Biological Selenite Reduction, Characterization and Bioactivities of Selenium Nanoparticles Biosynthesised by Pediococcus acidilactici DSM20284
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Bacterial Isolation
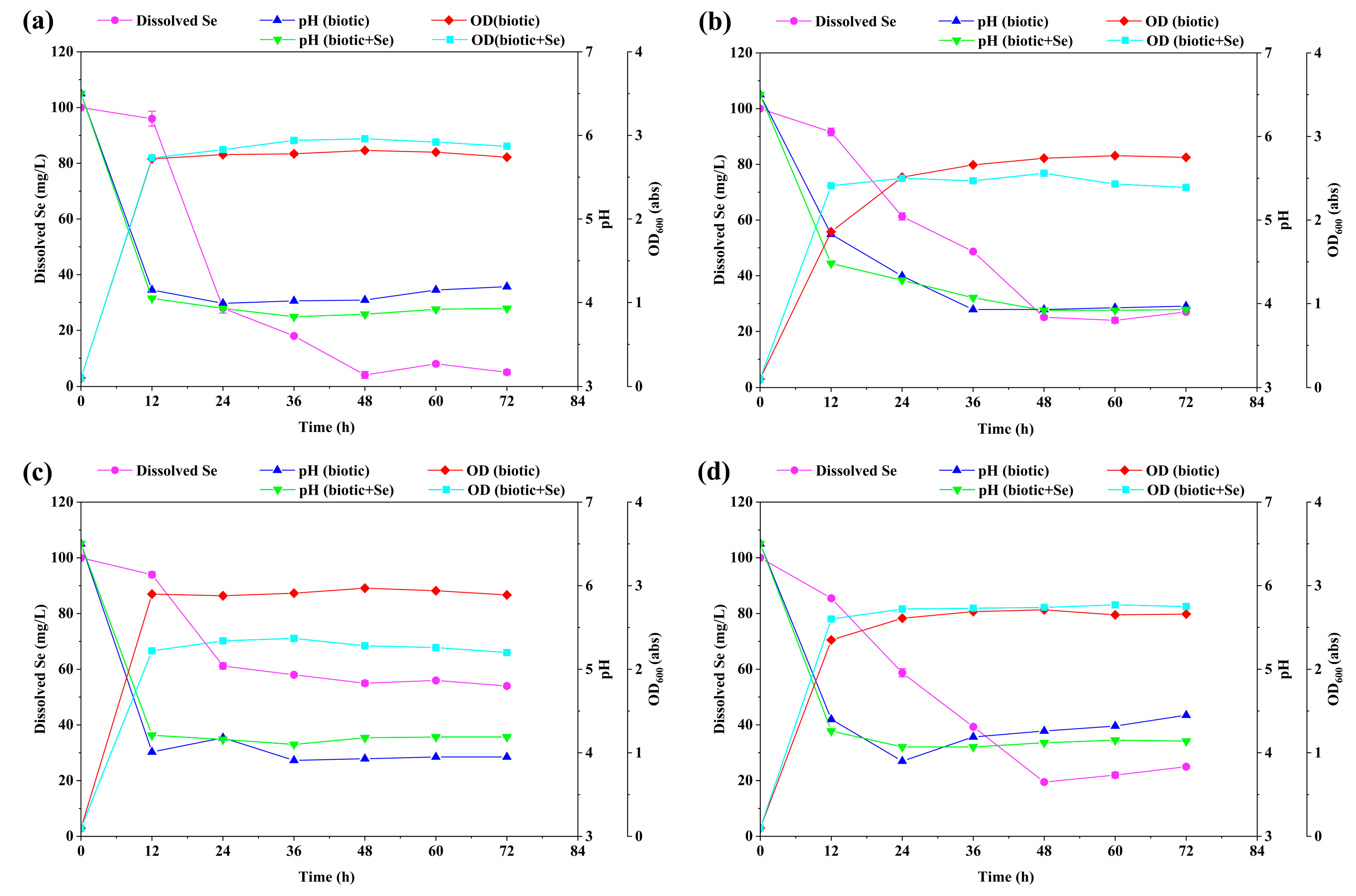
2.2. Selenite Reduction and Se Nanoparticle Production by Four Isolated Bacterial Strains
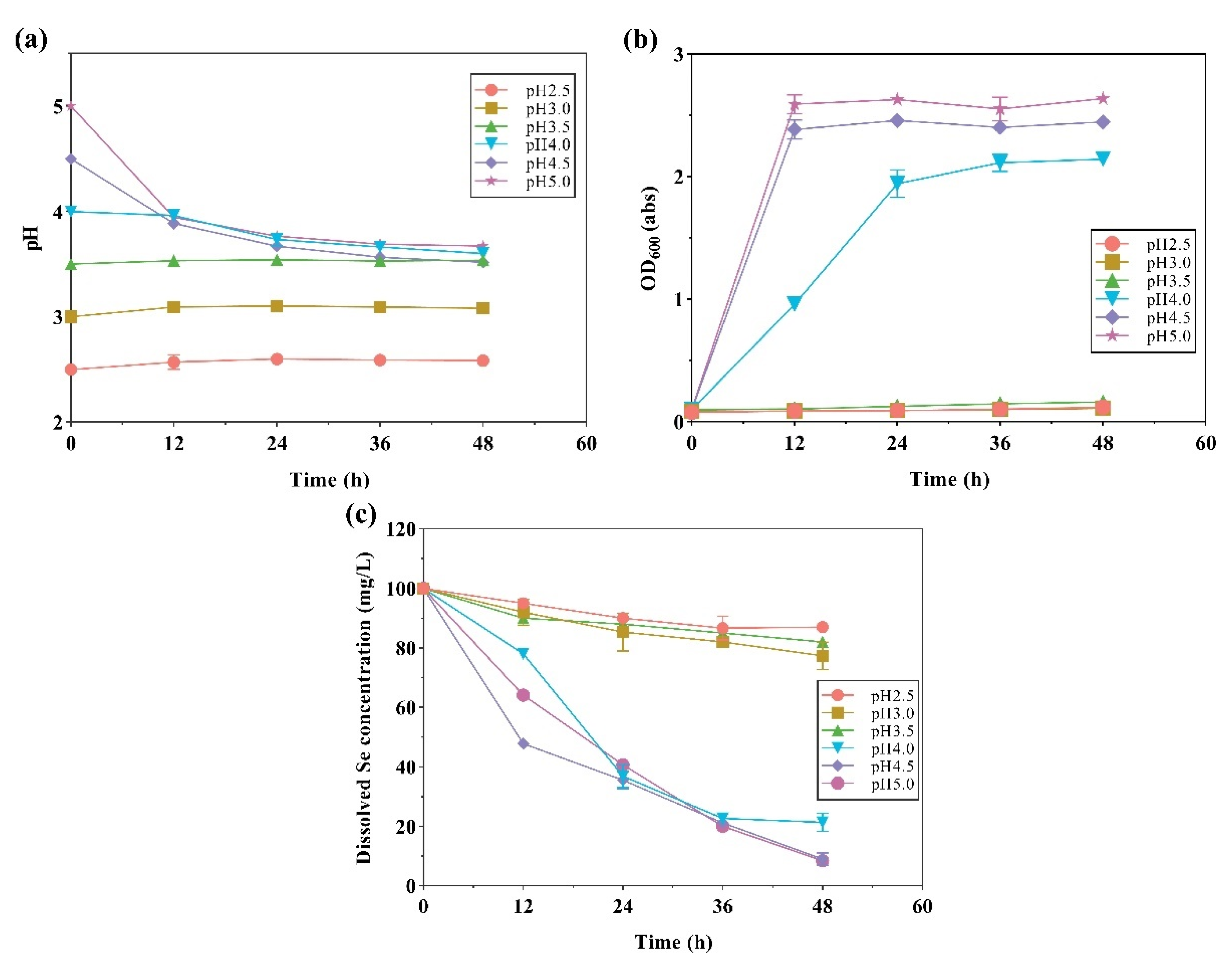
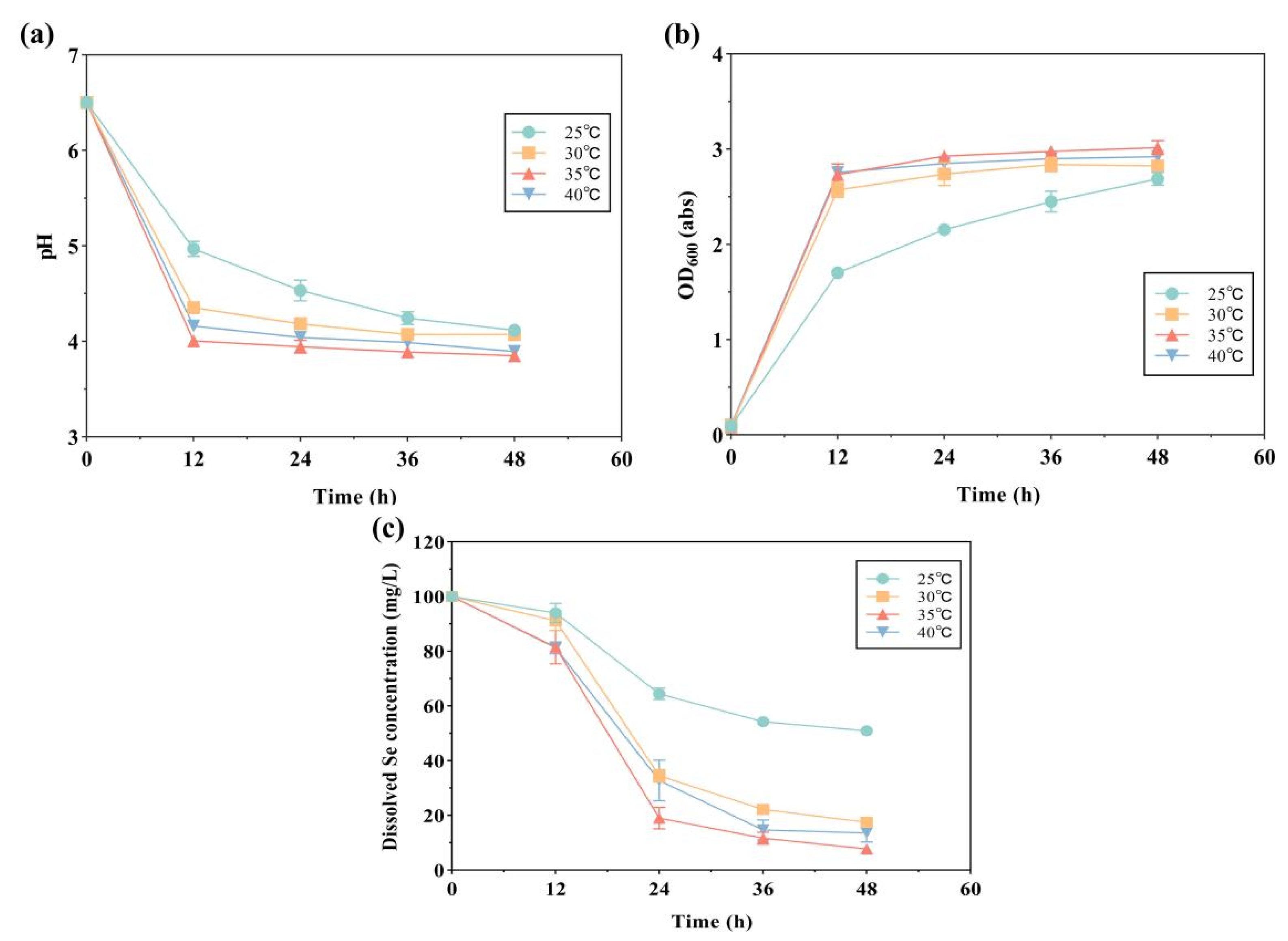
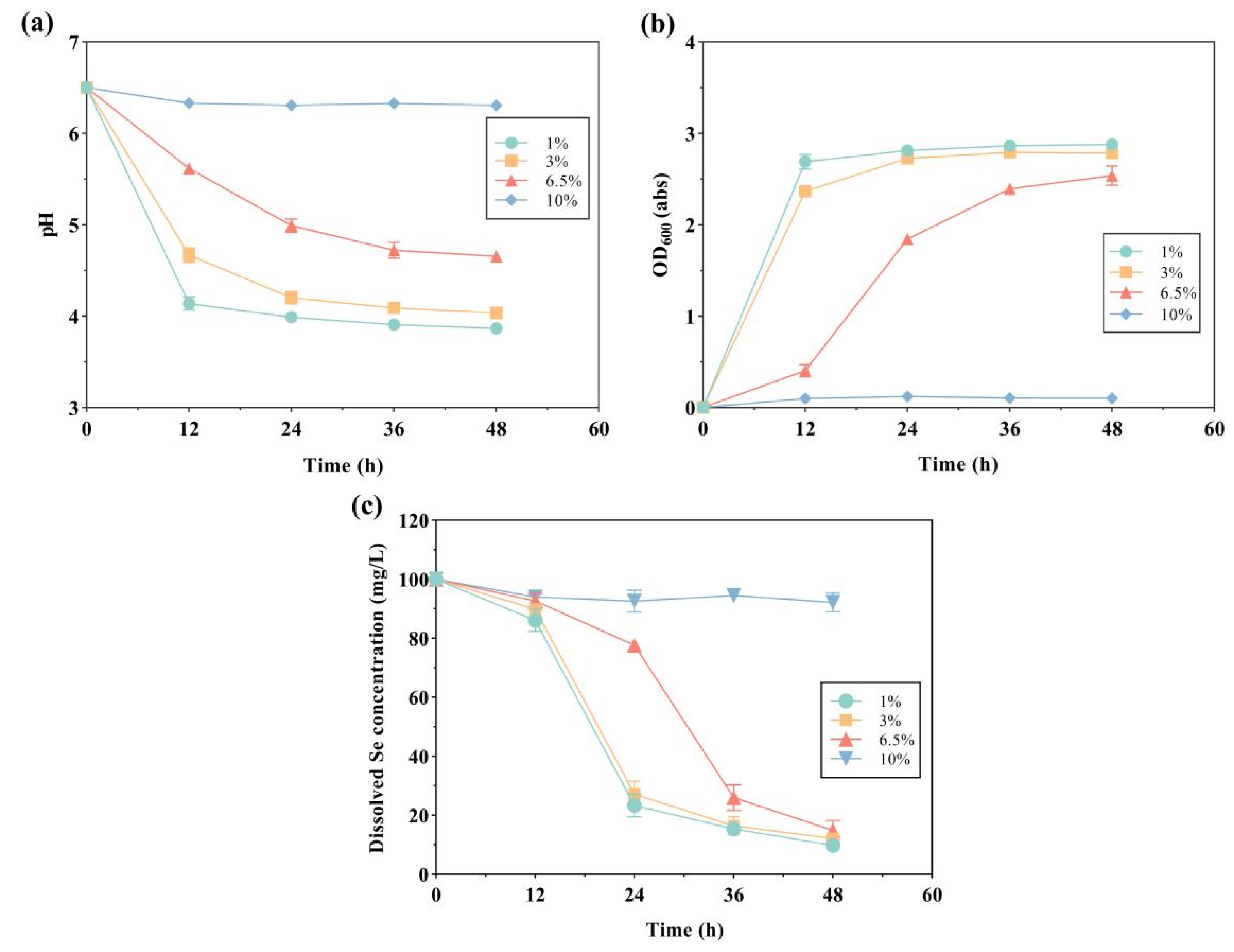
2.3. Selenite Reduction and Se Nanoparticle Production by Strain LAB-Se2, at Various Initial pH Values, Temperatures, and Salinities
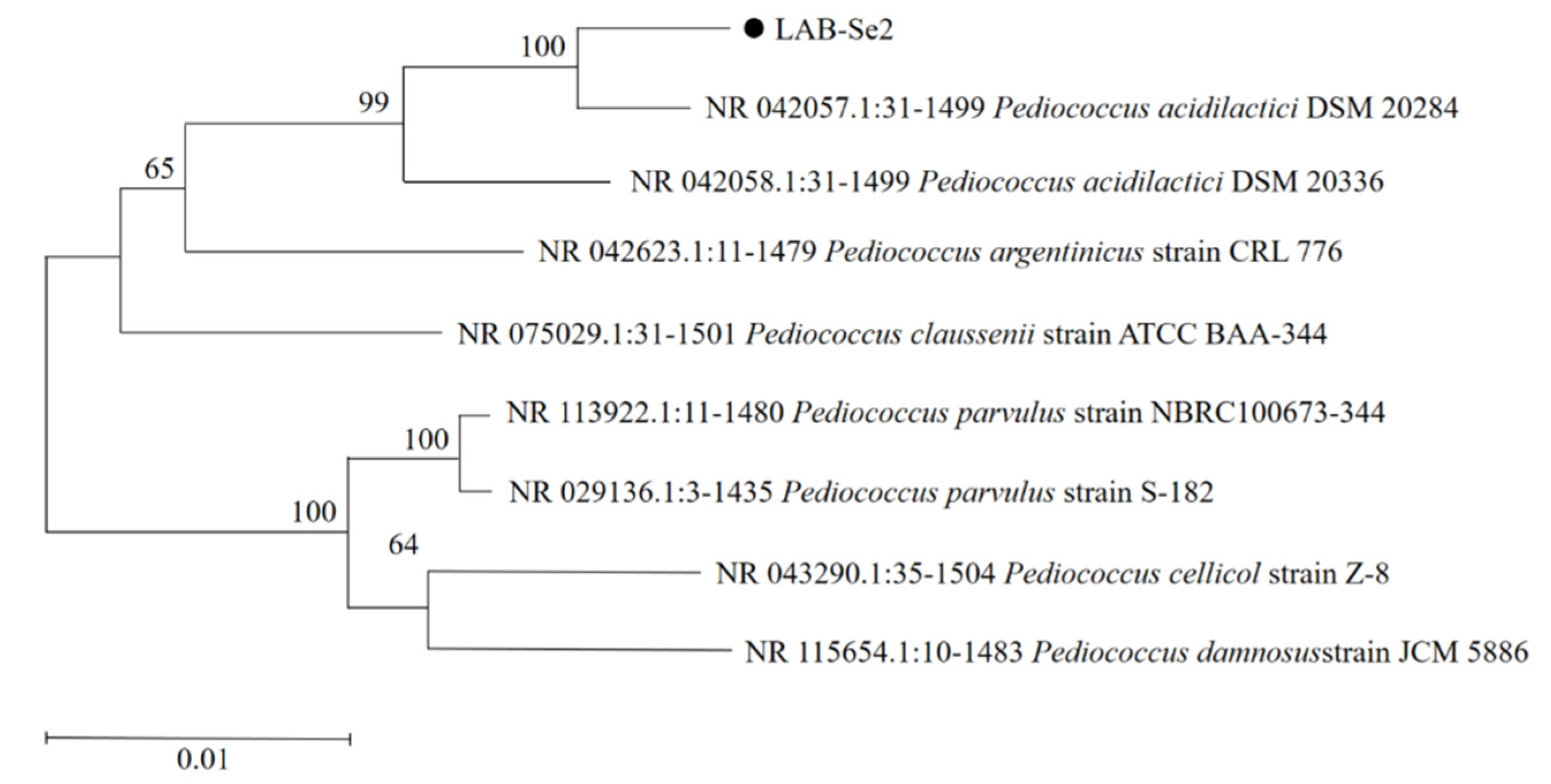
2.4. Identification of Bacterial Strain LAB-Se2
2.5. Biosynthesis of SeNPs
2.6. Characterisation of SeNPs
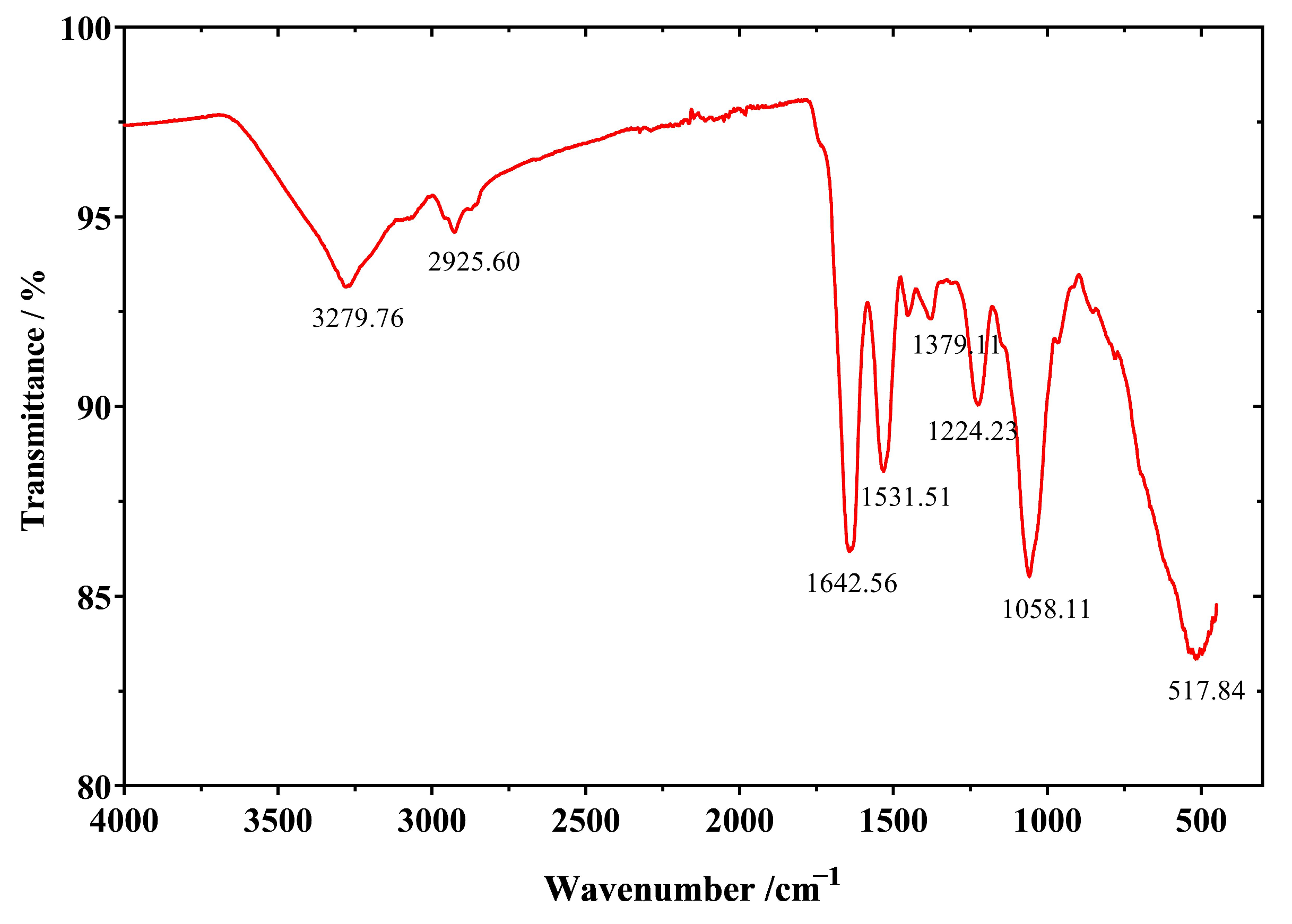
2.6.1. SeNPs Produced by Strain LAB-Se2 Contain an Organic Capping as Revealed by FTIR Spectroscopic Analysis
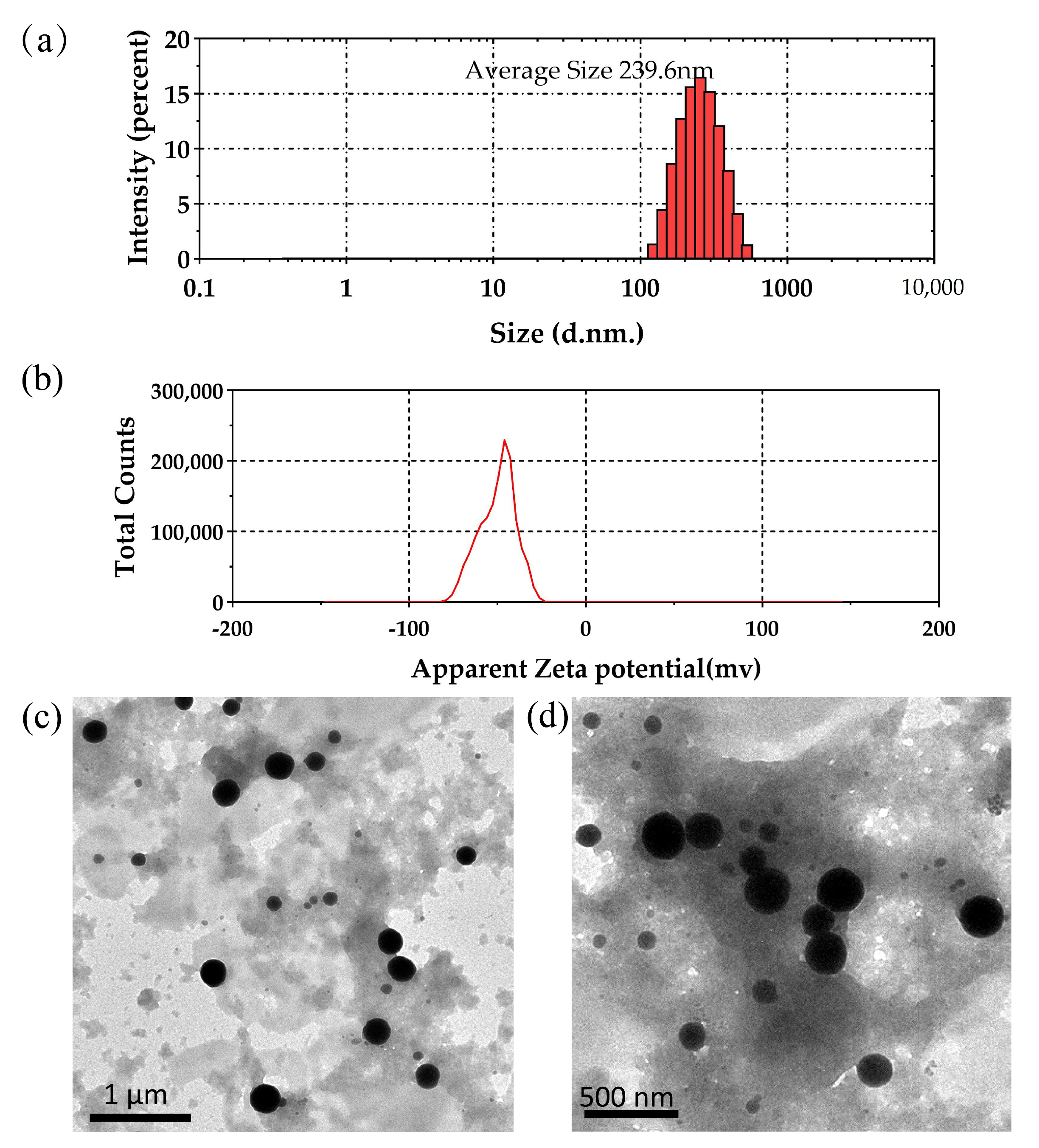
2.6.2. Particle Size, Zeta Potential Measurements, and TEM Analysis
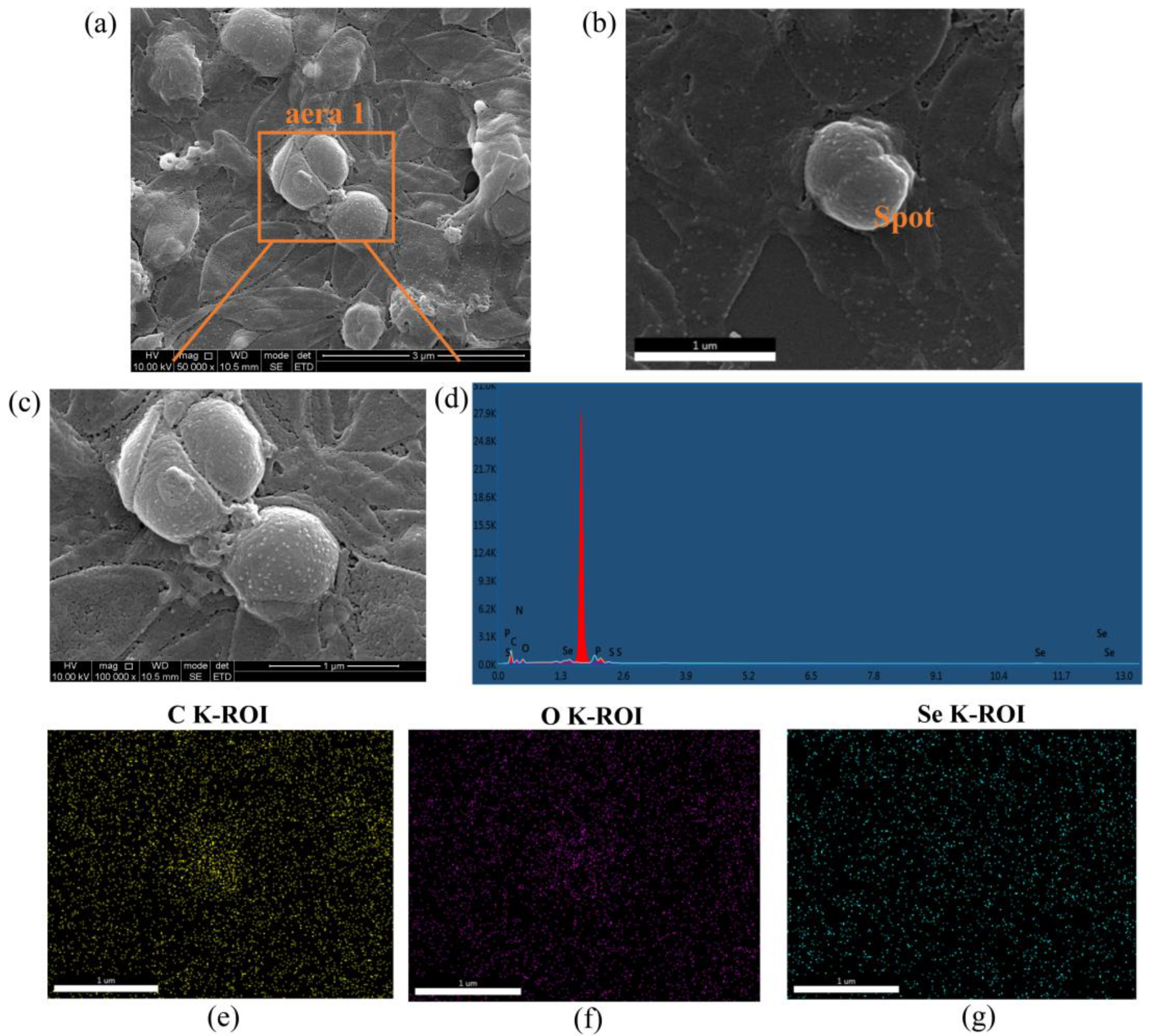
2.6.3. Spectroscopic and Ultramicroscopic Analyses Revealed the Shape and Size of SeNPs
2.7. Bioactivities of SeNPs
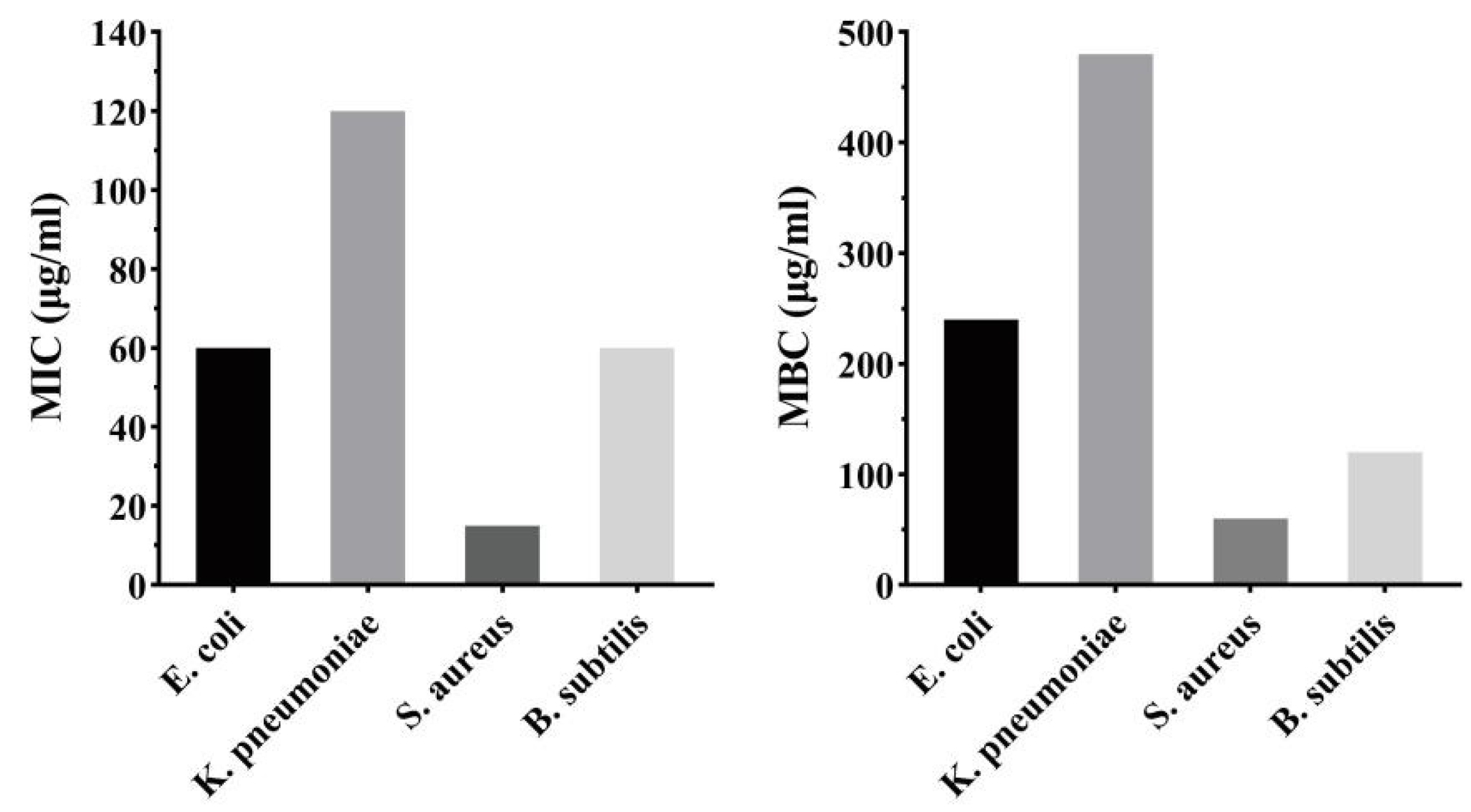
2.7.1. Antibacterial Activity
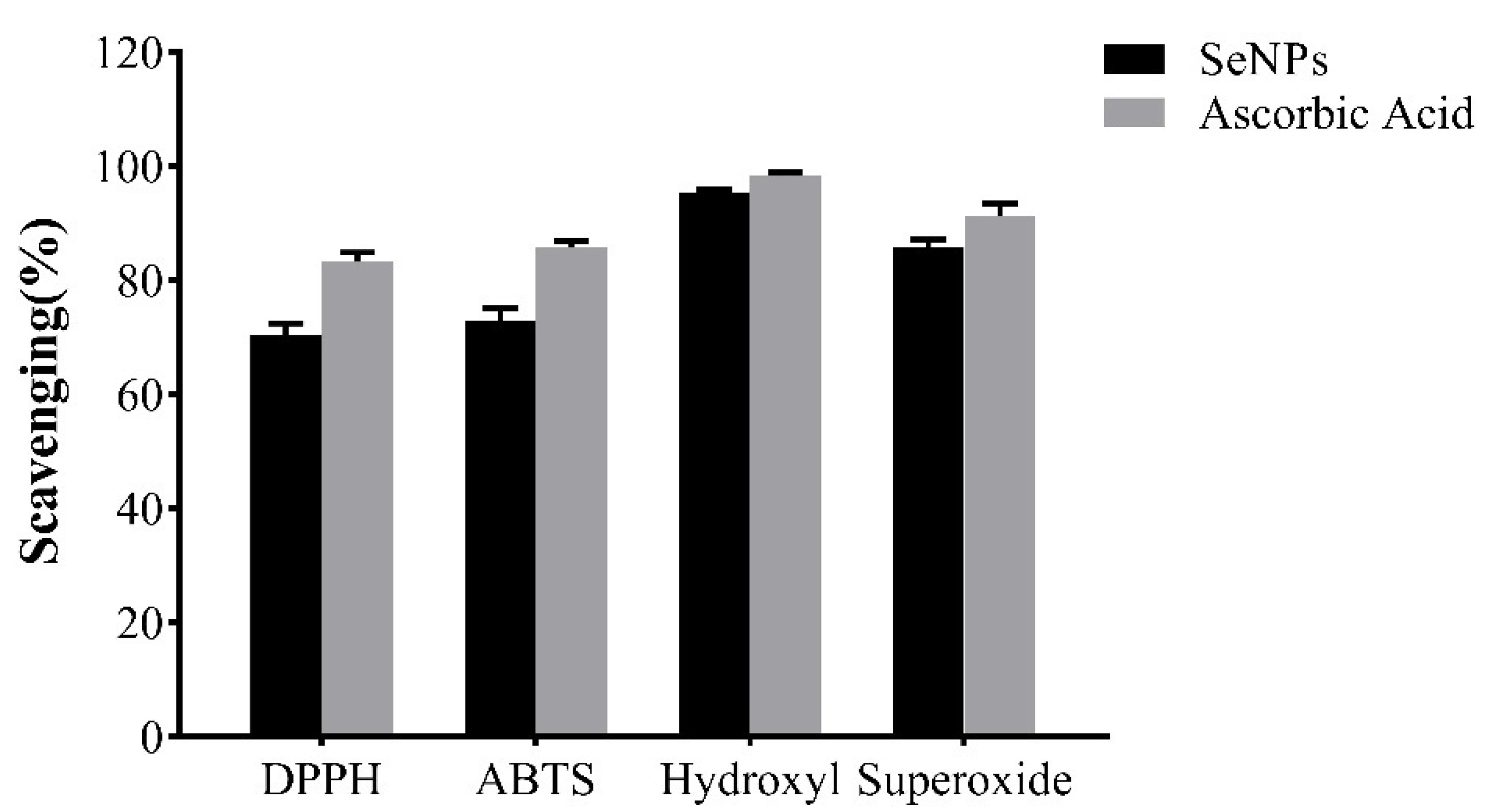
2.7.2. Antioxidant Activity
3. Material and Methods
3.1. Sample Collection and Strain Isolation
3.2. Selenite Reduction and Se Nanoparticle Production by Four Isolated Bacteria
3.3. Selenite Reduction and Se Nanoparticle Production by Strain LAB-Se2 under Various Conditions
3.4. Phylogenetic Analysis of New Selenite-Reducing Bacteria
3.5. Determination of Selenite Content
3.6. Biogenic Synthesis of Selenium Nanoparticles by Strain LAB-Se2
3.7. Characterisation of SeNPs
3.7.1. FTIR Spectroscopic Analysis
3.7.2. Particle Size and Zeta Potential Measurements
3.7.3. Transmission Electron Microscopy
3.7.4. Scanning Electron Microscopy with EDS
3.8. Antimicrobial Activity of SeNPs
3.8.1. Disk Diffusion Method
3.8.2. Minimal Inhibitory Concentration (MIC) Test
3.8.3. Minimum Bactericidal Concentration (MBC) Test
3.9. Antioxidant Activity of SeNPs
3.9.1. DPPH Scavenging Assay
3.9.2. ABTS Scavenging Assay
3.9.3. Hydroxyl Scavenging Assay
3.9.4. Superoxide Scavenging Assay
3.10. Statistical Analysis
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Sample Availability
References
- Mishra, R.R.; Prajapati, S.; Das, J.; Dangar, T.K.; Das, N.; Thatoi, H. Reduction of selenite to red elemental selenium by moderately halotolerant Bacillus megaterium strains isolated from Bhitarkanika mangrove soil and characterization of reduced product. Chemosphere 2011, 84, 1231–1237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiang, J.; Rao, S.; Chen, Q.; Zhang, W.; Cheng, S.; Cong, X.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, X.; Xu, F. Research Progress on the Effects of Selenium on the Growth and Quality of Tea Plants. Plants 2022, 11, 2491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandey, S.; Awasthee, N.; Shekher, A.; Rai, L.C.; Gupta, S.C.; Dubey, S.K. Biogenic synthesis and characterization of selenium nanoparticles and their applications with special reference to antibacterial, antioxidant, anticancer and photocatalytic activity. Bioprocess Biosyst. Eng. 2021, 44, 2679–2696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.; Bañuelos, G.S.; Wu, L.; Shi, W. The changing selenium nutritional status of Chinese residents. Nutrients 2014, 6, 1103–1114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, C.; Qiao, L.; Guo, Y.; Ma, L.; Cheng, Y. Preparation, characteristics and antioxidant activity of polysaccharides and proteins-capped selenium nanoparticles synthesized by Lactobacillus casei ATCC 393. Carbohydr Polym 2018, 195, 576–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, R.; Huang, J.; Wang, Z.; Chen, Y.; Dong, Y. Trace Element Selenium Effectively Alleviates Intestinal Diseases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 11708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Shu, X.; Hou, J.; Lu, W.; Zhao, W.; Huang, S.; Wu, L. Selenium Nanoparticle Synthesized by Proteus mirabilis YC801: An Efficacious Pathway for Selenite Biotransformation and Detoxification. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 3809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashengroph, M.; Hosseini, S.R. A newly isolated Bacillus amyloliquefaciens SRB04 for the synthesis of selenium nanoparticles with potential antibacterial properties. Int. Microbiol. 2021, 24, 103–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanna, A.L.; Hamouda, H.M.; Goda, H.A.; Sadik, M.W.; Moghanm, F.S.; Ghoneim, A.M.; Alenezi, M.A.; Alnomasy, S.F.; Alam, P.; Elsayed, T.R. Biosynthesis and Characterization of Silver Nanoparticles Produced by Phormidium ambiguum and Desertifilum tharense Cyanobacteria. Bioinorg. Chem. Appl. 2022, 2022, 9072508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Shu, X.; Zhou, Q.; Fan, T.; Wang, T.; Chen, X.; Li, M.; Ma, Y.; Ni, J.; Hou, J.; et al. Selenite Reduction and the Biogenesis of Selenium Nanoparticles by Alcaligenesfaecalis Se03 Isolated from the Gut of Monochamus alternatus (Coleoptera: Cerambycidae). Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 2799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, Y.; Yao, R.; Wang, R.; Wang, D.; Wang, G.; Zheng, S. Reduction of selenite to Se(0) nanoparticles by filamentous bacterium Streptomyces sp. ES2–5 isolated from a selenium mining soil. Microb. Cell Fact. 2016, 15, 157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simões, M.F.; Ottoni, C.A.; Antunes, A. Biogenic Metal Nanoparticles: A New Approach to Detect Life on Mars? Life 2020, 10, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Ren, Y.; Liang, Y.; Huang, L.; Yang, Y.; Zafar, A.; Hasan, M.; Yang, F.; Shu, X. Synthesis, Characterization, Immune Regulation, and Antioxidative Assessment of Yeast-Derived Selenium Nanoparticles in Cyclophosphamide-Induced Rats. ACS Omega 2021, 6, 24585–24594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, Y.H.; Li, L.L.; Zhou, N.Q.; Liu, J.H.; Huang, Q.; Wang, H.J.; Tian, J.; Yu, H.Q. In vivo synthesis of nano-selenium by Tetrahymena thermophila SB210. Enzyme Microb. Technol. 2016, 95, 185–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ullah, A.; Yin, X.; Wang, F.; Xu, B.; Mirani, Z.A.; Xu, B.; Chan, M.W.H.; Ali, A.; Usman, M.; Ali, N.; et al. Biosynthesis of Selenium Nanoparticles (via Bacillus subtilis BSN313), and Their Isolation, Characterization, and Bioactivities. Molecules 2021, 26, 5559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calomme, M.; Hu, J.; Van den Branden, K.; Vanden Berghe, D.A. Seleno-lactobacillus. An organic selenium source. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 1995, 47, 379–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Shi, L.; Tuo, X.; Ma, X.; Hou, X.; Jiang, S.; Lv, J.; Cheng, Y.; Guo, D.; Han, B. Preparation, characteristic and anti-inflammatory effect of selenium nanoparticle-enriched probiotic strain Enterococcus durans A8-1. J. Trace Elem. Med. Biol. 2022, 74, 127056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, L.; Ming, Y.; Yue, Y.; Peng, Y.; Jin, W.; Biteng, H. Development and Fermentation Performance Evalution of a Selenium-enriched Yogurt Starter and Evaluation. Food Sci. 2011, 32, 76–79. [Google Scholar]
- Peñas, E.; Martinez-Villaluenga, C.; Frias, J.; Sánchez-Martínez, M.J.; Pérez-Corona, M.T.; Madrid, Y.; Vidal-Valverde, C. Se improves indole glucosinolate hydrolysis products content, Se-methylselenocysteine content, antioxidant capacity and potential anti-inflammatory properties of sauerkraut. Food Chem. 2012, 132, 907–914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Li, Z.; Dai, C.; Wang, P.; Fan, S.; Yu, B.; Qu, Y. Antibacterial properties and mechanism of selenium nanoparticles synthesized by Providencia sp. DCX. Environ. Res. 2021, 194, 110630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, F.; Saeed, K.; Fatemeh, H. Nano-Bio Selenium Synthesized by Bacillus subtilis Modulates Broiler Performance, Intestinal Morphology and Microbiota, and Expression of Tight Junction’s Proteins. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2022, 200, 1811–1825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Won, S.; Ha, M.G.; Nguyen, D.D.; Kang, H.Y. Biological selenite removal and recovery of selenium nanoparticles by haloalkaliphilic bacteria isolated from the Nakdong River. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 280, 117001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palomo-Siguero, M.; Gutiérrez, A.M.; Pérez-Conde, C.; Madrid, Y. Effect of selenite and selenium nanoparticles on lactic bacteria: A multi-analytical study. Microchem. J. 2016, 126, 488–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kora, A.J.; Rastogi, L. Bacteriogenic synthesis of selenium nanoparticles by Escherichia coli ATCC 35218 and its structural characterisation. IET Nanobiotechnol. 2017, 11, 179–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mörschbächer, A.P.; Dullius, A.; Dullius, C.H.; Brandt, C.R.; Kuhn, D.; Brietzke, D.T.; José Malmann Kuffel, F.; Etgeton, H.P.; Altmayer, T.; Gonçalves, T.E.; et al. Assessment of selenium bioaccumulation in lactic acid bacteria. J. Dairy Sci. 2018, 101, 10626–10635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zúñiga, W.C.; Jones, V.; Anderson, S.M.; Echevarria, A.; Miller, N.L.; Stashko, C.; Schmolze, D.; Cha, P.D.; Kothari, R.; Fong, Y.; et al. Raman Spectroscopy for Rapid Evaluation of Surgical Margins during Breast Cancer Lumpectomy. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 14639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bright, C.M. The Effects of Hypoxia on Intracellular ion Activities in Mammalian Heart. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Edinburgh, Edinburgh, UK, 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Ahsan, A.; Farooq, M.A.; Ahsan Bajwa, A.; Parveen, A. Green Synthesis of Silver Nanoparticles Using Parthenium Hysterophorus: Optimization, Characterization and In Vitro Therapeutic Evaluation. Molecules 2020, 25, 3324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sirichokchatchawan, W.; Pupa, P.; Praechansri, P.; Am-In, N.; Tanasupawat, S.; Sonthayanon, P.; Prapasarakul, N. Autochthonous lactic acid bacteria isolated from pig faeces in Thailand show probiotic properties and antibacterial activity against enteric pathogenic bacteria. Microb. Pathog. 2018, 119, 208–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Wang, Q.; Dai, F.; Li, H. Reduction of selenite to selenium nanospheres by Se(IV)-resistant Lactobacillus paralimentarius JZ07. Food Chem. 2022, 393, 133385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagy, G.; Pinczes, G.; Pinter, G.; Pocsi, I.; Prokisch, J.; Banfalvi, G. In Situ Electron Microscopy of Lactomicroselenium Particles in Probiotic Bacteria. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 1047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tendenedzai, J.T.; Chirwa, E.M.N.; Brink, H.G. Enterococcus spp. Cell-Free Extract: An Abiotic Route for Synthesis of Selenium Nanoparticles (SeNPs), Their Characterisation and Inhibition of Escherichia coli. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dhanjal, S.; Cameotra, S.S. Aerobic biogenesis of selenium nanospheres by Bacillus cereus isolated from coalmine soil. Microb. Cell Fact. 2010, 9, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gunti, L.; Dass, R.S.; Kalagatur, N.K. Phytofabrication of Selenium Nanoparticles From Emblica officinalis Fruit Extract and Exploring Its Biopotential Applications: Antioxidant, Antimicrobial, and Biocompatibility. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Wang, Y.; Shao, Z.; Li, J.; Zan, S.; Zhou, S.; Yang, R. Two selenium tolerant Lysinibacillus sp. strains are capable of reducing selenite to elemental Se efficiently under aerobic conditions. J. Environ. Sci. 2019, 77, 238–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahbaz, M.; Akram, A.; Raja, N.I.; Mukhtar, T.; Mehak, A.; Fatima, N.; Ajmal, M.; Ali, K.; Mustafa, N.; Abasi, F. Antifungal activity of green synthesized selenium nanoparticles and their effect on physiological, biochemical, and antioxidant defense system of mango under mango malformation disease. PLoS ONE 2023, 18, 0274679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Negi, B.B.; Sinharoy, A.; Pakshirajan, K. Selenite removal from wastewater using fungal pelleted airlift bioreactor. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2020, 27, 992–1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.; Xiao, X.; Li, X.; Song, D.; Lu, Z.; Wang, F.; Wang, Y. Characterization, antioxidant property and cytoprotection of exopolysaccharide-capped elemental selenium particles synthesized by Bacillus paralicheniformis SR14. Carbohydr. Polym. 2017, 178, 18–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menon, S.; Sd, K.S.; Agarwal, H.; Shanmugam, V.K.J.C.; Communications, I.S. Efficacy of Biogenic Selenium Nanoparticles from an Extract of Ginger towards Evaluation on Anti-Microbial and Anti-Oxidant Activities. Colloid Interface Sci. Commun. 2019, 29, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez, F.G.; Moreno-Martin, G.; Pescuma, M.; Madrid-Albarrán, Y.; Mozzi, F. Biotransformation of Selenium by Lactic Acid Bacteria: Formation of Seleno-Nanoparticles and Seleno-Amino Acids. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2020, 8, 506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dacrory, S.; Hashem, A.H.; Hasanin, M. Synthesis of cellulose based amino acid functionalized nano-biocomplex: Characterization, antifungal activity, molecular docking and hemocompatibility. Environ. Nanotechnol. Monit. Manag. 2021, 15, 100453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, H.W.; Patel, K.D.; Kwak, J.H.; Jun, S.K.; Jang, T.S.; Lee, S.H.; Knowles, J.C.; Kim, H.W.; Lee, H.H.; Lee, J.H. Selenium Nanoparticles as Candidates for Antibacterial Substitutes and Supplements against Multidrug-Resistant Bacteria. Biomolecules 2021, 11, 1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boroumand, S.; Safari, M.; Shaabani, E. Selenium nanoparticles: Synthesis, characterization and study of their cytotoxicity, antioxidant and antibacterial activity(Article). Mater. Res. Express 2019, 6, 0850d0858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, W.; Hu, T.; Bakry, A.M.; Zheng, Z.; Xiao, Y.; Huang, Q. Effect of ultrasound on size, morphology, stability and antioxidant activity of selenium nanoparticles dispersed by a hyperbranched polysaccharide from Lignosus rhinocerotis. Ultrason. Sonochemistry 2018, 42, 823–831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, T.; Zhao, H.; Bi, Y.; Fan, X. Preparation and antioxidant activity of selenium nanoparticles decorated by polysaccharides from Sargassum fusiforme. J. Food Sci. 2021, 86, 977–986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sentkowska, A.; Pyrzynska, K. Does the Type Matter? Verification of Different Tea Types’ Potential in the Synthesis of SeNPs. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 2489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Jia, N.; Qiao, H.; Zhu, M.; Meng, Q.; Lu, Q.; Zu, Y. Synthesis and evaluation of a novel water-soluble high Se-enriched Astragalus polysaccharide nanoparticles. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 118, 1438–1448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

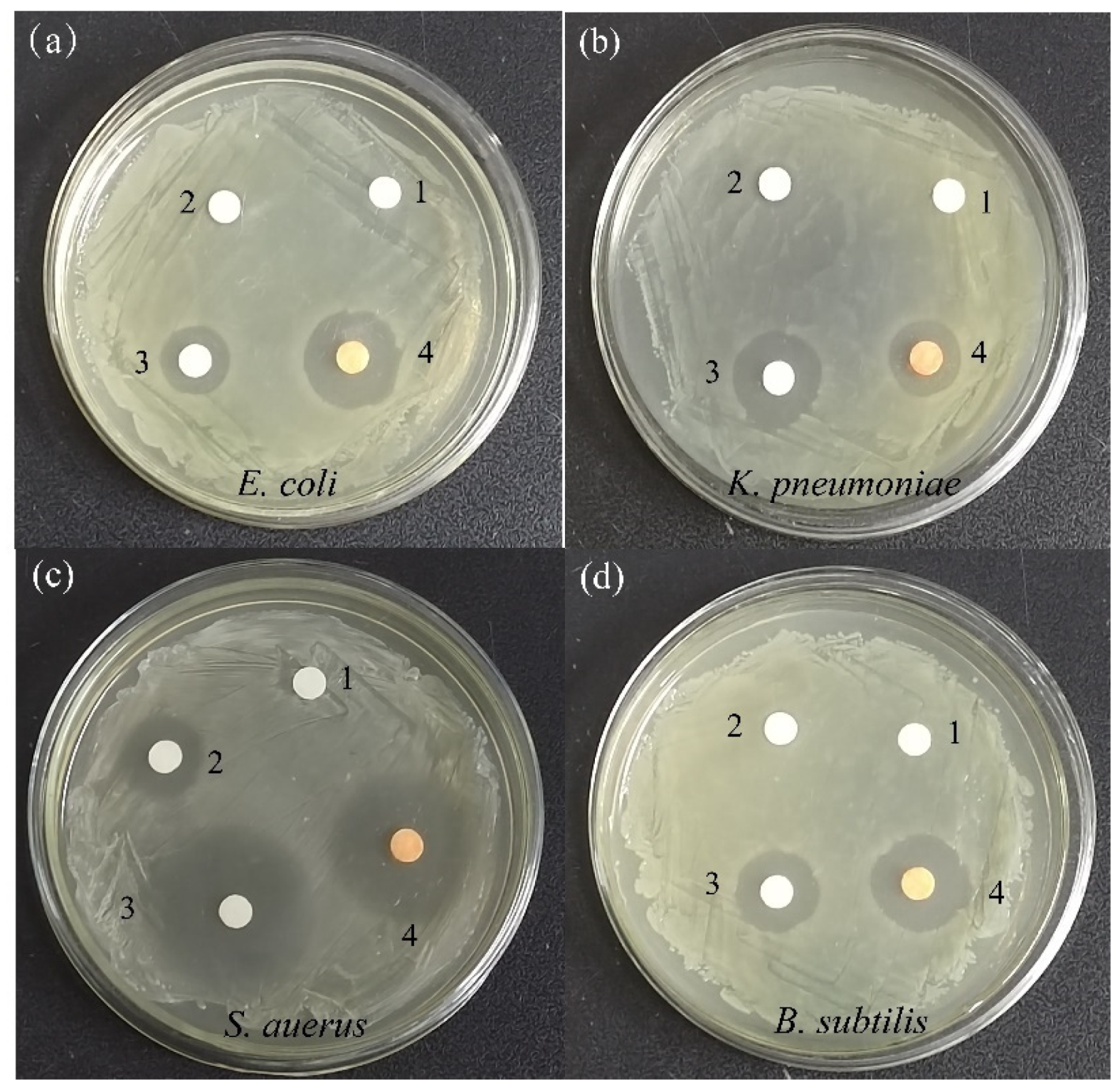
| Organisms | Diameter of Zone of Inhibition (in mm) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Deionised Water | Sodium Selenium | Ampicillin (10 μg/disk) | SeNPs | |
| E. Coli | 0.0 | 8.0 ± 1.1 | 14.1 ± 1.0 | 17.5 ± 0.8 |
| K. pneumoniae | 0.0 | 8.6 ± 1.0 | 16.0 ± 1.1 | 13.4 ± 0.9 |
| S. aureus | 0.0 | 13.1 ± 0.9 | 30.2 ± 1.3 | 27.9 ± 1.2 |
| B. subtilis | 0.0 | 7.6 ± 1.1 | 19.1 ± 1.0 | 16.2 ± 1.1 |
| Environmental Factors | Initial pH | Temperature/°C | Salinity/% |
|---|---|---|---|
| Initial pH | 2.5 | 35 | 1.0 |
| 3.0 | |||
| 3.5 | |||
| 4.0 | |||
| 4.5 | |||
| 5.0 | |||
| Temperature | 6.0 | 25 | |
| 30 | |||
| 35 | |||
| 40 | |||
| Salinity | 6.0 | 35 | 1.0 |
| 3.0 | |||
| 6.5 | |||
| 10 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, Q.; Wang, C.; Kuang, S.; Wang, D.; Shi, Y. Biological Selenite Reduction, Characterization and Bioactivities of Selenium Nanoparticles Biosynthesised by Pediococcus acidilactici DSM20284. Molecules 2023, 28, 3793. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28093793
Wang Q, Wang C, Kuang S, Wang D, Shi Y. Biological Selenite Reduction, Characterization and Bioactivities of Selenium Nanoparticles Biosynthesised by Pediococcus acidilactici DSM20284. Molecules. 2023; 28(9):3793. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28093793
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Qingdong, Chunyue Wang, Shanshan Kuang, Dezhen Wang, and Yuhua Shi. 2023. "Biological Selenite Reduction, Characterization and Bioactivities of Selenium Nanoparticles Biosynthesised by Pediococcus acidilactici DSM20284" Molecules 28, no. 9: 3793. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28093793
APA StyleWang, Q., Wang, C., Kuang, S., Wang, D., & Shi, Y. (2023). Biological Selenite Reduction, Characterization and Bioactivities of Selenium Nanoparticles Biosynthesised by Pediococcus acidilactici DSM20284. Molecules, 28(9), 3793. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28093793





