A New Class of Benzo[b]thiophene-chalcones as Cholinesterase Inhibitors: Synthesis, Biological Evaluation, Molecular Docking and ADME Studies
Abstract
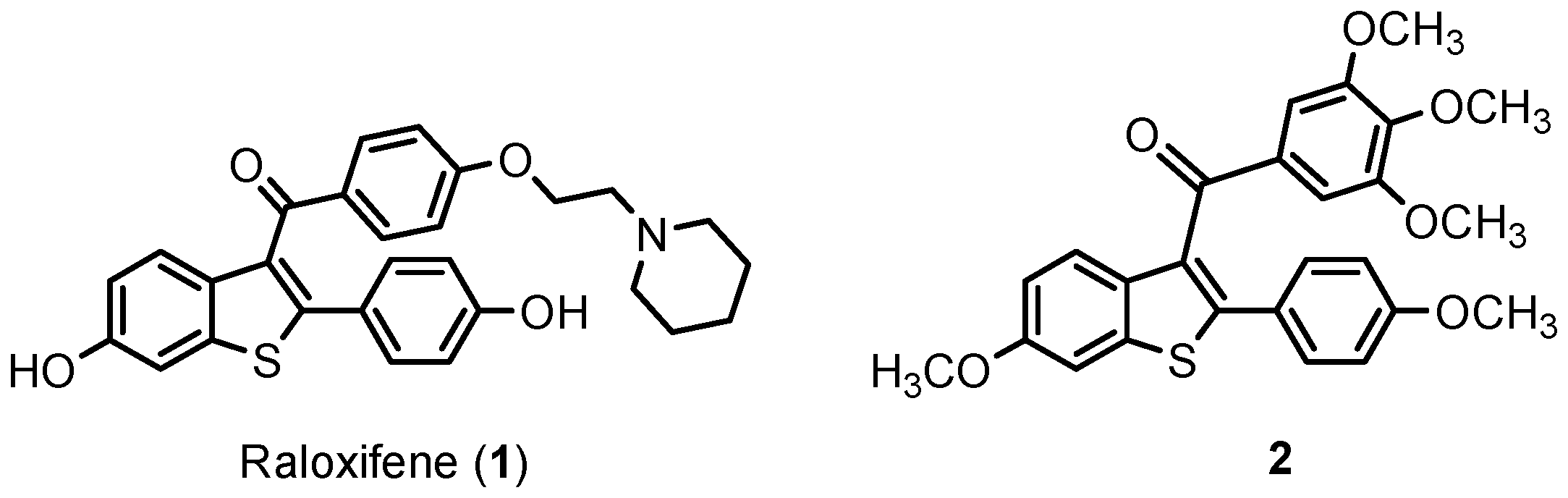
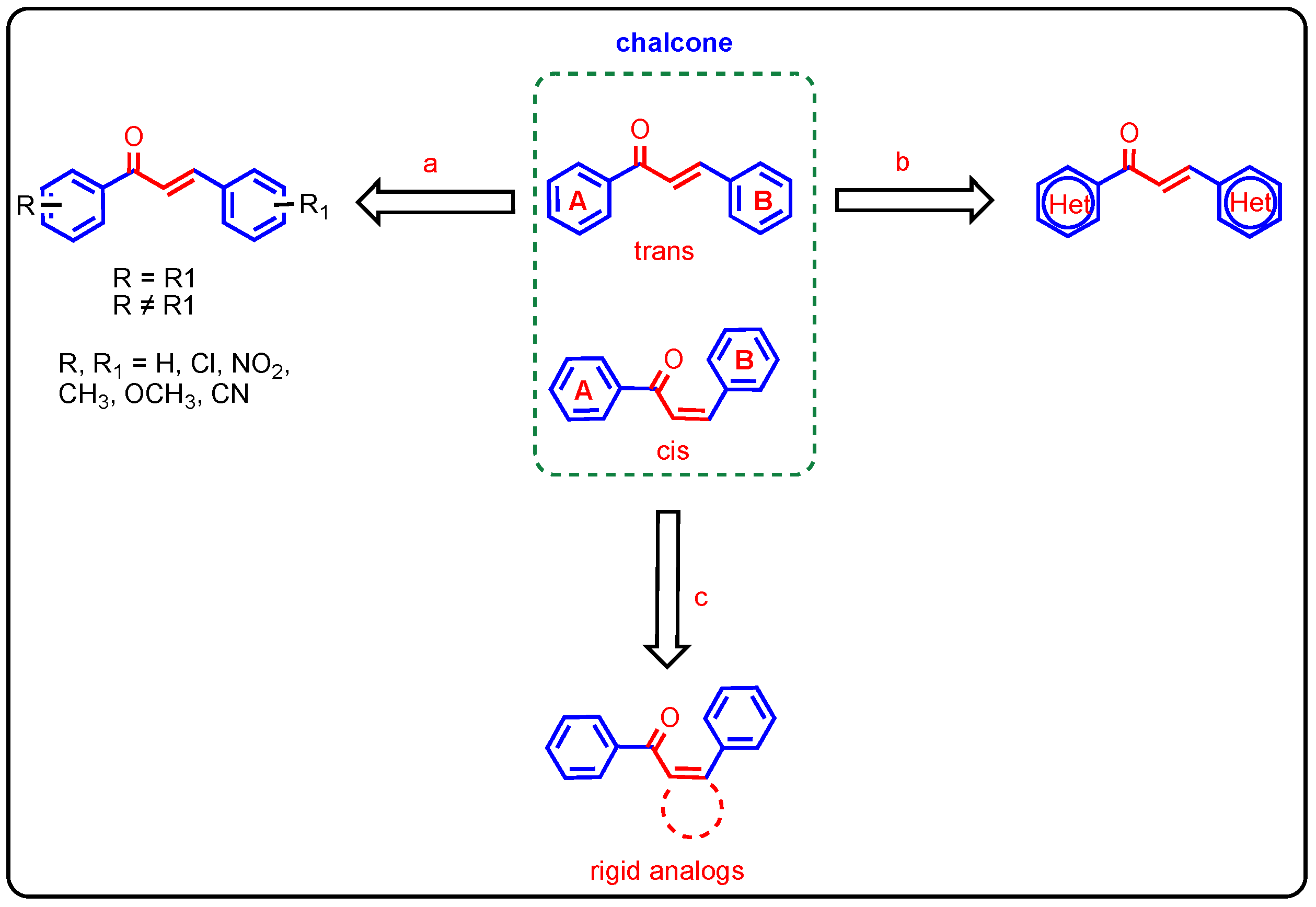
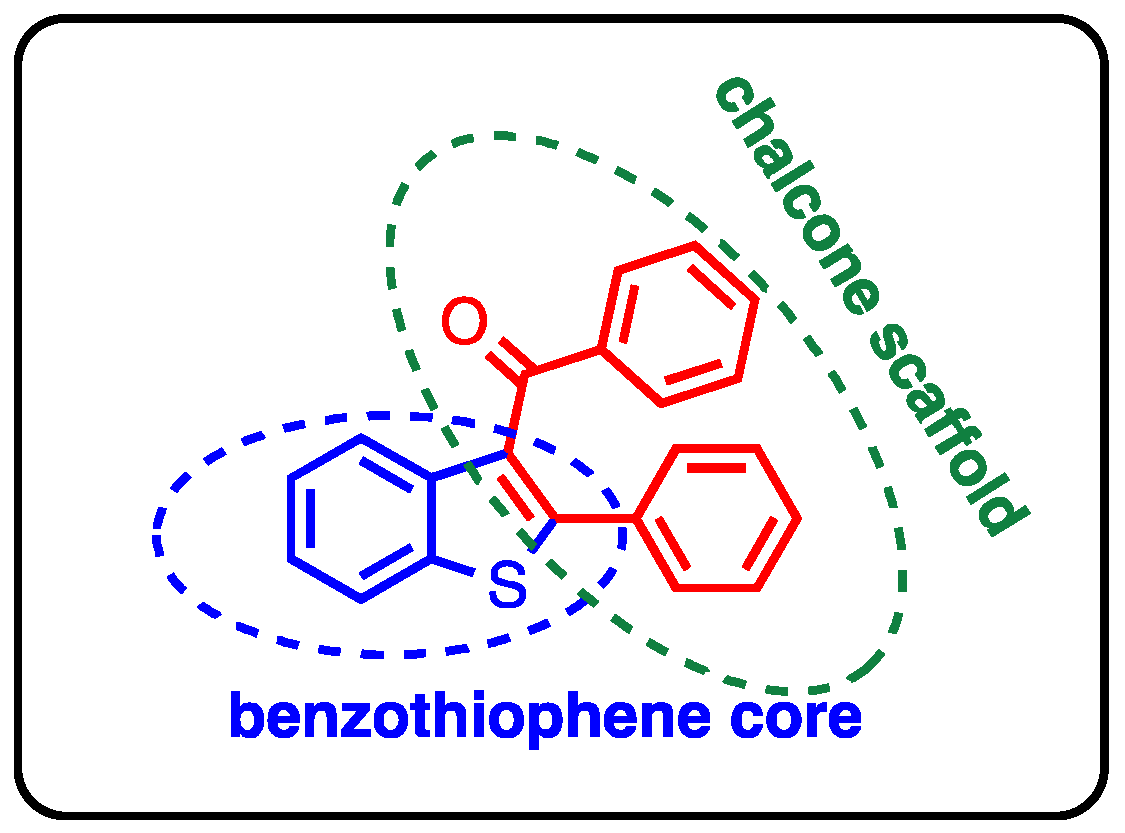
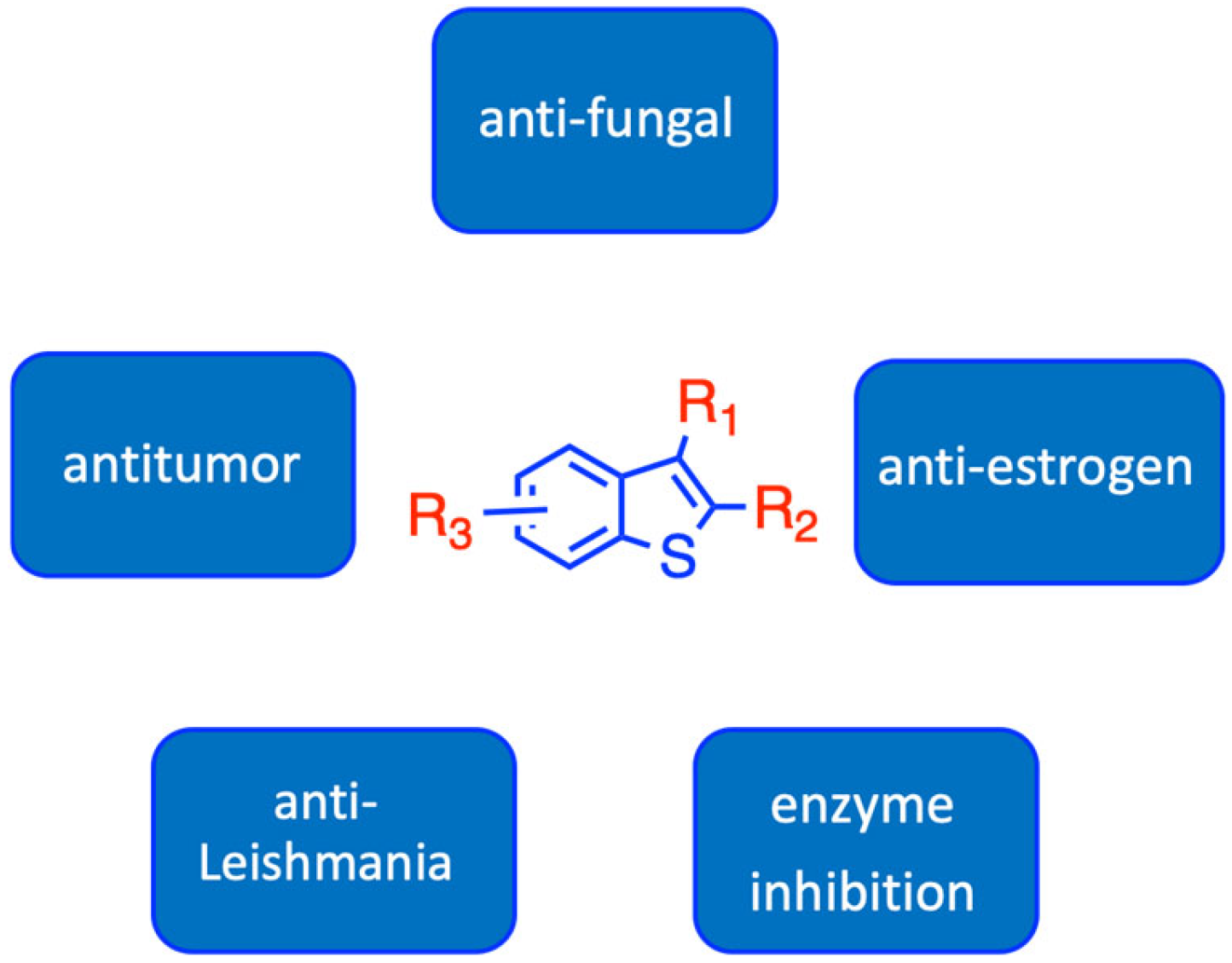
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Chemistry
2.2. Biological Activity
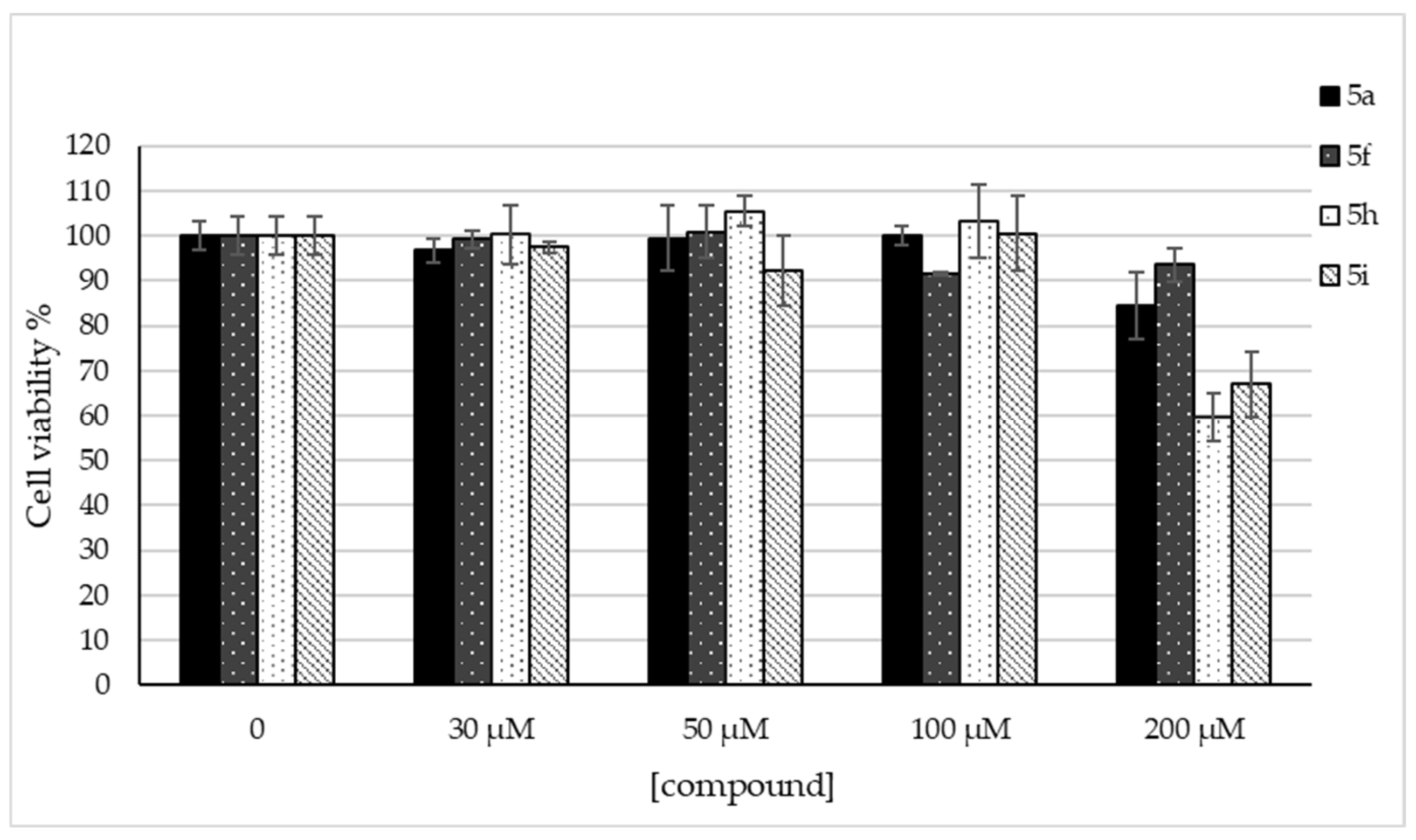
2.3. Cell Viability in SH-SY5Y Cells
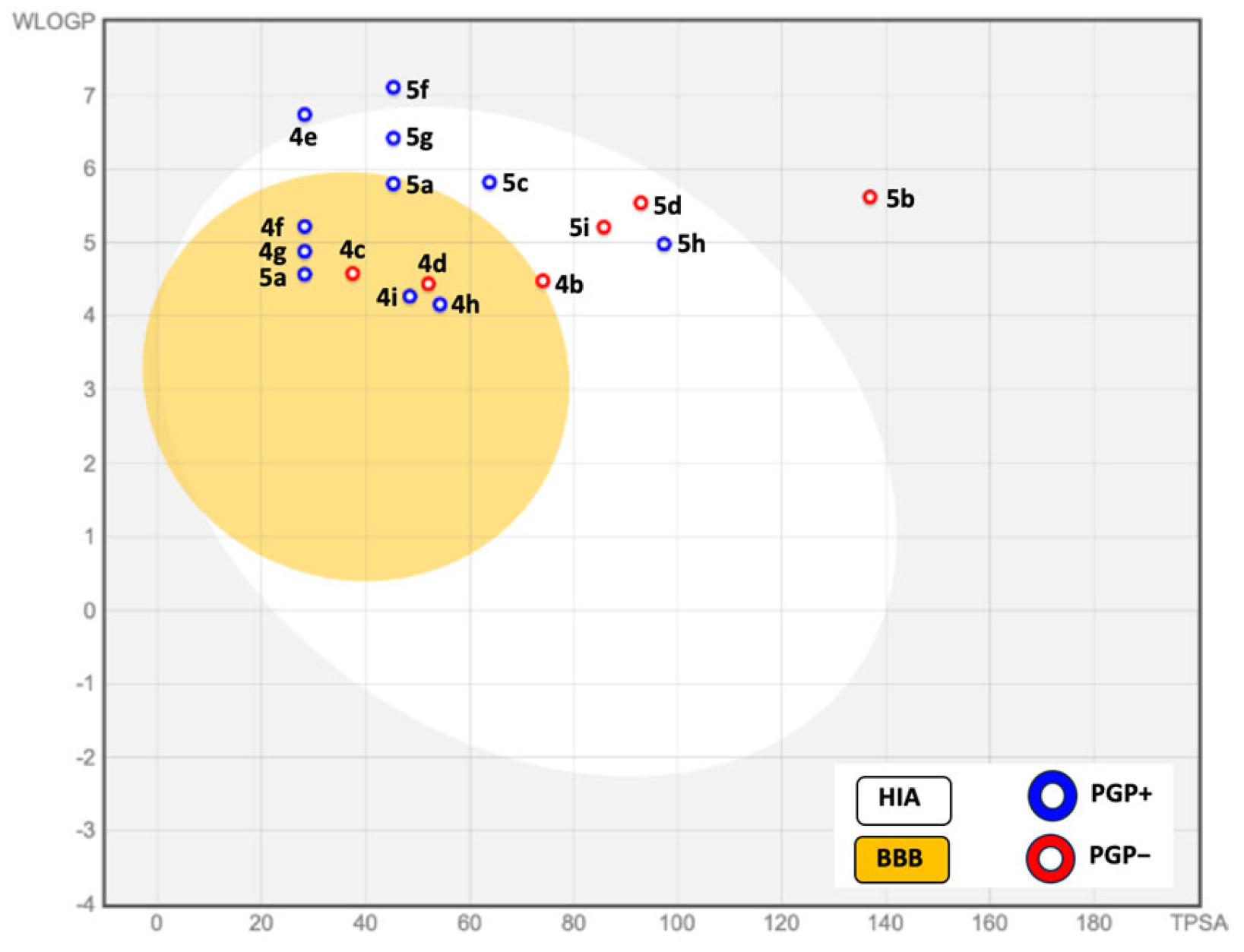
2.4. Absorption, Distribution, Metabolism and Excretion (ADME) Studies
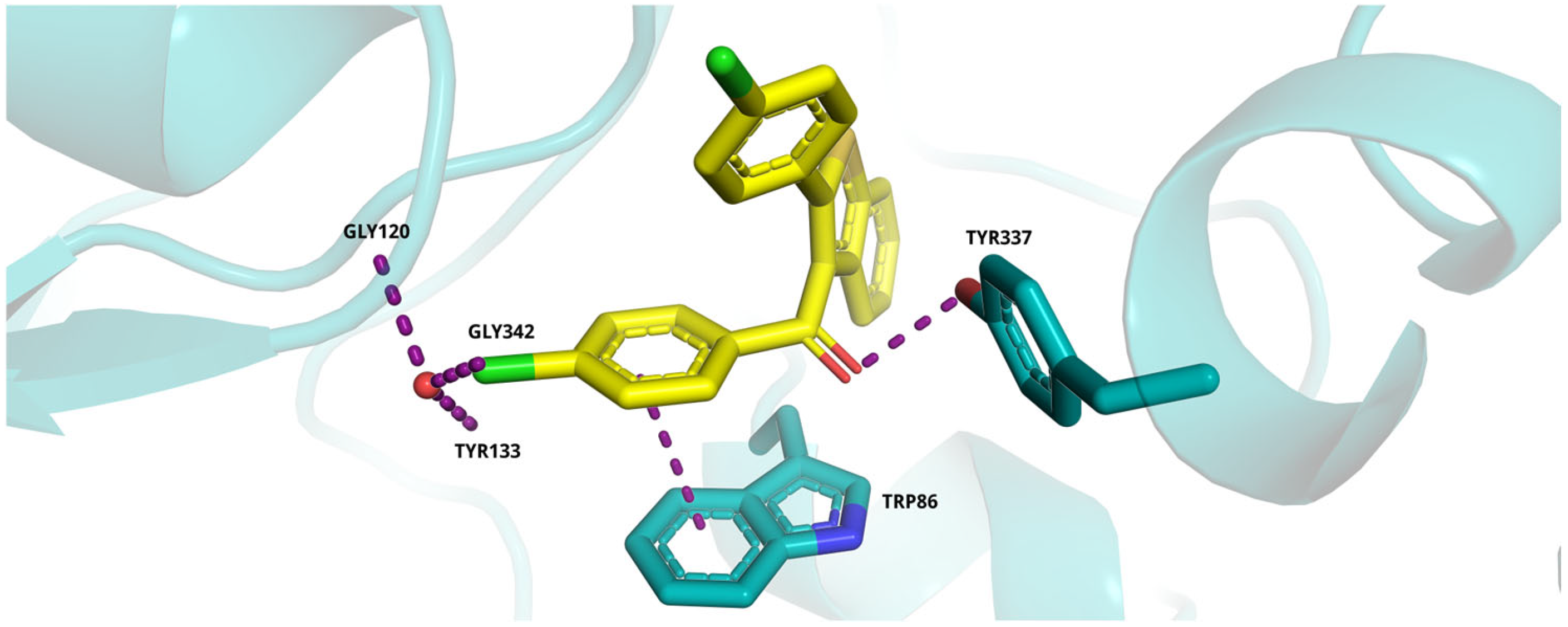
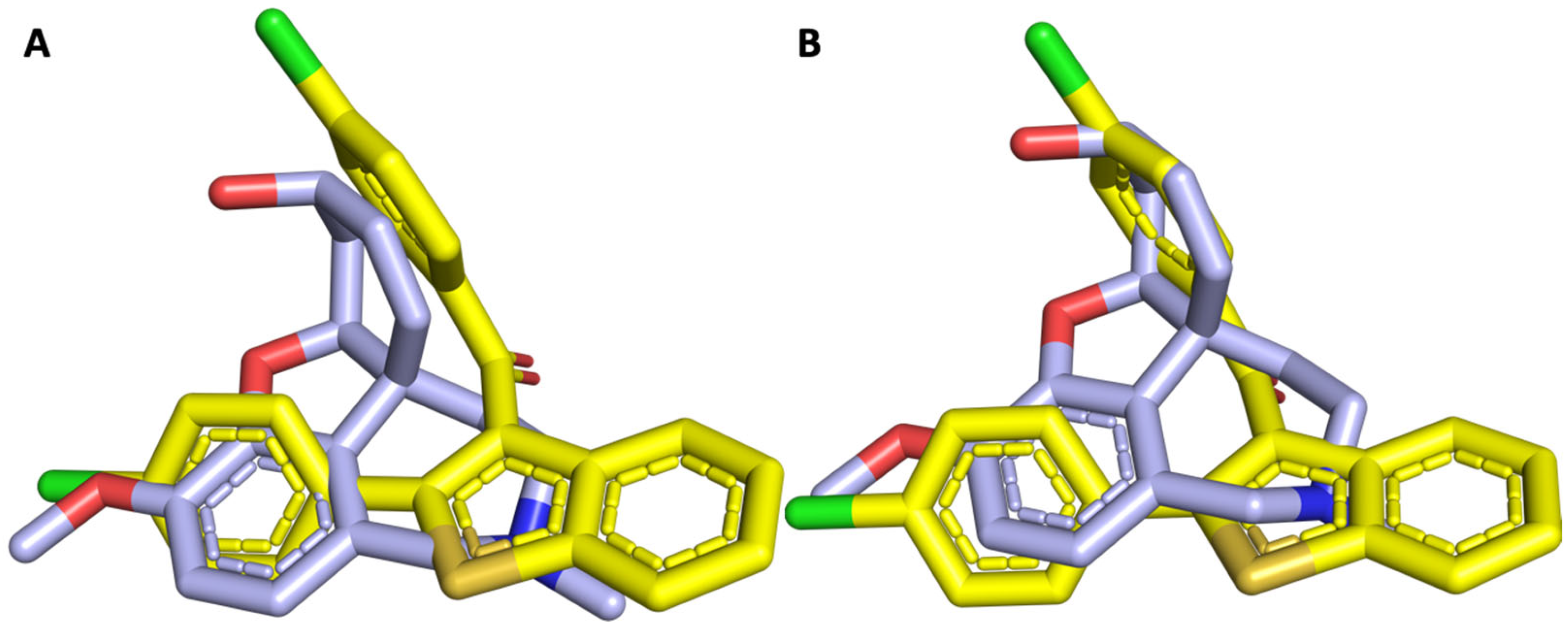
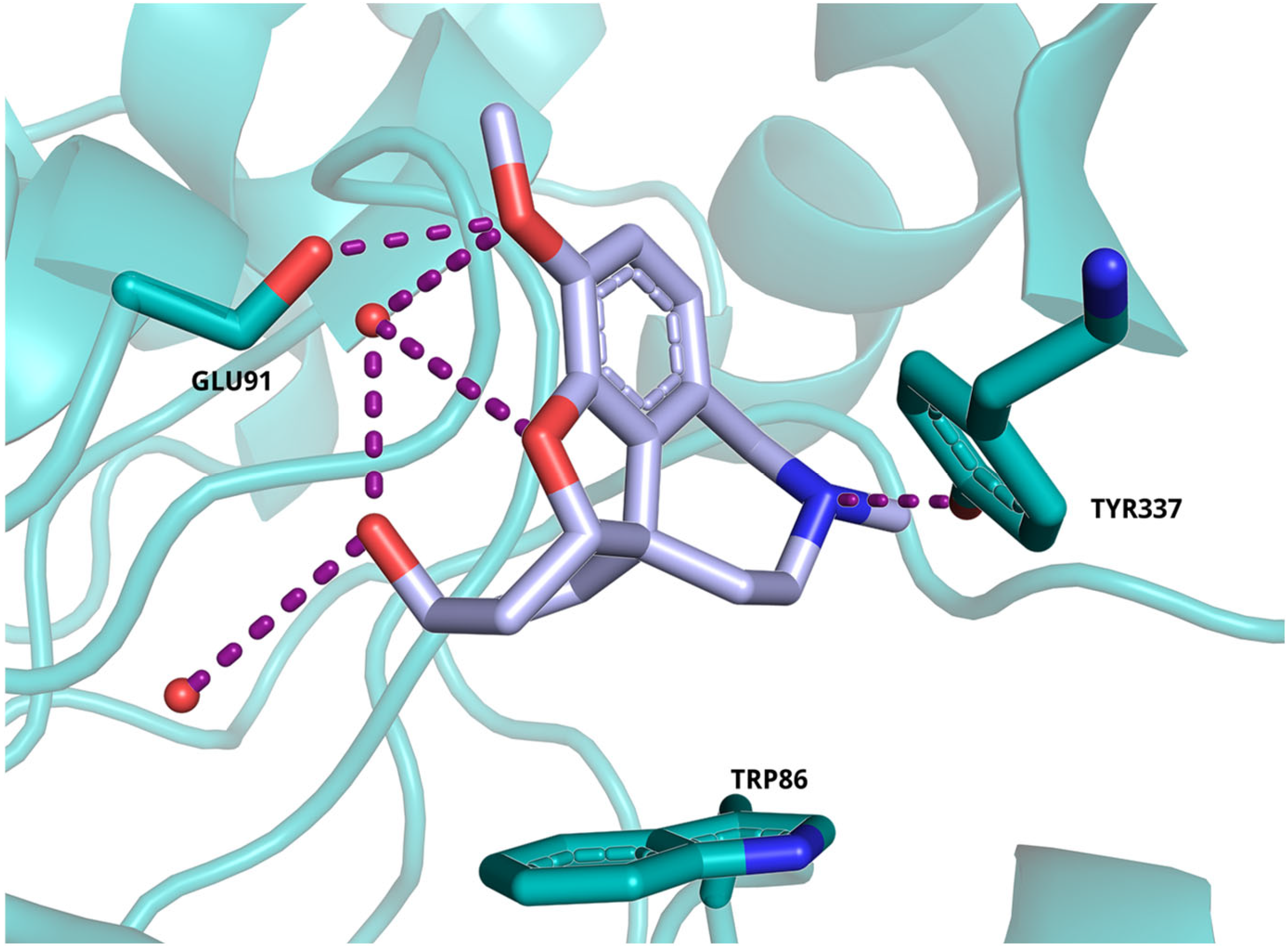
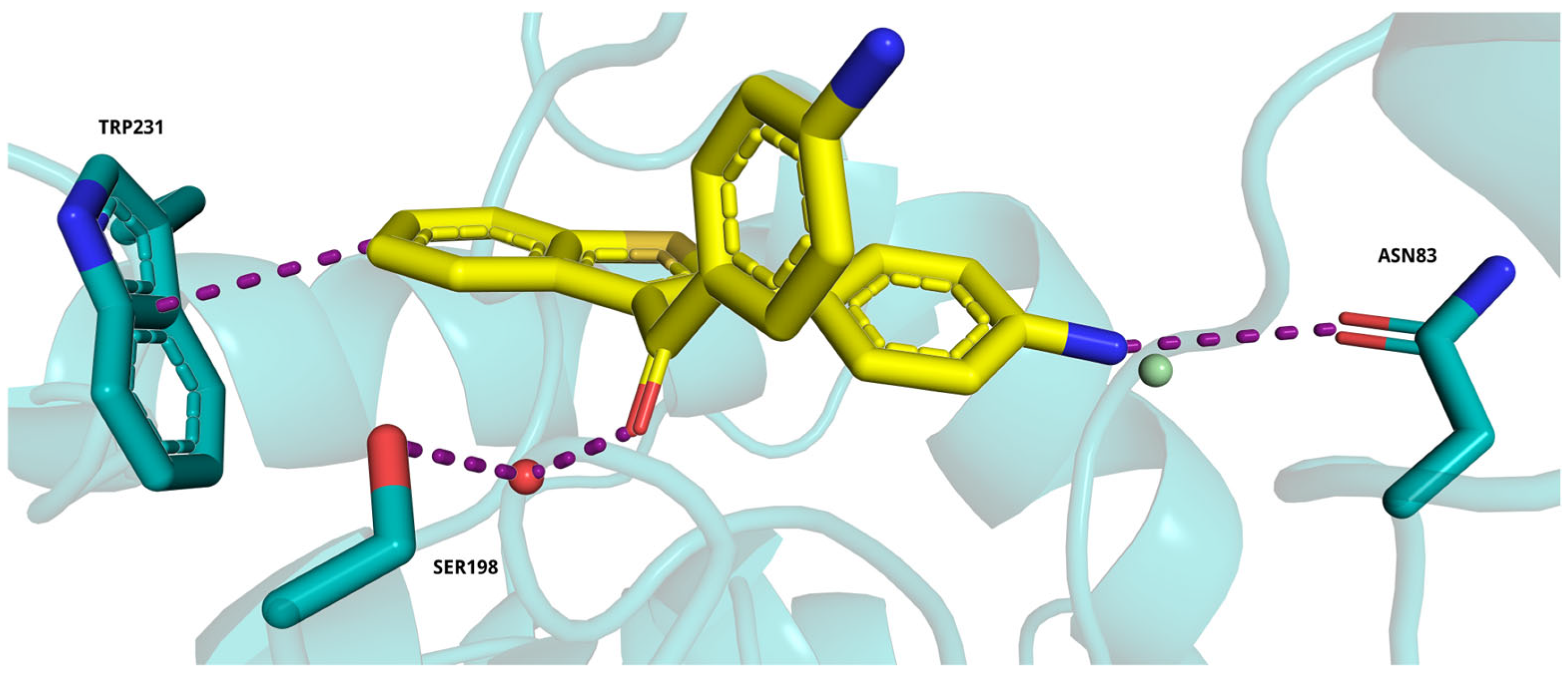
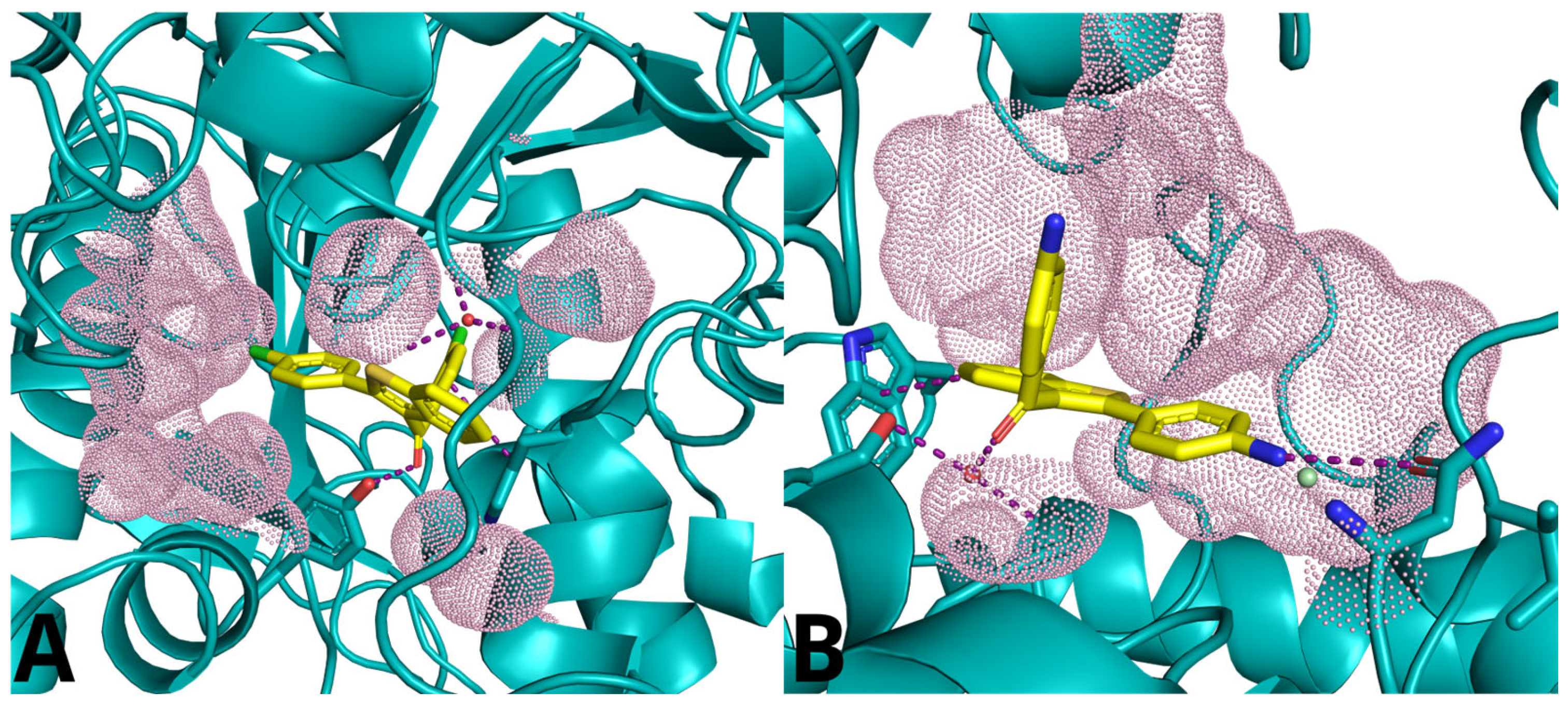
2.5. Molecular Docking Study
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Chemistry
3.2. Biological Activity
3.2.1. Determination of Cholinesterases Inhibition
3.2.2. Cell Viability
3.3. Computational Methods
3.3.1. Calculation of ADME Properties
3.3.2. Molecular Docking
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| Comp. | Physicochemical Properties | Lipophilicity | Drug-Likeness | Water Solubility | Pharmacokinetics | |||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MW (g/mol) | Fsp3 | RB | HBA | HBD | MR | tPSA | ilogP | XlogP3 | WlogP | MlogP | SILICOS-IT | Consensus logP | Lipinski | Ghose | Veber | Egan | Muegge | ESOL | Class | logKp (cm/s) | F | |
| 4a | 210.29 | 0.00 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 67.26 | 28.24 | 2.74 | 4.97 | 4.57 | 4.13 | 5.27 | 4.34 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | −4.95 | moderately | −4.05 | 0.55 |
| 5a | 314.40 | 0.00 | 3 | 1 | 0 | 97.14 | 45.31 | 3.19 | 5.94 | 5.80 | 4.43 | 6.66 | 5.20 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | −6.01 | poorly | −4.00 | 0.55 |
| 4b | 255.29 | 0.00 | 2 | 2 | 0 | 76.08 | 74.06 | 2.45 | 4.80 | 4.48 | 3.54 | 2.99 | 3.65 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | −4.93 | moderately | −4.45 | 0.55 |
| 5b | 404.40 | 0.00 | 5 | 5 | 0 | 114.78 | 136.95 | 1.67 | 5.60 | 5.62 | 2.30 | 2.27 | 3.49 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | −6.08 | poorly | −4.79 | 0.55 |
| 4c | 240.32 | 0.07 | 2 | 1 | 0 | 73.75 | 37.47 | 3.06 | 4.49 | 4.58 | 3.58 | 5.23 | 4.28 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | −4.96 | moderately | −4.26 | 0.55 |
| 5c | 374.45 | 0.09 | 5 | 3 | 0 | 110.12 | 63.77 | 3.79 | 5.89 | 5.82 | 3.60 | 6.73 | 5.17 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | −6.12 | poorly | −4.40 | 0.55 |
| 4d | 235.30 | 0.00 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 71.98 | 52.03 | 2.70 | 4.69 | 4.44 | 3.24 | 5.21 | 4.06 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | −4.84 | moderately | −4.41 | 0.55 |
| 5d | 364.42 | 0.00 | 3 | 3 | 0 | 106.57 | 92.89 | 3.04 | 5.38 | 5.54 | 2.92 | 6.69 | 4.71 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | −5.87 | moderately | −4.70 | 0.55 |
| 4e | 278.29 | 0.07 | 2 | 3 | 0 | 72.26 | 28.24 | 3.01 | 5.86 | 6.74 | 5.03 | 6.19 | 5.36 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 2 | −5.71 | moderately | −3.84 | 0.55 |
| 5e | 450.40 | 0.09 | 5 | 7 | 0 | 107.14 | 45.31 | 3.65 | 7.71 | 10.14 | 6.03 | 8.74 | 7.25 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | −7.66 | poorly | −3.57 | 0.55 |
| 4f | 244.74 | 0.07 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 72.27 | 28.24 | 3.02 | 5.60 | 5.22 | 4.65 | 5.86 | 4.87 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 2 | −5.51 | moderately | −3.82 | 0.55 |
| 5f | 383.29 | 0.00 | 3 | 1 | 0 | 107.16 | 45.31 | 3.64 | 7.20 | 7.11 | 5.40 | 7.91 | 6.25 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | −7.18 | poorly | −3.53 | 0.55 |
| 4g | 224.34 | 0.07 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 72.23 | 28.24 | 3.01 | 5.34 | 4.88 | 4.39 | 5.74 | 4.67 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 2 | −5.22 | moderately | −3.88 | 0.55 |
| 5g | 342.45 | 0.09 | 3 | 1 | 0 | 107.07 | 45.31 | 3.75 | 6.67 | 6.42 | 4.87 | 7.68 | 5.88 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | −6.59 | poorly | −3.65 | 0.55 |
| 4h | 225.31 | 0.00 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 71.67 | 54.26 | 2.38 | 4.29 | 4.16 | 3.33 | 4.50 | 3.73 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | −4.57 | moderately | −4.63 | 0.55 |
| 5h | 344.43 | 0.00 | 3 | 1 | 2 | 105.94 | 97.35 | 2.53 | 4.58 | 4.98 | 3.16 | 5.19 | 4.09 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | −5.28 | moderately | −5.15 | 0.55 |
| 4i | 226.29 | 0.00 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 69.28 | 48.47 | 2.38 | 4.62 | 4.27 | 3.33 | 4.74 | 3.87 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | −4.78 | moderately | −4.40 | 0.55 |
| 5i | 346.40 | 0.00 | 3 | 3 | 2 | 101.18 | 85.77 | 2.53 | 5.23 | 5.21 | 3.16 | 5.67 | 4.36 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | −5.71 | moderately | −4.70 | 0.55 |
| Galantamine | 287.35 | 0.53 | 1 | 4 | 1 | 84.05 | 41.93 | 2.66 | 1.84 | 1.32 | 1.74 | 2.03 | 1.92 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | −2.93 | soluble | −6.75 | 0.55 |
References
- Mishra, R.; Tomar, I.; Singhal, S.; Jha, K.K. Synthesis, Properties and Biological Activity of Thiophene: A Review. Der Pharma Chem. 2011, 3, 38–54. [Google Scholar]
- Katritzky, A. Advances in Heterocyclic Chemistry; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2002; Volume 82. [Google Scholar]
- Martins, P.; Jesus, J.; Santos, S.; Raposo, L.R.; Roma-Rodrigues, C.; Baptista, P.V.; Fernandes, A.R. Heterocyclic Anticancer Compounds: Recent Advances and the Paradigm Shift towards the Use of Nanomedicine’s Tool Box. Molecules 2015, 20, 16852–16891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomtsyan, A. Heterocycles in Drugs and Drug Discovery. Chem. Heterocycl. Compd. 2012, 48, 7–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keri, R.S.; Chand, K.; Budagumpi, S.; Balappa Somappa, S.; Patil, S.A.; Nagaraja, B.M. An Overview of Benzo[b]Thiophene-Based Medicinal Chemistry. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2017, 138, 1002–1033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dua, R.; Dua, R.; Shrivastava, S.; Sonwane, S.K.; Srivastava, S.K. Pharmacological Significance of Synthetic Heterocycles Scaffold: A Review. Adv. Biol. Res. 2011, 5, 120–144. [Google Scholar]
- Laxmikeshav, K.; Kumari, P.; Shankaraiah, N. Expedition of Sulfur-Containing Heterocyclic Derivatives as Cytotoxic Agents in Medicinal Chemistry: A Decade Update. Med. Res. Rev. 2022, 42, 513–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wright, C.D.; Stewart, S.F.; Kuipers, P.J.; Hoffman, M.D.; Devall, L.J.; Kennedy, J.A.; Ferin, M.A.; Thueson, D.O.; Conroy, M.C. Selective regulation of human neutrophil functions by the cell activation inhibitor CI-959. J. Leukoc. Biol. 1994, 55, 443–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Towle, M.J.; Lee, A.; Maduakor, E.C.; Schwartz, C.E.; Bridges, A.J. Inhibition of Urokinase by 4-Substituted Benzo[]Thiophene-2-Carboxamidines: An Important New Class of Selective Synthetic Urokinase Inhibitor. Cancer Res. 1993, 53, 2553–2559. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Carballo, M.; Conde, M.; Tejedo, J.; Gualberto, A.; Jimenez, J.; Monteseirín, J.; Santa María, C.; Bedoya, F.J.; Hunt, S.W.; Pintado, E.; et al. Macrophage Inducible Nitric Oxide Synthase Gene Expression Is Blocked by a Benzothiophene Derivative with Anti-HIV Properties. Mol. Genet. Metab. 2002, 75, 360–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ono, S.; Yamafuji, T.; Chaki, H.; Todo, Y.; Maekawa, M.; Kitamura, K.; Kimura, T.; Nakada, Y.; Mozumi, K.; Narita, H. A New Cognition. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 1995, 18, 1460–1462. [Google Scholar]
- Pinney, K.G.; Bounds, A.D.; Dingeman, K.M.; Mocharla, V.P.; Pettit, G.R.; Bai, R.; Hamel, E. A New Anti-Tubulin Agent Containing the Benzo[b]Thiophene Ring System. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 1999, 9, 1081–1086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vogel, V.G.; Costantino, J.P.; Wickerham, D.L.; Cronin, W.M.; Cecchini, R.S.; Atkins, J.N.; Bevers, T.B.; Fehrenbacher, L.; Pajon, E.R.; Wade, J.L.; et al. Effects of Tamoxifen vs Raloxifene on the Risk of Developing Invasive Breast Cancer and Other Disease Outcomes: The NSABP Study of Tamoxifen and Raloxifene (STAR) P-2 Trial. JAMA 2006, 295, 2727–2741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thapa, P.; Upadhyay, S.P.; Suo, W.Z.; Singh, V.; Gurung, P.; Lee, E.S.; Sharma, R.; Sharma, M. Chalcone and Its Analogs: Therapeutic and Diagnostic Applications in Alzheimer’s Disease. Bioorg. Chem. 2021, 108, 104681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hasan, A.; Khan, K.M.; Sher, M.; Maharvi, G.M.; Nawaz, S.A.; Choudhary, M.I.; Rahman, A.U.; Supuran, C.T. Synthesis and Inhibitory Potential towards Acetylcholinesterase, Butyrylcholinesterase and Lipoxygenase of Some Variably Substituted Chalcones. J. Enzym. Inhib. Med. Chem. 2005, 20, 41–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- George, G.; Koyiparambath, V.P.; Sukumaran, S.; Nair, A.S.; Pappachan, L.K.; Al-Sehemi, A.G.; Kim, H.; Mathew, B. Structural Modifications on Chalcone Framework for Developing New Class of Cholinesterase Inhibitors. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 3121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Ture, M.A.; Dickson, D.W. The Neuropathological Diagnosis of Alzheimer Disease. Mol. Neurodegener. 2019, 14, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scarpini, E.; Scheltens, P.; Feldman, H. Treatment of Alzheimer’s Disease: Current Status and New Perspectives. Lancet Neurol. 2003, 2, 539–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schneider, L.S. A Critical Review of Cholinesterase Inhibitors as a Treatment Modality in Alzheimer’s Disease. Dialogues Clin. Neurosci. 2000, 2, 111–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ismail, M.M.; Kamel, M.M.; Mohamed, L.W.; Faggal, S.I.; Galal, M.A. Synthesis and Biological Evaluation of Thiophene Derivatives as Acetylcholinesterase Inhibitors. Molecules 2012, 17, 7217–7231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barakat, A.; Alshahrani, S.; Al-Majid, A.M.; Ali, M.; Altowyan, M.S.; Islam, M.S.; Alamary, A.S.; Ashraf, S.; Ul-Haq, Z. Synthesis of a New Class of Spirooxindole-Benzo[b]Thiophene-Based Molecules as Acetylcholinesterase Inhibitors. Molecules 2020, 25, 4671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Wang, N.Y.; Song, X.J.; Lei, Q.; Ye, T.H.; You, X.Y.; Zuo, W.Q.; Xia, Y.; Zhang, L.D.; Yu, L.T. Discovery of Novel N-(5-(Tert-Butyl)Isoxazol-3-Yl)-N′-Phenylurea Analogs as Potent FLT3 Inhibitors and Evaluation of Their Activity against Acute Myeloid Leukemia in Vitro and in Vivo. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2015, 23, 4333–4343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chamberlain, K.; Carter, G.A. Fungitoxicity of Hydroxy- and Methoxy-substituted Phenyl- and Naphthyl-benzofurans, Phenylbenzo[b]Thiophenes and Phenylindoles. Pestic. Sci. 1981, 12, 539–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McInerney, E.M.; Katzenellenbogen, B.S. Different Regions in Activation Function-1 of the Human Estrogen Receptor Required for Antiestrogen- and Estradiol-Dependent Transcription Activation. J. Biol. Chem. 1996, 271, 24172–24178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Chang, L.; Pellet-Rostaing, S.; Liger, F.; Lemaire, M.; Buchet, R.; Wu, Y. Synthesis and Evaluation of Benzo[b]Thiophene Derivatives as Inhibitors of Alkaline Phosphatases. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2009, 17, 7290–7300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonano, V.I.; Yokoyama-Yasunaka, J.K.U.; Miguel, D.C.; Jones, S.A.; Dodge, J.A.; Uliana, S.R.B. Discovery of Synthetic Leishmania Inhibitors by Screening of a 2-Arylbenzothiophene Library. Chem. Biol. Drug Des. 2014, 83, 289–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Hu, Y.; Hong, X.; Li, G.; Huang, X.; Gao, W.; Liu, M.; Xia, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Wu, H. Direct synthesis of 3-acylbenzothiophenes via the radical cyclization of 2-alkynylthioanisoles with α-oxocarboxylic acids. Chem. Commun. 2018, 54, 14148–14151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Xiang, H.; Yang, L.; Zhou, X. Synthesis of 2-substituted benzo[b]thiophene via a Pd-catalyzed coupling of 2-iodothiophenol with phenylacetylene. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 7753–7757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kashiki, T.; Shinamura, S.; Kohara, M.; Miyazaki, E.; Takimiya, K.; Ikeda, M.; Kuwabara, H. One-pot Synthesis of Benzo[b]thiophenes and Benzo[b]selenophenes from o-Halo-Substituted Ethynylbenzenes: Convenient Approach to Mono-, Bis-, and Tris-Chalcogenophene-Annulated Benzenes. Org. Lett. 2009, 11, 365–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.H.; Chen, C.C.; Wu, M.J. Mercury(II)-Catalyzed Cyclization of 2-Alkynylphenyl Alkyl Sulfoxides Provides 3-Acylbenzo[b]Thiophenes. Chem.—A Eur. J. 2013, 19, 2578–2581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedel, A.; Crafts, J.; Ador, E.B. Einwirkung von Chloracetyl auf Azoresorcin. Dtsch. Chem. Ges. 1877, 10, 1854–1858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Begala, M.; Mancinelli, M.; Delogu, G.L. Unexpected Migration of a Benzoyl Group in the Intramolecular Wittig Reaction of O-Acyloxybenzylidenephosphoranes with Benzoyl Chlorides: One-Pot Synthesis of Isomeric 3-Benzoyl-2-Phenylbenzofurans. Tetrahedron Lett. 2020, 61, 151634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Begala, M.; Caboni, P.; Matos, M.J.; Delogu, G.L. Unexpected One-Step Synthesis of 3-Benzoyl-2-Phenylbenzofurans under Wittig Conditions. Tetrahedron Lett. 2018, 59, 1711–1714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, Y.S.; Jeong, J.M.; Lee, Y.S.; Kim, H.W.; Ganesha, R.B.; Kim, Y.J.; Lee, D.S.; Chung, J.K.; Lee, M.C. Synthesis and Evaluation of Benzothiophene Derivatives as Ligands for Imaging β-Amyloid Plaques in Alzheimer’s Disease. Nucl. Med. Biol. 2006, 33, 811–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arnoldi, A.; Carughi, M.A. No A Simple Synthesis of 2-Substituted 1-Benzothiophenes and 3-Substituted 2H-1-Benzothiopyrans. Synthesis 1988, 1988, 155–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, T.; Feng, C.; Shen, F.; Bian, K.; Wu, C.; Shen, R.; Gao, Y. Synthesis of 2-Substituted Benzothio(Seleno)Phenes and Indoles via Ag-Catalyzed Cyclization/Demethylation of 2-Alkynylthio(Seleno)Anisoles and 2-Alkynyldimethylanilines. Eur. J. Org. Chem. 2021, 2021, 653–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Sun, L.L.; Hu, B.L.; Zhang, X.G.; Chen, F. A Facile One-Pot Synthesis of Benzothiophenes via Copper-Catalyzed Thiolation Annulations of o-Halostyrenes with NaSH. Tetrahedron 2014, 70, 7969–7972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
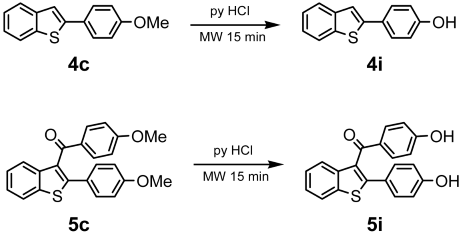
- Kulkarni, P.P.; Kadam, A.J.; Mane, R.B.; Desai, U.V.; Wadgaonkar, P.P. Demethylation of Methyl Aryl Ethers Using Pyridine Hydrochloride in Solvent-Free Conditions under Microwave Irradiation. J. Chem. Res.—Part S 1999, 6, 394–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fais, A.; Kumar, A.; Medda, R.; Pintus, F.; Delogu, F.; Matos, M.J.; Era, B.; Delogu, G.L. Synthesis, Molecular Docking and Cholinesterase Inhibitory Activity of Hydroxylated 2-Phenylbenzofuran Derivatives. Bioorg. Chem. 2019, 84, 302–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daina, A.; Michielin, O.; Zoete, V. SwissADME: A Free Web Tool to Evaluate Pharmacokinetics, Drug-Likeness and Medicinal Chemistry Friendliness of Small Molecules. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 42717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lipinski, C.A.; Lombardo, F.; Dominy, B.W.; Feeney, P.J. Experimental and Computational Approaches to Estimate Solubility and Permeability in Drug Discovery and Development Settings. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2001, 46, 3–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghose, A.K.; Viswanadhan, V.N.; Wendoloski, J.J. A Knowledge-Based Approach in Designing Combinatorial or Medicinal Chemistry Libraries for Drug Discovery. 1. A Qualitative and Quantitative Characterization of Known Drug Databases. J. Comb. Chem. 1999, 1, 55–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veber, D.F.; Johnson, S.R.; Cheng, H.-Y.; Smith, B.R.; Ward, K.W.; Kenneth, D.K. Molecular Properties That Influence the Oral Bioavailability of Drug Candidates. J. Med. Chem. 2002, 45, 2615–2623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Egan, W.J.; Merz, K.M.; Baldwin, J.J. Prediction of Drug Absorption Using Multivariate Statistics. J. Med. Chem. 2000, 43, 3867–3877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muegge, I.; Heald, S.L.; Brittelli, D. Simple Selection Criteria for Drug-like Chemical Matter. J. Med. Chem. 2001, 44, 1841–1846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wildman, S.A.; Crippen, G.M. Prediction of Physicochemical Parameters by Atomic Contributions. J. Chem. Inf. Comput. Sci. 1999, 39, 868–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delaney, J.S. ESOL: Estimating Aqueous Solubility Directly from Molecular Structure. J. Chem. Inf. Comput. Sci. 2004, 44, 1000–1005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daina, A.; Zoete, V. A BOILED-Egg to Predict Gastrointestinal Absorption and Brain Penetration of Small Molecules. ChemMedChem 2016, 11, 1117–1121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, Y.C. A Bioavailability Score. J. Med. Chem. 2005, 48, 3164–3170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vainio, M.J.; Puranen, J.S.; Johnson, M.S. ShaEP: Molecular Overlay Based on Shape and Electrostatic Potential. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2009, 49, 492–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Wang, R.; Yang, C.Y.; Wang, S. Analysis of Ligand-Bound Water Molecules in High-Resolution Crystal Structures of Protein-Ligand Complexes. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2007, 47, 668–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellman, G.L.; Courtney, K.D.; Andres, V.; Featherstone, R.M. A New and Rapid Colorimetric Determination of Acetylcholinesterase Activity. Biochem. Pharmacol. 1961, 7, 88–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Era, B.; Floris, S.; Sogos, V.; Porcedda, C.; Piras, A.; Medda, R.; Fais, A.; Pintus, F. Anti-Aging Potential of Extracts from Washingtonia Filifera Seeds. Plants 2021, 10, 151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eberhardt, J.; Santos-Martins, D.; Tillack, A.F.; Forli, S. AutoDock Vina 1.2.0: New Docking Methods, Expanded Force Field, and Python Bindings. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2021, 61, 3891–3898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eastman, P.; Swails, J.; Chodera, J.D.; McGibbon, R.T.; Zhao, Y.; Beauchamp, K.A.; Wang, L.P.; Simmonett, A.C.; Harrigan, M.P.; Stern, C.D.; et al. OpenMM 7: Rapid Development of High Performance Algorithms for Molecular Dynamics. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2017, 13, e1005659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maier, J.A.; Martinez, C.; Kasavajhala, K.; Wickstrom, L.; Hauser, K.E.; Simmerling, C. Ff14SB: Improving the Accuracy of Protein Side Chain and Backbone Parameters from Ff99SB. J. Chem. Theory Comput. 2015, 11, 3696–3713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Price, D.J.; Brooks, C.L. A Modified TIP3P Water Potential for Simulation with Ewald Summation. J. Chem. Phys. 2004, 121, 10096–10103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Genheden, S.; Ryde, U. The MM/PBSA and MM/GBSA Methods to Estimate Ligand-Binding Affinities. Expert Opin. Drug Discov. 2015, 10, 449–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toyota, K.; Tanaka, H.; Hanagasaki, T. Silica gel-assisted synthesis of benzo[b]thiophenes from o-(alkylsulfanyl)(ethynyl)benzenes. Results Chem. 2022, 4, 1000487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, F.; Wang, J.T.; Liu, L.L.; Ma, N.; Yang, C.; Gao, Y.; Xia, W. Synthesis of carbonylated heteroaromatic compounds via visible-light-driven intramolecular decarboxylative cyclization of o-alkynylated carboxylic acids. Chem. Commun. 2017, 53, 8533–8536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romero-Parra, J.; Mella-Raipan, J.; Palmieri, V.; Allara, M.; Torres, M.J.; Pessoa-Mahana, H.; Iturriaga-Vasquez, P.; Escobar, R.; Faúndez, M.; Di Marzo, V.; et al. Synthesis, binding assays, cytotoxic activity and docking studies of benzimidazole and benzothiophene derivatives with selective affinity for the CB2 cannabinoid receptor. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2016, 124, 17–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
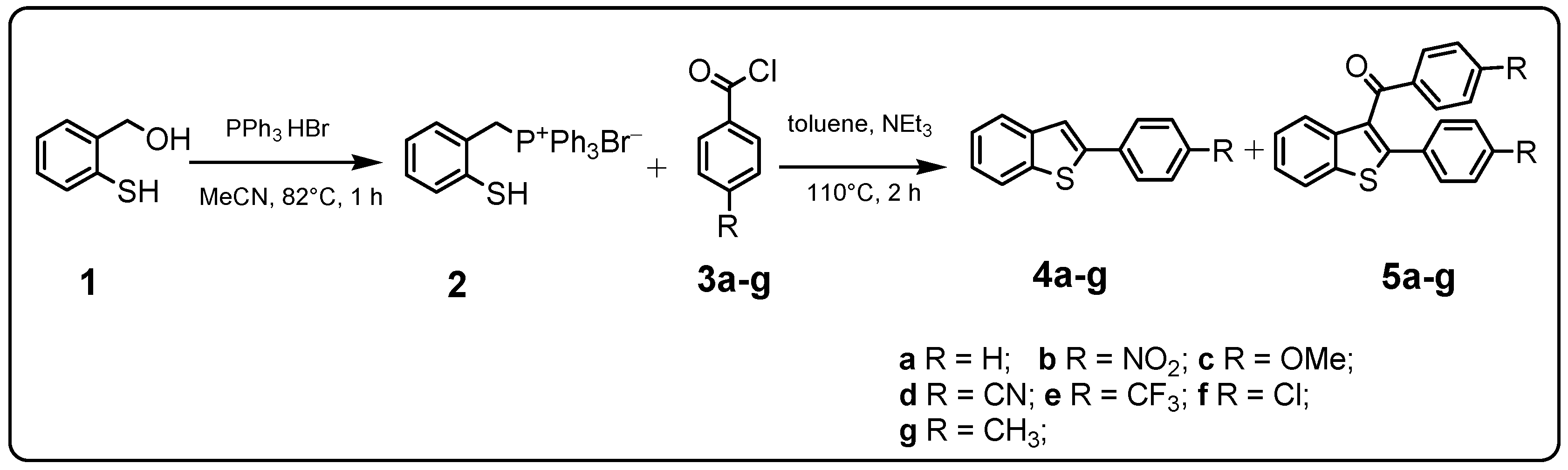
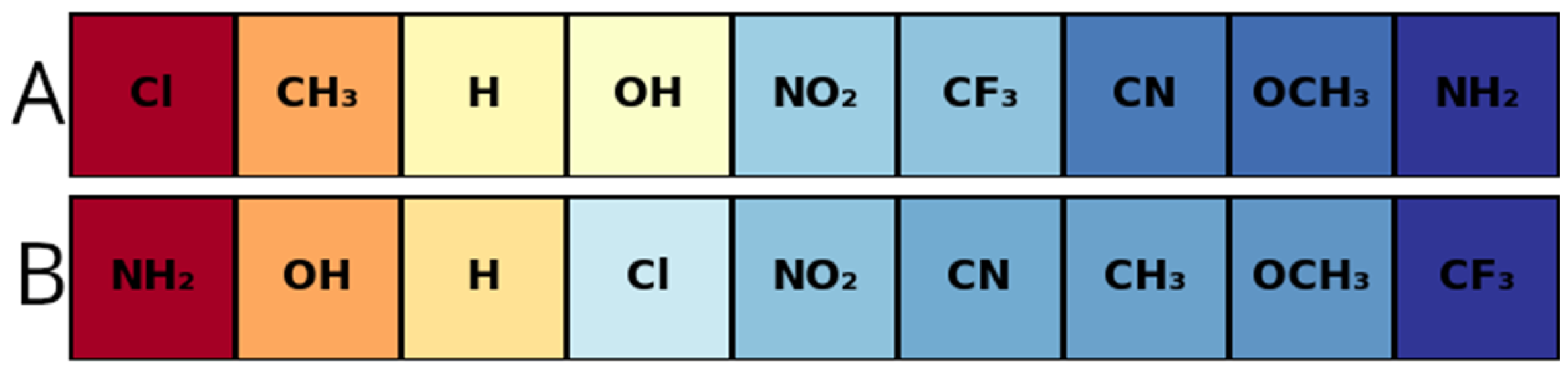
| Product 4a–g | Product 5a–g | Yield 4/5 (%) | |
|---|---|---|---|
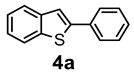 | + | 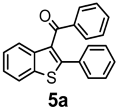 | 56/28 |
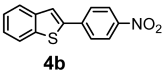 | + | 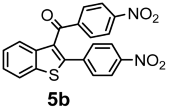 | 12/63 |
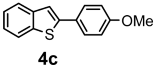 | + | 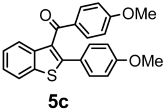 | 21/9 |
 | + | 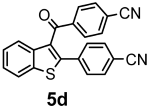 | 25/50 |
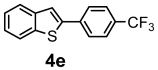 | + |  | 12/38 |
 | + |  | 31/47 |
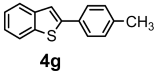 | + | 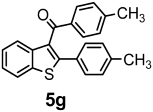 | 19/9 |
 | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Product | Yield | Product | Yield |
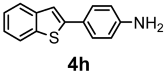 | 78% | 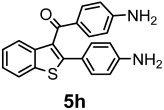 | 80% |
 | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Product | Yield | Product | Yield |
 | 90% | 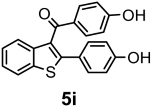 | 85% |
| Compounds | AChE (I %) | BChE (I %) | Compounds | AChE IC50 (µM) (I %) | BChE IC50 (µM) (I %) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 4a | Ins. | Ins. | 5a | (20.80 ± 4.20) | 83.40 ± 1.20 (35.70 ± 0.60) |
| 4b | (8.20 ± 2.40) | (2.29 ± 3.23) | 5b | (11.00 ± 0.04) | (16.80 ± 0.40) |
| 4c | (9.60 ± 1.50) | (1.20 ± 0.01) | 5c | (3.50 ± 0.10) | (11.90 ± 0.20) |
| 4d | Ins. | Ins. | 5d | (4.50 ± 3.90) | (14.00 ± 3.00) |
| 4e | Ins. | Ins. | 5e | (10.00 ± 1.10) | (3.10 ± 0.90) |
| 4f | Ins. | Ins. | 5f | 62.10 ± 1.20 (39.90 ± 0.10) | (23.10 ± 0.70) |
| 4g | Ins. | Ins. | 5g | (28.30 ± 8.40) | (13.10 ± 1.04) |
| 4h | NI | (10.20 ± 0.42) | 5h | NI | 24.30 ± 0.50 (58.30 ± 1.40) |
| 4i | (8.19 ± 1.55) | (13.57 ± 1.81) | 5i | (19.30 ± 0.90) | 59.60 ± 11.60 (42.20 ± 4.70) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Delogu, G.L.; Begala, M.; Matos, M.J.; Crucitti, D.; Sogos, V.; Era, B.; Fais, A. A New Class of Benzo[b]thiophene-chalcones as Cholinesterase Inhibitors: Synthesis, Biological Evaluation, Molecular Docking and ADME Studies. Molecules 2024, 29, 3748. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29163748
Delogu GL, Begala M, Matos MJ, Crucitti D, Sogos V, Era B, Fais A. A New Class of Benzo[b]thiophene-chalcones as Cholinesterase Inhibitors: Synthesis, Biological Evaluation, Molecular Docking and ADME Studies. Molecules. 2024; 29(16):3748. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29163748
Chicago/Turabian StyleDelogu, Giovanna Lucia, Michela Begala, Maria João Matos, Davide Crucitti, Valeria Sogos, Benedetta Era, and Antonella Fais. 2024. "A New Class of Benzo[b]thiophene-chalcones as Cholinesterase Inhibitors: Synthesis, Biological Evaluation, Molecular Docking and ADME Studies" Molecules 29, no. 16: 3748. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29163748
APA StyleDelogu, G. L., Begala, M., Matos, M. J., Crucitti, D., Sogos, V., Era, B., & Fais, A. (2024). A New Class of Benzo[b]thiophene-chalcones as Cholinesterase Inhibitors: Synthesis, Biological Evaluation, Molecular Docking and ADME Studies. Molecules, 29(16), 3748. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29163748










