Abstract
Synthetic efforts toward complex natural product (NP) scaffolds are useful ones, particularly those aimed at expanding their bioactive chemical space. Here, we utilised an orthogonal cheminformatics-based approach to predict the potential biological activities for a series of synthetic bis-indole alkaloids inspired by elusive sponge-derived NPs, echinosulfone A (1) and echinosulfonic acids A–D (2–5). Our work includes the first synthesis of desulfato-echinosulfonic acid C, an α-hydroxy bis(3′-indolyl) alkaloid (17), and its full NMR characterisation. This synthesis provides corroborating evidence for the structure revision of echinosulfonic acids A-C. Additionally, we demonstrate a robust synthetic strategy toward a diverse range of α-methine bis(3′-indolyl) acids and acetates (11–16) without the need for silica-based purification in either one or two steps. By integrating our synthetic library of bis-indoles with bioactivity data for 2048 marine indole alkaloids (reported up to the end of 2021), we analyzed their overlap with marine natural product chemical diversity. Notably, the C-6 dibrominated α-hydroxy bis(3′-indolyl) and α-methine bis(3′-indolyl) analogues (11, 14, and 17) were found to contain significant overlap with antibacterial C-6 dibrominated marine bis-indoles, guiding our biological evaluation. Validating the results of our cheminformatics analyses, the dibrominated α-methine bis(3′-indolyl) alkaloids (11, 12, 14, and 15) were found to exhibit antibacterial activities against methicillin-sensitive and -resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Further, while investigating other synthetic approaches toward bis-indole alkaloids, 16 incorrectly assigned synthetic α-hydroxy bis(3′-indolyl) alkaloids were identified. After careful analysis of their reported NMR data, and comparison with those obtained for the synthetic bis-indoles reported herein, all of the structures have been revised to α-methine bis(3′-indolyl) alkaloids.
1. Introduction
Marine indole alkaloids (MIAs) represent a diverse subclass of natural products (NPs) with increasing numbers continuing to be reported each year [1,2]. However, the majority of MIAs, and marine natural products (MNPs) more broadly, have been examined against a narrow breadth of disease and infection targets. In most cases, they are reported with potencies well below the threshold useful for further drug development [1,3]. To increase the likelihood of uncovering meaningful NP bioactivities, more thoughtful approaches toward their biological evaluations should be adopted. At the very least, more directed investigations of NP bioactivity will contribute to an expanded understanding of bioactive NP chemical space. Despite ongoing advancements in secondary metabolite omics methods, including metabolomics, genomics, proteomics, and transcriptomics, the translation of these data toward more sophisticated approaches for selecting biological targets for NP activity continues to lag behind [1].
With several online databases housing NP structures and their metadata [4], such as MarinLit [2], COCONUT [5], and the Dictionary of Natural Products [6], cheminformatics techniques have evolved into excellent analytical tools for handling large datasets. Recently, we have demonstrated the analytical power of cheminformatics, specifically utilising machine learning, self-organising maps (SOM), and principal component analyses. Our research has not only explored the structural diversity of NPs (by subclass, terrestrial vs. marine, and producing phyla) [1,3,7], but also examined the bioactivities and the diversity of bioassays used for their biological evaluations [1,3]. Despite advancements in 2D NMR spectroscopy and access to an ever-increasing toolbox of orthogonal structure elucidation and NMR fact-checking techniques [8,9,10], the reporting of incorrect NP structures continues to permeate the literature. Incorrectly assigned molecules can have far-reaching consequences, particularly in multidisciplinary fields where NPs are a central focus such as NP biosynthesis, molecular biology, chemical ecology, synthetic biology, agriculture, and drug discovery and development. To date, we have reported structure revisions for nearly twenty terrestrial and marine NPs, including a series of brominated sponge-derived bis-indole alkaloid sulfamates, echinosulfone A (1) and the echinosulfonic acids A−D (2–5, Figure 1) [11].
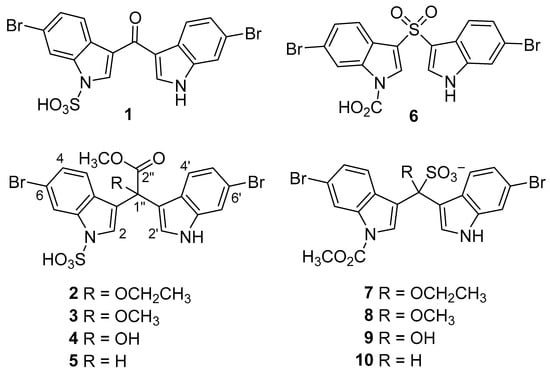
Figure 1.
Revised structures for echinosulfone A (1) and the echinosulfonic acids A-D (2–5), alongside their incorrectly reported structures 6–10.
The co-isolates, echinosulfone A (6) and the echinosulfonic acids A–C (7–9), inappropriately named based on their incorrectly assigned structures, were reported from the Australian sponge Echinodictyum sp. [12], while echinosulfonic acid D (10), its structure based on the incorrectly assigned co-isolate 8, was reported as part of a bioassay-guided investigation of the New Caledonian sponge Psammoclema sp. [13]. Their structures were subsequently revised to indole sulfamates 1–5 based on reinterpretation of their reported NMR and MS experimental data, the total synthesis of echinosulfone A (1), and what was clearly more plausible biosynthetic grounds [11]. The revised structures 1–5 were supported by the re-isolation of echinosulfone A (1) and echinosulfonic acid B (3) [14], while a second synthesis of echinosulfone A (1) was also published [15]. Recently, the total synthesis of echinosulfonic acid D (5) was reported by Abe et al. using a multi-step umpolung method with dimethylbarbituric acid [16].
While the structures of echinosulfone A (1) and echinosulfonic acids A–D (2–5) have now been formally revised, synthetic efforts toward these interesting marine bis-indole alkaloid scaffolds present both inspiration and challenges. Such endeavours prove valuable for exploring and expanding NP biological activities. Herein, we describe an acid-catalysed double Friedel–Crafts reaction affording relatively simple access to brominated and non-brominated α-methine bis(3′-indolyl) acetic acids and acetates (11–16, Figure 2). In addition, utilising the aforementioned bis(3′-indolyl) α-methine acetate scaffolds and exploiting a proposed indole azafulvenium pathway, we report the first synthesis of α-hydroxy bis(3′-indolyl) acetate scaffolds and the full NMR characterisation of 6-brominated α-hydroxy bis(3′-indolyl) alkaloid 17 (Figure 2). Despite the instability of 17 (and the partially purified debromo analogue 18), this marks the first successful synthetic approach toward the elusive echinosulfonic acid C (4) scaffold outside of sponge secondary metabolism.
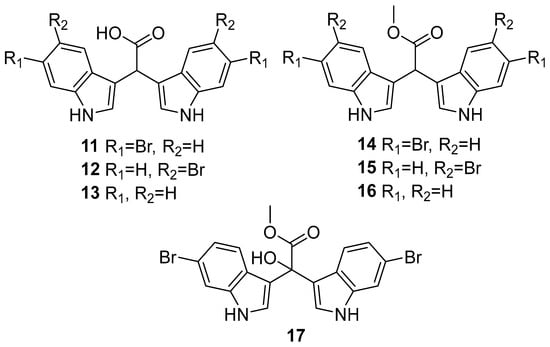
Figure 2.
Bis(3′-indolyl) α-methine acetic acids 11–13 and acetates 14–16, and 6-dibrominated bis(3′-indolyl) α-hydroxy acetate 17.
The synthesis of the bis-indoles presented herein also led to the re-examination of 16 synthetic bis(3′-indolyl) alkaloids (3o′, 5a–n, and 5ab′) [17]. This series of synthetic bis-indoles were assigned as α-hydroxy bis(3′-indolyl) alkaloids. However, discrepancies identified in the reported NMR and MS data for the synthetic α-hydroxy bis-indoles raised concerns regarding the accuracy of their assigned structures and the outcomes claimed for their acid-catalysed Friedel–Crafts synthetic strategy with acylsilane [17]. Comparative analyses of NMR and MS experimental data with the data obtained for the synthetic bis-indoles reported in this study (11–18) conclusively established the true identities of all 16 synthetic indoles as α-methine bis(3′-indolyl)s, further reinforcing the difficulties associated with the laboratory synthesis of α-hydroxy bis-indoles.
Furthermore, we employed cheminformatics analyses of MIA structural diversity (n = 2048) integrated with the findings from our recent meta-analysis of MIA bioactivities [1] to explore the biologically relevant chemical space of the synthetic bis(3′-indolyls) 11–17. Also included in these analyses were synthetic mono- and dibrominated bis(3′-indolyl) methanones 19–22 synthesised via our previously reported method [11]. Using a self-organising map (SOM) of MIA structural diversity scaled for biological activity, the synthetic bis-indoles were identified to share chemical space with other known marine bis-indoles reported with antibacterial activities. Their predicted antibacterial activities were subsequently examined against methicillin-susceptible and methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MSSA and MRSA) and Pseudomonas aeruginosa. The effectiveness of cheminformatics-guided approaches in targeting biological evaluations was underscored by the activity of dibrominated bis(3′-indolyl) α-methines 11, 12, 14, and 15 against both MSSA and MRSA. Notably, 6-dibromo bis(3′-indolyl) acetate 14 exhibited the highest potency with MIC50 values of 4 µg/mL and 8 µg/mL against MSSA and MRSA, respectively.
2. Results
2.1. Synthesis of α-Methine Bis(3′-indolyl) Acetic Acids and Methyl Acetates (11–16)
Our ongoing interest in exploring MIA diversity coupled with the recent total synthesis of echinosulfonic acid D (5), using a multi-step umpolung method with dimethylbarbituric acid [16], inspired design of a more direct approach toward accessing the structural diversity of desulfonated MNP-inspired α-methine bis(3′-indolyl) acetate scaffolds. A simple disconnection of the α-methine bis(3′-indolyl) methyl acetate (16) suggested the adoption of a two-step synthetic approach (Scheme 1).
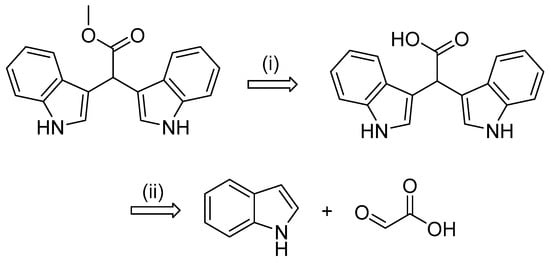
Scheme 1.
Retrosynthetic analysis of representative α-methine bis(3′-indolyl) methyl acetate scaffold (16); (i) esterification of carboxylic acid and (ii) bis-indole formation.
A modified Lewis-acid-catalysed Friedel–Crafts method, based on that reported by Sathieshkumar et al. for the total synthesis of the tris-indole natural product pseudellone C [18], formed the basis of our double Friedel–Craft bis-indole formation step. However, pyruvic acid was exchanged for glyoxylic acid in our strategy with the aim of accessing the required α-methine bis(3′-indolyl) acetic acid which we reasoned could be esterified to afford the bis-indole methyl acetate.
Using aluminium chloride (AlCl3) as the catalyst (20 mol%), 2 equivalents (eq.) of indole (either 5-bromo, 6-bromo, or non-brominated indole) were reacted with glyoxylic acid (1.2 eq.) in a stirred solution of anhydrous EtOH under an inert atmosphere, and the reaction mixture was monitored by thin-layer chromatography (TLC) for the disappearance of starting material (Scheme 2). After 4 h, the reaction mixture was quenched with cold H2O. After careful pH-monitored acid–base workup, the desired α-methine bis(3′-indolyl) acetic acids (11–13) were obtained in excellent yields (>88%) without the need for further purification. Following this, the α-methine bis(3′-indolyl) acetic acids (11–13, Figure 2) were esterified by stirring thionyl chloride in anhydrous MeOH at 0−5 °C under inert conditions for 2 h (Scheme 2). The reaction mixture was quenched with cold H2O, and after careful extraction with EtOAc and water, the organic phase was concentrated to dryness to afford quantitative yields of halogenated and non-halogenated α-methine bis(3′-indolyl) methyl acetates (14–16, Figure 2). The synthetic strategy outlined above provides a straightforward approach for synthesising a diverse range of bis-indole acids and esters, requiring only one step for bis-indole acids and two steps for bis-indole methyl esters. Furthermore, the synthetic bis-indoles were obtained in excellent yields without the need for any silica-based purification steps.
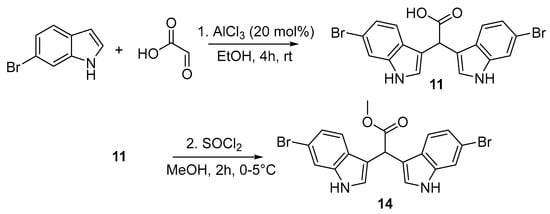
Scheme 2.
Acid-catalysed double Friedel–Crafts reaction to afford 6-dibromo α-methine bis(3′-indolyl) acetic acid 11 followed by thionyl chloride mediated esterification to 6-dibromo α-methine bis(3′-indolyl) methyl acetate 14.
2.2. Synthesis of α-Hydroxy Bis(3′-indolyl) Methylacetates (17−19)
With a robust approach in place for the synthesis of α-methine bis(3′-indolyl) methyl acetates (14–16), our focus shifted to the sponge NP α-hydroxy bis(3′-indolyl) acetate scaffolds, the echinosulfonic acids A–C (2–4). To the best of our knowledge, no syntheses of α-hydroxy bis(3′-indolyl) acetate scaffolds have been reported in the literature. Sala et al. reported the desulfonation products of echinosulfone A (22) and echinosulfonic acid B (3a, Figure S47) resulting from their chemical investigation of a Western Australian Crella sponge species [14]. The desulfonation products were rationalised to form via an acid-catalysed azafulvenium pathway initiated by the loss of sulfonic acid from indole, with the postulated azafulvenium intermediate reported as an intense purple colour. However, we propose that both desulfonated echinosulfone A and echinosulfonic acid B are more likely to have simply hydrolysed, losing sulfuric acid. Regardless, in both cases an azafulvenium intermediate would likely provide stability. With this in mind, we explored the prospect of bis-indole azafulveniums that we could generate from our synthetic α-methine bis(3′-indolyl) methyl acetates 14 and 16 to make α-hydroxy bis(3′-indolyl) methyl acetates. We hypothesised that compounds 11–16 could be oxidised under basic conditions by exploiting the acidity of the methine proton H-1″. We had previously noted intense deep purple colours in certain reaction mixtures during the optimisation of the Friedel–Crafts reaction for the synthesis of the bis-indole acids (11–13) and suspected that this colouration might be attributed to an aerial oxidation process. We reasoned that upon oxidation of the bis-indole scaffold to the bis-indole azafulvenium, we could then introduce the tertiary alcohol group at C-1″ to form the α-hydroxy bis(3′-indolyl) alkaloid scaffold (Scheme 3).
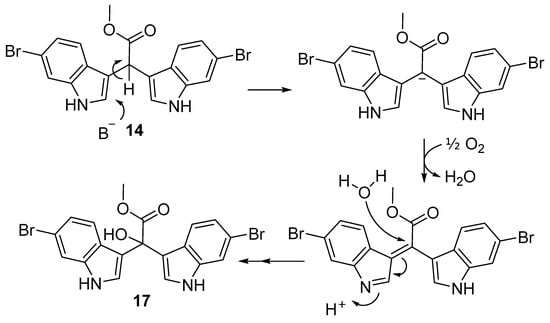
Scheme 3.
Proposed base-catalysed aerial oxidation bis-indole azafulvenium pathway from α-methine bis-indole scaffold 14 toward α-hydroxy bis-indole 17.
To preserve the integrity of bis-indole acetate scaffolds (14 and 16), we opted for the mild base cesium carbonate (Cs2CO3) in lieu of stronger alternatives. Our base-catalysed approach involved heating 14 in DMF to around 80 °C, followed by the addition of 1.5 eq. of Cs2CO3. The reaction mixture was left to stir for 12 h (Scheme 4). Upon a noticeable colour change from red to deep purple after several hours, the reaction mixture was quenched with H2O, cooled to room temperature, and stirred for an additional 15 min. Following careful extraction with EtOAc, the organic phase was adsorbed to C18-bonded silica gel and loaded into a refillable guard column. Subsequently, the C18-infused reaction mixture underwent purification via preparative reversed-phase high-pressure liquid chromatography (RP HPLC) using a decreasing polarity solvent gradient from H2O to CH3CN over 60 min, with fractions collected each minute. Fractional 1H NMR analysis confirmed that HPLC fractions 27–30 contained pure methyl-2,2-bis(6-bromo-1H-indol-3-yl)-2-hydroxyacetate (17).
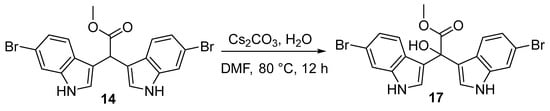
Scheme 4.
Synthesis of the desulfonated echinosulfonic acid C scaffold 6-dibromo α-hydroxy bis(3′-indolyl) acetate (17) from 6-dibromo α-methine bis(3′-indolyl) acetate (14) via what is likely a base-catalysed bis-indole azafulvenium intermediate.
The HSQC and 13C NMR spectra for 17 displayed an oxygenated, non-protonated carbon resonance at δC 73.8 (C-1″), while the 1H NMR and HSQC spectra contained a singlet proton resonance at δH 6.13 not directly attached to carbon, thereby representing the OH proton attached to C-1″. To the best of our knowledge, compound 17 represents the first reported synthesis and full NMR characterisation of a synthetic bis-indolyl-α-hydroxyacetate. The 1H and 13C NMR data for 17 were also identical to those reported for the non-sulfated 6-bromoindole, α-hydroxy carbon, and methyl ester resonances in echinosulfonic acid C (4), thus providing the first direct experimental evidence to corroborate the revised structure of echinosulfonic acid C.
Using our base-catalysed azafulvenium method, we were also able to synthesise the non-brominated α-hydroxy bis-indole 18; however, once the hydroxyl was installed at C-1″, the compound readily underwent oxidative decarboxylation to the bis-indole ketone 21 during HPLC purification (polar aprotic solvents) and concentration under vacuum (Scheme 5).
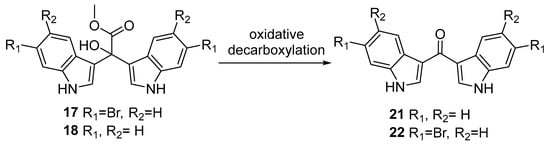
Scheme 5.
Oxidative decarboxylation of the bis-indolyl-α-hydroxyacetates 17 and 18 to their respective ketone-bridged bis-indole methanones 21 and 22.
The oxidative decarboxylation of C-1″ hydroxy bis(3′-indolyl) methyl acetates 17 and 18 to ketone-bridged bis-indoles 22 and 21 respectively, was observed during HPLC purification (particularly with MeOH as eluent) and concentration of samples in polar aprotic solvents under heat and vacuum. The 1H NMR spectra depicting the decarboxylation of non-brominated hydroxyacetate 18 to 21 during HPLC purification are displayed in Figure S30. The instability of the synthetic α-hydroxy bis-indole methyl acetates 17 and 18 provides evidence for the biosynthetic relationship between echinosulfone A (1) and the echinosulfonic acids A–D (2–5). Our findings suggest that 1 is likely the result of oxidative decarboxylation of any of the echinosulfonic acids A–D (2–5), most likely the hydroxy bis-indole sulfamate 4. Furthermore, we expect that the ethoxy and methoxy containing echinosulfonic acids A and B (2 and 3) are likely to be artifacts generated by solvolysis during extraction and purification with ethanol and methanol, respectively. Precedence for solvolysis was established during the original isolation of echinosulfonic acid A (2) extracted in ethanol [12], while echinosulfonic acid B (3) reportedly underwent solvolysis with deuterated MeOH [14]. All of these findings suggest that echinosulfonic acid C (3) is most likely the authentic sponge-derived NP, with the co-isolates (1, 2, 4, and 5) able to be reasonably linked to this scaffold via solvolysis and/or oxidative decarboxylation.
2.3. Structure Revision of α-Hydroxy Bis(3′-indolyl) Compounds 3o′, 5a–5n, and 5ab′
While reviewing the literature for synthetic methods reporting other C-1″ hydroxy bis-indoles, we encountered a study reporting the synthesis of 16 α-hydroxy bis(3′indolyl) indoles via an acid-catalysed double Friedel–Crafts strategy [17]. Using 5-hydroxyindole, camphorsulfonic acid, and tert-butyldimethylsilane (TBS) glyoxylate in water, the authors proposed a reaction mechanism in which selectivity for α-hydroxy bis-indole formation was attributed to an intermolecular hydrogen bond between C-3 TBS-substituted 5-hydroxyindole and water. After this, a Brook rearrangement occurs to form the 3-TBS 5-hydroxyindole azafulvenium, followed by the loss of TBS and coupling with another 5-hydroxyindole to form α-hydroxy bis(3′indolyl) compounds 3o′, 5a–n, and 5ab′ (Figure 3 and Figure S45) [17]. Given the challenges installing and maintaining a hydroxyl group at C-1″ encountered during our work, along with the difficulties reported by other research groups [19,20], we carefully examined the published experimental NMR and MS data reported for the 16 synthetic indoles [17].
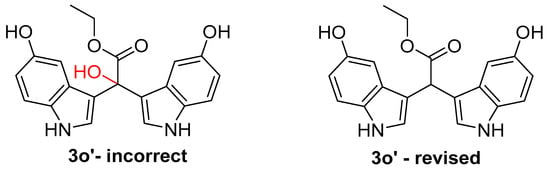
Figure 3.
Incorrectly assigned synthetic 1-hydroxy-bis(3′-indolyl) ethylacetate (3o′-incorrect) and revised structure of α-methine bis(3′-indolyl) ethylacetate (3o′-revised) based on reanalysis of reported NMR and MS experimental data.
Upon close inspection of the 1H and 13C NMR data for 3o′ and the other synthetic analogues, irregularities with its proposed structure were immediately obvious. Most notably, the α-hydroxy carbon C-1″ in 3o′ resonates at δC 40.6, a chemical shift too shielded for an oxygenated quaternary sp3 carbon. In contrast, C-1″ resonates at δC 73.8 in our synthetic α-hydroxy bis-indole 17, more than 30 ppm further downfield of that reported for 3o′. Consistent with the NMR data obtained for 11–16 reported herein, the C-1″ carbon resonance for 3o′ was in excellent agreement with the chemical shifts (ranging from δC 39.5 to 40.4) obtained for the α-methine bis(3′-indolyl) acids and methyl esters. In addition, the 1H NMR data for 3o′ clearly displayed a singlet proton resonance at δH 5.14 consistent with the α-methine proton at C-1″ in the synthetic bis-indoles (11–16), all of which resonated between δH 5.30 and 5.57. Moreover, confounding positive-mode HRMS (ESI) spectrometric data reported for the 16 α-hydroxy bis-indoles 3o′, 5a–n, and 5ab′ were also clearly refuted by the published NMR data. We can only speculate that the [M − (H2O) + H]+ dehydrated molecules, purportedly obtained from positive-mode HRMS, represent either the azafulvenium bis-indoles we have demonstrated can be generated from α-methine bis-indole acetates, or [M−H]- data acquired in negative-mode ESI HRMS.
Therefore, the structures for α-hydroxy bis(3′indolyl) indoles 3o′, 5a–n, and 5ab′ should be revised to the α-methine bis(3′indolyl) indole compounds shown in Figure 3 and Figure S45. It is regrettable that neither a 13C DEPT nor HSQC NMR experiment was utilised during the characterisation of the synthetic bis-indoles 3o′, 5a–n, and 5ab′. Such readily available NMR experiments would have likely revealed the true structural identities of the aforementioned synthetic indoles and avoided inaccuracies associated with the author’s proposed reaction mechanism (Brook rearrangement) and results of their acid-catalysed double Friedel–Crafts reaction with acylsilanes [17].
2.4. Cheminformatics-Directed Prediction of Synthetic Bis-Indole Bioactivities
The biological activities of the echinosulfonic acid series remain relatively unexplored, with only weak KB cell cytotoxicity reported for the echinosulfonic acids B and D (3 and 5) [13], alongside unquantified sponge crude extract anti-parasitic and antibacterial activities [12]. With this in mind, we were interested in exploring the chemical diversity of our synthetic library of bis-indoles compared with that present within MIAs to better direct their biological testing. Based on the results of our recent meta-analysis of MIA chemical diversity and bioactivities [1], we employed a cheminformatics-based approach to guide the biological evaluation of the marine-inspired synthetic bis-indole scaffolds reported herein. Using our existing MIA structure and bioactivity dataset (n = 2048 MIAs, with disease and infection targets and the potency of their reported bioactivities according to the formal classifications displayed in Table S1) [1], we integrated our library of synthetic bis-indoles 11–17 alongside an additional four ketone-bridged bis-indole methanones synthesised using our previously reported procedure [11]: bis(5-bromo-1H-indol-3-yl)methanone (19), (6-bromo-1H-indol-3-yl)(1H-indol-3-yl)methanone (20), di(1H-indol-3-yl)methanone (21), and bis(6-bromo-1H-indol-3-yl)methanone (22, Figure 4).
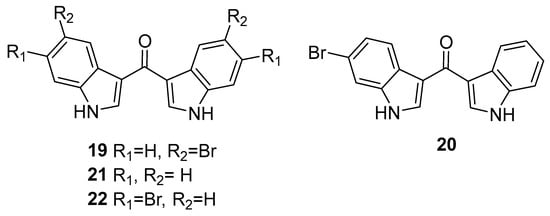
Figure 4.
Synthetic bis-indole methanones included in cheminformatics and antibacterial analyses: bis(5-bromo-1H-indol-3-yl)methanone (19), (6-bromo-1H-indol-3-yl)(1H-indol-3-yl)methanone (20), di(1H-indol-3-yl)methanone (21), and bis(6-bromo-1H-indol-3-yl)methanone (22).
Within the freely available cheminformatics platform Osiris Datawarrior [21], we examined the chemical diversity of the synthetic indoles 11–17 and 19–22 with that occupied by MIAs (n = 2048) visualised in a self-organising map (SOM, 50 × 50 neurons with the SkelSpheres chemical descriptor, Figure S46). SOMs are effective tools for examining chemical diversity and are generated from molecular fragment analyses using neural network algorithms that display structurally similar compounds in clusters of two-dimensional chemical space. The SOM clearly showed that all of the synthetic bis-indoles (11–17 and 19–22) occupied similar areas of chemical space with interesting overlap observed with structurally related bioactive MIAs (Figure 5). The synthetic 6-dibrominated α-hydroxy bis-indole acetate 17 (Figure 5A, red inset) clustered closely with dragmacidin G (23), a sponge-derived dibrominated guanidine bis-indole pyrazine reported with potent inhibitory activity against Staphylococcus aureus (MIC 0.62 μg/mL) [22] and weak cancer cell line cytotoxicity [23,24]. In addition, the 6-dibromo bis-indole acid 11 and acetate 14 clustered with two bioactive brominated MIAs, the bis-indole dihydrospongotine C (24) and the tris-indole tulongicin (25, Figure 5B) [25]. Both 24 and 25 were reported with moderate antibacterial activities against S. aureus at MIC 1.2 and 3.7 µg/mL, respectively. Moreover, both MIAs were found to be inactive against BSC-1 and HCG-116 cancer cell lines [25].
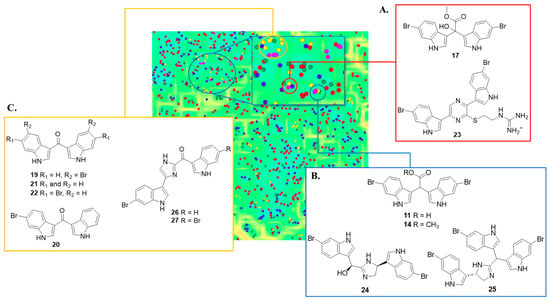
Figure 5.
Chemical cluster analysis of MIA dataset (n = 2048) integrated with synthetic bis-indoles 11–17 and 19–22 (pink circles) visualised as a self-organising map (SOM, 50 × 50 neurons) using the Skelspheres 1024-bit chemical fingerprint descriptor. MIAs are coloured according to their reported potency of biological activity (blue = not tested, red = inactive, green = weakly active, and yellow = moderate to potently active). (A). Red cluster of synthetic 17 with dragmacidin G (23). (B). Blue cluster of synthetic 6-dibrominated bis-indoles 11 and 14 with dihydrospongotine C (24) and tulongicin (25). (C). Yellow cluster with bis-indole methanones 19, 21, and 22 with bromodeoxytopsentin (26) and dibromodexoytopsentin (27).
While the remaining synthetic bis-indoles 12, 13, 15, 16, and 19–22 did not form clusters that directly overlapped with MIAs in our dataset, they did occupy regions of chemical space similar to other MIA bis-indole alkaloids. The bis-indole methanone analogues 19, 21, and 22 were clustered relatively closely with the bioactive sponge-derived bis-indoles, the topsentins (Figure 5C, yellow inset). While topsentin MIAs have been assigned diverse bioactivities, including cytotoxic, antiviral, and antifungal ones, of most interest was their inhibitory activity against methicillin-resistant S. aureus (MRSA) pyruvate kinase (PK) [26]. Both bromodeoxytopsentin (26) and dibromodexoytopsentin (27) were reported with nanomolar potent and selective inhibition of MRSA PK with IC50 values of 60 and 2.1 nM, respectively. Interestingly, structure–activity relationships (SARs) suggest that the halogenated topsentin analogues are favourable for MRSA PK activity [26]. These promising antibacterial results and predicted bioactivity from our cheminformatics analyses therefore prompted our evaluation of synthetic indoles 11–17 and 19–22 and synthetic echinosulfone A (1) [14] against Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria.
2.5. Antibacterial Testing of Synthetic Bis-Indoles 1, 11–17, and 19–22
The synthetic bis-indoles 1, 11–17, and 19–22 were evaluated against methicillin-susceptible and methicillin-resistant S. aureus (MSSA and MRSA, respectively) and Pseudomonas aeruginosa. It was found that four of the bis-indoles were active against MSSA and MRSA, while none displayed activity toward P. aeruginosa (Table 1). Most notably, the C-6 dibrominated α-methine bis-indole acetate 14 exhibited the highest potency toward both S. aureus strains, with MIC50 values of 4 and 8 µg/mL against MSSA and MRSA, respectively. The corresponding C-6 dibrominated α-methine bis-indole acid analogue 11 was also active against both S. aureus strains; however, four-fold and two-fold decreases in potency were observed toward MSSA and MRSA compared with the acetate 14. Additionally, the C-5 dibrominated α-methine bis-indole acid 12 and acetate 15 were also found to be active against MSSA and MRSA, but not at the potencies observed for C-6 dibrominated bis-indole acetate 14. In contrast, the non-brominated α-methine analogues 13 and 16 and the C-3 ketone-bridged bis-indoles 1, and 19–22 were all found to display no antibacterial activities. There appears to be a clear SAR among the bis-indoles screened with bromination and the presence of either the α-methine acetic acid or methyl acetate, essential for antibacterial activity. This is supported by the complete loss of antibacterial activity when either of the aforementioned structural features is absent. The potency of C-6 dibrominated α-methine bis-indole 14 compared with the acid 11 suggests that the ester is also an important discriminating feature between these two analogues. Consistent with the instability reported above for α-hydroxy bis-indole 17 and 18, we suggest that 17 likely underwent oxidative decarboxylation to 22 during the course of the antibacterial evaluation.

Table 1.
Antibacterial activities for synthetic indoles 1, 11–17, and 19–22.
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Chemistry
All anhydrous solvents and reagents used in reactions were purchased from Sigma-Aldrich, except for 5- and 6-bromoindole (Enamine). Further to this, bulk solvents (Merck) were distilled under a normal atmosphere prior to use to ensure non-volatile components were not present—they were not dried. All reactions were carried out under inert N2 or argon atmospheres under standard reaction conditions. NMR spectra were recorded at 25 °C on a Bruker® 400 MHz Avance III spectrometer equipped with a 5 mm BBFO probe with Z-gradient and automatic tuning with a SampleCase automatic sample changer, a Bruker Avance III 500 MHz spectrometer (BBFO Smartprobe, 5 mm 31P-109Ag), or a Bruker Avance III HDX 800 MHz with a triple (TCl) resonance 5 mm cryoprobe (all Bruker equipment sourced from Preston, Victoria, Australia). The 1H and 13C NMR chemical shifts were referenced to the solvent peak for DMSO-d6 at δH 2.50 and δC 39.52. High-resolution negative electrospray ionisation mass measurements were acquired using CH3CN as the mobile phase on an Agilent Technologies 6530 Accurate-Mass Q-TOF LC/MS (Mulgrave, Victoria, Australia) with a 1200 Series autosampler and 1290 Infinity HPLC, while low-resolution mass measurements were obtained using a Waters ZQ electrospray ionisation mass spectrometer (Rydalmere, NSW, Australia). A Merck Hitachi L7100 pump equipped with a Merck Hitachi L7455 PDA detector (Bayswater, Victoria, Australia) was used for HPLC purifications. Fractions were collected using a Gilson 215 liquid handler. The solvents used for chromatography were Scharlau HPLC-grade, and H2O was Millipore Milli-QPF-filtered (Bayswater, Victoria, Australia). Trifluoroacetic acid (TFA) was spectroscopy-grade from Alfa Aesar, while solvents used for HRESIMS were MS-grade.
3.2. Synthetic Procedures
3.2.1. Synthesis of Bis(1H-indol-3-yl)acetic Acids (11–13)
Based on a procedure described by Sathieshkumar et al. [18], glyoxylic acid monohydrate (1.2 eq.) and AlCl3 (20 mol%) were added to a stirred suspension of an appropriate indole (2 eq.) in EtOH under an argon atmosphere and left at room temperature for 3 h. The crude reaction mixture was quenched with cold distilled water (3.0 mL), basified with 1 M NaOH (5.0 mL, pH > 10), and extracted between CHCl3 and H2O (3 × 30 mL of CHCl3). The aqueous phase was collected, acidified with 1 M HCl (5.0 mL, pH < 3), and extracted with EtOAc (3 × 30 mL). The organic phase was dried with Na2SO4, filtered, and concentrated to dryness without the need for further purification. The α-methine bis-indole carboxylic acids 11–13 were afforded in yields greater than 85%.
3.2.2. Synthesis of Bis(1H-indol-3-yl)acetates (14–16)
Thionyl chloride was added dropwise (1.2 eq.) to the appropriate 2,2-bis(1H-indol-3-yl)acetic acid (11–13, 1 eq.) under an argon atmosphere; anhydrous MeOH (4–8.0 mL) was then added. The reaction mixture was stirred at 5 °C for 2 h, after which it was quenched with H2O (2.0 mL), extracted with EtOAc, dried over Na2SO4, filtered, and concentrated to dryness without the need for further purification. The α-methine bis-indole acetates 14–16 were acquired in yields greater than 90%.
3.2.3. Synthesis of Methyl 2,2-Bis(6-bromo-1H-indol-3-yl)-2-hydroxyacetate (17 and 18)
To a stirred suspension of 14 (72 mg, 0.15 mmol) in DMF (2.0 mL) at 80 °C, Cs2CO3 (145 mg, 0.3 mmol) was added under a normal atmosphere for 12 h. The reaction mixture was quenched with H2O (1.0 mL) and left to cool to room temperature. The reaction mixture was extracted in EtOAc, dried over Na2SO4, and concentrated to dryness. The crude reaction mixture was adsorbed to C18-bonded silica gel, loaded into a refillable guard column, and purified by preparative RP HPLC (Kinetex EVO C18 5 μm 100 Å, 21.2 mm × 150 mm) using a solvent gradient from H2O to CH3CN over 50 min with fractions collected each minute. Compound 17 was afforded in fractions 24 to 27.
3.2.4. Synthesis of Bis(1H-indol-3-yl)methanones (19–22)
In accordance with our previously reported method [11], 3 M ethyl magnesium bromide (1.2 eq.) was added dropwise under an argon atmosphere at 0 °C to a stirred solution of appropriate indole (1 eq.) in anhydrous diethyl ether (4.0 mL). The reaction mixture was then stirred at room temperature for 2 h, after which it was concentrated to dryness. The resultant indole magnesium salts were resuspended in anhydrous CH2Cl2 (4.0 mL); then, triphosgene (0.6 eq.) was added under inert conditions, and the reaction mixture was stirred for 24 h at 5 °C. The reaction was quenched with cold distilled H2O and carefully partitioned between ethyl acetate and water with the organic phase collected and dried with Na2SO4. After filtration, the organic phase was concentrated in vacuo. Bis-indoles 19, 21, and 22 (1H and 13C NMR spectra, Figures S43 and S44) were purified by column chromatography on silica gel (3:2 EtOAc/hexanes), while 20 was adsorbed to C18-bonded silica gel, loaded into a refillable guard column, and purified by preparative RP HPLC (Kinetex EVO C18 5 μm 100 Å, 21.2 mm × 150 mm) using a solvent gradient from H2O (0.1% TFA) to MeOH (0.1% TFA) over 50 min with fractions collected each minute. Compound 20 was afforded in fractions 37 to 39.
2,2-bis(6-bromo-1H-indol-3-yl)acetic acid (11): 350.6 mg (88.7% yield), red amorphous solid; UV(MeOH) λmax (log ε) 287 (5.9), 229 (6.7) nm; IR (neat); Vmax 3410, 1726, 1611, and 1453 cm−1; 1H NMR (400 MHz, DMSO) δ 11.06 (s, 2H), 7.53 (d, J = 1.6 Hz, 2H), 7.43 (d, J = 8.5 Hz, 2H), 7.23 (d, J = 2.2 Hz, 2H), 7.05 (dd, J = 8.5, 2.2 Hz, 2H), 5.30 (s, 1H); 13C NMR (101 MHz, DMSO) δ 174.1, 137.3, 125.6, 124.8, 121.4, 120.9, 114.2, 113.9, 113.3, 40.4. HRMS (ESI-QTOF) m/z: [M−H]− calcd. for C18H11N2O279Br81Br, (446.9164); found 446.9167. (NMR spectra, Figures S1–S4).
2,2-bis(5-bromo-1H-indol-3-yl)acetic acid (12): 205.7 mg (88.2% yield), red amorphous solid; UV(MeOH) λmax (log ε) 290 (3.1), 228 (3.9) nm; IR (neat); Vmax 3415, 1712, 1611, and 1453 cm−1; 1H NMR (500 MHz, DMSO) δ 11.16 (s, 2H), 7.68 (d, J = 1.8 Hz, 2H), 7.33 (d, J = 8.6 Hz, 2H), 7.30 (d, J = 2.3 Hz, 2H), 7.17 (dd, J = 8.6, 1.8 Hz, 2H), 5.35 (s, 1H); 13C NMR (101 MHz, DMSO) δ 174.0, 135.0, 128.2, 125.4, 123.5, 121.4, 113.6, 112.4, 111.1, 40.1; HRMS (ESI-QTOF) m/z: [M−H]- calcd. for C18H11N2O279Br81Br, (446.9168); found 446.9167. (NMR spectra, Figures S5–S8).
2,2-di(1H-indol-3-yl)acetic acid (13): 334.1 mg (88.5% yield), red amorphous solid; UV(MeOH) λmax (log ε) 282 (3.0), 222 (3.7) nm; IR (neat); Vmax 3417, 1710, 1614, and 1451 cm−1; 1H NMR (500 MHz, DMSO) δ 10.91 (s, 2H), 7.54 (d, J =7.9 Hz, 2H), 7.35 (d, J = 8.0f Hz, 2H), 7.21 (d, J = 2.2 Hz, 2H), 7.06 (dd, J = 8.0, 7.5 Hz, 2H), 6.94 (dd, J = 7.9, 7.5 Hz, 2H), 5.34 (s, 1H); 13C NMR (101 MHz, DMSO) δ 174.4, 136.3, 126.5, 123.6, 121.0, 119.0, 118.4, 112.8, 111.5, 40.4. HRMS (ESI-QTOF) m/z: [M−H]− calcd. for C18H13N2O2, (289.0978); found 289.0987. (NMR spectra, Figures S9–S12).
methyl 2,2-bis(6-bromo-1H-indol-3-yl)acetate (14): (300.5 mg, 94.4% yield), dark purple amorphous solid, UV(MeOH) λmax (log ε) 287 (3.2), 228 (4.1) nm; IR (neat); Vmax 3411, 1726, 1612, and 1453 cm−1; 1H NMR (400 MHz, DMSO) δ 11.12 (br s, 2H), 7.54 (d, J = 1.8 Hz, 2H), 7.42 (d, J = 8.5 Hz, 2H), 7.25 (d, J = 2.2 Hz, d), 7.07 (dd, J = 8.5, 1.8 Hz, 2H), 5.47 (s, 1H), 3.64 (s, 3H); 13C NMR (101 MHz, DMSO) δ 172.9, 137.2, 125.3, 124.9, 121.5, 120.6, 114.1, 113.9, 112.4, 52.0, 39.5. HRMS (ESI-QTOF) m/z: [M−H]- calcd. for C19H13N2O279Br81Br, (460.9324); found 460.9320. (NMR spectra, Figures S13–S16).
methyl 2,2-bis(5-bromo-1H-indol-3-yl)acetate (15): (176.1 mg, 93.3% yield), red amorphous solid; UV(MeOH) λmax (log ε) 290 (3.4), 222 (4.2) nm; IR (neat); Vmax 3410, 1728, 1610, and 1451 cm−1; 1H NMR (500 MHz, DMSO) δ 11.2 (s, 2H), 7.66 (d, J = 1.8 Hz, 2H), 7.33 (d, J = 8.6 Hz, 2H), 7.33 (d, J = 2.4 Hz, 2H), 7.17 (dd, J = 8.6, 1.9 Hz, 2H), 5.52 (s, 1H), 3.66 (s, 3H); 13C NMR (101 MHz, DMSO) δ 173.0 135.0, 128.0, 125.5, 123.6, 121.2, 113.6, 111.8, 111.2, 52.0, 39.6; HRMS (ESI-QTOF) m/z: [M−H]- calcd. for C19H13N2O279Br81Br, (460.9324); found 460.9324. (NMR spectra, Figures S17–S20).
methyl 2,2-di(1H-indol-3-yl)acetate (16): (281.0 mg, 92.5% yield), red amorphous solid; UV(MeOH) λmax (log ε) 336 (2.2), 281 (3.3) 222 (3.9); IR (neat); Vmax 3410, 1728, 1610, and 1451 cm−1; 1H NMR (500 MHz, DMSO) δ 10.96 (s, 2H), 7.52 (d, J = 7.9 Hz, 2H), 7.36 (d, J = 8.1 Hz, 2H), 7.06 (ddd, J = 8.1, 7.6. 1.0 Hz, 2H), 6.95 (ddd, J = 7.9, 7.6, 0.8 Hz, 2H), 5.47 (s, 1H), 3.65 (s, 3H); 13C NMR (101 MHz, DMSO) δ 173.1, 136.3, 126.3, 123.7, 121.1, 118.8, 118.5, 112.3, 111.5, 51.8, 40.0. HRMS (ESI-QTOF) m/z: [M−H]− calcd. for C19H15N2O2, (303.1135); found 303.1132. (NMR spectra, Figures S21–S24).
methyl 2,2-bis(6-bromo-1H-indol-3-yl)-2-hydroxyacetate (17): (7.1 mg, 7.5% yield), orange/brown amorphous solid, UV(MeOH) λmax (log ε) 286 (3.0), 226 (4.1) nm; IR (neat); Vmax 3410, 1726, 1612, and 1453 cm−1; 1H NMR (800 MHz, DMSO) δ 11.12 (br s, 2H), 7.53 (d, J = 1.8 Hz, 2H), 7.29 (d, J = 8.5 Hz, 2H), 7.15 (d, J = 2.2 Hz, d), 6.99 (dd, J = 8.5, 1.8 Hz, 2H), 6.13 (s, 1H), 3.65 (s, 3H); 13C NMR (201 MHz, DMSO) δ 174.0, 137.5, 124.9, 124.7, 122.4, 121.4, 117.6, 114.0, 113.8, 73.9, 52.2. HRMS (ESI-QTOF) m/z: [M−H]− calcd. for C19H13N2O379Br81Br, (476.9273); found 476.9268. (NMR spectra, Figures S25–S29).
bis(5-bromo-1H-indol-3-yl)methanone (19): (178.2 mg, 64.5% yield), brown amorphous solid; UV(MeOH) λmax (log ε) 322 (4.3), 281 (4.6), 253 (4.5), 222 (4.9) nm; IR (neat); Vmax 3419, 2910, 1681, 1597, 1520, and 1034 cm−1; 1H NMR (400 MHz, DMSO) δ 12.08 (s, 2H), 8.42 (d, J =2.0 Hz, 2H), 8.30 (s, 2H), 7.48 (d, J = 8.6 Hz, 2H), 7.36 (dd, J = 8.6, 2.0 Hz, 2H); 13C NMR (101 MHz, DMSO) δ 183.8, 135.2, 133.3, 128.3, 125.2, 123.6, 115.8, 114.0, 113.9. HRMS (ESI-QTOF) m/z: [M−H]− calcd. for C17H9N2O79Br81Br, (416.9062); found 416.9063. (NMR spectra, Figures S31–S34).
(6-bromo-1H-indol-3-yl)(1H-indol-3-yl)methanone (20): (20.1 mg, 24.5% yield), brown amorphous solid; UV(MeOH) λmax (log ε) 324 (4.1), 276 (4.2), 252 (4.1), 219 (4.6) nm; IR (neat); Vmax 3416, 2906, 1678, 1596, 1510, and 1032 cm−1; 1H NMR (500 MHz, DMSO) δ 11.92 (s, 1H), 11.86 (s, 1H), 8.25 (d, J = 8.0 Hz, 1H), 8.20 (s, 1H), 8.19 (d, J = 8.5 Hz, 1H), 8.19 (s, 1H), 7.68 (d, J = 1.8 Hz, 1H), 7.50 (d, J = 8.0 Hz, 1H), 7.32 (dd, J = 8.5, 1.8 Hz, 1H), 7.22 (ddd, J = 8.0, 7.1, 1.3 Hz, 1H), 7.18 (ddd, J = 8.0, 7.1, 1.0 Hz, 1H); 13C NMR (101 MHz, DMSO) δ 184.3, 137.4, 136.5, 132.6, 132.3, 126.5, 125.6, 123.9, 123.2, 122.6, 121.5, 121.1, 116.8, 116.6, 115.1, 114.5, 111.9. HRMS (ESI-QTOF) m/z: [M−H]- calcd. for C17H10N2O81Br, (338.9957); found 338.9963. (NMR spectra, Figures S35–S35).
di(1H-indol-3-yl)methanone (21): (100.3 mg, 70.1% yield), brown amorphous solid; UV(MeOH) λmax (log ε) 321 (4.3), 274 (4.4), 250 (4.3), 217 (4.8); IR (neat); Vmax 3416, 2914, 1676, 1594, 1518, and 1032 cm−1; 1H NMR (500 MHz, DMSO) δ 11.83 (s, 2H), 8.26 (d, J = 7.1 Hz, 2H), 8.16 (s, 2H), 7.50 (d, J = 7.8 Hz, 2H), 7.22 (ddd, J = 8.3, 7.1, 1.4 Hz, 2H), 7.18 (ddd, J = 8.3, 7.8, 1.3 Hz, 2H); 13C NMR (125 MHz, DMSO) δ 184.6, 136.5, 132.0, 126.6, 122.6, 121.5, 121.0, 116.8, 111.9. HRMS (ESI-QTOF) m/z: [M−H]− calcd. for C17H11N2O, (259.0872); found 259.0875. (Figures S9–S12). (NMR spectra, Figures S39–S40).
3.3. Cheminformatics Analyses of Marine and Synthetic Indole Chemical Diversity
The structures for 2048 marine indole alkaloids reported in the MarinLit database (up to the end of 2021) [2] were imported into the freely available cheminformatics software, Osiris DataWarrior [21]. The reported biological activities for the 2048 compounds were scaled to disease and infection targets and potency of activity classifications in Table S1 (as reported in our published meta-analysis of MIAs) [1]. After the integration of the synthetic indoles 11–17 and 19–22 into the MIA dataset, the chemical diversity of MIAs compared with the synthetic indoles reported herein was visualised using a 50 × 50-neuron self-organising map (SOM) and the SkelSpheres chemical descriptor (1024 bin resolution byte vector encoding for stereochemistry, heteroatoms, and duplicate fragment counts). The SOM output was colour-coded to the potency of the activity of MIAs.
3.4. Antibacterial Testing of Synthetic Bis-Indoles 1, 11–17, and 19–22
Compounds 1 (1H and 13C NMR spectra, Figures S41 and S42), 11–17, and 19–22 were tested for antibacterial activity against two Staphylococcus aureus strains (ATCC 25923 and ATCC 43300) and a Pseudomonas aeruginosa strain (ATCC 27853). A modified resazurin microtiter plate assay method developed by Sarker et al. was used to determine antibacterial activities [27]. A stock solution of each bis-indole was prepared at 1.5 mM in DMSO, from which a stock plate was prepared using a ten-fold, 1:2 serial dilution. Each assay employed several antibiotic controls which were compared to MIC quality control ranges reported by the Clinical and Laboratory Institute (CLSI) [27]. The positive controls rifampicin and ciprofloxacin were used for MSSA and MRSA strains, while the positive control tobramycin was used for P. aeruginosa. For both S. aureus stains, 5% DMSO was used as a negative control, while 2.5% DMSO was used for P. aeruginosa. Overnight cultures were prepared by aseptically transferring colonies into 10 mL of sterile Luria–Bertani (LB) broth and incubating them for 16–18 h at 37.5 °C. The inoculate was prepared by adjusting the overnight culture to 5 × 105 CFU/mL. The microdilution assay for S. aureus was performed in sterile 96-well plates, and to each well, 25 μL of double-strength LB broth, 5 μL of the stock solution, 20 μL of sterile H2O, and 50 μL of the inoculate were sequentially added. The volumes for P. aeruginosa were double that for S. aureus. Plates were incubated for 18 h at 37.5 °C while being shaken at 100 rpm, after which 10 μL of 704 μM resazurin (sodium salt, Sigma Aldrich, Melbourne, Victoria, Australia) was added to all wells and the assay plates were incubated for a further 1 h. Resazurin reduction was recorded on a BMG LABTECH, FLUOstar Omega (Mornington, Victoria, Australia) fluorescent plate reader (lex 544 nm, lem 590 nm). All experiments were run in triplicate over three consecutive days. MIC50 values were calculated in GraphPad Prism (version 5) using the log(inhibitor) vs. response (Variable slope) equation. Standard guidelines set by the Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute were closely followed during each step of the assay [27].
4. Conclusions
In conclusion, we report a cheminformatics-guided approach to exploring the bioactivities of MNP-inspired bis-indole alkaloids. Moreover, we also report the first synthesis of the unstable α-hydroxy bis(3′-indolyl) alkaloids (17–19) with full NMR and MS characterisation of the C-6 dibrominated analogue 17. The synthesis of desulfato-echinosulfonic acid C (17) provides experimental evidence to corroborate the structure revision of echinosulfonic acid C (4). In addition, we have demonstrated a robust synthetic strategy toward brominated and non-brominated α-methine bis(3′-indolyl) acids (11–13) and acetates (14–16) in one or two steps without the need for further purification. The synthetic results herein provide a simple strategy for accessing diverse bis-indole methanone scaffolds. The success of a cheminformatics-guided exploration of our library of synthetic bis-indoles with 2048 MIAs effectively directed the biological evaluation of 1, 11–17, and 19–22 toward their potential antibacterial activities. The promising MSSA and MRSA activities obtained for the brominated α-methine bis(3′-indolyl) alkaloids, in particular 6-dibrominated bis-indole acetate 14, validated our cheminformatics predictions based on MIA chemical similarity analyses coupled with reported bioactivity. A clear SAR suggested that both brominated and α-methine bis-indoles were favoured over non-brominated (13 and 16) and planar ketone-bridged ones (1 and 19–22). This work highlights the synergy of NP and synthetic chemistry and the inspiration provided by complex NP scaffolds and the pursuit of their biological potentials. Here we demonstrate the power of cheminformatics-guided approaches for directing the biological evaluation of NP and synthetic scaffolds. It is hoped that more thoughtful strategies aimed at leveraging the plethora of information residing in large NP databases will be used for examining the bioactivities of NPs and NP-inspired compounds. These approaches aim to expand our understanding of NP bioactive chemical space, ultimately maximising future NP drug discovery efforts.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/molecules29122806/s1: Figures S1–S44. Experimental NMR spectra for 1 and 11–22; Figure S45. Incorrectly assigned synthetic α-hydroxy bis-indoles (red) and revised α-methine bis-indoles structures (black) for 3o′, 5ab′, and 5a–n; Figure S46. Chemical diversity of marine indole alkaloids (n = 2048) integrated with synthetic bis-indoles 11–17 and 19–22 visualised as 50 × 50 self-organising map (SOM) using the Skelspheres 1024-bit chemical fingerprint descriptor; Figure S47. Desulfonated echinosulfone A (22) and echinosulfonic acid B (3a); Table S1. Bioactivity classifications used for cheminformatic analysis of marine indole alkaloids. References [1,3,14,17] are cited in the Supplementary Materials.
Author Contributions
Conceptualisation, D.C.H. and A.R.C.; methodology, D.C.H., M.J.K. and A.R.C.; analysis and writing, D.C.H. and A.R.C.; antibacterial evaluations, J.B.H.; draft, review, and editing, D.C.H., A.R.C., M.J.K. and J.B.H. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was funded by an Australian Postgraduate Award (APA) provided by the Australian Commonwealth Government to D.C.H.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Supporting data are available in the Electronic Supporting Information (ESI) provided.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Holland, D.C.; Carroll, A.R. Marine Indole Alkaloid Diversity and Bioactivity. What Do We Know and What Are We Missing? Nat. Prod. Rep. 2023, 40, 1596–1607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- MarinLit. Available online: http://pubs.rsc.org/marinlit/ (accessed on 11 May 2024).
- Carroll, A.R.; Copp, B.R.; Davis, R.A.; Keyzers, R.A.; Prinsep, M.R. Marine Natural Products. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2022, 39, 1111–1368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sorokina, M.; Steinbeck, C. Review on Natural Products Databases: Where to Find Data in 2020. J. Cheminform. 2020, 12, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sorokina, M.; Merseburger, P.; Rajan, K.; Yirik, M.A.; Steinbeck, C. COCONUT online: Collection of Open Natural Products database. J. Cheminform. 2021, 13, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dictionary of Natural Products. Available online: https://dnp.chemnetbase.com/chemical/ChemicalSearch.xhtml?dswid=5053 (accessed on 22 March 2024).
- Voser, T.M.; Campbell, M.D.; Carroll, A.R. How Different Are Marine Microbial Natural Products Compared to Their Terrestrial Counterparts? Nat. Prod. Rep. 2022, 39, 7–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, C.; Idelbayev, Y.; Roberts, N.; Tao, Y.; Nannapaneni, Y.; Duggan, B.M.; Min, J.; Lin, E.C.; Gerwick, E.C.; Cottrell, G.W.; et al. Small Molecule Accurate Recognition Technology (SMART) to Enhance Natural Products Research. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 14243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robien, W. Computer-Assisted Peer Reviewing of Spectral Data: The CSEARCH Protocol. Monatsh. Chem. 2019, 150, 927–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, Y.; Shree Sowndarya, S.V.; Gallegos, L.C.; St. John, P.C.; Paton, R.S. Real-time prediction of 1H and 13C chemical shifts with DFT accuracy using a 3D graph neural network. Chem. Sci. 2021, 12, 12012–12026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holland, D.C.; Kiefel, M.J.; Carroll, A.R. Structure Revisions of the Sponge-Derived Dibrominated Bis-Indole Alkaloids, Echinosulfone A and the Echinosulfonic Acids A to D. J. Org. Chem. 2020, 85, 3490–3496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ovenden, S.P.B.; Capon, R.J. Echinosulfonic Acids A-C and Echinosulfone A: Novel Bromoindole Sulfonic Acids and a Sulfone from a Southern Australian Marine Sponge, Echinodictyum. J. Nat. Prod. 1999, 62, 1246–1249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rubnov, S.; Chevallier, C.; Thoison, O.; Debitus, C.; Laprevote, O.; Guénard, D.; Sévenet, T. Echinosulfonic Acid D: An ESI MSn Evaluation of a New Cytotoxic Alkaloid from the New-Caledonian Sponge Psammoclemma sp. Nat. Prod. Res. 2005, 19, 75–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sala, S.; Nealon, G.L.; Sobolev, A.N.; Fromont, J.; Gomez, O.; Flematti, G.R. Structure Reassignment of Echinosulfone A and the Echinosulfonic Acids A − D Supported by Single-Crystal X-Ray Diffraction and Density Functional Theory Analysis. J. Nat. Prod. 2020, 83, 105–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neupane, P.; Salim, A.A.; Capon, R.J. Structure Revision of the Rare Sponge Metabolite Echinosulfone A, and Biosynthetically Related Echinosulfonic Acids A–D. Tetrahedron Lett. 2020, 61, 151651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abe, T.; Nakajima, R.; Yamashiro, T.; Sawada, D. First Total Synthesis of Reassigned Echinosulfonic Acid D. J. Nat. Prod. 2022, 85, 2122–2125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Q.; Liang, X.X.; Zhang, W.; Han, M.Y. Friedel–Crafts Reaction of Acylsilanes: Highly Chemoselective Synthesis of 1-Hydroxy-Bis(Indolyl)Methanes and 1-Silyl-Bis(Indolyl)Methanes Derivatives. Molecules 2023, 28, 5685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sathieshkumar, P.P.; Latha, P.; Nagarajan, R. Total Synthesis of Pseudellone C. Eur. J. Org. Chem. 2017, 2017, 3161–3164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elayaraja, R.; Joel Karunakaran, R. Cesium Carbonate Mediated Synthesis of 3-(α-Hydroxyaryl)Indoles. Tetrahedron Lett. 2012, 53, 6901–6904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deb, M.L.; Bhuyan, P.J. An Efficient and Clean Synthesis of Bis(Indolyl)Methanes in a Protic Solvent at Room Temperature. Tetrahedron Lett. 2006, 47, 1441–1443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sander, T.; Freyss, J.; Von Korff, M.; Rufener, C. DataWarrior: An Open-Source Program for Chemistry Aware Data Visualization and Analysis. J. Chem. Inf. Model 2015, 55, 460–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hitora, Y.; Takada, K.; Ise, Y.; Okada, S.; Matsunaga, S. Dragmacidins G and H, Bisindole Alkaloids Tethered by a Guanidino Ethylthiopyrazine Moiety, from a Lipastrotethya sp. Marine Sponge. J. Nat. Prod. 2016, 79, 2973–2976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McConnell, O.J.; Koehn, F.; Rinehart, K.L.; Kohmoto, S.; Wright, A.; Kashman, Y. Dragmacidin, a New Cytotoxic Bis(Indole) Alkaloid from a Deep Water Marine Sponge, Dragmacidon sp. J. Org. Chem. 2005, 53, 3116–3118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, A.E.; Killday, K.B.; Chakrabarti, D.; Guzmán, E.A.; Harmody, D.; McCarthy, P.J.; Pitts, T.; Pomponi, S.A.; Reed, J.K.; Roberts, B.F.; et al. Dragmacidin G, a Bioactive Bis-Indole Alkaloid from a Deep-Water Sponge of the Genus Spongosorites. Mar. Drugs 2017, 15, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.B.; Lauro, G.; O’Connor, R.D.; Lohith, K.; Kelly, M.; Colin, P.; Bifulco, G.; Bewley, C.A. Tulongicin, an Antibacterial Tri-Indole Alkaloid from a Deep-Water Topsentia sp. Sponge. J. Nat. Prod. 2017, 80, 2556–2560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Veale, C.G.L.; Zoraghi, R.; Young, R.M.; Morrison, J.P.; Pretheeban, M.; Lobb, K.A.; Reiner, N.E.; Andersen, R.J.; Davies-Coleman, M.T. Synthetic Analogues of the Marine Bisindole Deoxytopsentin: Potent Selective Inhibitors of MRSA Pyruvate Kinase. J. Nat. Prod. 2015, 78, 355–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarker, S.D.; Nahar, L.; Kumarasamy, Y. Microtitre Plate-Based Antibacterial Assay Incorporating Resazurin as an Indicator of Cell Growth, and Its Application in the in Vitro Antibacterial Screening of Phytochemicals. Methods 2007, 42, 321–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).