Research Progress of Bioactive Components in Sanghuangporus spp.
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Phylogenetic Progress
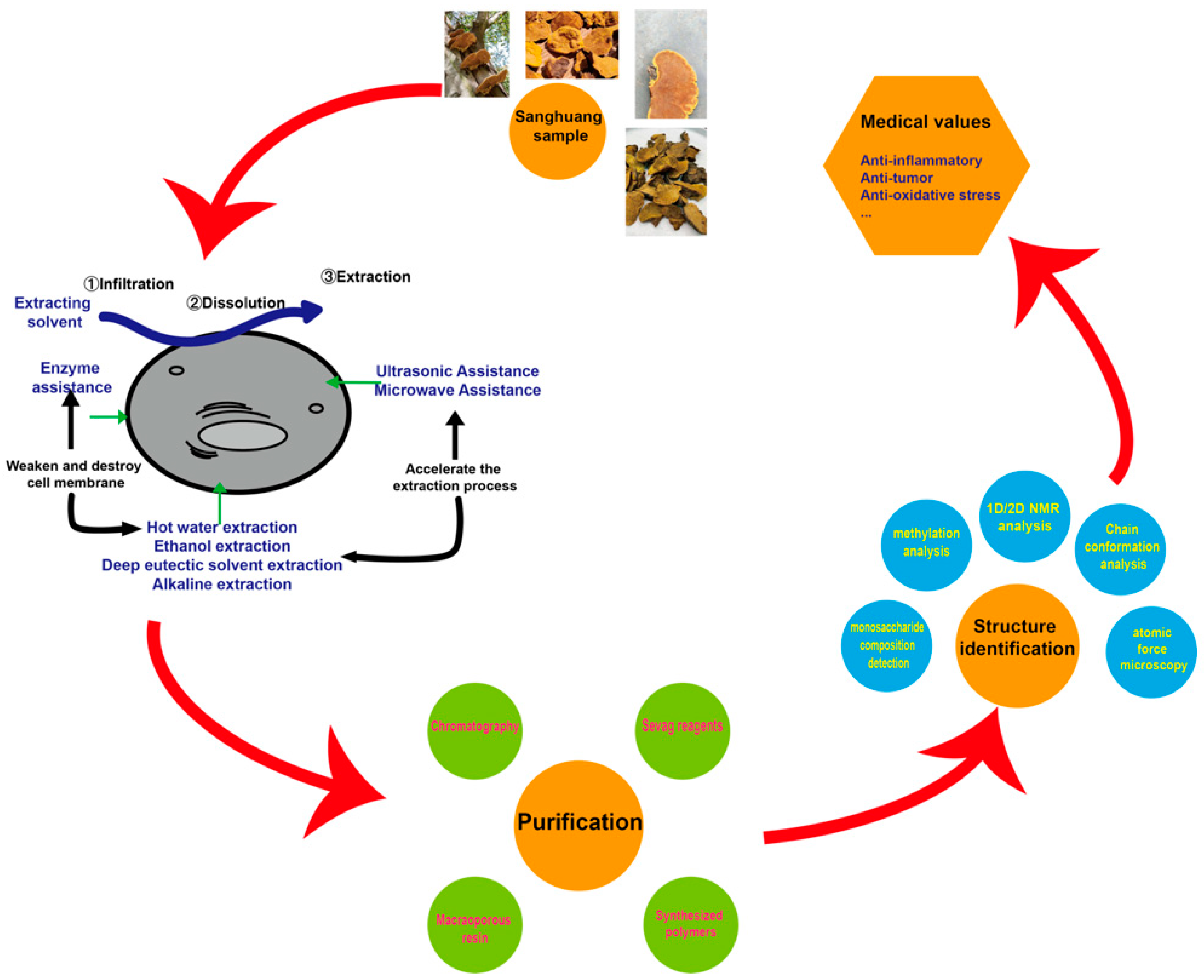
3. Extraction Methods
3.1. Hot Water Extraction
3.2. Ethanol Extraction
3.3. Deep Eutectic Solvent Extraction
3.4. Alkaline Extraction Methods
| Extraction Method | Material | Product | Purification Method | Optimized Condition | Final Yield | Reference | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Extraction Time | Liquid–Solid Ratio | Temperature/Power | ||||||
| Ethanol precipitation | Liquid culture broth | 4 Exopolysaccharides | DEAE-Sepharose Fast Flow column Sephacryl S-100 HR gel column | - | - | - | 11.77% 55.36% 17.12% 15.75% | [48] |
| Boiling water | Dried fruiting body | Polysaccharide and Polyphenol | - | - | - | - | 5.51% 23.00% | [4] |
| Boiling water | Fruiting body | Polysaccharide | - | 2.26 h | 21.61:1 mL/g | 99.24 °C | 9.40% | [22] |
| Boiling water | Mycelium | Polysaccharide | - | 2.5 h | 14:1 mL/g | 60 °C | 4.91% | [99] |
| Boiling water | Sanghuang powder | Polysaccharide | - | 8 h | 18:1 mL/g | 90 °C | 2.12% | [96] |
| Boiling water | Mycelium | Polysaccharide | - | 3.5 h | 45:1 mL/g | 100 °C | 3.99% | [100] |
| Boiling water | Fruiting body powder | Polysaccharide | DEAE-Sepharose Fast Flow column Sephacryl S-400 column Sephacryl S-200 column | 4.35 h | 26:1 mL/g | 100 °C | - | [106] |
| Ultrasonication | Mycelium powder | Polysaccharide | - | 30 min | 40:1 mL/g | 45 °C/120 W | 10.73% | [39] |
| Triterpenoid | - | 25 min | 50:1 mL/g | 45 °C/150 W | 1.51% | |||
| Ultrasonication | Mycelium powder | Polysaccharide | - | 260 s | 49:1 mL/g | 464 W | 13.19% | [36] |
| Ultrasonication | Dried fruiting body | Polysaccharide | - | 32.7 min | 32.5:1 mL/g | 360 W | 3.46% | [97] |
| Ethanol extraction | Mycelia and broth of S. sanghuang | 8 sesquiterpenoids and 6 polyphenols | Sephadex 200 column | - | - | - | - | [101] |
| Ethanol extraction and ultrasonication | Sanghuang powder | Flavonoid and polyphenol | - | 30 min | - | - | (10.18 ± 0.85)% (13.58 ± 1.33)% (14.62 ± 1.05)% (15.38 ± 0.76)% | [21] |
| Ultrasonication | S. baumii powder | Flavonoid and polyphenol | Macroporous membrane | 30 min | - | - | - | [28] |
| Ethanol extraction | Fermented broth of S. lonicericola | Polysaccharopeptide | DEAE exchange column | 24 h | - | - | 23.00% | [9] |
| Ethanol extraction | Mycelia of S. sanghuang | Triterpenoids | - | 20 min | - | 60 °C | 13.30% | [37] |
| DES extraction | Dried fruiting bodies of S. baumii | Phenolics | - | 42 min | 34:1 mL/mg | 58 °C | 12.58% | [35] |
| DES extraction | Fruiting body | Polyphenols | - | 21 min | 260:1 mL/g | 80 °C | (12.45 ± 1.88)% | [43] |
4. Purification Methods
4.1. Traditional Methods
4.2. Macroporous Resin Methods
4.3. Molecular Imprinting Technology
5. Conformational Properties of Sanghuang Polysaccharides

6. Medical Properties of the Sanghuang Species
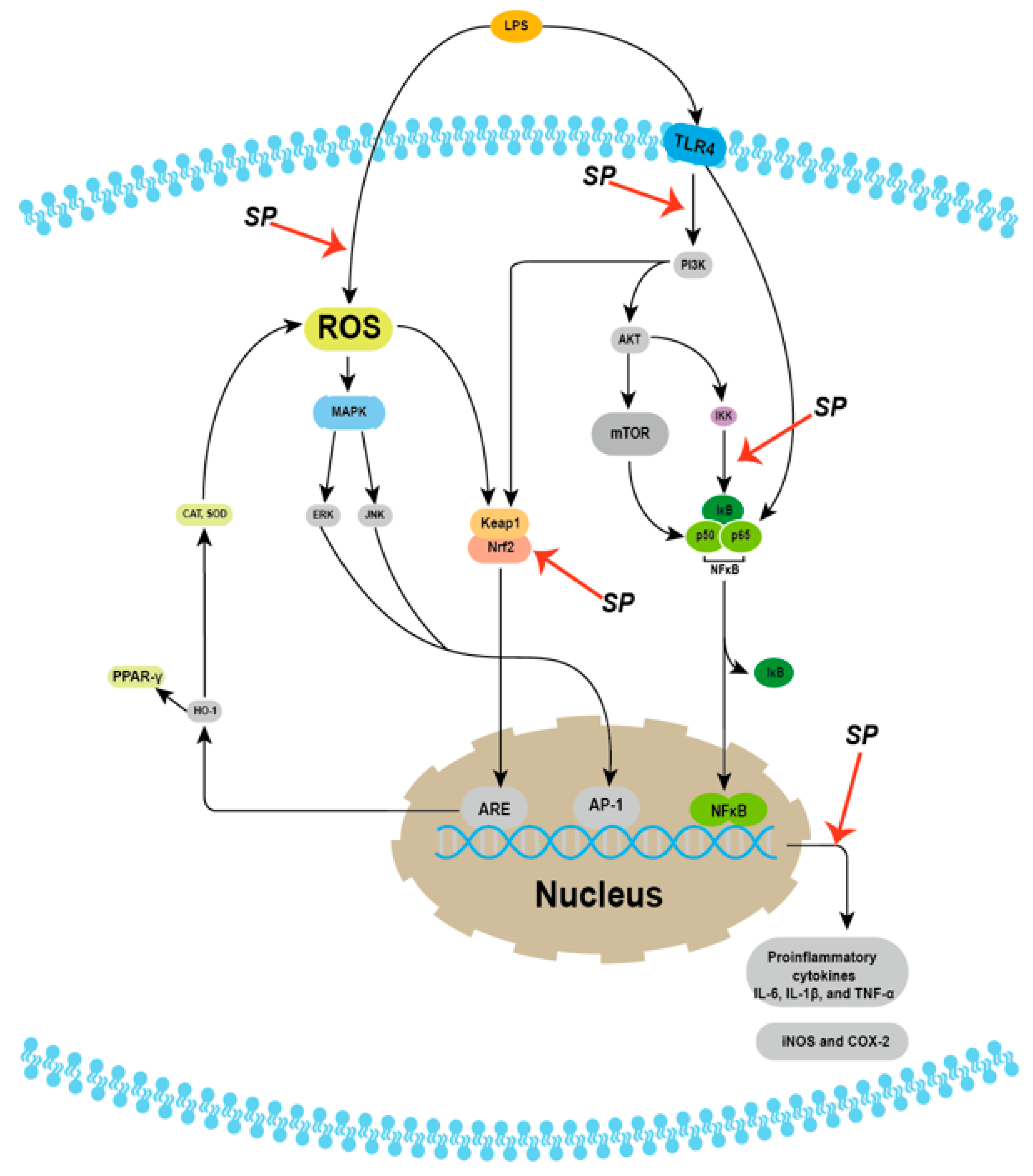
6.1. Anti-Inflammatory Effects
6.2. Antioxidant Effects
6.3. Antitumor Effects
6.4. Immunoregulation Effects
6.5. Antimicrobial Effects
7. Health-Improving Effects
7.1. Pulmonary Protection Effects
7.2. Hypoglycemia- and Diabetes-Mitigating Effects
7.3. Sleep-Improving Effects
7.4. Gout-Mitigating Effects
7.5. Antiaging Effects
7.6. Neuroprotective Effects
7.7. Effects on Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19)
7.8. Muscle Strengthening Effect
8. Toxicity Studies
9. Potential to Be Functional Food
10. Conclusions and Perspectives
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| DPPH | 2,2-diphenyl-1-picrylhydrazyl |
| ABTS | 2,2′-azino-bis |
| IR | infrared |
| AFM | atomic force microscopy |
| ITS | internal transcribed spacer |
| IBD | inflammatory bowel disease |
| FTRI | Fourier transform infrared spectrometry |
| DES | Deep eutectic solvent |
| DEAE | diethylaminoethanol |
| PLA | Phelligridin LA |
| MIPs | molecular imprinting polymers |
| MMIPs | magnetic molecularly imprinted polymers |
| VTES | Vinyltriethoxysilane |
| Fe3O4 NPs | Fe3O4 nanoparticles |
| ROS | oxygen species |
| CAT | catalase |
| SOD | superoxide dismutase |
| TEAC | Trolox equivalent antioxidant |
| T-AOC | total antioxidant capacity |
| POD | peroxidase |
| LPS | lipopolysaccharide |
| CTX | cyclophosphamide |
| IKK | IκB kinase |
| KAP1 | Kruppel-associated box (KRAB)-associated protein 1 |
| RA | Rheumatoid Arthritis |
| Vc | vitamin C |
| BHT | butylated hydroxytoluene |
| CDK | cyclin-dependent kinase |
References
- Wang, H.; Ma, J.X.; Zhou, M.; Si, J.; Cui, B.K. Current advances and potential trends of the polysaccharides derived from medicinal mushrooms sanghuang. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 965934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, S.; Duan, W.; Wang, Y.; Chen, L.; Yang, C.; Gu, X.; Xue, Q.; Li, R.; Zhang, Z. Component Analysis and Anti-Colorectal Cancer Mechanism via AKT/mTOR Signalling Pathway of Sanghuangporus vaninii Extracts. Molecules 2022, 27, 1153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, I.C.; Chang, F.C.; Kuo, C.C.; Chu, H.T.; Li, T.J.; Chen, C.C. Pilot Study: Nutritional and Preclinical Safety Investigation of Fermented Hispidin-Enriched Sanghuangporus sanghuang Mycelia: A Promising Functional Food Material to Improve Sleep. Front. Nutr. 2021, 8, 788965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, T.; Zhong, S.; Sun, Y.; Sun, H.; Chen, W.; Li, Y.; Zhu, J.; Lu, L.; Huo, J. Aqueous extracts of Sanghuangporus vaninii induce S-phase arrest and apoptosis in human melanoma A375 cells. Oncol. Lett. 2021, 22, 628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.K.; She, X.; Peterson, E.C.; Wang, Y.Z.; Zheng, P.; Ma, H.; Zhang, K.; Liang, J. A newly characterized exopolysaccharide from Sanghuangporus sanghuang. J. Microbiol. 2019, 57, 812–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Q.; Wang, J.; Jiang, H.; Wang, G.; Wang, Y. Deep sequencing of the Sanghuangporus vaninii transcriptome reveals dynamic landscapes of candidate genes involved in the biosynthesis of active compounds. Arch. Microbiol. 2021, 203, 2315–2324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, J.G.; Hyun, M.W.; Kim, C.S.; Jo, J.W.; Cho, J.H.; Lee, K.H.; Kong, W.S.; Han, S.K.; Oh, J.; Sung, G.H. Species identity of Phellinus linteus (sanghuang) extensively used as a medicinal mushroom in Korea. J. Microbiol. 2016, 54, 290–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, T.; Xu, F.; Shen, Y.; Fan, L.; Cai, W. The complete mitochondrial genome of Sanghuangporus vaninii Zhehuang-1 (Hymenochaetales, Basidiomycota). Mitochondrial DNA B Resour. 2021, 6, 1096–1097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zuo, K.; Tang, K.; Liang, Y.; Xu, Y.; Sheng, K.; Kong, X.; Wang, J.; Zhu, F.; Zha, X.; Wang, Y. Purification and antioxidant and anti-Inflammatory activity of extracellular polysaccharopeptide from sanghuang mushroom, Sanghuangporus lonicericola. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2021, 101, 1009–1020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kozarski, M.; Klaus, A.; Niksic, M.; Jakovljevic, D.; Helsper, J.P.F.G.; Van Griensven, L.J.L.D. Antioxidative and immunomodulating activities of polysaccharide extracts of the medicinal mushrooms Agaricus bisporus, Agaricus brasiliensis, Ganoderma lucidum and Phellinus linteus. Food Chem. 2011, 129, 1667–1675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Yang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Zhou, S.; Yan, M.Q.; Wu, D.; Zhang, J.; Tang, C. Physicochemical characteristics and biological activities of polysaccharide fractions from Phellinus baumii cultured with different methods. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2015, 81, 1082–1088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, W.C.; Deng, J.S.; Huang, S.S.; Wu, S.H.; Chen, C.C.; Lin, W.R.; Lin, H.Y.; Huang, G.J. Anti-Inflammatory Activity of Sanghuangporus sanghuang Mycelium. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, W.-C.; Deng, J.-S.; Huang, S.-S.; Lin, W.-R.; Wu, S.-H.; Lin, H.-Y.; Huang, G.-J. Anti-inflammatory activity of Sanghuangporus sanghuang by suppressing the TLR4-mediated PI3K/AKT/mTOR/IKKβ signaling pathway. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 21234–21251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, Y.; Wan, Y.Z.; Qiao, C.X.; Xu, X.F.; Wang, J.; Shen, Y. Immunoregenerative effects of the bionically cultured Sanghuang mushrooms (Inonotus sanghuagn) on the immunodeficient mice. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2019, 245, 112047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huo, J.; Sun, Y.; Pan, M.; Ma, H.; Lin, T.; Lv, Z.; Li, Y.; Zhong, S. Non-targeted metabonomics and transcriptomics revealed the mechanism of mulberry branch extracts promoting the growth of Sanghuangporus vaninii mycelium. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 1024987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Z.; Liu, R.; Tong, X.; Zou, L. New Insights into Methyl Jasmonate Regulation of Triterpenoid Biosynthesis in Medicinal Fungal Species Sanghuangporus baumii (Pilat) L.W. Zhou & Y.C. Dai. J. Fungi 2022, 8, 889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Gao, W.; Zhang, F.; Zhu, X.; Kong, W.; Niu, S.; Gao, K.; Yang, H. Community composition and trophic mode diversity of fungi associated with fruiting body of medicinal Sanghuangporus vaninii. BMC Microbiol. 2022, 22, 251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, M.; Xie, Y.; Su, X.; Liu, K.; Zhang, Y.; Pang, W.; Wang, J. Inonotus sanghuang Polyphenols Attenuate Inflammatory Response Via Modulating the Crosstalk Between Macrophages and Adipocytes. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, S.; Jin, L.; Lei, P.; Shao, C.; Wu, S.; Yang, Y.; He, Y.; Ren, R.; Xu, J. Whole-genome assembly and analysis of a medicinal fungus: Inonotus hispidus. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 967135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, P.Y.; Hou, Y.H.; Yang, Y.; Li, N. The anticancer effect of extract of medicinal mushroom Sanghuangprous vaninii against human cervical cancer cell via endoplasmic reticulum stress-mitochondrial apoptotic pathway. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2021, 279, 114345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyu, G.; Song, T.; Cai, W.; Zhang, Z. Comparative study of chemical components and antioxidant activities of wild Sanghuangporus sanghuang and Sanghuangporus vaninii. Mycosystema 2021, 40, 1833–1843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, M.; Fu, T.; Xu, C.; Chen, A.; Shao, Y. The Optimum Extracting Technology and Antioxidant Activity of Polysaccharides from Fruiting Body of Phellinus igniarius. Food Ind. 2021, 42, 103–108. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.; Xie, Y.; Wang, H.; Li, J.; Liu, J.; Hu, L.; Wang, S. Comparison of chemical constituents and antioxidant activities of Sanghuangporus vaninii in different substrates. J. Food Saf. Qual. 2021, 12, 9183–9188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huo, J.; Sun, Y.; Zhong, S.; Li, Y.; Yang, R.; Xia, L.; Wang, J.; Zhang, M.; Zhu, J. Safety evaluation of aqueous extracts of Sanghuangporus vaninii fruiting body in Sprague-Dawley rats. Food Sci. Nutr. 2020, 8, 5107–5113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, T.; Zhang, Z.; Jin, Q.; Feng, W.; Shen, Y.; Fan, L.; Cai, W. Nutrient profiles, functional compositions, and antioxidant activities of seven types of grain fermented with Sanghuangporus sanghuang fungus. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 58, 4091–4101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, I.C.; Chen, C.C.; Sheu, S.J.; Huang, I.H.; Chen, C.C. Optimized production and safety evaluation of hispidin-enriched Sanghuangporus sanghuang mycelia. Food Sci. Nutr. 2020, 8, 1864–1873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, Y.; Yang, C.; Liu, X.; Wang, G.; Xiong, Z.; Song, X.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, H.; Ai, L. Enhancement of triterpene production via in situ extractive fermentation of Sanghuangporus vaninii YC-1. Biotechnol. Appl. Biochem. 2021, 69, 2561–2572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, Q.H.; Huang, Q.; Xie, J.Y.; Wang, K.; Qian, Z.M.; Li, D.Q. A rapid analysis of antioxidants in Sanghuangporus baumii by online extraction-HPLC-ABTS. RSC Adv. 2021, 11, 25646–25652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, X.; Liu, K.; Xie, Y.; Zhang, M.; Wu, X.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, J. Mushroom Inonotus sanghuang alleviates experimental pulmonary fibrosis: Implications for therapy of pulmonary fibrosis. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2021, 133, 110919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Q.; Zhao, L.; Zhu, Y.; Wu, J.; Hao, C.; Song, S.; Shi, W. Optimization of culture medium for Sanghuangporus vaninii and a study on its therapeutic effects on gout. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2021, 135, 111194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Mo, J.; Pan, D.; Liu, G. Research Progress on Pharmacological Actions and Extraction Methods of Polysaccharide from Phellinus igniarius. Biotechnol. Bull. 2018, 34, 63–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Gao, D.; Paudel, Y.N.; Li, X.; Zheng, M.; Liu, G.; Ma, Y.; Chu, L.; He, F.; Jin, M. Anti-Parkinson’s Disease Activity of Sanghuangprous vaninii Extracts in the MPTP-Induced Zebrafish Model. ACS Chem. Neurosci. 2022, 13, 330–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, J.H.; Wu, S.H.; Zhou, L.W. The First Whole Genome Sequencing of Sanghuangporus sanghuang Provides Insights into Its Medicinal Application and Evolution. J. Fungi 2021, 7, 787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, K.; Zhang, S.; Geng, Y.; Tian, B.; Cai, M.; Guan, R.; Li, Y.; Ye, B.; Sun, P. Anti-Inflammatory Properties In Vitro and Hypoglycaemic Effects of Phenolics from Cultivated Fruit Body of Phellinus baumii in Type 2 Diabetic Mice. Molecules 2021, 26, 2285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, N.; Ming, Y.; Chu, J.; Yang, S.; Wu, G.; Li, W.; Zhang, R.; Cheng, X. Optimization of Extraction Process and the Antioxidant Activity of Phenolics from Sanghuangporus baumii. Molecules 2021, 26, 3850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Xu, J.; Yang, J.; He, K.; Li, Y.; Duan, Y. Progresses on the effects of Phellinus linteus on tumors. Jiangsu Sci. Technol. Inf. 2021, 38, 60–64. [Google Scholar]
- Cai, C.; Ma, J.; Han, C.; Jin, Y.; Zhao, G.; He, X. Extraction and antioxidant activity of total triterpenoids in the mycelium of a medicinal fungus, Sanghuangporus sanghuang. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 7418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, S.; Bao, H.; Wei, Y.; Liu, Y.; Liu, J. Antitumor effect and mechanism of different extracts of cultivated Phellinus vaninii on H22 tumor bearing mice. Chin. J. Biotech. 2022, 38, 1025–1038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, D.; Ma, H.; Cao, Y.; Wang, W.; Wang, Y.; Wang, W. Ultrasonic wave–assisted Extraction of Active Substances from Phellinus igniarius. J. Chin. Inst. Food Sci. Technol. 2015, 15, 87–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, W.-C.; Deng, J.-S.; Huang, S.-S.; Wu, S.-H.; Lin, H.-Y.; Huang, G.-J. Evaluation of antioxidant, anti-inflammatory and anti-proliferative activities of ethanol extracts from different varieties of Sanghuang species. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 7780–7788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, M.; Park, H.J. Anti-inflammatory effect of Phellinus linteus grown on germinated brown rice on dextran sodium sulfate-induced acute colitis in mice and LPS-activated macrophages. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2014, 154, 311–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chien, L.H.; Deng, J.S.; Jiang, W.P.; Chen, C.C.; Chou, Y.N.; Lin, J.G.; Huang, G.J. Study on the potential of Sanghuangporus sanghuang and its components as COVID-19 spike protein receptor binding domain inhibitors. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2022, 153, 113434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Song, T.; Chen, C.; Cai, W.; Lyu, G. Optimization of extraction process and examination of antioxidant activities of polyphenols extracted from Sanghuangporus vaninii by using deep eutectic solvent. Mycosystema 2022, 41, 1694–1703. [Google Scholar]
- Yuan, W.; Zhou, R.; Sun, M.; Yang, H.; Lu, T.; Zhao, Y.; Zheng, W. Effects of nitric oxide on the accumulation of polyphenols and triterpenoids in the submerged cultures of Sanghuangporus vaninii. Mycosystema 2023, 42, 932–938. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, K.; Ding, Z.; Pei, J.; Yan, J. Antioxidant Activities of Polysaccharides from Phellinus linteus Mycelia by Alkaline Extraction. Sci. Technol. Food Ind. 2020, 41, 289–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Wang, Y.; Xia, J.; Luo, D.; Wang, T. Optimization of Extraction Process of Polysaccharide of Phellinus igniarius Mycelium and Analysis of Its Antioxidant Activity in vitro. Chin. Agric. Sci. Bull. 2019, 35, 143–150. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, J.; Song, J.; Wei, H.; Wang, Y.; Huang, X.; Liu, Y.; Lu, N.; He, L.; Lv, G.; Ding, H.; et al. Structural characterization and hypoglycemic activity of an intracellular polysaccharide from Sanghuangporus sanghuang mycelia. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 164, 3305–3314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, J.; Song, J.; Liu, Y.; Lu, N.; Wang, Y.; Hu, C.; He, L.; Wei, H.; Lv, G.; Yang, S.; et al. Conformational properties and biological activities of alpha-D-mannan from Sanghuangporus sanghuang in liquid culture. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 164, 3568–3579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, X.; Jin, X.; Xie, M.; Liu, J.; Gontcharov, A.A.; Wang, H.; Lv, R.; Liu, D.; Wang, Q.; Li, Y. Characterization of a polysaccharide from Sanghuangporus vaninii and its antitumor regulation via activation of the p53 signaling pathway in breast cancer MCF-7 cells. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 163, 865–877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Tian, T.; Miao, H.; Zhao, Y.Y. Traditional uses, fermentation, phytochemistry and pharmacology of Phellinus linteus: A review. Fitoterapia 2016, 113, 6–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Liu, Z.; Wang, X.; Liu, R.; Zou, L. Mushrooms Do Produce Flavonoids: Metabolite Profiling and Transcriptome Analysis of Flavonoid Synthesis in the Medicinal Mushroom Sanghuangporus baumii. J. Fungi 2022, 8, 582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, Y.; Han, H.; Qi, J.; Gao, J.M.; Xu, Z.; Wang, P.; Zhang, J.; Liu, C. Genome sequencing of Inonotus obliquus reveals insights into candidate genes involved in secondary metabolite biosynthesis. BMC Genom. 2022, 23, 314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, T.; Wang, G.; Zhang, G.; Hou, R.; Zhou, L.; Tian, X. Systematic analysis of the lysine malonylome in Sanghuangporus sanghuang. BMC Genom. 2021, 22, 840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Wang, S.; Xu, X.; Sun, J.; Ma, Y.; Liu, Z.; Sun, T.; Zou, L. Molecular cloning, characterization, and heterologous expression of an acetyl-CoA acetyl transferase gene from Sanghuangporus baumii. Protein Expr. Purif. 2020, 170, 105592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wan, X.; Jin, X.; Wu, X.; Yang, X.; Lin, D.; Li, C.; Fu, Y.; Liu, Y.; Liu, X.; Lv, J.; et al. Structural characterisation and antitumor activity against non-small cell lung cancer of polysaccharides from Sanghuangporus vaninii. Carbohydr. Polym. 2022, 276, 118798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, G.-Y.; Park, S.-K.; Lee, M.-K.; Lee, S.-H.; Oh, Y.-H.; Kwak, J.-Y.; Yoon, S.; Lee, J.-D.; Park, Y.-M. Proteoglycan isolated from Phellinus linteus activates murine B lymphocytes via protein kinase C and protein tyrosine kinase. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2003, 3, 1281–1292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, J.; He, R.; Sun, P.; Zhang, F.; Linhardt, R.J.; Zhang, A. Molecular mechanisms of bioactive polysaccharides from Ganoderma lucidum (Lingzhi), a review. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 150, 765–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qu, J.; Huang, P.; Zhang, L.; Qiu, Y.; Qi, H.; Leng, A.; Shang, D. Hepatoprotective effect of plant polysaccharides from natural resources: A review of the mechanisms and structure-activity relationship. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 161, 24–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shon, Y.H.; Nam, K.S. Inhibition of cytochrome P450 isozymes in rat liver microsomes by polysaccharides derived from Phellinus linteus. Biotechnol. Lett. 2003, 25, 167–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, F.; Xiang, R.; Jing, L.; Chen, M.; Guo, W.; Zhang, C.; Jiang, F. Research Progresses of the Hypolipidemic and Antioxidant Effects of Phellinus fungi. J. Chin. Med. Mater. 2018, 41, 2721–2725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.; Liu, X.; Li, Y.; Ji, H.; Liu, C.; Zhou, L.; Huang, Y.; Bai, C.; Jiang, Z.; Wu, X. Screening for proteins related to the biosynthesis of hispidin and its derivatives in Phellinus igniarius using iTRAQ proteomic analysis. BMC Microbiol. 2021, 21, 81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, J.S.; Lee, J.S.; Lee, J.H.; Kwon, D.S.; Lee, K.E.; Lee, S.Y.; Hong, E.K. Hispidin produced from Phellinus linteus protects pancreatic beta-cells from damage by hydrogen peroxide. Arch. Pharm. Res. 2010, 33, 853–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, I.-H.; Chung, S.-K.; Lee, K.-B.; Yoo, Y.-C.; Kim, S.-K.; Kim, G.-S.; Song, K.-S. An antioxidant hispidin from the mycelial cultures of Phellinus linteus. Arch. Pharmacal Res. 2004, 27, 615–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, W.; Luo, Y.; Xie, Z.; Kong, C.; Na, Z. Extraction and detection of morin from Sanghuangporus lonicericola by magnetic molecularly imprinted polymers coupled with HPLC analysis. J. Food Sci. 2022, 87, 1575–1585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajput, S.A.; Wang, X.Q.; Yan, H.C. Morin hydrate: A comprehensive review on novel natural dietary bioactive compound with versatile biological and pharmacological potential. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2021, 138, 111511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heo, Y.M.; Kim, K.; Kwon, S.L.; Na, J.; Lee, H.; Jang, S.; Kim, C.H.; Jung, J.; Kim, J.J. Investigation of Filamentous Fungi Producing Safe, Functional Water-Soluble Pigments. Mycobiology 2018, 46, 269–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, H.; Pan, J.; Guo, M.; Li, J.; Yu, L.; Fan, L. Dietary strategies with anti-aging potential: Dietary patterns and supplements. Food Res. Int. 2022, 158, 111501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Atlante, A.; Amadoro, G.; Bobba, A.; Latina, V. Functional Foods: An Approach to Modulate Molecular Mechanisms of Alzheimer’s Disease. Cells 2020, 9, 2347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Serafini, M.; Peluso, I. Functional Foods for Health: The Interrelated Antioxidant and Anti-Inflammatory Role of Fruits, Vegetables, Herbs, Spices and Cocoa in Humans. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2017, 22, 6701–6715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaturvedi, V.K.; Agarwal, S.; Gupta, K.K.; Ramteke, P.W.; Singh, M.P. Medicinal mushroom: Boon for therapeutic applications. 3 Biotech 2018, 8, 334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, J.; Ali, L.; Khan, A.L.; Rehman, N.U.; Jabeen, F.; Kim, J.S.; Al-Harrasi, A. Isolation and bioactivities of the flavonoids morin and morin-3-O-β-D-glucopyranoside from Acridocarpus orientalis—A wild Arabian medicinal plant. Molecules 2014, 19, 17763–17772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Zeng, J. Research Progress on Chemical Constituents of Phellinus and Its Antitumor Mechanism. Chin. J. Exp. Tradit. Med. Formulae 2023, 29, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Song, J.; Yan, J.; Lu, N.; Fu, L.; Yuan, W.; Zhou, Z. Effects of harvest time on content of active components and antioxidant activities of fruiting bodies of Sanghuangporus cultivated with substitute materials. Mycosystema 2020, 39, 2369–2379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, J.G.; Oh, J.; Jo, J.W.; Kim, C.S.; Kwag, Y.N.; Han, S.K.; Sung, G.H. The complete mitochondrial genome of Sanghuangporus sanghuang (Hymenochaetaceae, Basidiomycota). Mitochondrial DNA B Resour. 2018, 3, 456–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, Y.W.; Lee, J.S.; Jung, H.S. Type studies on Phellinus baumii and Phellinus linteus. Mycotaxon 2003, 85, 201–210. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, L.-W.; Vlasák, J.; Decock, C.; Assefa, A.; Stenlid, J.; Abate, D.; Wu, S.-H.; Dai, Y.-C. Global diversity and taxonomy of the Inonotus linteus complex (Hymenochaetales, Basidiomycota): Sanghuangporus gen. nov., Tropicoporus excentrodendri and T. guanacastensis gen. et spp. nov., and 17 new combinations. Fungal Divers. 2015, 77, 335–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.J.; Gao, W.Q.; Zhu, X.T.; Kong, W.B.; Zhang, F.; Yang, H.Q. Identification and profiling of the community structure and potential function of bacteria from the fruiting bodies of Sanghuangporus vaninii. Arch. Microbiol. 2022, 204, 564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, T.; Chepkirui, C.; Decock, C.; Matasyoh, J.C.; Stadler, M. Sesquiterpenes from an Eastern African Medicinal Mushroom Belonging to the Genus Sanghuangporus. J. Nat. Prod. 2019, 82, 1283–1291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agnestisia, R.; Ono, A.; Nakamura, L.; Chino, R.; Nodera, K.; Aiso-Sanada, H.; Nezu, I.; Ishiguri, F.; Suzuki, T.; Yokota, S. The complete mitochondrial genome sequence of the medicinal fungus Inonotus obliquus (Hymenochaetaceae, Basidiomycota). Mitochondrial DNA B Resour. 2019, 4, 3504–3506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, S.; Liu, S.L.; Jiang, J.H.; Zhou, L.W. Addressing widespread misidentifications of traditional medicinal mushrooms in Sanghuangporus (Basidiomycota) through ITS barcoding and designation of reference sequences. IMA Fungus 2021, 12, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, S.H.; Chang, C.C.; Wei, C.L.; Jiang, G.Z.; Cui, B.K. Sanghuangporus toxicodendri sp. nov. (Hymenochaetales, Basidiomycota) from China. MycoKeys 2019, 57, 101–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Francis, A.; Huber, K.T.; Moulton, V. Tree-Based Unrooted Phylogenetic Networks. Bull. Math. Biol. 2018, 80, 404–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McLennan, D.A. How to Read a Phylogenetic Tree. Evol. Educ. Outreach 2010, 3, 506–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, X.-M.; Yu, H.-Y.; Zhou, L.-W.; Decock, C.; Vlasák, J.; Dai, Y.-C. Phylogeny and taxonomy of the Inonotus linteus complex. Fungal Divers. 2012, 58, 159–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, L.; Song, J.; Zhou, J.L.; Si, J.; Cui, B.K. Species Diversity, Phylogeny, Divergence Time, and Biogeography of the Genus Sanghuangporus (Basidiomycota). Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Chen, X.; Zhang, A. Research progress in purification, bio-activity and product development of polysaccharides from Sanghuangporus. Edible Med. Mushrooms 2022, 30, 26–31+61. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, Y.; Huo, J.; Zhong, S.; Zhu, J.; Li, Y.; Li, X. Chemical structure and anti-inflammatory activity of a branched polysaccharide isolated from Phellinus baumii. Carbohydr. Polym. 2021, 268, 118214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, J.-K.; Wang, Y.-Y.; Ma, H.-L.; Wang, Z.-B.; Pei, J.-J. Structural characteristics and antioxidant activity in vivo of a polysaccharide isolated from Phellinus linteus mycelia. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 2016, 65, 110–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, C.Y.; Li, W.Q.; Shao, S.S.; He, L.; Cheng, J.; Han, S.; Liu, Y. Structure and chain conformation of a neutral intracellular heteropolysaccharide from mycelium of Paecilomyces cicadae. Carbohydr. Polym. 2016, 136, 728–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, Q.; Zhao, L.; Li, Z.; Harqin, C.; Peng, Y.; Liu, J. Physicochemical analysis, structural elucidation and bioactivities of a high-molecular-weight polysaccharide from Phellinus igniarius mycelia. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 120, 1855–1864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galinari, E.; Sabry, D.A.; Sassaki, G.L.; Macedo, G.R.; Passos, F.M.L.; Mantovani, H.C.; Rocha, H.A.O. Chemical structure, antiproliferative and antioxidant activities of a cell wall alpha-d-mannan from yeast Kluyveromyces marxianus. Carbohydr. Polym. 2017, 157, 1298–1305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.C.; Yang, X.M.; Ma, H.L.; Yan, J.K.; Guo, D.Z. Purification, characterization and antitumor activity of polysaccharides extracted from Phellinus igniarius mycelia. Carbohydr. Polym. 2015, 133, 24–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, S.; Huang, H.; Huang, G. Extraction, derivatization and antioxidant activity of cucumber polysaccharide. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 140, 1047–1053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Shang, Z.Z.; Li, Q.M.; Zha, X.Q.; Wu, D.L.; Yu, N.J.; Han, L.; Peng, D.Y.; Luo, J.P. Structural features and anti-gastric cancer activity of polysaccharides from stem, root, leaf and flower of cultivated Dendrobium huoshanense. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 143, 651–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, S.; Rausch, W.D. Compare of antioxidant and anti-inflammatory activity of different Phellinus. Chin. J. Pharmacovigil. 2017, 14, 394–398. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, H.; Jin, Q.; Li, P.; Yu, T.; Han, C.; Cui, C. Extraction and antioxidation of polysaccharide from Phellinus linteus. Food Sci. Technol. 2013, 38, 201–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, J.W.; He, L.; Wei, H.L.; Song, J.L.; Hu, C.J.; Zou, J.Q.; Li, H.B.; Jiang, Y.H. Ultrasonic-assisted Enzymatic Method Extraction of Polysaccharide from Inonotus sanghuang. J. Zhejiang For. Sci. Tech. 2017, 37, 33–38. [Google Scholar]
- Gong, L.; Liu, G.; Bai, J.; Liu, D.; He, Y. Optimization of Extraction of Phellinus igniarius and Antioxidant and Antibacterial ActivitieS of Lyophilized Powder. Food Res. Dev. 2021, 42, 143–149. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, Y.; Wang, J.; Yin, X.; Jin, L.; Liu, J.; Zhang, C. Optimization of extraction process of Phellinus linteus polysaccharide. J. Med. Sci. Yanbian Univ. 2021, 44, 242–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Z.; Bao, H. Progresses on extraction methods of polysaccharides of Phellinus fungi. North. Hortic. 2017, 01, 191–195. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.-J.; Chen, B.-S.; Dai, H.-Q.; Ren, J.-W.; Zhou, L.-W.; Wu, S.-H.; Liu, H.-W. Sesquiterpenes and polyphenols with glucose-uptake stimulatory and antioxidant activities from the medicinal mushroom Sanghuangporus sanghuang. Chin. J. Nat. Med. 2021, 19, 693–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Lang, K.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Q. Research on Process of Ultrasonic Assisted Extraction of Phellinus igniarius Polysaccharide. Agric. Sci. Technol. Equip. 2018, 02, 42–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbott, A.P.; Capper, G.; Davies, D.L.; Rasheed, R.K.; Tambyrajah, V. Novel solvent properties of choline chloride/urea mixtures. Chem. Commun. 2003, 39, 70–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, D.; Qin, F.; Liu, B.; Tang, Y.; Chen, W. Effect of dietary supplementation of Phellinus linteus polysaccharide on lipopolysaccharide induced production performance serum biochemistry, immunity and antioxidant capacity of laying hens. Feed Res. 2022, 45, 46–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pei, J.J.; Wang, Z.B.; Ma, H.L.; Yan, J.K. Structural features and antitumor activity of a novel polysaccharide from alkaline extract of Phellinus linteus mycelia. Carbohydr. Polym. 2015, 115, 472–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, S.; Zeng, P.; Lang, M.; Xie, H.; Chen, Y.; Li, C.; Shen, Z.; Li, Y.; Shi, L. Study on the Antioxidant Effects of the Polysaccharide from Phellinus baumii in Vitro. Bull. Seric. 2019, 50, 12–14+22. [Google Scholar]
- Qiu, P.; Liu, J.; Zhao, L.; Zhang, P.; Wang, W.; Shou, D.; Ji, J.; Li, C.; Chai, K.; Dong, Y. Inoscavin A, a pyrone compound isolated from a Sanghuangporus vaninii extract, inhibits colon cancer cell growth and induces cell apoptosis via the hedgehog signaling pathway. Phytomedicine 2022, 96, 153852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, S.P.; Du, X.X.; Zhou, Q.S.; Jie, M.; Hui, L. Study on Deproteinization and Decoloration in Fucoidan. Adv. Mater. Res. 2011, 354–355, 62–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Zhao, R.; Zhou, H.L.; Wu, D.H. Deproteinization of Polysaccharide from the Stigma Maydis by Sevag Method. Adv. Mater. Res. 2011, 340, 416–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Yuan, Y.; Wang, K.; Zhang, D.; Yang, Z.; Xu, P. Deproteinization of gellan gum produced by Sphingomonas paucimobilis ATCC 31461. J. Biotechnol. 2007, 128, 403–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ran, L.; Zou, Y.; Cheng, J.; Lu, F. Silver nanoparticles in situ synthesized by polysaccharides from Sanghuangporus sanghuang and composites with chitosan to prepare scaffolds for the regeneration of infected full-thickness skin defects. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 125, 392–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, J.; Song, J.; Wang, Y.; Wei, H.; He, L.; Liu, Y.; Ding, H.; Huang, Q.; Hu, C.; Huang, X.; et al. Conformation and anticancer activity of a novel mannogalactan from the fruiting bodies of Sanghuangporus sanghuang on HepG2 cells. Food Res. Int. 2022, 156, 111336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, L.; Liu, G.; Yu, G.; Song, Y.; Li, Q. Simultaneous decoloration and purification of crude oligosaccharides from pumpkin (Cucurbita moschata Duch) by macroporous adsorbent resin. Food Chem. 2018, 277, 744–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Shi, S.; Tu, M.; Via, B.; Sun, F.F.; Adhikari, S. Detoxification of Organosolv-Pretreated Pine Prehydrolysates with Anion Resin and Cysteine for Butanol Fermentation. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2018, 186, 662–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Luo, J.; Sun, Y.; Ye, H.; Lu, Z.; Zeng, X. A simple method for the simultaneous decoloration and deproteinization of crude levan extract from Paenibacillus polymyxa EJS-3 by macroporous resin. Bioresour. Technol. 2010, 101, 6077–6083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Chase, H.A. Development of adsorptive (non-ionic) macroporous resins and their uses in the purification of pharmacologically-active natural products from plant sources. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2010, 27, 1493–1510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, M.; Jiao, P.; Qin, T.; Jiang, K.; Zhou, J.; Zhuang, W.; Chen, Y.; Liu, D.; Zhu, C.; Chen, X.; et al. Recovery of lactic acid from the pretreated fermentation broth based on a novel hyper-cross-linked meso-micropore resin: Modeling. Bioresour. Technol. 2017, 241, 593–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, T.; Sun, S.; Liang, C.; Li, H.; Liu, A.; Zhu, H. Effective isolation of antioxidant Phelligridin LA from the fermentation broth of Inonotus baumii by macroporous resin. Bioprocess. Biosyst. Eng. 2020, 43, 2095–2106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, J.; Zheng, Y.; Lin, Z.; Han, X.; Liao, W. Macroporous resin purification and characterization of flavonoids from Platycladus orientalis (L.) Franco and their effects on macrophage inflammatory response. Food Funct. 2017, 8, 86–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mulder, H.A.; Halquist, M.S. Growing Trends in the Efficient and Selective Extraction of Compounds in Complex Matrices Using Molecularly Imprinted Polymers and Their Relevance to Toxicological Analysis. J. Anal. Toxicol. 2021, 45, 312–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, J.; Shen, C.; Wang, X.; Zhu, Y.; Bao, S.; Wu, X.; Fu, Y. A porous cellulose-based molecular imprinted polymer for specific recognition and enrichment of resveratrol. Carbohydr. Polym. 2021, 251, 117026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bereli, N.; Cimen, D.; Huseynli, S.; Denizli, A. Detection of amoxicillin residues in egg extract with a molecularly imprinted polymer on gold microchip using surface plasmon resonance and quartz crystal microbalance methods. J. Food Sci. 2020, 85, 4152–4160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, M.J.; Yang, H.L.; Si, Y.M.; Tang, Q.; Chow, C.F.; Gong, C.B. Photoresponsive Surface Molecularly Imprinted Polymers for the Detection of Profenofos in Tomato and Mangosteen. Front. Chem. 2020, 8, 583036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, C.; He, J.; Chen, N.; Li, Y.; Yuan, L.; Zhao, D.; He, L.; Gu, K.; Zhang, S. Synthesis of cobalt-based magnetic nanoporous carbon core-shell molecularly imprinted polymers for the solid-phase extraction of phthalate plasticizers in edible oil. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2018, 410, 6943–6954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zan, X.; Cui, F.; Li, Y.; Yang, Y.; Wu, D.; Sun, W.; Ping, L. Hericium erinaceus polysaccharide-protein HEG-5 inhibits SGC-7901 cell growth via cell cycle arrest and apoptosis. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2015, 76, 242–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, P.; Liu, H.P.; Ji, H.H.; Sun, N.X.; Feng, Y.Y. A cold-water soluble polysaccharide isolated from Grifola frondosa induces the apoptosis of HepG2 cells through mitochondrial passway. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 125, 1232–1241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, W.; Zhu, X.; Ma, J.; Zhang, M.; Wu, H. Structural Elucidation of a Novel Pectin-Polysaccharide from the Petal of Saussurea laniceps and the Mechanism of its Anti-HBV Activity. Carbohydr. Polym. 2019, 223, 115077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, Y.; Lin, Q.; Luo, F. Effects of Non-Starch Polysaccharides on Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 1372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.L.; Wang, Z.H.; Zhao, Y.X.; Luo, S.J.; Zhang, D.W.; Xiao, S.X.; Peng, Z.H. Isolation and antitumor activities of acidic polysaccharide from Gynostemma pentaphyllum Makino. Carbohydr. Polym. 2012, 89, 942–947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, P.; Wu, S.; Zheng, K.; Xu, C. Molecular Structure and Antioxidant Activity of Polysaccharides from Phellinus vaninii. J. Food Sci. Biotechnol. 2015, 37, 1673–1689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, W.; Zhou, X.; Wang, J.; Zhang, K.; Zhou, Y.; Chen, S.; Nie, S.; Xie, M. Cordyceps sinensis polysaccharide inhibits colon cancer cells growth by inducing apoptosis and autophagy flux blockage via mTOR signaling. Carbohydr. Polym. 2020, 237, 116113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, W.P.; Deng, J.S.; Huang, S.S.; Wu, S.H.; Chen, C.C.; Liao, J.C.; Chen, H.Y.; Lin, H.Y.; Huang, G.J. Sanghuangporus sanghuang Mycelium Prevents Paracetamol-Induced Hepatotoxicity through Regulating the MAPK/NF-kappaB, Keap1/Nrf2/HO-1, TLR4/PI3K/Akt, and CaMKKbeta/LKB1/AMPK Pathways and Suppressing Oxidative Stress and Inflammation. Antioxidants 2021, 10, 897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, C.Y.; Deng, J.S.; Huang, W.C.; Jiang, W.P.; Huang, G.J. Attenuation of Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Acute Lung Injury by Hispolon in Mice, Through Regulating the TLR4/PI3K/Akt/mTOR and Keap1/Nrf2/HO-1 Pathways, and Suppressing Oxidative Stress-Mediated ER Stress-Induced Apoptosis and Autophagy. Nutrients 2020, 12, 1742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, X.Y.; Xu, L.H.; Ouyang, D.Y.; Liu, K.P.; Pan, H.; He, J.; He, X.H. Ginsenoside Rg1 regulates innate immune responses in macrophages through differentially modulating the NF-kappaB and PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathways. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2014, 23, 77–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keppler-Noreuil, K.M.; Parker, V.E.; Darling, T.N.; Martinez-Agosto, J.A. Somatic overgrowth disorders of the PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway & therapeutic strategies. Am. J. Med. Genet. C Semin. Med. Genet. 2016, 172, 402–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thimmulappa, R.K.; Lee, H.; Rangasamy, T.; Reddy, S.P.; Yamamoto, M.; Kensler, T.W.; Biswal, S. Nrf2 is a critical regulator of the innate immune response and survival during experimental sepsis. J. Clin. Investig. 2006, 116, 984–995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, J.; Zhang, W.; Wang, J.; Yang, H.; Zhao, X.; Zhou, Q.; Wang, H.; Li, L.; Du, G. Activation of Nrf2 signaling by salvianolic acid C attenuates NF-kappaB mediated inflammatory response both in vivo and in vitro. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2018, 63, 299–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Hao, W.; Hu, J.; Mi, X.; Han, Y.; Ren, S.; Jiang, S.; Wang, Y.; Li, X.; Li, W. Maltol Improves APAP-Induced Hepatotoxicity by Inhibiting Oxidative Stress and Inflammation Response via NF-kappaB and PI3K/Akt Signal Pathways. Antioxidants 2019, 8, 395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsuruma, R.; Ohbayashi, N.; Kamitani, S.; Ikeda, O.; Sato, N.; Muromoto, R.; Sekine, Y.; Oritani, K.; Matsuda, T. Physical and functional interactions between STAT3 and KAP1. Oncogene 2008, 27, 3054–3059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, N.; Li, C.; Tian, G.; Zhu, M.; Bu, W.; Chen, J.; Hou, X.; Di, L.; Jia, X.; Dong, Z.; et al. Organic acid component from Taraxacum mongolicum Hand.-Mazz alleviates inflammatory injury in lipopolysaccharide-induced acute tracheobronchitis of ICR mice through TLR4/NF-kappaB signaling pathway. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2016, 34, 92–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.H.; Choo, Y.Y.; Tae, N.; Min, B.S.; Lee, J.H. The anti-inflammatory effect of 3-deoxysappanchalcone is mediated by inducing heme oxygenase-1 via activating the AKT/mTOR pathway in murine macrophages. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2014, 22, 420–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, C.; Zhu, L.; Wang, J.; He, H.; Chang, X.; Gao, J.; Shumin, W.; Yan, T. Anti-inflammatory effects of water extract of Taraxacum mongolicum hand.-Mazz on lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammation in acute lung injury by suppressing PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling pathway. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2015, 168, 349–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Gui, Y.S.; Tian, X.L.; Cai, B.Q.; Wang, D.T.; Zhang, D.; Zhao, H.; Xu, K.F. Inactivation of mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) by rapamycin in a murine model of lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury. Chin. Med. J. 2011, 124, 3112–3117. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, G.J.; Deng, J.S.; Chiu, C.S.; Liao, J.C.; Hsieh, W.T.; Sheu, M.J.; Wu, C.H. Hispolon Protects against Acute Liver Damage in the Rat by Inhibiting Lipid Peroxidation, Proinflammatory Cytokine, and Oxidative Stress and Downregulating the Expressions of iNOS, COX-2, and MMP-9. Evid. Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2012, 2012, 480714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, G.J.; Deng, J.S.; Huang, S.S.; Hu, M.L. Hispolon induces apoptosis and cell cycle arrest of human hepatocellular carcinoma Hep3B cells by modulating ERK phosphorylation. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2011, 59, 7104–7113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, G.-J.; Yang, C.-M.; Chang, Y.-S.; Amagaya, S.; Wang, H.-C.; Hou, W.-C.; Huang, S.-S.; Hu, M.-L. Hispolon Suppresses SK-Hep1 Human Hepatoma Cell Metastasis by Inhibiting Matrix Metalloproteinase-2/9 and Urokinase-Plasminogen Activator through the PI3K/Akt and ERK Signaling Pathways. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2010, 58, 9468–9475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsieh, Y.H.; Deng, J.S.; Chang, Y.S.; Huang, G.J. Ginsenoside Rh2 Ameliorates Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Acute Lung Injury by Regulating the TLR4/PI3K/Akt/mTOR, Raf-1/MEK/ERK, and Keap1/Nrf2/HO-1 Signaling Pathways in Mice. Nutrients 2018, 10, 1208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mu, C.; Zhou, G.; Qin, H.; Chen, J.; Li, C. Effect Of Phellinus Polysaccharide On Canonical Wnt Signaling In Synovium In Rats With Rheumatoid Arthritis. J. Sichuan Univ. (Med. Sci. Ed.) 2015, 46, 376–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iyengar, S.; Farnham, P.J. KAP1 protein: An enigmatic master regulator of the genome. J. Biol. Chem. 2011, 286, 26267–26276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamitani, S.; Togi, S.; Ikeda, O.; Nakasuji, M.; Sakauchi, A.; Sekine, Y.; Muromoto, R.; Oritani, K.; Matsuda, T. Kruppel-associated box-associated protein 1 negatively regulates TNF-alpha-induced NF-kappaB transcriptional activity by influencing the interactions among STAT3, p300, and NF-kappaB/p65. J. Immunol. 2011, 187, 2476–2483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gegotek, A.; Niklinski, J.; Charkiewicz, R.; Bielawska, K.; Kozlowski, M.; Skrzydlewska, E. Relationships between level of lipid peroxidation products and expression of Nrf2 and its activators/inhibitors in non-small cell lung cancer tissue. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2014, 75 (Suppl. 1), S31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maruyama, A.; Nishikawa, K.; Kawatani, Y.; Mimura, J.; Hosoya, T.; Harada, N.; Yamamato, M.; Itoh, K. The novel Nrf2-interacting factor KAP1 regulates susceptibility to oxidative stress by promoting the Nrf2-mediated cytoprotective response. Biochem. J. 2011, 436, 387–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, H.J.; Jeong, J.B.; Kim, K.J.; Lee, S.H. Anti-inflammatory activity of mushroom-derived hispidin through blocking of NF-kappaB activation. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2015, 95, 2482–2486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Yuan, J.; Zhang, Y.; Shui, B.; Fan, Y.; Ding, X. Therapeutic Effects of Phellinus igniarius Mycelium Polysaccharide on Collagen-induced Arthritis Rats. J. Zhejiang Chin. Med. Univ. 2014, 38, 526–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noh, J.R.; Kim, Y.H.; Hwang, J.H.; Gang, G.T.; Kim, K.S.; Lee, I.K.; Yun, B.S.; Lee, C.H. Davallialactone protects against acetaminophen overdose-induced liver injuries in mice. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2013, 58, 14–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsieh, Y.H.; Deng, J.S.; Pan, H.P.; Liao, J.C.; Huang, S.S.; Huang, G.J. Sclareol ameliorate lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury through inhibition of MAPK and induction of HO-1 signaling. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2017, 44, 16–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fitzgerald, K.A.; Kagan, J.C. Toll-like Receptors and the Control of Immunity. Cell 2020, 180, 1044–1066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katsanos, K.H.; Papadakis, K.A. Inflammatory Bowel Disease: Updates on Molecular Targets for Biologics. Gut Liver 2017, 11, 455–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, J.S.; Choi, J.; Hwang, S.H.; Kim, J.K.; Kim, E.K.; Lee, S.Y.; Lee, B.I.; Park, S.H.; Cho, M.L. Cottonseed Oil Protects Against Intestinal Inflammation in Dextran Sodium Sulfate-Induced Inflammatory Bowel Disease. J. Med. Food 2019, 22, 672–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.-B.; Shin, Y.-O.; Bae, J.-S.; Min, Y.-K.; Yang, H.-M.; Seo, H.-S.; Kwon, D.-K.; Kang, J.-Y.; Song, Y.-J. Effect of Phellinus linteus extract supplementation on cortisol and related cytokines in young male adults. Food Sci. Biotechnol. 2010, 19, 671–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Su, G.; Zhao, T.; Wang, S.; Sun, B.; Zheng, L.; Zhao, M. The memory improving effects of round scad (Decapterus maruadsi) hydrolysates on sleep deprivation-induced memory deficits in rats via antioxidant and neurotrophic pathways. Food Funct. 2019, 10, 7733–7744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Im, K.H.; Baek, S.A.; Choi, J.; Lee, T.S. Antioxidant, Anti-Melanogenic and Anti-Wrinkle Effects of Phellinus vaninii. Mycobiology 2019, 47, 494–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bailly, C.; Corbineau, F.; van Doorn, W.G. Free radical scavenging and senescence in Iris tepals. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2001, 39, 649–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valko, M.; Leibfritz, D.; Moncol, J.; Cronin, M.T.D.; Mazur, M.; Telser, J. Free radicals and antioxidants in normal physiological functions and human disease. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2007, 39, 44–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aseervatham, G.S.B.; Sivasudha, T.; Jeyadevi, R.; Arul Ananth, D. Environmental factors and unhealthy lifestyle influence oxidative stress in humans—An overview. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2013, 20, 4356–4369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lyu, G.; Wang, X.; Song, T.; Zhang, Z. Comparison of Antioxidant Activity of Liquid Fermentation Products of Two Wild Phellinus Strain. Edible Med. Mushrooms 2018, 26, 175–177+183. [Google Scholar]
- Ververidis, F.; Trantas, E.; Douglas, C.; Vollmer, G.; Kretzschmar, G.; Panopoulos, N. Biotechnology of flavonoids and other phenylpropanoid-derived natural products. Part I: Chemical diversity, impacts on plant biology and human health. Biotechnol. J. 2007, 2, 1214–1234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, T.; Kim, S.-H.; Chen, C.-Y. A Medicinal Mushroom: Phellinus linteus. Curr. Med. Chem. 2008, 15, 1330–1335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mustafa, R.A.; Hamid, A.A.; Mohamed, S.; Bakar, F.A. Total Phenolic Compounds, Flavonoids, and Radical Scavenging Activity of 21 Selected Tropical Plants. J. Food Sci. 2010, 75, C28–C35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Wang, C.; Bao, H. Antitumor Effect of Water Extracts from Fruiting Bodies of Different “Sanghuang” Fungi. Biotechnol. Bull. 2018, 34, 138–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Lu, N.; Yan, J.; Fu, L.; Song, J.; Yuan, W.; Zhou, Z. Effects of growth age on nutrition, content of active components and antioxidant activities of fruiting bodies of Sanghuangporus baumii cultivated on oak segment. Mycosystema 2021, 40, 668–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Pang, D.; Zou, Y.; Liao, S.; Xiao, G. The Total Flavone Content and in Vitro Antioxidant Activity of Phellinus sp. Edible Fungi China 2014, 33, 47–49+56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Ma, J.X.; Wu, D.M.; Gao, N.; Si, J.; Cui, B.K. Identifying Bioactive Ingredients and Antioxidant Activities of Wild Sanghuangporus Species of Medicinal Fungi. J. Fungi 2023, 9, 242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shao, Y.; Guo, H.; Zhang, J.; Liu, H.; Wang, K.; Zuo, S.; Xu, P.; Xia, Z.; Zhou, Q.; Zhang, H.; et al. The Genome of the Medicinal Macrofungus Sanghuang Provides Insights Into the Synthesis of Diverse Secondary Metabolites. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 3035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Zhang, J.; Wu, D.; Zhang, Z.; Li, W.; Wang, W.; Wang, K.; Yang, Y. HPLC fingerprint and spectrum effect relationship of antioxidant activities of Sanghuangporus baumii. Mycosystema 2021, 40, 2364–2375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mapari, S.A.S.; Nielsen, K.F.; Larsen, T.O.; Frisvad, J.C.; Meyer, A.S.; Thrane, U. Exploring fungal biodiversity for the production of water-soluble pigments as potential natural food colorants. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2005, 16, 231–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fox, E.M.; Howlett, B.J. Secondary metabolism: Regulation and role in fungal biology. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 2008, 11, 481–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nirlane da Costa Souza, P.; Luiza Bim Grigoletto, T.; Alberto Beraldo de Moraes, L.; Abreu, L.M.; Henrique Souza Guimarães, L.; Santos, C.; Ribeiro Galvão, L.; Gomes Cardoso, P. Production and chemical characterization of pigments in filamentous fungi. Microbiology 2016, 162, 12–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teixeira, M.F.S.; Martins, M.S.; da Silva, J.C.; Kirsch, L.S.; Fernandes, O.C.C.; Carneiro, A.L.B.; de Conti, R.; Durán, N. Amazonian biodiversity: Pigments from Aspergillus and Penicillium-characterizations, antibacterial activities and their Toxicities. Curr. Trends Biotechnol. Pharm. 2012, 6, 300–311. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, J.; Liu, J.; Sun, Y.; Ye, H.; Zhou, C.; Zeng, X. Medium optimization, preliminary characterization and antioxidant activity in vivo of mycelial polysaccharide from Phellinus baumii Pilát. Carbohydr. Polym. 2010, 81, 533–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, L.; Cai, W.; Jin, Q.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, J.; Zhang, X. Effect of Sanghuang Decoction on Oxidative Damage Induced by D-galactose in Mice. Chin. J. Mod. Appl. Pharm. 2019, 36, 2144–2148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Wang, G.; Zhou, S. Protective Effects of Isoliquiritigenin on LPS-Induced Acute Lung Injury by Activating PPAR-γ. Inflammation 2018, 41, 1290–1296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; He, F.; Ma, Y.; Liu, G.; Chu, L.; Zheng, M. The Growth Characteristics and Antioxidant Activity of Different Sanghuang Strain in Fermentation Broth. Edible Fungi China 2021, 40, 57–61+66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, L.; Lu, N.; Yan, J.; Wang, W.; Song, J.; Yuan, W.; Zhou, Z. Analyses and evaluation of nutrition, active component and antioxidant activities of fruiting bodies of three species of Sanghuangporus. Mycosystema 2021, 40, 2148–2158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Xu, Z.; Li, J.; Wang, J.; Bian, Y.; Chen, Z. Selection of a High Antioxidant Capacity Sanghuangporus sanghuang Strain and Elicitation of It with Phytohormones for Increased Intracellular Flavonoids. J. Edible Mushrooms 2020, 27, 61–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Yin, C.; Fan, X.; Shi, D.; Yao, F.; Li, C.; Liu, Y.; Cheng, Y.; Gao, H. In Vitro Anti-oxidant, Hypoglycemic, and Hypouricemic Activities of Sanghuangporus vaninii Extracts. Mod. Food Sci. Technol. 2022, 38, 71–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyu, G.; Song, T.; Zhang, Y.; Cai, W.; Zhang, Z. Comparative study on antioxidant activities of fermentation products of Sanghuangporus sanghuang and S. vaninii based on UPLC-triple-TOF-MS. Mycosystema 2023, 42, 939–948. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, L.; Yang, H.; Que, S.; Ban, L. Comparative Analysis of the Antioxidant Activity of the Different Components from Phellinus igniarius. Food Res. Dev. 2016, 37, 208–210. [Google Scholar]
- Gong, R.; Tian, X.; Ou, X.; Li, S.; Ma, L.; He, X.; Miao, T. Effects of Phellinus linteus Ploysaccharide on Growth Performance, Hematological Parameters and Immunological Indexes of Growing-laying Hens. Chin. J. Vet. Med. 2021, 57, 86–90. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, J.; Wang, Z.; Yuan, X.; Shan, Q.; Wang, X. Mechanism of inhibitory effect of Phelinus linteus polysaccharide on glioma cell proliferation and migration through PI3K/Akt signaling pathway. Chin. J. Cancer Prev. Treat. 2020, 27, 840–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lang, M.; Zeng, P.; Liu, M.; Xie, H.; Li, X.; Shi, L. Research Progress on Polysaccharide from Phellinus baumii. Bull. Seric. 2017, 48, 14–18. [Google Scholar]
- Fotsis, T.; Pepper, M.S.; Aktas, E.; Breit, S.; Rasku, S.; Adlercreutz, H.; Wähälä, K.; Montesano, R.; Schweigerer, L. Flavonoids, dietary-derived inhibitors of cell proliferation and in vitro angiogenesis. Cancer Res. 1997, 57, 2916–2921. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Sun, J.; Lyu, F.; Gao, G.; Zhao, M.; Zhang, K. Isolation and bioactive characters of a novel lectin SHL24 from the liquid fermentation of Phellinus baumii. Microbiol. China 2018, 45, 420–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, P.Y.; Yang, Y.; Di, L.; Li, J.L.; Li, N. A comparative study on in vitro antitumor activities of the medicinal fungus Sanghuangporus baumii cultivated in different substrates. Mycosystema 2020, 39, 1400–1409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Liu, F.; Zhao, S.; Guo, B.; Ling, P.; Han, G.; Cui, Z. Purification of an acidic polysaccharide from Suaeda salsa plant and its anti-tumor activity by activating mitochondrial pathway in MCF-7 cells. Carbohydr. Polym. 2019, 215, 99–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, X.; Liang, H.; Luo, L. Antitumor polysaccharides from mushrooms: A review on the structural characteristics, antitumor mechanisms and immunomodulating activities. Carbohydr. Res. 2016, 424, 30–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, H.; Zhou, J.; Qi, Y. The effects of Phellinus igniarius Polysaccharides on regulating PI3K/AKT/mTOR Pathway to Inhibit Abdominal Tumor Bearing Tumor of Liver Cancer and to Reduce the Toxicity and Increase the Efficacy of Chemotherapy. Chin. J. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 2020, 25, 401–407. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, J.; Li, J.; Wen, C.; Fan, Y.; Ding, X. Therapeutic Effect of Polysaccharides from Phellinus igniarius on Liver Cancer in H22 Bearing Mice. J. Chin. Med. Mater. 2016, 39, 2868–2870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyu, F.; Zhang, N.; Yu, S. Research progress on the anti-tumor mechanism of Sanghuang polysaccharides. Shanghai J. Tradit. Chin. Med. 2015, 49, 87–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Wang, X.; Yu, Z. Influence of Phellinus igniarius Polysaccharides on Growth and Peripheral Blood Cells of Rats Treated by Cyclophosphamide. Chin. J. Mod. Appl. Pharm. 2017, 34, 832–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, S.; Li, Y.G.; Ji, D.F.; Lin, T.B.; Lv, Z.Q. Protocatechualdehyde Induces S-Phase Arrest and Apoptosis by Stimulating the p27(KIP1)-Cyclin A/D1-CDK2 and Mitochondrial Apoptotic Pathways in HT-29 Cells. Molecules 2016, 21, 934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, M.; Chen, H.; Huang, J.; Li, Z.; Zhu, C.; Zhang, S. Effect of lycium barbarum polysaccharide on human hepatoma QGY7703 cells: Inhibition of proliferation and induction of apoptosis. Life Sci. 2005, 76, 2115–2124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Yao, L.; Jin, Y.; Jin, C.; Dong, Y.; Shou, D.; Wang, Y. Activation Effect of Human TLR4 Signaling Pathway by Polysaccharide from Phellinus igniarius. Chin. J. Mod. Appl. Pharm. 2019, 36, 1178–1182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.; An, C.; Liu, D.; Pan, Y. Effects of liquid fermented flavonoids of Phellinus igniarus on antitumor activity and cell cycle. J. Shandong Univ. Technol. (Nat. Sci. Ed.) 2019, 33, 65–68+73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Bitar, S.; Gali-Muhtasib, H. The Role of the Cyclin Dependent Kinase Inhibitor p21(cip1/waf1) in Targeting Cancer: Molecular Mechanisms and Novel Therapeutics. Cancers 2019, 11, 1475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moussa, R.S.; Park, K.C.; Kovacevic, Z.; Richardson, D.R. Ironing out the role of the cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor, p21 in cancer: Novel iron chelating agents to target p21 expression and activity. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2019, 133, 276–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hennessy, E.J. Selective inhibitors of Bcl-2 and Bcl-xL: Balancing antitumor activity with on-target toxicity. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2016, 26, 2105–2114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, K.F.; Chiu, T.L.; Chang, S.F.; Wang, M.J.; Chiu, S.C. Hispolon Induces Apoptosis, Suppresses Migration and Invasion of Glioblastoma Cells and Inhibits GBM Xenograft Tumor Growth In Vivo. Molecules 2021, 26, 4497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.; Li, D.; Xu, X.-B.; Qiu, S.; Luo, S.; Qiu, E.; Rong, Z.; Zhang, J.; Zheng, D. Galangin inhibits epithelial-mesenchymal transition and angiogenesis by downregulating CD44 in glioma. J. Cancer 2019, 10, 4499–4508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, G.H.; Kang, J.H. Efficacy of Phellinus linteus (sanghuang) extract for improving immune functions: Study protocol for a randomized, double-blinded, placebo-controlled pilot trial. Medicine 2020, 99, e18829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Liu, H.; Su, B.; Liu, Z. Study on the Effect of Polysaccharides from Phellinus baumii on Tumor Microenvironment. J. Taishan Med. Coll. 2020, 41, 318–320. [Google Scholar]
- Ying, R.; Wu, C.; Huang, M.; Wang, Y. Anti-tumor activity of polysaccharides from Phellinus igniarius fruiting body and mycelium. China Food Addit. 2017, 38, 57–61. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, W.; Zhang, N.; Yu, S. Research progress in anti-tumor effects and mechanism of Phellinus fungi. China J. Chin. Mater. Medica 2014, 39, 4165–4168. [Google Scholar]
- Li, T.; Yang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Bao, D. Research progress in structural characteristics, preparation methods, and biological activities of polysaccharides from Phellinus fungi. J. Edible Mushrooms 2013, 20, 65–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, C.; Zhang, Z.; Sun, S.; Zhong, Y. Research Progress on Fermentation Culture, Chemical Compnents and Bioactivity of Phellinus linteus. Edible Fungi China 2021, 40, 14–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, B.O.; Yamada, K.; Cho, B.-G.; Jeon, T.; Hwang, S.-G.; Park, T.; Kang, S.A.; Park, D.K. Comparative Study on the Modulation of IgE and Cytokine Production by Phellinus linteus Grown on Germinated Brown Rice, Phellinus linteus and Germinated Brown Rice in Murine Splenocytes. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2004, 68, 2391–2394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.N.; Qu, H.Y.; Zhang, J.M.; Feng, J.M.; Song, W.J.; Yuan, F.H. Polysaccharide from Phellinus igniarius alleviates oxidative stress and hepatic fibrosis in Schistosoma japonicum-infected mice. Chin. J. Schisto Control 2019, 31, 615–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chien, L.H.; Deng, J.S.; Jiang, W.P.; Chou, Y.N.; Lin, J.G.; Huang, G.J. Evaluation of lung protection of Sanghuangporus sanghuang through TLR4/NF-kappaB/MAPK, keap1/Nrf2/HO-1, CaMKK/AMPK/Sirt1, and TGF-beta/SMAD3 signaling pathways mediating apoptosis and autophagy. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2023, 165, 115080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, X.; La, X.; Zhang, B.; Wang, Z.; Li, Y.; Bo, Y.; Chang, H.; Gao, X.; Tian, C.; Wu, C.; et al. Sanghuang Tongxie Formula Ameliorates Insulin Resistance in Drosophila Through Regulating PI3K/Akt Signaling. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 874180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Magkos, F.; Hjorth, M.F.; Astrup, A. Diet and exercise in the prevention and treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2020, 16, 545–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, Y.; Sidell, M.A.; Arterburn, D.; Daley, M.F.; Desai, J.; Fitzpatrick, S.L.; Horberg, M.A.; Koebnick, C.; McCormick, E.; Oshiro, C.; et al. Racial/Ethnic Disparities in the Prevalence of Diabetes and Prediabetes by BMI: Patient Outcomes Research To Advance Learning (PORTAL) Multisite Cohort of Adults in the U.S. Diabetes Care 2019, 42, 2211–2219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirmiran, P.; Bahadoran, Z.; Azizi, F. Functional foods-based diet as a novel dietary approach for management of type 2 diabetes and its complications: A review. World J. Diabetes 2014, 5, 267–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ballali, S.; Lanciai, F. Functional food and diabetes: A natural way in diabetes prevention? Int. J. Food Sci. Nutr. 2012, 63 (Suppl. 1), 51–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khursheed, R.; Singh, S.K.; Wadhwa, S.; Gulati, M.; Awasthi, A. Therapeutic potential of mushrooms in diabetes mellitus: Role of polysaccharides. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 164, 1194–1205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, D.; Cui, Q.; Qi, X.; Cui, C.; Chen, Z. Effect of Phellinus igniarius polysaccharide on type I diabetes mice model. Agric. Sci. J. Yanbian Univ. 2017, 39, 33–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Q.; Lin, P.; Wang, M.; Chen, H.; Zheng, D.; Huang, Q.; Zhang, S.; Shi, Z. Phellinus igniarius polysaccharide attenuates renal fibrosis in diabetic nephropathy mice based on P311/TGF- β1/Snail1 Pathway. Pharmacol. Clin. Tradit. Chin. Med. 2019, 35, 28–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Littlewood, D.L.; Russell, K. Is there a role for sleep medicine in suicide prevention? Sleep Med. 2020, 66, 262–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Godos, J.; Ferri, R.; Caraci, F.; Cosentino, F.I.I.; Castellano, S.; Shivappa, N.; Hebert, J.R.; Galvano, F.; Grosso, G. Dietary Inflammatory Index and Sleep Quality in Southern Italian Adults. Nutrients 2019, 11, 1324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wible, R.S.; Ramanathan, C.; Sutter, C.H.; Olesen, K.M.; Kensler, T.W.; Liu, A.C.; Sutter, T.R. NRF2 regulates core and stabilizing circadian clock loops, coupling redox and timekeeping in Mus musculus. Elife 2018, 7, e31656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frigato, E.; Benedusi, M.; Guiotto, A.; Bertolucci, C.; Valacchi, G. Circadian Clock and OxInflammation: Functional Crosstalk in Cutaneous Homeostasis. Oxid. Med. Cell Longev. 2020, 2020, 2309437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.-Q.; Sun, X.; Zhang, T.; Zhang, L.-L.; Wu, C.-J. Phytochemicals in traditional Chinese medicine can treat gout by regulating intestinal flora through inactivating NLRP3 and inhibiting XOD activity. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2022, 74, 919–929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chi, X.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, S.; Ma, K.A.-O. Chinese herbal medicine for gout: A review of the clinical evidence and pharmacological mechanisms. Chin. Med. 2020, 15, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mattson, M.P.; Arumugam, T.V. Hallmarks of Brain Aging: Adaptive and Pathological Modification by Metabolic States. Cell Metab. 2018, 27, 1176–1199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soukas, A.A.; Hao, H.; Wu, L. Metformin as Anti-Aging Therapy: Is It for Everyone? Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 2019, 30, 745–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okoro, N.O.; Odiba, A.S.; Osadebe, P.O.; Omeje, E.O.; Liao, G.; Fang, W.A.-O.; Jin, C.A.-O.; Wang, B.A.-O. Bioactive Phytochemicals with Anti-Aging and Lifespan Extending Potentials in Caenorhabditis elegans. Molecules 2021, 26, 7323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Zhang, J.; Yang, Y.; Yan, M.; Wu, D.; Wu, N.; Zhang, H. A Comparative Study on Antioxidant and Anti-aging Activities of Ten Edible/Medicinal Fungi. Nat. Prod. Res. Dev. 2013, 25, 1027–1032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papaemmanouil, C.D.; Peña-García, J.; Banegas-Luna, A.A.-O.; Kostagianni, A.D.; Gerothanassis, I.A.-O.; Pérez-Sánchez, H.A.-O.; Tzakos, A.A.-O. ANTIAGE-DB: A Database and Server for the Prediction of Anti-Aging Compounds Targeting Elastase, Hyaluronidase, and Tyrosinase. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 2268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ooyama, T.; Sakamato, H. Elastase in the prevention of arterial aging and the treatment of atherosclerosis. In Ciba Foundation Symposium 192-The Molecular Biology and Pathology of Elastic Tissues: The Molecular Biology and Pathology of Elastic Tissues: Ciba Foundation Symposium; John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.: Chichester, UK, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Dong, Z.; Wang, Y.; Hao, C.; Cheng, Y.; Guo, X.; He, Y.; Shi, Y.; Wang, S.; Li, Y.; Shi, W. Sanghuangporus sanghuang extract extended the lifespan and healthspan of Caenorhabditis elegans via DAF-16/SIR-2.1. Front. Pharmacol. 2023, 14, 1136897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, K.; Qi, C.; Liu, Y.; Huai, Y.; Hu, H.; Xiao, X.; Wang, J. Phenolic composition and neuroprotective effects of the ethyl-acetate fraction from Inonotus sanghuang against H2O2-induced apoptotic cell death of primary cortical neuronal cells. Food Sci. Biotechnol. 2022, 31, 1213–1223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jayasena, T.; Poljak, A.; Smythe, G.; Braidy, N.; Münch, G.; Sachdev, P. The role of polyphenols in the modulation of sirtuins and other pathways involved in Alzheimer’s disease. Ageing Res. Rev. 2013, 12, 867–883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phan, C.-W.; David, P.; Naidu, M.; Wong, K.-H.; Sabaratnam, V. Therapeutic potential of culinary-medicinal mushrooms for the management of neurodegenerative diseases: Diversity, metabolite, and mechanism. Crit. Rev. Biotechnol. 2015, 35, 355–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, D.J.; Cho, S.; Seo, J.Y.; Lee, H.B.; Park, Y.I. Neuroprotective effects of the Phellinus linteus ethyl acetate extract against H2O2-induced apoptotic cell death of SK-N-MC cells. Nutr. Res. 2016, 36, 31–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.; Nan, S.; Fan, J.; Chen, Q.; Zhang, Y. Inonotus obliquus polysaccharides protect against Alzheimer’s disease by regulating Nrf2 signaling and exerting antioxidative and antiapoptotic effects. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 131, 769–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitamura, Y.; Sakanashi, M.; Ozawa, A.; Saeki, Y.; Nakamura, A.; Hara, Y.; Saeki, K.I.; Arimoto-Kobayashi, S. Protective effect of Actinidia arguta in MPTP-induced Parkinson’s disease model mice. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2021, 555, 154–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezaei, O.; Nateghinia, S.; Estiar, M.A.; Taheri, M.; Ghafouri-Fard, S. Assessment of the role of non-coding RNAs in the pathophysiology of Parkinson’s disease. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2021, 896, 173914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rai, S.N.; Singh, P.; Varshney, R.; Chaturvedi, V.K.; Vamanu, E.; Singh, M.P.; Singh, B.K. Promising drug targets and associated therapeutic interventions in Parkinson’s disease. Neural Regen. Res. 2021, 16, 1730–1739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rai, S.N.; Chaturvedi, V.K.; Singh, P.; Singh, B.K.; Singh, M.P. Mucuna pruriens in Parkinson’s and in some other diseases: Recent advancement and future prospective. 3 Biotech 2020, 10, 522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hemmati-Dinarvand, M.; Saedi, S.; Valilo, M.; Kalantary-Charvadeh, A.; Alizadeh Sani, M.; Kargar, R.; Safari, H.; Samadi, N. Oxidative stress and Parkinson’s disease: Conflict of oxidant-antioxidant systems. Neurosci. Lett. 2019, 709, 134296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fiolet, T.; Kherabi, Y.; MacDonald, C.J.; Ghosn, J.; Peiffer-Smadja, N. Comparing COVID-19 vaccines for their characteristics, efficacy and effectiveness against SARS-CoV-2 and variants of concern: A narrative review. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2022, 28, 202–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Long, B.; Carius, B.M.; Chavez, S.; Liang, S.Y.; Brady, W.J.; Koyfman, A.; Gottlieb, M. Clinical update on COVID-19 for the emergency clinician: Presentation and evaluation. Am. J. Emerg. Med. 2022, 54, 46–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peeling, R.W.; Heymann, D.L.; Teo, Y.Y.; Garcia, P.J. Diagnostics for COVID-19: Moving from pandemic response to control. Lancet 2021, 399, 757–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffmann, M.; Kleine-Weber, H.; Schroeder, S.; Kruger, N.; Herrler, T.; Erichsen, S.; Schiergens, T.S.; Herrler, G.; Wu, N.H.; Nitsche, A.; et al. SARS-CoV-2 Cell Entry Depends on ACE2 and TMPRSS2 and Is Blocked by a Clinically Proven Protease Inhibitor. Cell 2020, 181, 271–280.e8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glowacka, I.; Bertram, S.; Muller, M.A.; Allen, P.; Soilleux, E.; Pfefferle, S.; Steffen, I.; Tsegaye, T.S.; He, Y.; Gnirss, K.; et al. Evidence that TMPRSS2 activates the severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus spike protein for membrane fusion and reduces viral control by the humoral immune response. J. Virol. 2011, 85, 4122–4134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia, H. Pulmonary Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme 2 (ACE2) and Inflammatory Lung Disease. Shock 2016, 46, 239–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, I.C.; Lu, T.Y.; Lin, T.W.; Chen, A.Y.; Chu, H.T.; Chen, Y.L.; Li, T.J.; Chen, C.C. Hispidin-enriched Sanghuangporus sanghuang mycelia SS-MN4 ameliorate disuse atrophy while improving muscle endurance. J. Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle 2023, 14, 2226–2238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, J.; Zhao, S.; Ma, S.; Liang, Y. Effect of Phellinus Linzeus Polysaccharide on Anti-fatigue and Enhancing Anoxia Endurance Function. Edible Fungi China 2012, 31, 42–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, H. Effect of the Phellinus linteus Polysaccharides on Chromosome and Micronucleus of Murine Bone Marrow. Strait Pharm. J. 2014, 26, 16–18. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, H.; Lin, Y. Study on the PoIysaccharides from Phellinus linteus on Sperm AbnormaIity and Chromosome Aberration in TesticIe CeII of Mice. Strait Pharm. J. 2017, 29, 23–25. [Google Scholar]
- Hussain, S.; Sher, H.; Ullah, Z.; Elshikh, M.S.; Al Farraj, D.A.; Ali, A.; Abbasi, A.M. Traditional Uses of Wild Edible Mushrooms among the Local Communities of Swat, Pakistan. Foods 2023, 12, 1705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardwell, G.; Bornman, J.F.; James, A.P.; Black, L.J. A Review of Mushrooms as a Potential Source of Dietary Vitamin D. Nutrients 2018, 10, 1498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jo Feeney, M.; Miller, A.M.; Roupas, P. Mushrooms-Biologically Distinct and Nutritionally Unique: Exploring a “Third Food Kingdom”. Nutr. Today 2014, 49, 301–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khazai, N.; Judd, S.E.; Tangpricha, V. Calcium and vitamin D: Skeletal and extraskeletal health. Curr. Rheumatol. Rep. 2008, 10, 110–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lu, J.; Su, M.; Zhou, X.; Li, D.; Niu, X.; Wang, Y. Research Progress of Bioactive Components in Sanghuangporus spp. Molecules 2024, 29, 1195. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29061195
Lu J, Su M, Zhou X, Li D, Niu X, Wang Y. Research Progress of Bioactive Components in Sanghuangporus spp. Molecules. 2024; 29(6):1195. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29061195
Chicago/Turabian StyleLu, Jungu, Manman Su, Xuan Zhou, Deming Li, Xinhui Niu, and Yi Wang. 2024. "Research Progress of Bioactive Components in Sanghuangporus spp." Molecules 29, no. 6: 1195. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29061195
APA StyleLu, J., Su, M., Zhou, X., Li, D., Niu, X., & Wang, Y. (2024). Research Progress of Bioactive Components in Sanghuangporus spp. Molecules, 29(6), 1195. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29061195







