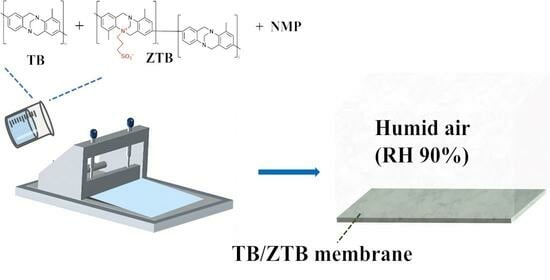
Zwitterionic Tröger’s Base Microfiltration Membrane Prepared via Vapor-Induced Phase Separation with Improved Demulsification and Antifouling Performance
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
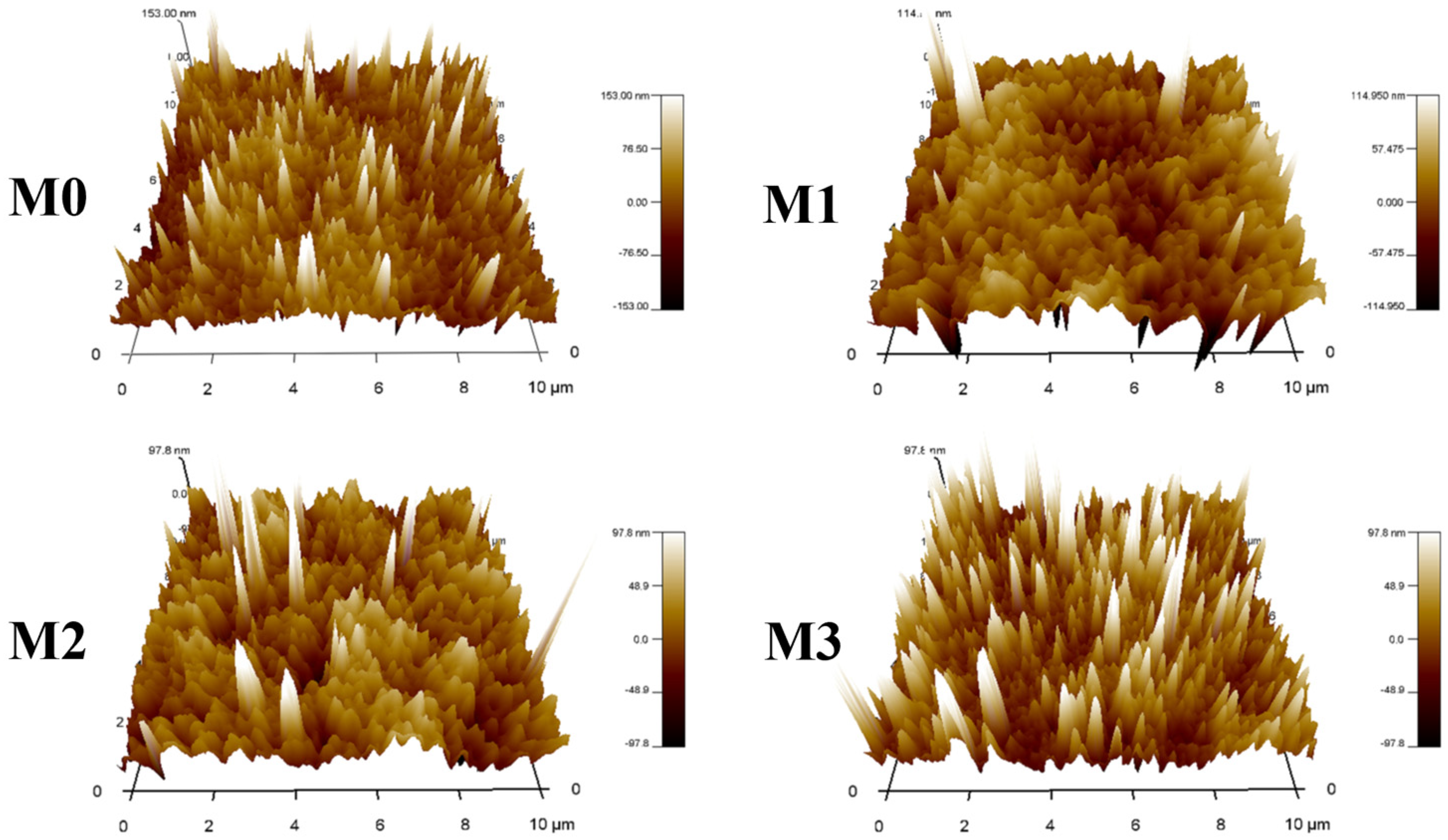
2.1. MF Membrane Morphology
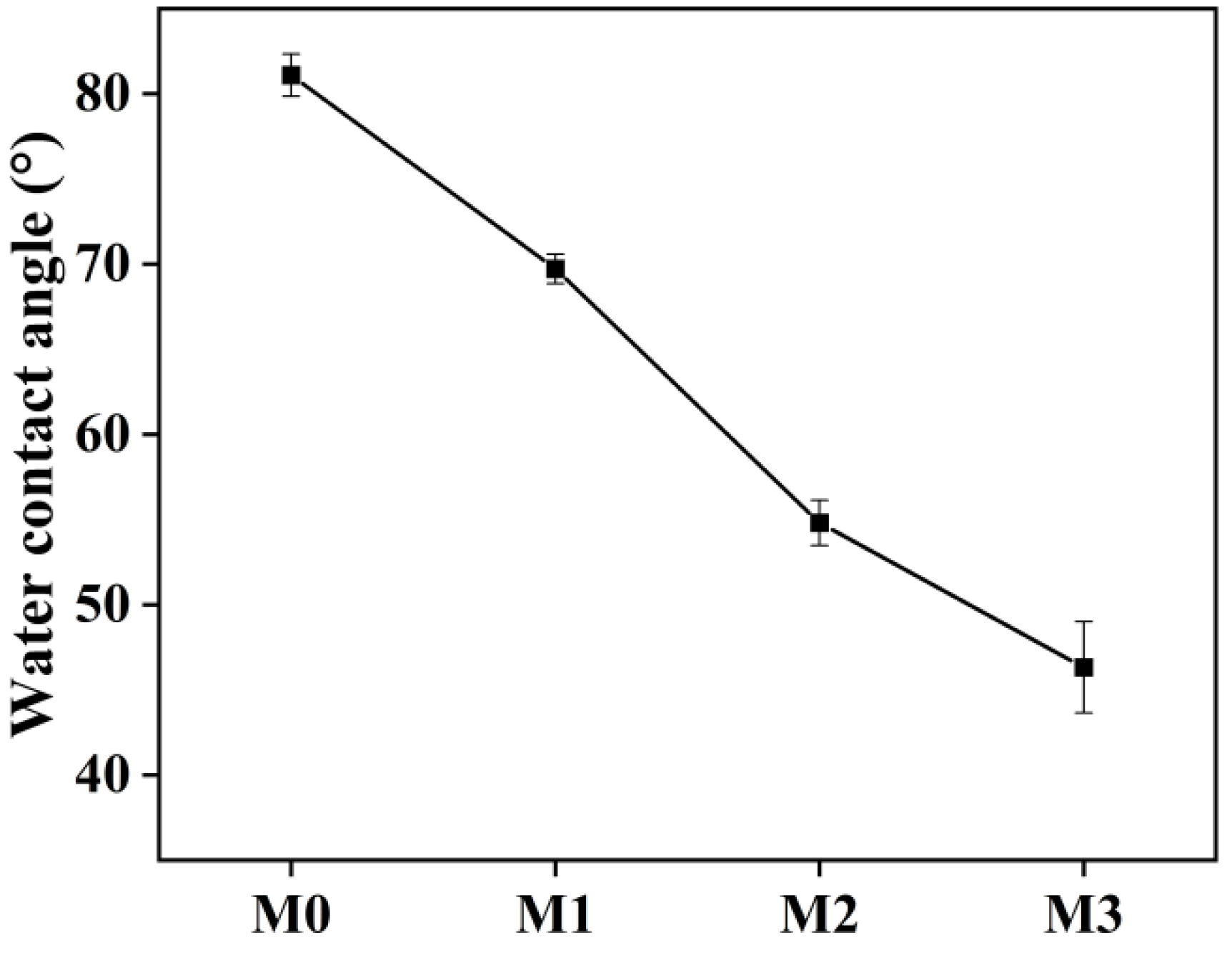
2.2. Hydrophilicity of MF Membrane
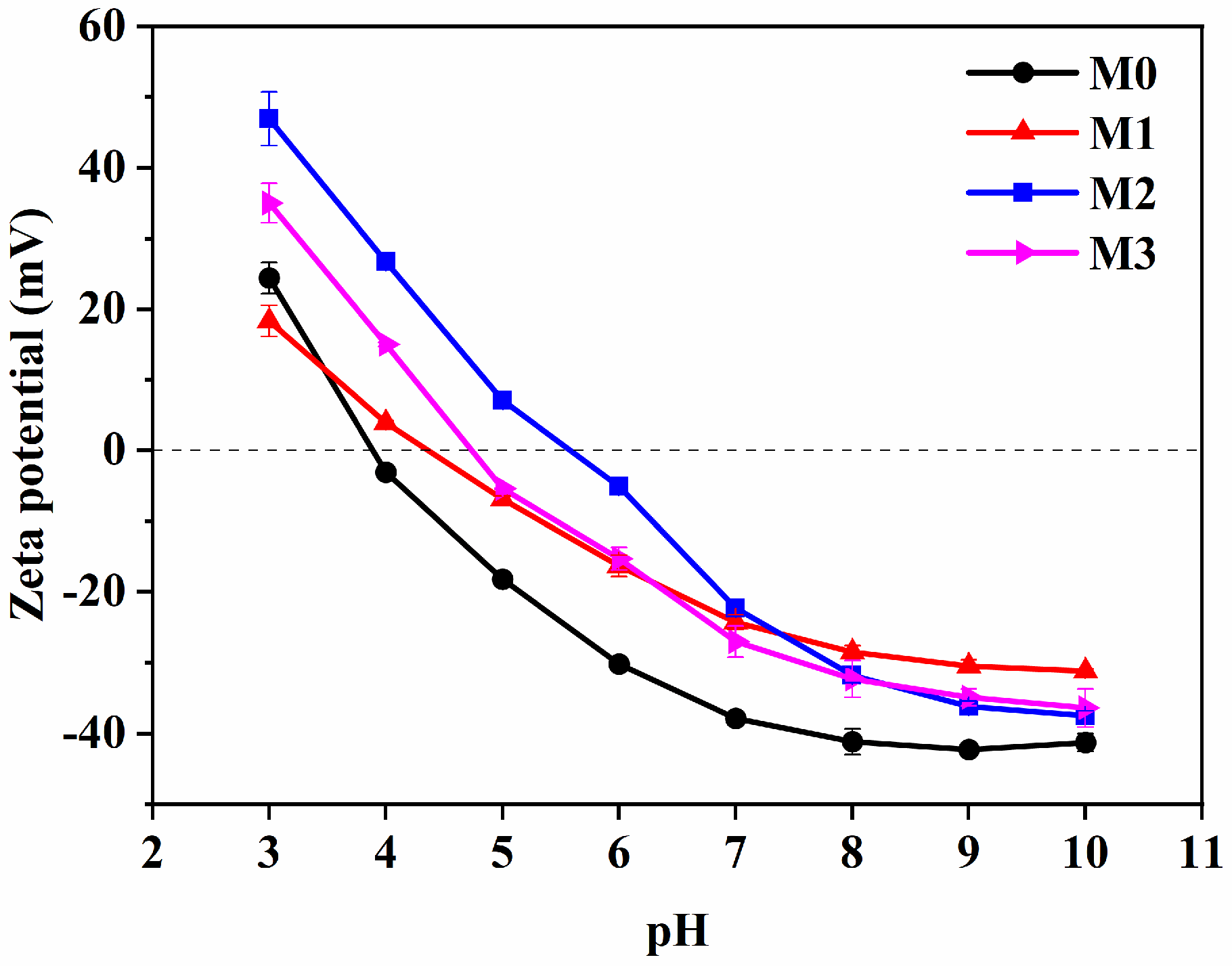
2.3. Zeta Potential of Oily Wastewater and MF Membrane
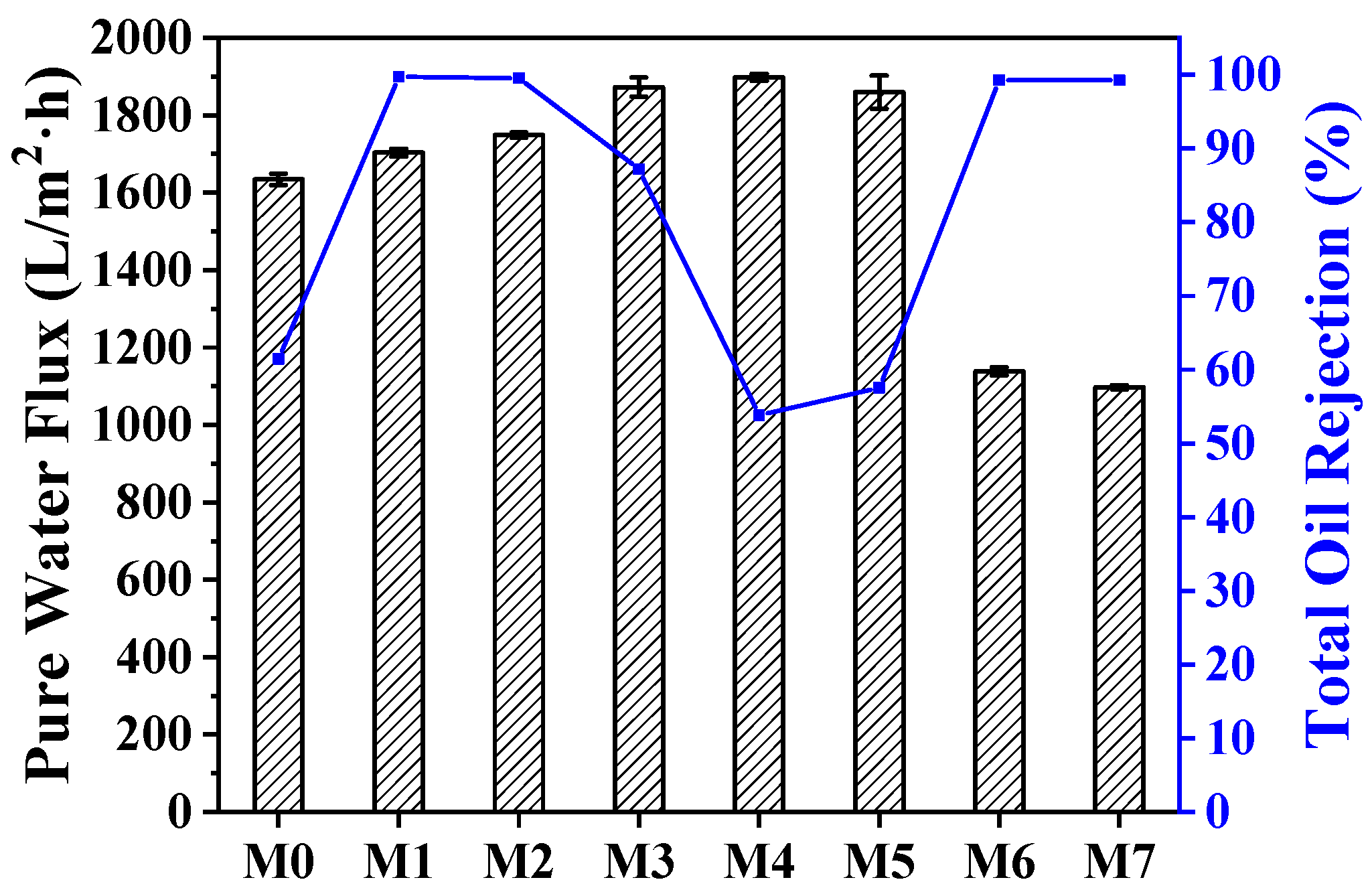
2.4. Penetration and Rejection Performance
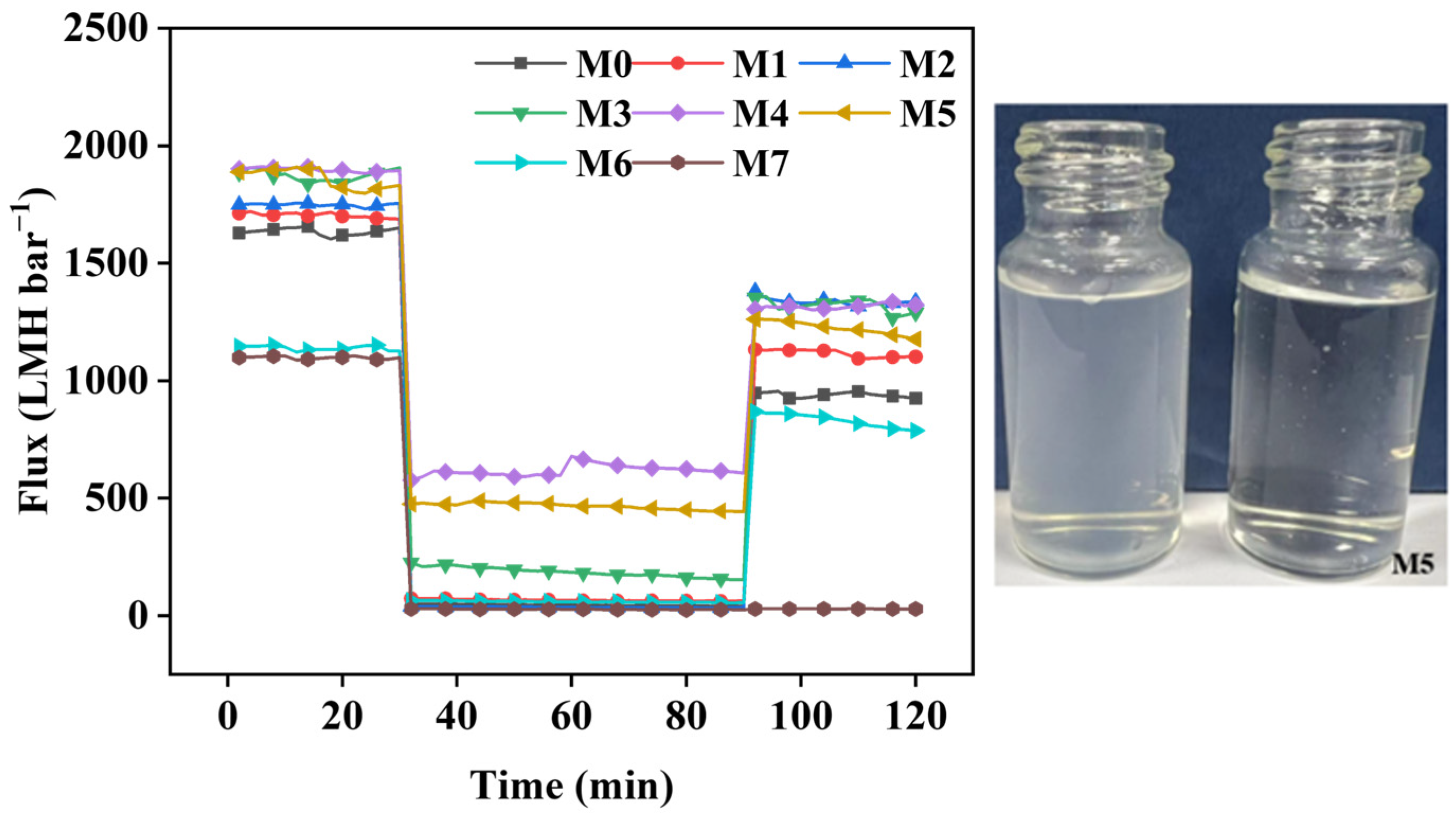
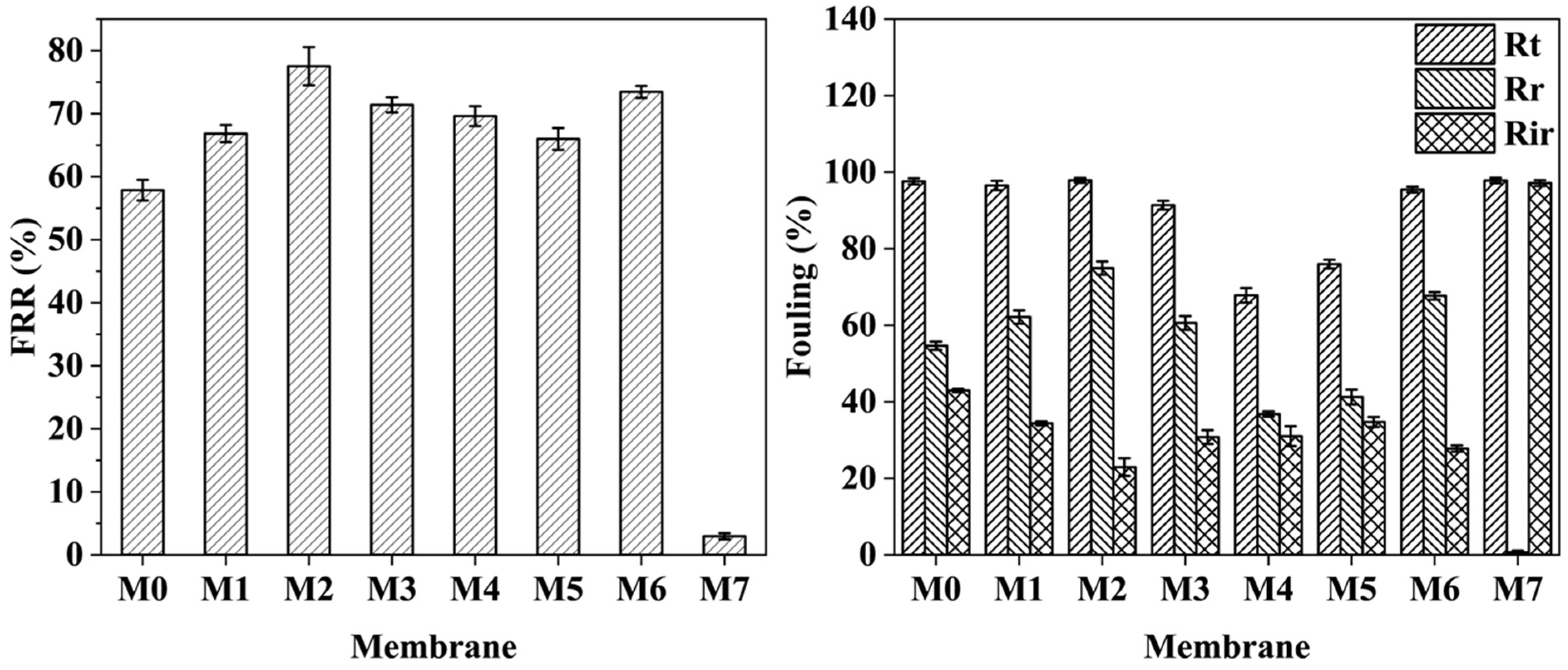
2.5. Antifouling Performance of Membranes
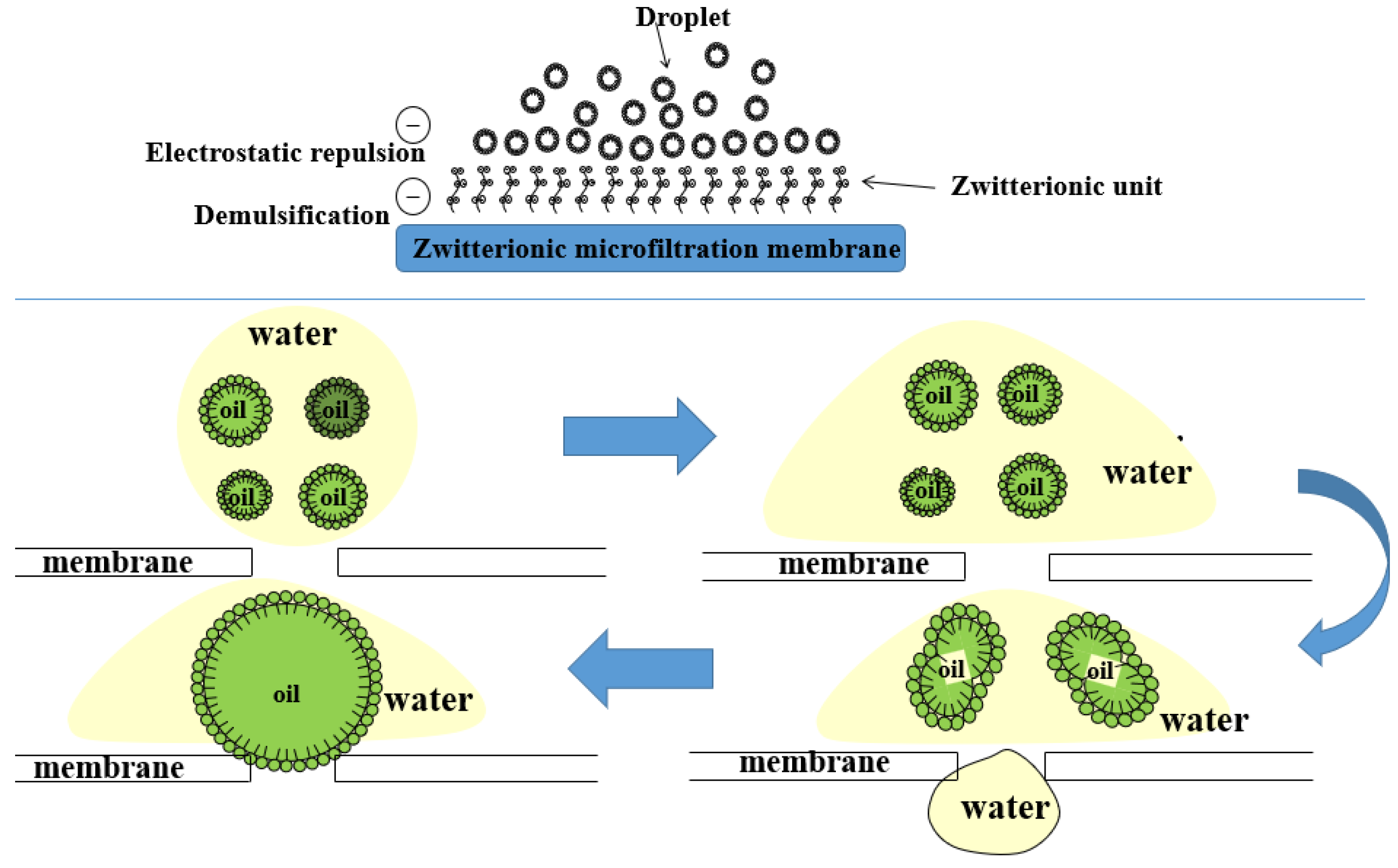
2.6. Possible Antifouling and Demulsification Mechanism
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials and Chemicals
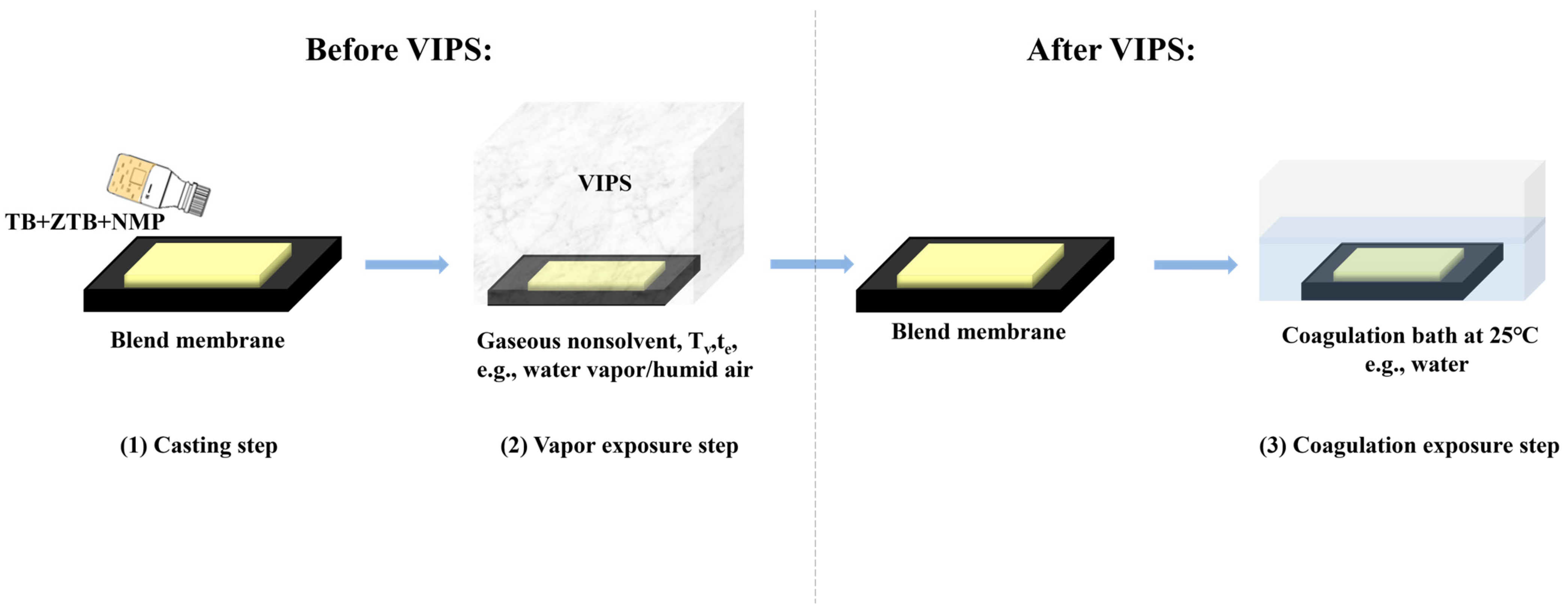
3.2. Preparation of MF Membranes
3.3. Membrane Characterization
3.4. Simulated Stabilized Oil-in-Water Emulsions
3.5. Zeta Potential of the MF Membrane and Emulsified Oil
3.6. Membrane Filtration and Antifouling Performance
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Shi, P.; Zhang, R.; Pu, W.; Liu, R.; Fang, S. Coalescence and separation of surfactant-stabilized water-in-oil emulsion via membrane coalescer functionalized by demulsifier. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 330, 129945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, B.; Shi, G.; Mu, P.; Li, J. Eco-friendly WBF/PAN nanofiber composite membrane for efficient separation various surfactant-stabilized oil-in-water emulsions. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2022, 645, 128917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, X.; Liao, Y.; Tian, M.; Chew, J.W.; Wang, R. Engineering highly effective nanofibrous membranes to demulsify surfactant-stabilized oil-in-water emulsions. J. Membr. Sci. 2020, 611, 118398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Y.; Dai, M.; Wu, Y.; Peng, C. Emulsion system, demulsification and membrane technology in oil–water emulsion separation: A comprehensive review. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2023, 53, 1254–1278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Si, Y.; Zhu, H.; Jiang, T.; Guo, Z. A study on the fabrication of porous PVDF membranes by in-situ elimination and their applications in separating oil/water mixtures and nano-emulsions. J. Membr. Sci. 2016, 520, 760–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, S.; Yang, H.; Zhou, C.; Cheng, J.; Jiang, Z.; Lu, Z.; Miao, J. Underwater superoleophobic mesh based on BiVO4 nanoparticles with sunlight-driven self-cleaning property for oil/water separation. Chem. Eng. J. 2017, 320, 342–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.; Tang, B.; Wu, P. Development of Hybrid Ultrafiltration Membranes with Improved Water Separation Properties Using Modified Superhydrophilic Metal–Organic Framework Nanoparticles. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 21473–21484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Su, Y.; Cao, J.; Guan, J.; Zhang, R.; He, M.; Fan, L.; Zhang, Q.; Jiang, Z. Antifouling, high-flux oil/water separation carbon nanotube membranes by polymer-mediated surface charging and hydrophilization. J. Membr. Sci. 2017, 542, 254–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mat Nawi, N.I.; Chean, H.M.; Shamsuddin, N.; Bilad, M.R.; Narkkun, T.; Faungnawakij, K.; Khan, A.L. Development of Hydrophilic PVDF Membrane Using Vapour Induced Phase Separation Method for Produced Water Treatment. Membranes 2020, 10, 121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, M.; Xu, Z.; Guo, Y.; Hou, Y.; Li, P.; Niu, Q.J. Engineering a superwettable polyolefin membrane for highly efficient oil/water separation with excellent self-cleaning and photo-catalysis degradation property. J. Membr. Sci. 2020, 611, 118409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, S.; Kang, Y.; Tiraferri, A.; Giannelis, E.P.; Huang, X.; Elimelech, M. Highly Hydrophilic Polyvinylidene Fluoride (PVDF) Ultrafiltration Membranes via Postfabrication Grafting of Surface-Tailored Silica Nanoparticles. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2013, 5, 6694–6703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Safarpour, M.; Hosseinpour, S.; Haddad Irani-nezhad, M.; Orooji, Y.; Khataee, A. Fabrication of Ti2SnC-MAX Phase Blended PES Membranes with Improved Hydrophilicity and Antifouling Properties for Oil/Water Separation. Molecules 2022, 27, 8914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, C.; Rutledge, G.C. Electrospun Liquid-Infused Membranes for Emulsified Oil/Water Separation. Langmuir 2022, 38, 2301–2313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Ge, Q. Membrane Surface Engineering with Bifunctional Zwitterions for Efficient Oil–Water Separation. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 11, 31328–31337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Qiu, M.; He, C. A zwitterionic polymer/PES membrane for enhanced antifouling performance and promoting hemocompatibility. J. Membr. Sci. 2020, 606, 118119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zang, L.; Zheng, S.; Wang, L.; Ma, J.; Sun, L. Zwitterionic nanogels modified nanofibrous membrane for efficient oil/water separation. J. Membr. Sci. 2020, 612, 118379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghaffar, A.; Zhu, X.; Chen, B. Biochar composite membrane for high performance pollutant management: Fabrication, structural characteristics and synergistic mechanisms. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 233, 1013–1023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Venault, A.; Wei, T.-C.; Shih, H.-L.; Yeh, C.-C.; Chinnathambi, A.; Alharbi, S.A.; Carretier, S.; Aimar, P.; Lai, J.-Y.; Chang, Y. Antifouling pseudo-zwitterionic poly(vinylidene fluoride) membranes with efficient mixed-charge surface grafting via glow dielectric barrier discharge plasma-induced copolymerization. J. Membr. Sci. 2016, 516, 13–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Cheng, L.; Wang, R.; Jia, N.; Liu, L.; Gao, C. Bioinspired synthesis of polyzwitterion/titania functionalized carbon nanotube membrane with superwetting property for efficient oil-in-water emulsion separation. J. Membr. Sci. 2019, 589, 117257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Wang, J.; Zhang, F.; Gao, S.; Wang, A.; Fang, W.; Jin, J. Zwitterionic Nanohydrogel Grafted PVDF Membranes with Comprehensive Antifouling Property and Superior Cycle Stability for Oil-in-Water Emulsion Separation. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2018, 28, 1804121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maggay, I.V.; Suba, M.C.A.M.; Aini, H.N.; Wu, C.-J.; Tang, S.-H.; Aquino, R.B.; Chang, Y.; Venault, A. Thermostable antifouling zwitterionic vapor-induced phase separation membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 2021, 627, 119227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Folgado, E.; Ladmiral, V.; Semsarilar, M. Towards permanent hydrophilic PVDF membranes. Amphiphilic PVDF-b-PEG-b-PVDF triblock copolymer as membrane additive. Eur. Polym. J. 2020, 131, 109708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venault, A.; Chiang, C.-H.; Chang, H.-Y.; Hung, W.-S.; Chang, Y. Graphene oxide/PVDF VIPS membranes for switchable, versatile and gravity-driven separation of oil and water. J. Membr. Sci. 2018, 565, 131–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nayak, M.C.; Isloor, A.M.; Moslehyani, A.; Ismail, N.; Ismail, A.F. Fabrication of novel PPSU/ZSM-5 ultrafiltration hollow fiber membranes for separation of proteins and hazardous reactive dyes. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 2018, 82, 342–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dehban, A.; Kargari, A.; Ashtiani, F.Z. Preparation and optimization of antifouling PPSU/PES/SiO2 nanocomposite ultrafiltration membranes by VIPS-NIPS technique. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2020, 88, 292–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, H.-T.; Venault, A.; Chang, Y. Reducing the pathogenicity of wastewater with killer vapor-induced phase separation membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 2020, 614, 118543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venault, A.; Chang, C.-Y.; Tsai, T.-C.; Chang, H.-Y.; Bouyer, D.; Lee, K.-R.; Chang, Y. Surface zwitterionization of PVDF VIPS membranes for oil and water separation. J. Membr. Sci. 2018, 563, 54–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Y.; Fan, H.; Dong, Y.; Song, Y.; Han, H. Effects of exposure time on variations in the structure and hydrophobicity of polyvinylidene fluoride membranes prepared via vapor-induced phase separation. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2012, 258, 7872–7881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdulazeez, I.; Salhi, B.; Elsharif, A.M.; Ahmad, M.S.; Baig, N.; Abdelnaby, M.M. Hemin-Modified Multi-Walled Carbon Nanotube-Incorporated PVDF Membranes: Computational and Experimental Studies on Oil–Water Emulsion Separations. Molecules 2023, 28, 391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Wang, M.; Chen, J.; Dong, L.; Tian, Y.; Cui, Z.; Li, J.; He, B.; Yan, F. Demulsifier-Inspired Superhydrophilic/Underwater Superoleophobic Membrane Modified with Polyoxypropylene Polyoxyethylene Block Polymer for Enhanced Oil/Water Separation Properties. Molecules 2023, 28, 1282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Long, N.; Xiao, T.; Yang, X. Tuning the Pore Structure of Poly(vinylidene fluoride) Membrane for Efficient Oil/Water Separation: A Novel Vapor-Induced Phase Separation Method Based on a Lower Critical Solution Temperature System. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2020, 59, 14947–14959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, T.; Yin, J.; Tang, H.; Zhang, Z.; Liu, D.; Liu, S.; Xu, Z.; Li, N. Improved permeability and antifouling performance of Tröger’s base polymer-based ultrafiltration membrane via zwitterionization. J. Membr. Sci. 2022, 646, 120251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venault, A.; Chang, Y.; Wang, D.-M.; Bouyer, D. A Review on Polymeric Membranes and Hydrogels Prepared by Vapor-Induced Phase Separation Process. Polym. Rev. 2013, 53, 568–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, T.-H.; Chen, L.-W. Pore formation mechanism of membranes from phase inversion process. Desalination 1995, 103, 233–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ismail, N.; Venault, A.; Mikkola, J.-P.; Bouyer, D.; Drioli, E.; Tavajohi Hassan Kiadeh, N. Investigating the potential of membranes formed by the vapor induced phase separation process. J. Membr. Sci. 2020, 597, 117601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Q.; Xie, R.; Luo, F.; Faraj, Y.; Liu, Z.; Ju, X.-J.; Wang, W.; Chu, L.-Y. Preparation of high strength poly(vinylidene fluoride) porous membranes with cellular structure via vapor-induced phase separation. J. Membr. Sci. 2018, 549, 151–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guillen, G.R.; Pan, Y.; Li, M.; Hoek, E.M.V. Preparation and Characterization of Membranes Formed by Nonsolvent Induced Phase Separation: A Review. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2011, 50, 3798–3817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.-B.; Shi, W.-Y.; Zhang, Y.-F.; Liu, D.-Q.; Liu, X.-F. Effects of Additives on the Morphology and Performance of PPTA/PVDF in Situ Blend UF Membrane. Polymers 2014, 6, 1846–1861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Liu, Y.; Liu, T.; Xu, X.; Hu, Y. Improving the perm-selectivity and anti-fouling property of UF membrane through the micro-phase separation of PSf-b-PEG block copolymers. J. Membr. Sci. 2020, 599, 117851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, M.-H.; Xie, R.; Ju, X.-J.; Wang, W.; Liu, Z.; Chu, L.-Y. Antifouling membranes with bi-continuous porous structures and high fluxes prepared by vapor-induced phase separation. J. Membr. Sci. 2020, 611, 118256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dehban, A.; Hosseini Saeedavi, F.; Kargari, A. A study on the mechanism of pore formation through VIPS-NIPS technique for membrane fabrication. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2022, 108, 54–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Y.; Dong, Y.; Fan, H.; Chen, P.; Li, Z.; Jiang, Q. Preparation of polysulfone membranes via vapor-induced phase separation and simulation of direct-contact membrane distillation by measuring hydrophobic layer thickness. Desalination 2013, 316, 53–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, G.; Chen, S.; Quan, X.; Wei, G.; Fan, X.; Yu, H. Enhanced separation performance of carbon nanotube–polyvinyl alcohol composite membranes for emulsified oily wastewater treatment under electrical assistance. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2018, 197, 107–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dehban, A.; Kargari, A.; Zokaee Ashtiani, F. Preparation and characterization of an antifouling poly (phenyl sulfone) ultrafiltration membrane by vapor-induced phase separation technique. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2019, 212, 986–1000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venault, A.; Chang, Y.; Wang, D.-M.; Lai, J.-Y. Surface anti-biofouling control of PEGylated poly(vinylidene fluoride) membranes via vapor-induced phase separation processing. J. Membr. Sci. 2012, 423–424, 53–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, D.; Zhang, T.; Gutierrez, L.; Ma, J.; Croué, J.-P. Influence of Surface Properties of Filtration-Layer Metal Oxide on Ceramic Membrane Fouling during Ultrafiltration of Oil/Water Emulsion. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 50, 4668–4674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Xu, Z.; Liu, C.; Zhao, Y.; Xia, Q.; Fang, M.; Min, X.; Huang, Z.; Liu, Y.G.; Wu, X. Polydopamine Nanocluster Embedded Nanofibrous Membrane via Blow Spinning for Separation of Oil/Water Emulsions. Molecules 2021, 26, 3258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, B.; Huo, Z.; Wu, P. Study on a novel polyester composite nanofiltration membrane by interfacial polymerization of triethanolamine (TEOA) and trimesoyl chloride (TMC): I. Preparation, characterization and nanofiltration properties test of membrane. J. Membr. Sci. 2008, 320, 198–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Su, Y.; Liu, Y.; Li, Y.; Jiang, Z. Free-Standing Graphene Oxide-Palygorskite Nanohybrid Membrane for Oil/Water Separation. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 8247–8256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, J.T.; Su, Y.S.; Wang, D.M.; Kuo, J.L.; Lai, J.Y.; Deratani, A. Retainment of pore connectivity in membranes prepared with vapor-induced phase separation. J. Membr. Sci. 2010, 362, 360–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Su, Y.; Zhao, X.; Li, Y.; Zhang, R.; Jiang, Z. Improved antifouling properties of polyethersulfone membrane by blending the amphiphilic surface modifier with crosslinked hydrophobic segments. J. Membr. Sci. 2015, 486, 195–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barambu, N.U.; Bilad, M.R.; Bustam, M.A.; Huda, N.; Jaafar, J.; Narkkun, T.; Faungnawakij, K. Development of Polysulfone Membrane via Vapor-Induced Phase Separation for Oil/Water Emulsion Filtration. Polymers 2020, 12, 2519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Han, Q.; Lin, H.; Zhang, S.; Yang, Q.; Liu, F. Fine regulation on hour-glass like spongy structure of polyphenylsulfone (PPSU)/sulfonated polysulfone (SPSf) MF membranes via a vapor-liquid induced phase separation (V-LIPS) technique. J. Membr. Sci. 2022, 660, 120872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, H.-Y.; Venault, A. Adjusting the morphology of poly(vinylidene fluoride-co-hexafluoropropylene) membranes by the VIPS process for efficient oil-rich emulsion separation. J. Membr. Sci. 2019, 581, 178–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Yang, H.; Yang, Y.; Zhu, L.; Zeng, Z.; Liu, S.; Li, Y.; Liang, Z. Poly(vinylidene fluoride) membranes with underwater superoleophobicity for highly efficient separation of oil-in-water emulsions in resisting fouling. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2022, 285, 120298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ong, C.; Shi, Y.; Chang, J.; Alduraiei, F.; Wehbe, N.; Ahmed, Z.; Wang, P. Tannin-inspired robust fabrication of superwettability membranes for highly efficient separation of oil-in-water emulsions and immiscible oil/water mixtures. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2019, 227, 115657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.-N.; Yang, J.; Xu, Z.-K. Hollow fiber membranes with Janus surfaces for continuous deemulsification and separation of oil-in-water emulsions. J. Membr. Sci. 2020, 602, 117964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, P.; Liang, S.; Qiu, L.; Gao, Y.; Wang, Q. Thin film nanocomposite forward osmosis membranes based on layered double hydroxide nanoparticles blended substrates. J. Membr. Sci. 2016, 504, 196–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Huang, R.; Tang, H.; Zhang, Z.; Xu, Z.; Li, N. Enhanced antifouling and separation properties of Tröger’s base polymer ultrafiltration membrane via ring-opening modification. J. Membr. Sci. 2020, 597, 117763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Membranes | Ps/% | rs/μm | rmax/μm | T/μm |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| M0 | 1.2 ± 0.2 | 0.178 ± 0.002 | 0.462 ± 0.008 | 0.035 ± 0.004 |
| M1 | 1.6 ± 0.1 | 0.203 ± 0.001 | 0.550 ± 0.039 | 0.030 ± 0.002 |
| M2 | 2.9 ± 0.1 | 0.212 ± 0.008 | 0.660 ± 0.117 | 0.030 ± 0.005 |
| M3 | 5.1 ± 0.1 | 0.247 ± 0.005 | 0.867 ± 0.070 | 0.025 ± 0.005 |
| M4 | 3.9 ± 0.1 | 0.263 ± 0.006 | 0.963 ± 0.025 | 0.055 ± 0.011 |
| M5 | 5.7 ± 0.4 | 0.278 ± 0.001 | 0.992 ± 0.209 | 0.036 ± 0.007 |
| M6 | 4.0 ± 0.1 | 0.293 ± 0.001 | 1.311 ± 0.103 | 0.050 ± 0.012 |
| M7 | 2.7 ± 0.1 | 0.214 ± 0.001 | 0.621 ± 0.035 | 0.021 ± 0.003 |
| Membranes | Ra (nm) | Rq (nm) | −ΔGML (mJ m−2) |
|---|---|---|---|
| M0 | 21.79 ± 2.22 | 29.57 ± 2.24 | 83.0 |
| M1 | 22.38 ± 2.08 | 33.50 ± 3.34 | 95.9 |
| M2 | 23.73 ± 3.35 | 34.76 ± 3.90 | 111.1 |
| M3 | 24.24 ± 3.06 | 45.93 ± 1.25 | 118.1 |
| Membrane Material/Fabrication | Oil/Surfactant Content | Driving Force (bar) | Separation Efficiency (%) | Flux (LMH bar−1) | Flux Recovery Rate (%) | Refs |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PVDF (VIPS + TIPS/VIPS + NIPS) | SDS:oil = 1:6 (w/w) | 0.2 | / | ~3028 | ~77% | [31] |
| PSF(VISP) | SDS:oil = 1:99 (w/w) | 0.2 | ~98.48 | ~501.89 | ~49.57% | [52] |
| PPSU/SPSf (V-LIPS) | Water:oil = 1:99 (w/w) | 0.2 | 99.5–99.5 | 508.4~414.1 | / | [53] |
| PVDF-co-HFP(VIPS) | oil/water = 1% (v/v) | 1.0 | 99.5% | 600 | / | [54] |
| PVDF/PHEMA (VIPS) | 20 mg SDS + 10 mL oil + 990 m water | 1.0 | 99.1% (crude oil) | 1866 ± 162 (pump oil) | / | [55] |
| zwitterionization PVDF(VIPS) | oil/water = 1:99 (w/w) | 0.5 | 99.0% | 180–240 | [27] | |
| tannic acid deposited onto PVDF MF membrane | Tween-80 + 2-dichloroethane/hexane/iso-octane and water (v/v/v = 1:50:0.02) | 0.8 | 98% | 38 ± 13~401 ± 97 | 84 | [56] |
| PMCSMA grafted PES MF membrane | Span-80 (4000 mg/L) + Kerosene (50 mg/L) | 0.25 | 99.5% | 43 | / | [1] |
| Polydopamine/polyelectrolyte co-deposited onto PP MF membrane | SDS(1000 mg/L) + Oi/waterl (v:v = 1:5/) | / | 99% | 0.65 | / | [57] |
| Zwitterionic Tröger’s base/VISP | SDS(50 mg/L) + Cutting oil(50 mg/L) | 0.1 | 99% | 1328 | 74% | This work |
| Membranes | Composition | Temperature of VIPS Chamber | Exposure Time | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TB (wt%) | ZTB (wt%) | NMP (wt%) | Tv (°C) | te (min) | |
| M0 | 18 | 0 | 82 | 50 | 10 |
| M1 | 17 | 1 | 82 | 50 | 10 |
| M2 | 16 | 2 | 82 | 50 | 10 |
| M3 | 15 | 3 | 82 | 50 | 10 |
| M4 | 16 | 2 | 82 | 50 | 5 |
| M5 | 16 | 2 | 82 | 50 | 15 |
| M6 | 16 | 2 | 82 | 30 | 10 |
| M7 | 16 | 2 | 82 | 80 | 10 |
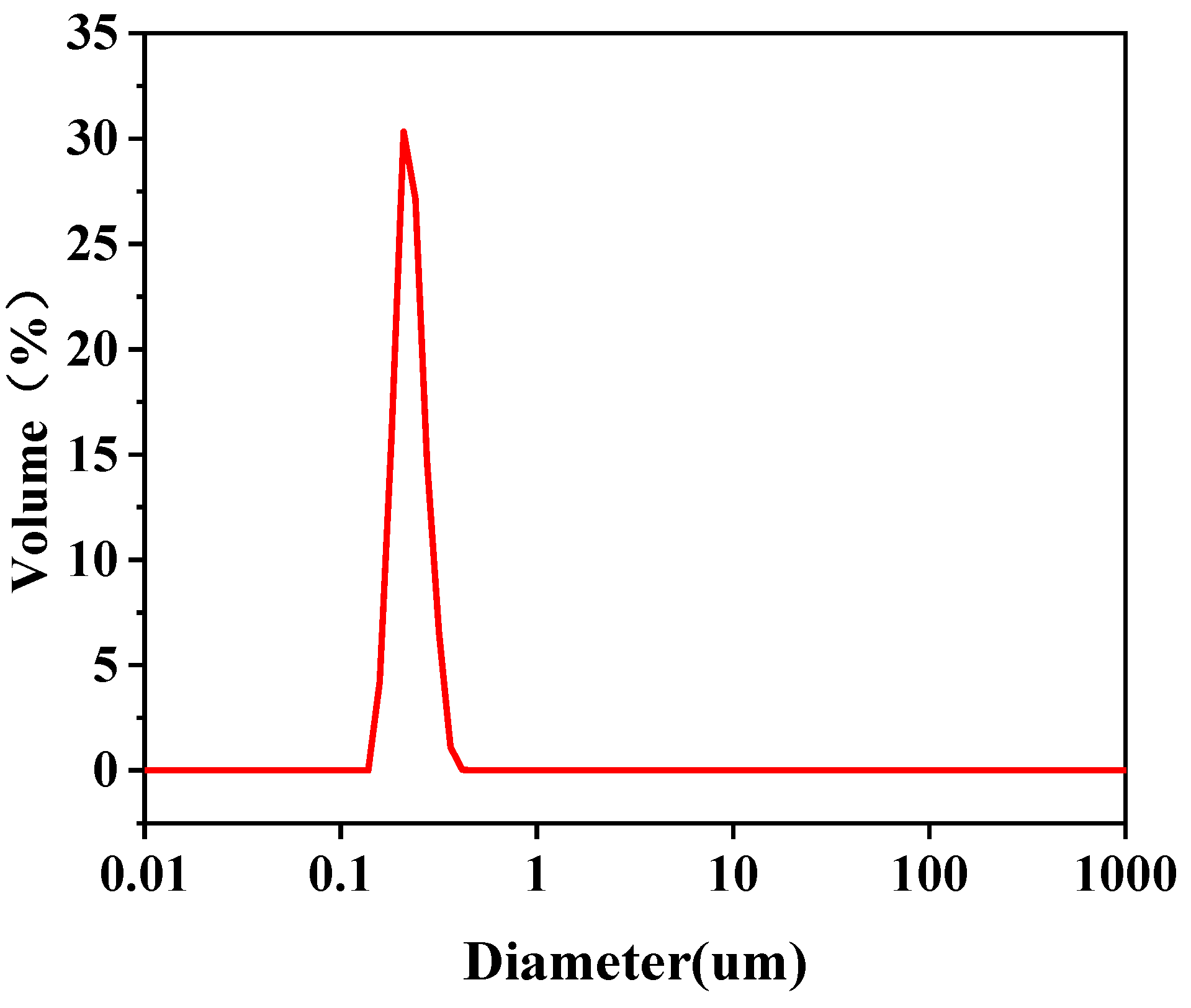
| Emulsified Oil Droplet Size (μm) | D10 | D50 | D90 | D(3,2) | D(4,3) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Feed liquid | 0.171 | 0.209 | 0.266 | 0.208 | 0.214 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, M.; Huang, T.; Shan, M.; Sun, M.; Liu, S.; Tang, H. Zwitterionic Tröger’s Base Microfiltration Membrane Prepared via Vapor-Induced Phase Separation with Improved Demulsification and Antifouling Performance. Molecules 2024, 29, 1001. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29051001
Wang M, Huang T, Shan M, Sun M, Liu S, Tang H. Zwitterionic Tröger’s Base Microfiltration Membrane Prepared via Vapor-Induced Phase Separation with Improved Demulsification and Antifouling Performance. Molecules. 2024; 29(5):1001. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29051001
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Meng, Tingting Huang, Meng Shan, Mei Sun, Shasha Liu, and Hai Tang. 2024. "Zwitterionic Tröger’s Base Microfiltration Membrane Prepared via Vapor-Induced Phase Separation with Improved Demulsification and Antifouling Performance" Molecules 29, no. 5: 1001. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29051001
APA StyleWang, M., Huang, T., Shan, M., Sun, M., Liu, S., & Tang, H. (2024). Zwitterionic Tröger’s Base Microfiltration Membrane Prepared via Vapor-Induced Phase Separation with Improved Demulsification and Antifouling Performance. Molecules, 29(5), 1001. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29051001