Design and Synthesis of a Novel ICT Bichromophoric pH Sensing System Based on 1,8-Naphthalimide Fluorophores as a Two-Input Logic Gate and Its Antibacterial Evaluation
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
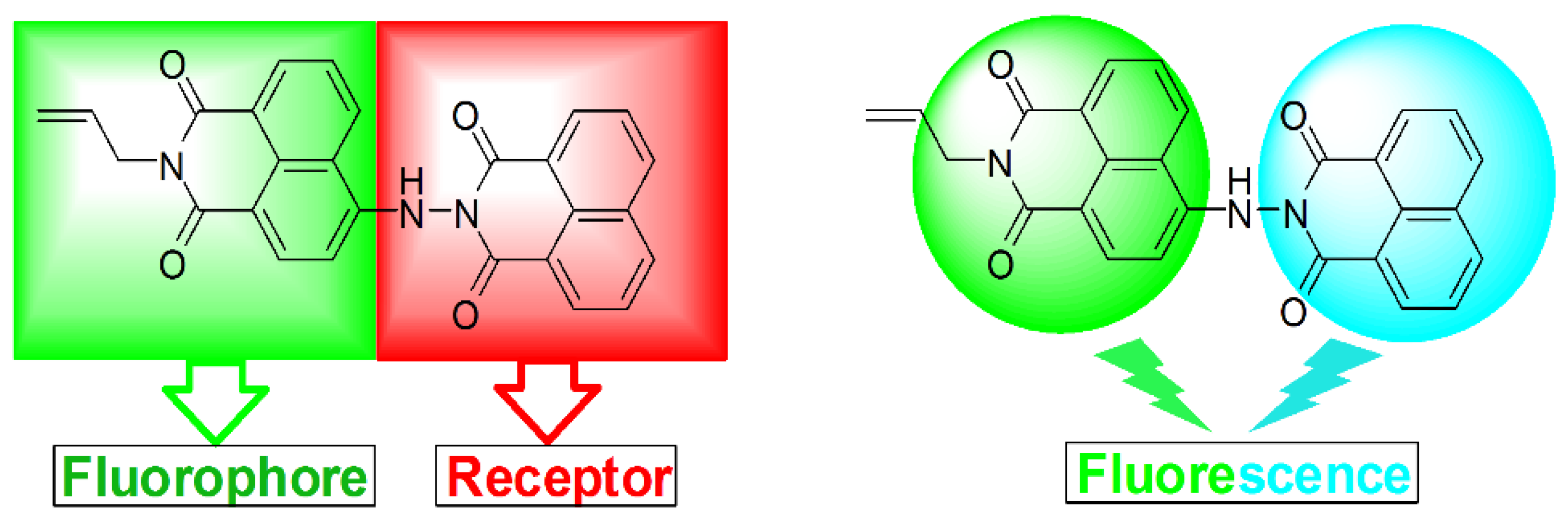
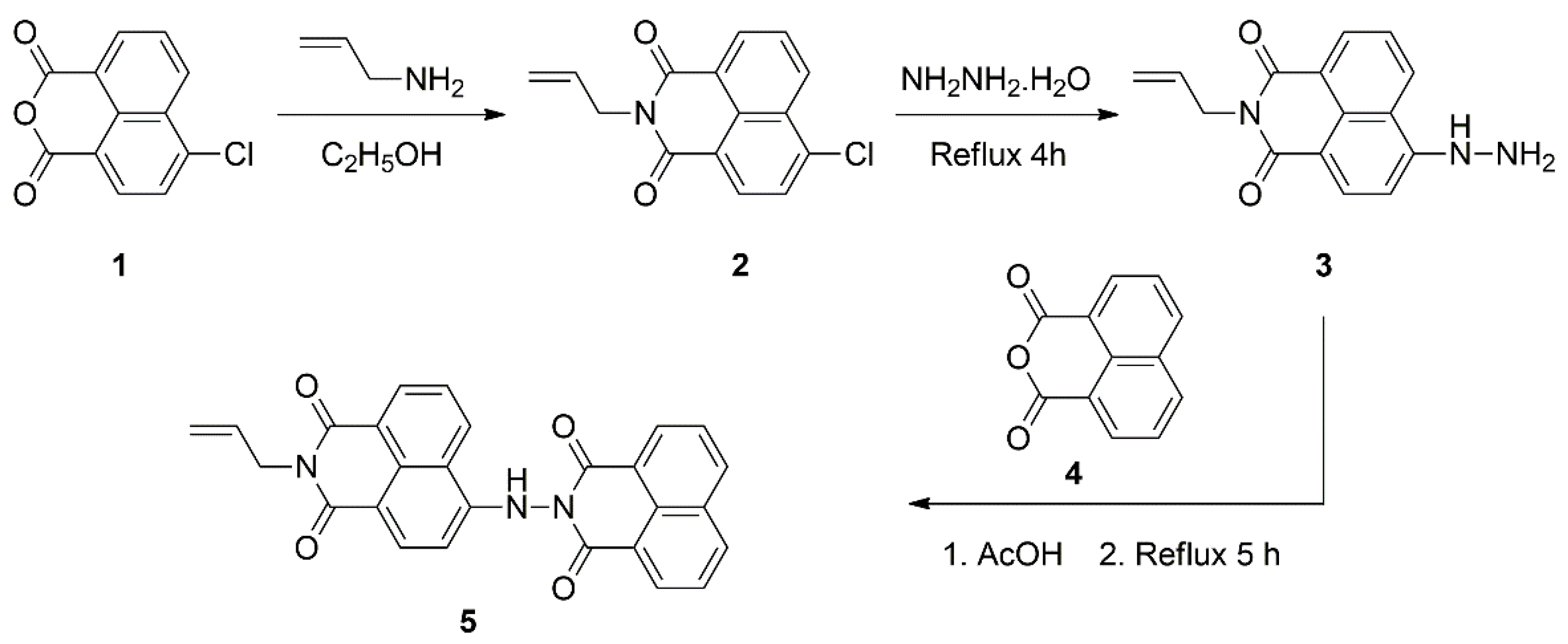
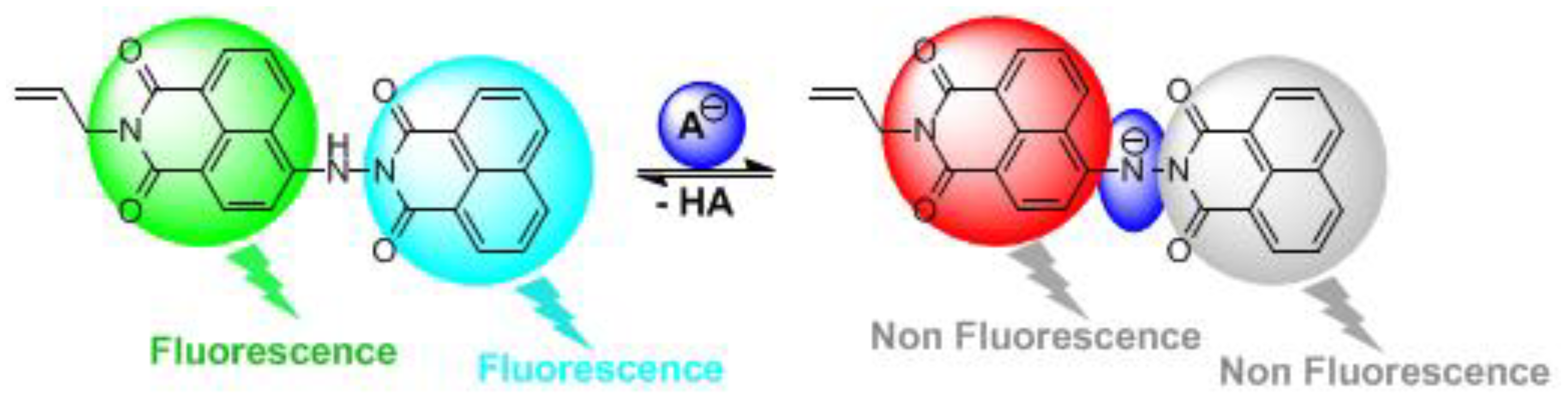
2.1. Design and Synthesis of Bichromophoric System 5
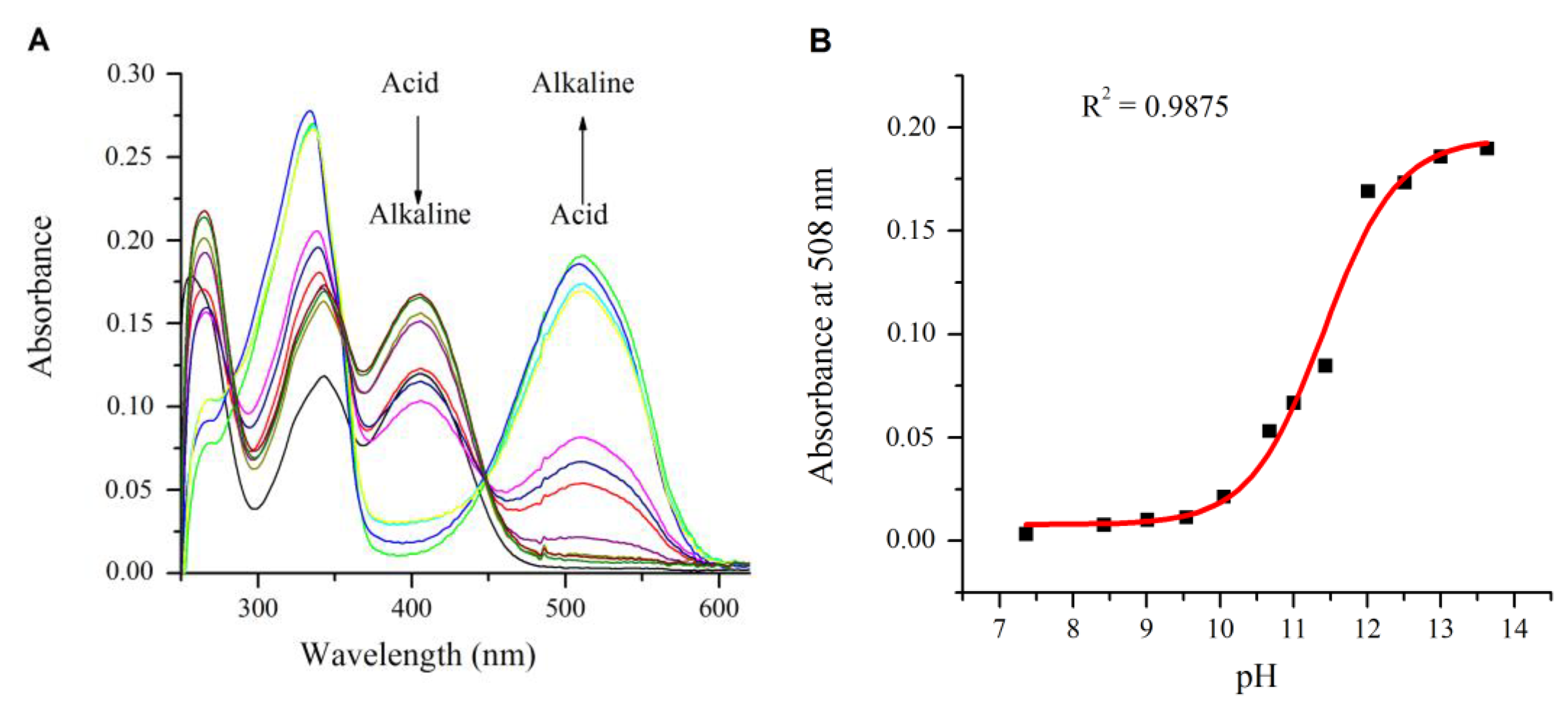
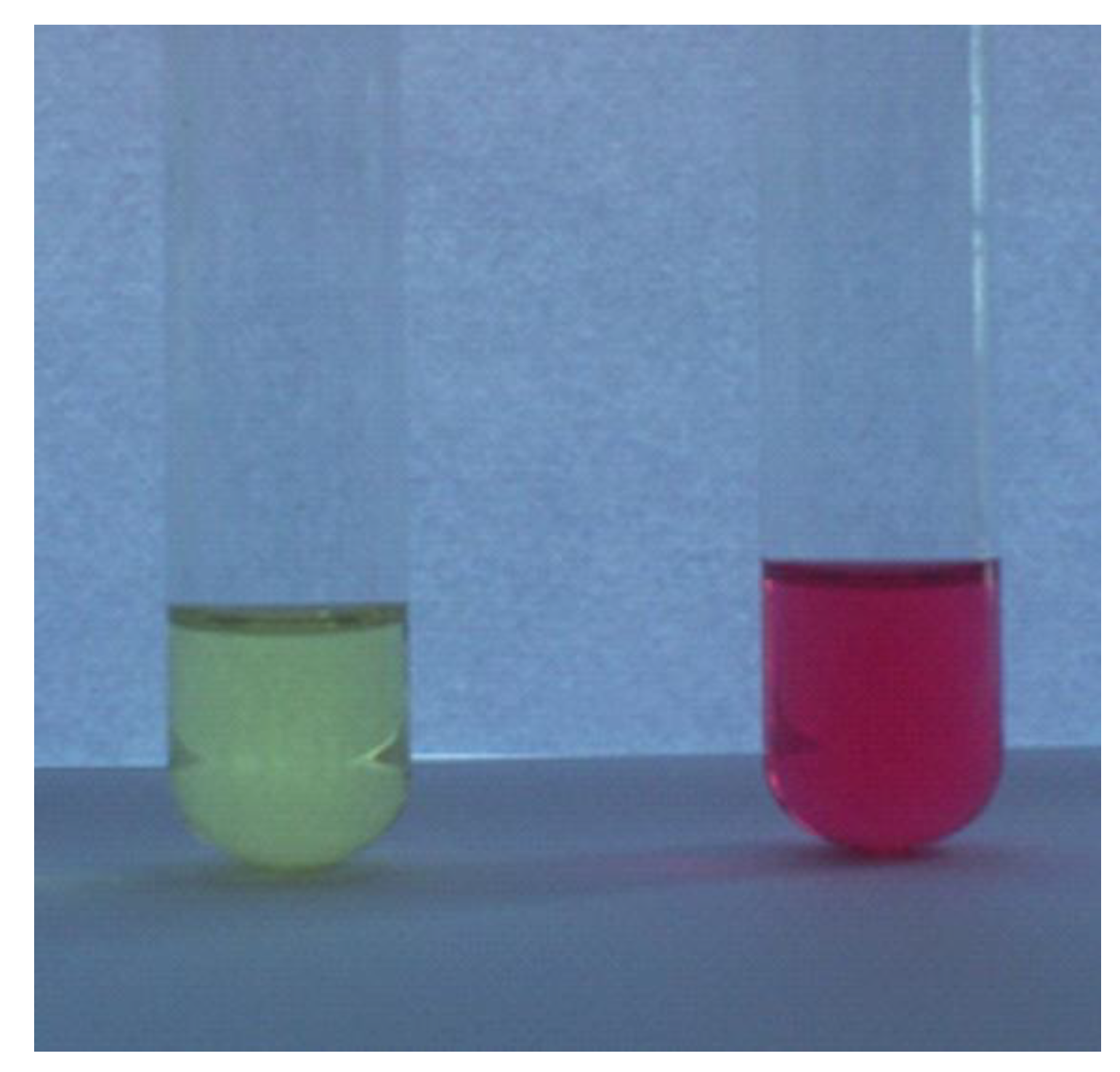
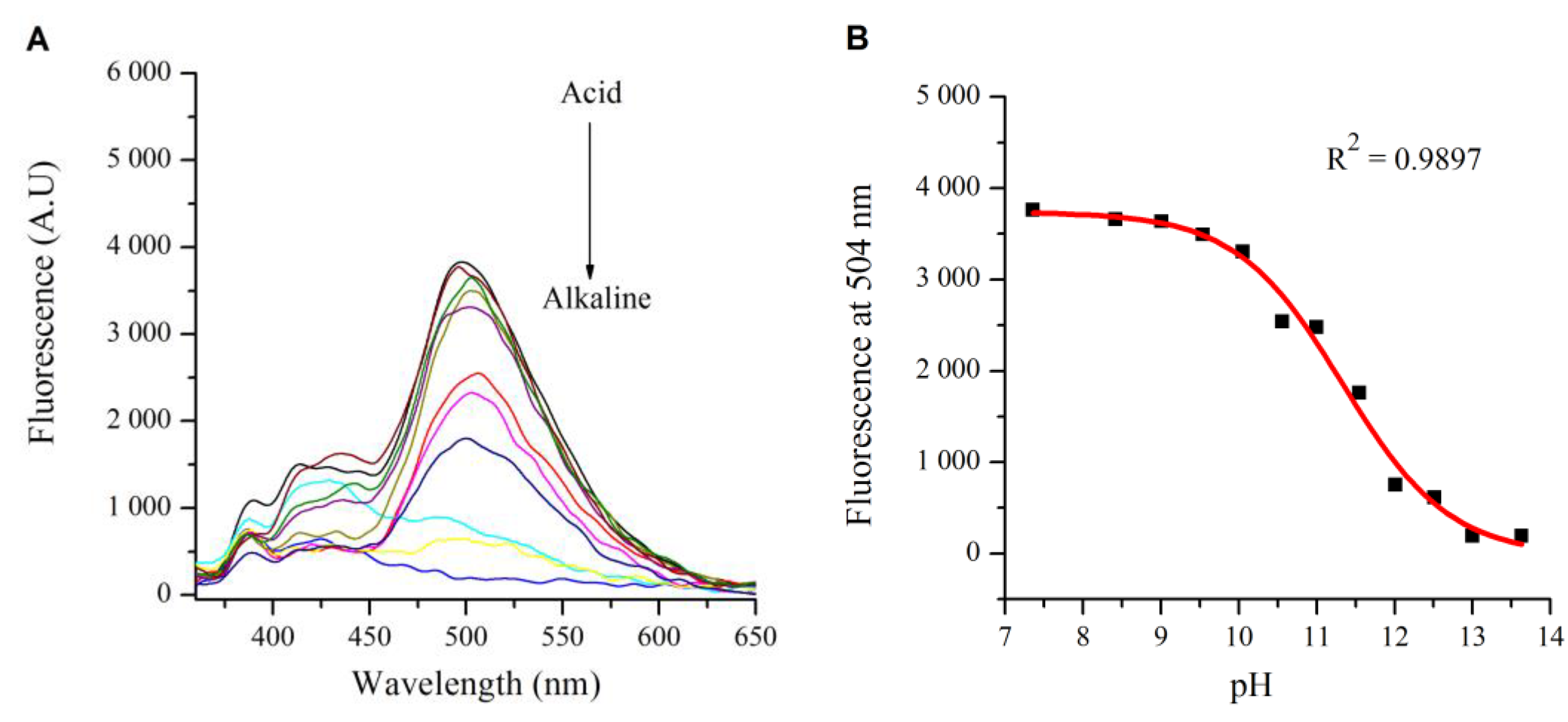
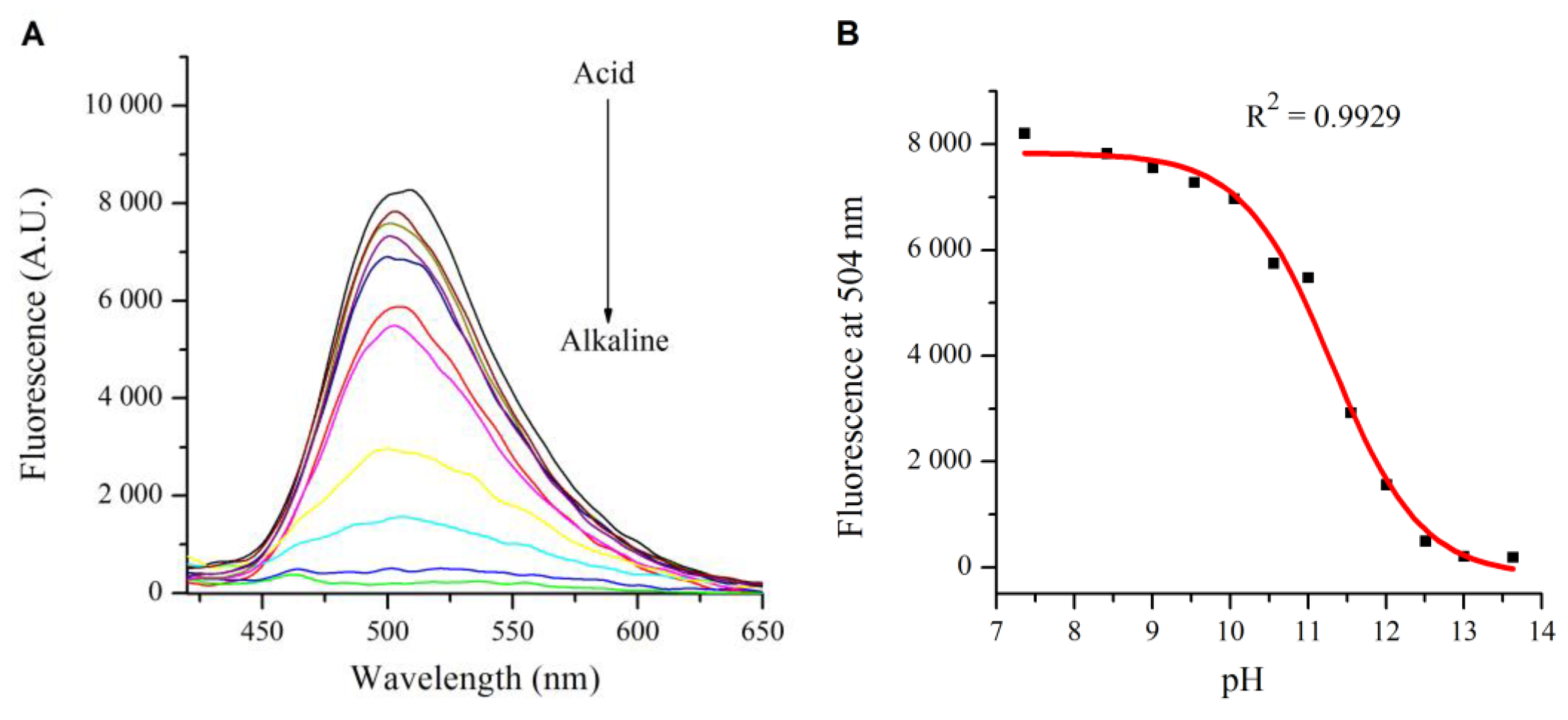
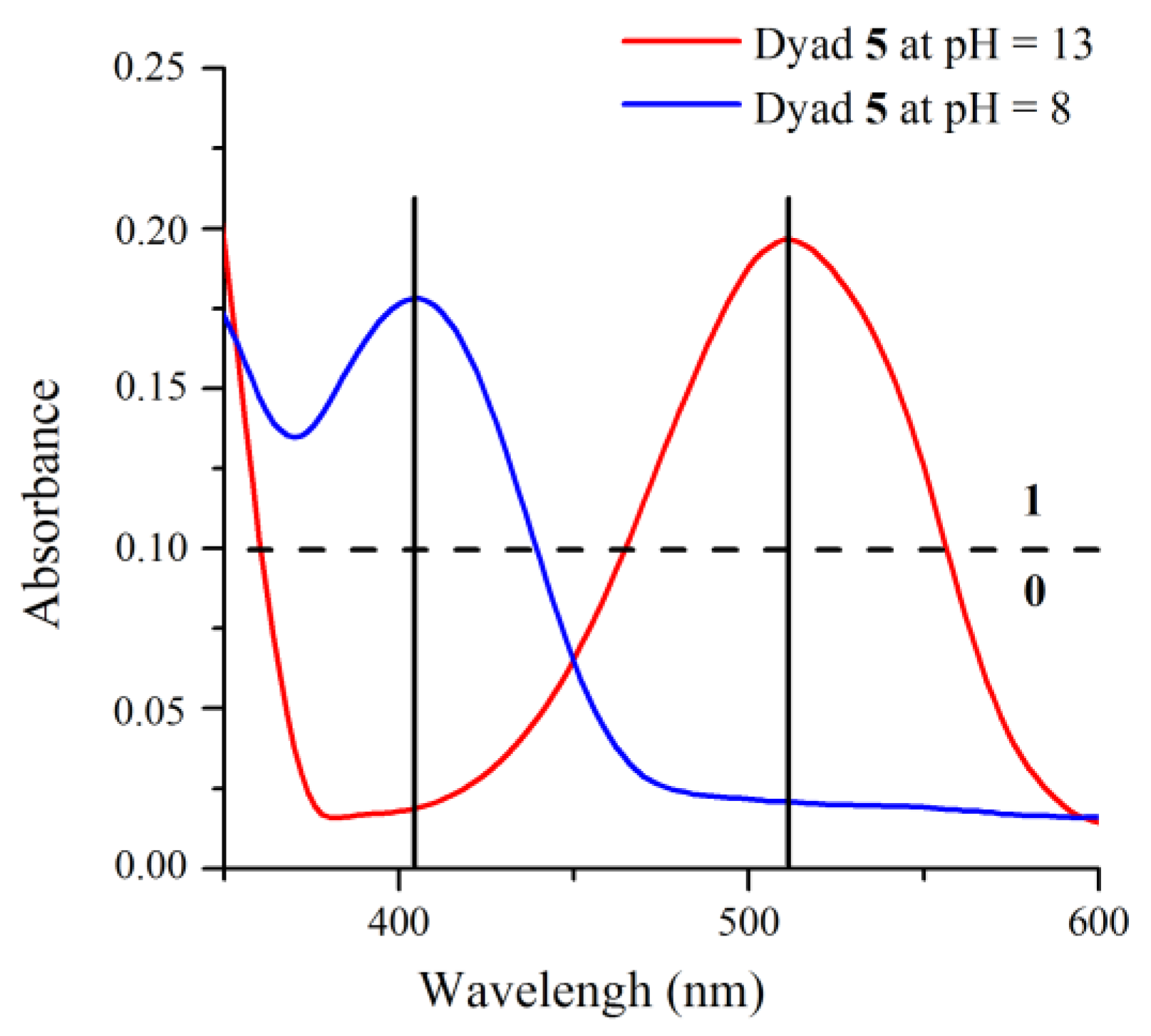
2.2. Influence of pH on the Absorption and Fluorescence Characteristics of Bichromophoric System 5
2.3. Logic Gates of Probe 5
2.4. Antibacterial Evaluation of the Synthesized Dyes
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials
3.2. Methods
3.3. Synthetic Procedures
3.3.1. Synthesis of 4-Chloro-N-allyl-1,8-naphthalimide (2)
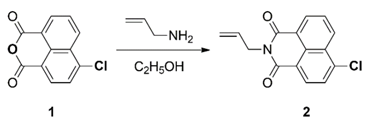
3.3.2. Synthesis of 4-Hydrazinyl-N-allyl-1,8-naphthalimide (3)
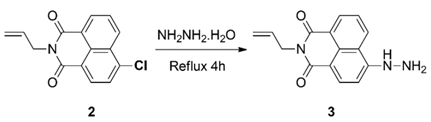
3.3.3. Synthesis of Dyad 5
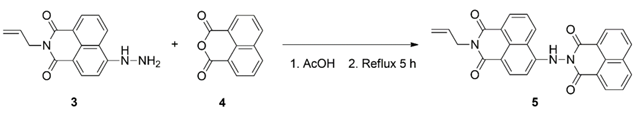
3.4. Antibacterial Screening of the Synthesized Compounds
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Sample Availability
References
- Dickert, F.; Sikorski, R. Supramolecular strategies in chemical sensing. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 1999, 10, 39–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Liu, W.; Ge, J.; Zhang, H.; Wang, P. New sensing mechanisms for design of fluorescent chemosensors emerging in recent years. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2011, 40, 3483–3495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, L.; Dong, B.; Liu, Y.; Lin, W. Fluorescent chemosensors manipulated by dual/triple interplaying sensing mechanisms. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2016, 45, 6449–6461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saleem, M.; Lee, K. Optical sensor: A promising strategy for environmental and biomedical monitoring of ionic species. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 72150–72287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rouhani, S.; Haghgoo, S. A novel fluorescence nanosensor based on1,8-naphthalimide-thiophene doped silica nanoparticles, and its application to the determination ofmethamphetamine. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2015, 209, 957–965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Georgiev, N.; Bakov, V.; Anichina, K.; Bojinov, V. Fluorescent probes as a tool in diagnostic and drug delivery systems. Pharmaceuticals 2023, 16, 381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, M.; Yu, F.; Lv, C.; Choo, J.; Chen, L. Fluorescent chemical probes for accurate tumor diagnosis and targeting therapy. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2017, 46, 2237–2271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ji, L.; Zhou, X.; Liu, R.; Wang, L.; Hu, Y.; Gu, J.; Li, Z.; Li, C.; Huang, T.; Yu, Y. Design of a selective and water-soluble fluorescent probe targeting Tau fibrils for intracellular and in vivo imaging. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2023, 380, 133415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Georgiev, N.; Bryaskova, R.; Tzoneva, R.; Ugrinova, I.; Detrembleur, C.; Miloshev, S.; Asiri, A.; Qusti, A.; Bojinov, V. A novel pH sensitive water soluble fluorescent nanomicellar sensor for potential biomedical applications. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2013, 21, 6292–6302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lang, W.; Yuan, C.; Zhu, L.; Du, S.; Qian, L.; Gea, J.; Yao, S.Q. Recent advances in construction of small molecule-based fluorophore-drug conjugates. J. Pharm. Anal. 2020, 10, 434–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnson, A.D.; Zammit, R.; Vella, J.; Valentino, M.; Buhagiar, J.A.; Magri, D.C. Aminonaphthalimide hybrids of mitoxantrone and amonafide as anticancer and fluorescent cellular imaging agents. Bioorg. Chem. 2019, 93, 103287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, P.; Pan, W.; Li, N.; Tang, B. Fluorescent probes for organelle-targeted bioactive species imaging. Chem. Sci. 2019, 10, 6035–6071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valeur, B.; Leray, I. Design principles of fluorescent molecular sensors for cation recognition. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2000, 205, 3–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Silva, A.P.; Vance, T.; West, M.; Wright, G. Bright molecules with sense, logic, numeracy and utility. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2008, 6, 2468–2481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zammit, R.; Pappova, M.; Zammit, E.; Gabarretta, J.; Magri, D. 1,3,5-Triarylpyrazolines—pH-driven off-on-off molecular logic devices based on a “receptor1–fluorophore–spacer–receptor2” format with internal charge transfer (ICT) and photoinduced electron transfer (PET) mechanisms. Can. J. Chem. 2015, 93, 199–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daly, B.; Ling, J.; de Silva, A. Current developments in fluorescent PET (photoinduced electron transfer) sensors and switches. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2015, 44, 4203–4211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Georgiev, N.; Krasteva, P.; Bakov, V.; Bojinov, V. A highly water-soluble and solid state emissive 1,8-naphthalimide as a fluorescent PET probe for determination of pHs, acid/base vapors, and water content in organic solvents. Molecules 2022, 27, 4229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badugu, R. Fluorescence sensor design for transition metal ions: The role of the PIET interaction efficiency. J. Fluoresc. 2005, 15, 71–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bakov, V.; Georgiev, N.; Bojinov, V. A novel fluorescent probe for determination of pH and viscosity based on a highly water-soluble 1,8-naphthalimide rotor. Molecules 2022, 27, 7556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sareen, P.; Kaur, D.; Singh, K. Strategies in detection of metal ions using dyes. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2014, 265, 125–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Georgiev, N.; Bojinov, V.; Nikolov, P. The design, synthesis and photophysical properties of two novel 1,8-naphthalimide fluorescent pH sensors based on PET and ICT. Dyes Pigm. 2011, 88, 350–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakr, A.; Georgiev, N.; Bojinov, V. Design, photochemistry, logic gates behavior and antibacterial evaluation of ICT systems based on 1,8-naphthalimides. J. Fluoresc. 2023, 33, 43–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dash, N.; Malakar, A.; Kumar, M.; Mandal, B.; Krishnamoorthy, G. Metal ion dependent “ON” intramolecular charge transfer (ICT) and “OFF” normal switching of the fluorescence: Sensing of Zn2+ by ICT emission in living cells. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2014, 202, 1154–1163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Wu, F.; Feng, S.; Xu, J.; Xu, Z.; Chen, Y.; Tang, T.; Weng, X.; Zhou, X. A convenient ratiomeric pH probe and its application for monitoring pH change in living cells. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2014, 196, 194–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Georgiev, N.; Dimitrova, M.; Krasteva, P.; Bojinov, V. A novel water-soluble 1,8-naphthalimide as a fluorescent pH-probe and a molecular logic circuit. J. Lumin. 2017, 187, 383–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerbich, T.; Schmitt, H.; Fischer, I.; Mitrić, R.; Petersen, J. Dynamics of isolated 1,8-naphthalimide and N-methyl-1,8-naphthalimide: An experimental and computational study. J. Phys. Chem. A 2016, 120, 2089–2095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Georgiev, N.; Yaneva, I.; Surleva, A.; Asiri, A.; Bojinov, V. Synthesis, sensor activity and logic behavior of a highly water-soluble naphthalimide derivative. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2013, 184, 54–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magri, D.; de Silva, A. From PASS 1 to YES to AND logic: Building parallel processing into molecular logic gates by sequential addition of receptors. New J. Chem. 2010, 34, 476–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amelia, M.; Zou, L.; Credi, A. Signal processing with multicomponent systems based on metal complexes. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2010, 254, 2267–2280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balzani, V. Photochemical molecular devices. Photochem. Photobiol. Sci. 2003, 2, 459–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dimov, S.; Georgiev, N.; Asiri, A.; Bojinov, V. Synthesis and sensor activity of a PET-based 1,8-naphthalimide probe for Zn2+ and pH determination. J. Fluoresc. 2014, 24, 1621–1628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, L.; Lu, M.; Tian, H. Selective supramolecular bindings for stepwise signal output. Tetrahedron 2012, 68, 79–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alamry, K.; Georgiev, N.; Abdullah El-Daly, S.; Taib, L.; Bojinov, V. A highly selective ratiometric fluorescent pH probe based on a PAMAM wavelength-shifting bichromophoric system. Spectrochim. Acta Part A 2015, 135, 792–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamilton, G.; Sahoo, S.; Kamila, S.; Singh, N.; Kaur, N.; Hyland, B.; Callan, J. Optical probes for the detection of protons, and alkali and alkaline earth metal cations. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2015, 44, 4415–4432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Georgiev, N.; Asiri, A.; Qusti, A.; Alamry, K.; Bojinov, V. Design and synthesis of pH-selective fluorescence sensing PAMAM light-harvesting dendrons based on 1,8-naphthalimides. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2014, 190, 185–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, L.; Qian, J.; Tian, H.; Lan, M.; Zhang, W. A colorimetric and fluorescent dual probe for specific detection of cysteine based on intramolecular nucleophilic aromatic substitution. Analyst 2012, 137, 5046–5050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alamry, K.; Georgiev, N.; Abdullah El-Daly, S.; Taib, L.; Bojinov, V. A ratiometric rhodamine-naphthalimide pH selective probe built on the basis of a PAMAM light-harvesting architecture. J. Lumin. 2015, 158, 50–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, S.; Zhang, X.; Bai, S.; Miao, J.; Zhao, B. A novel ratiometric pH probe for extreme acidity based on FRET and PET. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 13341–13346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Georgiev, N.; Asiri, A.; Alamry, K.; Obaid, A.; Bojinov, V. Selective ratiometric pH-sensing PAMAM light-harvesting dendrimer based on Rhodamine 6G and 1,8-naphthalimide. J. Photochem. Photobiol. A Chem. 2014, 277, 62–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alam, M.Z.; Alimuddin; Khan, S.A. A review on Schiff base as a versatile fluorescent chemo-sensors tool for detection of Cu2+ and Fe3+ metal ion. J. Fluoresc. 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alam, M.Z.; Khan, S.A. A review on rhodamine-based Schiff base derivatives: Synthesis and fluorescent chemo-sensors behaviour for detection of Fe3+ and Cu2+ ions. J. Coord. Chem. 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Thaqafy, S.H.; Asiri, A.M.; Zayed, M.E.M.; Alam, M.Z.; Ahmad, A.; Fatima, M.; Kumar, S.; Khan, S.A. Physicochemical investigation and fluorescence quenching of biologically active pyrrole-containing push-pull chromophore by Ag nanoparticles. J. Mol. Struct. 2023, 1274, 134421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aviram, A. Molecules for memory, logic, and amplification. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1988, 110, 5687–5692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Silva, A.P.; Gunaratne, H.; McCoy, C. A molecular photoionic AND gate based on fluorescent signaling. Nature 1993, 364, 42–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bojinov, V.; Georgiev, N. Molecular sensors and molecular logic gates. J. Univ. Chem. Technol. Metall. 2011, 46, 3–26. [Google Scholar]
- Georgiev, N.; Lyulev, M.; Bojinov, V. Sensor activity and logic behavior of PET based dihydroimidazonaphthalimide diester. Spectrochim. Acta Part A 2012, 97, 512–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaur, N. Supramolecular switches-advanced molecular logic and computation molecular logic gates. Curr. Org. Chem. 2014, 18, 2892–2909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Georgiev, N.; Dimitrova, M.; Asiri, A.; Alamry, K.; Bojinov, V. Synthesis, sensor activity and logic behaviour of a novel bichromophoric system based on rhodamine 6G and 1,8-naphthalimide. Dyes Pigm. 2015, 115, 172–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, J.; Qian, X.; Xu, Y.; Zhang, S. Multiple molecular logic functions and molecular calculations facilitated by surfactant’s versatility. Chem. Commun. 2008, 35, 4141–4143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andréasson, J.; Pischel, U. Molecules with a sense of logic: A progress report. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2015, 44, 1053–1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marinova, N.; Georgiev, N.; Bojinov, V. Facile synthesis, sensor activity and logic behaviour of 4-aryloxy substituted 1,8-naphthalimide. J. Photochem. Photobiol. A Chem. 2013, 254, 54–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pais, V.; Remon, P.; Collado, D.; Andréasson, J.; Perez-Inestrosa, E.; Pischel, U. OFF–ON–OFF fluorescence switch with T-latch function. Org. Lett. 2011, 13, 5572–5575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pu, F.; Ju, E.; Ren, J.; Qu, X. Multiconfigurable logic gates based on fluorescence switching in adaptive coordination polymer nanoparticles. Adv. Mater. 2014, 26, 1111–1117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Magri, D.; Fava, M.; Mallia, C. A sodium-enabled ‘Pourbaix sensor’: A three-input AND logic gate as a ‘lab-on-a-molecule’ for monitoring Na+, PH and PE. Chem. Commun. 2014, 50, 1009–1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ling, J.; Naren, G.; Kelly, J.; Moody, T.; de Silva, A.P. Building pH sensors into paper-based small-molecular logic systems for very simple detection of edges of objects. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2015, 137, 3763–3766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Silva, A.P.; McClenaghan, N. Molecular-scale logic gates. Chem. Eur. J. 2004, 10, 574–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Georgiev, N.; Sakr, A.; Bojinov, V. Design and synthesis of a novel PET and ICT based 1,8-naphthalimide FRET bichromophore as a four-input Disabled–Enabled-OR logic gate. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2015, 221, 625–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magri, D.; Vance, T.; de Silva, A.P. From complexation to computation: Recent progress in molecular logic. Inorg. Chim. Acta 2007, 360, 751–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Georgiev, N.; Dimitrova, M.; Todorova, Y.; Bojinov, V. Synthesis, chemosensing properties and logic behaviour of a novel ratiometric 1,8-naphthalimide probe based on ICT and PET. Dyes Pigm. 2016, 131, 9–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Silva, A.P.; Uchiyama, S. Molecular logic gates and luminescent sensors based on photoinduced electron transfer. Top. Curr. Chem. 2011, 300, 1–28. [Google Scholar]
- Said, A.; Georgiev, N.; Bojinov, V. Synthesis of a single 1,8-naphthalimide fluorophore as a molecular logic lab for simultaneously detecting of Fe3+, Hg2+ and Cu2+. Spectrochim. Acta Part A 2018, 196, 76–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Silva, A.P. Molecular Logic-Based Computation; Royal Society of Chemistry: Cambridge, UK, 2013; p. 417. [Google Scholar]
- Said, A.; Georgiev, N.; Bojinov, V. A smart chemosensor: Discriminative multidetection and various logic operations in aqueous solution at biological pH. Spectrochim. Acta Part A 2019, 223, 117304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, W.; Zhang, H.; Liu, Y. Unimolecular half-adders and half-subtractors based on acid-base reaction. Front. Chem. China 2009, 4, 292–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Said, A.; Georgiev, N.; Bojinov, V. A fluorescent bichromophoric “off-on-off” pH probe as a molecular logic device (half-subtractor and digital comparator) operating by controlled PET and ICT processes. Dyes Pigm. 2019, 162, 377–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Margulies, D.; Melman, G.; Shanzer, A. Full-adder and full-subtractor, an additional step toward a moleculator. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2006, 128, 4865–4871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amelia, M.; Baroncini, M.; Credi, A. A simple unimolecular multiplexer/demultiplexer. Angew. Chem. 2008, 120, 6336–6339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ceroni, P.; Bergamini, G.; Balzani, V. Old molecules, new concepts: [Ru(bpy)3]2+ as a molecular encoder–decoder. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2009, 48, 8516–8518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Georgiev, N.; Dimov, S.; Asiri, A.; Alamry, K.; Obaid, A.; Bojinov, V. Synthesis, selective pH-sensing activity and logic behavior of highly water-soluble 1,8-naphthalimide and dihydroimidazonaphthalimide derivatives. J. Lumin. 2014, 149, 325–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Said, A.; Georgiev, N.; Hamdan, S.; Bojinov, V. A chemosensoring molecular lab for various analytes and its ability to execute a molecular logical digital comparator. J. Fluoresc. 2019, 29, 1431–1443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Georgiev, N.; Lyulev, M.; Alamry, K.; El-Daly, S.; Taib, L.; Bojinov, V. Synthesis, sensor activity and logic behavior of a highly water-soluble 9,10-dihydro-7H-imidazo[1,2-b]benz[d,e]isoqionolin-7-one dicarboxylic acid. J. Photochem. Photobiol. A Chem. 2014, 297, 31–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Said, A.; Georgiev, N.; Bojinov, V. A novel dual naked eye colorimetric and fluorescent pH chemosensor and its ability to execute three INHIBIT based digital comparator. Dyes Pigm. 2022, 205, 110489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Yue, Y.; Guo, Y.; Shao, S. Fluoride anions triggered “OFF–ON” fluorescent sensor for hydrogen sulfate anions based on a BODIPY scaffold that works as a molecular keypad lock. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2012, 173, 797–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thottiparambil, A.; Kumar, P.; Chakkumkumarath, L. Styrylcyanine-based ratiometric and tunable fluorescent pH sensors. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 56063–56067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Huang, D.; Niu, C.; Guo, L.; Cui, J.; Hu, L.; Zeng, G. An internal reference fluorescent pH sensor with two pH-sensitive fluorophores carrier. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2016, 234, 593–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gotor, R.; Ashokkumar, P.; Hecht, M.; Keil, K.; Rurack, K. Optical pH sensor covering the range from pH 0-14 compatible with mobile-device readout and based on a set of rationally designed indicator dyes. Anal. Chem. 2017, 89, 8437–8444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.; Mukherjee, K.; Shoukat, R.; Dong, H. A review on pH sensitive materials for sensors and detection methods. Microsyst. Technol. 2017, 23, 4391–4404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spiteri, J.; Johnson, A.; Denisov, S.; Jonusauskas, G.; McClenaghan, N.; Magri, D. A fluorescent AND logic gate based on a ferrocene-naphthalimide-piperazine format responsive to acidity and oxidizability. Dyes Pigm. 2018, 157, 278–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Zhang, L.; Tian, Y. Micro electrochemical pH sensor applicable for real-time ratiometric monitoring of pH values in rat brains. Anal. Chem. 2016, 88, 2113–2118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, M.; Du, L.; Yu, H.; Zhang, K.; Liu, Y.; Wang, S. An intramolecular charge transfer process based fluorescent probe for monitoring subtle pH fluctuation in living cells. Talanta 2017, 162, 180–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Bu, F.; Zhao, Y.; Zhao, B.; Wang, L.; Song, B. A hemicyanine fluorescent probe with intramolecular charge transfer (ICT) mechanism for highly sensitive and selective detection of acidic pH and its application in living cells. Anal. Chim. Acta 2020, 1098, 155–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Georgiev, N.I.; Said, A.I.; Toshkova, R.A.; Tzoneva, R.D.; Bojinov, V.B. A novel water-soluble perylenetetracarboxylic diimide as a fluorescent pH probe: Chemosensing, biocompatibility and cell imaging. Dyes Pigm. 2019, 160, 28–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Fang, C.; Chang, T.; Liu, X.; Shangguan, D. A pH sensitive ratiometric fluorophore and its application for monitoring the intracellular and extracellular pHs simultaneously. J. Mater. Chem. B 2013, 1, 661–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, Y.; Zhou, J.; Gao, Z.; Sun, X.; Liu, C.; Shangguan, D.; Yang, W.; Gao, M. Protease-activated ratiometric fluorescent probe for pH mapping of malignant tumors. ACS Nano 2015, 9, 3199–3205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daffy, L.; de Silva, A.; Gunaratne, H.; Huber, C.; Lynch, P.; Werner, T.; Wolfbeis, O. Arenedicarboximide building blocks for fluorescent photoinduced electron transfer pH sensors applicable with different media and communication wavelengths. Chem. Eur. J. 1998, 4, 1810–1815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, J.; Xu, Y.; Qian, X.; Zhang, S. Molecular logic operations based on surfactant nanoaggregates. ChemPhysChem 2008, 9, 1891–1898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Chen, H.; Kirillov, A.; Xie, Y.; Shan, C.; Wang, B.; Shia, C.; Tang, Y. A paper-based lanthanide smart device for acid–base vapour detection, anti-counterfeiting and logic operations. Inorg. Chem. Front. 2016, 3, 1014–1020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez, A.W.; Phillips, S.T.; Whitesides, G.M. Diagnostics for the developing world: Microfluidic paper-based analytical devices. Anal. Chem. 2010, 82, 3–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nery, E.W.; Kubota, L.T. Sensing approaches on paper-based devices: A review. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2013, 405, 7573–7595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sackmann, E.K.; Fulton, A.L.; Beebe, D.J. The present and future role of microfluidics in biomedical research. Nature 2014, 507, 181–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cate, D.M.; Adkins, J.A.; Mettakoonpitak, J.; Henry, C.S. Recent developments in paper-based microfluidic devices. Anal. Chem. 2015, 87, 19–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Georgiev, N.; Bakov, V.; Bojinov, V. Photoinduced electron transfer and aggregation-induced emission in 1,8-naphthalimide probes as a platform for detection of acid/base vapors. Photonics 2022, 9, 994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Refalo, M.V.; Spiteri, J.C.; Magri, D.C. Covalent attachment of a fluorescent ‘Pourbaix sensor’ onto a polymer bead for sensing in water. New J. Chem. 2018, 42, 16474–16477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Silva, A.P. Crossing the divide: Experiences of taking fluorescent PET (photoinduced electron transfer) sensing/switching systems from solution to solid. Dyes Pigm. 2022, 204, 110453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Georgiev, N.I.; Bryaskova, R.G.; Ismail, S.R.; Philipova, N.D.; Uzunova, V.P.; Bakov, V.V.; Tzoneva, R.D.; Bojinov, V.B. Aggregation induced emission in 1,8-naphthalimide embedded nanomicellar architecture as a platform for fluorescent ratiometric pH-probe with biomedical applications. J. Photochem. Photobiol. A Chem. 2021, 418, 113380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahajan, V.A.; Shinde, A.P.; Borate, H.B.; Wakhrakar, R.D. Convenient synthesis of 5-methylene-4-substituted-2(5H)-furanones. Tetrahedron Lett. 2005, 46, 1009–1012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Husain, A.; Khan, M.S.Y.; Hasan, S.M.; Alam, M.M. 2-Arylidene-4-(4-phenoxy-phenyl)but-3-en-4-olides: Synthesis, reactions and biological activity. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2005, 40, 1394–1404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Compound | Yield (%) | M.p. (°C) | Rf | λA (nm) | λF (nm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2 | 94 | 120–122 | 0.80 1 | 342 | - |
| 3 | 97 | 228–230 | 0.70 2 | 448 | 538 |
| 5 | 88 | 341–343 | 0.33 2 | 342 404 | 410 504 |
| Input 1 (H+) | Input 2 (HO−) | Output 1 (A404) | Output 2 (A508) | Output 3 (FI504) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 |
| 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| INHIBIT | IMPLICATION | INHIBIT |
| Compound | 2 | 3 | 5 | Control | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tested microorganisms | Mean IZ | Mean IZ | Mean IZ | Mean IZ | ±SD |
| Gram-positive bacteria: | Gentamycin | ||||
| Bacillus subtilis: RCMB 015 (1) NRRL B-543 | 14 | 15 | 19 | 26.02 | 0.03 |
| Gram-negative bacteria: | Gentamycin | ||||
| Escherichia coli: (RCMB 010052) ATCC 25955 | 15 | 18 | 18 | 29.90 | 0.01 |
| Pseudomonas aeruginosa | 12 | 17 | 19 | 21.01 | 0.04 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sakr, A.R.; Georgiev, N.I.; Bojinov, V.B. Design and Synthesis of a Novel ICT Bichromophoric pH Sensing System Based on 1,8-Naphthalimide Fluorophores as a Two-Input Logic Gate and Its Antibacterial Evaluation. Molecules 2023, 28, 3631. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28083631
Sakr AR, Georgiev NI, Bojinov VB. Design and Synthesis of a Novel ICT Bichromophoric pH Sensing System Based on 1,8-Naphthalimide Fluorophores as a Two-Input Logic Gate and Its Antibacterial Evaluation. Molecules. 2023; 28(8):3631. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28083631
Chicago/Turabian StyleSakr, Alaa R., Nikolai I. Georgiev, and Vladimir B. Bojinov. 2023. "Design and Synthesis of a Novel ICT Bichromophoric pH Sensing System Based on 1,8-Naphthalimide Fluorophores as a Two-Input Logic Gate and Its Antibacterial Evaluation" Molecules 28, no. 8: 3631. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28083631
APA StyleSakr, A. R., Georgiev, N. I., & Bojinov, V. B. (2023). Design and Synthesis of a Novel ICT Bichromophoric pH Sensing System Based on 1,8-Naphthalimide Fluorophores as a Two-Input Logic Gate and Its Antibacterial Evaluation. Molecules, 28(8), 3631. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28083631








