Effects of Hydraulic Retention Time on Removal of Cr (VI) and p-Chlorophenol and Electricity Generation in L. hexandra-Planted Constructed Wetland–Microbial Fuel Cell
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
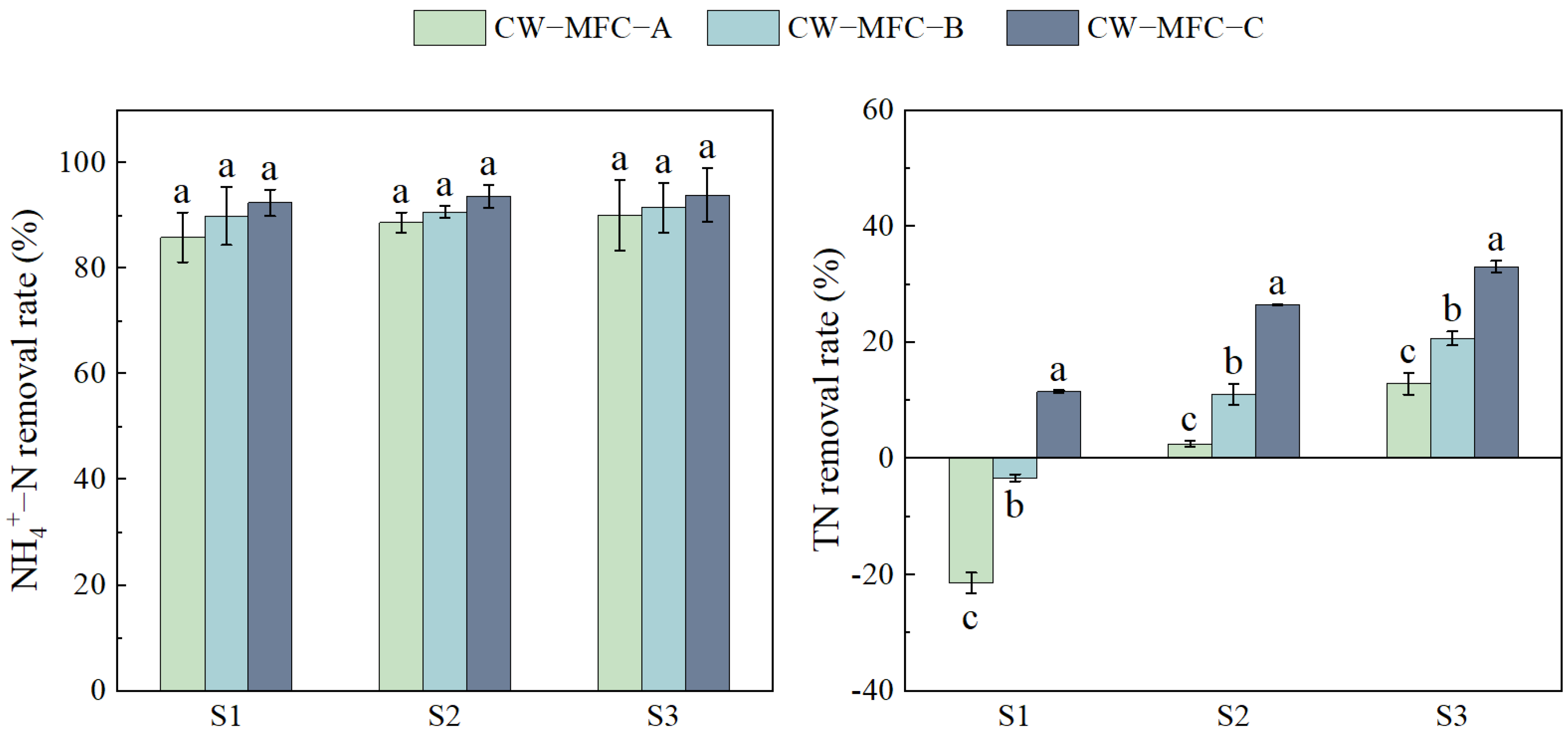
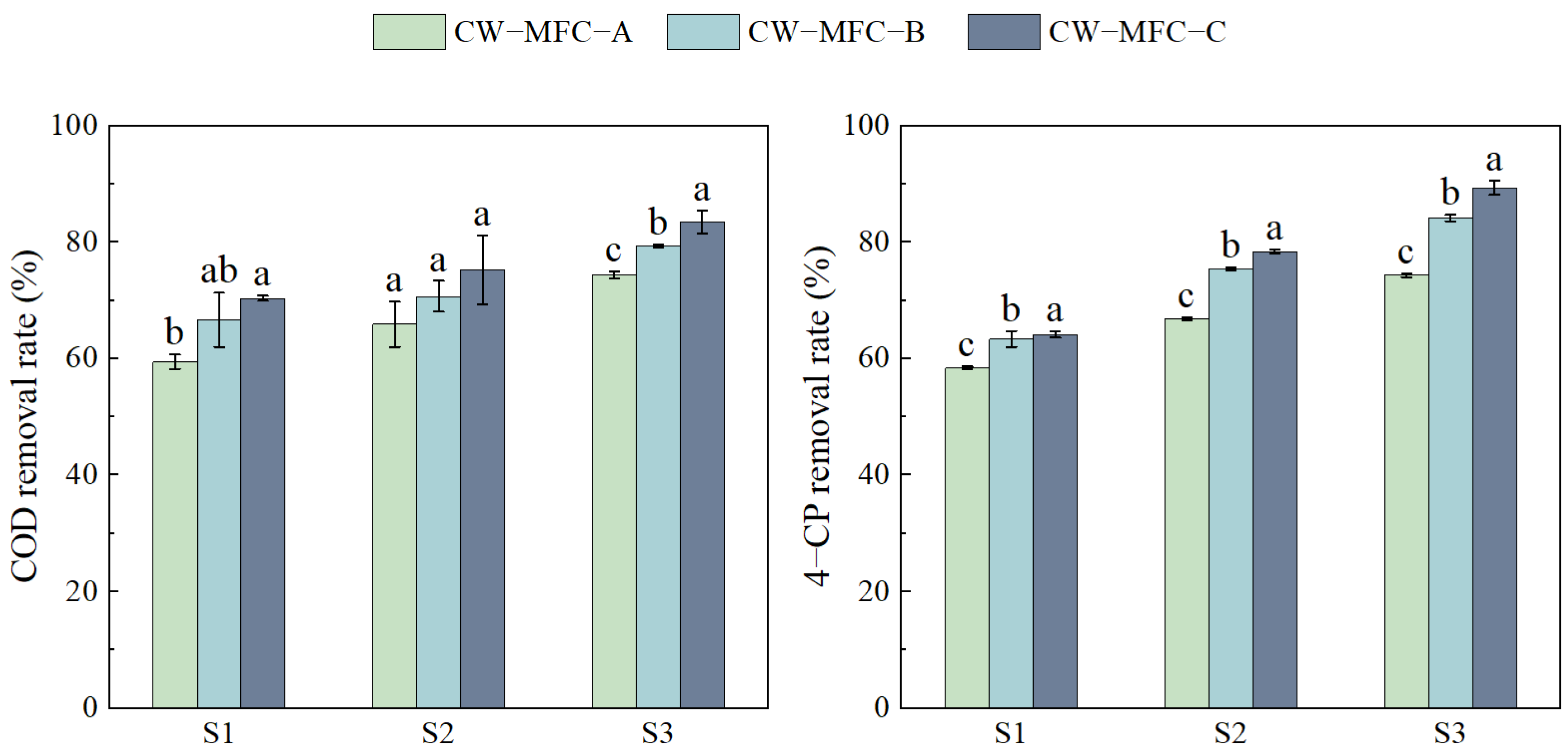
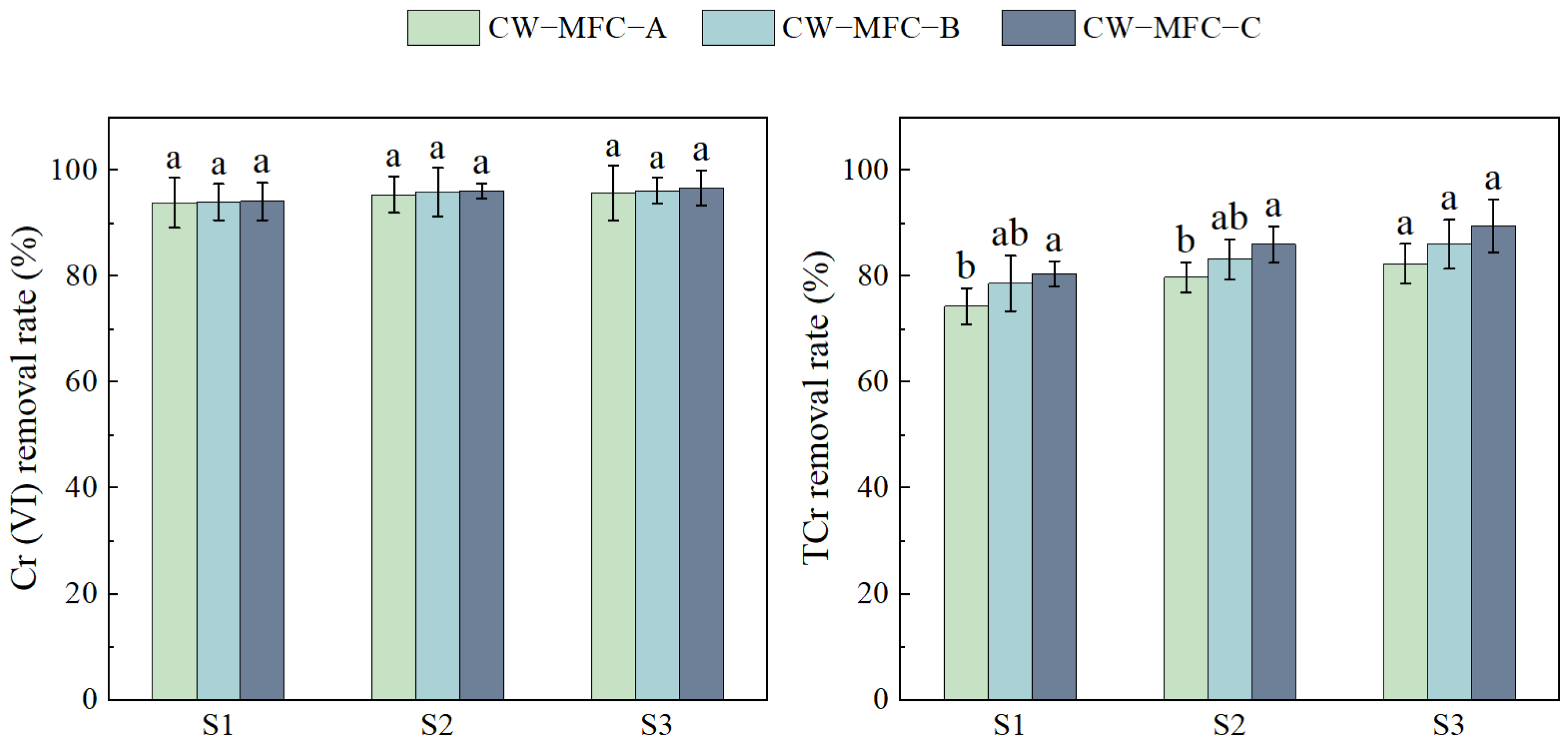
2.1. The Effect of the HRT on Wastewater Purification Performance with Different Configurations
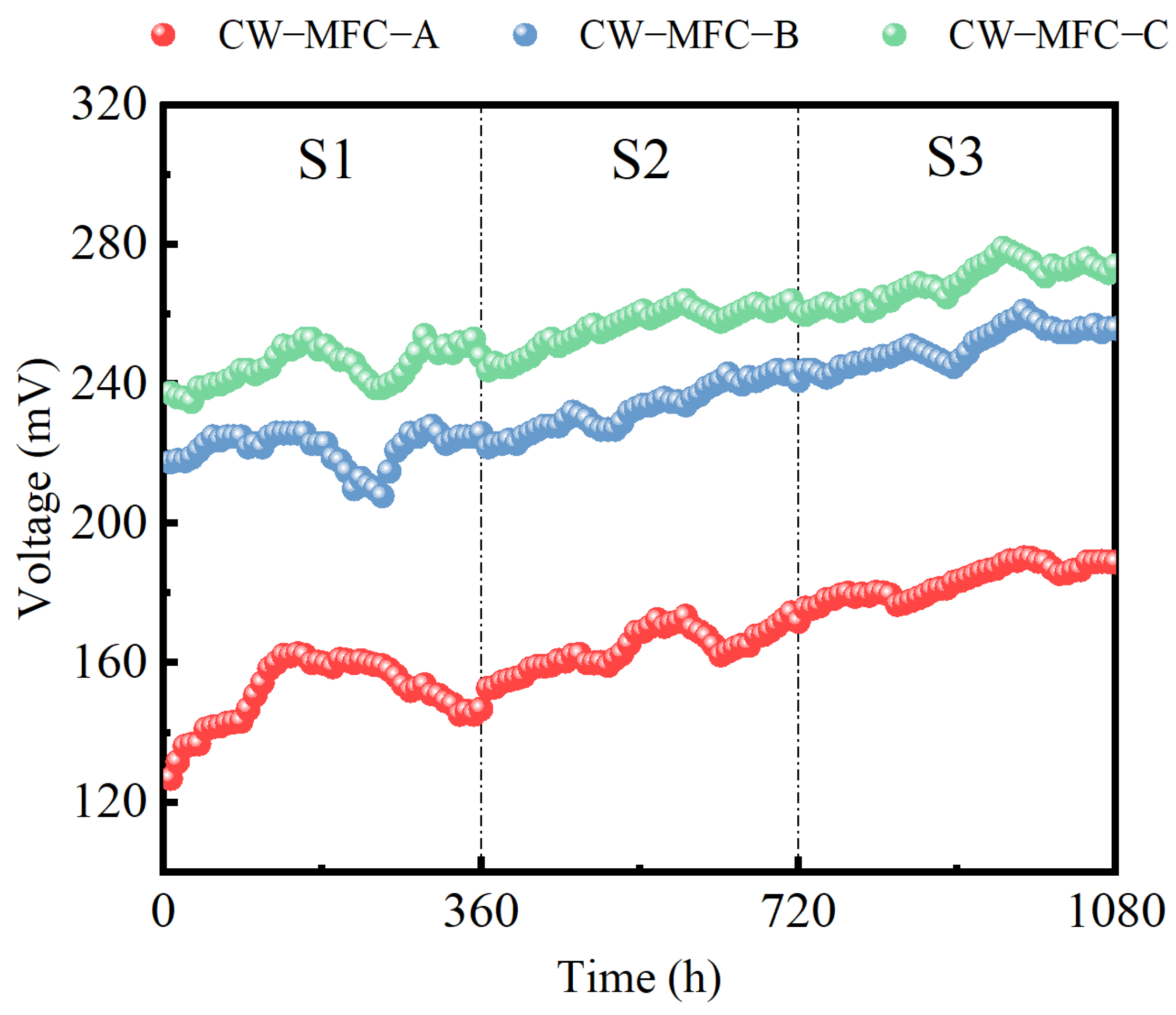
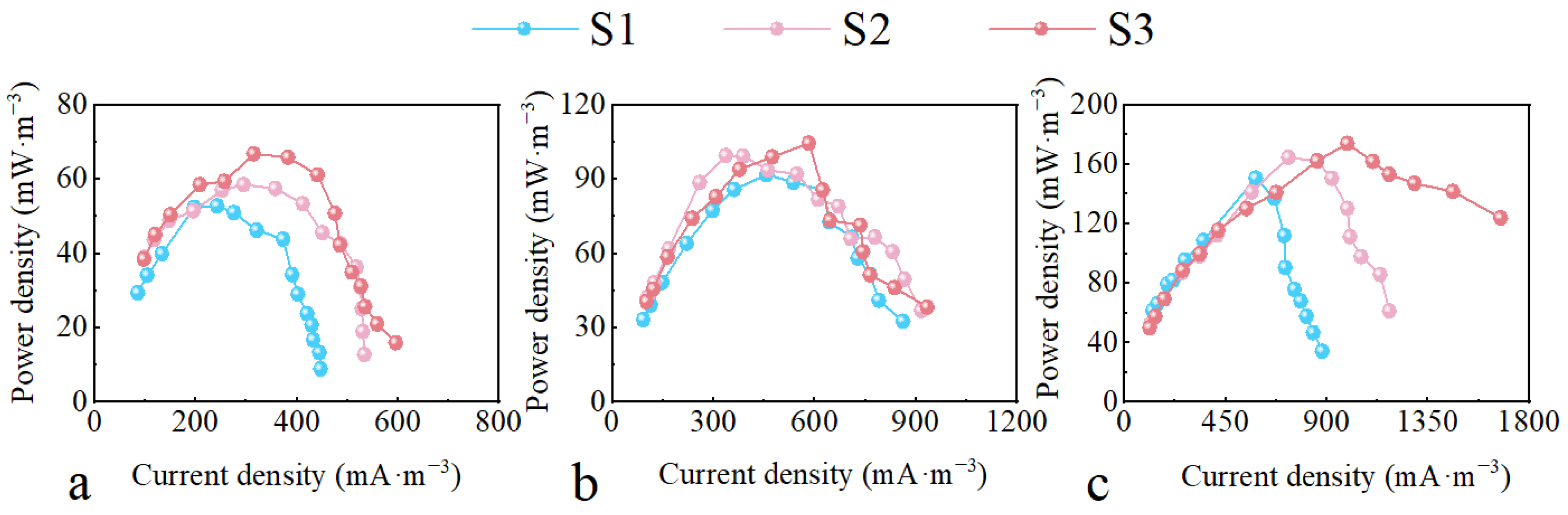
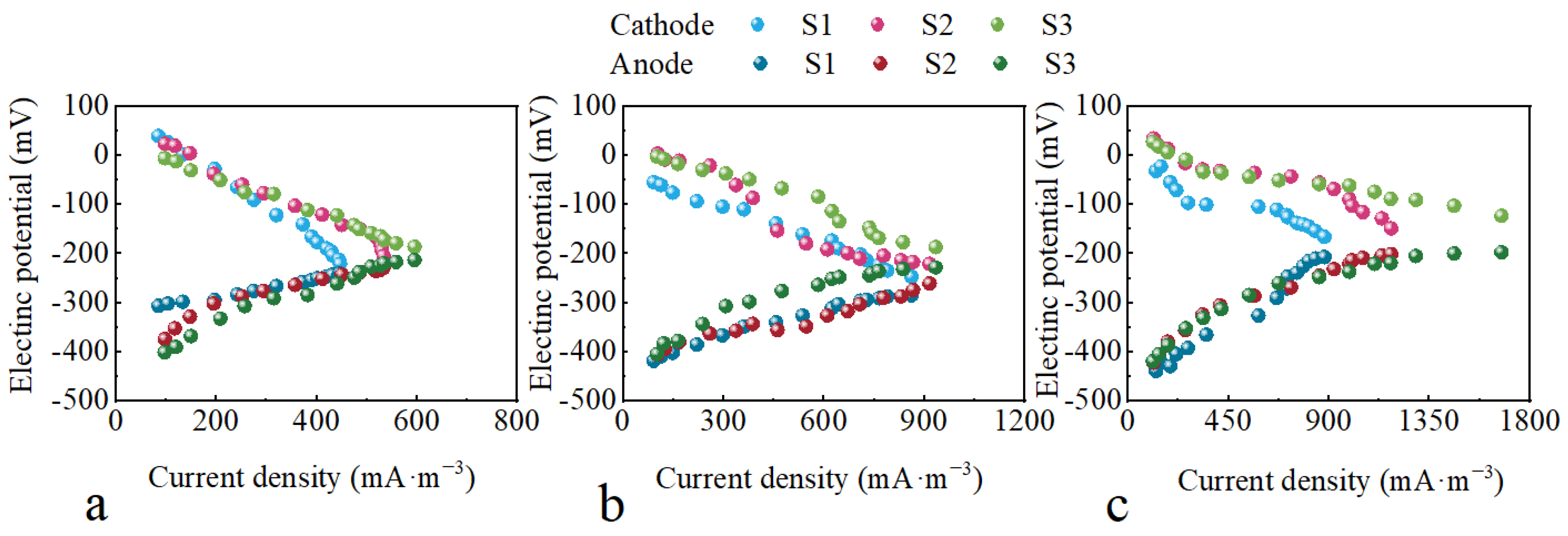
2.2. The Effect of the HRT on Electrochemical Performance with Different Configurations
| HRT | Plant | Pollutant and Removal Rate | Maximum Power Density | Voltage | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 10 h | Lycoris radiata | Cr (Ⅵ) (99.8%) TCr (99.6%) | 23.72 W/m3 | 400 mV | [70] |
| 1.5 d | L. hexandra | Cr (Ⅵ) (99%) | 64.2 mW/m2 | 500 mV | [71] |
| 2.5 d | L. hexandra | Cr (Ⅵ) (98.5%) 4-CP (42.1%) | 64.6 mW/m3 | 516 mV | [8] |
| 3 d | Iris tectorum | Pb (84.86%) | 7.43 mW/m2 | 343 mV | [72] |
| 3 d | N/A | Cr (Ⅵ) (93%) COD (89.2%) | 426.8 mW/m3 | 558.1 mV | [73] |
| 4 d | Acorus calamus L. | TCr (95.6%) COD (86.5%) | 46.63 mW/m2 | 650 mV | [74] |
| 5 d | L. hexandra | Cr (Ⅵ) (96.7%) 4-CP (89.3%) | 174 mW/m3 | 279.1 mV | Present study |
| 6.5 d | L. hexandra | Cr (Ⅵ) (99%) 4-CP (78.6%) | 72.25 mW/m3 | 543 mV | [8] |
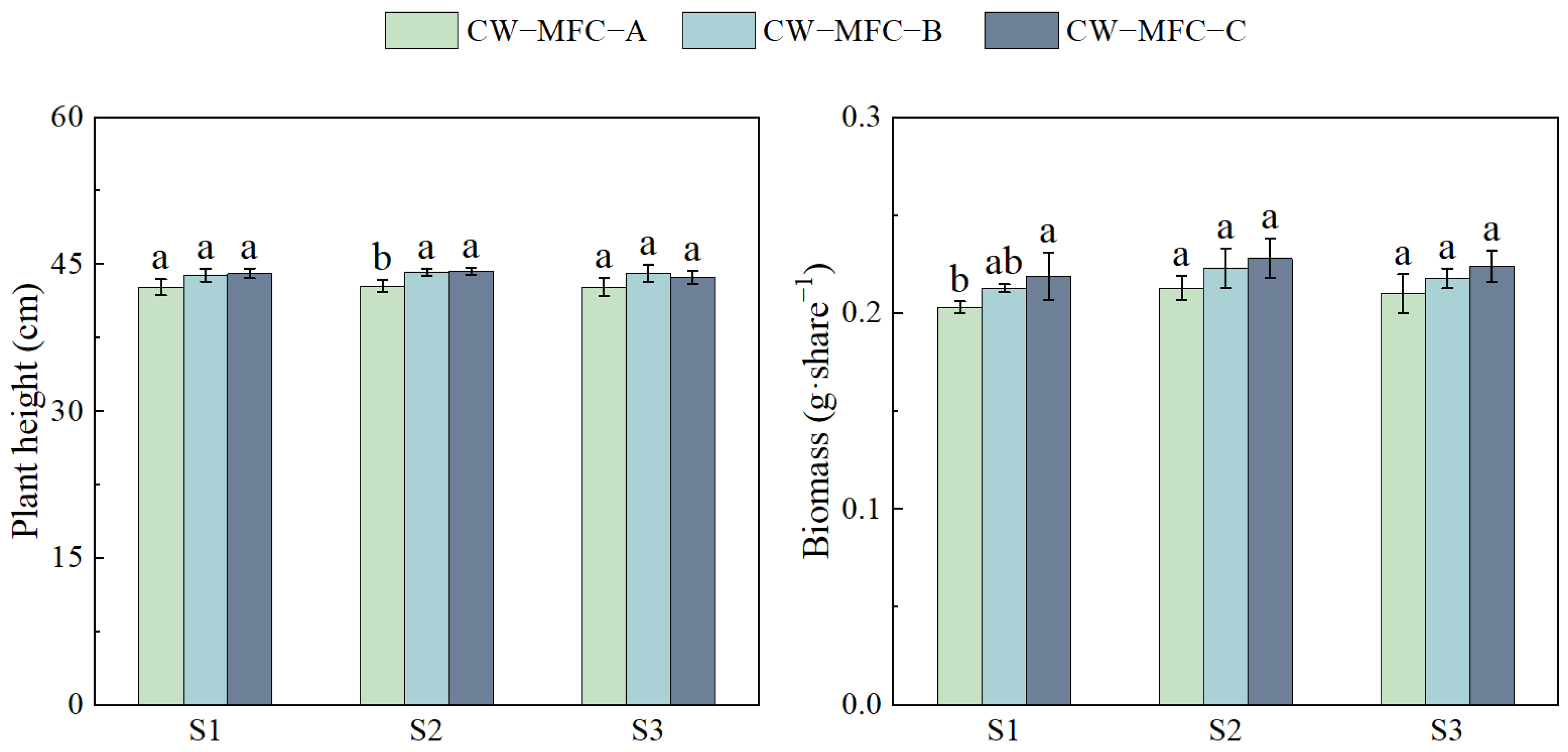
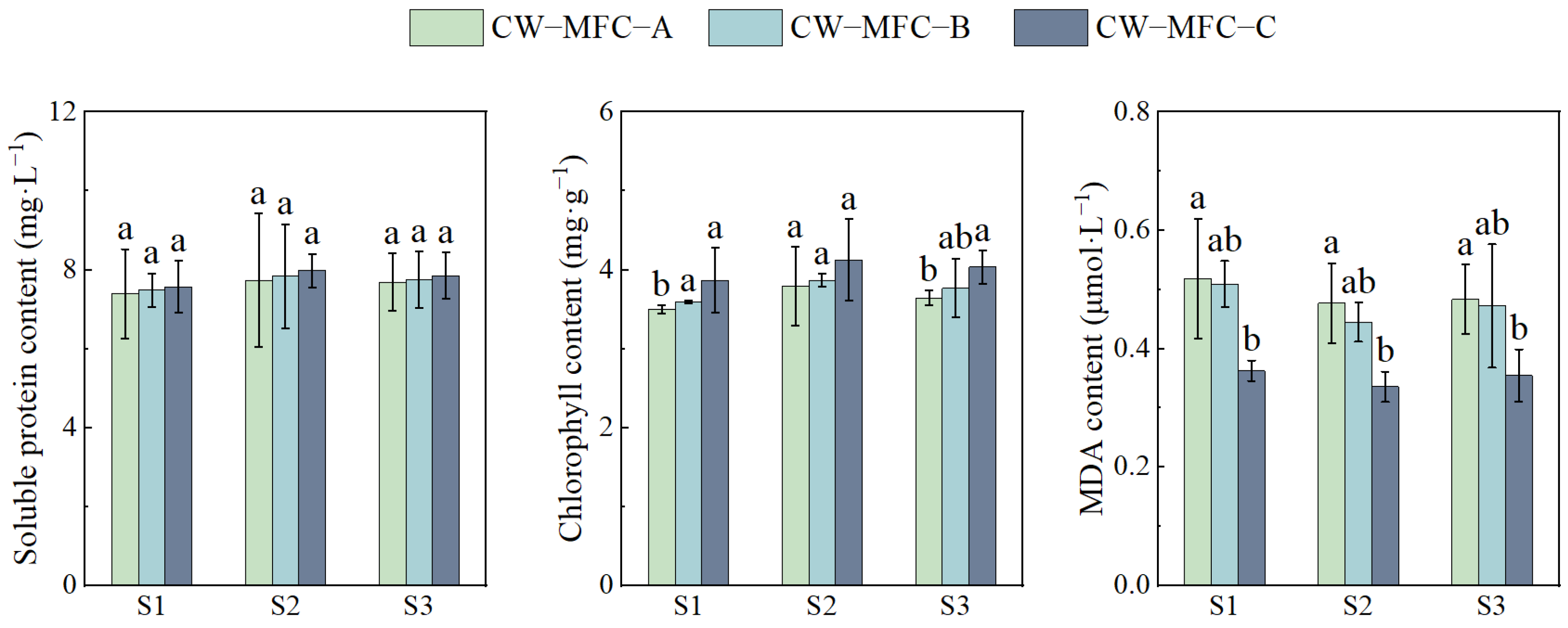
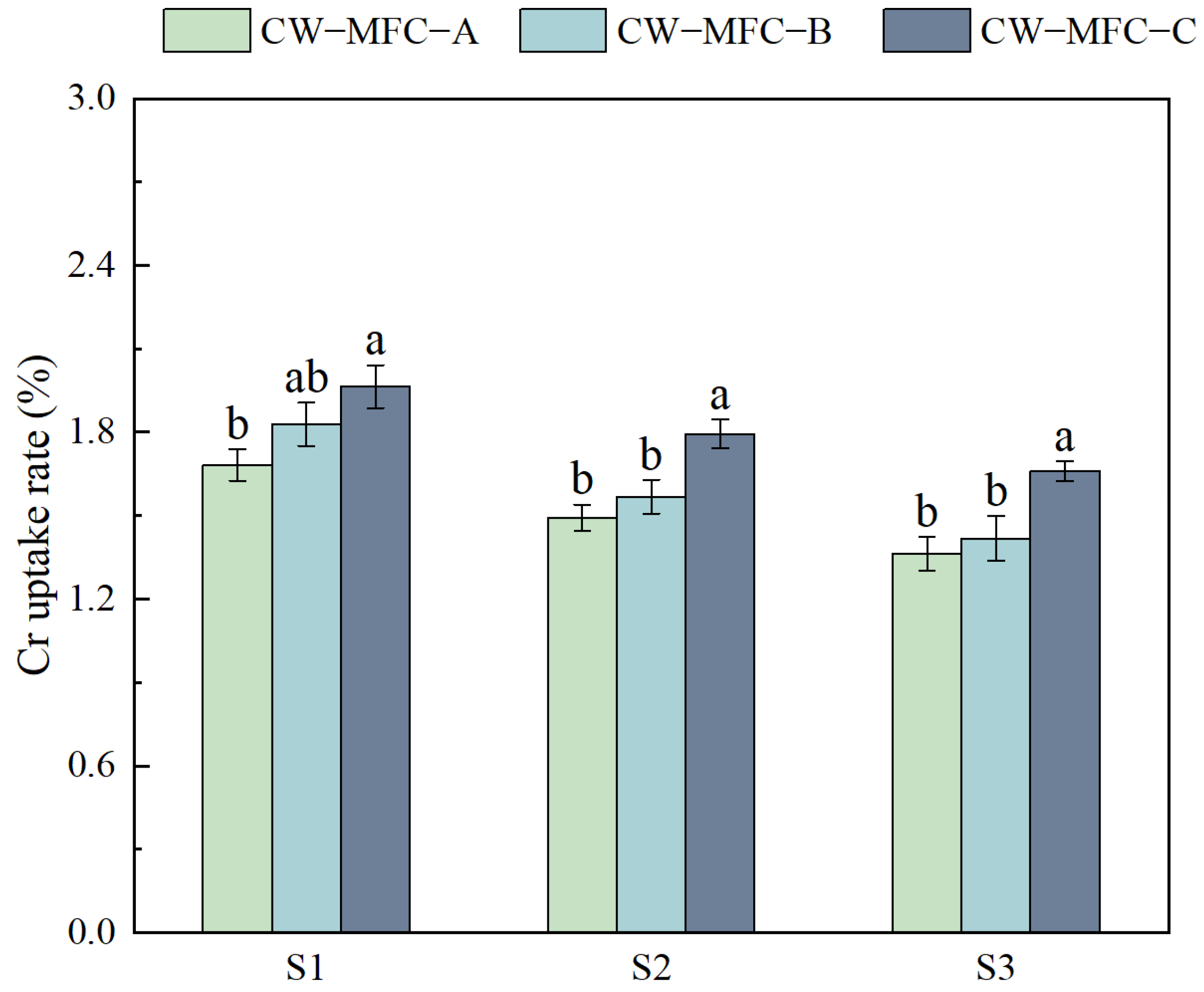
2.3. Effects of HRT on Physiological and Biochemical Responses of L. hexandra with Different Configurations
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. System Setup
3.2. Inoculation and Initiation of CW–MFC
3.3. Water Quality Analysis
3.4. Electrochemical Performance
3.5. Physiological and Biochemical Response and Cr Concentration of L. hexandra
3.6. Methods of Analysis
3.7. Information of Analysis Equipment
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lofrano, G.; Meriç, S.; Zengin, G.E.; Orhon, D. Chemical and Biological Treatment Technologies for Leather Tannery Chemicals and Wastewaters: A Review. Sci. Total Environ. 2013, 461–462, 265–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- China MoEaEotPsRo—2023. Available online: https://www.stats.gov.cn/sj/ndsj/2023/indexch.htm (accessed on 16 August 2024).
- Wang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Lin, H. Effects of pH on Simultaneous Cr(VI) and p-Chlorophenol Removal and Electrochemical Performance in Leersia Hexandra Constructed Wetland-Microbial Fuel Cell. Environ. Technol. 2024, 45, 483–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, S.; Liu, P.; Niu, Y.; Chen, Z.; Khan, A.; Zhang, P.; Li, X. A Novel Early Warning System Based on a Sediment Microbial Fuel Cell for In Situ and Real Time Hexavalent Chromium Detection in Industrial Wastewater. Sensors 2018, 18, 642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Z. Environmental Behavior Characteristics and Research Progress of Persistent Organic Pollutants. Res. Environ. Sci. 2005, 18, 93–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, H.; Yuan, N.; Li, S. Phenol compound harm and measurement method in water. Cience Technol. Inf. 2007, 38, 66. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, A.K.; Chandra, R. Pollutants Released from the Pulp Paper Industry: Aquatic Toxicity and Their Health Hazards. Aquat. Toxicol. 2019, 211, 202–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Lin, H. Removal of Cr (VI) and p-Chlorophenol and Generation of Electricity Using Constructed Wetland-Microbial Fuel Cells Based on Leersia Hexandra Swartz: P-Chlorophenol Concentration and Hydraulic Retention Time Effects. RSC Adv. 2022, 12, 15123–15132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Owlad, M.; Aroua, M.K.; Daud, W.A.W.; Baroutian, S. Removal of Hexavalent Chromium-Contaminated Water and Wastewater: A Review. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2009, 200, 59–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sripriya, R.; Chandrasekaran, M.; Subramanian, K.; Asokan, K.; Noel, M. Electrochemical Destruction of p-Chlorophenol and p-Nitrophenol—Influence of Surfactants and Anode Materials. Chemosphere 2007, 69, 254–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez, J.; Espinosa, C.; Pooch, F.; Tenhu, H.; Pizarro, G.d.C.; Oyarzún, D.P. Poly(N,N-Dimethylaminoethyl Methacrylate) for Removing Chromium (VI) through Polymer-Enhanced Ultrafiltration Technique. React. Funct. Polym. 2018, 127, 67–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xavier, S.; Gandhimathi, R.; Nidheesh, P.V.; Ramesh, S.T. Comparison of Homogeneous and Heterogeneous Fenton Processes for the Removal of Reactive Dye Magenta MB from Aqueous Solution. Desalination Water Treat. 2015, 53, 109–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kickuth, R. A Low-Cost Process for Purification of Municipal and Industrial Waste Water. Der Tropenlandwirt J. Agric. Trop. Subtrop. 1982, 83, 141–154. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Xiao, L.; Lin, H. The In-Depth Revelation of the Mechanism by Which a Downflow Leersia hexandra Swartz Constructed Wetland-Microbial Fuel Cell Synchronously Removes Cr(VI) and p-Chlorophenol and Generates Electricity. Environ. Res. 2023, 216, 114451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Luo, Y.; Huang, H.; Liu, J.; Zhu, Y.; Zeng, Q. Leersia hexandra Swartz: A newly discovered hygrophyte with chromium hyperaccumulator properties. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2006, 26, 950–953. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Z.; Lin, H.; Wang, Y.; Qin, H.; Chhuon, K. Effect of phosphate forms on enrichment of Cu and Cr by Leersia Hexandra Swartz and physiological response. Ecol. Environ. Sci. 2021, 30, 412–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Zhang, X.; You, S.; Wu, Q.; Zhou, K. Function of Leersia hexandra Swartz in Constructed Wetlands for Cr(VI) Decontamination: A Comparative Study of Planted and Unplanted Mesocosms. Ecol. Eng. 2015, 81, 70–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Q.; Liu, J.; You, S.; Zhou, K. Decontamination mechanism of Cr(VI)-polluted water in constructed we-tland planted with Leersia hexandra Swartz. Acta Sci. Circumstantiae 2014, 34, 2306–2312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, S.; Zhang, X.; Liu, J.; Tao, J.; Zhao, Y.; Jin, X.; Yang, M. Study on the decontamination of electroplating wastewater by Leersia hexandra Swartz constructed wetland. Ind. Water Treat. 2014, 34, 23–26. [Google Scholar]
- Ji, W.; Zhu, M.; Zhang, S.; Wang, W.; Fan, X. Research progress on constructed wetland for advanced treatment of municipal tailwater. Water Purif. Technol. 2024, 43, 9–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, Z.; Song, H.; Cang, N.; Li, X. Electricity Production from Azo Dye Wastewater Using a Microbial Fuel Cell Coupled Constructed Wetland Operating under Different Operating Conditions. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2015, 68, 135–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abourached, C.; Catal, T.; Liu, H. Efficacy of Single-Chamber Microbial Fuel Cells for Removal of Cadmium and Zinc with Simultaneous Electricity Production. Water Res. 2014, 51, 228–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doherty, L.; Zhao, Y.; Zhao, X.; Wang, W. Nutrient and Organics Removal from Swine Slurry with Simultaneous Electricity Generation in an Alum Sludge-Based Constructed Wetland Incorporating Microbial Fuel Cell Technology. Chem. Eng. J. 2015, 266, 74–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strik, D.P.B.T.B.; Hamelers (Bert), H.V.M.; Snel, J.F.H.; Buisman, C.J.N. Green Electricity Production with Living Plants and Bacteria in a Fuel Cell. Int. J. Energy Res. 2008, 32, 870–876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, C.; Wang, L.; Wang, L. Removal of Cr(VI) and Electricity Production by Constructed Wetland Combined with Microbial Fuel Cell (CW-MFC): Influence of Filler Media. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 320, 128860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Tang, G.; You, S.; Jiang, P. Effect of External Aeration on Cr (VI) Reduction in the Leersia Hexandra Swartz Constructed Wetland-Microbial Fuel Cell System. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 3309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, T.; Liu, R.; Gao, F. Energy Capture and Nutrients Removal Enhancement through a Stacked Constructed Wetland Incorporated with Microbial Fuel Cell. Water Sci. Technol. 2017, 76, 28–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Yang, X.-L.; Li, H.; Song, H.-L.; Wang, R.-C.; Dai, Z.-Q. Degradation of Sulfamethoxazole in Bioelectrochemical System with Power Supplied by Constructed Wetland-Coupled Microbial Fuel Cells. Bioresour. Technol. 2017, 244, 345–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, B.; Wang, T.; Zhao, Y. Two-Stage Hybrid Constructed Wetland-Microbial Fuel Cells for Swine Wastewater Treatment and Bioenergy Generation. Chemosphere 2021, 268, 128803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srivastava, P.; Yadav, A.K.; Garaniya, V.; Lewis, T.; Abbassi, R.; Khan, S.J. Electrode Dependent Anaerobic Ammonium Oxidation in Microbial Fuel Cell Integrated Hybrid Constructed Wetlands: A New Process. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 698, 134248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, P.; Lin, Y.; Lin, H.; Xiao, L.; Gan, S.; Wang, Y. Effect of the constructed wetland-microbial fuel cells with different configurations on the purification of 4-chlorophenol in wastewater and the power generation performance. Chin. J. Environ. Eng. 2023, 17, 507–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamta, P.; Rani, N.; Yadav, A.K. Enhanced Wastewater Treatment and Electricity Generation Using Stacked Constructed Wetland–Microbial Fuel Cells. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2020, 18, 871–879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muhammad Nashafi, A.; Thiravetyan, P.; Dolphen, R.; Treesubsuntorn, C. Using Stacked Pot Connection of Wetland Microbial Fuel Cells to Charge the Battery: Potential and Effecting Factor. Environ. Res. 2024, 252, 119066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verma, P.; Ray, S. Critical Evaluation of Electroactive Wetlands: Traditional and Modern Advances. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2024, 31, 14349–14366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, S.; Nayak, A.; Roy, C.; Yadav, A.K. An Algal Assisted Constructed Wetland-Microbial Fuel Cell Integrated with Sand Filter for Efficient Wastewater Treatment and Electricity Production. Chemosphere 2021, 263, 128132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Hu, J.; Tang, L.; Liu, Z.; Hou, J.; Yang, S.; Li, Y. Microbial Fuel Cell and Building Energy Efficiency. Chem. Bioeng. 2015, 32, 11–13. [Google Scholar]
- He, W. The Modular Design and Key Factors Iscaling-Up of Air Cathode Microbial Fuel Cell; Harbin Institute of Technology: Harbin, China, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, H.; Duan, J.; Ma, H.; Zhu, Y.; Zhou, Z.; Shi, M.; Li, J. The effect of the configurations of constructed wetland microbial fuel cells on ammonia nitrogen removal under low temperatures. J. Chem. Eng. Chin. Univ. 2023, 37, 153–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meylani, V.; Surahman, E.; Fudholi, A.; Almalki, W.H.; Ilyas, N.; Sayyed, R.Z. Biodiversity in Microbial Fuel Cells: Review of a Promising Technology for Wastewater Treatment. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2023, 11, 109503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Tian, Y.; Liu, H.; Zhao, X.; Peng, S. Optimizing the Performance of Organics and Nutrient Removal in Constructed Wetland–Microbial Fuel Cell Systems. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 653, 860–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Song, X.; Wang, Y.; Bai, J.; Bai, H.; Yan, D.; Cao, Y.; Li, Y.; Yu, Z.; Dong, G. Bioelectricity Generation, Contaminant Removal and Bacterial Community Distribution as Affected by Substrate Material Size and Aquatic Macrophyte in Constructed Wetland-Microbial Fuel Cell. Bioresour. Technol. 2017, 245, 372–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, T.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, C.; Dai, K.; Guo, M.; Xu, T.; Ma, J. Hydraulic retention time and purification effect of two kinds of constructed wetlands. Chin. J. Environ. Eng. 2012, 6, 883–890. [Google Scholar]
- Ding, C.; Yang, T.; Yu, Q.; Li, Z.; Yang, C. Treatment of 1,2-dichlorobenzene in Wastewater by Using Horizontal Subsurface Flow Constructed Wetlands. Environ. Sci. 2011, 32, 2582–2587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Zhang, M.; Lin, H.; Liu, X.; Wang, X.; Hai, R. Research on Constructed Wetland Coupled with Microbial Fuel Cell for Electricity Production and Wastewater Treatment. Technol. Water Treat. 2022, 48, 94–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Zhang, S.; Yang, X.-L.; Yang, Y.-L.; Xu, H.; Li, X.-N.; Song, H.-L. Enhanced Degradation of Bisphenol A and Ibuprofen by an Up-Flow Microbial Fuel Cell-Coupled Constructed Wetland and Analysis of Bacterial Community Structure. Chemosphere 2019, 217, 599–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Minakshi, D.; Sharma, P.K.; Rani, A.; Malaviya, P.; Srivastava, V.; Kumar, M. Performance Evaluation of Vertical Constructed Wetland Units with Hydraulic Retention Time as a Variable Operating Factor. Groundw. Sustain. Dev. 2022, 19, 100834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Yu, Q.; Yuan, S.; Zhu, L.; Yang, L.; Chen, C. Power production performance and water purification of composite vertical flow constructed wetland-microbial fuel cell (CW-MFC) coupling system. Ind. Catal. 2024, 32, 80–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Wang, Z. An eco-type microbial fuel cell for simultaneous electricity generation and nitrogen removal. Environ. Eng. 2023, 41, 116–122, 149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Wang, L.; Wang, L. Study on the Performance of Microbial Fuel Cell-Constructed Wetland for Wastewater Treatment and Simultaneous Electricity Generation. Technol. Water Treat. 2018, 44, 109–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, D.; Curtis, M.; Troop, E.; Scheible, K.; McGrath, J.; Hu, B.; Suib, S.; Raymond, D.; Li, B. A Pilot-Scale Study on Utilizing Multi-Anode/Cathode Microbial Fuel Cells (MAC MFCs) to Enhance the Power Production in Wastewater Treatment. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2011, 36, 876–884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagner, T.V.; de Wilde, V.; Willemsen, B.; Mutaqin, M.; Putri, G.; Opdam, J.; Parsons, J.R.; Rijnaarts, H.H.M.; de Voogt, P.; Langenhoff, A.A.M. Pilot-Scale Hybrid Constructed Wetlands for the Treatment of Cooling Tower Water Prior to Its Desalination and Reuse. J. Environ. Manag. 2020, 271, 110972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ieropoulos, I.; Winfield, J.; Greenman, J. Effects of Flow-Rate, Inoculum and Time on the Internal Resistance of Microbial Fuel Cells. Bioresour. Technol. 2010, 101, 3520–3525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Chen, S.; Wang, B.; Li, M.; Zhou, M.; Zhou, R.; Yan, J.; Song, T. Purification effect of combined artificial wetlands on the dispersed domestic sewage and analysis of microbial community structure. Environ. Chem. 2019, 38, 2535–2545. [Google Scholar]
- Ho, K.F.; Lee, S.C.; Louie, P.K.K.; Zou, S.C. Seasonal Variation of Carbonyl Compound Concentrations in Urban Area of Hong Kong. Atmos. Environ. 2002, 36, 1259–1265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Fu, J.; Addo-Bankas, O.; Wei, T. Electron Flow in Constructed Wetland-Microbial Fuel Cells and Its Effect on Wastewater Treatment Enhancement. China Water Wastewater 2021, 37, 27–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, C.; Lee, C.R.; Song, Y.E.; Heo, J.; Choi, S.M.; Lim, D.-H.; Cho, J.; Park, C.; Jang, M.; Kim, J.R. Hexavalent Chromium as a Cathodic Electron Acceptor in a Bipolar Membrane Microbial Fuel Cell with the Simultaneous Treatment of Electroplating Wastewater. Chem. Eng. J. 2017, 328, 703–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeppilli, M.; Matturro, B.; Dell’Armi, E.; Cristiani, L.; Papini, M.P.; Rossetti, S.; Majone, M. Reductive/Oxidative Sequential Bioelectrochemical Process for Perchloroethylene (PCE) Removal: Effect of the Applied Reductive Potential and Microbial Community Characterization. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 104657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez-Acata, S.; Esquivel-Ríos, I.; Pérez-Sandoval, M.V.; Navarro-Noya, Y.; Rojas-Valdez, A.; Thalasso, F.; Luna-Guido, M.; Dendooven, L. Bacterial Community Structure within an Activated Sludge Reactor Added with Phenolic Compounds. Appl Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2017, 101, 3405–3414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montenegro, I.P.F.M.; Mucha, A.P.; Tomasino, M.P.; Gomes, C.R.; Almeida, C.M.R. Alkylphenols and Chlorophenols Remediation in Vertical Flow Constructed Wetlands: Removal Efficiency and Microbial Community Response. Water 2021, 13, 715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, X.; Jin, M.; Xu, H.; Chen, W.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, M.; Shao, X.; Xu, Z.; Wang, W. Enhanced Simultaneous Nitrogen and Phosphorus Removal in A Denitrifying Biological Filter Using Waterworks Sludge Ceramsite Coupled with Iron-Carbon. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 2646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, F.; Cao, F.; Kong, Q.; Zhou, L.; Yuan, Q.; Zhu, Y.; Wang, Q.; Du, Y.; Wang, Z. Electricity Production and Evolution of Microbial Community in the Constructed Wetland-Microbial Fuel Cell. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 339, 479–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oon, Y.-L.; Ong, S.-A.; Ho, L.-N.; Wong, Y.-S.; Dahalan, F.A.; Oon, Y.-S.; Lehl, H.K.; Thung, W.-E.; Nordin, N. Role of Macrophyte and Effect of Supplementary Aeration in Up-Flow Constructed Wetland-Microbial Fuel Cell for Simultaneous Wastewater Treatment and Energy Recovery. Bioresour. Technol. 2017, 224, 265–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, C.; Lin, H.; Zhang, X.; Chhuon, K. Research progress on constructed wetland-microbial fuel cell coupling system. Mod. Chem. Ind. 2021, 41, 21–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Zheng, J.; Zhang, Y.; Lin, H. Electrochemical properties and microbial community structure of constructed wetland microbial fuel cell under different matrix carbon source. Chin. J. Environ. Eng. 2021, 15, 3696–3706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pepè Sciarria, T.; Arioli, S.; Gargari, G.; Mora, D.; Adani, F. Monitoring Microbial Communities’ Dynamics during the Start-up of Microbial Fuel Cells by High-Throughput Screening Techniques. Biotechnol. Rep. 2019, 21, e00310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Song, X.; Wang, Y.; Abayneh, B.; Li, Y.; Yan, D.; Bai, J. Nitrate Removal and Bioenergy Production in Constructed Wetland Coupled with Microbial Fuel Cell: Establishment of Electrochemically Active Bacteria Community on Anode. Bioresour. Technol. 2016, 221, 358–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vilajeliu-Pons, A.; Bañeras, L.; Puig, S.; Molognoni, D.; Vilà-Rovira, A.; Amo, E.H.; Balaguer, M.D.; Colprim, J. External Resistances Applied to MFC Affect Core Microbiome and Swine Manure Treatment Efficiencies. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0164044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, H.; Pritchard, P.H.; Sewell, G.W. Microbial Reduction of Cr(VI) during Anaerobic Degradation of Benzoate. Environ. Sci. Technol. 1996, 30, 1667–1674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erensoy, A.; Çek, N. Investigation of Polymer Biofilm Formation on Titanium-Based Anode Surface in Microbial Fuel Cells with Poplar Substrate. Polymers 2021, 13, 1833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.-X.; Yang, H.-C.; Guo, S.; Qi, C.-F.; Wu, K.-J.; Guo, F.-F. Remediation of Chromium Contaminated Soil by Microbial Electrochemical Technology. Int. J. Electrochem. Sci. 2020, 15, 6143–6154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Yu, G.; Yao, Y.; Lin, H. Effects of Flow Pattern, Leersia hexandra, and Circuit Mode on the Cr (Ⅵ) Removal Capacity, Electricity Generation Performance, and Microbial Community of Constructed Wetland-Microbial Fuel Cells. Fuel 2023, 338, 127326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.; Shang, D.; Zou, Y.; Du, Y.; Wang, Q.; Xu, F.; Ren, L.; Kong, Q. Changes in Electricity Production and Microbial Community Evolution in Constructed Wetland-Microbial Fuel Cell Exposed to Wastewater Containing Pb(II). Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 732, 139127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, C.; Wang, L.; Wang, L. Performance of Lab-Scale Microbial Fuel Cell Coupled with Unplanted Constructed Wetland for Hexavalent Chromium Removal and Electricity Production. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 25140–25148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, S.; Qiu, D.; Lu, F.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Z.; Feng, X.; Pyo, S.-H. Acorus calamus L. Constructed Wetland-Microbial Fuel Cell for Cr(VI)-Containing Wastewater Treatment and Bioelectricity Production. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2022, 10, 107801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, F. Physiological and Molecular Mechanisms of Chromium Stress and Tolerance in Rice; Zhejiang University: Hangzhou, China, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Qin, H.; Lin, H.; Xu, H.; Liu, Z.; Wang, Y.; Gan, S. The Enrichment Characteristics of Leersia Hexandra Swartz to Ni in Water and its Photosynthetic Physiological Response. Technol. Water Treat. 2022, 48, 92–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Han, P.; Pan, Y.; Wu, M.; Zhao, Y.; Jia, Y.; Jiang, B.; Zhang, L.; Xu, Q.; Liu, S. Effects of cadmium stress on photosynthetic physiology and chlorophyll fluorescence in Solanum nigrum and Solanum americanum. J. Agro-Environ. Sci. 2021, 40, 26–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farquhar, G.D.; Sharkey, T.D. Stomatal Conductance and Photosynthesis. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 1982, 33, 317–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vera, I.; Verdejo, N.; Chávez, W.; Jorquera, C.; Olave, J. Influence of Hydraulic Retention Time and Plant Species on Performance of Mesocosm Subsurface Constructed Wetlands during Municipal Wastewater Treatment in Super-Arid Areas. J. Environ. Sci. Health Part A 2016, 51, 105–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ilyas, H.; van Hullebusch, E.D. Role of Design and Operational Factors in the Removal of Pharmaceuticals by Constructed Wetlands. Water 2019, 11, 2356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, X.; Shen, Y.; Yang, Q.; Kawi, S.; He, Z.; Yang, X.; Wang, C.-H. Simultaneous Syngas and Biochar Production during Heavy Metal Separation from Cd/Zn Hyperaccumulator (Sedum alfredii) by Gasification. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 347, 543–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.-Y.; Oh, S.; Park, Y.-K. Overview of Biochar Production from Preservative-Treated Wood with Detailed Analysis of Biochar Characteristics, Heavy Metals Behaviors, and Their Ecotoxicity. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 384, 121356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Valdez, E.; Alarcón, A.; Ferrera-Cerrato, R.; Vega-Carrillo, H.R.; Maldonado-Vega, M.; Salas-Luévano, M.Á.; Argumedo-Delira, R. Induced Accumulation of Au, Ag and Cu in Brassica napus Grown in a Mine Tailings with the Inoculation of Aspergillus niger and the Application of Two Chemical Compounds. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2018, 154, 180–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, X.; Zhang, J.; Wang, X.; Pan, M.; Lin, Q.; Khan, K.Y.; Yan, B.; Li, T.; He, Z.; Yang, X.; et al. A Review on the Thermal Treatment of Heavy Metal Hyperaccumulator: Fates of Heavy Metals and Generation of Products. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 405, 123832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, S.; Song, H.; Wei, S.; Yang, F.; Li, X. Bio-Cathode Materials Evaluation and Configuration Optimization for Power Output of Vertical Subsurface Flow Constructed Wetland—Microbial Fuel Cell Systems. Bioresour. Technol. 2014, 166, 575–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, G.; Guo, Y.; Cai, J.; Wen, H.; Mao, Z.; Zhang, H.; Wang, X.; Ma, L.; Zhu, M. Electricity Production and the Analysis of the Anode Microbial Community in a Constructed Wetland-Microbial Fuel Cell. RSC Adv. 2019, 9, 21460–21472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ministry of Ecology and Environment of the People’s Republic of China. Water quality-Determination of Total Nitrogen-Alkaline Potassium Persulfate Digestion UV Spectrophotometric Method. Available online: https://www.mee.gov.cn/ywgz/fgbz/bz/bzwb/jcffbz/201203/t20120307_224383.shtml (accessed on 19 August 2024).
- Xing, C.; Xu, X.; Xu, Z.; Wang, R.; Xu, L. Study on the Decontamination Effect of Biochar-Constructed Wetland under Different Hydraulic Conditions. Water 2021, 13, 893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurnik, K.; Treder, K.; Skorupa-Kłaput, M.; Tretyn, A.; Tyburski, J. Removal of Phenol from Synthetic and Industrial Wastewater by Potato Pulp Peroxidases. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2015, 226, 254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, Y.; Wang, W.; Yu, P.; Xi, Z.; Xu, L.; Li, X.; He, N. Comparison of Taurine, GABA, Glu, and Asp as Scavengers of Malondialdehyde in Vitro and in Vivo. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2013, 8, 190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boxman, A.W.; Krabbendam, H.; Bellemakers, M.J.S.; Roelofs, J.G.M. Effects of Ammonium and Aluminium on the Development and Nutrition of Pinus nigra in Hydroculture. Environ. Pollut. 1991, 73, 119–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sonawane, J.M.; Al-Saadi, S.; Singh Raman, R.K.; Ghosh, P.C.; Adeloju, S.B. Exploring the Use of Polyaniline-Modified Stainless Steel Plates as Low-Cost, High-Performance Anodes for Microbial Fuel Cells. Electrochim. Acta 2018, 268, 484–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Full Name | Abbreviation |
|---|---|
| Constructed wetland | CW |
| Constructed wetland–microbial fuel cell | CW-MFC |
| Hexavalent chromium | Cr (VI) |
| p-chlorophenol | 4-CP |
| Electrochemically active bacteria | EABs |
| Hydraulic retention time | HRT |
| Leersia hexandra Swartz | L. hexandra |
| Chemical oxygen demand | COD |
| Ammonia nitrogen | NH4+-N |
| Total nitrogen | TN |
| Malondialdehyde | MDA |
| Nutrient Substance | Chemical | Concentration (mg·L−1) |
|---|---|---|
| Carbon source | CH3COONa | 192.31 |
| Nitrogen source | NH4Cl | 107.70 |
| Phosphorus source | KH2PO4·2H2O | 19.68 |
| K2HPO4 | 29.16 | |
| Trace element | MgSO4·7H2O | 2.46 |
| FeSO4·7H2O | 0.009 | |
| ZnSO4·7H2O | 0.04 | |
| CuSO4·5H2O | 0.0028 | |
| CaCl2 | 0.0082 | |
| MnCl2·4H2O | 0.008 | |
| CoCl2·6H2O | 0.0029 | |
| NiCl2·6H2O | 0.014 | |
| Na2MoO4·6H2O | 0.011 |
| Period | HRT (d) |
|---|---|
| Stage 1 (S1) | 3 |
| Stage 2 (S2) | 4 |
| Stage 3 (S3) | 5 |
| No. | Instrument Name | Manufacturer |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | UV/Vis Spectrophotometer | Shanghai Metash Instruments Co., Ltd., Shanghai, China |
| 2 | Digital multimeter | Shanghai Fluke Test Instruments Co., Ltd., Shanghai, China |
| 3 | Peristaltic pump | BaoDing Lead Fluid Technology Co., Ltd., BaoDing, China |
| 4 | COD digestion instrument | QingDao Source Enviromental Protection Equipment Co., Ltd., QingDao, China |
| 5 | Voltage data sensor | Vernier, Oregon, America |
| 6 | ICP-OES | Agilent, California, America |
| 7 | Photosynthesizer | Zhe Jiang TOP Instrument Co., Ltd., Hang Zhou, China |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, T.; Yang, P.; Yan, J.; Chen, M.; You, S.; Bai, J.; Yu, G.; Ullah, H.; Chen, J.; Lin, H. Effects of Hydraulic Retention Time on Removal of Cr (VI) and p-Chlorophenol and Electricity Generation in L. hexandra-Planted Constructed Wetland–Microbial Fuel Cell. Molecules 2024, 29, 4773. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29194773
Li T, Yang P, Yan J, Chen M, You S, Bai J, Yu G, Ullah H, Chen J, Lin H. Effects of Hydraulic Retention Time on Removal of Cr (VI) and p-Chlorophenol and Electricity Generation in L. hexandra-Planted Constructed Wetland–Microbial Fuel Cell. Molecules. 2024; 29(19):4773. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29194773
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Tangming, Peiwen Yang, Jun Yan, Mouyixing Chen, Shengxiong You, Jiahuan Bai, Guo Yu, Habib Ullah, Jihuan Chen, and Hua Lin. 2024. "Effects of Hydraulic Retention Time on Removal of Cr (VI) and p-Chlorophenol and Electricity Generation in L. hexandra-Planted Constructed Wetland–Microbial Fuel Cell" Molecules 29, no. 19: 4773. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29194773
APA StyleLi, T., Yang, P., Yan, J., Chen, M., You, S., Bai, J., Yu, G., Ullah, H., Chen, J., & Lin, H. (2024). Effects of Hydraulic Retention Time on Removal of Cr (VI) and p-Chlorophenol and Electricity Generation in L. hexandra-Planted Constructed Wetland–Microbial Fuel Cell. Molecules, 29(19), 4773. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29194773







