Ketonization of Ginsenoside C-K by Novel Recombinant 3-β-Hydroxysteroid Dehydrogenases and Effect on Human Fibroblast Cells
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Bacterial Strain Isolation and Screening for Ketonzation of C-K
2.2. Phylogenetic Analysis
2.3. Expression and Purification of Recombinant HSDLb1
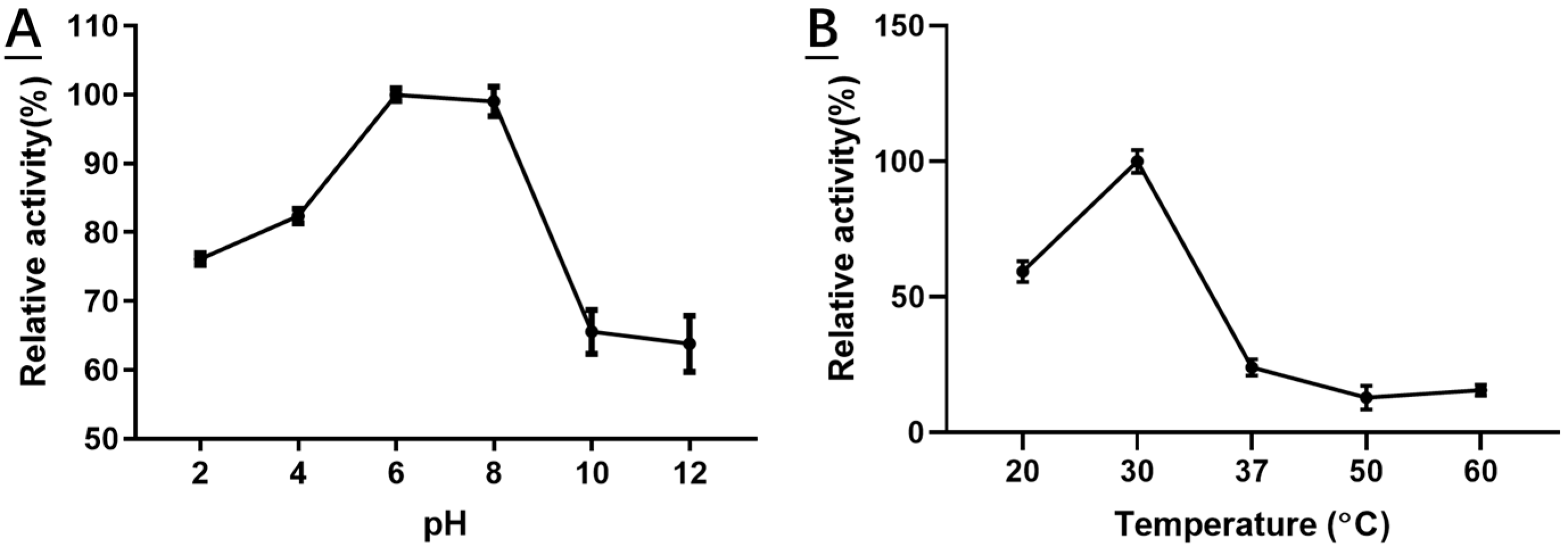
2.4. Characterization of Recombinant HSDLb1
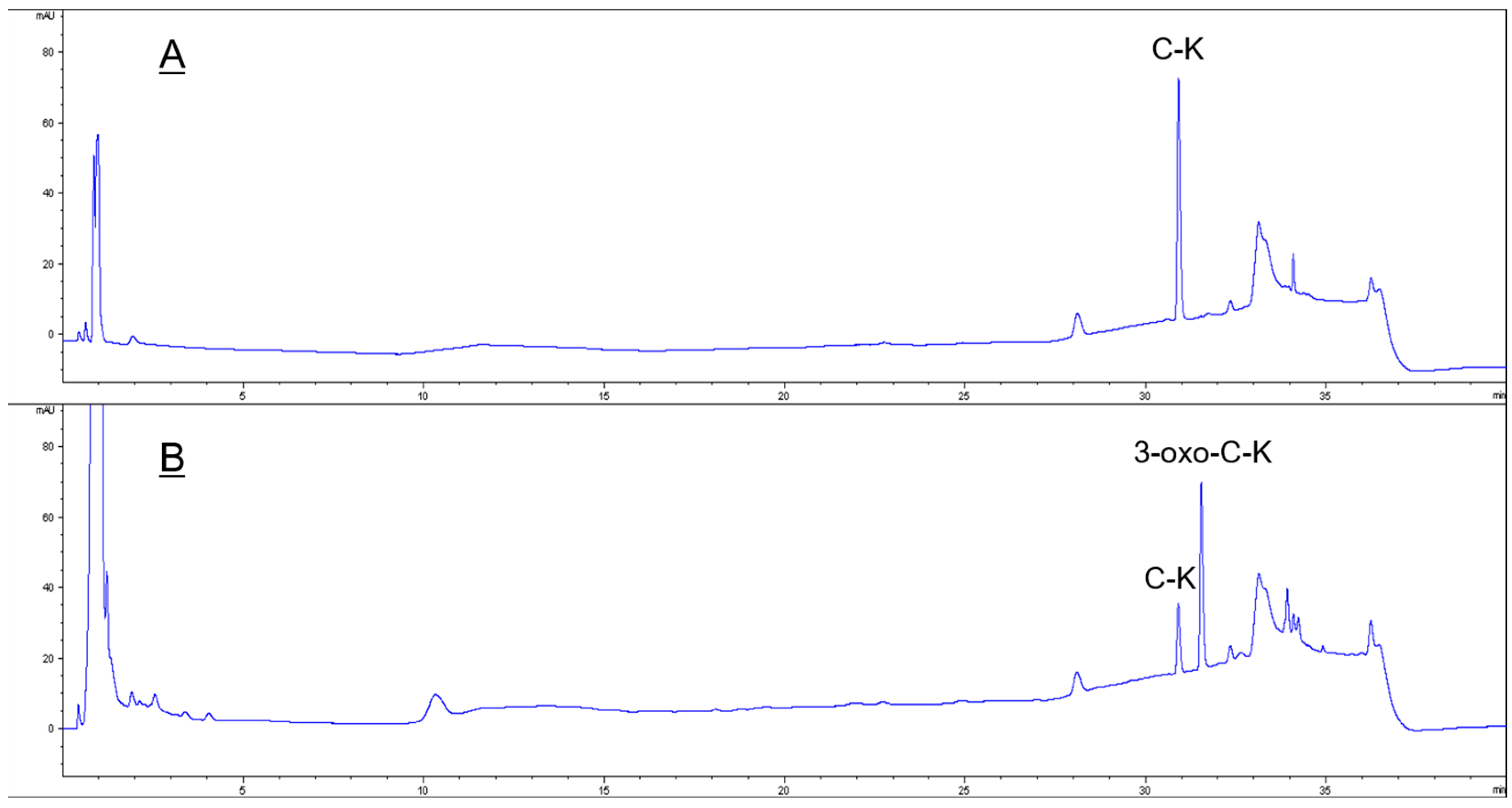
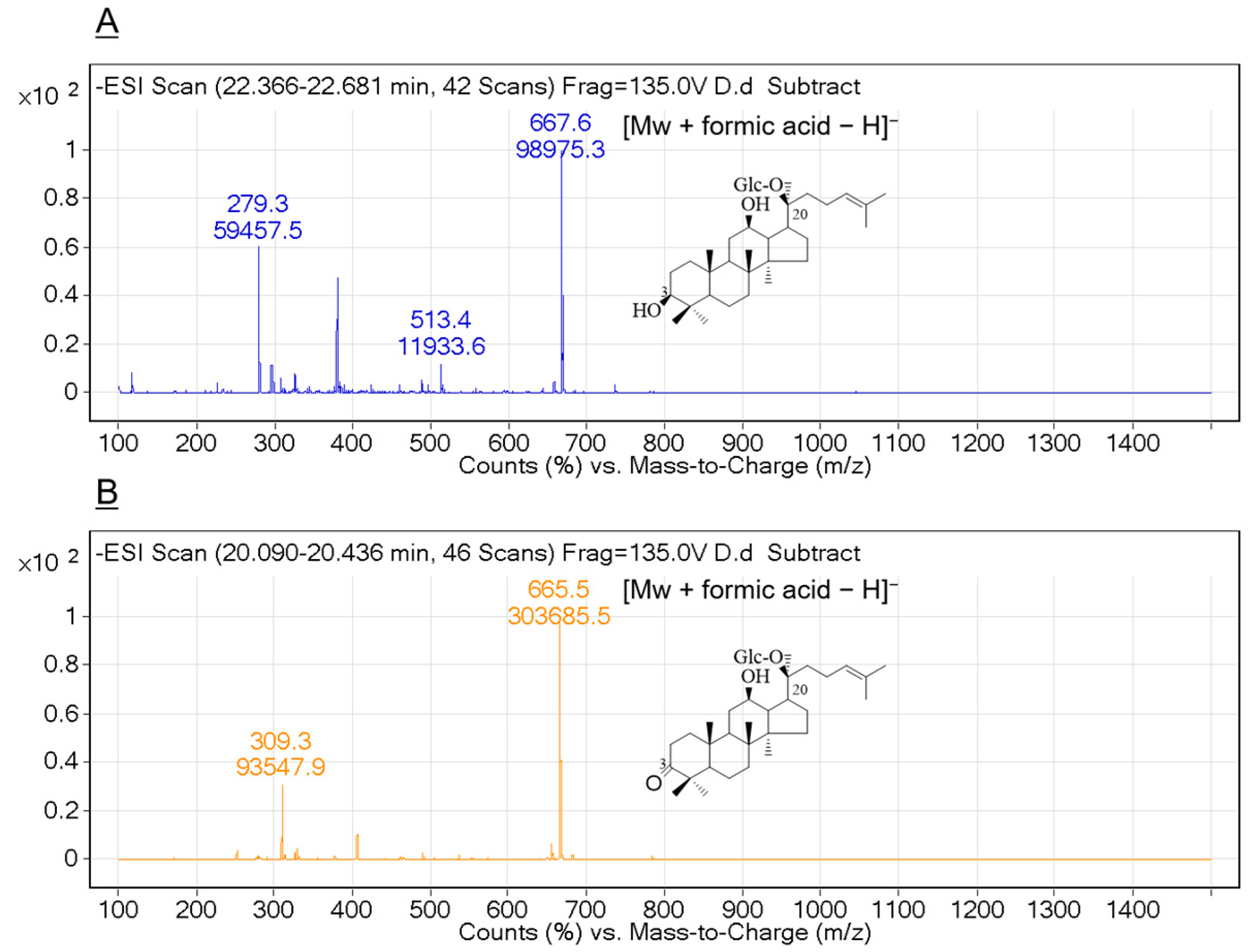
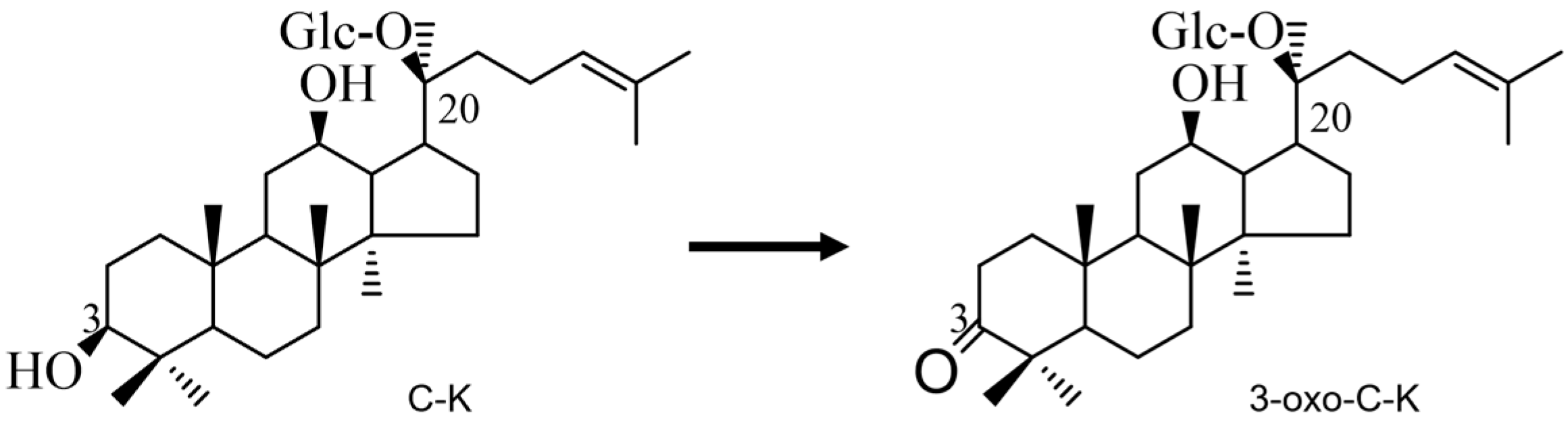
2.5. Bioconversion of Ginsenoside C-K by Recombinant HSDLb1
2.6. Cell Cytotoxicity
2.6.1. Effect of C-K and 3-oxo-C-K on HDF Cell Viability
2.6.2. Effect of C-K and 3-oxo-C-K on the Synthesis of MMP-1 and Procollagen Type I
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Chemical Reagents and Ginsenoside Standards
3.1.1. Strain Isolation and Ketonization of Ginsenoside C-K
3.1.2. Gene Cloning, Expression and Purification of Recombinant HSDLb1
3.1.3. Effect of Different pH, Temperature, and Metal Ions
3.2. TLC, HPLC and LC/MS Analysis
3.3. In Vitro Cell Viability Analysis
3.3.1. Ultraviolet Irradiation
3.3.2. Assay for Inhibition of Matrix Metalloproteinase-1 (MMP-1) Expression and Production of Procollagen Type I
3.3.3. Cytotoxicity of Ginsenoside C-K and 3-oxo-C-K
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Sample Availability
References
- Chang-Xiao, L.; Pei-Gen, X. Recent advances on ginseng research in China. J. Ethnopharmacol. 1992, 36, 27–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ratan, Z.A.; Haidere, M.F.; Hong, Y.H.; Park, S.H.; Lee, J.O.; Lee, J.; Cho, J.Y. Pharmacological potential of ginseng and its major component ginsenosides. J. Ginseng Res. 2021, 45, 199–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.; Qiao, X.; Li, K.; Fan, J.; Bo, T.; Guo, D.A.; Ye, M. Identification and differentiation of Panax ginseng, Panax quinquefolium, and Panax notoginseng by monitoring multiple diagnostic chemical markers. Acta Pharm. Sin. B 2016, 6, 568–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christensen, L.P. Chapter 1. Ginsenosides: Chemistry, biosynthesis, analysis, and potential health effects. Adv. Food Nutr. Res. 2008, 55, 1–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.H.; Yi, Y.S.; Kim, M.Y.; Cho, J.Y. Role of ginsenosides, the main active components of Panax ginseng, in inflammatory responses and diseases. J. Ginseng Res. 2017, 41, 435–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.H. Pharmacological and medical applications of Panax ginseng and ginsenosides: A review for use in cardiovascular diseases. J. Ginseng Res. 2018, 42, 264–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.H.; Lee, D.; Lee, H.L.; Kim, C.E.; Jung, K.; Kang, K.S. Beneficial effects of Panax ginseng for the treatment and prevention of neurodegenerative diseases: Past findings and future directions. J. Ginseng Res. 2018, 42, 239–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, I.S.; Uh, I.; Kim, K.S.; Kim, K.H.; Park, J.; Kim, Y.; Jung, J.H.; Jung, H.J.; Jang, H.J. Anti-inflammatory effects of ginsenoside Rg3 via NF−B pathway in A549 cells and human asthmatic lung tissue. J. Immunol. Res. 2016, 2016, 7521601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, H.; Baatar, D. Hwang SG. Anticancer activities of ginsenosides, the main active components of ginseng. Evid. Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2021, 2021, 8858006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, M.; Kim, K.H.; Jaiswal, V.; Choi, J.; Chun, J.L.; Seo, K.M.; Lee, M.J.; Lee, H.J. Effect of black ginseng and silkworm supplementation on obesity, the transcriptome, and the gut microbiome of diet-induced overweight dogs. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 16334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.Y.; Zhang, F.; Pan, W.; Yang, Y.F.; Jiang, X.Y. Clinical potentials of ginseng polysaccharide for treating gestational diabetes mellitus. World J. Clin. Cases 2021, 9, 4959–4979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.Y.; Irfan, M.; Quah, Y.; Saba, E.; Kim, S.D.; Park, S.C.; Jeong, M.-G.; Kwak, Y.-S.; Rhee, M.H. The increasing hematopoietic effect of the combined treatment of Korean Red ginseng and Colla corii asini on cyclophosphamide-induced immunosuppression in mice. J. Ginseng Res. 2021, 45, 591–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hyun, S.H.; Bhilare, K.D.; In, G.; Park, C.K.; Kim, J.H. Effects of Panax ginseng and ginsenosides on oxidative stress and cardiovascular diseases: Pharmacological and therapeutic roles. J. Ginseng Res. 2022, 46, 33–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, C.J.; Ryu, H.Y.; Lee, S.; Lee, H.J.; Chun, Y.S.; Kim, J.K.; Yu, C.Y.; Ghimire, B.K.; Lee, J.G. Neuroprotective Effect and Antioxidant Potency of Fermented Cultured Wild ginseng Root Extracts of Panax ginseng C.A. Meyer in Mice. Molecules 2021, 26, 3001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, M.M.; Xu, F.X.; Li, Y.J.; Xi, X.Z.; Cui, X.W.; Han, C.C.; Zhang, X.L. Study on transformation of ginsenosides in different methods. BioMed Res. Int. 2017, 2017, 8601027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siddiqi, M.Z.; Ximenes, H.A.; Song, B.K.; Park, H.Y.; Lee, W.H.; Han, H.; Im, W.T. Enhanced production of ginsenoside Rh2(S) from PPD-type major ginsenosides using BglSk cloned from Saccharibacillus kuerlensis together with two glycosidase in series. Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 2021, 28, 4668–4676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Y.; Jung, S.Y.; Kim, Y.J.; Lee, D.Y.; Min, J.W.; Wang, C.; Yang, D.C. Microbial ketonization of ginsenosides F1 and C-K by Lactobacillus brevis. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 2014, 106, 1215–1221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Qiao, L.R.; Xie, D.; Dai, J.G. Microbial deglycosylation and ketonization of ginsenosides Rg1 and Rb1 by Fusarium oxysporum. J. Asian Nat. Prod. Res. 2011, 13, 652–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.M.; Ni, P.; Wang, Y.X.; Shi, L.; Deng, G.G.; Zhu, M. Selection of composite microbial system for the transformation of ginsenoside compound K and optimization of the biotransformation conditions. J. Beihua Univ. 2016, 17, 473–476. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, G.; Yang, M.; Nong, S.; Yang, X.; Ling, Y.; Wang, D.; Wang, X.; Zhang, W. Microbial transformation of 20(S)-protopanaxadiol by Absidia corymbifera. Cytotoxic activity of the metabolites against human prostate cancer cells. Fitoterapia 2013, 84, 6–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tam, D.N.H.; Truong, D.H.; Nguyen, T.T.H.; Quynh, L.N.; Tran, L.; Nguyen, H.D.; Shamandy, B.E.; Le, T.M.H.; Tran, D.K.; Sayed, D.; et al. Ginsenoside Rh1: A systematic review of its pharmacological properties. Planta Med. 2018, 84, 139–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.Y. Synergistic effect of maclurin on ginsenoside compound K induced inhibition of the transcriptional expression of matrix metalloproteinase-1 in HaCaT human keratinocyte cells. J. Ginseng Res. 2018, 42, 229–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Meng, Y.; Sun, Q.; Zhang, Z.Y.; Guo, X.Q.; Sheng, X.T.; Tai, G.H.; Cheng, H.R.; Zhou, Y.F. Ginsenoside compound K sensitizes human colon cancer cells to TRAILinduced apoptosis via autophagy-dependent and -independent DR5 upregulation. Cell Death Dis. 2016, 7, e2334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, E.; Kim, D.; Yoo, S.; Hong, Y.H.; Han, S.Y.; Jeong, S.; Jeong, D.; Kim, J.H.; Cho, J.Y.; Park, J. The skin protective effects of compound K, a metabolite of ginsenoside Rb1 from Panax ginseng. J. Ginseng Res. 2018, 42, 218–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.Y.; Xiao, Y.K.; Hwang, E.; Haeng, J.J.; Yi, T.H. Antiphotoaging and Antimelanogenesis Properties of Ginsenoside C-Y,a Ginsenoside Rb2 Metabolite from American Ginseng PDD-Ginsenoside. Photochem. Photobiol. 2019, 95, 1412–1423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.Y.; Hwang, E.; Park, B.; Ngo, H.T.T.; Xiao, Y.K.; Yi, T.H. Ginsenoside C-Mx Isolated from Notoginseng Stem-leaf Ginsenosides Attenuates Ultraviolet B-mediated Photoaging in Human Dermal Fibroblasts. Photochem. Photobiol. 2018, 94, 1040–1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, L.; Guo, J.; Ge, R.S. Environmental pollutants and hydroxysteroid dehydrogenases. Vitam. Horm. 2014, 94, 349–390. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Penning, T.M. Molecular endocrinology of hydroxysteroid dehydrogenases. Endocr. Rev. 1997, 18, 281–305. [Google Scholar]
- Hofmann, A.F.; Roda, A. Physicochemical properties of bile acids and their relationship to biological properties: An overview of the problem. J. Lipid Res. 1984, 25, 1477–1489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watanabe, M.; Fukiya, S.; Yokota, A. Comprehensive evaluation of the bactericidal activities of free bile acids in the large intestine of humans and rodents. J. Lipid Res. 2017, 58, 1143–1152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makishima, M.; Lu, T.T.; Xie, W.; Whitfield, G.K.; Domoto, H.; Evans, R.M.; Haussler, M.R.; Mangelsdorf, D.J. Vitamin D receptor as an intestinal bile acid sensor. Science 2002, 296, 1313–1317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herl, V.; Rankenstein, J.; Meitinger, N.; Müller-Uri, F.; Kreis, W. Delta 5-3beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase (3βHSD) from Digitalis lanata. Heterologous expression and characterisation of the recombinant enzyme. Planta Med. 2007, 73, 704–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Persson, B.; Kallberg, Y.; Bray, J.E.; Bruford, E.; Dellaporta, S.L.; Favia, A.D.; Duarte, R.G.; Jornvall, H.; Kavanagh, K.L.; Kedishvili, N.; et al. The SDR (short-chain dehydrogenase/reductase and related enzymes) nomenclature initiative. Chem. Biol. Interact. 2009, 178, 94–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Persson, B.; Kallberg, Y. Classification and nomenclature of the superfamily of shortchain dehydrogenases/reductases (SDRs), Chem. Biol. Interact. 2013, 202, 111–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kisiela, M.; Skarka, A.; Ebert, B.; Maser, E. Hydroxysteroid dehydrogenases (HSDs) in bacteria: A bioinformatic perspective. J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2012, 129, 31–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kallberg, Y.; Oppermann, U.; Jornvall, H.; Persson, B. Short-chain dehydrogenase/ reductase (SDR) relationships: A large family with eight clusters common to human, animal, and plant genomes. Protein Sci. 2002, 11, 636–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, Y.H.; Hong, S.M.; Kim, C.H. Isolation and Characterization of Lactic Acid Bacteria from Kimchi, Korean Traditional Fermented Food to Apply into Fermented Dairy Products. Food Sci. Anim. Resour. 2013, 33, 75–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.S.; Bae, I.H.; Han, J.; Choi, G.Y.; Hwang, K.H.; Kim, D.H.; Yeom, M.H.; Park, Y.H.; Park, M. Compound K inhibits MMP-1 expression through suppression of c-Src-dependent ERK activation in TNF-α-stimulated dermal fibroblast. Exp. Dermatol. 2014, 23, 819–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tawab, M.A.; Bahr, U.; Karas, M.; Wurglics, M.; Schubert-Zsilavecz, M. Degradation of ginsenosides in humans after oral administration. Drug Metab. Dispos. 2003, 31, 1065–1071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.; Park, Y.G.; Lee, H.-J.; Lim, S.J.; Nho, C.W. Youngiasides A and C isolated from Youngia denticulatum inhibit UVB-Induced MMP expression and promote type I procollagen pro-duction via repression of MAPK/AP-1/NF-jB and activation ofAMPK/Nrf2 in HaCaT cells and human dermal fibroblasts. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2015, 63, 5428–5438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwok, H.-H.; Yue, P.Y.-K.; Mak, N.-K.; Wong, R.N.-S. Ginsenoside Rb1 induces type I collagen expression through peroxi-some proliferator-activated receptor-delta. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2012, 84, 532–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, D.; Sun, J.; Zhu, X.; Nian, S.; Liu, J. Compound K increases type I procollagen level and decreases matrix metalloproteinase-1 activity and level in ultraviolet-A-irradiated fibroblasts. J. Med. Assoc. 2011, 110, 153–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shenton, J.M.; Teranishi, M.; Abu-Asab, M.S.; Yager, J.A.; Uetrecht, J.P. Characterization of a potential animal model of anidiosyncratic drug reaction: Nevirapine-induced skin rash in the rat. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2003, 16, 1078–1089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weiss, R.B.; Donehower, R.; Wiernik, P.; Ohnuma, T.; Gralla, R.; Trump, D.; Baker, J., Jr.; Van Echo, D.; Von Hoff, D.; Leyland-Jones, B. Hypersensitivity reactions from taxol. J. Clin. Oncol. 1990, 8, 1263–1268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, G.S.; Shin, J.S.; Kim, W.; Baik, M.Y. Increases in Ginsenoside Rg3, Compound K, and Antioxidant Activity of Cultivated Wild Panax Ginseng (CWPG) by Puffing. Foods 2022, 11, 2936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chittasupho, C.; Manthaisong, A.; Okonogi, S.; Tadtong, S.; Samee, W. Effects of Quercetin and Curcumin Combination on Antibacterial, Antioxidant, In Vitro Wound Healing and Migration of Human Dermal Fibroblast Cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 23, 142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Metal Ions or Reagents | Relative Activity ± SD (%) 10 mM |
|---|---|
| Control | 100.0 ± 5.4 |
| CoCl2 | 19.8 ± 1.0 |
| MgCl2 | 138.1 ± 8.5 |
| FeCl3 | 15.6 ± 1.3 |
| NaCl | 85.6 ± 6.2 |
| CuSO4 | 10.6 ± 0.5 |
| NH4Cl | 89.4 ± 5.1 |
| KCl | 76.7 ± 6.0 |
| CaCl2 | 63.4 ± 3.4 |
| ZnSO4 | 6.5 ± 0.9 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jin, Y.; Wang, D.; Im, W.-T.; Siddiqi, M.Z.; Yang, D.-C. Ketonization of Ginsenoside C-K by Novel Recombinant 3-β-Hydroxysteroid Dehydrogenases and Effect on Human Fibroblast Cells. Molecules 2023, 28, 3792. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28093792
Jin Y, Wang D, Im W-T, Siddiqi MZ, Yang D-C. Ketonization of Ginsenoside C-K by Novel Recombinant 3-β-Hydroxysteroid Dehydrogenases and Effect on Human Fibroblast Cells. Molecules. 2023; 28(9):3792. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28093792
Chicago/Turabian StyleJin, Yan, Dandan Wang, Wan-Taek Im, Muhammad Zubair Siddiqi, and Deok-Chun Yang. 2023. "Ketonization of Ginsenoside C-K by Novel Recombinant 3-β-Hydroxysteroid Dehydrogenases and Effect on Human Fibroblast Cells" Molecules 28, no. 9: 3792. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28093792
APA StyleJin, Y., Wang, D., Im, W.-T., Siddiqi, M. Z., & Yang, D.-C. (2023). Ketonization of Ginsenoside C-K by Novel Recombinant 3-β-Hydroxysteroid Dehydrogenases and Effect on Human Fibroblast Cells. Molecules, 28(9), 3792. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28093792







