, N. Computational Design and Evaluation of Peptides to Target SARS-CoV-2 Spike–ACE2 Interaction. Molecules 2025, 30, 1750. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30081750
Almabhouh S, Cecon E, Basubas F, Molina-Fernandez R, Maciej Stepniewski T, Selent J, Jockers R, Rahmeh A, Oliva B, Fernandez-Fuentes N. Computational Design and Evaluation of Peptides to Target SARS-CoV-2 Spike–ACE2 Interaction. Molecules. 2025; 30(8):1750. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30081750
Chicago/Turabian StyleAlmabhouh, Saja, Erika Cecon, Florence Basubas, Ruben Molina-Fernandez, Tomasz Maciej Stepniewski, Jana Selent, Ralf Jockers, Amal Rahmeh, Baldo Oliva, and Narcis Fernandez-Fuentes. 2025. "Computational Design and Evaluation of Peptides to Target SARS-CoV-2 Spike–ACE2 Interaction" Molecules 30, no. 8: 1750. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30081750
APA StyleAlmabhouh, S., Cecon, E., Basubas, F., Molina-Fernandez, R., Maciej Stepniewski, T., Selent, J., Jockers, R., Rahmeh, A., Oliva, B., & Fernandez-Fuentes, N. (2025). Computational Design and Evaluation of Peptides to Target SARS-CoV-2 Spike–ACE2 Interaction. Molecules, 30(8), 1750. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30081750








