Abstract
A series of bitopic ligands based on Fallypride with a flexible secondary binding fragment (SBF) were prepared with the goal of preparing a D3R-selective compound. The effect of the flexible linker ((R,S)-trans-2a–d), SBFs ((R,S)-trans-2h–j), and the chirality of orthosteric binding fragments (OBFs) ((S,R)-trans-d, (S,R)-trans-i, (S,S)-trans-d, (S,S)-trans-i, (R,R)-trans-d, and (R,R)-trans-i) were evaluated in in vitro binding assays. Computational chemistry studies revealed that the interaction of the fragment binding to the SBF increased the distance between the pyrrolidine nitrogen and ASP1103.32 of the D3R, thereby reducing the D3R affinity to a suboptimal level.
1. Introduction
Dopamine receptors are a class of G protein-coupled receptors. Five subtypes of dopamine receptors have been identified, and they are divided into two classes based on their sequence and functional roles. The dopamine 1-like receptors include the dopamine 1 receptor (D1R) and the dopamine 5 receptor (D5R), and the dopamine 2-like receptors consist of the dopamine 2 receptor (D2R), the dopamine 3 receptor (D3R), and the dopamine 4 receptor (D4R) [1,2,3]. Previous studies showed that the dysregulation of D2R and D3R is related to many central nervous system (CNS) diseases [4,5]. These two dopamine receptors have been used as therapeutic targets for treating neurological and neuropsychiatric disorders, including schizophrenia, drug addiction, and Parkinson’s disease (PD) [4,6,7,8].
The D2R and D3R have a differential distribution in the human brain [9,10,11]. For example, in the globus pallidus internal part, thalamus, red nucleus, and substantia nigra, the D3R has a higher density than the D2R [12,13]. Moreover, an autoradiography study in chronic cocaine abuse showed that the density of the D2R and D3R changed differently (the D2R had no change vs. the D3R increased) [4,14,15,16,17,18]. An in vitro autoradiography study of PD brain samples yielded similar results as above [12,14]. These results indicate that these two dopamine receptors play different roles in the CNS; the D3R is thought to play a key role in mediating L-DOPA-induced dyskinesia [16].
Positron emission tomography (PET) is a functional imaging technique that uses radiotracers to image receptors in the CNS. Over the past several years, [18F]Fallypride [19,20,21,22], [11C]Raclopride [23,24,25,26,27], [11C]FLB 457 [20,26,28], and [11C]-(+)-PHNO [29,30,31] have been used as radiotracers for PET imaging studies of the D2-like receptors in humans (Figure 1). Unfortunately, all four radiotracers cannot image the D3R independently of the D2R. The lack of highly selective D3R PET radiotracers has prevented the imaging of the D3R independently of the D2R. Therefore, developing a D3R selective radiotracer that can bind independently of the D2R is of high importance to further understand the behavior of the D3R in the CNS.
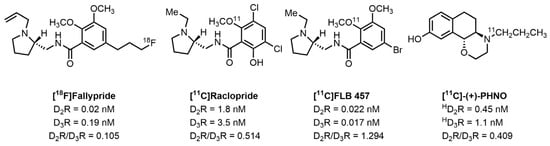
Figure 1.
Structure and data of radiotracers for imaging D2-like receptors.
The high structural similarity of the D2R and D3R (78% similar in the transmembrane spanning region) [4], has presented a challenge in the development of a D3R versus a D2R selective ligand [32]. During the past decade, a number of D3R selective ligands with the phenylpiperazine structure have been reported. Our group has reported Fluortriopride (FTP; LS-3-134) [33] (Figure 2), which has high D3R affinity (Ki = 0.17 nM) and good selectivity versus the D2R (163-fold). The 1,2,4-triazole-based scaffold also has notable D3R versus D2R selectivity. For example, GSK598,809 (D3R Ki = 3.2 nM) [34] represents a D3R selective ligand with this scaffold and has a 670-fold D3R vs. D2R selectivity. Based on the structure of tranylcypromine, Chen et al. [35] reported a D3R ligand (CJ-1882) with 2.8 nM affinity for the D3R and 223-fold D3R versus D2R selectivity. Recently, we reported a flexible scaffold structure (HY-2-93) with 0.8 nM affinity for the D3R and 180-fold D3R versus D2R selectivity [36].
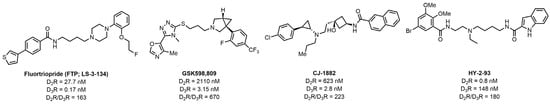
Figure 2.
The D3R versus D2R selective ligands.
This report describes the continuation of our effort to identify D3R antagonists having a high selectivity versus the D2R as a potential PET radiotracer for in vivo imaging studies. Our recent structure–activity relationship (SAR) studies based on Fallypride revealed some critical factors for designing a D3R versus D2R selective ligand [37]. These results, together with the flexible D3R ligands we reported previously [36], inspired us to design a D3R selective antagonist by introducing a flexible secondary binding fragment (SBF) based on Fallypride.
2. Results
2.1. Chemistry
As shown in Scheme 1, we used a two-step route to prepare the Fallypride-based bitopic ligands. First, a mixture of (S,R)-trans-1 and 1,1-carbonyldiimidazole (CDI) in acetonitrile was stirred overnight. Second, the corresponding amines reacted with the crude product from the previous step in toluene at 100 °C, delivering the designed bitopic ligands (R,S)-trans-2a–j in good yield.
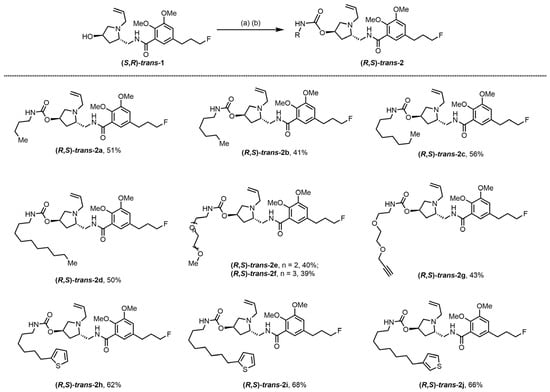
Scheme 1.
Synthesis of bitopic ligands (R,S)-trans-2a–j based on Fallypride. Reagents and conditions: (a) 1,1′-Carbonyldiimidazole (CDI), MeCN, rt, overnight; (b) RNH2, toluene, 100 °C, overnight.
Next, in Scheme 2, the chirality of orthosteric binding fragments (OBFs) was explored. The diastereomers and enantiomers of (R,S)-trans-2d and (R,S)-trans-2i were prepared. (R,S)-trans-1, (S,S)-trans-1 or (R,R)-trans-1, the diastereomers and enantiomers of (S,R)-trans-1, reacted with CDI in acetonitrile. The generated intermediate was further treated with the corresponding amines in toluene at 100 °C to give the diastereomers and enantiomers of (R,S)-trans-2d and (R,S)-trans-2i.
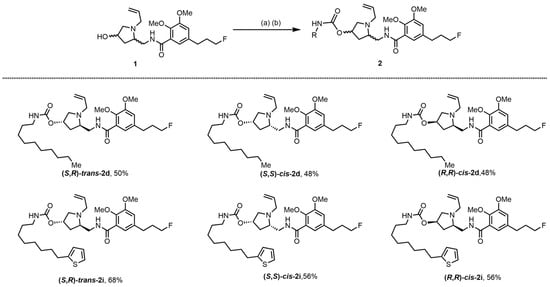
Scheme 2.
Synthesis of bitopic ligands based Fallypride. Reagents and conditions: (a) 1,1′-Carbonyldiimidazole (CDI), MeCN, rt, overnight; (b) RNH2, toluene, 100 °C, overnight.
2.2. SAR Study of Flexible Bitopic Ligands towards D2R and D3R
The compounds synthesized in Scheme 1 and Scheme 2 were submitted for in vitro binding assays measuring their affinity for D3R and D2R. The results of the binding assays are shown in Table 1 and Table 2.

Table 1.
The results of D3R vs. D2R affinity and β-arrestin assay IC50 a.

Table 2.
The results of D3R vs. D2R affinity and β-arrestin assay IC50 a.
Ligands with a flexible aliphatic linker (i.e., (R,S)-trans-2a–d) have a high affinity for the D3R; as the length of the aliphatic linkers increased, their affinity for the D2R decreased. These results suggest that bitopic ligands with longer aliphatic linkers increase the selectivity for the D3R versus the D2R. Bitopic ligands with a polyethylene glycol (PEG) as a flexible linker were also evaluated ((R,S)-trans-2e–g). Although these bitopic ligands maintained high affinity for the D3R, they did not have the expected higher D3R versus D2R selectivity. The ligands (R,S)-trans-2h–j, which have a flexible linker containing a thiophene in the SBF, were evaluated for their affinity for the D2R and D3R. The 2-thiophene analog with a 6-carbon spacer, (R,S)-trans-2h, had a sub-nanomolar affinity for the D3R (Ki = 0.6 ± 0.1 nM); increasing the spacer group to 8 carbon atoms did not affect the D3R affinity (Ki = 0.7 ± 0.1 nM). The analog having a 6-carbon spacer with a 3-thiophene had lower D3R affinity relative to its 2-thiophene congener, (R,S)-trans-2h.
We next evaluated the effect of the chirality of OBFs (Table 2). The enantiomers and diastereomers of (R,S)-trans-2d and (R,S)-trans-2i were utilized for this as these two ligands have comparatively better affinity for the D3R. Changing the chiral centers of OBFs has a dramatic effect on their affinity for the D2R and D3R. (S,R)-trans-2d is an enantiomer of (R,S)-trans-2d. The affinity for the D2R and the D3R decreased one thousand-fold to 1945 nM and 2628 nM, respectively. Meanwhile, the D2R and D3R affinity of (S,S)-cis-2d and (R,R)-cis-2d, the diastereomers of (R,S)-trans-2d, were decreased by one hundred to one thousand-fold. These results were also observed for the enantiomer and diastereomers of (R,S)-trans-2i.
2.3. β-Arrestin Competition Assay
A β-arrestin competition assay was conducted to determine the potency of the above-mentioned compounds for competing with dopamine (30 nM) for the D3R. High potency in this assay (EC50 ~2 nM) is needed in order to compete with synaptic dopamine for binding to the D3R in vivo [39]. As shown in Table 1, (R,S)-trans-2a has high potency in the β-arrestin assay. Compounds having a longer aliphatic linker ((R,S)-trans-2b–d) have a similar IC50 value in this assay. As expected, the IC50 value of β-arrestin assay parallels the Ki value in the D3R binding assay. It is of interest to note that the potency of (R,S)-trans-2a in the β-arrestin assay is higher than its potency in the in vitro binding assay for the D3R.
2.4. Molecular Dynamic Simulation (MDS) Studies
The representative binding poses for the D3R or D2R from the MDS production runs for four compounds with different lengths of aliphatic groups in the SBFs ((R,S)-trans-2a, (R,S)-trans-2b, (R,S)-trans-2c, and (R,S)-trans-2d) are shown in Figure 3. The “Fallypride” fragment of all four compounds posed in the orthosteric binding pocket interacted with the amino acid residues at transmembrane (TM) 3, 5, and 6 in both the D2R and the D3R. The SBF of all four compounds interacted with the amino acid residues in TM 2 and 7 in the secondary binding site for the D3R. For the D2R, the SBF of the four compounds interacted with the secondary binding pocket (TM 2 and 7) or the loop region, EC1 or EC2. Hydrogen bonds formed between ASP1103.32 and the protonated nitrogen in the pyrrolidine ring, the key interaction that has been reported for the D3R [39,40], were observed in all four compounds in the D3R (Figure 3A–D). The benzene rings of (R,S)-trans-2a, (R,S)-trans-2b, and (R,S)-trans-2c formed a π-stacking interaction with PHE3456.51 in the orthosteric binding pocket of the D3R (Figure 3A–C). For the D2R, a hydrogen bond or salt bridge formed between ASP1143.32 and the protonated nitrogen in the pyrrolidine ring (the key interaction that has been reported for D2R [41,42]) was observed in the MDS for all four compounds (Figure 3F–I). The absence of a π-stacking interaction in the orthosteric binding site of the D2R may partially explain the higher affinity of the four compounds for the D3R.
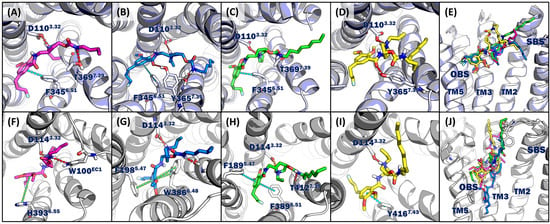
Figure 3.
Representative ligand–protein complex from MDS with the key interaction residues of D3R (A–E) or D2R (F–J) with four compounds having different lengths of SBFs. Ligand–D3R complex of (A) (R,S)-trans-2a, (B) (R,S)-trans-2b, (C) (R,S)-trans-2c, (D) (R,S)-trans-2d, and (E) superposition of four ligand–D3R complexes. Ligand–D2R complex of (F) (R,S)-trans-2a, (G) (R,S)-trans-2b, (H) (R,S)-trans-2c, (I) (R,S)-trans-2d, and (J) superposition of four ligand–D2R complexes. Red: hydrogen bond; orange: salt bridge; green: π–π interaction; cyan: π-stacking; OBS: orthosteric binding site; SBS: secondary binding site; TM: transmembrane.
The distance between the protonated nitrogen in the pyrrolidine ring of six ligands ((R,S)-trans-2a-d, (R,S)-trans-2h, and (R,S)-trans-2i) and ASP1103.32 in the D3R was in the range of 3.28 to 3.79 Å (Table 3); this distance is greater than that with Fallypride (3.17 ± 0.21 Å) [39]. This indicates that these compounds have weaker interactions with ASP1103.32 in the D3R compared to Fallypride, resulting in a reduction in the binding affinity for the D3R. Furthermore, the distance between ASP1143.32 in the D2R and the protonated nitrogen in the pyrrolidine ring of the six ligands was greater (3.45 to 9.32 Å; Table 3) and had a higher standard deviation (0.94 to 2.20 Å; Table 3); these results are consistent with the low stability of these compounds in the binding pocket and are reflected in the lower binding affinity of the six compounds for the D2R.

Table 3.
The distance between the protonated nitrogen in the pyrrolidine ring of ligand and ASP1103.32 in the D3R and ASP1143.32 in the D2R.
Another method for studying ligand–protein interactions is to measure the frequency of the contact between the ligand and amino acid residues in the ligand binding site. The summary of the frequency of contacts for each compound in the D3R or D2R is shown in Figure 4. A stable salt bridge or hydrogen bound was formed between ASP1103.32 in the D3R and the pyrrolidine nitrogen in all six compounds (frequency of contact > 0.8; Figure 4A). Consequently, (R,S)-trans-2a-d, (R,S)-trans-2h, and (R,S)-trans-2i all had high affinity for the D3R (0.6–3.4 nM). For the D2R, (R,S)-trans-2a-d, (R,S)-trans-2h, and (R,S)-trans-2i displayed a poor to moderate probability of forming a hydrogen bound with ASP1143.32 (frequency of contact = 0.01–0.81; Figure 4B). There was also a wide range in the probability of forming hydrophobic interactions (0.15–0.87) in the orthosteric binding pocket (TM 3 and 5; Figure 4B). The low interaction with ASP1143.32 and variable hydrophobic interactions likely explain the high range in the D2R affinity for the six compounds.
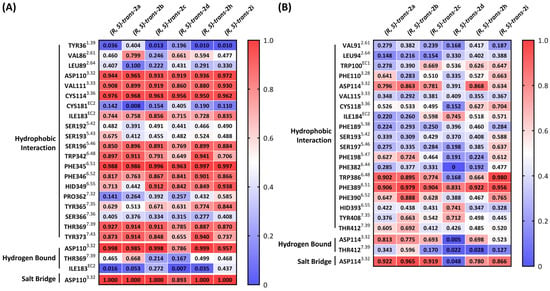
Figure 4.
Summary of frequency of interactions between ligands and the residues in the binding pocket of (A) D3R and (B) D2R.
Although there were differences in the interaction of (R,S)-trans-2a-d, (R,S)-trans-2h, and (R,S)-trans-2i with VAL862.61 in the secondary binding pocket of the D3R, this interaction was inconsequential since all six compounds had similar affinity for the D3R. On the other hand, the interaction of the SBF with the D2R may play a role in the D2R affinity of the six ligands. (R,S)-trans-2c, (R,S)-trans-2d, (R,S)-trans-2h, and (R,S)-trans-2i, which have a longer length of the SBF (8 and 10 carbon spacer group), displayed a higher frequency of contact of TRP100EC1 in the loop between TM 2 and 3 (EC1) and ILE184EC2 in the loop between TM 4 and 5 (EC2; Figure 4B). The favorable interaction of (R,S)-trans-2c and (R,S)-trans-2d with the loop region of EC2 interferes with the formation of the hydrogen bond with ASP1143.32, and this likely explains the lower D2R affinity of (R,S)-trans-2c and (R,S)-trans-2d.
3. Discussion
We prepared a panel of bitopic D3R ligands based on Fallypride with the goal of developing a D3R selective antagonist. The most D3R selective compounds were (R,S)-trans-2c and (R,S)-trans-2d, which had a ~3 nM affinity for the D3R and 5–10-fold selectivity versus the D2R. This selectivity was attributed to their reduced affinity for the D2R, which was likely caused by the lower interactions in the orthosteric binding site of the D2R. (R,S)-trans-2a had higher potency (IC50 = 0.8 ± 0.5 nM) to compete with dopamine than Fallypride (IC50 = 1.7 ± 0.8 nM) in the β-arrestin recruitment assay, which was unexpected given its lower affinity for the D3R relative to Fallypride. The reason for this discrepancy between the receptor affinity and potency in the β-arrestin competition assay is not clear. (R,S)-trans-2d had modest D3R versus D2R selectivity (~12.7-fold) and a much better ability to compete with endogenous dopamine (IC50 = 21.2 ± 9.8 nM) than the highly D3R-selective radiotracer FTP (IC50 = 611.7 ± 101.3 nM). Increasing the length and steric bulk of the flexible linker in the SBF did not improve the D3R versus D2R selectivity. This structural modification also reduced the affinity of the bitopic compounds for both the D3R and the D2R relative to that of Fallypride, which is largely due to the effect of the substituent in the SBF increasing the distance between the pyrrolidine nitrogen and the key ASP3.32 residues in the orthosteric binding site of the D3R and the D2R. Consequently, the SAR studies described above indicate that the modification of Fallypride to contain an SBF does not improve the selectivity of this scaffold that is needed to generate a D3R-selective PET radiotracer.
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Chemistry
The starting materials and anhydrous solvents were purchased from Sigma-Aldrich, TCI America, Alfa Aesar, and Ambeed and were used without further purification. 5-(3-fluoropropyl)-2,3-dimethoxybenzoic acid was prepared using a reported method. The NMR spectra were taken on a Bruker DMX 400 MHz. The chemical shifts (δ) in the NMR spectra (1H and 13C) were referenced by assigning the residual solvent peaks. The purification of organic compounds was carried out on a Biotage Isolera One with a dual-wavelength UV−vis detector (silica gel: 230−400 mesh, 60 Å). The compound structures and identity were confirmed by 1H- and 13C NMR and mass spectrometry (Supplementary Materials). The procedure for the synthesis of 1 can be found in our previous report [37].
General Methods for the Synthesis of 2
A mixture of 1 (0.2 mmol) and 1,1′-Carbonyldiimidazole (CDI) (0.2 mmol) in acetonitrile (4 mL) was stirred at room temperature overnight. The solvent was removed under a vacuum, and the crude product was used for the next step directly.
A solution of the crude product mentioned above and the corresponding amine (0.4 mmol) in toluene was heated to 100 °C overnight. The solvent was removed under vacuum, and the crude product was purified by flash silica chromatography (CH2Cl2/MeOH = 95:5) to afford 2.
(3R,5S)-1-allyl-5-((5-(3-fluoropropyl)-2,3-dimethoxybenzamido)methyl)pyrrolidin-3-yl butylcarbamate ((R,S)-trans-2a). A total of 49 mg colorless oil, 51% yield. 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ 8.40 (s, 1H), 7.53 (d, J = 2.1 Hz, 1H), 6.87 (d, J = 2.1 Hz, 1H), 6.00–5.72 (m, 1H), 5.21 (d, J = 17.1 Hz, 1H), 5.12 (d, J = 9.4 Hz, 1H), 5.05 (s, 1H), 4.62 (s, 1H), 4.51 (t, J = 5.9 Hz, 1H), 4.39 (t, J = 5.9 Hz, 1H), 3.89 (s, 3H), 3.87 (s, 3H), 3.85–3.81 (m, 1H), 3.54–3.48 (m, 2H), 3.36 (s, 1H), 3.14 (q, J = 6.7 Hz, 2H), 2.98 (s, 2H), 2.77–2.66 (m, 2H), 2.42 (s, 1H), 2.08–1.90 (m, 4H), 1.50–1.41 (m, 2H), 1.39–1.28 (m, 2H), 0.91 (t, J = 7.3 Hz, 3H); 13C NMR (101 MHz, CDCl3) δ 165.7, 156.1, 152.6, 146.0, 137.5, 135.2, 126.4, 122.3, 117.6, 115.8, 83.2 (d, J = 164.9 Hz), 72.7, 61.5, 60.6, 59.7, 56.5, 56.2, 40.8, 39.8, 35.8, 32.2, 32.0 (d, J = 19.8 Hz), 31.3 (d, J = 5.4 Hz), 20.0, 13.8. HRMS (ESI) calculated for C25H38FN3O5Na+ ([M + Na+]) 502.2693, found: 502.2688.
(3R,5S)-1-allyl-5-((5-(3-fluoropropyl)-2,3-dimethoxybenzamido)methyl)pyrrolidin-3-yl hexylcarbamate ((R,S)-trans-2b). A total of 42 mg colorless oil, 41% yield. 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ 8.42 (s, 1H), 7.53 (d, J = 2.1 Hz, 1H), 6.87 (d, J = 2.1 Hz, 1H), 5.89 (s, 1H), 5.22 (d, J = 17.2 Hz, 1H), 5.13 (d, J = 9.1 Hz, 1H), 5.06 (s, 1H), 4.62 (s, 1H), 4.51 (t, J = 5.9 Hz, 1H), 4.39 (t, J = 5.9 Hz, 1H), 3.89 (s, 7H), 3.60–3.50 (t, J = 6.5 Hz, 2H), 3.37 (s, 1H), 3.14 (q, J = 6.8 Hz, 2H), 2.98 (s, 2H), 2.77–2.70 (m, 2H), 2.43 (s, 1H), 2.09–1.91 (m, 4H), 1.50–1.43 (m, 2H), 1.32–1.25 (m, 6H), 0.88 (t, J = 6.8 Hz, 3H); 13C NMR (101 MHz, CDCl3) δ 165.8, 156.0, 152.6, 146.1, 137.5, 135.3, 126.3, 122.3, 117.7, 115.9, 83.2 (d, J = 164.9 Hz), 72.7, 61.5, 60.5, 59.7, 56.2, 41.1, 39.8, 35.8, 32.0 (d, J = 19.8 Hz), 31.6, 31.3 (d, J = 5.3 Hz), 30.0, 26.5, 22.7, 14.1. HRMS (ESI) calculated for C27H43FN3O5 + ([M + H+]) 508.3181, found: 508.3178.
(3R,5S)-1-allyl-5-((5-(3-fluoropropyl)-2,3-dimethoxybenzamido)methyl)pyrrolidin-3-yl octylcarbamate ((R,S)-trans-2c). A total of 60 mg colorless oil, 56% yield. 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ 8.41 (s, 1H), 7.53 (d, J = 2.2 Hz, 1H), 6.87 (d, J = 2.2 Hz, 1H), 5.96–5.81 (m, 1H), 5.22 (d, J = 17.1 Hz, 1H), 5.13 (d, J = 9.3 Hz, 1H), 5.06 (s, 1H), 4.63 (s, 1H), 4.51 (t, J = 5.9 Hz, 1H), 4.39 (t, J = 5.9 Hz, 1H), 3.88 (s, 7H), 3.63–3.47 (m, 2H), 3.37 (s, 1H), 3.13 (q, J = 6.8 Hz, 2H), 2.98 (s, 2H), 2.76–2.70 (m, 2H), 2.43 (s, 1H), 2.09–1.88 (m, 4H), 1.50–1.43 (m, 2H), 1.31–1.25 (m, 10H), 0.89–0.84 (m, 3H); 13C NMR (101 MHz, CDCl3) δ 165.8, 156.1, 152.6, 146.1, 137.5, 135.1, 126.3, 122.3, 117.6, 115.8, 83.2 (d, J = 164.9 Hz), 72.6, 61.5, 60.6, 59.7, 56.2, 41.1, 39.8, 35.8, 32.0 (d, J = 19.8 Hz), 31.9, 31.3 (d, J = 5.3 Hz), 29.3, 29.3, 26.9, 22.8, 14.2. HRMS (ESI) calculated for C29H47FN3O5+ ([M + H+]) 536.3494, found: 536.3506.
(3R,5S)-1-allyl-5-((5-(3-fluoropropyl)-2,3-dimethoxybenzamido)methyl)pyrrolidin-3-yl decylcarbamate ((R,S)-trans-2d) and (3S,5R)-1-allyl-5-((5-(3-fluoropropyl)-2,3-dimethoxybenzamido)methyl)pyrrolidin-3-yl decylcarbamate ((S,R)-trans-2d). A total of 56 mg colorless oil, 50% yield. 1H-NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ 8.47–8.32 (m, 1H), 7.53 (d, J = 2.2 Hz, 1H), 6.86 (d, J = 2.1 Hz, 1H), 5.94–5.80 (m, 1H), 5.20 (d, J = 17.1 Hz, 1H), 5.12 (d, J = 10.0 Hz, 1H), 5.05 (s, 1H), 4.64 (s, 1H), 4.50 (t, J = 5.9 Hz, 1H), 4.38 (t, J = 5.9 Hz, 1H), 3.88–3.80 (m, 7H), 3.59–3.45 (m, 2H), 3.36 (s, 1H), 3.13 (q, J = 6.8 Hz, 2H), 2.98 (s, 2H), 2.75–2.71 (m, 2H), 2.41 (s, 1H), 2.09–1.88 (m, 4H), 1.50–1.43 (m, 2H), 1.30–1.24 (m, 14H), 0.86 (t, J = 6.7 Hz, 3H); 13C NMR (101 MHz, CDCl3) δ 165.7, 156.1, 152.6, 146.0, 137.5, 135.2, 126.3, 122.3, 117.6, 115.8, 83.1 (d, J = 165.0 Hz), 72.6, 61.4, 60.6, 59.7, 56.5, 56.2, 41.1, 39.8, 35.8, 32.0, 32.0 (d, J = 19.8 Hz), 31.3 (d, J = 5.2 Hz), 30.1, 29.6, 29.4, 29.4, 26.9, 22.8, 14.2. HRMS (ESI) calculated for C31H51FN3O5+ ([M + H+]) 564.3807, found: 564.3838.
(3R,5S)-1-allyl-5-((5-(3-fluoropropyl)-2,3-dimethoxybenzamido)methyl)pyrrolidin-3-yl (2-(2-(2-methoxyethoxy)ethoxy)ethyl)carbamate ((R,S)-trans-2e). A total of 46 mg colorless oil, 40% yield. 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ 8.40 (s, 1H), 7.51 (d, J = 2.1 Hz, 1H), 6.85 (d, J = 2.2 Hz, 1H), 5.91–5.85 (m, 1H), 5.27 (s, 1H), 5.20 (d, J = 17.1 Hz, 1H), 5.11 (d, J = 10.2 Hz, 1H), 5.04 (s, 1H), 4.49 (t, J = 5.9 Hz, 1H), 4.37 (t, J = 5.9 Hz, 1H), 3.87–3.79 (d, J = 3.2 Hz, 7H), 3.70–3.59 (m, 9H), 3.54–3.50 (m, 5H), 3.36 (s, 3H), 3.32 (q, J = 5.2 Hz, 2H), 2.98 (s, 2H), 2.71 (t, J = 7.7 Hz, 2H), 2.43 (s, 1H), 2.07–1.91 (m, 4H); 13C NMR (101 MHz, CDCl3) δ 165.7, 156.2, 152.6, 146.0, 137.4, 135.0, 126.3, 122.2, 117.8, 115.8, 83.1 (d, J = 164.9 Hz), 72.7, 72.0, 70.59, 70.56, 70.3, 70.1, 61.4, 60.6, 59.6, 59.1, 56.5, 56.2, 40.8, 39.7, 35.7, 31.9 (d, J = 19.8 Hz), 31.3 (d, J = 5.2 Hz). HRMS (ESI) calculated for C28H45FN3O8+ ([M + H+]) 570.3185, found: 570.3204.
(3R,5S)-1-allyl-5-((5-(3-fluoropropyl)-2,3-dimethoxybenzamido)methyl)pyrrolidin-3-yl (2,5,8,11-tetraoxatridecan-13-yl)carbamate ((R,S)-trans-2f). A total of 48 mg colorless oil, 39% yield. 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ 8.42 (s, 1H), 7.52 (s, 1H), 6.87 (d, J = 2.2 Hz, 1H), 5.89 (s, 1H), 5.36–4.97 (m, 4H), 4.51 (t, J = 5.9 Hz, 1H), 4.39 (t, J = 5.9 Hz, 1H), 3.89 (s, 7H), 3.72–3.57 (m, 12H), 3.55–3.53(m, 5H), 3.37 (s, 3H), 3.36–3.30 (m, 2H), 3.10–2.86 (m, 2H), 2.76–2.71 (m, 2H), 2.43 (s, 1H), 2.12–1.88 (m, 4H); 13C NMR (101 MHz, CDCl3) δ 165.7, 156.1, 152.5, 146.0, 137.4, 134.9, 126.2, 122.2, 117.8, 115.7, 83.1 (d, J = 164.9 Hz), 72.6, 72.0, 70.63, 70.61, 70.58, 70.51, 70.3, 70.1, 61.4, 60.6, 59.6, 59.1, 56.5, 56.1, 40.8, 39.7, 35.7, 31.9 (d, J = 19.7 Hz), 31.2 (d, J = 5.2 Hz). HRMS (ESI) calculated for C30H48FN3O9Na+ ([M + H+]) 636.3267, found: 636.3267.
(3R,5S)-1-allyl-5-((5-(3-fluoropropyl)-2,3-dimethoxybenzamido)methyl)pyrrolidin-3-yl (2-(2-(prop-2-yn-1-yloxy)ethoxy)ethyl)carbamate ((R,S)-trans-2g). A total of 47 mg colorless oil, 43% yield. 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ 8.41 (s, 1H), 7.52 (d, J = 2.1 Hz, 1H), 6.86 (d, J = 2.1 Hz, 1H), 5.97–5.80 (m, 1H), 5.26–5.02 (m, 4H), 4.50 (t, J = 5.8 Hz, 1H), 4.39 (t, J = 5.8 Hz, 1H), 4.19 (s, 2H), 3.88– 3.81 (m, 7H), 3.71–3.62 (m, 5H), 3.59–3.48 (m, 4H), 3.35 (q, J = 5.5 Hz, 2H), 3.00 (s, 2H), 2.73 (t, J = 7.7 Hz, 2H), 2.45–2.44 (m, 2H), 2.11–1.91 (m, 4H); 13C NMR (101 MHz, CDCl3) δ 165.7, 156.1, 152.6, 146.0, 137.5, 135.2, 126.3, 122.3, 117.7, 115.8, 83.2 (d, J = 164.9 Hz), 79.6, 74.9, 72.8, 70.3, 70.2, 69.2, 61.5, 60.6, 59.6, 58.6, 56.6, 56.2, 40.8, 39.8, 35.8, 32.0 (d, J = 19.7 Hz), 31.3 (d, J = 5.2 Hz). HRMS (ESI) calculated for C28H41FN3O7+ ([M + H+]) 550.2923, found: 550.2917.
(3R,5S)-1-allyl-5-((5-(3-fluoropropyl)-2,3-dimethoxybenzamido)methyl)pyrrolidin-3-yl (6-(thiophen-2-yl)hexyl)carbamate ((R,S)-trans-2h). A total of 73 mg colorless oil, 62% yield. 1H-NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ 8.40 (d, J = 5.9 Hz, 1H), 7.53 (d, J = 2.2 Hz, 1H), 7.09 (dd, J = 5.2, 1.2 Hz, 1H), 6.91–6.85 (m, 2H), 6.76–6.74 (m, 1H), 5.91–5.81 (m, 1H), 5.20 (dd, J = 17.0, 1.8 Hz, 1H), 5.11 (d, J = 10.2 Hz, 1H), 5.04 (s, 1H), 4.67 (s, 1H), 4.50 (t, J = 5.9 Hz, 1H), 4.38 (t, J = 5.9 Hz, 1H), 3.89–3.81 (m, 7H), 3.58–3.44 (m, 2H), 3.38–3.27 (m, 1H), 3.13 (q, J = 6.7 Hz, 2H), 3.04–2.90 (m, 2H), 2.80 (t, J = 7.6 Hz, 2H), 2.76–2.69 (m, 2H), 2.41 (s, 1H), 2.09–1.91 (m, 4H), 1.70–1.63 (m, 2H), 1.51–1.44 (m, 2H), 1.38–1.32 (m, 4H); 13C NMR (101 MHz, CDCl3) δ 165.7, 156.1, 152.6, 146.0, 145.6, 137.5, 135.2, 126.7, 126.3, 124.1, 122.9, 122.3, 117.6, 115.8, 83.1 (d, J = 165.0 Hz), 72.6, 61.4, 60.5, 59.7, 56.4, 56.2, 41.0, 39.7, 35.7, 32.0 (d, J = 19.7 Hz), 31.7, 31.3 (d, J = 5.2 Hz), 30.0, 29.9, 28.8, 26.5. HRMS (ESI) calculated forC31H45FN3O5S+ ([M + H+]) 590.3058, found: 590.3052.
(3R,5S)-1-allyl-5-((5-(3-fluoropropyl)-2,3-dimethoxybenzamido)methyl)pyrrolidin-3-yl (8-(thiophen-2-yl)octyl)carbamate ((R,S)-trans-2i) or (3S,5R)-1-allyl-5-((5-(3-fluoropropyl)-2,3-dimethoxybenzamido)methyl)pyrrolidin-3-yl (8-(thiophen-2-yl)octyl)carbamate ((S,R)-trans-2i). A total of 84 mg colorless oil, 68% yield. 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ 8.40 (d, J = 5.3 Hz, 1H), 7.54 (d, J = 2.1 Hz, 1H), 7.09 (d, J = 5.1 Hz, 1H), 6.92–6.89 (m, 1H), 6.87 (d, J = 2.1 Hz, 1H), 6.76 (d, J = 3.4 Hz, 1H), 5.94–5.80 (m, 1H), 5.21 (d, J = 17.1 Hz, 1H), 5.11 (d, J = 10.2 Hz, 1H), 5.05 (s, 1H), 4.64 (s, 1H), 4.51 (t, J = 5.9 Hz, 1H), 4.39 (t, J = 5.9 Hz, 1H), 3.88 (d, 6H), 3.85–3.79 (m, 1H), 3.57–3.47 (m, 2H), 3.40–3.27 (m, 1H), 3.13 (q, J = 6.8 Hz, 2H), 3.03–2.91 (m, 2H), 2.80 (t, J = 7.6 Hz, 2H), 2.77–2.66 (m, 2H), 2.41 (s, 1H), 2.11–1.87 (m, 4H), 1.69–1.62 (m, 2H), 1.50–1.45 (m, 2H), 1.35–1.29 (m, 8H); 13C NMR (101 MHz, CDCl3) δ 165.7, 156.1, 152.6, 146.0, 145.8, 137.5, 135.2, 126.7, 126.4, 124.0, 122.8, 122.3, 117.5, 115.8, 83.1 (d, J = 165.0 Hz), 72.7, 61.4, 60.5, 59.7, 56.5, 56.2, 41.1, 39.7, 35.8, 32.0 (d, J = 19.9 Hz), 31.8, 31.3 (d, J = 5.3 Hz), 30.1, 30.0, 29.3, 29.3, 29.1, 26.8. HRMS (ESI) calculated for C33H48FN3O5SNa+ ([M + Na+]) 618.3371, found: 618.3379.
(3R,5S)-1-allyl-5-((5-(3-fluoropropyl)-2,3-dimethoxybenzamido)methyl)pyrrolidin-3-yl (8-(thiophen-3-yl)octyl)carbamate ((R,S)-trans-2j). A total of 81 mg colorless oil, 66% yield. 1H-NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ 8.42 (s, 1H), 7.53 (s, 1H), 7.23 (t, J = 4.0 Hz, 1H), 6.93–6.87 (m, 2H), 6.87 (s, 1H), 6.00–5.80 (m, 1H), 5.30–5.05 (m, 3H), 4.62 (s, 1H), 4.51 (t, J = 5.9 Hz, 1H), 4.39 (t, J = 5.9 Hz, 1H), 3.89 (s, 7H), 3.64–3.43 (m, 2H), 3.35 (s, 1H), 3.14 (q, J = 6.8 Hz, 2H), 3.03–2.88 (m, 2H), 2.73 (t, J = 7.7 Hz, 2H), 2.61 (t, J = 7.7 Hz, 2H), 2.43 (s, 1H), 2.08–1.92 (m, 4H), 1.62–1.57 (m, 2H), 1.49–1.43 (m, 2H), 1.33–1.30 (m, 8H); 13C NMR (101 MHz, CDCl3) δ 165.7, 155.9, 152.5, 146.0, 143.1, 137.4, 135.2, 128.3, 126.2, 125.1, 122.1, 119.8, 117.7, 115.8, 83.0 (d, J = 165.0 Hz), 72.5, 61.4, 59.5, 56.1, 41.0, 39.8, 35.7, 31.9 (d, J = 19.8 Hz), 31.2 (d, J = 5.3 Hz), 30.5, 30.2, 29.9, 29.3, 29.21, 29.19, 26.7. HRMS (ESI) calculated for C33H48FN3O5SNa+ ([M + Na+]) 640.3191, found: 640.3209.
(3S,5S)-1-allyl-5-((5-(3-fluoropropyl)-2,3-dimethoxybenzamido)methyl)pyrrolidin-3-yl decylcarbamate ((S,S)-cis-2d) and (3R,5R)-1-allyl-5-((5-(3-fluoropropyl)-2,3-dimethoxybenzamido)methyl)pyrrolidin-3-yl decylcarbamate ((R,R)-cis-2d). A total of 54 mg colorless oil, 48% yield. 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ 8.49 (s, 1H), 7.56 (s, 1H), 6.86 (s, 1H), 5.88–5.85 (m, 1H), 5.33 (s, 1H), 5.21 (d, J = 17.1 Hz, 1H), 5.13–5.07 (m, 2H), 4.52 (t, J = 5.9 Hz, 1H), 4.40 (t, J = 5.9 Hz, 1H), 3.87 (s, 6H), 3.68 (s, 1H), 3.49 (d, J = 14.0 Hz, 2H), 3.20 (d, J = 8.8 Hz, 1H), 3.10–2.81 (m, 4H), 2.74 (t, J = 7.7 Hz, 2H), 2.48–2.31 (m, 2H), 2.08 –1.95 (m, 2H), 1.77–1.73 (m, 2H), 1.30–1.24 (m, 16H), 0.87 (t, J = 6.6 Hz, 3H); 13C NMR (101 MHz, CDCl3) δ 165.7, 156.3, 152.6, 137.8, 135.2, 123.4, 122.4, 117.5, 115.3, 83.2 (d, J = 165.0 Hz), 72.3, 61.4, 60.1, 56.5, 55.9, 41.2, 41.0, 35.6, 32.0 (d, J = 19.9 Hz), 32.0, 31.4 (d, J = 5.3 Hz), 30.0, 29.7, 29.7, 29.5, 29.4, 26.9, 22.8, 14.2. HRMS (ESI) calculated for C31H51FN3O5+ ([M + H+]) 564.3807, found: 564.3806.
(3S,5S)-1-allyl-5-((5-(3-fluoropropyl)-2,3-dimethoxybenzamido)methyl)pyrrolidin-3-yl (8-(thiophen-2-yl)octyl)carbamate ((S,S)-cis-2i) and (3R,5R)-1-allyl-5-((5-(3-fluoropropyl)-2,3-dimethoxybenzamido)methyl)pyrrolidin-3-yl (8-(thiophen-2-yl)octyl)carbamate ((R,R)-cis-2i). A total of 69 mg colorless oil, 56% yield. 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ 8.49 (s, 1H), 7.57 (s, 1H), 7.10 (d, J = 5.0 Hz, 1H), 6.92–6.90 (m, 1H), 6.86 (s, 1H), 6.77 (d, J = 3.4 Hz, 1H), 5.86 (s, 1H), 5.33 (s, 1H), 5.21 (d, J = 17.1 Hz, 1H), 5.16–5.06 (m, 2H), 4.51 (t, J = 5.9 Hz, 1H), 4.40 (t, J = 5.9 Hz, 1H), 3.87 (s, 6H), 3.68 (s, 1H), 3.49 (s, 2H), 3.20 (s, 1H), 3.10–2.98 (m, 2H), 2.94–2.88 (m, 2H), 2.80 (t, J = 7.6 Hz, 2H), 2.74 (t, J = 7.8 Hz, 2H), 2.52–2.30 (m, 2H), 2.08–1.95 (m, 2H), 1.76 (d, J = 14.2 Hz, 1H), 1.77–1.62 (m, 4H), 1.38–1.23 (m, 9H); 13C NMR (101 MHz, CDCl3) δ 165.7, 156.4, 152.6, 145.9, 137.8, 135.5, 126.8, 124.1, 122.9, 122.4, 117.6, 115.3, 83.2 (d, J = 165.1 Hz), 72.4, 61.4, 60.1, 56.4, 56.0, 41.2, 41.0, 35.6, 32.0 (d, J = 19.8 Hz), 31.9, 31.4 (d, J = 5.2 Hz), 30.0, 30.0, 29.4, 29.4, 29.2, 26.9. HRMS (ESI) calculated for C33H48FN3O5SNa+ ([M + H+]) 640.3191, found: 640.3200.
4.2. Receptor Binding and β-Arrestin Assays
The receptor binding assay for the D2R and the D3R and the β-arrestin recruitment assay for the D3R were performed by following the previously reported methods [37].
4.3. Molecular Docking and Molecular Dynamics Simulation (MDS) Studies
The X-ray structures of the D2R (PDB ID: 6CM4, resolution 2.87 Å) and the D3R (PDB ID: 3PBL, resolution 2.89 Å) were obtained from the RCSB Protein Data Bank (https://www.rcsb.org/ (accessed on 12 November 2023)) to conduct the docking and MDS studies with (R,S)-trans-2a, (R,S)-trans-2b, (R,S)-trans-2c, (R,S)-trans-2d, (R,S)-trans-2h, and (R,S)-trans-2i. The docking and MDS studies were performed using the previously reported methods [37,39].
5. Conclusions
A panel of bitopic D3R ligands based on Fallypride was synthesized with the goal of developing a D3R selective ligand. The most selective compound, (R,S)-trans-2d, had a modest D3R versus D2R selectivity (~12.7-fold) and a much better ability to compete with endogenous dopamine (IC50 = 21.2 ± 9.8 nM) than the highly D3R-selective radiotracer FTP (IC50 = 611.7 ± 101.3 nM). Increasing the length and steric bulk of the flexible linker in the SBF did not improve the D3R versus D2R selectivity and resulted in a reduction in the affinity for the D3R. Computational chemistry studies revealed that this reduction in affinity was caused by an increase in the distance between the pyrrolidine nitrogen and ASP1103.32 in the D3R caused by the interaction of the substituents with the SBF.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/molecules29010123/s1, chemical purity, 1H and 13C NMP spectra.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, G.-L.T. and R.H.M.; Methodology, G.-L.T., J.Y.L., C.-J.H. and M.T.; Validation, R.R.L. and R.H.M.; Formal analysis, G.-L.T., J.Y.L., C.-J.H. and R.H.M.; Investigation, G.-L.T., J.Y.L., C.-J.H., M.T. and R.H.M.; Resources, R.R.L. and R.H.M.; Data curation, R.R.L. and R.H.M.; Writing—original draft, G.-L.T., J.Y.L., C.-J.H. and R.H.M.; Writing—review and editing, G.-L.T., C.-J.H. and R.H.M. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by a grant from the National Institute on Drug Abuse, grant number DA029840.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The article contains complete data used to support the findings of this study.
Acknowledgments
The molecular dynamic simulation studies were conducted on the high-performance computing cluster (https://www.med.upenn.edu/cbica/cubic.html (accessed on 12 November 2023)) at the University of Pennsylvania Center for Biomedical Image Computing and Analytics and supported by the National Institutes of Health, grant number: 1S10OD023495-01.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Gingrich, J.A.; Caron, M.G. Recent advances in the molecular biology of dopamine receptors. Annu. Rev. Neurosci. 1993, 16, 299–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Missale, C.; Nash, S.R.; Robinson, S.W.; Jaber, M.; Caron, M.G. Dopamine receptors: From structure to function. Physiol. Rev. 1998, 78, 189–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackson, D.M.; Westlind-Danielsson, A. Dopamine receptors: Molecular biology, biochemistry and behavioural aspects. Pharmacol. Ther. 1994, 64, 291–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luedtke, R.R.; Rangel-Barajas, C.; Malik, M.; Reichert, D.E.; H Mach, R. Bitropic D3 dopamine receptor selective compounds s potential antipsychotics. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2015, 21, 3700–3724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sokoloff, P.; Le Foll, B. The dopamine D3 receptor, a quarter century later. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2017, 45, 2–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keck, T.M.; John, W.S.; Czoty, P.W.; Nader, M.A.; Newman, A.H. Identifying medication targets for psychostimulant addiction: Unraveling the dopamine D3 receptor hypothesis. J. Med. Chem. 2015, 58, 5361–5380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leggio, G.M.; Bucolo, C.; Platania, C.B.M.; Salomone, S.; Drago, F. Current drug treatments targeting dopamine D3 receptor. Pharmacol. Ther. 2016, 165, 164–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, P.; Perlmutter, J.S.; Benzinger, T.L.; Morris, J.C.; Xu, J. Dopamine D3 receptor: A neglected participant in Parkinson Disease pathogenesis and treatment? Ageing Res. Rev. 2020, 57, 100994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gurevich, E.V.; Bordelon, Y.; Shapiro, R.M.; Arnold, S.E.; Gur, R.E.; Joyce, J.N. Mesolimbic dopamine D3 receptors and use of antipsychotics in patients with schizophrenia: A postmortem study. Arch. Gen. Psychiatry 1997, 54, 225–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gurevich, E.V.; Joyce, J.N. Distribution of dopamine D3 receptor expressing neurons in the human forebrain: Comparison with D2 receptor expressing neurons. Neuropsychopharmacology 1999, 20, 60–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morissette, M.; Goulet, M.; Grondin, R.; Blanchet, P.; Bédard, P.J.; Di Paolo, T.; Lévesque, D. Associative and limbic regions of monkey striatum express high levels of dopamine D3 receptors: Effects of MPTP and dopamine agonist replacement therapies. Eur. J. Neurosci. 1998, 10, 2565–2573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, J.; Cairns, N.J.; Perlmutter, J.S.; Mach, R.H.; Xu, J. Regulation of dopamine D3 receptor in the striatal regions and substantia nigra in diffuse Lewy body disease. Neuroscience 2013, 248, 112–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, J.; Xu, J.; Cairns, N.J.; Perlmutter, J.S.; Mach, R.H. Dopamine D1, D2, D3 receptors, vesicular monoamine transporter type-2 (VMAT2) and dopamine transporter (DAT) densities in aged human brain. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e49483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ledonne, A.; Mercuri, N.B. Current concepts on the physiopathological relevance of dopaminergic receptors. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2017, 11, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Volkow, N.D.; Fowler, J.S.; Wang, G.-J.; Swanson, J.M. Dopamine in drug abuse and addiction: Results from imaging studies and treatment implications. Mol. Psychiatry 2004, 9, 557–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Visanji, N.P.; Fox, S.H.; Johnston, T.; Reyes, G.; Millan, M.J.; Brotchie, J.M. Dopamine D3 receptor stimulation underlies the development of L-DOPA-induced dyskinesia in animal models of Parkinson’s disease. Neurobiol. Dis. 2009, 35, 184–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mash, D.C.; Staley, J.K. D3 dopamine and kappa opioid receptor alterations in human brain of cocaine-overdose victims. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 1999, 877, 507–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Staley, J.K.; Mash, D.C. Adaptive increase in D3 dopamine receptors in the brain reward circuits of human cocaine fatalities. J. Neurosci. Off. J. Soc. Neurosci. 1996, 16, 6100–6106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukherjee, J.; Christian, B.T.; Dunigan, K.A.; Shi, B.; Narayanan, T.K.; Satter, M.; Mantil, J. Brain imaging of 18F-fallypride in normal volunteers: Blood analysis, distribution, test-retest studies, and preliminary assessment of sensitivity to aging effects on dopamine D-2/D-3 receptors. Synapse 2002, 46, 170–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Paulis, T. The discovery of epidepride and its analogs as high-affinity radioligands for imaging extrastriatal dopamine D2 receptors in human brain. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2003, 9, 673–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elsinga, P.H.; Hatano, K.; Ishiwata, K. PET tracers for imaging of the dopaminergic system. Curr. Med. Chem. 2006, 13, 2139–2153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patel, N.H.; Vyas, N.S.; Puri, B.K.; Nijran, K.S.; Al-Nahhas, A. Positron emission tomography in schizophrenia: A new perspective. J. Nucl. Med. Off. Publ. Soc. Nucl. Med. 2010, 51, 511–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Volkow, N.D.; Fowler, J.S.; Wang, G.-J.; Dewey, S.L.; Schlyer, D.; MacGregor, R.; Logan, J.; Alexoff, D.; Shea, C.; Hitzemann, R. Reproducibility of repeated measures of carbon-11-raclopride binding in the human brain. J. Nucl. Med. 1993, 34, 609–613. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Caravaggio, F.; Porco, N.; Kim, J.; Torres-Carmona, E.; Brown, E.; Iwata, Y.; Nakajima, S.; Gerretsen, P.; Remington, G.; Graff-Guerrero, A. Measuring amphetamine-induced dopamine release in humans: A comparative meta-analysis of [11C]-raclopride and [11C]-(+)-PHNO studies. Synapse 2021, 75, e22195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Le Foll, B.; Wilson, A.A.; Graff, A.; Boileau, I.; Di Ciano, P. Recent methods for measuring dopamine D3 receptor occupancy in vivo: Importance for drug development. Front. Pharmacol. 2014, 5, 161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.; Zakiniaeiz, Y.; Cosgrove, K.P.; Morris, E.D. Toward whole-brain dopamine movies: A critical review of PET imaging of dopamine transmission in the striatum and cortex. Brain Imaging Behav. 2019, 13, 314–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nord, M.; Farde, L. Antipsychotic occupancy of dopamine receptors in schizophrenia. CNS Neurosci. Ther. 2011, 17, 97–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halldin, C.; Farde, L.; Högberg, T.; Mohell, N.; Hall, H.; Suhara, T.; Karlsson, P.; Nakashima, Y.; Swahn, C.-G. Carbon-11-FLB 457: A radioligand for extrastriatal D2 dopamine receptors. J. Nucl. Med. 1995, 36, 1275–1281. [Google Scholar]
- Galineau, L.; Wilson, A.A.; Garcia, A.; Houle, S.; Kapur, S.; Ginovart, N. In vivo characterization of the pharmacokinetics and pharmacological properties of [11C]-(+)-PHNO in rats using an intracerebral beta-sensitive system. Synapse 2006, 60, 172–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Payer, D.; Balasubramaniam, G.; Boileau, I. What is the role of the D3 receptor in addiction? A mini review of PET studies with [11C]-(+)-PHNO. Prog. Neuro-Psychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry 2014, 52, 4–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vyas, N.S.; Patel, N.H.; Herscovitch, P.; Puri, B.K.; Lanzenberger, R. Recent developments in neurochemical imaging in schizophrenia: An update. Curr. Med. Chem. 2013, 20, 351–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mach, R.H.; Luedtke, R.R. Challenges in the development of dopamine D2-and D3-selective radiotracers for PET imaging studies. J. Label. Compd. Radiopharm. 2018, 61, 291–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tu, Z.; Li, S.; Cui, J.; Xu, J.; Taylor, M.; Ho, D.; Luedtke, R.R.; Mach, R.H. Synthesis and pharmacological evaluation of fluorine-containing D3 dopamine receptor ligands. J. Med. Chem. 2011, 54, 1555–1564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mugnaini, M.; Iavarone, L.; Cavallini, P.; Griffante, C.; Oliosi, B.; Savoia, C.; Beaver, J.; Rabiner, E.A.; Micheli, F.; Heidbreder, C. Occupancy of brain dopamine D3 receptors and drug craving: A translational approach. Neuropsychopharmacology 2013, 38, 302–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Levant, B.; Jiang, C.; Keck, T.M.; Newman, A.H.; Wang, S. Tranylcypromine substituted cis-hydroxycyclobutylnaphthamides as potent and selective dopamine D3 receptor antagonists. J. Med. Chem. 2014, 57, 4962–4968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.Y.; Lee, J.Y.; Hsieh, C.-J.; Taylor, M.; Luedtke, R.R.; Mach, R.H. Design and Synthesis of Conformationally Flexible Scaffold as Bitopic Ligands for Potent D3-Selective Antagonists. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, G.L.; Hsieh, C.J.; Taylor, M.; Lee, J.Y.; Riad, A.A.; Luedtke, R.R.; Mach, R.H. Synthesis of bitopic ligands based on fallypride and evaluation of their affinity and selectivity towards dopamine D2 and D3 receptors. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2023, 261, 115751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Mukherjee, J. N-[(1-Cyclopropylmethyl-2-pyrrolidinyl)methyl]-substituted benzamides: Synthesis and dopamine D-2 and D-3 receptor binding affinities. Med. Chem. Res. 1999, 9, 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Hsieh, C.-J.; Riad, A.; Lee, J.Y.; Sahlholm, K.; Xu, K.; Luedtke, R.R.; Mach, R.H. Interaction of ligands for PET with the dopamine D3 receptor: In silico and in vitro methods. Biomolecules 2021, 11, 529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayatshahi, H.S.; Xu, K.; Griffin, S.A.; Taylor, M.; Mach, R.H.; Liu, J.; Luedtke, R.R. Analogues of arylamide phenylpiperazine ligands to investigate the factors influencing D3 dopamine receptor bitropic binding and receptor subtype selectivity. ACS Chem. Neurosci. 2018, 9, 2972–2983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Che, T.; Levit, A.; Shoichet, B.K.; Wacker, D.; Roth, B.L. Structure of the D2 dopamine receptor bound to the atypical antipsychotic drug risperidone. Nature 2018, 555, 269–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Im, D.; Inoue, A.; Fujiwara, T.; Nakane, T.; Yamanaka, Y.; Uemura, T.; Mori, C.; Shiimura, Y.; Kimura, K.T.; Asada, H. Structure of the dopamine D2 receptor in complex with the antipsychotic drug spiperone. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 6442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).