Zinc and Lead Leaching from Sphalerite–Galena Concentrate Using Deep Eutectic Solvents Based on Choline Chloride: Effect of Roasting and Iodine as Oxidizing Agent
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Physical, Chemical, and Mineralogical Characterization of the Concentrate
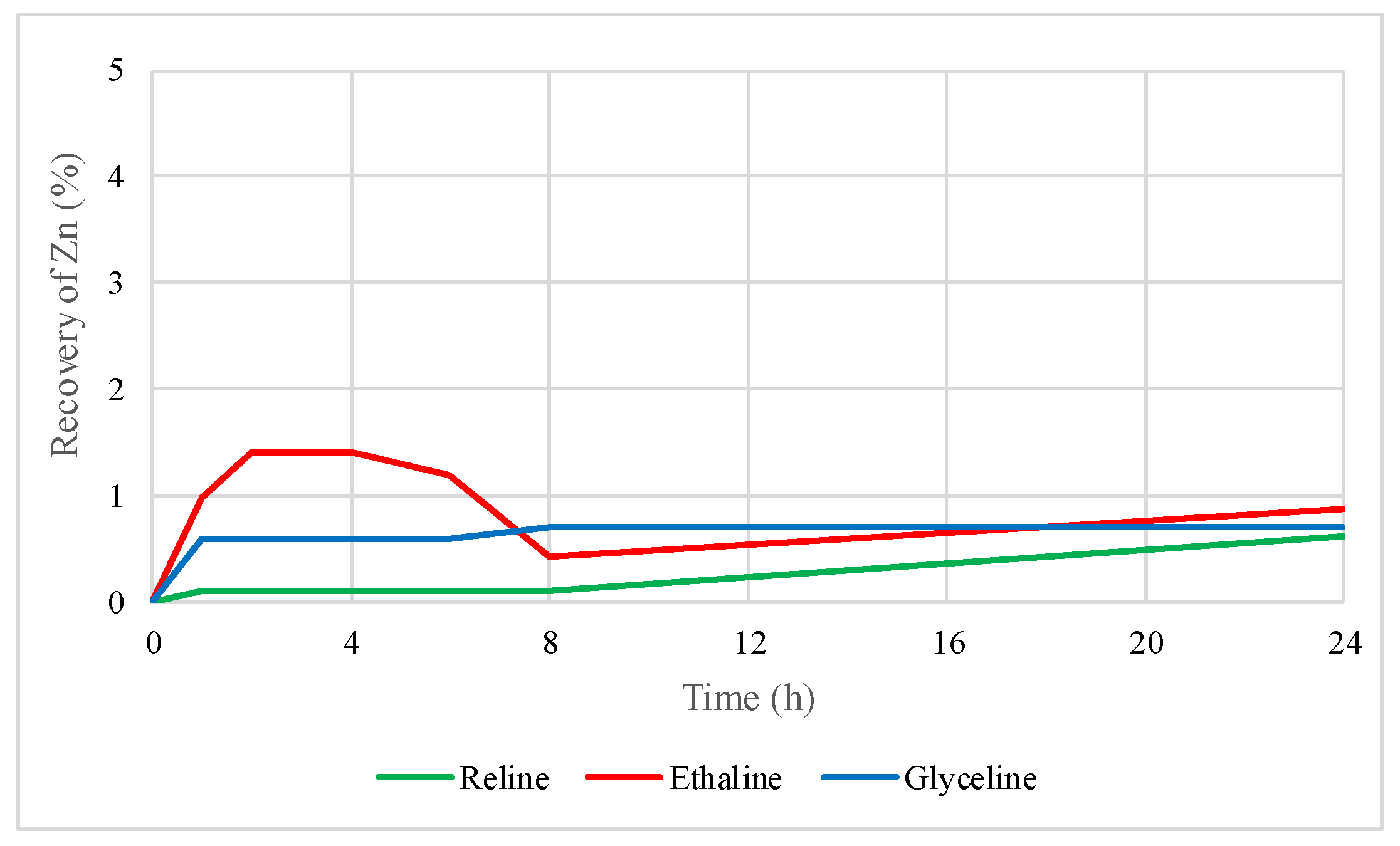
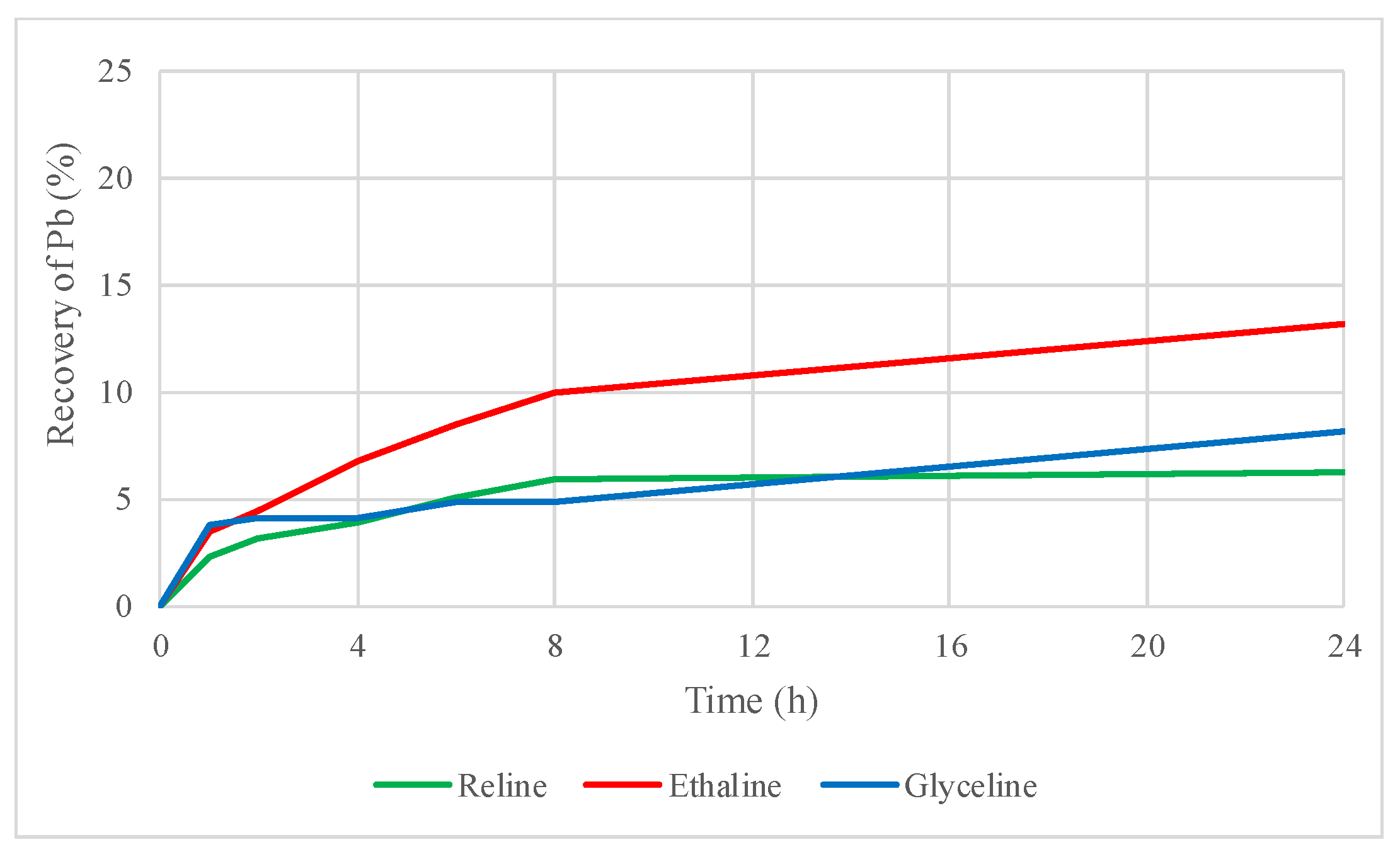
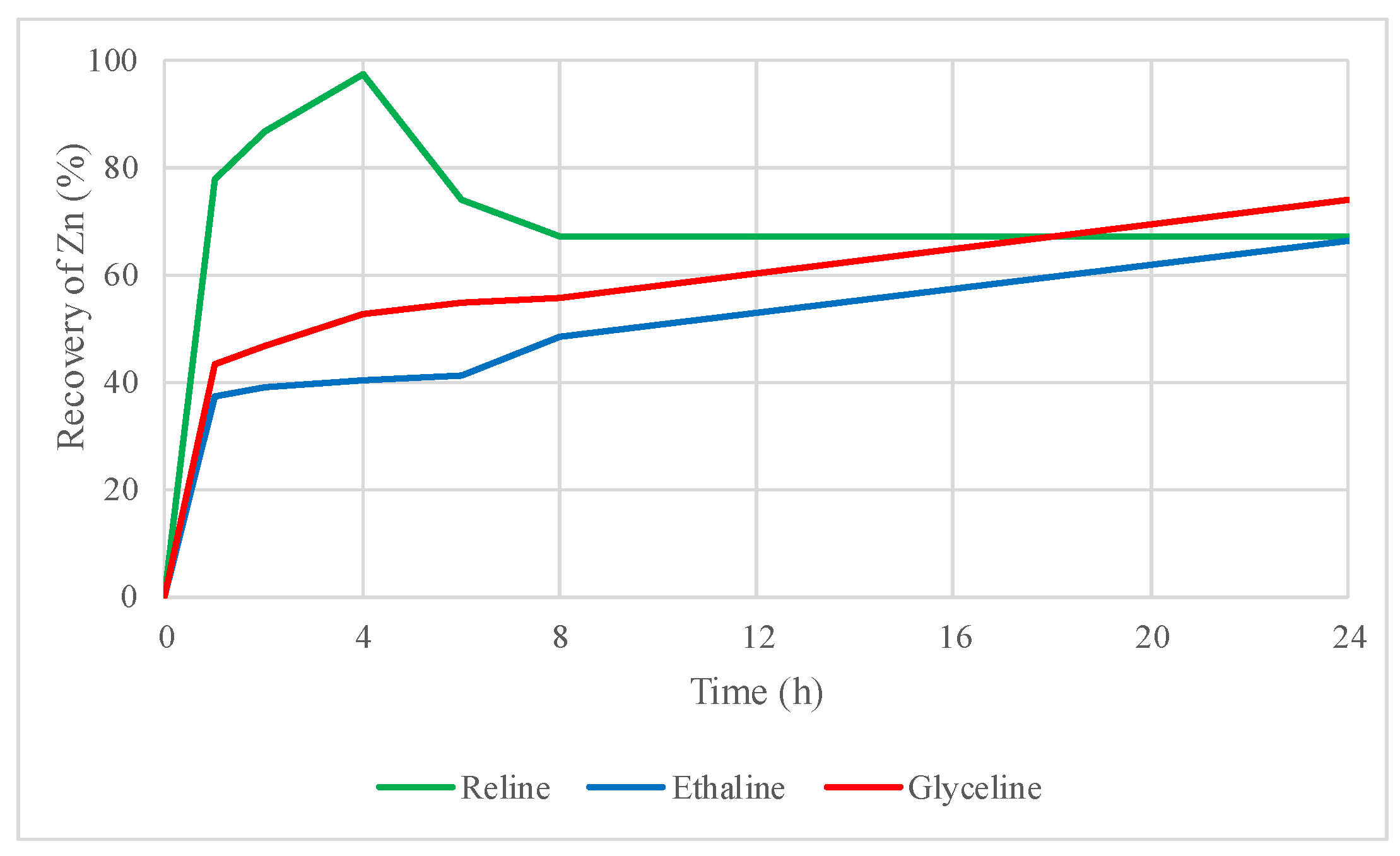
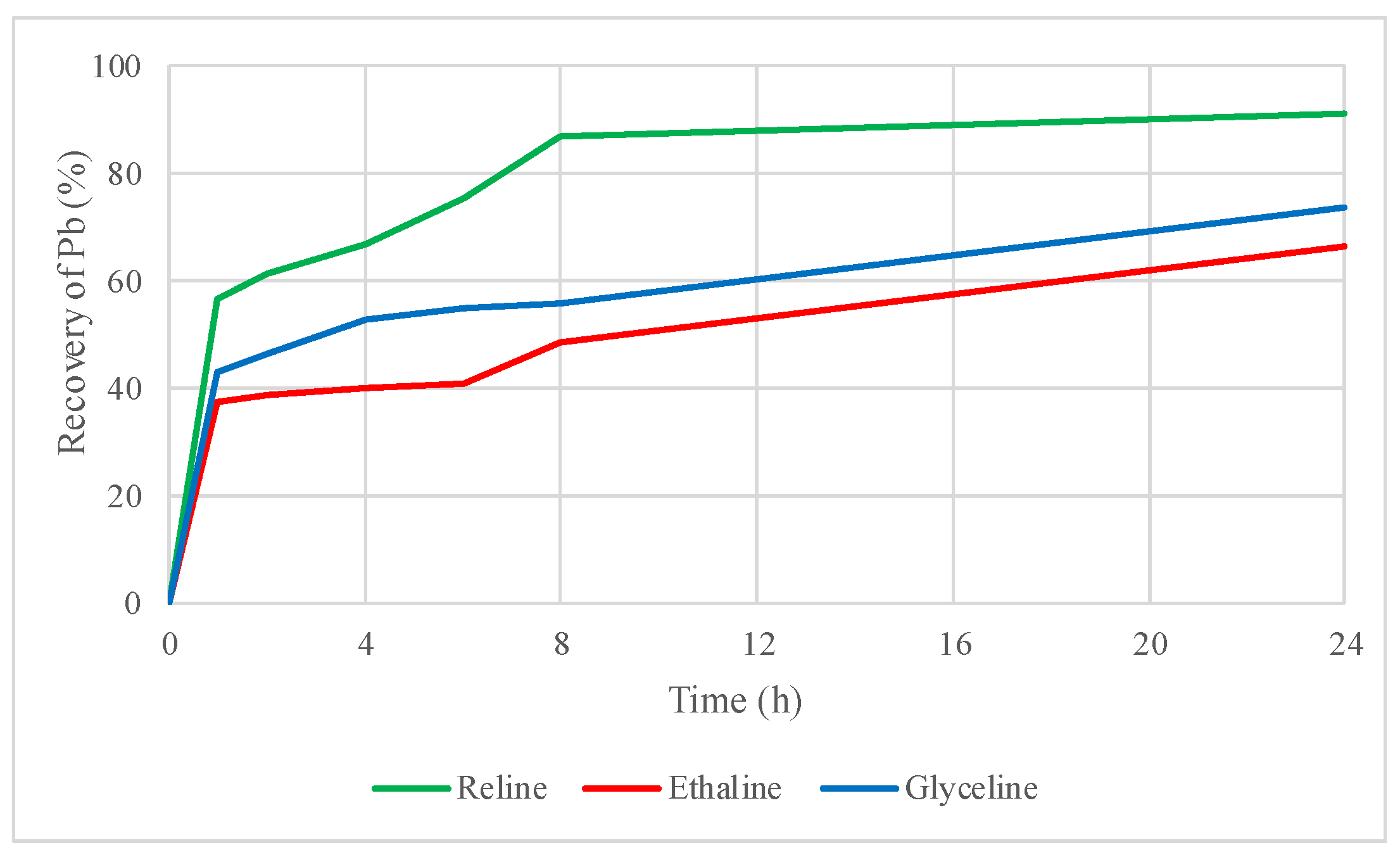
2.2. Preliminary Leaching Tests with DESs
2.3. Influence of Oxidizing Agent in the DES Leaching Process
2.4. Influence of Thermal Treatment of the Concentrate in the DES Leaching Process
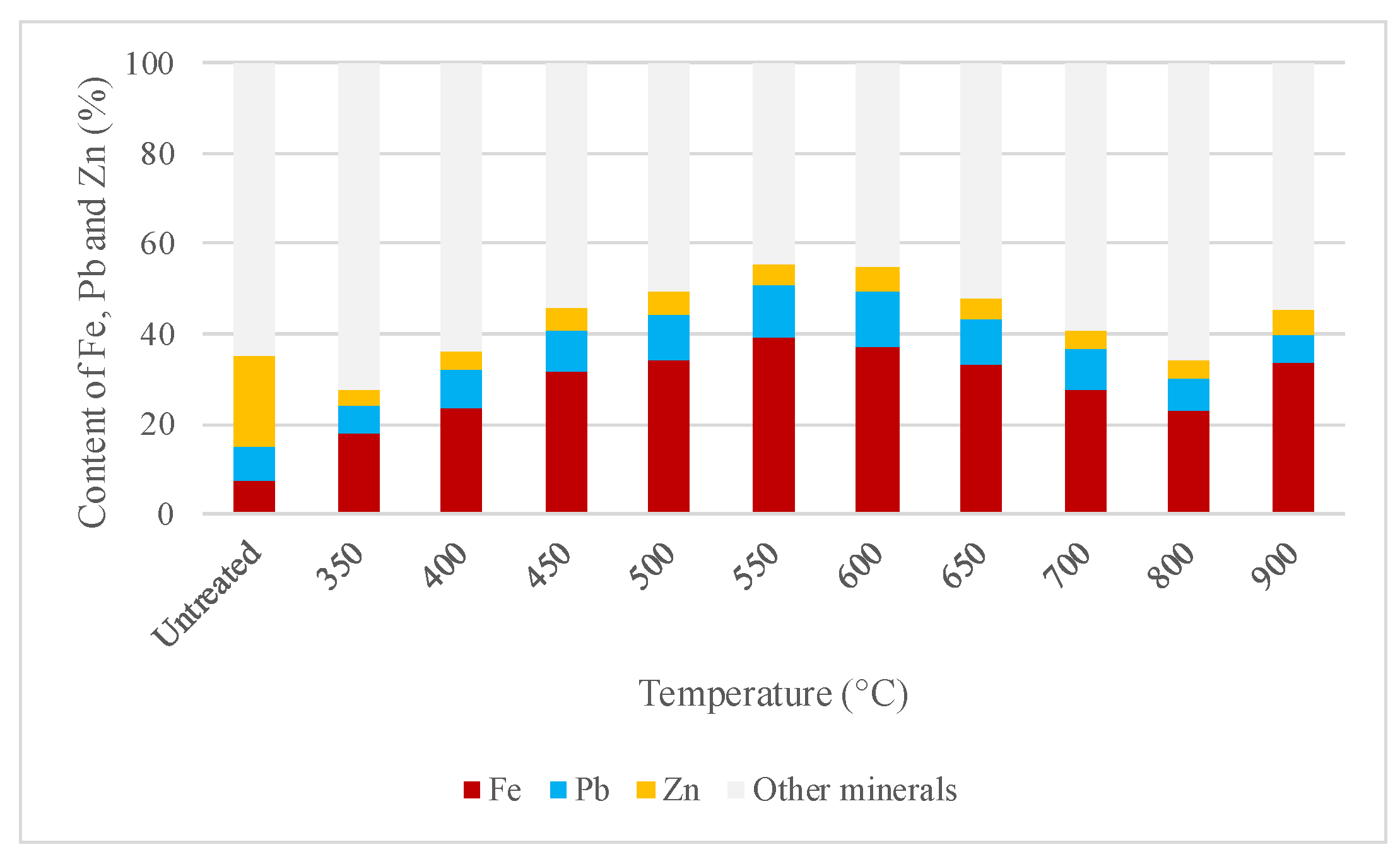
2.4.1. Establishing the Best Roasting Conditions for the Concentrate
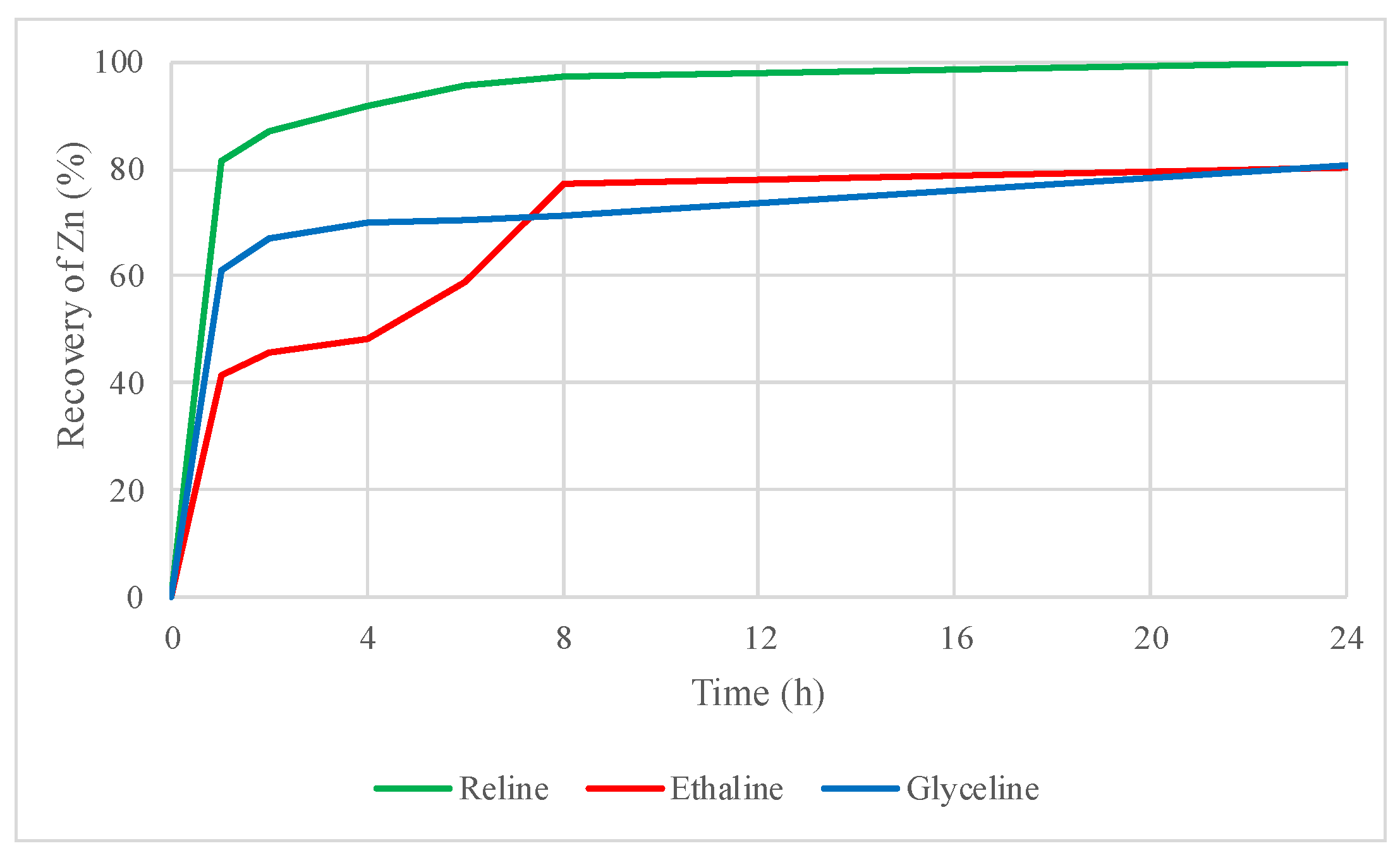
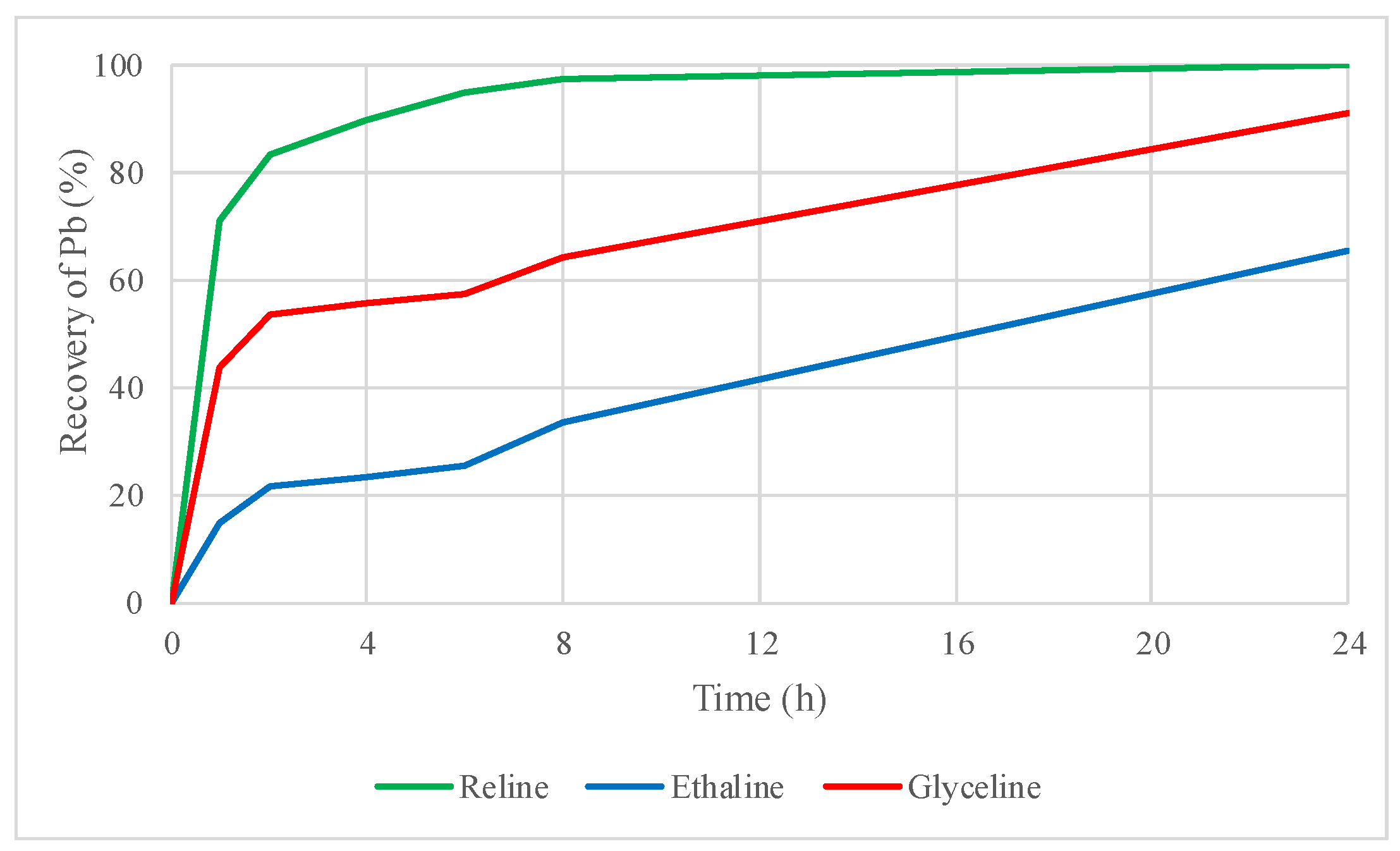
2.4.2. Leaching Tests of the Roasted Concentrate with DESs
2.4.3. Leaching Tests of the Roasted Concentrate with DESs plus I2 as an Oxidizing Agent
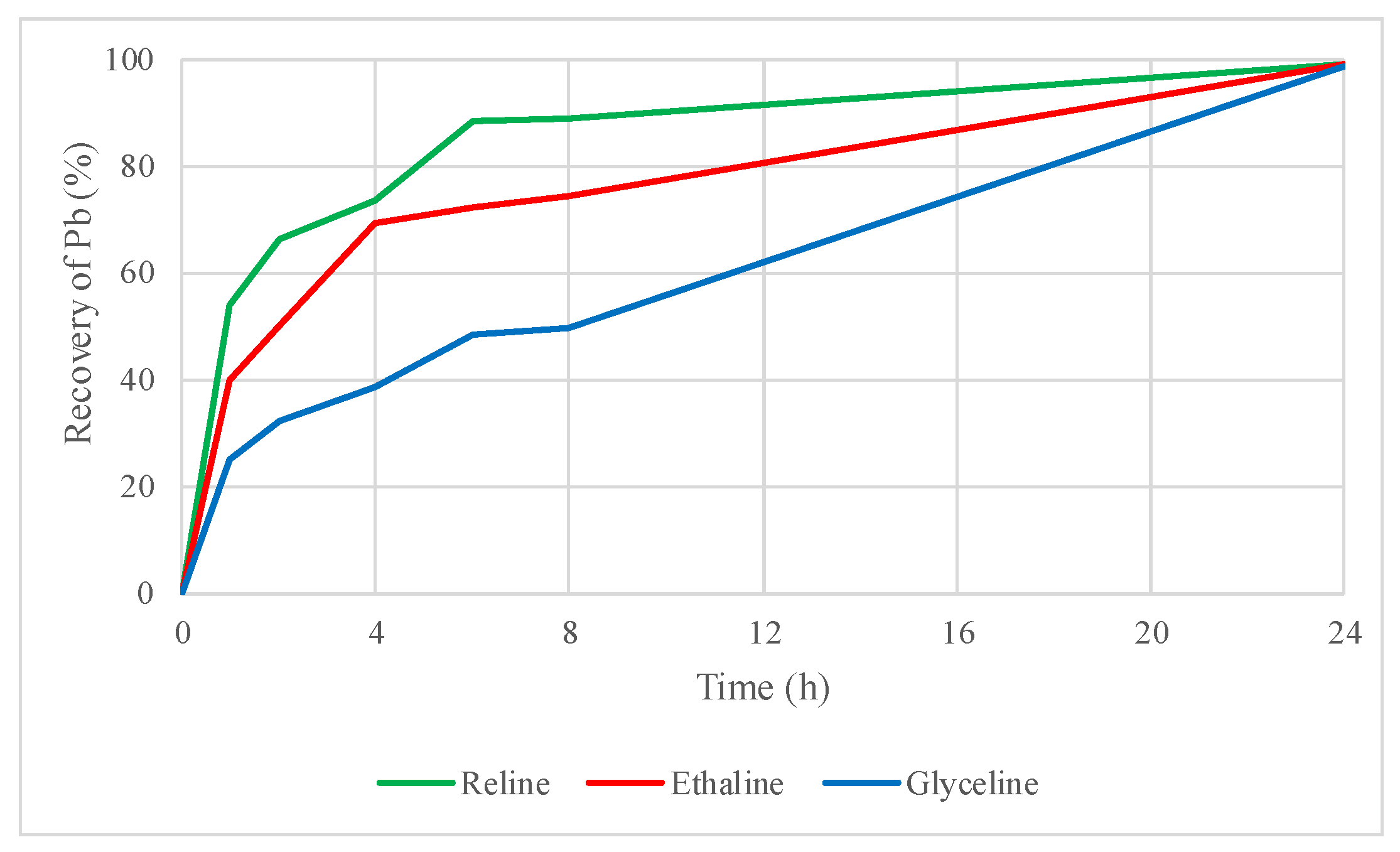
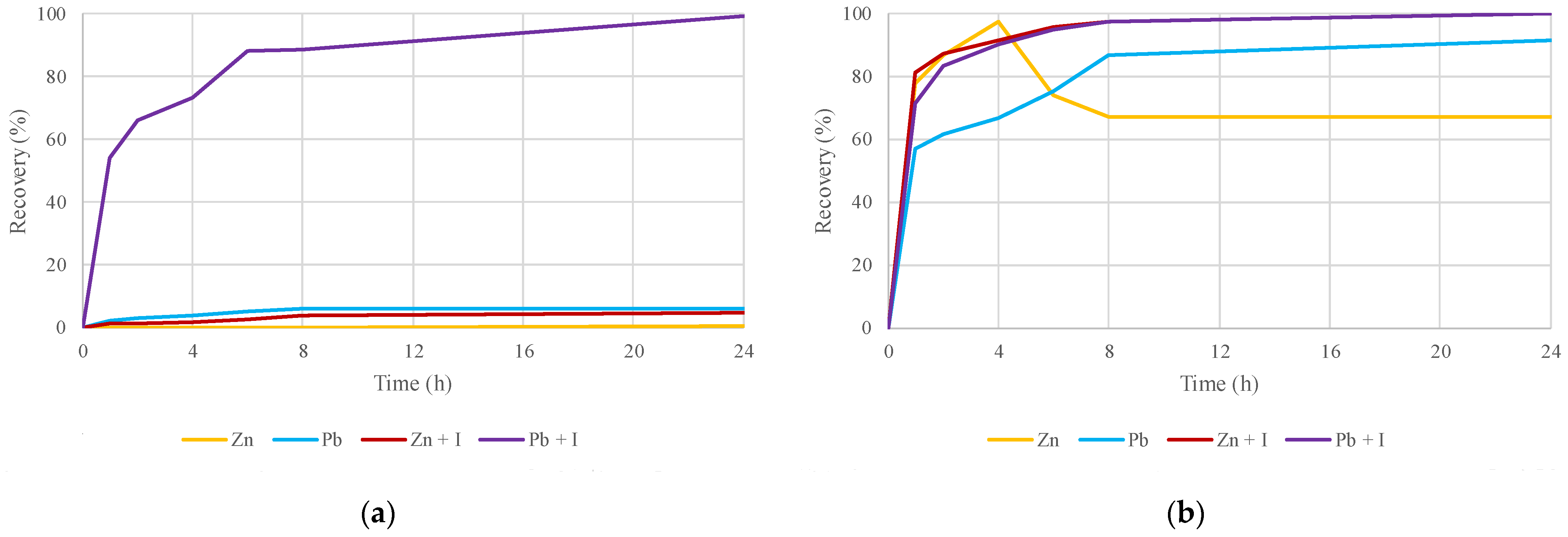
2.5. Evaluation of Zinc and Lead Recovery by DES Leaching with the Influences of Thermal Treatment and the Addition of Iodine as an Oxidizing Agent
3. Discussion
3.1. Influence of Mineralogy in the DES Leaching Process
3.2. Influence of the Oxidizing Agent in the DES Leaching Process
3.3. Influence of Thermal Treatment in the DES Leaching Process
3.4. Influence of the Oxidizing Agent and Thermal Treatment at the Same Time in the DES Leaching Process
3.5. Comparison with Conventional Acid Leaching Routes
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Characterization of the Concentrate
4.2. Thermal Treatments of Sulfide-Rich Concentrate
4.3. Leaching Tests Using DESs
4.4. Leaching Tests Using Acids
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rodriguez, N.; Machiels, L.; Onghena, B.; Spooren, J.; Binnemans, K. Selective recovery of zinc from goethite residue in the zinc industry using deep-eutectic solvents. RSC Adv. 2020, 10, 7328–7335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xing, P.; Wang, C.; Wang, L.; Ma, B.; Chen, Y. Hydrometallurgical recovery of lead from spent lead-acid battery paste via leaching and electrowinning in chloride solution. Hydrometallurgy 2019, 189, 105134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anugrah, R.I.; Mubarok, M.Z.; Amalia, D. Study on the leaching behavior of galena concentrate in fluosilicic acid solution using hydrogen peroxide as oxidant. In Proceedings of the 1st International Process Metallurgy Conference (IPMC 2016), West Java, Indonesia, 10–11 November 2016; AIP Conference Proceedings; American Institute of Physics Inc.: College Park, MD, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peters, E. Hydrometallurgical process innovation. Hydrometallurgy 1992, 29, 431–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pateli, I.M.; Abbott, A.P.; Jenkin, G.R.T.; Hartley, J.M. Electrochemical oxidation as alternative for dissolution of metal oxides in deep eutectic solvents. Green. Chem. 2020, 22, 8360–8368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbott, A.; Capper, G.; Davies, D.; McKenzie, K.; Obi, S. Solubility of Metal Oxides in Deep Eu-tectic Solvents Based on Choline Chloride. J. Chem. Eng. Data 2006, 51, 1280–1282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbott, A.; Capper, G.; Davies, D.; Rasheed, R.; Shikotra, P. Selective extraction of metals from mixed oxide matrixes using choline-based ionic liquids. Inorg. Chem. 2005, 44, 6497–6499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sverdrup, H.U.; Ragnarsdottir, K.V.; Koca, D. An assessment of metal supply sustainability as an input to policy: Security of supply extraction rates, stocks-in-use, recycling, and risk of scarcity. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 140, 359–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zante, G.; Boltoeva, M. Review on Hydrometallurgical Recovery of Metals with Deep Eutectic Solvents. Sustain. Chem. 2020, 1, 238–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Binnemans, K.; Jones, P. Solvometallurgy: An Emerging Branch of Extractive Metallurgy. J. Sustain. Metall. 2017, 3, 570–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riaño, S.; Petranikova, M.; Onghena, B.; Hoogerstraete, T.V.; Banerjee, D.; Foreman, M.R.S.; Ekberg, C.; Binnemans, K. Separation of rare earths and other valuable metals from deep-eutectic solvents: A new alternative for the recycling of used NdFeB magnets. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 32100–32113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martins, M.; Pinho, S.; Coutinho, J. Insights into the Nature of Eutectic and Deep Eutectic Mix-tures. J. Solut. Chem. 2019, 48, 962–982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcus, Y. Deep Eutectic Solvents, 1st ed.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, J.-H.; Wu, P.-C.; Bai, Y.-H. Eutectic mixture of choline chloride/urea as a green solvent in synthesis of a coordination polymer: [Zn(O3PCH2CO2)] · NH4. Inorg. Chem. Commun. 2005, 8, 390–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbott, A.; Capper, G.; Mckenzie, K.; Ryder, K. Electrodeposition of Zinc-Tin Alloys From Deep Eutectic Solvents Based on Choline Chloride. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2007, 599, 288–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbott, A.P.; Boothby, D.; Capper, G.; Davies, D.L.; Rasheed, R.K. Deep Eutectic Solvents Formed between Choline Chloride and Carboxylic Acids: Versatile Alternatives to Ionic Liquids. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2004, 126, 9142–9147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aragón-Tobar, C.F.; Endara, D.; de la Torre, E. Dissolution of Metals (Cu, Fe, Pb, and Zn) from Different Metal-Bearing Species (Sulfides, Oxides, and Sulfates) Using Three Deep Eutectic Solvents Based on Choline Chloride. Molecules 2024, 29, 290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Maria, A.; Van Acker, K. Turning Industrial Residues into Resources: An Environmental Impact Assessment of Goethite Valorization. Engineering 2018, 4, 421–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinche, M.; Fornasiero, D. Understanding the effect of sulphate in mining-process water on sul-phide flotation. Min. Eng. 2021, 165, 106865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, M.K.; Rodrigues, M.-T.F.; Kato, K.; Babu, G.; Ajayan, P.M. Deep eutectic solvents for cathode recycling of Li-ion batteries. Nat. Energy 2019, 4, 339–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salgado, B.; Endara, D.; Aragón-Tobar, C.F.; de la Torre, E.; Ullauri, L. Recovery of Residual Lead from Automotive Battery Recycling Slag Using Deep Eutectic Solvents. Molecules 2024, 29, 394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukhopadhyay, S.; Mukherjee, S.; Adnan, N.F.; Hayyan, A.; Hayyan, M.; Hashim, M.A.; Gupta, B.S. Ammonium-based deep eutectic solvents as novel soil washing agent for lead removal. Chem. Eng. J. 2016, 294, 316–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petračić, A.; Sander, A.; Cvetnić, M. A novel approach for the removal of trace elements from waste fats and oils. Sep. Sci. Technol. 2020, 55, 3487–3501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cen, P.; Spahiu, K.; Tyumentsev, M.S.; Foreman, M.R.S.J. Metal extraction from a deep eu-tectic solvent, an insight into activities. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2020, 22, 11012–11024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Entezari-Zarandi, A.; Larachi, F. Selective dissolution of rare-earth element carbonates in deep eutectic solvents. J. Rare Earths 2019, 37, 528–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spathariotis, S.; Peeters, N.; Ryder, K.S.; Abbott, A.P.; Binnemans, K.; Riaño, S. Separation of iron(iii), zinc(ii) and lead(ii) from a choline chloride-ethylene glycol deep eutectic solvent by solvent extraction. RSC Adv. 2020, 10, 33161–33170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jenkin, G.R.T.; Al-Bassam, A.Z.; Harris, R.C.; Abbott, A.P.; Smith, D.J.; Holwell, D.A.; Chapman, R.J.; Stanley, C.J. The application of deep eutectic solvent ionic liquids for environmental-ly-friendly dissolution and recovery of precious metals. Min. Eng. 2016, 87, 18–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahin, M.; Akcil, A.; Erust, C.; Altynbek, S.; Gahan, C.S.; Tuncuk, A. A Potential Alternative for Precious Metal Recovery from E-waste: Iodine Leaching. Sep. Sci. Technol. 2015, 50, 2587–2595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konyratbekova, S.S.; Baikonurova, A.; Akcil, A. Non-cyanide leaching processes in gold hy-drometallurgy and iodine-iodide applications: A review. In Mineral Processing and Extractive Met-Allurgy Review; Taylor and Francis Inc.: Abingdon, UK, 2015; Volume 36, pp. 198–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbott, A.P.; Frisch, G.; Gurman, S.J.; Hillman, A.R.; Hartley, J.; Holyoak, F.; Ryder, K.S. Ionometallurgy: Designer redox properties for metal processing. Chem. Commun. 2011, 47, 10031–10033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abbott, A.P.; Ballantyne, A.; Harris, R.C.; Juma, J.A.; Ryder, K.S. A Comparative Study of Nickel Electrodeposition Using Deep Eutectic Solvents and Aqueous Solutions. Electrochim. Acta 2015, 176, 718–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabzkoohi, H.A.; Kolliopoulos, G. Green Zero-Waste Metal Extraction and Recycling from Printed Circuit Boards. Mater. Proc. 2021, 5, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukano, Y.; Miura, A. Chalcopyrite leaching with iodine (JX Iodine Process) for various ore types. Hydrometallurgy 2021, 206, 105752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dimitrov, R.; Boyanov, B. Investigation of the oxidation of metal sulphides and sulphide con-centrates. Thermochim. Acta 1983, 64, 27–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbott, A.P.; Capper, G.; Davies, D.L.; Rasheed, R.K.; Tambyrajah, V. Novel solvent properties of choline chloride/urea mixtures. Chem. Commun. 2003, 39, 70–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prabhu, G.M.; Ulrichson, D.L.; Pulsher’, A.H. Kinetics of the Oxidation of Zinc sulfide. Ind. Eng. Chem. Fundam. 1984, 23, 271–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deer, W.A.; Howie, R.A.; Zussman, J. An Introduction to the Rock-Forming Minerals, 2nd ed.; Longman: Harlow, UK, 1992; Volume 1. [Google Scholar]
- Shahrezaei, F.; Karimi, S.; Behnajady, B. Experimental and dynamic molecular study of zinc extraction from sphalerite concentrate in ternary deep eutectic solvent. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2024, 695, 134241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlesi, C.; Harris, R.C.; Abbott, A.P.; Jenkin, G.R.T. Chemical Dissolution of Chalcopyrite Concentrate in Choline Chloride Ethylene Glycol Deep Eutectic Solvent. Minerals 2022, 12, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartley, J.M.; Scott, S.; Dilruba, Z.; Lucio, A.J.; Bird, P.J.; Harris, R.C.; Jenkin, G.R.T.; Abbott, A.P. Iodine speciation in deep eutectic solvents. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2022, 24, 24105–24115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anggara, S.; Bevan, F.; Harris, R.C.; Hartley, J.M.; Frisch, G.; Jenkin, G.R.T.; Abbott, A.P. Direct extraction of copper from copper sulfide minerals using deep eutectic solvents. Green. Chem. 2019, 21, 6502–6512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartley, J.M.; Al-Bassam, A.Z.M.; Harris, R.C.; Frisch, G.; Jenkin, G.R.T.; Abbott, A.P. In-vestigating the dissolution of iron sulfide and arsenide minerals in deep eutectic solvents. Hydrometallurgy 2020, 198, 105511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Element | Content (%) |
|---|---|
| Zn | 20 |
| S | 12 |
| Pb | 8 |
| Fe | 7 |
| Si | 6 |
| Al | 2 |
| Mn | 1 |
| K, Ca, Cu, Na and Mg | <1 |
| Mineral | Formula | Content (%) |
|---|---|---|
| Sphalerite | ZnS | 63 |
| Galena | PbS | 9 |
| Pyrite | FeS2 | 8 |
| Anglesite | PbSO4 | 7 |
| Quartz | SiO2 | 6 |
| Muscovite | KAl2(AlSi3O10)(OH)2 | 4 |
| Calcite | CaCO3 | 2 |
| Plagioclase | (Na,Ca)Al(Si,Al)Si2O8 | 1 |
| Leaching Agent | Untreated Concentrate | Untreated Concentrate + I2 | Roasted Concentrate | Roasted Concentrate + I2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Reline | 0.6 | 5 | 67 | 99 |
| Ethaline | 1 | 11 | 66 | 80 |
| Glyceline | 0.7 | 9 | 74 | 80 |
| Sulfuric Acid * | 10 | - | 96 | - |
| Leaching Agent | Untreated Concentrate | Untreated Concentrate + I2 | Roasted Concentrate | Roasted Concentrate + I2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Reline | 6 | 99 | 91 | 100 |
| Ethaline | 13 | 99 | 47 | 66 |
| Glyceline | 8 | 99 | 62 | 91 |
| Nitric Acid * | 22 | - | 80 | - |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Moreno, K.; Díaz, X.; Endara, D.; Sánchez, F.; Aragón-Tobar, C.F. Zinc and Lead Leaching from Sphalerite–Galena Concentrate Using Deep Eutectic Solvents Based on Choline Chloride: Effect of Roasting and Iodine as Oxidizing Agent. Molecules 2024, 29, 3742. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29163742
Moreno K, Díaz X, Endara D, Sánchez F, Aragón-Tobar CF. Zinc and Lead Leaching from Sphalerite–Galena Concentrate Using Deep Eutectic Solvents Based on Choline Chloride: Effect of Roasting and Iodine as Oxidizing Agent. Molecules. 2024; 29(16):3742. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29163742
Chicago/Turabian StyleMoreno, Katherine, Ximena Díaz, Diana Endara, Fernando Sánchez, and Carlos F. Aragón-Tobar. 2024. "Zinc and Lead Leaching from Sphalerite–Galena Concentrate Using Deep Eutectic Solvents Based on Choline Chloride: Effect of Roasting and Iodine as Oxidizing Agent" Molecules 29, no. 16: 3742. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29163742
APA StyleMoreno, K., Díaz, X., Endara, D., Sánchez, F., & Aragón-Tobar, C. F. (2024). Zinc and Lead Leaching from Sphalerite–Galena Concentrate Using Deep Eutectic Solvents Based on Choline Chloride: Effect of Roasting and Iodine as Oxidizing Agent. Molecules, 29(16), 3742. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29163742






