Therapeutic Uses of Retinol and Retinoid-Related Antioxidants
Abstract
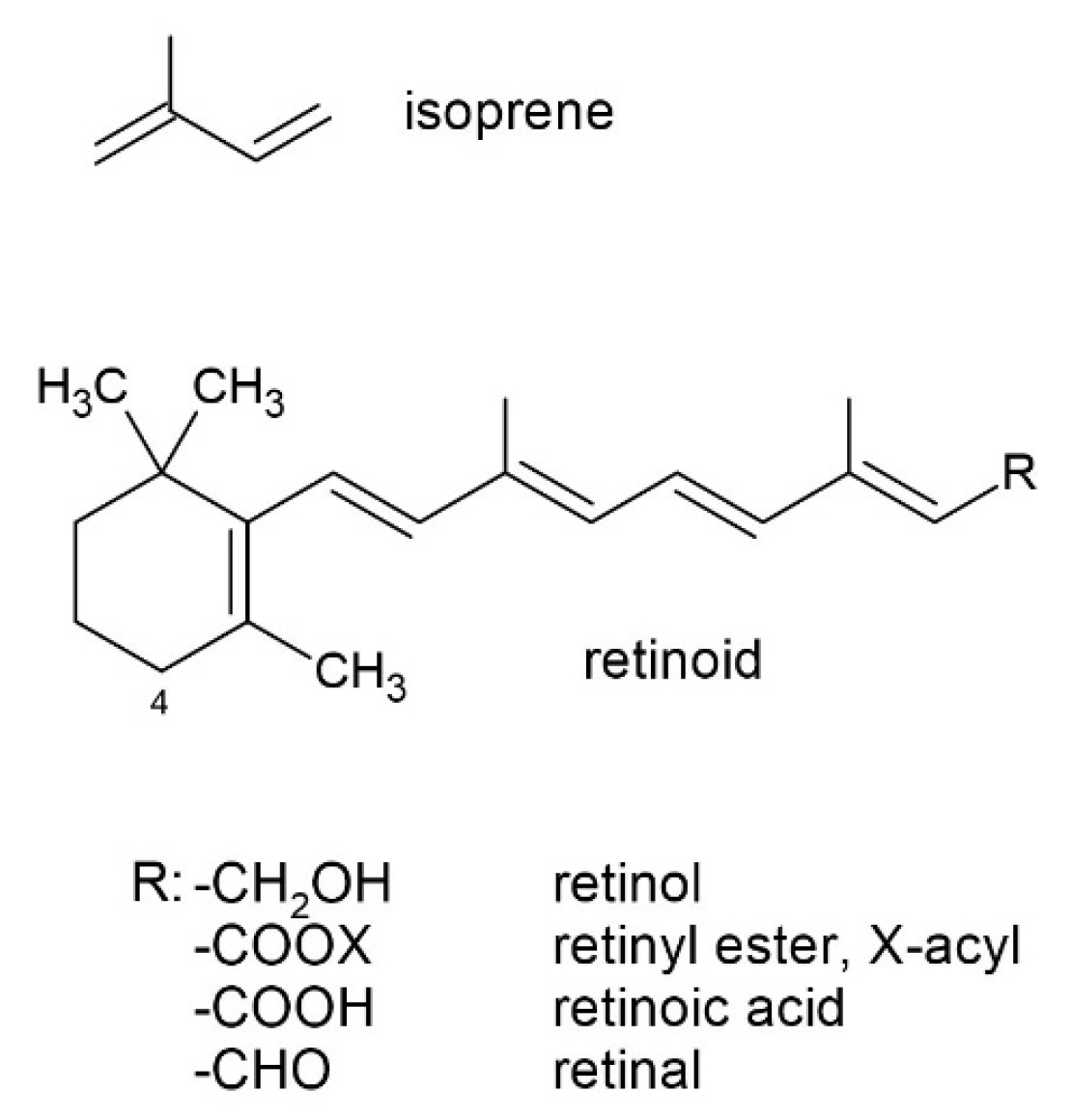
1. Introduction
2. Methods
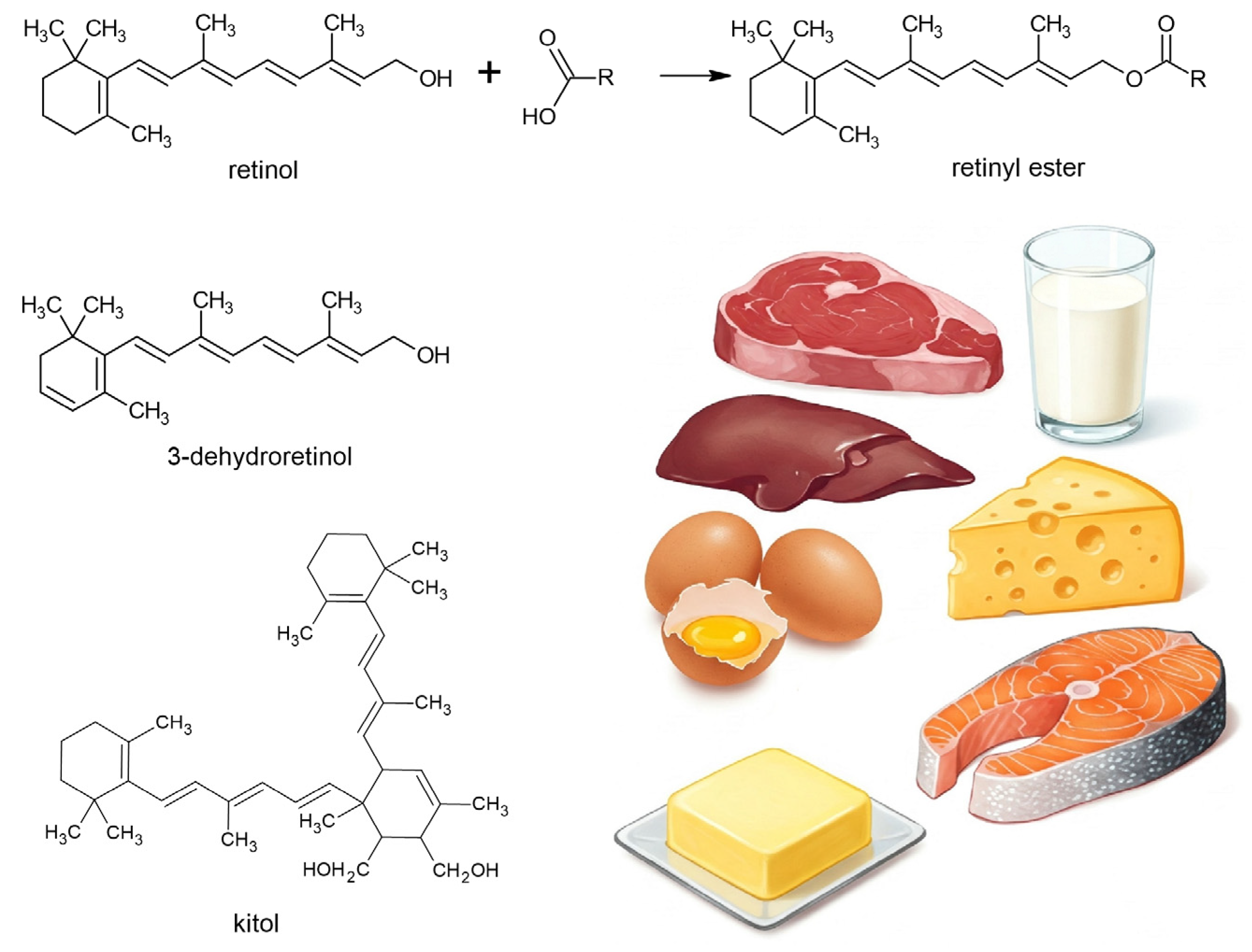
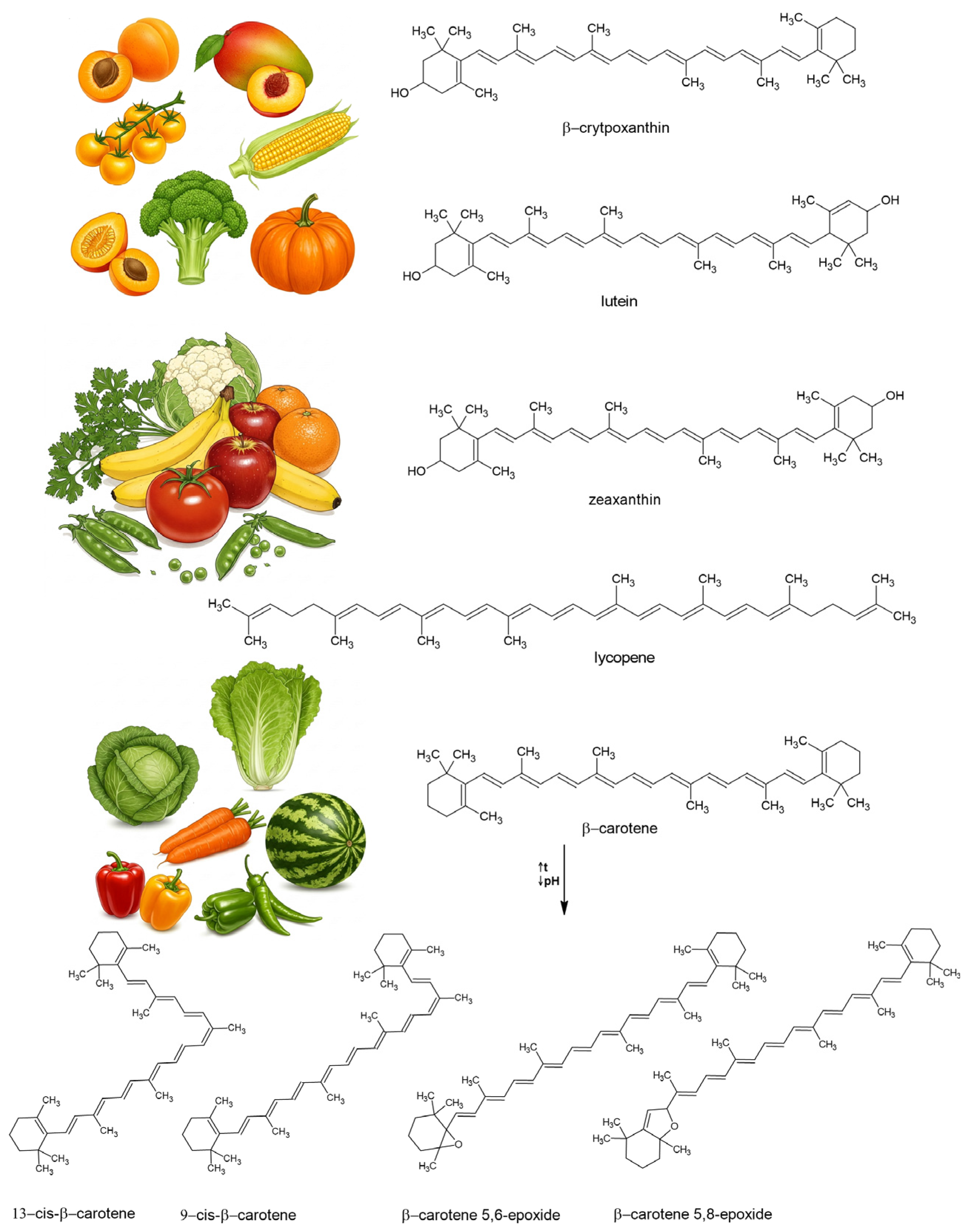
3. Food Sources
4. Overview of Digestion, Absorption, and Distribution into Tissues
4.1. Oral Cavity
4.2. Stomach
4.3. Intestinum
4.4. Liver
4.5. Bloodstream
5. Antioxidant Properties and Oxidation of Retinoid-Related Compounds
- (a)
- A high molar absorption coefficient, enabling protection against photo-oxidation;
- (b)
- Their ability to quench singlet oxygen (1O2);
- (c)
- Their capacity to lose protons upon interacting with reactive species, forming a less reactive radical center stabilized by the polyene network [130].
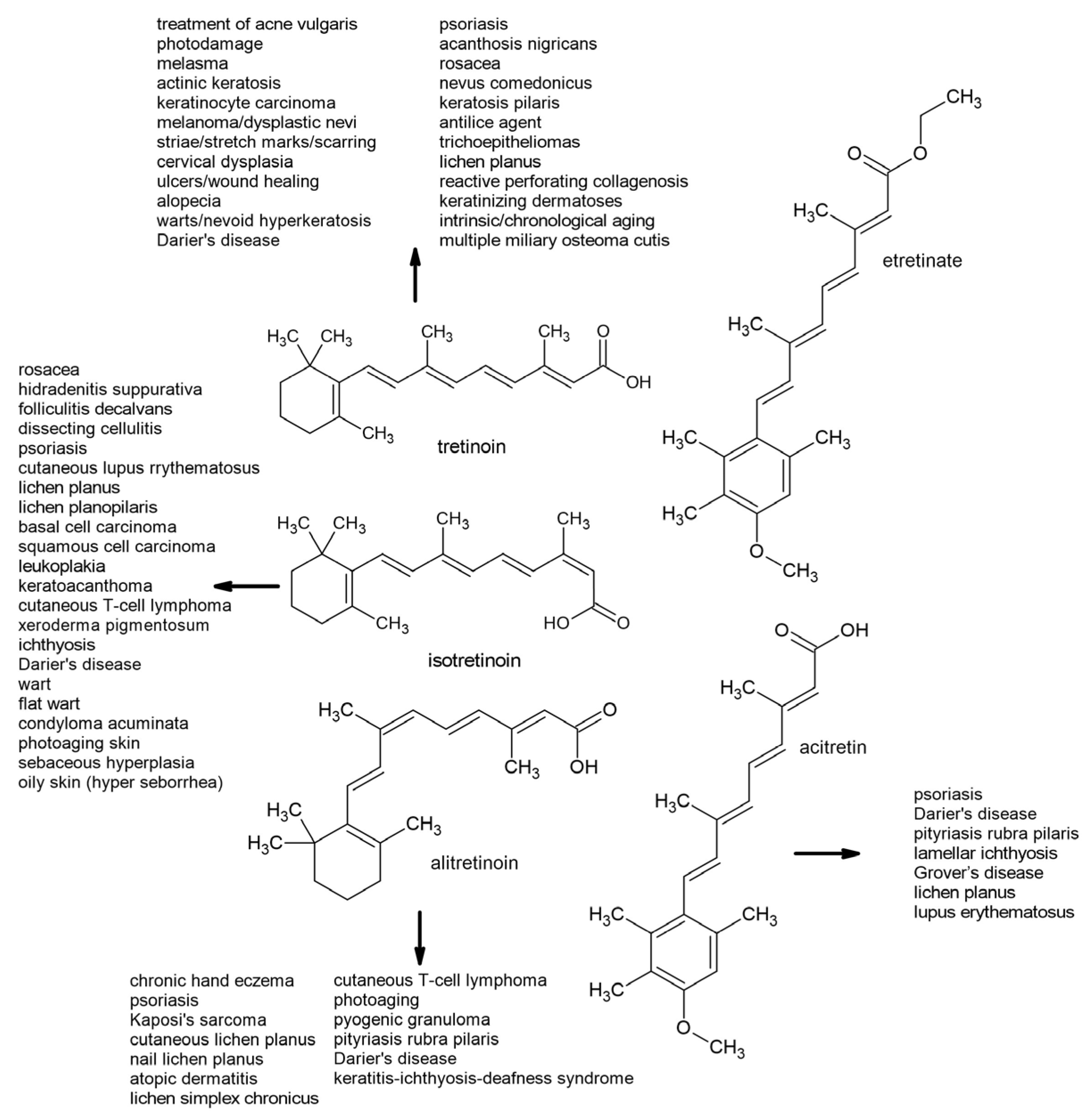
6. Therapeutic Uses of First- and Second-Generation Retinoids
6.1. First-Generation Retinoids
6.2. Second-Generation Retinoids
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ARAT | acyl-CoA acyl transferase |
| ATRA | all-trans-retinoic acid |
| BCMO1 | β-carotene-15,15′-dioxygenase |
| BCDO2 | β-carotene-9′,10′-dioxygenase |
| CD36 | Cluster Determinant 36 |
| CEL | carboxyl ester lipase |
| CRBP | cellular retinol-binding protein |
| HDL | High-Density Lipoprotein |
| LOX | lipoxygenase |
| LDL | Low-Density Lipoprotein |
| LP | pancreatic lipase |
| LRAT | lecithin retinol acyl transferase |
| MRP-8 | migration inhibitory factor-related protein-8 |
| PGHS | prostaglandin H synthase |
| RAR | retinoic acid receptor |
| RARE | retinoic acid response element |
| ROS | reactive oxygen species |
| RBP | retinol-binding protein |
| RXR | retinoid X receptor |
| STRA6 | STimulated by Retinoic Acid 6 |
| VLDL | Very Low-Density Lipoprotein |
References
- Castillo, V.; Giacomini, D.; Páez-Pereda, M.; Stalla, J.; Labeur, M.; Theodoropoulou, M.; Holsboer, F.; Grossman, A.B.; Stalla, G.K.; Arzt, E. Retinoic Acid as a Novel Medical Therapy for Cushing’s Disease in Dogs. Endocrinology 2006, 147, 4438–4444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berenguer, M.; Duester, G. Retinoic Acid, RARs and Early Development. J. Mol. Endocrinol. 2022, 69, T59–T67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burzyński, J.; Fichna, J.; Tarasiuk, A. Putative molecular targets for vitamin A in neutralizing oxidative stress in acute and chronic pancreatitis—A systematic review. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg’s Arch. Pharmacol. 2023, 396, 1361–1370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belyaeva, O.V.; Adams, M.K.; Popov, K.M.; Kedishvili, N.Y. Generation of Retinaldehyde for Retinoic Acid Biosynthesis. Biomolecules 2019, 10, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kedishvili, N.Y. Enzymology of Retinoic Acid Biosynthesis and Degradation. J. Lipid Res. 2013, 54, 1744–1760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edem, D.O. Vitamin A: A Review. Asian J. Clin. Nutr. 2009, 1, 65–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bender, D.A. Nutritional Biochemistry of the Vitamins; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Mao, G.E.; Collins, M.D.; Derguini, F. Teratogenicity, Tissue Distribution, and Metabolism of the Retro-Retinoids, 14-Hydroxy-4,14-Retro-Retinol and Anhydroretinol, in the C57BL/6J Mouse. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2000, 163, 38–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maurya, V.K.; Shakya, A.; Bashir, K.; Kushwaha, S.C.; McClements, D.J. Vitamin A Fortification: Recent Advances in Encapsulation Technologies. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2022, 21, 2772–2819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrison, E.H.; Curley, R.W. Carotenoids and Retinoids: Nomenclature, Chemistry, and Analysis. Sub-Cell. Biochem./Subcell. Biochem. 2016, 81, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrison, E.H. Carotenoids, Β-Apocarotenoids, and Retinoids: The Long and the Short of It. Nutrients 2022, 14, 1411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasmussen, S.C. Polyenes and Polyvinylenes. In Springer Briefs in Molecular Science; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2018; pp. 67–83. [Google Scholar]
- Manzanares, W.; Dhaliwal, R.; Jiang, X.; Murch, L.; Heyland, D.K. Antioxidant micronutrients in the critically ill: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Crit. Care 2012, 16, R66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koekkoek, W.A.C.K.; van Zanten, A.R.H. Antioxidant vitamins and trace elements in critical illness. Nutr. Clin. Pract. 2016, 31, 457–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palace, V.P.; Khaper, N.; Qin, Q.; Singal, P.K. Antioxidant Potentials of Vitamin A and Carotenoids and Their Relevance to Heart Disease. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 1999, 26, 746–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabbani, E.; Golgiri, F.; Janani, L.; Moradi, N.; Fallah, S.; Abiri, B.; Vafa, M. Randomized Study of the Effects of Zinc, Vitamin A, and Magnesium Co-supplementation on Thyroid Function, Oxidative Stress, and hs-CRP in Patients with Hypothyroidism. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2021, 199, 4074–4083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kayalar, O.; Bayrak, B.B.; Yildirim, M.; Yanardag, R.; Oztay, F. Retinoic acid reduces kidney injury by regulating oxidative stress, NRF-2, and apoptosis in hyperoxic mice. Cell Biochem. Funct. 2024, 42, e4094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iqbal, A.; Hafeez Kamran, S.; Siddique, F.; Ishtiaq, S.; Hameed, M.; Manzoor, M. Modulatory effects of rutin and vitamin A on hyperglycemia induced glycation, oxidative stress and inflammation in high-fat-fructose diet animal model. PLoS ONE 2024, 19, e0303060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, D.; Takahashi, G.; Zheng, Y.W.; Matsuo-Takasaki, M.; Li, J.; Takami, M.; An, Y.; Hemmi, Y.; Miharada, N.; Fujioka, T.; et al. Retinoids rescue ceruloplasmin secretion and alleviate oxidative stress in Wilson’s disease-specific hepatocytes. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2022, 31, 3652–3671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, P.; Shen, N.; Feng, S.; Liu, W.; Wang, J.; Wang, C. Oxidative stress and apoptosis of the spinal cord in a rat model of retinoic acid-induced neural tube defects. Int. J. Dev. Neurosci. 2025, 85, e10399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eggersdorfer, M.; Wyss, A. Carotenoids in Human Nutrition and Health. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2018, 652, 18–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xavier, A.A.O.; Pérez-Gálvez, A. Carotenoids as a Source of Antioxidants in the Diet. Sub-Cell. Biochem./Subcell. Biochem. 2016, 79, 359–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bondi, A.; Sklan, D. Vitamin A and Carotene in Animal Nutrition. Prog. Food Nutr. Sci. 1984, 8, 165–191. [Google Scholar]
- Blomhoff, R.; Blomhoff, H.K. Overview of Retinoid Metabolism and Function. J. Neurobiol. 2006, 66, 606–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schieber, A.; Carle, R. Occurrence of Carotenoid Cis-Isomers in Food: Technological, Analytical, and Nutritional Implications. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2005, 16, 416–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khoo, H.-E.; Prasad, K.N.; Kong, K.-W.; Jiang, Y.; Ismail, A. Carotenoids and Their Isomers: Color Pigments in Fruits and Vegetables. Molecules 2011, 16, 1710–1738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rao, A.; Rao, L. Carotenoids and Human Health. Pharmacol. Res. 2007, 55, 207–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Rigal, D.; Gauillard, F.; Richard-Forget, F. Changes in the Carotenoid Content of Apricot (Prunus Armeniaca, Var Bergeron) During Enzymatic Browning: Β-carotene Inhibition of Chlorogenic Acid Degradation. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2000, 80, 763–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waché, Y.; Bosser-DeRatuld, A.; Lhuguenot, J.-C.; Belin, J.-M. Effect of Cis/Trans Isomerism of β-Carotene on the Ratios of Volatile Compounds Produced during Oxidative Degradation. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2003, 51, 1984–1987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dugave, C.; Demange, L. CIS−Trans Isomerization of Organic Molecules and Biomolecules: Implications and Applications. Chem. Rev. 2003, 103, 2475–2532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moltedo, A.; Álvarez-Sánchez, C.; Grande, F.; Charrondiere, U.R. The Complexity of Producing and Interpreting Dietary Vitamin A Statistics. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2021, 100, 103926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maurya, V.K.; Shakya, A.; Aggarwal, M.; Gothandam, K.M.; Bohn, T.; Pareek, S. Fate of β-Carotene within Loaded Delivery Systems in Food: State of Knowledge. Antioxidants 2021, 10, 426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dzakovich, M.P.; Gas-Pascual, E.; Orchard, C.J.; Sari, E.N.; Riedl, K.M.; Schwartz, S.J.; Francis, D.M.; Cooperstone, J.L. Analysis of Tomato Carotenoids: Comparing Extraction and Chromatographic Methods. J. AOAC Int. 2019, 102, 1069–1079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saini, R.K.; Nile, S.H.; Park, S.W. Carotenoids from Fruits and Vegetables: Chemistry, Analysis, Occurrence, Bioavailability and Biological Activities. Food Res. Int. 2015, 76, 735–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, G. Bioconversion of Dietary Provitamin A Carotenoids to Vitamin A in Humans. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2010, 91, 1468S–1473S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vitamin A Deficiency. Available online: https://www.who.int/data/nutrition/nlis/info/vitamin-a-deficiency (accessed on 29 March 2025).
- Wiseman, E.M.; Dadon, S.B.-E.; Reifen, R. The Vicious Cycle of Vitamin a Deficiency: A Review. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2016, 57, 3703–3714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- González-Peña, M.A.; Ortega-Regules, A.E.; De Parrodi, C.A.; Lozada-Ramírez, J.D. Chemistry, Occurrence, Properties, Applications, and Encapsulation of Carotenoids—A Review. Plants 2023, 12, 313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wüstenberg, B.; Müller, M.-A.; Schütz, J.; Wyss, A.; Schiefer, G.; Litta, G.; John, M.; Hähnlein, W. Vitamins, 2. Vitamin A (Retinoids). Ullmann’s Encycl. Ind. Chem. 2020, 1, 1–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonrath, W.; Gao, B.; Houston, P.; McClymont, T.; Müller, M.-A.; Schäfer, C.; Schweiggert, C.; Schütz, J.; Medlock, J.A. 75 Years of Vitamin A Production: A Historical and Scientific Overview of the Development of New Methodologies in Chemistry, Formulation, and Biotechnology. Org. Process Res. Dev. 2023, 27, 1557–1584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, L.H.; Haskell, M. Estimating the Potential for Vitamin A Toxicity in Women and Young Children. J. Nutr. 2002, 132, 2907S–2919S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reboul, E. Proteins Involved in Fat-Soluble Vitamin and Carotenoid Transport across the Intestinal Cells: New Insights from the Past Decade. Prog. Lipid Res. 2022, 89, 101208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kopec, R.E.; Failla, M.L. Recent Advances in the Bioaccessibility and Bioavailability of Carotenoids and Effects of Other Dietary Lipophiles. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2017, 68, 16–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chacón-Ordóñez, T.; Carle, R.; Schweiggert, R. Bioaccessibility of Carotenoids from Plant and Animal Foods. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2018, 99, 3220–3239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ben-Amotz, A.; Levy, Y. Bioavailability of a Natural Isomer Mixture Compared with Synthetic All-Trans Beta-Carotene in Human Serum. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 1996, 63, 729–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaziano, J.; Johnson, E.; Russell, R.; Manson, J.; Stampfer, M.; Ridker, P.; Frei, B.; Hennekens, C.; Krinsky, N. Discrimination in Absorption or Transport of Beta-Carotene Isomers after Oral Supplementation with Either All-Trans- or 9-Cis-Beta-Carotene. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 1995, 61, 1248–1252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Erdman, J.W.; Thatcher, A.J.; Hofmann, N.E.; Lederman, J.D.; Block, S.S.; Lee, C.M.; Mokady, S. All-Trans β-Carotene Is Absorbed Preferentially to 9-Cis β-Carotene, but the Latter Accumulates in the Tissues of Domestic Ferrets (Mustela Putorius Puro). J. Nutr. 1998, 128, 2009–2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deming, D.M.; Teixeira, S.R.; Erdman, J.W. All-Trans β-Carotene Appears to Be More Bioavailable than 9-Cis or 13-Cis β-Carotene in Gerbils Given Single Oral Doses of Each Isomer. J. Nutr. 2002, 132, 2700–2708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amengual, J.; Widjaja-Adhi, M.A.K.; Rodriguez-Santiago, S.; Hessel, S.; Golczak, M.; Palczewski, K.; Von Lintig, J. Two Carotenoid Oxygenases Contribute to Mammalian Provitamin A Metabolism. J. Biol. Chem. 2013, 288, 34081–34096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, W.Y.W.; Chua, J.W.M.; Gill, S.; Brownlee, I.A. Analysis of the Lipolytic Activity of Whole-Saliva and Site-Specific Secretions from the Oral Cavity of Healthy Adults. Nutrients 2019, 11, 191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niot, I.; Besnard, P. Appetite Control by the Tongue-Gut Axis and Evaluation of the Role of CD36/SR-B2. Biochimie 2017, 136, 27–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Isola, G.; Polizzi, A.; Muraglie, S.; Leonardi, R.; Lo Giudice, A. Assessment of Vitamin C and Antioxidant Profiles in Saliva and Serum in Patients with Periodontitis and Ischemic Heart Disease. Nutrients 2019, 11, 2956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blakeley, M.; Sobczyńska-Malefora, A.; Carpenter, G. The Origins of Salivary Vitamin A, Vitamin B12 and Vitamin D-Binding Proteins. Nutrients 2020, 12, 3838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mensi, A.; Borel, P.; Goncalves, A.; Nowicki, M.; Gleize, B.; Roi, S.; Chobert, J.-M.; Haertlé, T.; Reboul, E. Β-Lactoglobulin as a Vector for Β-Carotene Food Fortification. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2014, 62, 5916–5924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bourassa, P.; N’soukpoé-Kossi, C.N.; Tajmir-Riahi, H.A. Binding of Vitamin A with Milk α- and β-Caseins. Food Chem. 2012, 138, 444–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mensi, A.; Choiset, Y.; Haertlé, T.; Reboul, E.; Borel, P.; Guyon, C.; de Lamballerie, M.; Chobert, J.-M. Interlocking of β-Carotene in Beta-Lactoglobulin Aggregates Produced under High Pressure. Food Chem. 2013, 139, 253–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbé, F.; Ménard, O.; Gouar, Y.L.; Buffière, C.; Famelart, M.-H.; Laroche, B.; Feunteun, S.L.; Dupont, D.; Rémond, D. The Heat Treatment and the Gelation Are Strong Determinants of the Kinetics of Milk Proteins Digestion and of the Peripheral Availability of Amino Acids. Food Chem. 2012, 136, 1203–1212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sporn, M.B.; Roberts, A.B.; Goodman, D.S. The Retinoids, 2nd ed.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, S.C.; Yuk, H.G.; Lee, D.H.; Lee, K.E.; Hwang, Y.I.; Ludescher, R. Stabilization of Retinol through Incorporation into Liposomes. J. Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2002, 35, 358–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Low, D.Y.; D’Arcy, B.; Gidley, M.J. Mastication Effects on Carotenoid Bioaccessibility from Mango Fruit Tissue. Food Res. Int. 2014, 67, 238–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tyssandier, V.; Reboul, E.; Dumas, J.-F.; Bouteloup-Demange, C.; Armand, M.; Marcand, J.; Sallas, M.; Borel, P. Processing of Vegetable-Borne Carotenoids in the Human Stomach and Duodenum. AJP Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2003, 284, G913–G923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brodkorb, A.; Egger, L.; Alminger, M.; Alvito, P.; Assunção, R.; Ballance, S.; Bohn, T.; Bourlieu-Lacanal, C.; Boutrou, R.; Carrière, F.; et al. INFOGEST Static in Vitro Simulation of Gastrointestinal Food Digestion. Nat. Protoc. 2019, 14, 991–1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salvia-Trujillo, L.; Verkempinck, S.H.E.; Sun, L.; Van Loey, A.M.; Grauwet, T.; Hendrickx, M.E. Lipid Digestion, Micelle Formation and Carotenoid Bioaccessibility Kinetics: Influence of Emulsion Droplet Size. Food Chem. 2017, 229, 653–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donhowe, E.G.; Kong, F. Beta-Carotene: Digestion, Microencapsulation, and in Vitro Bioavailability. Food Bioprocess. Technol. 2014, 7, 338–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, C.; Zhao, M.; Decker, E.A.; McClements, D.J. Influence of Protein Type on Oxidation and Digestibility of Fish Oil-in-Water Emulsions: Gliadin, Caseinate, and Whey Protein. Food Chem. 2014, 175, 249–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iddir, M.; Degerli, C.; Dingeo, G.; Desmarchelier, C.; Schleeh, T.; Borel, P.; Larondelle, Y.; Bohn, T. Whey Protein Isolate Modulates Beta-Carotene Bioaccessibility Depending on Gastro-Intestinal Digestion Conditions. Food Chem. 2019, 291, 157–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konovalov, V.V.; Kispert, L.D. AM1, INDO/S and Optical Studies of Carbocations of Carotenoid Molecules. Acid Induced Isomerization. J. Chem. Society. Perkin Trans. II 1999, 4, 901–910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Failla, M.L.; Chitchumroonchokchai, C.; Ishida, B.K. In Vitro Micellarization and Intestinal Cell Uptake of Cis Isomers of Lycopene Exceed Those of All-Trans Lycopene. J. Nutr. 2008, 138, 482–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferruzzi, M.G.; Lumpkin, J.L.; Schwartz, S.J.; Failla, M. Digestive Stability, Micellarization, and Uptake of Β-Carotene Isomers by CACO-2 Human Intestinal Cells. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2006, 54, 2780–2785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kopec, R.E.; Gleize, B.; Borel, P.; Desmarchelier, C.; Caris-Veyrat, C. Are Lutein, Lycopene, and β-Carotene Lost through the Digestive Process? Food Funct. 2017, 8, 1494–1503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sy, C.; Dangles, O.; Borel, P.; Caris-Veyrat, C. Iron-Induced Oxidation of (All-E)-β-Carotene under Model Gastric Conditions: Kinetics, Products, and Mechanism. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2013, 63, 195–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sy, C.; Dangles, O.; Borel, P.; Caris-Veyrat, C. Stability of Bacterial Carotenoids in the Presence of Iron in a Model of the Gastric Compartment—Comparison with Dietary Reference Carotenoids. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2015, 572, 89–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kopec, R.E.; Caris-Veyrat, C.; Nowicki, M.; Gleize, B.; Carail, M.; Borel, P. Production of Asymmetric Oxidative Metabolites of [13C]-β-Carotene During Digestion in the Gastrointestinal Lumen of Healthy Men. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2018, 108, 803–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carriere, F.; Barrowman, J.A.; Verger, R.; René, L. Secretion and Contribution to Lipolysis of Gastric and Pancreatic Lipases during a Test Meal in Humans. Gastroenterology 1993, 105, 876–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blaner, W.S.; Olson, J.A. Retinol and Retinoic Acid Metabolism. In The Retinoids: Biology, Chemistry and Medicine; Sporn, M.B., Roberts, A.B., Goodman, D.S., Eds.; Raven Press: New York, NK, USA, 1994; pp. 229–256. [Google Scholar]
- Murillo, A.; Hu, S.; Fernandez, M. Zeaxanthin: Metabolism, Properties, and Antioxidant Protection of Eyes, Heart, Liver, and Skin. Antioxidants 2019, 8, 390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reboul, E.; Berton, A.; Moussa, M.; Kreuzer, C.; Crenon, I.; Borel, P. Pancreatic Lipase and Pancreatic Lipase-Related Protein 2, but Not Pancreatic Lipase-Related Protein 1, Hydrolyze Retinyl Palmitate in Physiological Conditions. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA) Mol. Cell Biol. Lipids 2006, 1761, 4–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chitchumroonchokchai, C.; Failla, M.L. Hydrolysis of Zeaxanthin Esters by Carboxyl Ester Lipase during Digestion Facilitates Micellarization and Uptake of the Xanthophyll by Caco-2 Human Intestinal Cells. J. Nutr. 2006, 136, 588–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rigtrup, K.M.; Kakkad, B.; Ong, D.E. Purification and Partial Characterization of a Retinyl Ester Hydrolase from the Brush Border of Rat Small Intestine Mucosa: Probable Identity with Brush Border Phospholipase B. Biochemistry 1994, 33, 2661–2666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dhuique-Mayer, C.; Borel, P.; Reboul, E.; Caporiccio, B.; Besancon, P.; Amiot, M.-J. β-Cryptoxanthin from Citrus juices: Assessment of Bioaccessibility Using Anin Vitrodigestion/Caco-2 Cell Culture Model. Br. J. Nutr. 2007, 97, 883–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sy, C.; Gleize, B.; Dangles, O.; Landrier, J.-F.; Caris-Veyrat, C.; Borel, P. Effects of Physicochemical Properties of Carotenoids on Their Bioaccessibility, Intestinal Cell Uptake, and Blood and Tissue Concentrations. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2012, 56, 1385–1397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marques, C.S.; Lima, M.J.R.; Oliveira, J.; Teixeira-Lemos, E. Tomato Lycopene: Functional Proprieties and Health. Int. J. Nutr. Food Eng. 2015, 9, 1089–1099. [Google Scholar]
- Bohn, T.; Desmarchelier, C.; Dragsted, L.O.; Nielsen, C.S.; Stahl, W.; Rühl, R.; Keijer, J.; Borel, P. Host-related Factors Explaining Interindividual Variability of Carotenoid Bioavailability and Tissue Concentrations in Humans. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2017, 61, 1600685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corte-Real, J.; Desmarchelier, C.; Borel, P.; Richling, E.; Hoffmann, L.; Bohn, T. Magnesium Affects Spinach Carotenoid Bioaccessibility In Vitro Depending on Intestinal Bile and Pancreatic Enzyme Concentrations. Food Chem. 2017, 239, 751–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roodenburg, A.J.; Leenen, R.; Van Het Hof, K.H.; Weststrate, J.A.; Tijburg, L.B. Amount of Fat in the Diet Affects Bioavailability of Lutein Esters but Not of α-Carotene, β-Carotene, and Vitamin E in Humans. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2000, 71, 1187–1193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soukoulis, C.; Bohn, T. A Comprehensive Overview on the Micro- and Nano-Technological Encapsulation Advances for Enhancing the Chemical Stability and Bioavailability of Carotenoids. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2015, 58, 1–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borel, P.; Desmarchelier, C.; Dumont, U.; Halimi, C.; Lairon, D.; Page, D.; Sébédio, J.L.; Buisson, C.; Buffière, C.; Rémond, D. Dietary Calcium Impairs Tomato Lycopene Bioavailability in Healthy Humans. Br. J. Nutr. 2016, 116, 2091–2096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirilenko, V.; Gregoriadis, G. Fat Soluble Vitamins in Liposomes: Studies on Incorporation Efficiency and Bile Salt Induced Vesicle Disintegration. J. Drug Target. 1993, 1, 361–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noy, N.; Kelleher, D.J.; Scotto, A.W. Interactions of Retinol with Lipid Bilayers: Studies with Vesicles of Different Radii. J. Lipid Res. 1995, 36, 375–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rocha, H.R.; Coelho, M.C.; Gomes, A.M.; Pintado, M.E. Carotenoids Diet: Digestion, Gut Microbiota Modulation, and Inflammatory Diseases. Nutrients 2023, 15, 2265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
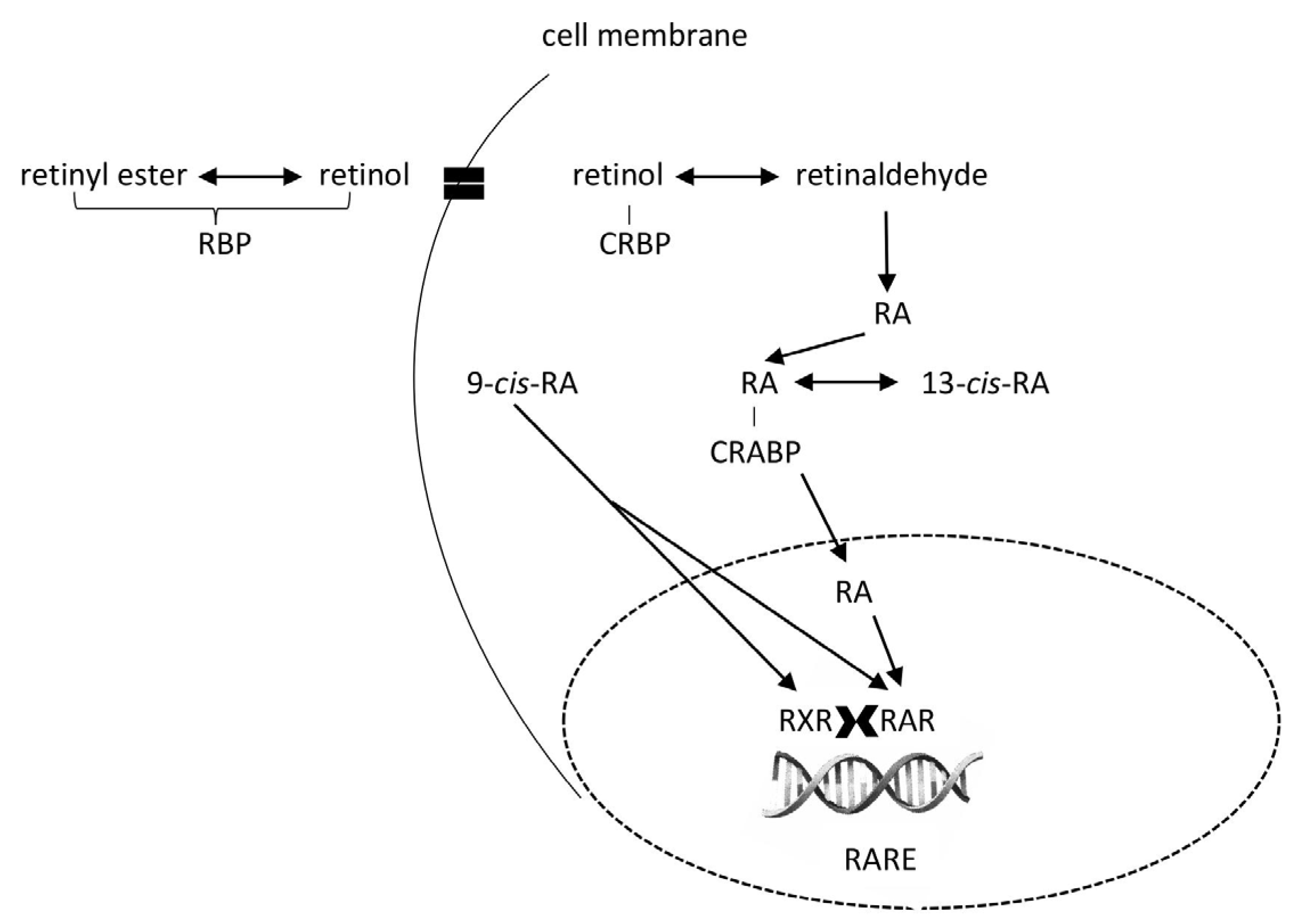
- Reboul, E. Absorption of Vitamin A and Carotenoids by the Enterocyte: Focus on Transport Proteins. Nutrients 2013, 5, 3563–3581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- During, A.; Harrison, E.H. Mechanisms of Provitamin A (Carotenoid) and Vitamin A (Retinol) Transport into and out of Intestinal Caco-2 Cells. J. Lipid Res. 2007, 48, 2283–2294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawaguchi, R.; Yu, J.; Honda, J.; Hu, J.; Whitelegge, J.; Ping, P.; Wiita, P.; Bok, D.; Sun, H. A Membrane Receptor for Retinol Binding Protein Mediates Cellular Uptake of Vitamin A. Science 2007, 315, 820–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isken, A.; Golczak, M.; Oberhauser, V.; Hunzelmann, S.; Driever, W.; Imanishi, Y.; Palczewski, K.; Von Lintig, J. RBP4 Disrupts Vitamin A Uptake Homeostasis in a STRA6-Deficient Animal Model for Matthew-Wood Syndrome. Cell Metab. 2008, 7, 258–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blaner, W.S.; Li, Y. Vitamin A Metabolism, Storage and Tissue Delivery Mechanisms. In The Retinoids: Biology, Biochemistry, and Disease; Doll, E.P., Niederreither, K., Eds.; Wiley Blackwell: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2015; pp. 3–34. [Google Scholar]
- Blaner, W.S.; Brun, P.-J.; Calderon, R.M.; Golczak, M. Retinol-Binding Protein 2 (RBP2): Biology and Pathobiology. Crit. Rev. Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2020, 55, 197–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lobo, M.V.T.; Huerta, L.; Ruiz–Velasco, N.; Teixeiro, E.; De La Cueva, P.; Celdrán, A.; Martín–Hidalgo, A.; Vega, M.A.; Bragado, R. Localization of the Lipid Receptors CD36 and CLA-1/SR-BI in the Human Gastrointestinal Tract: Towards the Identification of Receptors Mediating the Intestinal Absorption of Dietary Lipids. J. Histochem. Cytochem. 2001, 49, 1253–1260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Terpstra, V.; Van Amersfoort, E.S.; Van Velzen, A.G.; Kuiper, J.; Van Berkel, T.J.C. Hepatic and Extrahepatic Scavenger Receptors. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2000, 20, 1860–1872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- During, A.; Dawson, H.D.; Harrison, E.H. Carotenoid Transport Is Decreased and Expression of the Lipid Transporters SR-BI, NPC1L1, and ABCA1 Is Downregulated in Caco-2 Cells Treated with Ezetimibe. J. Nutr. 2005, 135, 2305–2312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Von Lintig, J. Colors with Functions: Elucidating the Biochemical and Molecular Basis of Carotenoid Metabolism. Annu. Rev. Nutr. 2010, 30, 35–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ong, D.E.; Newcomer, M.E.; Chytil, F. Cellular Retinoid-Binding Proteins. In The Retinoids: Biology, Chemistry and Medicine; Sporn, M.B., Roberts, A.B., Goodman, D.S., Eds.; Raven Press: New York, NK, USA, 1994; pp. 283–318. [Google Scholar]
- O’Byrne, S.M.; Blaner, W.S. Retinol and Retinyl Esters: Biochemistry and Physiology. J. Lipid Res. 2013, 54, 1731–1743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lobo, G.P.; Amengual, J.; Palczewski, G.; Babino, D.; Von Lintig, J. Mammalian Carotenoid-Oxygenases: Key Players for Carotenoid Function and Homeostasis. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA) Mol. Cell Biol. Lipids 2011, 1821, 78–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harrison, E.H. Mechanisms of Digestion and Absorption of Dietary Vitamin A. Annu. Rev. Nutr. 2005, 25, 87–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.Y.; Meng, L.; Shen, L.; Ji, H.F. Regulation of gut microbiota by vitamin C, vitamin E and β-carotene. Food Res. Int. 2023, 169, 112749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pham, V.T.; Dold, S.; Rehman, A.; Bird, J.K.; Steinert, R.E. Vitamins, the gut microbiome and gastrointestinal health in humans. Nutr. Res. 2021, 95, 35–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, C.; Li, Z.; Tu, H.; Sun, F.; Guo, W.; Di, C.; He, R.; Ze, X.; Zhang, L.; Gao, R.; et al. 2’-FL and cross-feeding bifidobacteria reshaped the gut microbiota of infants with atopic dermatitis ex vivo and prevented dermatitis in mice post-microbiota transplantation through retinol metabolism activation. Gut Microbes 2025, 17, 2474148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, H.; Zhang, S.; Wang, M.; Yi, B.; Zhao, Y.; Schroyen, M.; Zhang, H. Retinol metabolism signaling participates in microbiota-regulated fat deposition in obese mice. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2025, 136, 109787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Wongsiriroj, N.; Blaner, W.S. The Multifaceted Nature of Retinoid Transport and Metabolism. Hepatobiliary Surg. Nutr. 2014, 3, 126–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blaner, W.S.; O’Byrne, S.M.; Wongsiriroj, N.; Kluwe, J.; D’Ambrosio, D.M.; Jiang, H.; Schwabe, R.F.; Hillman, E.M.C.; Piantedosi, R.; Libien, J. Hepatic Stellate Cell Lipid Droplets: A Specialized Lipid Droplet for Retinoid Storage. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA) Mol. Cell Biol. Lipids 2008, 1791, 467–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lapshina, E.A.; Belyaeva, O.V.; Chumakova, O.V.; Kedishvili, N.Y. Differential Recognition of the Free versus Bound Retinol by Human Microsomal Retinol/Sterol Dehydrogenases: Characterization of the Holo-CRBP Dehydrogenase Activity of RoDH-4. Biochemistry 2002, 42, 776–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noy, N. Retinoid-Binding Proteins: Mediators of Retinoid Action. Biochem. J. 2000, 348, 481–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Friedman, S.L. Hepatic Stellate Cells: Protean, Multifunctional, and Enigmatic Cells of the Liver. Physiol. Rev. 2008, 88, 125–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moriwaki, H.; Blaner, W.S.; Piantedosi, R.; Goodman, D.S. Effects of Dietary Retinoid and Triglyceride on the Lipid Composition of Rat Liver Stellate Cells and Stellate Cell Lipid Droplets. J. Lipid Res. 1988, 29, 1523–1534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanumihardjo, S.A.; Furr, H.C.; Amedée-Manesme, O.; Olson, J.A. Retinyl Ester (Vitamin A Ester) and Carotenoid Composition in Human Liver. Int. J. Vitam. Nutr. Res. 1990, 60, 307–313. [Google Scholar]
- Blomhoff, R.; Berg, T.; Norum, K.R. Distribution of Retinol in Rat Liver Cells: Effect of Age, Sex and Nutritional Status. Br. J. Nutr. 1988, 60, 233–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barua, A.B.; Sidell, N. Retinoyl Β-Glucuronide: A Biologically Active Interesting Retinoid. J. Nutr. 2004, 134, 286S–289S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nadin, L.; Murray, M. Arachidonic Acid-mediated Cooxidation of All-trans-retinoic Acid in Microsomal Fractions from Human Liver. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2000, 131, 851–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gudas, J.M.; Sporn, M.B.; Roberts, A.B. Cellular Biology and Biochemistry of the Retinoids. In The Retinoids: Biology, Chemistry and Medicine; Sporn, M.B., Roberts, A.B., Goodman, D.S., Eds.; Raven Press: New York, NK, USA, 1994; pp. 443–520. [Google Scholar]
- Berry, D.C.; Jacobs, H.; Marwarha, G.; Gely-Pernot, A.; O’Byrne, S.M.; DeSantis, D.; Klopfenstein, M.; Feret, B.; Dennefeld, C.; Blaner, W.S.; et al. The STRA6 Receptor Is Essential for Retinol-Binding Protein-Induced Insulin Resistance but Not for Maintaining Vitamin A Homeostasis in Tissues Other than the Eye. J. Biol. Chem. 2013, 288, 24528–24539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz, A.; Mark, M.; Jacobs, H.; Klopfenstein, M.; Hu, J.; Lloyd, M.; Habib, S.; Tosha, C.; Radu, R.A.; Ghyselinck, N.B.; et al. Retinoid Content, Visual Responses, and Ocular Morphology Are Compromised in the Retinas of Mice Lacking the Retinol-Binding Protein Receptor, STRA6. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2012, 53, 3027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terra, R.; Wang, X.; Hu, Y.; Charpentier, T.; Lamarre, A.; Zhong, M.; Sun, H.; Mao, J.; Qi, S.; Luo, H.; et al. To Investigate the Necessity of STRA6 Upregulation in T Cells During T Cell Immune Responses. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e82808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adamantidi, T.; Lafara, M.-P.; Venetikidou, M.; Likartsi, E.; Toganidou, I.; Tsoupras, A. Utilization and Bio-Efficacy of Carotenoids, Vitamin A and Its Vitaminoids in Nutricosmetics, Cosmeceuticals, and Cosmetics’ Applications with Skin-Health Promoting Properties. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 1657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crupi, P.; Faienza, M.F.; Naeem, M.Y.; Corbo, F.; Clodoveo, M.L.; Muraglia, M. Overview of the Potential Beneficial Effects of Carotenoids on Consumer Health and Well-Being. Antioxidants 2023, 12, 1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, F.; Khan, J.; Zehravi, M.; Das, R.; Haque, M.A.; Banu, A.; Parwaiz, S.; Nainu, F.; Nafady, M.H.; Shahriar, S.M.S.; et al. Synergistic Effects of Carotenoids: Therapeutic Benefits on Human Health. Process Biochem. 2023, 136, 254–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortega-Regules, A.E.; Martínez-Thomas, J.A.; Schürenkämper-Carrillo, K.; de Parrodi, C.A.; López-Mena, E.R.; Mejía-Méndez, J.L.; Lozada-Ramírez, J.D. Recent Advances in the Therapeutic Potential of Carotenoids in Preventing and Managing Metabolic Disorders. Plants 2024, 13, 1584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rasmus, P.; Kozłowska, E. Antioxidant and Anti-Inflammatory Effects of Carotenoids in Mood Disorders: An Overview. Antioxidants 2023, 12, 676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rocha, H.R.; Pintado, M.E.; Gomes, A.M.; Coelho, M.C. Carotenoids and Intestinal Harmony: Exploring the Link for Health. Foods 2024, 13, 1599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terao, J. Revisiting Carotenoids as Dietary Antioxidants for Human Health and Disease Prevention. Food Funct. 2023, 14, 7799–7824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Landrum, J.T. Reactive Oxygen and Nitrogen Species in Biological Systems: Reactions and Regulation by Carotenoids. In Carotenoids and Human Health; Humana: Totowa, NJ, USA, 2012; pp. 57–101. [Google Scholar]
- Washington, I.; Jockusch, S.; Itagaki, Y.; Turro, N.J.; Nakanishi, K. Superoxidation of Bisretinoids. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2005, 44, 7097–7100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ben-Shabat, S.; Itagaki, Y.; Jockusch, S.; Sparrow, J.R.; Turro, N.J.; Nakanishi, K. Formation of a Nonaoxirane from A2E, a Lipofuscin Fluorophore Related to Macular Degeneration, and Evidence of Singlet Oxygen Involvement. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2002, 41, 814–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amarie, S.; Standfuss, J.; Barros, T.; Kühlbrandt, W.; Dreuw, A.; Wachtveitl, J. Carotenoid Radical Cations as a Probe for the Molecular Mechanism of Nonphotochemical Quenching in Oxygenic Photosynthesis. J. Phys. Chem. B 2007, 111, 3481–3487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samokyszyn, V.M.; Chen, T.; Maddipati, K.R.; Franz, T.J.; Lehman, P.A.; Lloyd, R.V. Free Radical Oxidation of (E)-Retinoic Acid by Prostaglandin H Synthase. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 1995, 8, 807–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Edge, R.; Land, E.J.; McGarvey, D.; Mulroy, L.; Truscott, T.G. Relative One-Electron Reduction Potentials of Carotenoid Radical Cations and the Interactions of Carotenoids with the Vitamin E Radical Cation. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1998, 120, 4087–4090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edge, R.; El-Agamey, A.; Land, E.J.; Navaratnam, S.; Truscott, T.G. Studies of Carotenoid One-Electron Reduction Radicals. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2006, 458, 104–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, R.-M.; Chen, C.-H.; Tian, Y.-X.; Zhang, J.-P.; Skibsted, L.H. Fast Regeneration of Carotenoids from Radical Cations by Isoflavonoid Dianions: Importance of the Carotenoid Keto Group for Electron Transfer. J. Phys. Chem. A 2009, 114, 126–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Agamey, A.; McGarvey, D.J. First Direct Observation of Reversible Oxygen Addition to a Carotenoid-Derived Carbon-Centered Neutral Radical. Org. Lett. 2005, 7, 3957–3960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devasagayam, T.P.A.; Werner, T.; Ippendorf, H.; Martin, H.; Sies, H. Synthetic Carotenoids, Novel Polyene Polyketones and New Capsorubin Isomers as Efficient Quenchers of Singlet Molecular Oxygen. Photochem. Photobiol. 1992, 55, 511–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
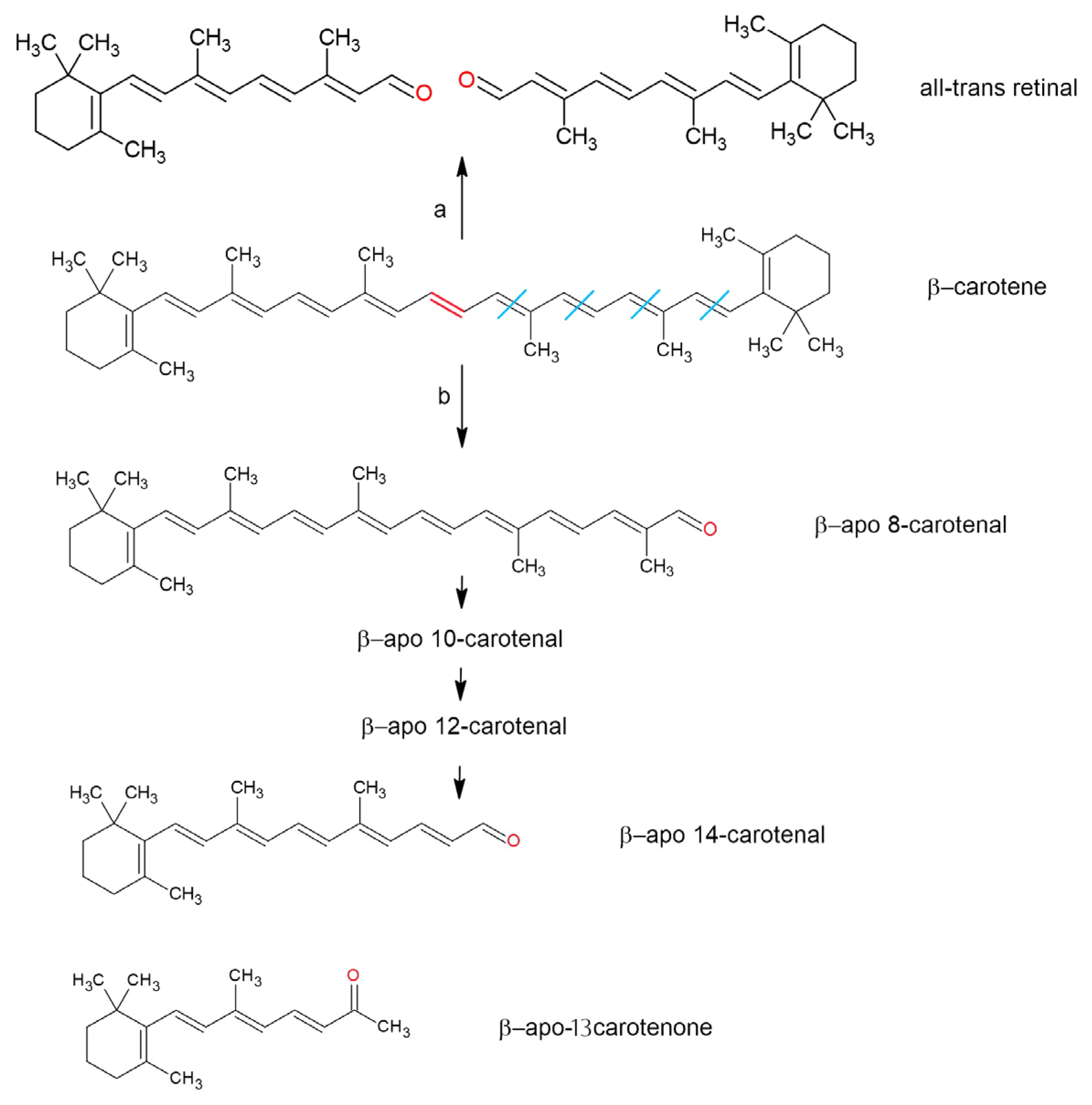
- Nagao, A. Oxidative Conversion of Carotenoids to Retinoids and Other Products. J. Nutr. 2004, 134, 237S–240S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McClure, T.D.; Liebler, D.C. A Rapid Method for Profiling the Products of Antioxidant Reactions by Negative Ion Chemical Ionization Mass Spectrometry. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 1995, 8, 128–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stratton, S.P.; Schaefer, W.H.; Liebler, D.C. Isolation and Identification of Singlet Oxygen Oxidation Products of Beta-Carotene. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 1993, 6, 542–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bausch, N.; Liechti, N.; Oesterhelt, N.; Kistler, N. Isolation and Identification of a Major Urinary Canthaxanthin Metabolite in Rats. Int. J. Vitam. Nutr. Res. 1999, 69, 268–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolz, E.; Liechti, H.; Notter, B.; Oesterhelt, G.; Kistler, A. Characterization of Metabolites of Astaxanthin in Primary Cultures of Rat Hepatocytes. Drug Metab. Dispos. 1999, 27, 456–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khachik, F.; Spangler, C.J.; Smith, J.C.; Canfield, L.M.; Steck, A.; Pfander, H. Identification, Quantification, and Relative Concentrations of Carotenoids and Their Metabolites in Human Milk and Serum. Anal. Chem. 1997, 69, 1873–1881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kiokias, S.; Varzakas, T.; Oreopoulou, V. In Vitro Activity of Vitamins, Flavonoids, and Natural Phenolic Antioxidants Against the Oxidative Deterioration of Oil-Based Systems. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2008, 48, 78–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.-D.; Tang, G.-W.; Fox, J.G.; Krinsky, N.I.; Russell, R.M. Enzymatic Conversion of β-Carotene into β-Apo-Carotenals and Retinoids by Human, Monkey, Ferret, and Rat Tissues. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 1991, 285, 8–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrison, E.H.; Sena, C.D.; Eroglu, A.; Fleshman, M.K. The Formation, Occurrence, and Function of β-Apocarotenoids: β-Carotene Metabolites That May Modulate Nuclear Receptor Signaling. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2012, 96, 1189S–1192S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chedea, V.S.; Jisaka, M. Lipoxygenase and Carotenoids: A Co-Oxidation Story. Afr. J. Biotechnol. 2013, 12, 2786–2791. [Google Scholar]
- Chedea, V.S.; Jisaka, M. Inhibition of Soybean Lipoxygenases–Structural and Activity Models for the Lipoxygenase Isoenzymes Family. In Recent Trends for Enhancing the Diversity and Quality of Soybean Products; Krezhova, D., Ed.; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Goldreich, D.; Grossman, S.; Sofer, Y.; Breitbart, E.; Sklan, D. The Effect of Retinol and Retinoic Acids on Lipoxygenase Activity. Int. J. Vitam. Nutr. Res. 1997, 67, 4–9. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hazai, E.; Bikádi, Z.; Zsila, F.; Lockwood, S.F. Molecular Modeling of the Non-Covalent Binding of the Dietary Tomato Carotenoids Lycopene and Lycophyll, and Selected Oxidative Metabolites with 5-Lipoxygenase. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2006, 14, 6859–6867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lockwood, S.F.; Penn, M.S.; Hazen, S.L.; Bikádi, Z.; Zsila, F. The Effects of Oral CardaxTM (Disodium Disuccinate Astaxanthin) on Multiple Independent Oxidative Stress Markers in a Mouse Peritoneal Inflammation Model: Influence on 5-Lipoxygenase in Vitro and in Vivo. Life Sci. 2006, 79, 162–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Samokyszyn, V.M.; Marnett, L.J. Hydroperoxide-Dependent Cooxidation of 13-Cis-Retinoic Acid by Prostaglandin H Synthase. J. Biol. Chem. 1987, 262, 14119–14133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoham, A.L.; Casadesus, D. Tretinoin. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK557478/ (accessed on 31 March 2025).
- Baldwin, H.E.; Nighland, M.; Kendall, C.; Mays, D.A.; Grossman, R.; Newburger, J. 40 Years of Topical Tretinoin Use in Review. J. Drugs Dermatol. 2013, 12, 638–642. [Google Scholar]
- Kang, S. The Mechanism of Action of Topical Retinoids. Cutis 2005, 75, 10–13; discussion 13. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.-Y. Mechanism of Action of All-Trans Retinoic Acid and Arsenic Trioxide in the Treatment of Acute Promyelocytic Leukemia. Gan Kagaku Ryoho 2002, 29, 214–218. [Google Scholar]
- Sitohang, I.B.S.; Makes, W.I.; Sandora, N.; Suryanegara, J. Topical Tretinoin for Treating Photoaging: A Systematic Review of Randomized Controlled Trials. Int. J. Women’s Dermatol. 2022, 8, e003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mambwe, B.; Mellody, K.T.; Kiss, O.; O’Connor, C.; Bell, M.; Watson, R.E.B.; Langton, A.K. Cosmetic retinoid use in photoaged skin: A review of the compounds, their use and mechanisms of action. Int. J. Cosmet. Sci. 2025, 47, 45–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saleem, R.; Rehman, M.; Ahmed Khan, T.; Khalid, Q.; Ahmad, A.; Awais, M.; Ahmad, A.; Ijaz, S. Tretinoin loaded NLCs-based sunscreen cream; preparation and characterization. Pak. J. Pharm. Sci. 2025, 38, 315–323. [Google Scholar]
- Del Rosso, J.Q. Status Report on Oral Isotretinoin in the Management of Acne Vulgaris: Why All the Discussion about Drug Absorption and Relapse Rates? Curr. Dermatol. Rep. 2013, 2, 177–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Tolino, E.; Skroza, N.; Proietti, I.; Mambrin, A.; Balduzzi, V.; Marchesiello, A.; Maddalena, P.; Michelini, S.; Volpe, S.; Bernardini, N.; et al. Efficacy and Safety of Systemic Isotretinoin Treatment for Moderate to Severe Acne (Insights from the Real-life Clinical Setting). Dermatol. Ther. 2020, 33, e14392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saadet, E.D. Investigation of Relapse Rate and Factors Affecting Relapse after Oral Isotretinoin Treatment in Patients with Acne Vulgaris. Dermatol. Ther. 2021, 34, e15109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zaenglein, A.L.; Pathy, A.L.; Schlosser, B.J.; Alikhan, A.; Baldwin, H.E.; Berson, D.S.; Bowe, W.P.; Graber, E.M.; Harper, J.C.; Kang, S.; et al. Guidelines of Care for the Management of Acne Vulgaris. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2016, 74, 945–973.e33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- On, S.C.J.; Zeichner, J. Isotretinoin Updates. Dermatol. Ther. 2013, 26, 377–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagatin, E.; Costa, C.S.; da Rocha, M.A.D.; Picosse, F.R.; Kamamoto, C.S.L.; Pirmez, R.; Ianhez, M.; Miot, H.A. Consensus on the Use of Oral Isotretinoin in Dermatology-Brazilian Society of Dermatology. An. Bras. Dermatol. 2020, 95, 19–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dispenza, M.C.; Wolpert, E.B.; Gilliland, K.L.; Dai, J.P.; Cong, Z.; Nelson, A.M.; Thiboutot, D.M. Systemic Isotretinoin Therapy Normalizes Exaggerated TLR-2-Mediated Innate Immune Responses in Acne Patients. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2012, 132, 2198–2205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sami, N. Topical Retinoids. In Comprehensive Dermatologic Drug Therapy; Harper, J.C., Wolverton, S.E., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2007; pp. 625–641. [Google Scholar]
- Werner, B.; Bresch, M.; Brenner, F.M.; Lima, H.C. Comparative Study of Histopathological and Immunohistochemical Findings in Skin Biopsies from Patients with Psoriasis Before and After Treatment with Acitretin. J. Cutan. Pathol. 2007, 35, 302–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bissonnette, R.; Diepgen, T.L.; Elsner, P.; English, J.; Graham-Brown, R.; Homey, B.; Luger, T.; Lynde, C.; Maares, J.; Maibach, H.I. Redefining Treatment Options in Chronic Hand Eczema (CHE). J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2010, 24, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, C.; Michaels, J.; Scheinfeld, N. Alitretinoin: A Comprehensive Review. Expert Opin. Investig. Drugs 2008, 17, 437–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molin, S.; Ruzicka, T. Alitretinoin. Der Hautarzt 2008, 59, 703–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bodsworth, N.J.; Bloch, M.; Bower, M.; Donnell, D.; Yocum, R. Phase III Vehicle-Controlled, Multi-Centered Study of Topical Alitretinoin Gel 0.1% in Cutaneous AIDS-Related Kaposi’s Sarcoma. Am. J. Clin. Dermatol. 2001, 2, 77–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bouvy, M.L.; Sturkenboom, M.C.; Cornel, M.C.; de Jong-van den Berg, L.T.W.; Stricker, B.H.C.; Wesseling, H. Acitretin (Neotigason®). Pharm. Weekbl. 1992, 14, 33–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sturkenboom, M.; de Jong-Van den Berg, L.; van Voorst-Vader, P.; Cornel, M.; Stricker, B.; Wesseling, H. Inability to Detect Plasma Etretinate and Acitretin Is a Poor Predictor of the Absence of These Teratogens in Tissue after Stopping Acitretin Treatment. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 1994, 38, 229–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katugampola, R.P.; Finlay, A.Y. Oral Retinoid Therapy for Disorders of Keratinization: Single-Centre Retrospective 25 Years’ Experience on 23 Patients. Br. J. Dermatol. 2005, 154, 267–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meyer, E.; de Bersaques, J.; Lambert, W.E.; de Leenheer, A.P.; Kint, A.H. Skin, Adipose Tissue and Plasma Levels of Acitretin with Rare Occurrence of Esterified Acitretin during Long/Term Treatment. Acta Derm. Venereol. 1993, 73, 113–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, W.; Peng, C.; Zhu, W.; Chen, X. Polymorphisms of SLCO1B1 Rs4149056 and SLC22A1 Rs2282143 Are Associated with Responsiveness to Acitretin in Psoriasis Patients. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 13182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guenther, L.C.; Kunynetz, R.; Lynde, C.W.; Sibbald, R.G.; Toole, J.; Vender, R.; Zip, C. Acitretin Use in Dermatology. J. Cutan. Med. Surg. 2017, 21, 2S–12S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zito, P.M.; Patel, P.; Mazzoni, T. Acitretin. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK519571/ (accessed on 1 April 2025).
- Larsen, F.G.; Steinkjer, B.; Jakobsen, P.; Hjorter, A.; Brockhoff, P.B.; Nielsen-Kudsk, F. Acitretin Is Converted to Etretinate Only during Concomitant Alcohol Intake. Br. J. Dermatol. 2000, 143, 1164–1169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, J.H.; Hyun, G.H.; Park, Y.J.; Kwon, S.W.; Lee, A.-Y. Clinical Factors Affecting the Serum Retention of a Teratogenic Etretinate After the Acitretin Administration. Biomol. Ther. 2022, 30, 562–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ighani, A.; Partridge, A.C.R.; Shear, N.H.; Lynde, C.; Gulliver, W.P.; Sibbald, C.; Fleming, P. Comparison of Management Guidelines for Moderate-to-Severe Plaque Psoriasis: A Review of Phototherapy, Systemic Therapies, and Biologic Agents. J. Cutan. Med. Surg. 2018, 23, 204–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaushik, S.B.; Lebwohl, M.G. Review of Safety and Efficacy of Approved Systemic Psoriasis Therapies. Int. J. Dermatol. 2018, 58, 649–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paichitrojjana, A.; Paichitrojjana, A. Oral Isotretinoin and Its Uses in Dermatology: A Review. Drug Des. Dev. Ther. 2023, 17, 2573–2591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bubna, A. Alitretinoin in Dermatology—An Update. Indian. J. Dermatol. 2015, 60, 520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Vašková, J.; Stupák, M.; Vidová Ugurbaş, M.; Židzik, J.; Mičková, H. Therapeutic Uses of Retinol and Retinoid-Related Antioxidants. Molecules 2025, 30, 2191. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30102191
Vašková J, Stupák M, Vidová Ugurbaş M, Židzik J, Mičková H. Therapeutic Uses of Retinol and Retinoid-Related Antioxidants. Molecules. 2025; 30(10):2191. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30102191
Chicago/Turabian StyleVašková, Janka, Marek Stupák, Martina Vidová Ugurbaş, Jozef Židzik, and Helena Mičková. 2025. "Therapeutic Uses of Retinol and Retinoid-Related Antioxidants" Molecules 30, no. 10: 2191. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30102191
APA StyleVašková, J., Stupák, M., Vidová Ugurbaş, M., Židzik, J., & Mičková, H. (2025). Therapeutic Uses of Retinol and Retinoid-Related Antioxidants. Molecules, 30(10), 2191. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30102191