Stability Evaluation and Pharmacokinetic Profiling of Vepdegestrant in Rodents Using Liquid Chromatography–Tandem Mass Spectrometry
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
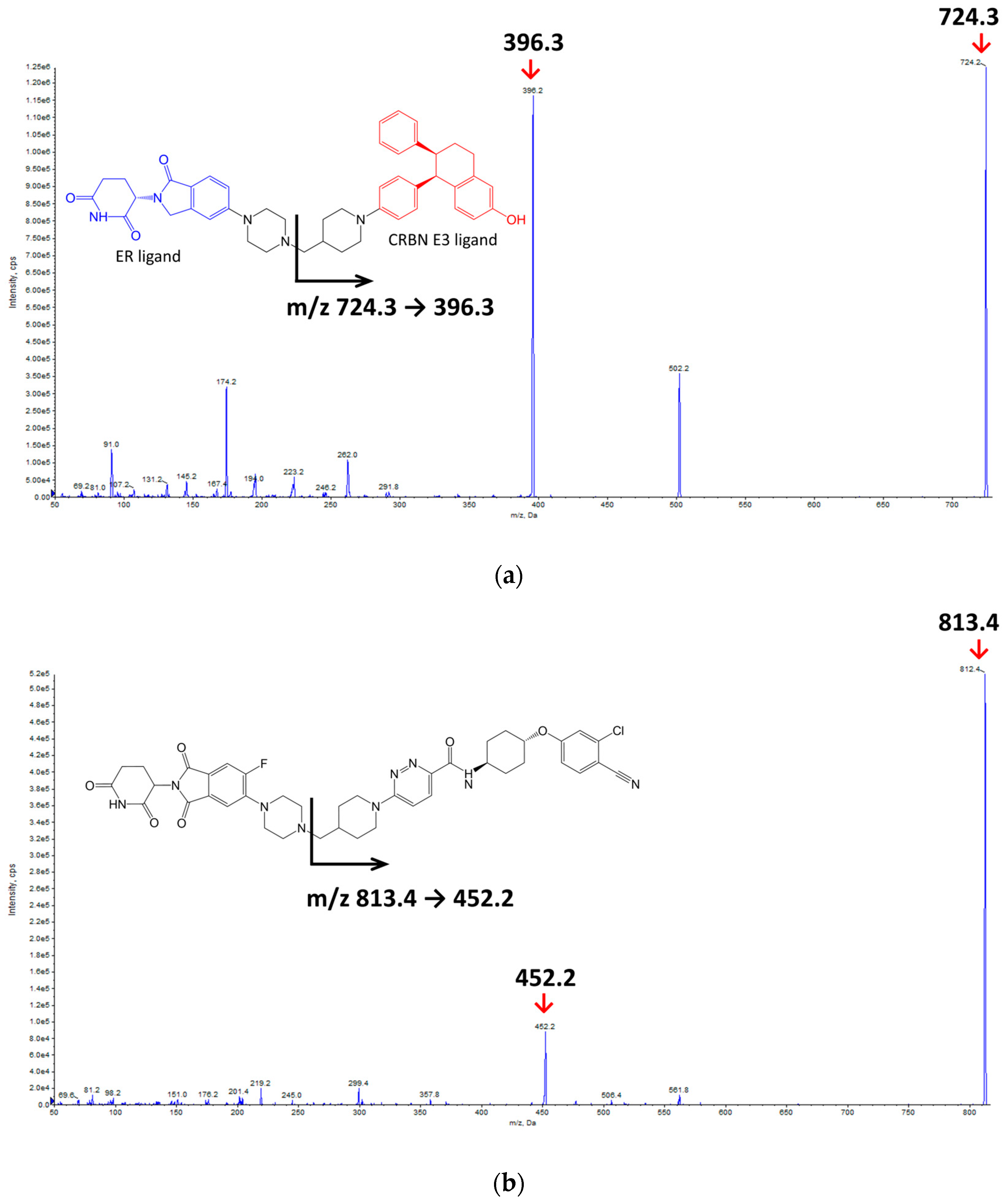
2.1. HPLC-MS/MS Method Development
2.2. HPLC-MS/MS Method Validation
2.3. In Vitro Stability Tests
2.4. Rodent Pharmacokinetic Studies
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials
3.2. Selection of Internal Standard
3.3. Analytical Methods
3.4. Preparation of the Standard and Quality Control Samples
3.5. Method Validation
3.6. In Vitro Stability Tests
3.7. Rodent Pharmacokinetic Studies
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- International Agency for Research on Cancer. Available online: https://gco.iarc.who.int/media/globocan/factsheets/cancers/20-breast-fact-sheet.pdf (accessed on 25 June 2024).
- Miziak, P.; Baran, M.; Błaszczak, E.; Przybyszewska-Podstawka, A.; Kałafut, J.; Smok-Kalwat, J.; Dmoszyńska-Graniczka, M.; Kiełbus, M.; Stepulak, A. Estrogen Receptor Signaling in Breast Cancer. Cancers 2023, 15, 4689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patel, H.K.; Bihani, T. Selective estrogen receptor modulators (SERMs) and selective estrogen receptor degraders (SERDs) in cancer treatment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2018, 186, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fanning, S.W.; Greene, G.L. Next-Generation ER α Inhibitors for Endocrine-Resistant ER+ Breast Cancer. Endocrinology 2019, 160, 759–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pepermans, R.A.; Prossnitz, E.R. ERα-targeted endocrine therapy, resistance and the role of GPER. Steroids 2019, 152, 108493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakamoto, K.M.; Kim, K.B.; Kumagai, A.; Mercurio, F.; Crews, C.M.; Deshaies, R.J. Protacs: Chimeric molecules that target proteins to the Skp1–Cullin–F box complex for ubiquitination and degradation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2001, 98, 8554–8559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gadd, M.S.; Testa, A.; Lucas, X.; Chan, K.-H.; Chen, W.; Lamont, D.J.; Zengerle, M.; Ciulli, A. Structural basis of PROTAC cooperative recognition for selective protein degradation. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2017, 13, 514–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Hu, M.; Yang, Y.; Du, C.; Zhou, H.; Liu, C.; Chen, Y.; Fan, L.; Ma, H.; Gong, Y. An overview of PROTACs: A promising drug discovery paradigm. Mol. Biomed. 2022, 3, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cecchini, C.; Tardy, S.; Ceserani, V.; Theurillat, J.-P.; Scapozza, L. Exploring the ubiquitin-proteasome system (UPS) through PROTAC technology. Chimia 2020, 74, 274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burke, M.R.; Smith, A.R.; Zheng, G. Overcoming cancer drug resistance utilizing PROTAC technology. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2022, 10, 872729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sincere, N.I.; Anand, K.; Ashique, S.; Yang, J.; You, C. PROTACs: Emerging targeted protein degradation approaches for advanced druggable strategies. Molecules 2023, 28, 4014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Rao, Y. PROTACs as potential therapeutic agents for cancer drug resistance. Biochemistry 2019, 59, 240–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Snyder, L.B.; Flanagan, J.J.; Qian, Y.; Gough, S.M.; Andreoli, M.; Bookbinder, M.; Cadelina, G.; Bradley, J.; Rousseau, E.; Chandler, J. The discovery of ARV-471, an orally bioavailable estrogen receptor degrading PROTAC for the treatment of patients with breast cancer. Cancer Res. 2021, 81, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flanagan, J.; Qian, Y.; Gough, S.; Andreoli, M.; Bookbinder, M.; Cadelina, G.; Bradley, J.; Rousseau, E.; Willard, R.; Pizzano, J. Abstract P5-04-18: ARV-471, an oral estrogen receptor PROTAC degrader for breast cancer. Cancer Res. 2019, 79, P5-04-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gough, S.M.; Flanagan, J.J.; Teh, J.; Andreoli, M.; Rousseau, E.; Pannone, M.; Bookbinder, M.; Willard, R.; Davenport, K.; Bortolon, E. Oral estrogen receptor PROTAC® vepdegestrant (ARV-471) is highly efficacious as monotherapy and in combination with CDK4/6 or PI3K/mTOR pathway inhibitors in preclinical ER+ breast cancer models. Clin. Cancer Res. 2024, 30, 3549–3563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamilton, E.; Vahdat, L.; Han, H.S.; Ranciato, J.; Gedrich, R.; Keung, C.F.; Chirnomas, D.; Hurvitz, S. First-in-human safety and activity of ARV-471, a novel PROTAC estrogen receptor degrader, in ER+/HER2-locally advanced or metastatic breast cancer. Cancer Res. 2022, 82, PD13-08. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schott, A.F.; Hurvitz, S.; Ma, C.; Hamilton, E.; Nanda, R.; Zahrah, G.; Hunter, N.; Tan, A.R.; Telli, M.; Mesias, J.A. Abstract GS3-03: GS3-03 ARV-471, a PROTAC® estrogen receptor (ER) degrader in advanced ER-positive/human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 (HER2)-negative breast cancer: Phase 2 expansion (VERITAC) of a phase 1/2 study. Cancer Res. 2023, 83, GS3-03. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Hou, P.; Long, Z.; Zheng, Y.; Tang, C.; Jones, E.; Diao, X.; Zhu, M. Application of Electro-Activated Dissociation Fragmentation Technique to Identifying Glucuronidation and Oxidative Metabolism Sites of Vepdegestrant by Liquid Chromatography-High Resolution Mass Spectrometry. Drug Metab. Dispos. 2024, 52, 634–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamilton, E.; Ma, C.; De Laurentiis, M.; Iwata, H.; Hurvitz, S.; Wander, S.; Danso, M.; Lu, D.; Perkins, J.; Liu, Y. 257TiP VERITAC-2: A global, randomized phase III study of ARV-471, a PROteolysis TArgeting Chimera (PROTAC) estrogen receptor (ER) degrader, vs fulvestrant in ER+/human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 (HER2)-advanced breast cancer. ESMO Open 2023, 8, 101445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niessen, J.; Nilsson, J.M.; Peters, K.; Indulkar, A.; Borchardt, T.; Koziolek, M.; Lennernäs, H.; Dahlgren, D.; Hedeland, M. Development and Validation of Lc-Ms/Ms Methods for the Pharmacokinetic Assessment of the Protacs Bavdeglutamide (Arv-110) and Vepdegestrant (Arv-471). J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2024, 249, 116348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Medicines Agency. Guideline on Bioanalytical Method Validation; Committee for Medicinal Products for Human Use: London, UK, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- US-FDA. FDA Guidance for Industry: Bioanalytical Method Validation; Center for Drug Evaluation and Research (CDER): Rockville, MD, USA, 2018. Available online: https://www.fda.gov/media/70858/download (accessed on 3 March 2023).
- Sun, X.; Gao, H.; Yang, Y.; He, M.; Wu, Y.; Song, Y.; Tong, Y.; Rao, Y. PROTACs: Great opportunities for academia and industry. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2019, 4, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, N.; Zhou, S.; Palmisano, M. Clinical pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of lenalidomide. Clin. Pharmacokinet. 2017, 56, 139–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, T.-T.-L.; Kim, J.W.; Choi, H.-I.; Maeng, H.-J.; Koo, T.-S. Development of an LC-MS/MS Method for ARV-110, a PROTAC Molecule, and Applications to Pharmacokinetic Studies. Molecules 2022, 27, 1977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davies, B.; Morris, T. Physiological parameters in laboratory animals and humans. Pharm. Res. 1993, 10, 1093–1095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwon, Y. Distribution. In Handbook of Essential Pharmacokinetics, Pharmacodynamics and Drug Metabolism for Industrial Scientists, 1st ed.; Springer: Boston, MA, USA, 2002; pp. 73–82. [Google Scholar]
- Pike, A.; Williamson, B.; Harlfinger, S.; Martin, S.; McGinnity, D.F. Optimising proteolysis-targeting chimeras (PROTACs) for oral drug delivery: A drug metabolism and pharmacokinetics perspective. Drug Discov. Today 2020, 25, 1793–1800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hornberger, K.R.; Araujo, E.M. Physicochemical property determinants of oral absorption for PROTAC protein degraders. J. Med. Chem. 2023, 66, 8281–8287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, H.-I.; Kim, T.; Kim, J.W.; Lee, G.J.; Choi, J.; Chae, Y.-J.; Kim, E.; Koo, T.-S. Rat Pharmacokinetics and In Vitro Metabolite Identification of KM-819, a Parkinson’s Disease Candidate, Using LC-MS/MS and LC-HRMS. Molecules 2024, 29, 1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| Nominal Concentration (ng/mL) | Measured Concentration (ng/mL) | Precision (CV, %) | Accuracy (RE, %) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mouse plasma | |||
| Intra-day (n = 5) | |||
| 1 | 1.029 ± 0.105 | 8.33 | 2.86 |
| 3 | 3.338 ± 0.355 | 10.64 | 11.27 |
| 30 | 33.60 ± 3.21 | 9.54 | 12.00 |
| 900 | 1007 ± 78 | 7.70 | 11.91 |
| Inter-day (n = 15) | |||
| 1 | 1.057 ± 0.142 | 13.43 | 5.69 |
| 3 | 3.271 ± 0.210 | 6.43 | 9.04 |
| 30 | 31.47 ± 3.83 | 12.16 | 4.91 |
| 900 | 898.1 ± 86.4 | 9.62 | 0.21 |
| Rat plasma | |||
| Intra-day (n = 5) | |||
| 1 | 1.021 ± 0.109 | 10.63 | 2.10 |
| 3 | 2.974 ± 0.218 | 7.32 | 0.87 |
| 30 | 30.10 ± 2.78 | 9.30 | 0.33 |
| 900 | 905.6 ± 48.4 | 5.35 | 0.62 |
| Inter-day (n = 15) | |||
| 1 | 1.023 ± 0.132 | 12.94 | 2.27 |
| 3 | 3.033 ± 0.365 | 12.02 | 1.11 |
| 30 | 31.15 ± 4.19 | 13.43 | 3.84 |
| 900 | 925.9 ± 109.9 | 11.87 | 2.87 |
| Storage Conditions | Nominal Concentration (ng/mL) | Stability in Mouse Plasma (%) | Stability in Rat Plasma (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 6 h at room temperature (25 °C) | 3 | 97.70 ± 4.12 | 100.3 ± 7.1 |
| 900 | 110.7 ± 2.8 | 99.59 ± 4.12 | |
| Freeze–thaw three-cycle (−20 °C → RT) | 3 | 99.78 ± 1.60 | 98.70 ± 7.09 |
| 900 | 103.3 ± 4.1 | 94.98 ± 1.40 | |
| 1 month at −20 °C | 3 | 103.1 ± 5.4 | 98.83 ± 12.58 |
| 900 | 107.7 ± 4.0 | 104.3 ± 8.5 | |
| Processed sample in 10 °C autosampler for 24 h | 3 | 104.0 ± 7.2 | 99.86 ± 0.84 |
| 900 | 98.49 ± 8.79 | 92.18 ± 6.32 |
| Nominal Concentration (ng/mL) | Matrix Effect (%) | Recovery (%) | Process Efficiency (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mouse plasma | |||
| 3 | 106.8 ± 4.86 | 92.89 ± 2.12 | 99.16 ± 2.26 |
| 30 | 108.8 ± 2.13 | 95.95 ± 0.49 | 104.4 ± 0.53 |
| 900 | 92.02 ± 4.76 | 106.0 ± 3.91 | 97.58 ± 3.60 |
| IS (300 ng/mL) | 92.66 ± 7.72 | 94.73 ± 4.94 | 87.78 ± 4.57 |
| Rat plasma | |||
| 3 | 91.35 ± 8.96 | 93.34 ± 5.31 | 88.64 ± 5.05 |
| 30 | 90.78 ± 6.60 | 88.54 ± 3.09 | 81.45 ± 2.84 |
| 900 | 92.26 ± 3.00 | 85.94 ± 2.61 | 87.80 ± 2.66 |
| IS (300 ng/mL) | 91.99 ± 6.23 | 90.05 ± 7.45 | 87.60 ± 7.25 |
| Parameters | Mouse | Rat | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| IV | PO | IV | PO | |
| Tmax (h) | 0.050 ± 0.000 | 1.000 ± 0.000 | 0.083 ± 0.000 | 3.200 ± 2.950 |
| Cmax (μg/mL) | 2.180 ± 0.442 | 0.393 ± 0.133 | 0.850 ± 0.095 | 0.108 ± 0.038 |
| T1/2 (h) | 3.790 ± 1.151 | 3.637 ± 1.399 | 3.970 ± 0.284 | 4.068 ± 0.418 |
| AUClast (μg/h/mL) | 6.396 ± 1.080 | 2.869 ± 0.704 | 1.881 ± 0.084 | 1.123 ± 0.428 |
| AUCinf (μg/h/mL) | 6.507 ± 1.057 | 2.913 ± 0.707 | 1.902 ± 0.090 | 1.147 ± 0.446 |
| CL (mL/h/kg) | 313.3 ± 44.2 | - | 1053 ± 49 | - |
| Vss (mL/kg) | 1434 ± 472 | - | 4354 ± 300 | - |
| MRT (h) | 4.607 ± 1.431 | 5.581 ± 1.344 | 4.140 ± 0.348 | 6.541 ± 0.965 |
| BA (%) | - | 17.91 ± 4.35 | - | 24.12 ± 9.39 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Choi, H.-I.; Choi, J.; Kim, J.W.; Lee, Y.H.; Cho, K.H.; Koo, T.-S. Stability Evaluation and Pharmacokinetic Profiling of Vepdegestrant in Rodents Using Liquid Chromatography–Tandem Mass Spectrometry. Molecules 2024, 29, 4048. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29174048
Choi H-I, Choi J, Kim JW, Lee YH, Cho KH, Koo T-S. Stability Evaluation and Pharmacokinetic Profiling of Vepdegestrant in Rodents Using Liquid Chromatography–Tandem Mass Spectrometry. Molecules. 2024; 29(17):4048. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29174048
Chicago/Turabian StyleChoi, Hae-In, Jinyoung Choi, Jin Woo Kim, Yoon Ha Lee, Kwan Hyung Cho, and Tae-Sung Koo. 2024. "Stability Evaluation and Pharmacokinetic Profiling of Vepdegestrant in Rodents Using Liquid Chromatography–Tandem Mass Spectrometry" Molecules 29, no. 17: 4048. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29174048
APA StyleChoi, H.-I., Choi, J., Kim, J. W., Lee, Y. H., Cho, K. H., & Koo, T.-S. (2024). Stability Evaluation and Pharmacokinetic Profiling of Vepdegestrant in Rodents Using Liquid Chromatography–Tandem Mass Spectrometry. Molecules, 29(17), 4048. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29174048







