Discovery and Optimization of Ergosterol Peroxide Derivatives as Novel Glutaminase 1 Inhibitors for the Treatment of Triple-Negative Breast Cancer
Abstract
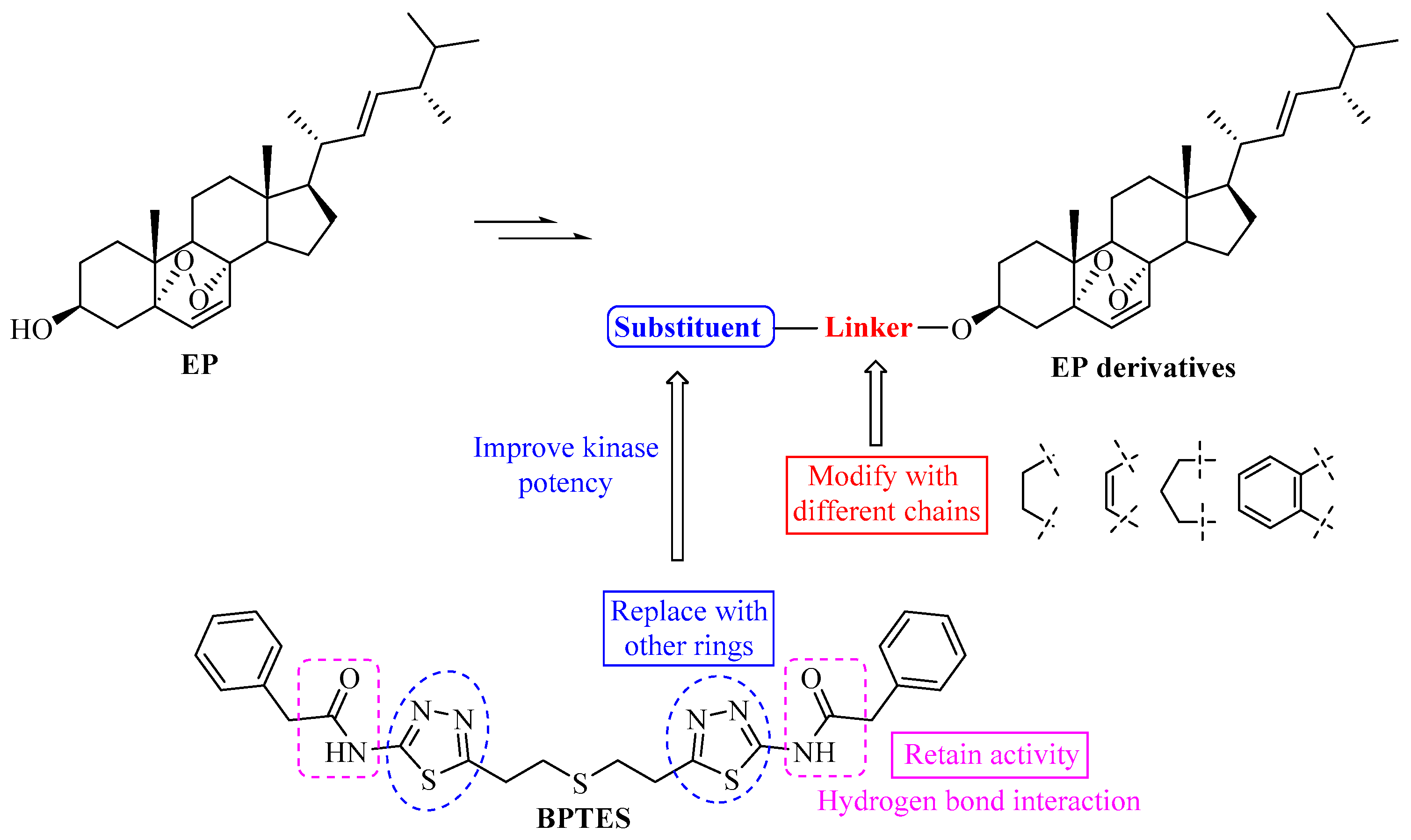
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
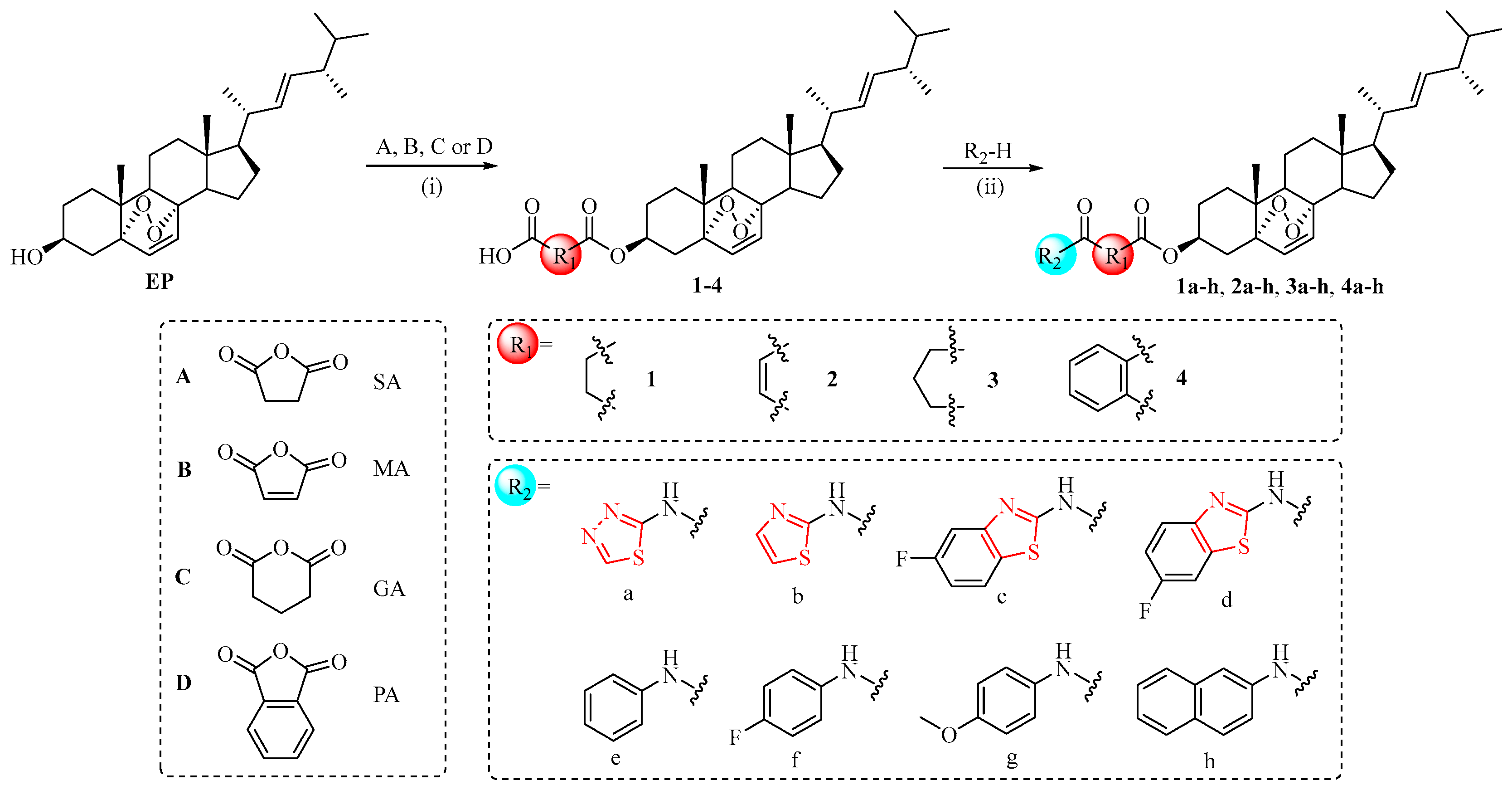
2.1. Chemistry
2.2. In Vitro Antiproliferative Activity of EP Derivatives
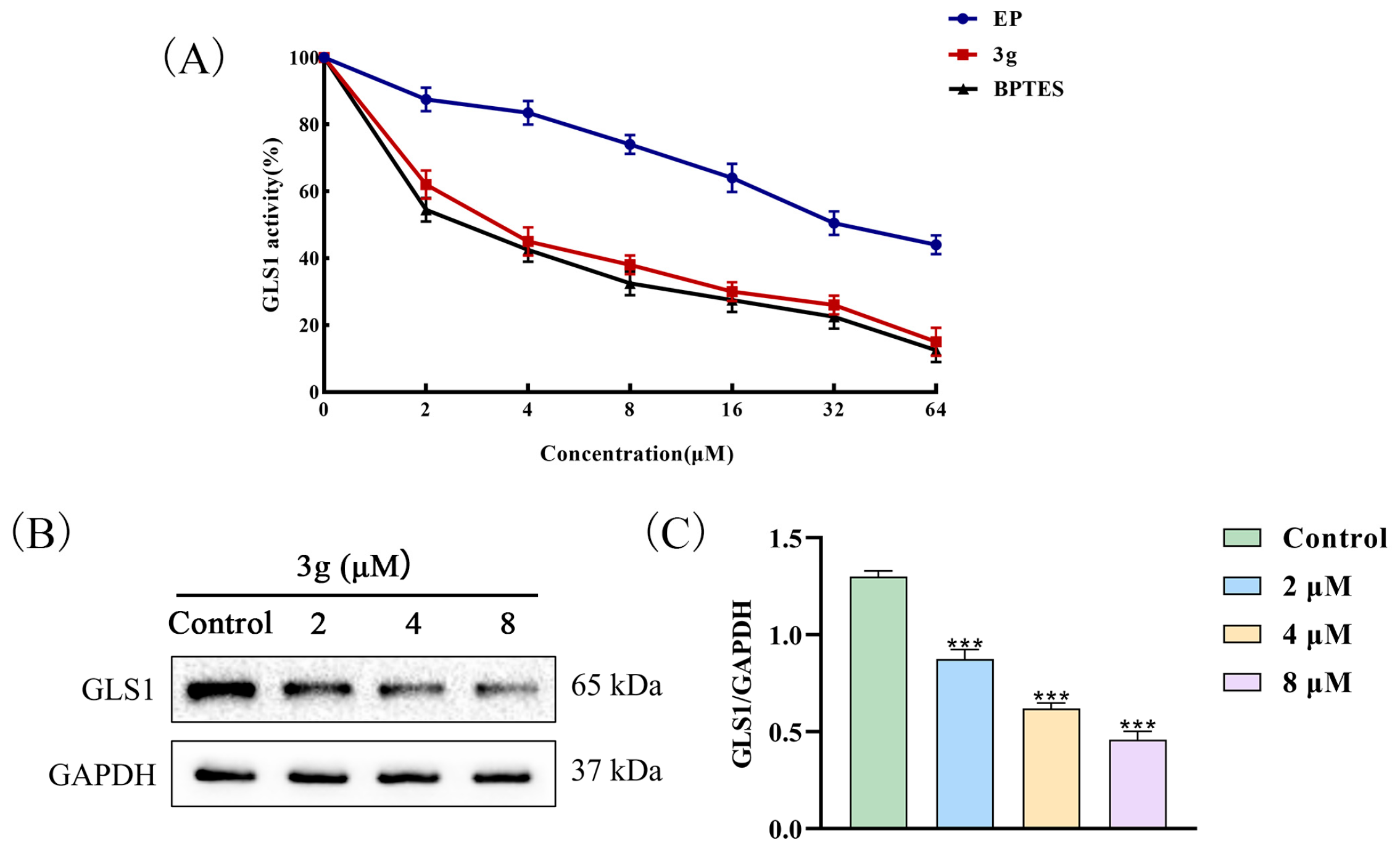
2.3. Compound 3g Inhibited the GLS1 Activity of MDA-MB-231 Cells
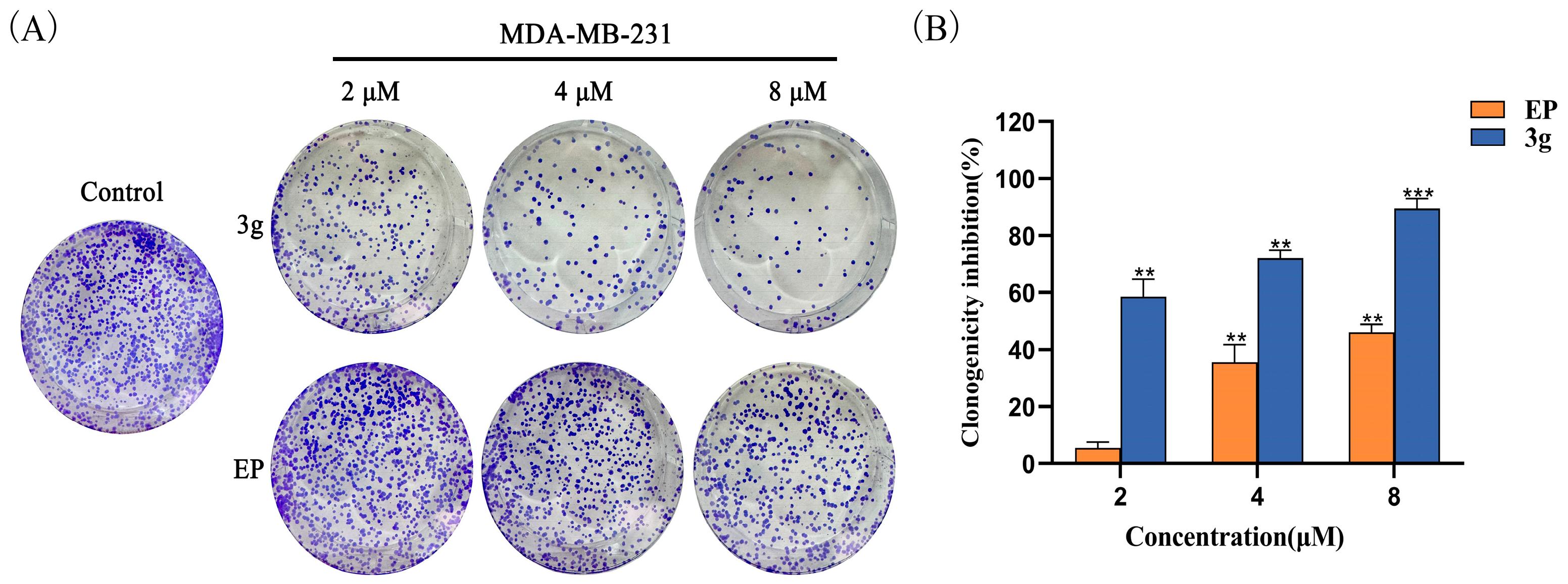
2.4. Compound 3g Inhibited the Colony Formation of MDA-MB-231 Cells
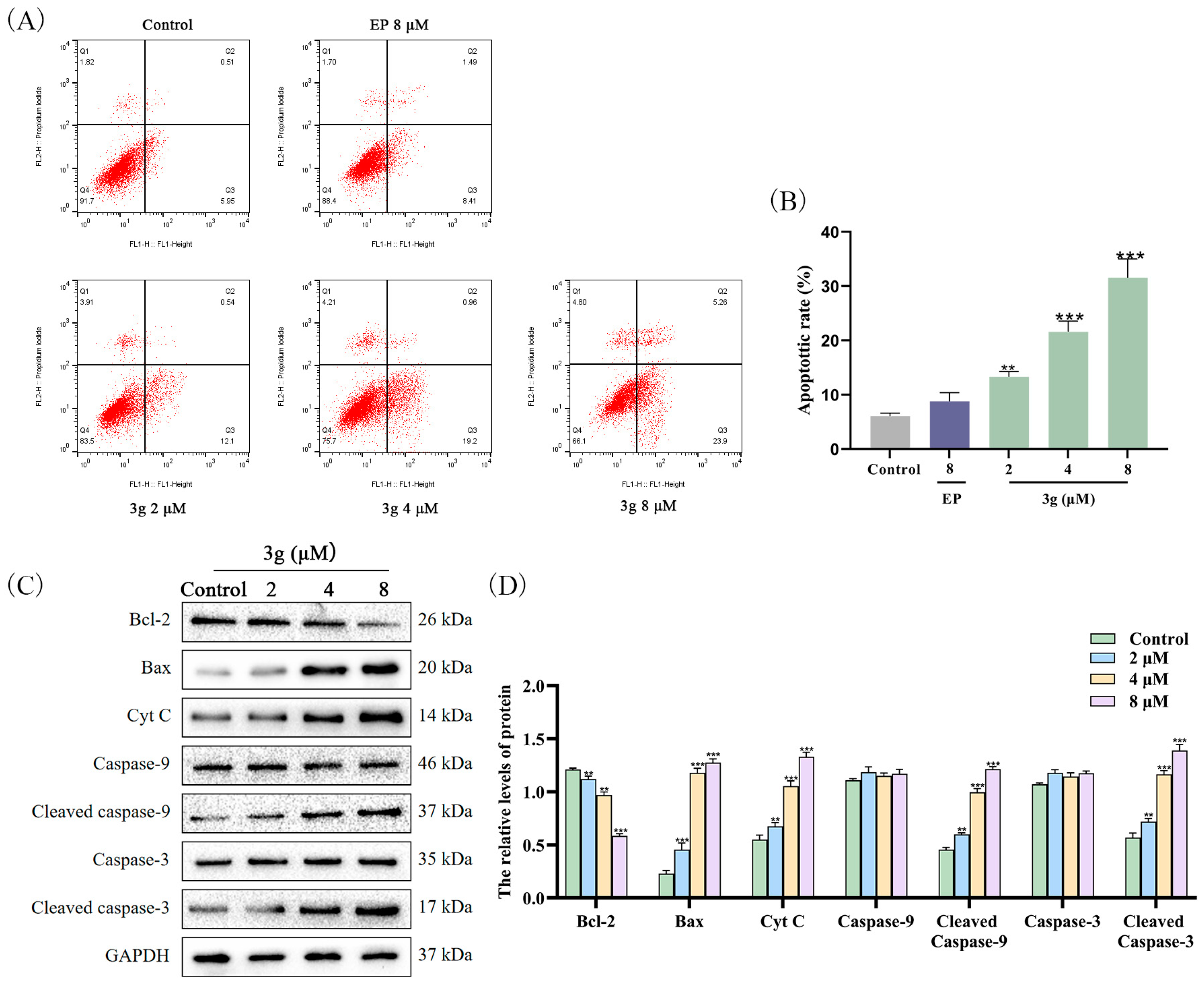
2.5. Compound 3g Induced Apoptosis in MDA-MB-231 Cells
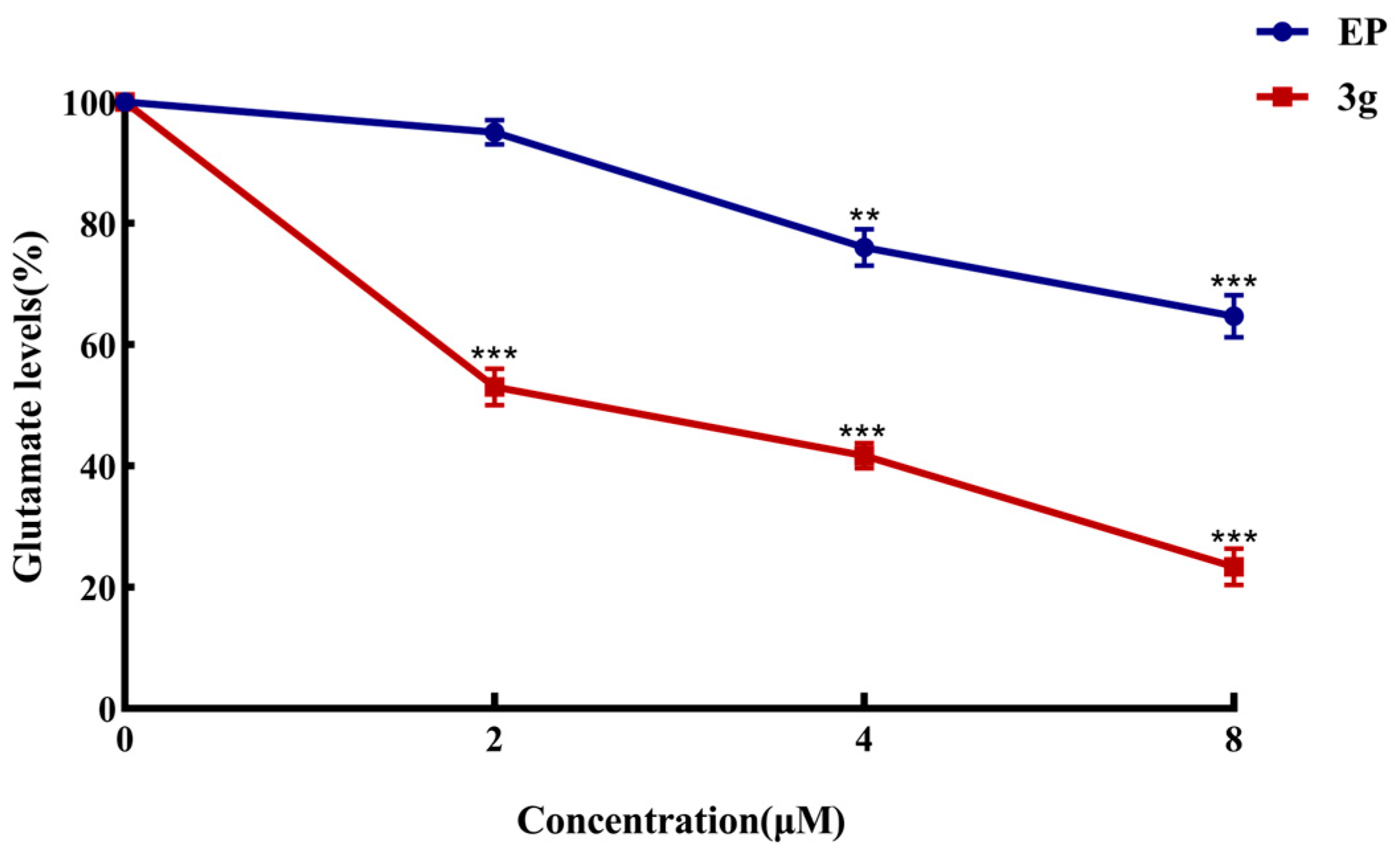
2.6. Compound 3g Inhibited Glutamate Production in MDA-MB-231 Cells
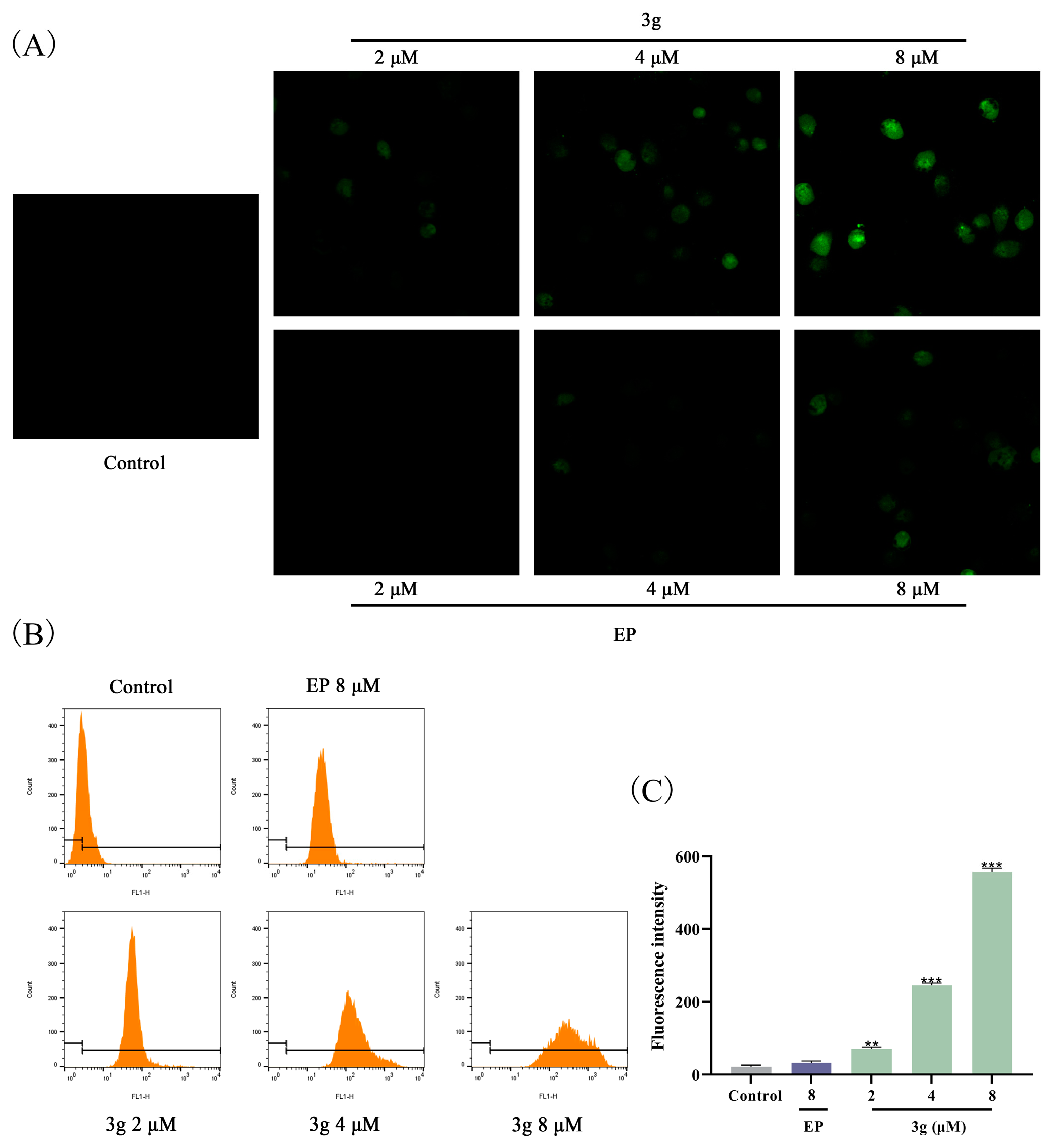
2.7. Compound 3g Induced ROS Generation in MDA-MB-231 Cells
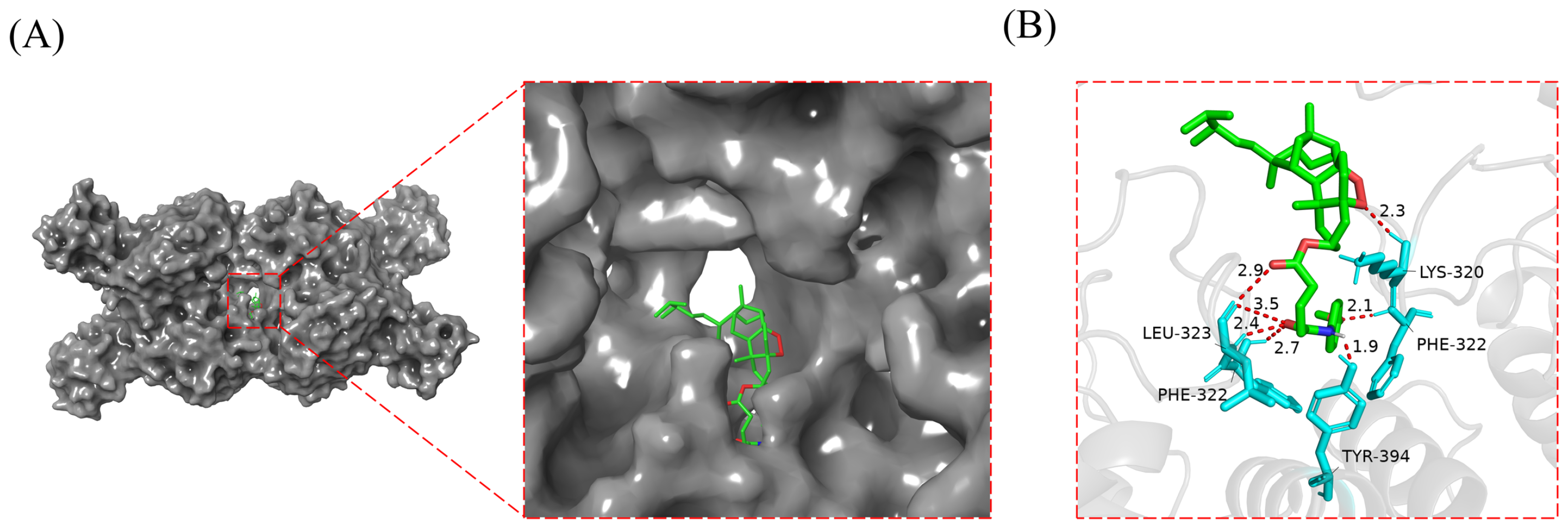
2.8. Compound 3g Docked with GLS1 Molecule
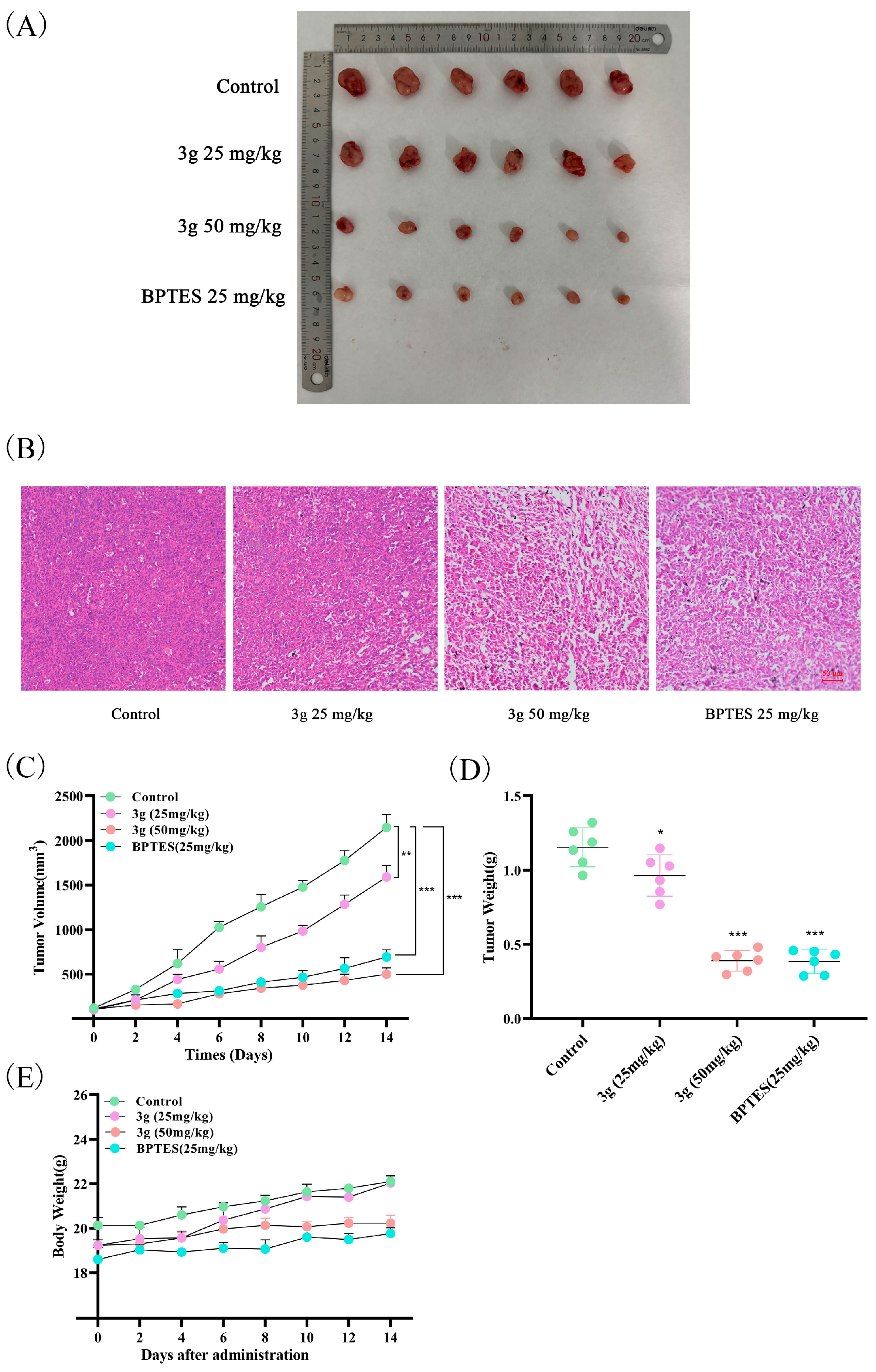
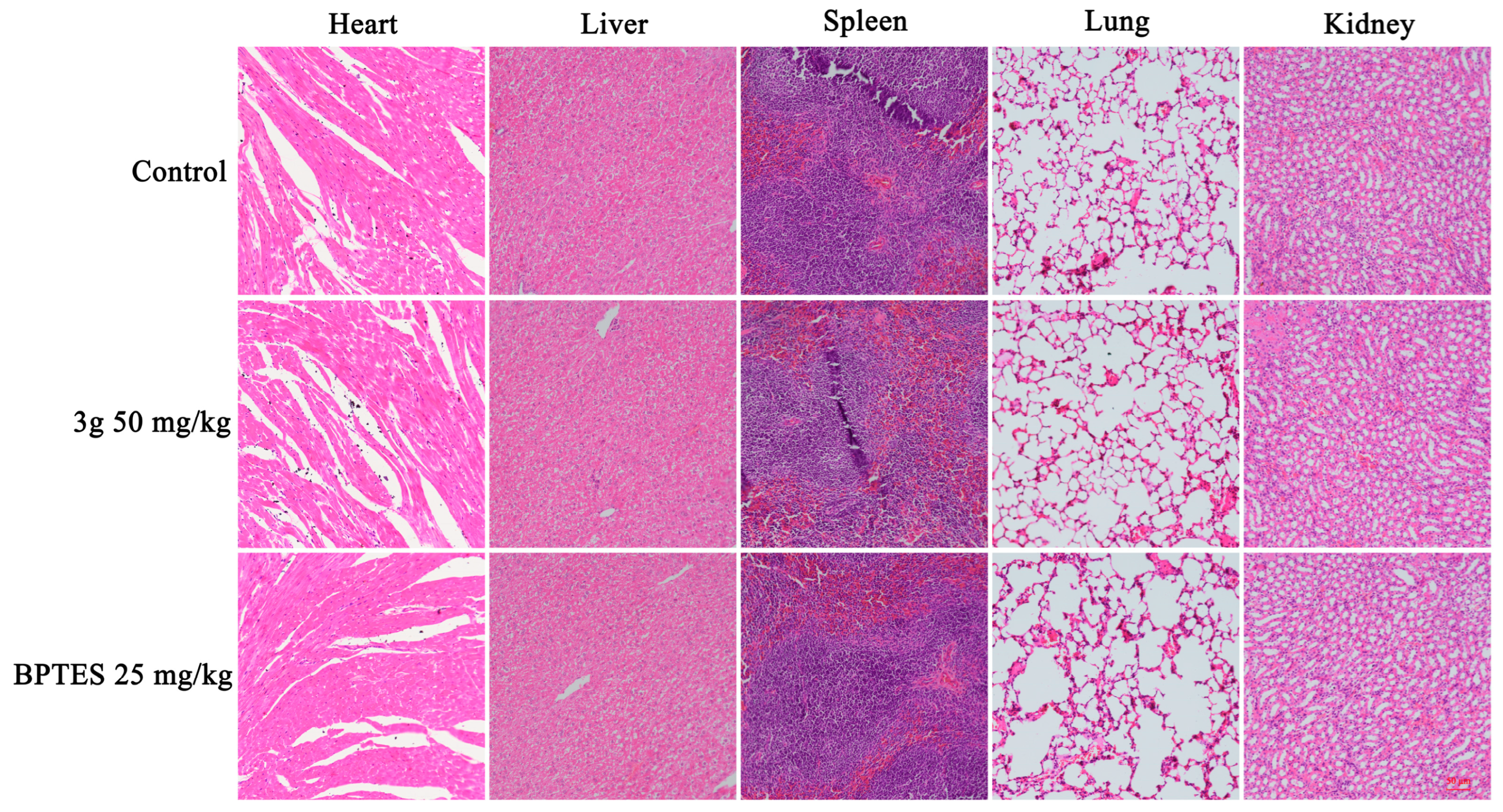
2.9. Compound 3g Inhibited Tumor Growth In Vivo
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Chemistry
3.1.1. General Procedure to Prepare Intermediates 1–4
- Ergosterol peroxide-3-(4-oxobut-2-enoic acid) (1)
- Ergosterol peroxide-3-(4-oxobutanoic acid) (2)
- Ergosterol peroxide-3-(5-oxopentanoic acid) (3)
- Ergosterol peroxide-3-(2-carbonyl-benzoic acid) (4)
3.1.2. General Procedure to Prepare Compounds 1a–h, 2a–h, 3a–h, and 4a–h
- Ergosterol peroxide-3-(4-((1,3,4-thiadiazol-2-yl)amino)-4-oxobut-2-enoate) (1a)
- Ergosterol peroxide-3-(4-(thiazol-2-ylamino)-4-oxobut-2-enoate) (1b)
- Ergosterol peroxide-3-(4-((5-fluorobenzo[d]thiazol-2-yl)amino)-4-oxobut-2-enoate) (1c)
- Ergosterol peroxide-3-(4-((6-fluorobenzo[d]thiazol-2-yl)amino)-4-oxobut-2-enoate) (1d)
- Ergosterol peroxide-3-(4-oxo-4-(phenylamino)but-2-enoate) (1e)
- Ergosterol peroxide-3-(4-((4-fluorophenyl)amino)-4-oxobut-2-enoate) (1f)
- Ergosterol peroxide-3-(4-((4-methoxyphenyl)amino)-4-oxobut-2-enoate) (1g)
- Ergosterol peroxide-3-(4-(naphthalen-2-ylamino)-4-oxobut-2-enoate) (1h)
- Ergosterol peroxide-3-(4-((1,3,4-thiadiazol-2-yl)amino)-4-oxobutanoate) (2a)
- Ergosterol peroxide-3-(4-oxo-4-(thiazol-2-ylamino)butanoate) (2b)
- Ergosterol peroxide-3-(4-((5-fluorobenzo[d]thiazol-2-yl)amino)-4-oxobutanoate) (2c)
- Ergosterol peroxide-3-(4-((6-fluorobenzo[d]thiazol-2-yl)amino)-4-oxobutanoate) (2d)
- Ergosterol peroxide-3-(4-oxo-4-(phenylamino)-4-oxobutanoate) (2e)
- Ergosterol peroxide-3-(4-((4-fluorophenyl)amino)-4-oxobutanoate) (2f)
- Ergosterol peroxide-3-(4-((4-methoxyphenyl)amino)-4-oxobutanoate) (2g)
- Ergosterol peroxide-3-(4-(naphthalen-2-ylamino)-4-oxobutanoate) (2h)
- Ergosterol peroxide-3-(5-((1,3,4-thiadiazol-2-yl)amino)-5-oxopentanoate) (3a)
- Ergosterol peroxide-3-(5-oxo-5-(thiazol-2-ylamino)pentanoate) (3b)
- Ergosterol peroxide-3-(5-((5-fluorobenzo[d]thiazol-2-yl)amino)-5-oxopentanoate) (3c)
- Ergosterol peroxide-3-(5-((6-fluorobenzo[d]thiazol-2-yl)amino)-5-oxopentanoate) (3d)
- Ergosterol peroxide-3-(5-oxo-5-(phenylamino)pentanoate) (3e)
- Ergosterol peroxide-3-(5-((4-fluorophenyl)amino)-5-oxopentanoate) (3f)
- Ergosterol peroxide-3-(5-((4-(dimethylamino)phenyl)amino)-5-oxopentanoate) (3g)
- Ergosterol peroxide-3-(5-(naphthalen-2-ylamino)-5-oxopentanoate) (3h)
- Ergosterol peroxide-3-(2-((1,3,4-thiadiazol-2-yl)carbamoyl)benzoate) (4a)
- Ergosterol peroxide-3-(2-oxo-5-((thiazol-2-yl)carbamoyl)benzoate) (4b)
- Ergosterol peroxide-3-(2-((5-fluorobenzo[d]thiazol-2-yl)carbamoyl)benzoate) (4c)
- Ergosterol peroxide-3-(2-((6-fluorobenzo[d]thiazol-2-yl)carbamoyl)benzoate) (4d)
- Ergosterol peroxide-3-(2-oxo-5-((phenyl)carbamoyl)benzoate) (4e)
- Ergosterol peroxide-3-(2-((4-fluorophenyl)carbamoyl)benzoate) (4f)
- Ergosterol peroxide-3-(2-((4-(dimethylamino)phenyl)carbamoyl)benzoate) (4g)
- Ergosterol peroxide-3-(2-(naphthalen-2-ylcarbamoyl)benzoate) (4h)
3.2. GLS1 Enzyme Assay
3.3. Cell Proliferation Assay
3.4. Colony Formation Assay
3.5. Apoptosis Assays
3.6. Western Blot Analysis
3.7. Determination of Intracellular Glutamate Levels
3.8. ROS Assay
3.9. Molecular Docking
3.10. In Vivo Model
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wolf, A.; Agnihotri, S.; Guha, A. Targeting metabolic remodeling in glioblastoma multiforme. Oncotarget 2010, 1, 552–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhong, X.; He, Z.; Yin, L.; Fan, Y.; Tong, Y.; Kang, Y.; Bi, Q. Glutamine metabolism in tumor metastasis: Genes, mechanisms and the therapeutic targets. Heliyon 2023, 9, e20656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergers, G.; Fendt, S.M. The metabolism of cancer cells during metastasis. Nat. Rev. Cancer. 2021, 21, 162–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cruzat, V.; Macedo Rogero, M.; Noel Keane, K.; Curi, R.; Newsholme, P. Glutamine: Metabolism and Immune Function, Supplementation and Clinical Translation. Nutrients 2018, 10, 1564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, J.; Byun, J.K.; Choi, Y.K.; Park, K.G. Targeting glutamine metabolism as a therapeutic strategy for cancer. Exp. Mol. Med. 2023, 55, 706–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erickson, J.W.; Cerione, R.A. Glutaminase: A hot spot for regulation of cancer cell metabolism? Oncotarget 2010, 1, 734–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leone, R.D.; Zhao, L.; Englert, J.M.; Sun, I.M.; Oh, M.H.; Sun, I.H.; Arwood, M.L.; Bettencourt, I.A.; Patel, C.H.; Wen, J.; et al. Glutamine blockade induces divergent metabolic programs to overcome tumor immune evasion. Science 2019, 366, 1013–1021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, L.; Zhu, X.; Wu, Y. Effects of Glucose Metabolism, Lipid Metabolism, and Glutamine Metabolism on Tumor Microenvironment and Clinical Implications. Biomolecules 2022, 12, 580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sullivan, L.B.; Gui, D.Y.; Hosios, A.M.; Bush, L.N.; Freinkman, E.; Vander Heiden, M.G. Supporting Aspartate Biosynthesis Is an Essential Function of Respiration in Proliferating Cells. Cell 2015, 162, 552–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Cao, Y.; Meng, G.; Qian, L.; Xu, T.; Yan, C.; Luo, O.; Wang, S.; Wei, J.; Ding, Y.; et al. Targeting glutaminase 1 attenuates stemness properties in hepatocellular carcinoma by increasing reactive oxygen species and suppressing Wnt/beta-catenin pathway. EBioMedicine 2019, 39, 239–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, J.; Liu, P.P.; Hou, G.; Shao, J.; Yang, J.; Liu, K.; Lu, W.; Wen, S.; Hu, Y.; Huang, P. Regulation of stem-like cancer cells by glutamine through β-catenin pathway mediated by redox signaling. Mol. Cancer 2017, 16, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, X.; An, B.; Lin, Y.; Ni, Y.; Zhao, X.; Liang, X. Molecular mechanisms of ROS-modulated cancer chemoresistance and therapeutic strategies. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2023, 165, 115036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, S.; Fukumoto, T.; Lin, J.; Nacarelli, T.; Wang, Y.; Ong, D.; Liu, H.; Fatkhutdinov, N.; Zundell, J.A.; Karakashev, S.; et al. Targeting glutamine dependence through GLS1 inhibition suppresses ARID1A-inactivated clear cell ovarian carcinoma. Nat. Cancer 2021, 2, 189–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wise, D.R.; Thompson, C.B. Glutamine addiction: A new therapeutic target in cancer. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2010, 35, 427–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katt, W.P.; Cerione, R.A. Glutaminase regulation in cancer cells: A druggable chain of events. Drug Discov. Today 2014, 19, 450–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gameiro, P.A.; Yang, J.; Metelo, A.M.; Pérez-Carro, R.; Baker, R.; Wang, Z.; Arreola, A.; Rathmell, W.K.; Olumi, A.; López-Larrubia, P.; et al. In vivo HIF-mediated reductive carboxylation is regulated by citrate levels and sensitizes VHL-deficient cells to glutamine deprivation. Cell Metab. 2013, 17, 372–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, B.; Zhang, J.; Zhao, G.; Liu, M.; Hu, J.; Lin, F.; Wang, J.; Zhao, W.; Ma, H.; Zhang, C.; et al. Filamentous GLS1 promotes ROS-induced apoptosis upon glutamine deprivation via insufficient asparagine synthesis. Mol. Cell 2022, 82, 1821–1835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.Q.; Lei, H.M.; Hu, Q.Y.; Li, G.H.; Zhao, P.J. Recent Advances in the Synthetic Biology of Natural Drugs. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2021, 9, 691152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bu, M.; Yang, B.B.; Hu, L. Natural Endoperoxides as Drug Lead Compounds. Curr. Med. Chem. 2016, 23, 383–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.J.; Lu, T.M.; Lai, M.N.; Ng, L.T. Immunomodulatory activities of medicinal mushroom Grifola frondosa extract and its bioactive constituent. Am. J. Chin. Med. 2013, 41, 131–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, C.; Ge, X.; Wang, J.; Wei, Z.; Feng, W.H.; Wang, J. Ergosterol peroxide exhibits antiviral and immunomodulatory abilities against porcine deltacoronavirus (PDCoV) via suppression of NF-κB and p38/MAPK signaling pathways in vitro. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2021, 93, 107317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martínez-Montemayor, M.M.; Ling, T.; Suárez-Arroyo, I.J.; Ortiz-Soto, G.; Santiago-Negrón, C.L.; Lacourt-Ventura, M.Y.; Valentín-Acevedo, A.; Lang, W.H.; Rivas, F. Identification of Biologically Active Ganoderma lucidum Compounds and Synthesis of Improved Derivatives That Confer Anti-cancer Activities in vitro. Front. Pharmacol. 2019, 10, 115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Govindharaj, M.; Arumugam, S.; Nirmala, G.; Bharadwaj, M.; Murugiyan, K. Effect of Marine Basidiomycetes Fulvifomes sp.-Derived Ergosterol Peroxide on Cytotoxicity and Apoptosis Induction in MCF-7 Cell Line. J. Fungi. 2019, 5, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, W.; Pan, M.; Liu, H.; Tian, H.; Ye, Q.; Liu, H. Ergosterol peroxide inhibits ovarian cancer cell growth through multiple pathways. Onco Targets Ther. 2017, 10, 3467–3474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, L.; Shi, W.; Liu, X.; Zhao, X.; Zhang, Z. Anticancer Action and Mechanism of Ergosterol Peroxide from Paecilomyces cicadae Fermentation Broth. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 3935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, J.H.; Jang, J.E.; Mishra, S.K.; Lee, H.J.; Nho, C.W.; Shin, D.; Jin, M.; Kim, M.K.; Choi, C.; Oh, S.H. Ergosterol peroxide from Chaga mushroom (Inonotus obliquus) exhibits anti-cancer activity by down-regulation of the β-catenin pathway in colorectal cancer. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2015, 173, 303–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobori, M.; Yoshida, M.; Ohnishi-Kameyama, M.; Shinmoto, H. Ergosterol peroxide from an edible mushroom suppresses inflammatory responses in RAW264.7 macrophages and growth of HT29 colon adenocarcinoma cells. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2007, 150, 209–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Luo, X.; Yasheng, M.; Zhao, J.; Li, J.; Li, J. Ergosterol peroxide from Pleurotus ferulae inhibits gastrointestinal tumor cell growth through induction of apoptosis via reactive oxygen species and endoplasmic reticulum stress. Food Funct. 2020, 11, 4171–4184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.Y.; Yang, F.L.; Li, L.H.; Rao, Y.K.; Ju, T.C.; Wong, W.T.; Hsieh, C.Y.; Pivkin, M.V.; Hua, K.F.; Wu, S.H. Ergosterol peroxide from marine fungus Phoma sp. induces ROS-dependent apoptosis and autophagy in human lung adenocarcinoma cells. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 17956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bu, M.; Li, H.; Wang, H.; Wang, J.; Lin, Y.; Ma, Y. Synthesis of Ergosterol Peroxide Conjugates as Mitochondria Targeting Probes for Enhanced Anticancer Activity. Molecules 2019, 24, 3307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bu, M.; Cao, T.; Li, H.; Guo, M.; Yang, B.B.; Zeng, C.; Hu, L. Synthesis of 5α,8α-Ergosterol Peroxide 3-Carbamate Derivatives and a Fluorescent Mitochondria-Targeting Conjugate for Enhanced Anticancer Activities. ChemMedChem 2017, 12, 466–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, W.K.; Wu, J.L.; Wang, J.F.; Wang, H.J.; Han, Y.L.; Lin, Y.; Bu, M. Mitochondria-Targeted Ergosterol Peroxide Derivatives: Synthesis, Anticancer Properties and Their Preliminary Mechanism of Inhibiting MCF-7 Cell Proliferation. J. Braz. Chem. Soc. 2023, 34, 1420–1431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shapiro, R.A.; Clark, V.M.; Curthoys, N.P. Inactivation of rat renal phosphate-dependent glutaminase with 6-diazo-5-oxo-L-norleucine. Evidence for interaction at the glutamine binding site. J. Biol. Chem. 1979, 254, 2835–2838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shapiro, R.A.; Clark, V.M.; Curthoys, N.P. Covalent interaction of L-2-amino-4-oxo-5-chloropentanoic acid with rat renal phosphate-dependent glutaminase. Evidence for a specific glutamate binding site and of subunit heterogeneity. J. Biol. Chem. 1978, 253, 7086–7090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuneva, M.O.; Fan, T.W.; Allen, T.D.; Higashi, R.M.; Ferraris, D.V.; Tsukamoto, T.; Matés, J.M.; Alonso, F.J.; Wang, C.; Seo, Y.; et al. The metabolic profile of tumors depends on both the responsible genetic lesion and tissue type. Cell Metab. 2012, 15, 157–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newcomb, R.W.; Newocmb, M. Selective Inhibition of Glutaminase by BisThiadiazoles. U.S. Patent 6451828B1, 17 September 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Robinson, M.M.; McBryant, S.J.; Tsukamoto, T.; Rojas, C.; Ferraris, D.V.; Hamilton, S.K.; Hansen, J.C.; Curthoys, N.P. Novel mechanism of inhibition of rat kidney-type glutaminase by bis-2-(5-phenylacetamido-1,2,4-thiadiazol-2-yl)ethyl sulfide (BPTES). Biochem. J. 2007, 406, 407–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shukla, K.; Ferraris, D.V.; Thomas, A.G.; Stathis, M.; Duvall, B.; Delahanty, G.; Alt, J.; Rais, R.; Rojas, C.; Gao, P.; et al. Design, synthesis, and pharmacological evaluation of bis-2-(5-phenylacetamido-1,2,4-thiadiazol-2-yl)ethyl sulfide 3 (BPTES) analogs as glutaminase inhibitors. J. Med. Chem. 2012, 55, 10551–10563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zimmermann, S.C.; Wolf, E.F.; Luu, A.; Thomas, A.G.; Stathis, M.; Poore, B.; Nguyen, C.; Le, A.; Rojas, C.; Slusher, B.S.; et al. Allosteric Glutaminase Inhibitors Based on a 1,4-Di(5-amino-1,3,4-thiadiazol-2-yl)butane Scaffold. ACS Med. Chem. Lett. 2016, 7, 520–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, W.X.; Chen, C.; Liu, X.Q.; Li, Y.; Lin, Y.L.; Wu, X.T.; Kong, L.Y.; Luo, J.G. Discovery and optimization of withangulatin A derivatives as novel glutaminase 1 inhibitors for the treatment of triple-negative breast cancer. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2021, 210, 112980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vagia, E.; Mahalingam, D.; Cristofanilli, M. The Landscape of Targeted Therapies in TNBC. Cancers 2020, 12, 916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, L.; Duan, J.J.; Bian, X.W.; Yu, S.C. Triple-negative breast cancer molecular subtyping and treatment progress. Breast Cancer Res. 2020, 22, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- MacDonald, I.; Nixon, N.A.; Khan, O.F. Triple-Negative Breast Cancer: A Review of Current Curative Intent Therapies. Curr. Oncol. 2022, 29, 4768–4778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, M.J.; Kim, D.H.; Jung, W.H.; Koo, J.S. Expression of metabolism-related proteins in triple-negative breast cancer. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Pathol. 2013, 7, 301–312. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ju, Y.; Ben-David, Y.; Rotin, D.; Zacksenhaus, E. Inhibition of eEF2K synergizes with glutaminase inhibitors or 4EBP1 depletion to suppress growth of triple-negative breast cancer cells. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 9181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Compound | IC50 a (μM) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| A549 | HepG2 | MCF-7 | MDA-MB-231 | |
| 1a | 12.45 ± 0.84 | 8.89 ± 0.41 | 8.44 ± 0.82 | 11.61 ± 1.54 |
| 1b | 16.76 ± 1.33 | 10.97 ± 0.82 | 9.07 ± 0.52 | 17.66 ± 1.71 |
| 1c | 12.88 ± 0.91 | 11.35 ± 0.76 | 15.35 ± 1.22 | 19.89 ± 1.08 |
| 1d | 17.28 ± 1.12 | 13.31 ± 1.05 | 10.85 ± 1.32 | 12.73 ± 0.26 |
| 1e | 10.01 ± 0.61 | 15.17 ± 1.03 | 11.61 ± 0.96 | 11.69 ± 0.57 |
| 1f | 13.99 ± 0.87 | 8.99 ± 0.67 | 8.03 ± 0.68 | 9.24 ± 0.41 |
| 1g | 15.96 ± 1.42 | 11.53 ± 0.87 | 9.05 ± 0.49 | 10.10 ± 0.85 |
| 1h | 17.93 ± 1.21 | 12.09 ± 1.11 | 9.27 ± 0.38 | 9.05 ± 1.02 |
| 2a | 18.40 ± 1.40 | 10.98 ± 0.93 | 7.66 ± 1.01 | 16.83 ± 0.95 |
| 2b | 16.23 ± 1.17 | 9.83 ± 0.76 | 6.39 ± 0.28 | 17.10 ± 0.83 |
| 2c | 14.08 ± 0.98 | 9.78 ± 0.81 | 13.45 ± 1.03 | 16.55 ± 0.72 |
| 2d | 9.86 ± 1.64 | 9.51 ± 0.73 | 12.93 ± 0.78 | 14.79 ± 1.27 |
| 2e | 17.13 ± 1.22 | 18.17 ± 0.71 | 7.40 ± 0.28 | 5.19 ± 0.69 |
| 2f | 13.42 ± 0.71 | 15.76 ± 1.27 | 10.93 ± 0.84 | 8.11 ± 0.76 |
| 2g | 10.28 ± 0.38 | 12.20 ± 1.15 | 5.38 ± 0.38 | 6.02 ± 0.71 |
| 2h | 14.88 ± 1.10 | 12.63 ± 1.08 | 14.74 ± 1.34 | 14.00 ± 0.79 |
| 3a | 9.73 ± 0.42 | 10.66 ± 0.82 | 5.16 ± 0.93 | 7.06 ± 0.35 |
| 3b | 11.69 ± 0.82 | 13.06 ± 1.22 | 9.47 ± 0.75 | 6.92 ± 0.28 |
| 3c | 11.38 ± 0.79 | 11.87 ± 1.07 | 11.04 ± 0.62 | 11.99 ± 0.72 |
| 3d | 9.09 ± 0.64 | 14.67 ± 0.35 | 8.39 ± 0.34 | 10.79 ± 0.53 |
| 3e | 10.52 ± 0.79 | 14.91 ± 1.13 | 11.55 ± 0.66 | 4.78 ± 0.41 |
| 3f | 11.08 ± 0.93 | 9.79 ± 1.01 | 8.09 ± 0.71 | 7.19 ± 0.39 |
| 3g | 13.52 ± 1.14 | 15.48 ± 0.63 | 4.57 ± 0.62 | 3.20 ± 0.29 |
| 3h | 9.30 ± 0.66 | 13.84 ± 1.30 | 8.65 ± 0.73 | 4.98 ± 0.84 |
| 4a | 7.07 ± 0.47 | 8.08 ± 0.64 | 8.20 ± 0.68 | 10.19 ± 0.62 |
| 4b | 12.80 ± 1.08 | 10.95 ± 0.76 | 12.64 ± 0.94 | 15.77 ± 1.26 |
| 4c | 11.69 ± 1.02 | 11.40 ± 0.98 | 10.71 ± 0.47 | 7.32 ± 0.58 |
| 4d | 8.99 ± 0.81 | 15.32 ± 1.31 | 10.56 ± 0.52 | 11.31 ± 0.44 |
| 4e | 12.58 ± 0.99 | 18.54 ± 1.18 | 15.40 ± 1.21 | 9.07 ± 0.93 |
| 4f | 18.79 ± 0.64 | 9.02 ± 0.87 | 9.64 ± 0.51 | 13.39 ± 1.24 |
| 4g | 17.62 ± 1.39 | 15.59 ± 0.84 | 9.49 ± 0.24 | 8.16 ± 0.80 |
| 4h | 10.13 ± 1.16 | 14.29 ± 1.55 | 11.39 ± 0.42 | 14.57 ± 0.47 |
| EP | 14.95 ± 1.27 | 18.05 ± 1.71 | 19.42 ± 1.50 | 17.26 ± 1.05 |
| BPTES | 49.08 ± 11.60 | 60.23 ± 8.35 | 21.26 ± 6.89 | 9.10 ± 0.26 |
| Cisplatin | 11.64 ± 0.38 | 6.29 ± 0.30 | 4.23 ± 0.24 | 10.37 ± 0.34 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Luo, R.; Zhao, H.; Deng, S.; Wu, J.; Wang, H.; Guo, X.; Han, C.; Ren, W.; Han, Y.; Zhou, J.; et al. Discovery and Optimization of Ergosterol Peroxide Derivatives as Novel Glutaminase 1 Inhibitors for the Treatment of Triple-Negative Breast Cancer. Molecules 2024, 29, 4375. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29184375
Luo R, Zhao H, Deng S, Wu J, Wang H, Guo X, Han C, Ren W, Han Y, Zhou J, et al. Discovery and Optimization of Ergosterol Peroxide Derivatives as Novel Glutaminase 1 Inhibitors for the Treatment of Triple-Negative Breast Cancer. Molecules. 2024; 29(18):4375. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29184375
Chicago/Turabian StyleLuo, Ran, Haoyi Zhao, Siqi Deng, Jiale Wu, Haijun Wang, Xiaoshan Guo, Cuicui Han, Wenkang Ren, Yinglong Han, Jianwen Zhou, and et al. 2024. "Discovery and Optimization of Ergosterol Peroxide Derivatives as Novel Glutaminase 1 Inhibitors for the Treatment of Triple-Negative Breast Cancer" Molecules 29, no. 18: 4375. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29184375
APA StyleLuo, R., Zhao, H., Deng, S., Wu, J., Wang, H., Guo, X., Han, C., Ren, W., Han, Y., Zhou, J., Lin, Y., & Bu, M. (2024). Discovery and Optimization of Ergosterol Peroxide Derivatives as Novel Glutaminase 1 Inhibitors for the Treatment of Triple-Negative Breast Cancer. Molecules, 29(18), 4375. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29184375







