Simultaneous Adsorption and Purification of Low-Concentration SO2 and H2S
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experiments and Simulation
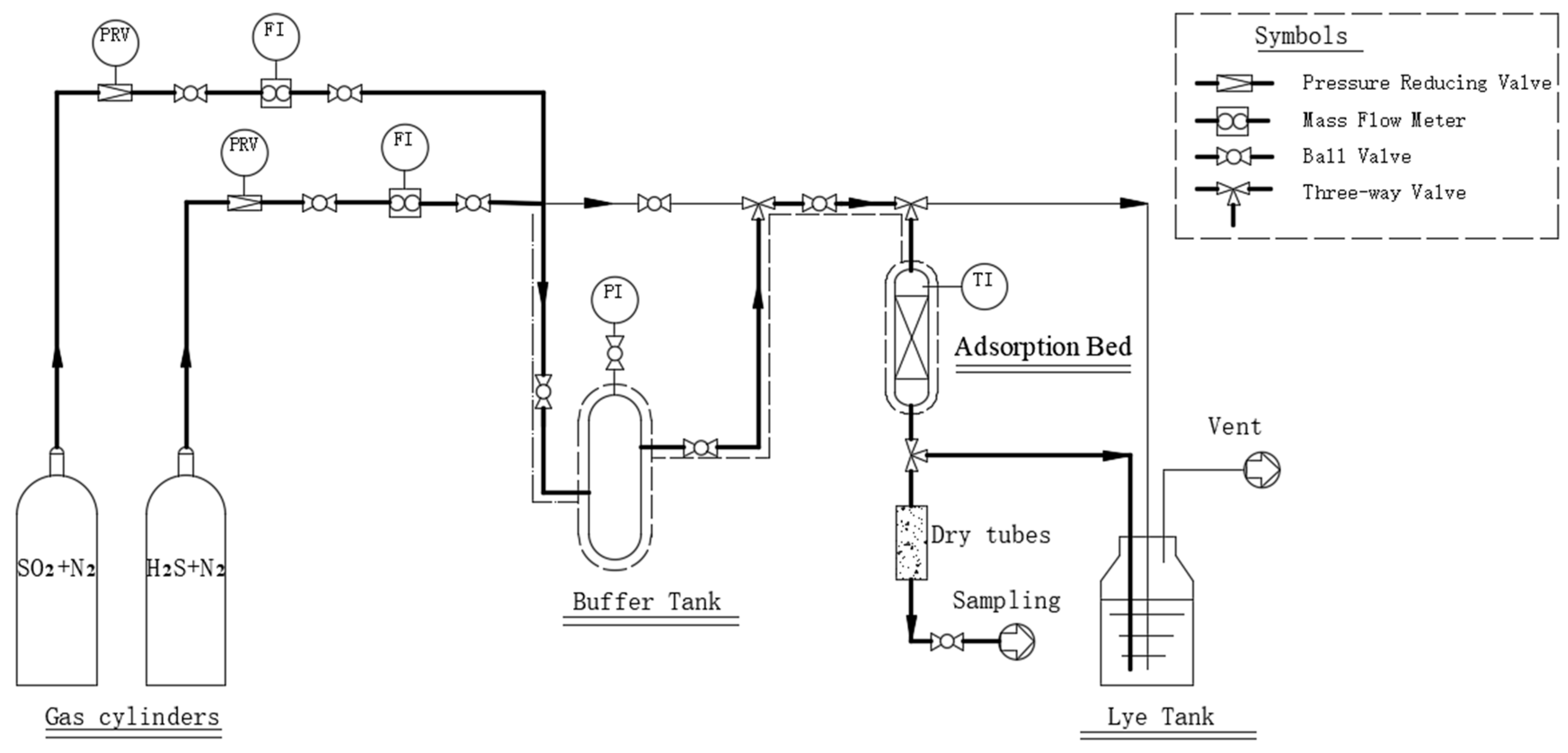
2.1. Experimental
2.2. Simulations
2.2.1. Model Selection
2.2.2. Parameters for Simulation Calculations
3. Results and Discussion
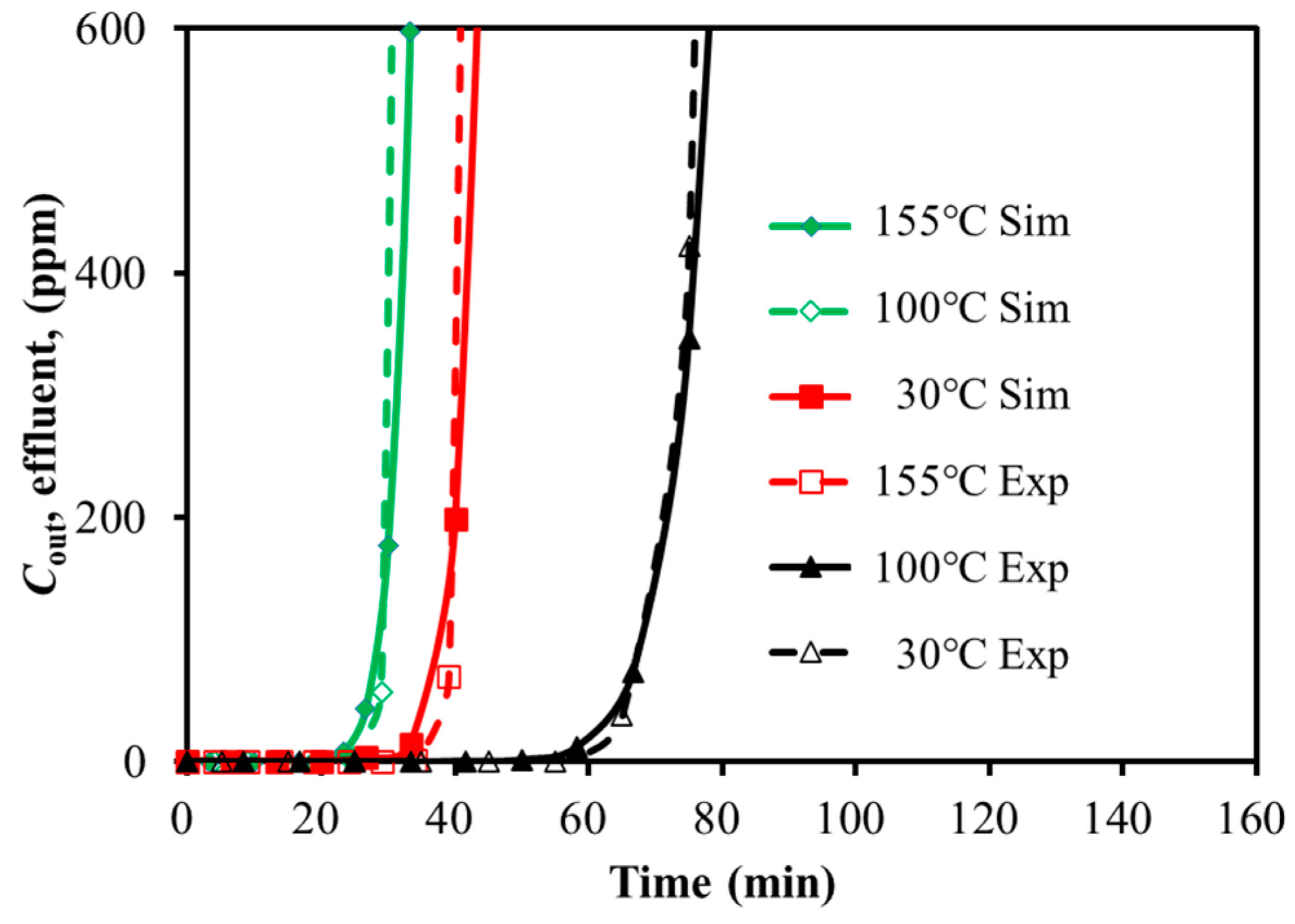
3.1. Comparison of Single-Component Adsorption Experiments and Simulation
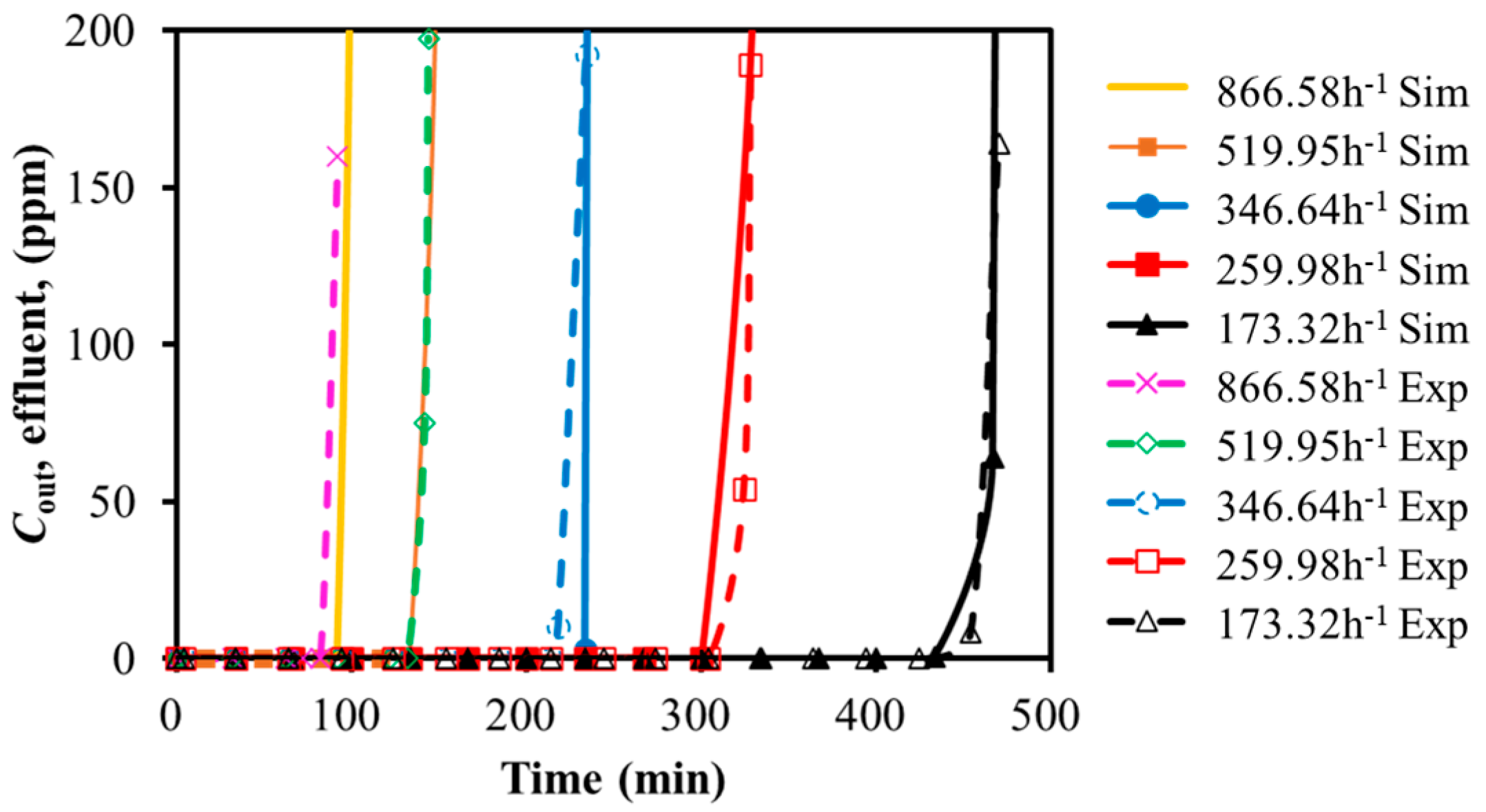
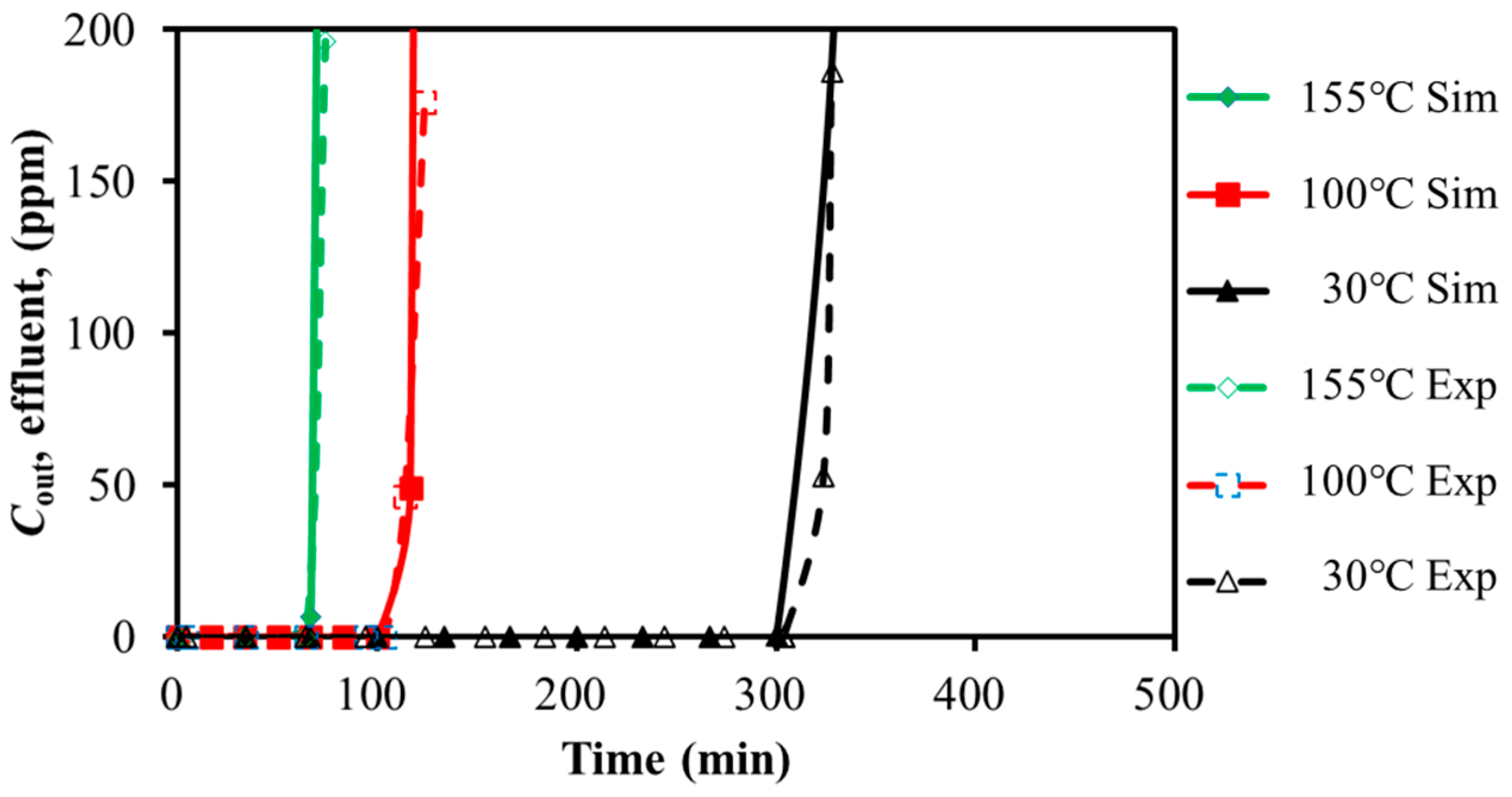
3.1.1. SO2 Adsorption
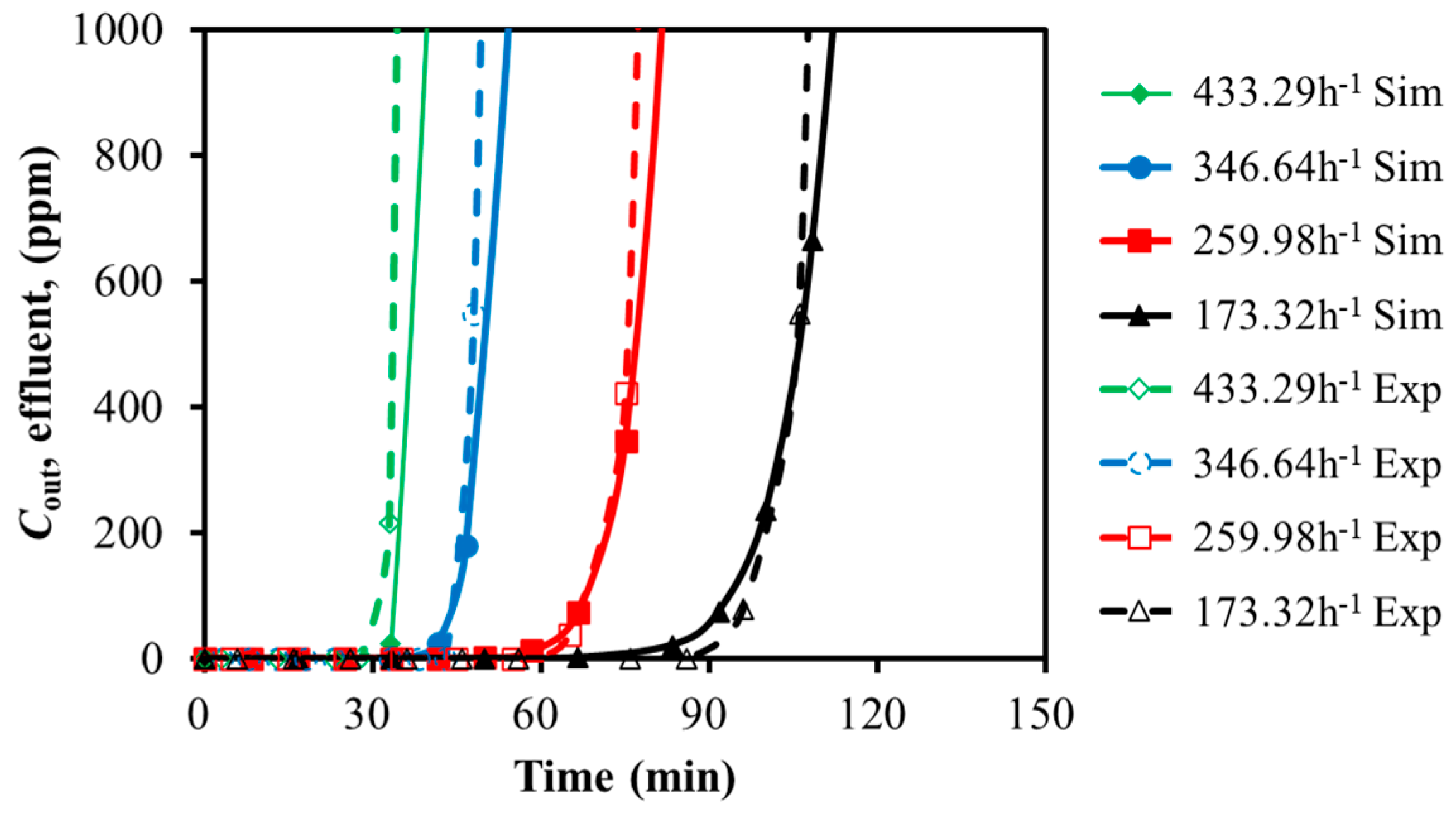
3.1.2. H2S Adsorption
3.2. Simulation Calculation of Bi-Component Adsorption
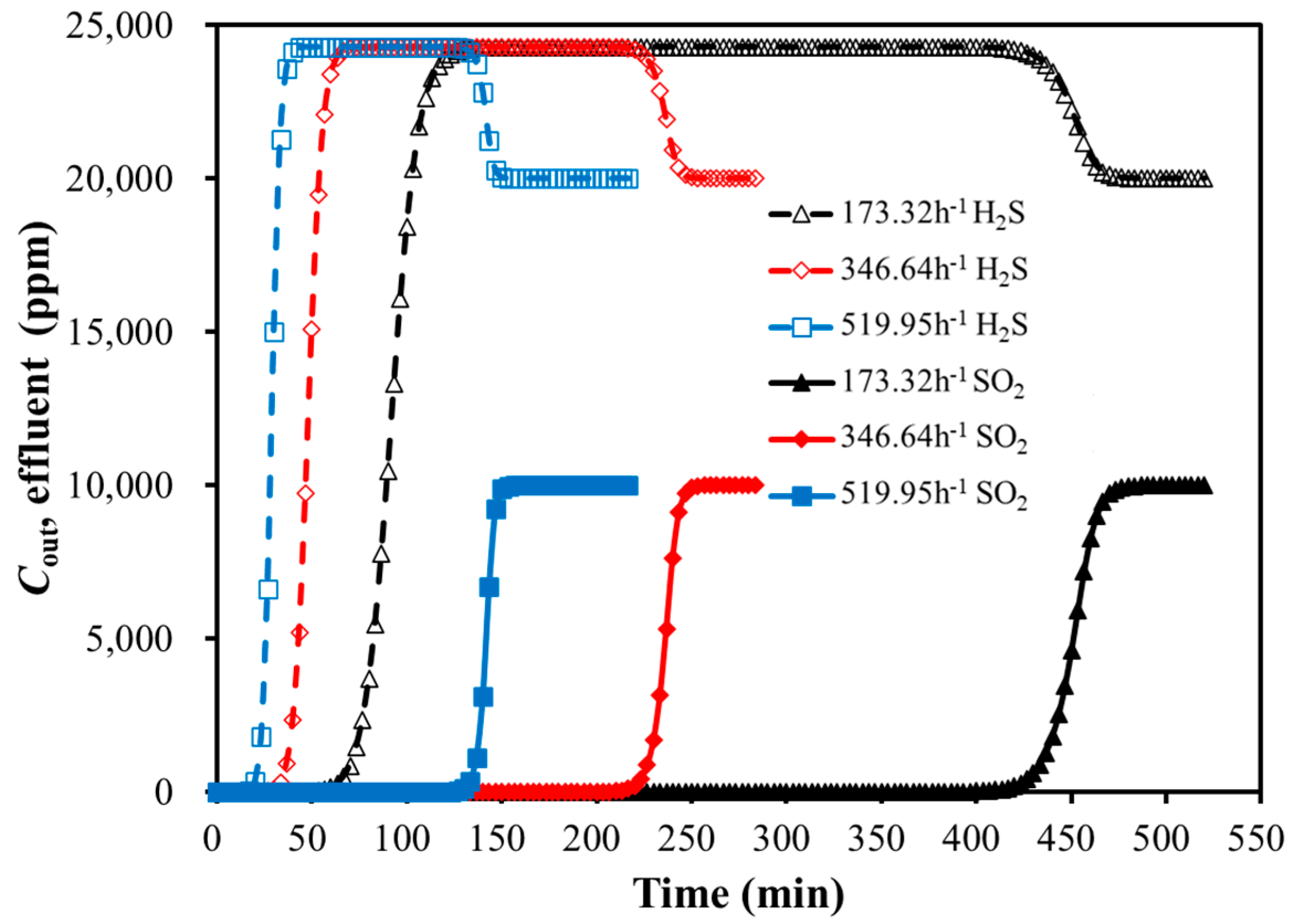
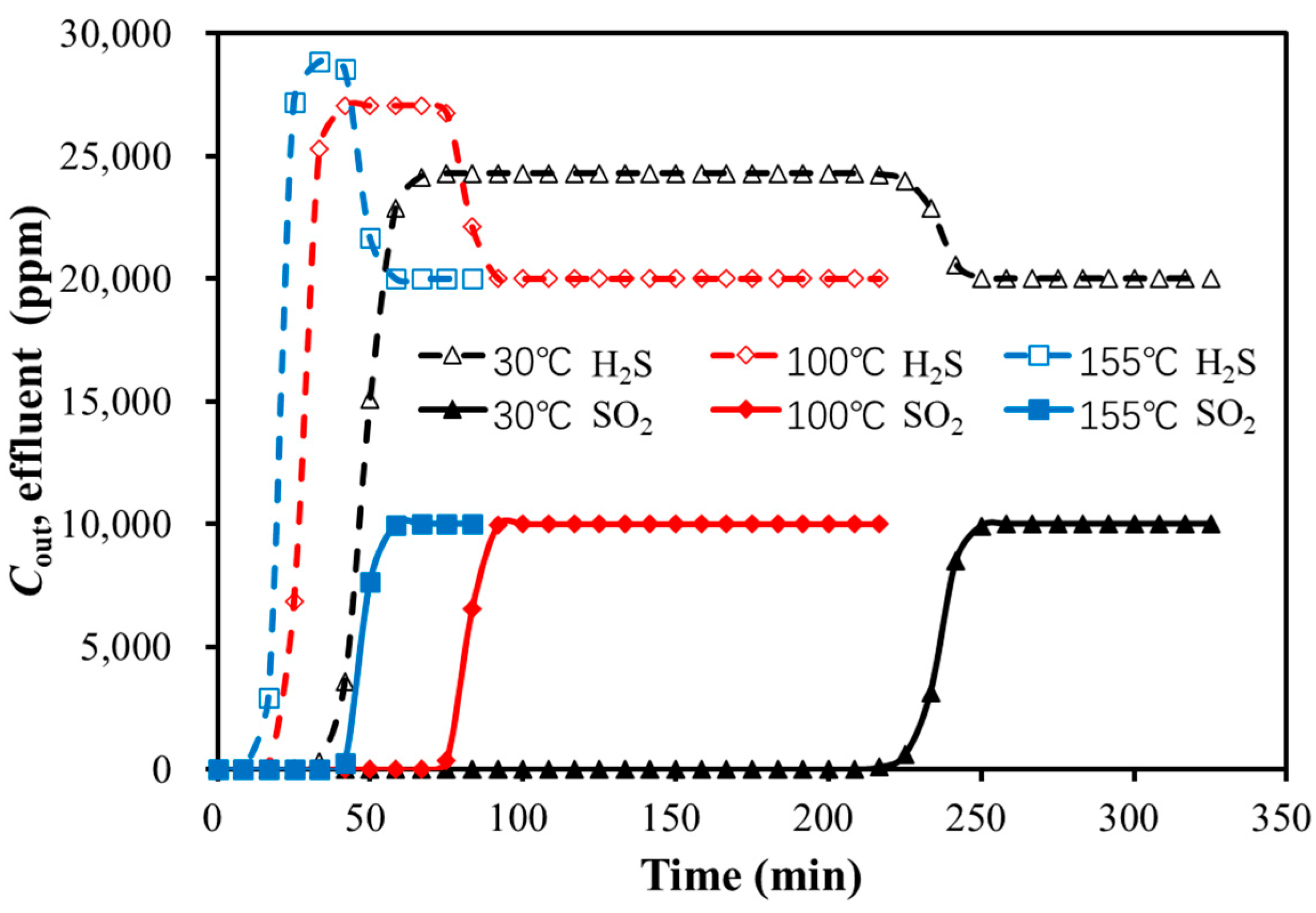
3.2.1. Effects of GHSV and Temperature on Dynamic Adsorption Characteristics
GHSV
Temperature
3.2.2. Comparison of Bi-Component and Single-Component Adsorption Breakthrough Time
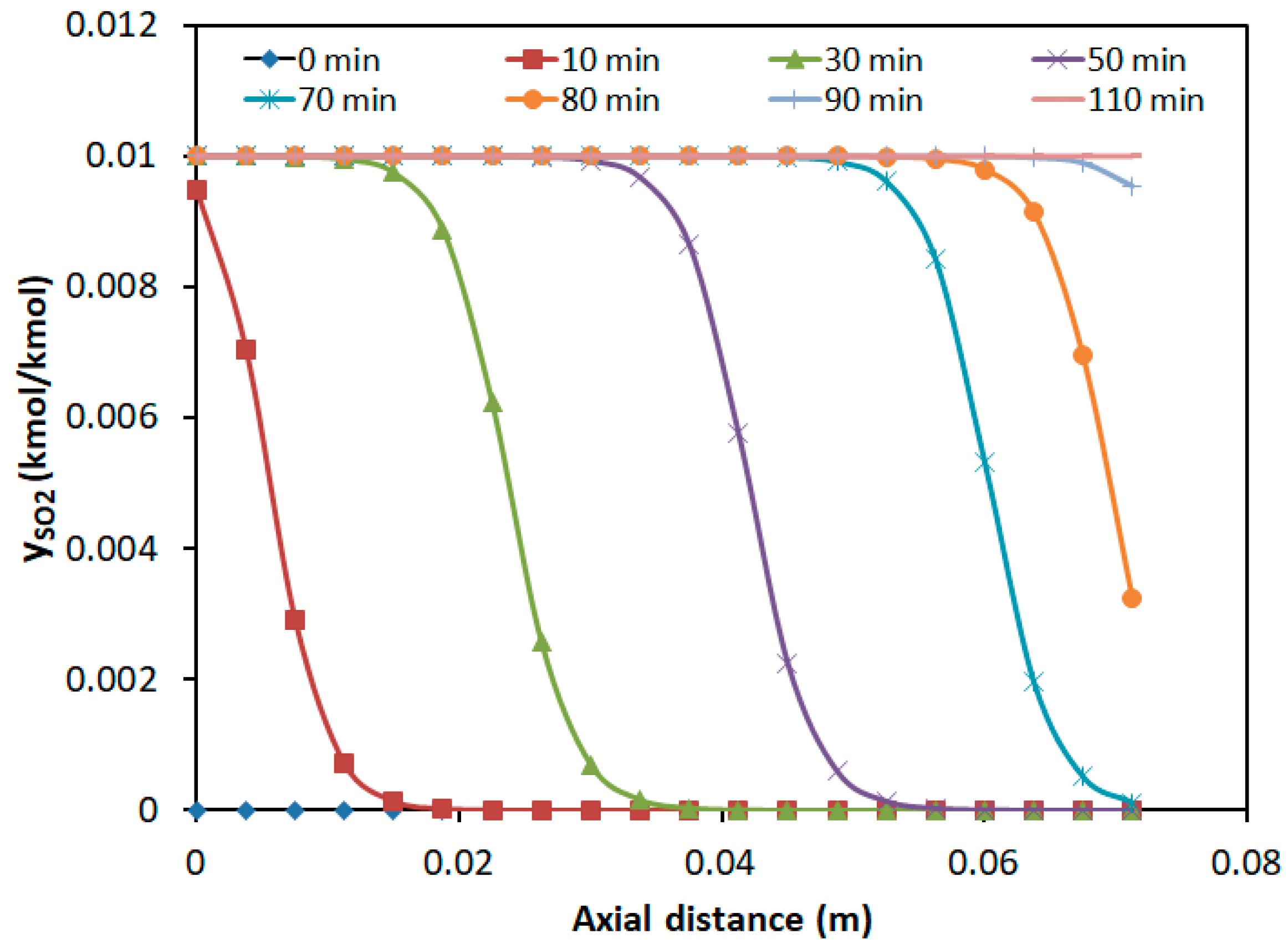
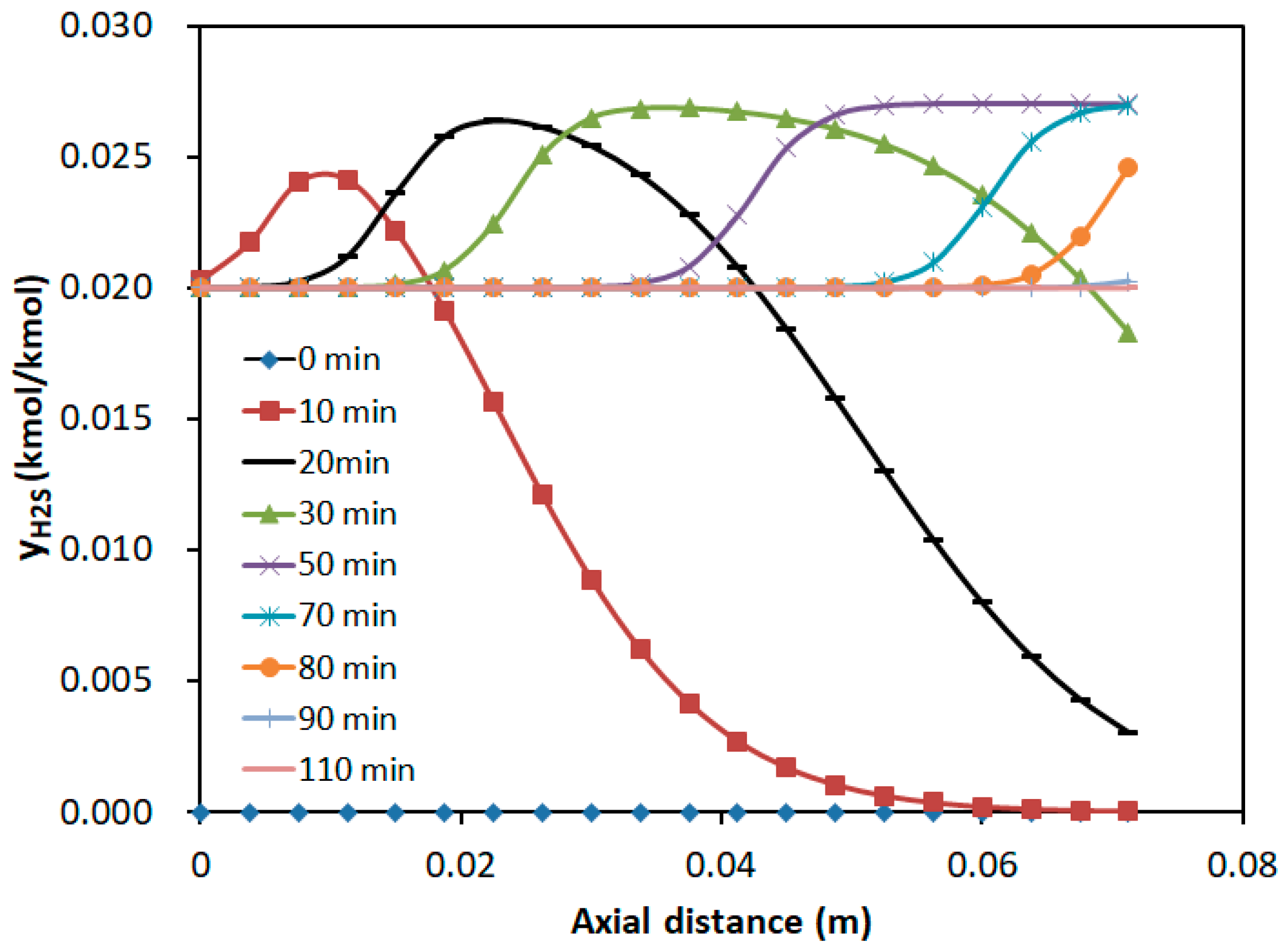
3.2.3. Concentration Distribution in the Adsorption Bed
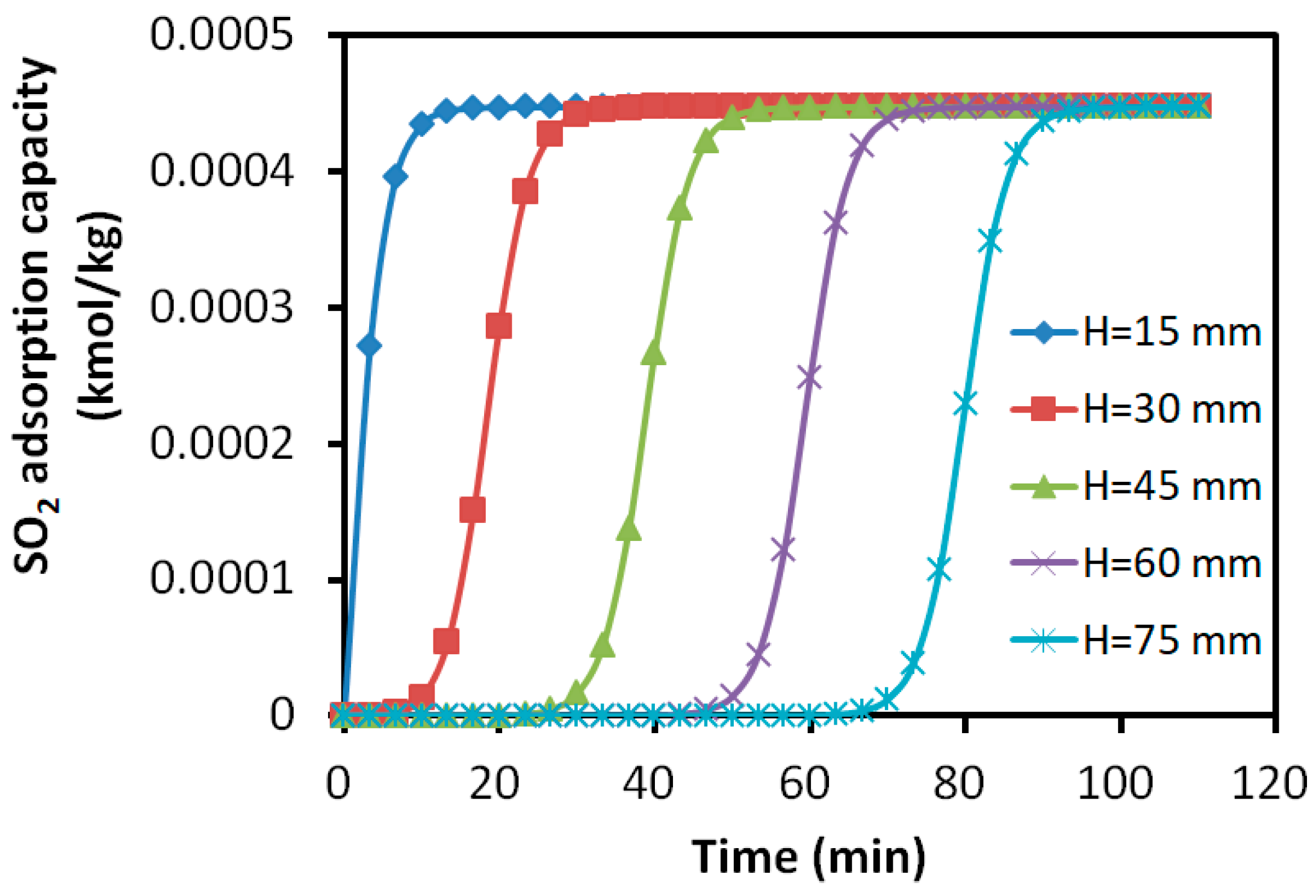
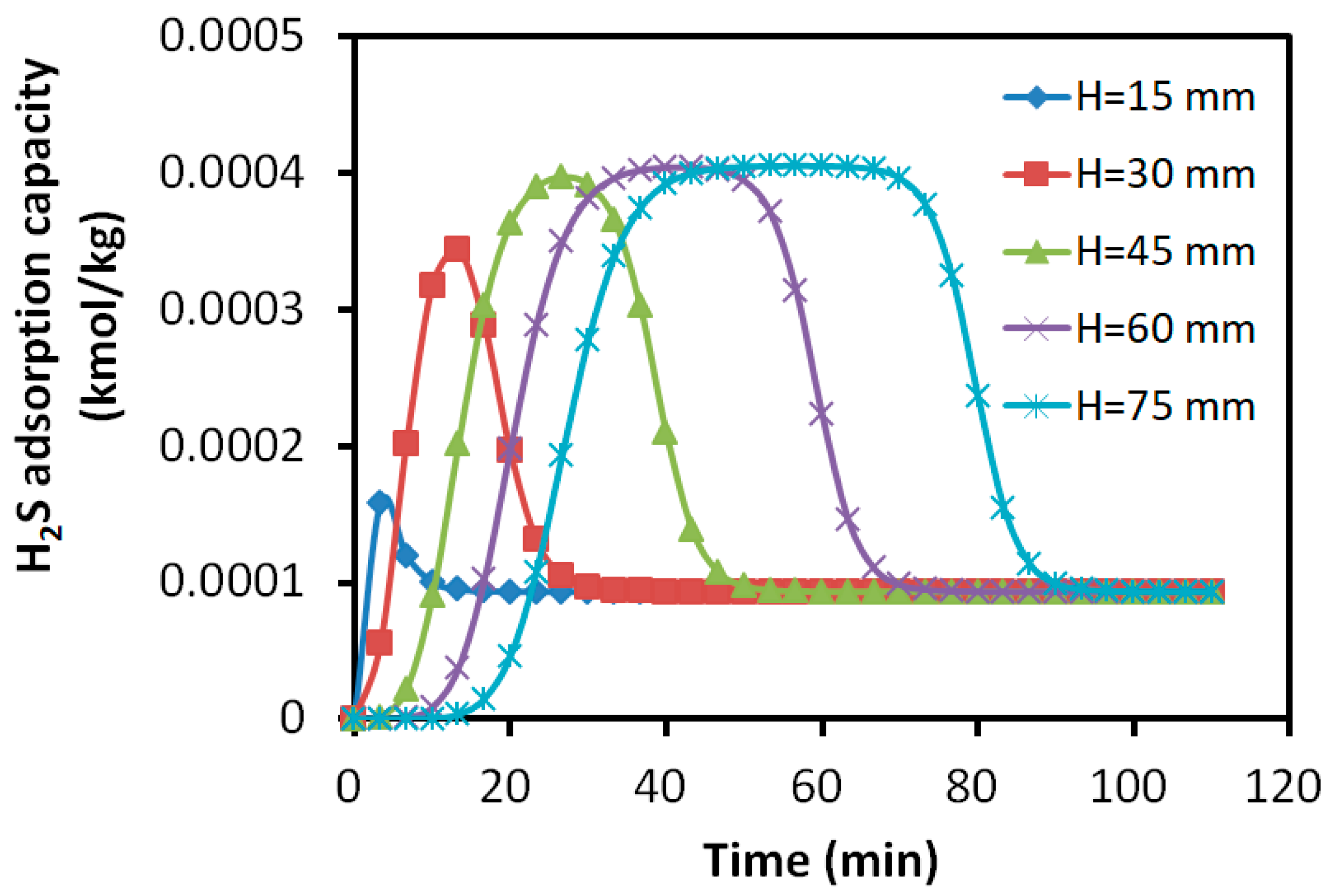
3.2.4. Distribution of Adsorption Amount in the Adsorption Bed
3.2.5. Limitations of the Bi-Component Simulation
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Nomenclature
| C | Concentration of adsorbate (kg/m3) |
| Cout, effluent | Species concentration at the outlet (ppm) |
| ySO2 | Dimensionless concentration of SO2 (kmol/kmol) |
| yH2S | Dimensionless concentration of H2S (kmol/kmol) |
| v | Flow rate of the fluid (m/s) |
| z | Axial direction of adsorption bed (m) |
| εb | Bed porosity (-) |
| ρp | Adsorbent particle density (kg/m3) |
| ρb | Bed bulk density (kg/m3) |
| ρs | Particle skeletal density (kg/m3) |
| q | Adsorption phase concentration (kg adsorbed/kg adsorbent) |
| q* | Equilibrium adsorption capacity (kg adsorbed/kg adsorbent) |
| kf | Overall mass transfer coefficient (1/s) |
| RP | Particle radius of adsorbent (m) |
| t | Adsorption time (s) |
| Hb | Height of adsorption bed (m) |
| Db | Adsorption bed inner diameter (m) |
| S | Spherical particle size of adsorbent (-) |
| IP1 | Langmuir isothermal parameter (kmol/kg/bar) |
| IP2 | Langmuir isothermal parameter (1/bar) |
References
- Kohl, A.L.; Nielsen, R.B. Gas Purification, 5th ed.; Gulf Publishing Company: Houston, TX, USA, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Eow, J.S. Recovery of Sulfur from Sour Acid Gas: A Review of the Technology. Environ. Prog. 2002, 21, 143–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Léveillé, V.; Claessens, T. Cansolv® SO2 Scrubbing System: Review of Commercial Applications for Smelter SO2 Emissions Control. S. Afr. Inst. Min. Metall. 2009, 109, 485–489. [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt, R.; Cross, J.B.; Latimer, E.G. Tail-Gas Cleanup by Simultaneous SO2 and H2S Removal. Energy Fuels 2009, 23, 3612–3616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, Y.; Ren, X.; Sun, Q.; Wennersten, R.; Cao, F.; Liu, Y.; Hao, M.; Yu, H. Performance of Nitrogen-Containing Functional Groups on SO2 Adsorption by Active Coke. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2024, 337, 126192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kisiela-Czajka, A.M.; Dziejarski, B. Linear and Non-Linear Regression Analysis for the Adsorption Kinetics of SO2 in a Fixed Carbon Bed Reactor—A Case Study. Energies 2022, 15, 633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Li, Z.; Yang, Y.; Jian, W.; Ma, D.; Jia, F. Kinetics and Thermodynamics of SO2 Adsorption on Metal-Loaded Multiwalled Carbon Nanotubes. Open Phys. 2020, 18, 1201–1214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Liu, Y.; Wang, H.; Tsai, C.-J.; Yang, X.; Xing, Y.; Zhang, C.; Xiao, P.; Webley, P.A. A Numerical Modelling Study of SO2 Adsorption on Activated Carbons with New Rate Equations. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 353, 858–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, S.-C.; Yao, J.-J.; Gao, L.; Ma, X.-Y.; Zhao, Y. Experimental Study on Removals of SO2 and NOx Using Adsorption of Activated Carbon/Microwave Desorption. J. Air Waste Manag. Assoc. 2012, 62, 1012–1021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, H.; Yi, H.; Tang, X.; Yu, Q.; Ning, P.; Yang, L. Adsorption Equilibrium for Sulfur Dioxide, Nitric Oxide, Carbon Dioxide, Nitrogen on 13x and 5a Zeolites. Chem. Eng. J. 2012, 188, 77–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lua, A.C.; Yang, T. Theoretical and Experimental SO2 Adsorption onto Pistachio-Nut-Shell Activated Carbon for a Fixed-Bed Column. Chem. Eng. J. 2009, 155, 175–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez, D.; Buitrago, R.; Sepulveda-Escribano, A.; Rodríguez-Reinoso, F.; Mondragón, F. Low Temperature Catalytic Adsorption of SO2 on Activated Carbon. J. Phys. Chem. C 2008, 112, 15335–15340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Xu, S.; Gao, S.; Xiao, P.; Jiang, M.; Zhao, H.; Huang, B.; Liu, L.; Niu, H.; Wang, J.; et al. Simultaneous Removal of SO2 and NOx from Flue Gas by Low-Temperature Adsorption over Activated Carbon. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 11003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pudi, A.; Rezaei, M.; Signorini, V.; Andersson, M.P.; Baschetti, M.G.; Mansouri, S.S. Hydrogen Sulfide Capture and Removal Technologies: A Comprehensive Review of Recent Developments and Emerging Trends. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2022, 298, 121448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saleh, A.M.; Mahdi, H.H.; Alias, A.B.; Hadi, N.K.A.; Qarizada, D.; Jawad, A.H.; Saleh, N.M. Equilibrium and Kinetic Studies in Adsorption of H2s Using Coconut Shell Activated Carbon Xerogel: Effect of Mass Adsorbent and Temperature. Desalin. Water Treat. 2024, 317, 100149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadighi, S.; Masoudian, S.K.; Mohaddecy, S.R.S.; Karimi, A. Sub-Dew Point Claus Process for Reducing Hydrogen Sulfide Emission from Sulfur Recovery Units. Petrol. Sci. Technol. 2024, 43, 1166–1181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.H. Hydrogen Sulfide Removal Technology: A Focused Review on Adsorption and Catalytic Oxidation. Korean J. Chem. Eng. 2021, 38, 674–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moradi, H.; Azizpour, H.; Bahmanyar, H.; Mohammadi, M. Molecular Dynamics Simulation of H2S Adsorption Behavior on the Surface of Activated Carbon. Inorg. Chem. Commun. 2020, 118, 108048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, X.; Chen, H.; Liu, Y.; Pan, J. Study on Removal of Gaseous Hydrogen Sulfide Based on Macroalgae Biochars. Nat. Gas Sci. Eng. 2020, 73, 103068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, A. A Computational Study of Adsorption of H2S and SO2 on the Activated Carbon Surfaces. J. Mol. Graph. Model. 2023, 122, 108463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parinyakit, S.; Worathanakul, P. Static and Dynamic Simulation of Single and Binary Component Adsorption of CO2 and CH4 on Fixed Bed Using Molecular Sieve of Zeolite 4A. Processes 2021, 9, 1250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, L.; Yang, K.; Zhao, Q.; Wang, H.; Cui, Q. Characterization and Mechanisms of H2S and SO2 Adsorption by Activated Carbon. Energy Fuels 2015, 29, 6678–6685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xuan, J.; Wang, C.; Zhang, L.; Cui, Q.; Wang, H. Effect of CO2/H2O on Adsorptive Removal of H2S/SO2 Mixture. Environ. Technol. 2022, 43, 2069–2079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wan, J.; Liu, M.; Liu, W.; Ding, W.; Duan, Y. Effect of Multi-Component Gas on Removal of Trace Hydrogen Sulfide Activity from Blast Furnace Gas Using Activated Carbon Adsorbent. Int. J. Chem. React. Eng. 2024, 22, 867–878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mudhoo, A.; Pittman, C.U., Jr. Adsorption Data Modeling and Analysis under Scrutiny: A Clarion Call to Redress Recently Found Troubling Flaws. Chem. Eng. Res. Des. 2023, 192, 371–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortiz, F.J.G.; Rodríguez, M.B.; Yang, R.T. Modeling of Fixed-Bed Columns for Gas Physical Adsorption. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 378, 121985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreira, D.D.S.; Goncalves, D.V.; Coelho, J.A.; de Azevedo, D.C.; Rios, R.B.; de Lucena, S.M.; Bastos-Neto, M. Influence of SO2 on CO2 Capture by Adsorption on Activated Carbon: Individual Pore Performance Via Multiscale Simulation. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2024, 336, 126219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capelo-Aviles, S.; De Fez-Febré, M.; Balestra, S.R.G.; Cabezas-Giménez, J.; de Oliveira, R.T.; Stampino, I.I.G.; Vidal-Ferran, A.; González-Cobos, J.; Lillo, V.; Fabelo, O.; et al. Selective Adsorption of CO2 in Tamof-1 for the Separation of CO2/CH4 Gas Mixtures. Nat. Commun. 2025, 16, 3243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GB 31570-2015; Emission Standard of Pollutants for Petroleum Refining Industry. The Standards Press of China: Beijing, China, 2015.
- GBZ 2.1-2019; Occupational Exposure Limits for Hazardous Agents in the Workplace—Part 1: Chemical Hazardous Agents. The Standards Press of China: Beijing, China, 2019.
- Riaz, Z. Modelling of Gas Separations Using Aspen Adsorption® Software. Master’s Thesis, LUT School of Engineering Science, Lappeenranta—Lahti University of Technology, Lahti, Finland, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Boki, K.; Tanada, S. Adsorption of Hydrogen Sulfide on Activated Carbon. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 1980, 28, 1270–1275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
| Temperature (°C) | IP1 (kmol/kg/bar) | IP2 (bar−1) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SO2 | H2S | SO2 | H2S | |
| 30 | 1.410 | 0.056 | 890 | 21.1 |
| 100 | 0.300 | 0.031 | 474 | 17.2 |
| 155 | 0.134 | 0.023 | 319 | 15.5 |
| Adsorption Process Parameters | Units | Value |
|---|---|---|
| Hb | m | 0.075 |
| Db | m | 0.015 |
| εb | m3/m3 | 0.6774 |
| ρb | kg/m3 | 450 |
| RP | (m) | 0.125 |
| S | - | 0.91 |
| kf of SO2 [31] | 1/s | 0.016 |
| kf of H2S [31] | 0.022 |
| Feed Gas GHSV (h−1) | Breakthrough Time (min) | Relative Deviation (%) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Experimental | Simulation | ||
| 173.32 | 474 | 470 | 0.9 |
| 259.98 | 336 | 328 | 2.4 |
| 346.64 | 240 | 247 | 2.8 |
| 519.95 | 142 | 144 | 1.4 |
| 866.58 | 87 | 92 | 5.4 |
| Temperatures of the Adsorption Bed (°C) | Breakthrough Time (min) | Relative Deviation (%) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Experimental | Simulation | ||
| 30 | 330 | 328 | 0.6 |
| 100 | 127 | 124 | 2.4 |
| 155 | 76 | 74 | 2.7 |
| Feed Gas GHSV (1/h) | Breakthrough Time (min) | Relative Deviation (%) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Experimental | Simulation | ||
| 173.32 | 93 | 89 | 4.5 |
| 259.98 | 65 | 64 | 1.6 |
| 346.64 | 43 | 44 | 2.3 |
| 433.29 | 31 | 33 | 6.1 |
| Temperatures of the Adsorption Bed (°C) | Breakthrough Time (min) | Relative Deviation (%) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Experimental | Simulation | ||
| 30 | 66 | 65 | 1.5 |
| 100 | 41 | 39 | 4.9 |
| 155 | 31 | 29 | 6.4 |
| Feed Gas GHSV (1/h) | Breakthrough Time (min) | |
|---|---|---|
| H2S | SO2 | |
| 173.32 | 59 | 431 |
| 346.64 | 36 | 221 |
| 519.95 | 10 | 134 |
| Temperatures of the Adsorption Bed (°C) | Breakthrough Time (min) | |
|---|---|---|
| H2S | SO2 | |
| 30 | 36 | 221 |
| 100 | 16 | 76 |
| 155 | 11 | 43 |
| Type | Breakthrough Time (min) | |
|---|---|---|
| H2S | SO2 | |
| Bi-component | 36 | 221 |
| Single-component | 44 | 247 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cao, X.; Zhang, L.; Cui, Q.; Wang, H. Simultaneous Adsorption and Purification of Low-Concentration SO2 and H2S. Molecules 2025, 30, 2302. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30112302
Cao X, Zhang L, Cui Q, Wang H. Simultaneous Adsorption and Purification of Low-Concentration SO2 and H2S. Molecules. 2025; 30(11):2302. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30112302
Chicago/Turabian StyleCao, Xiaoli, Lin Zhang, Qun Cui, and Haiyan Wang. 2025. "Simultaneous Adsorption and Purification of Low-Concentration SO2 and H2S" Molecules 30, no. 11: 2302. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30112302
APA StyleCao, X., Zhang, L., Cui, Q., & Wang, H. (2025). Simultaneous Adsorption and Purification of Low-Concentration SO2 and H2S. Molecules, 30(11), 2302. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30112302






