Interaction of Water and Oxygen Molecules with Phosphorene: An Ab Initio Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
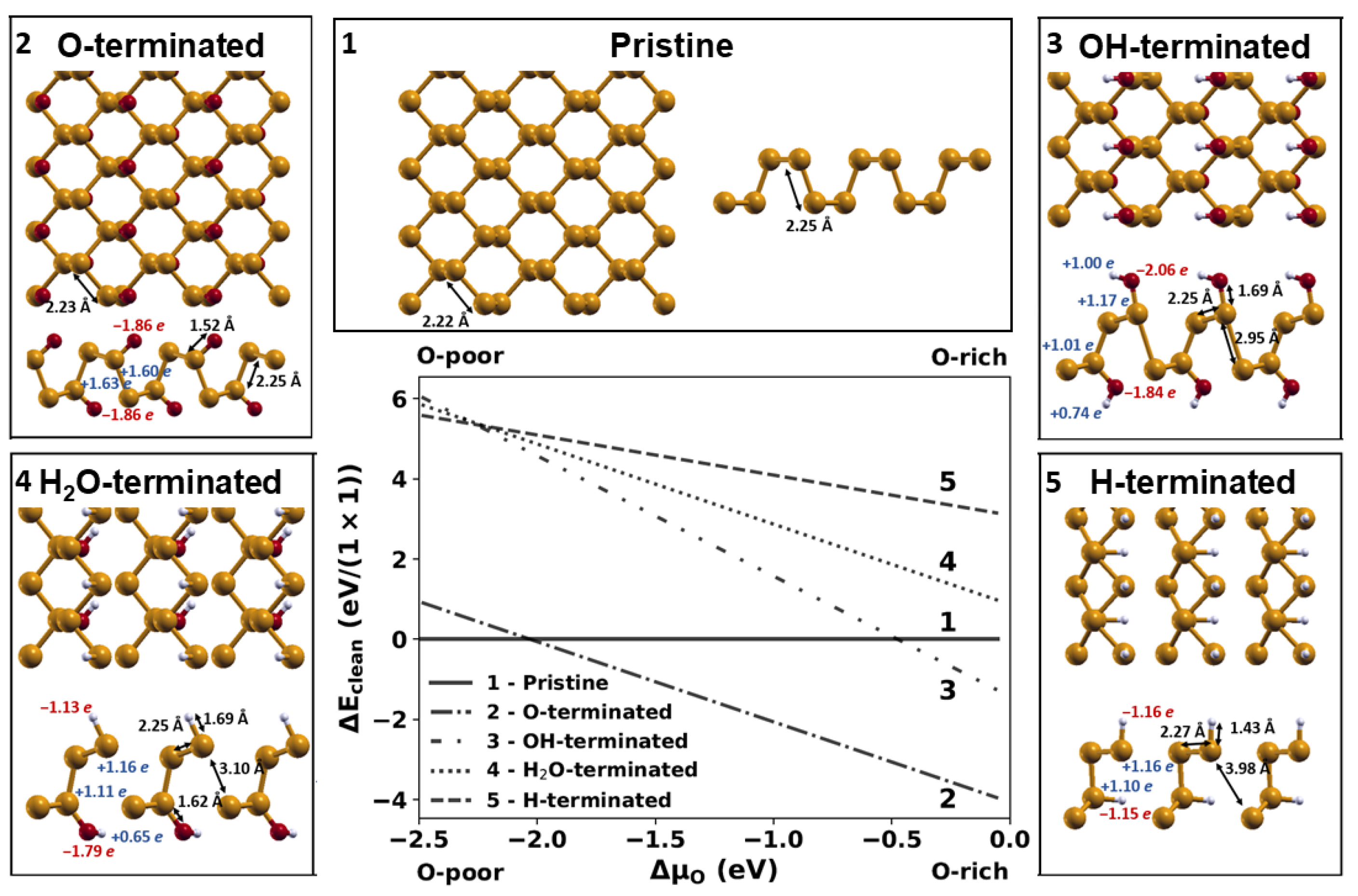
2.1. Relative Stability of Phosphorene Layers with Different Terminations
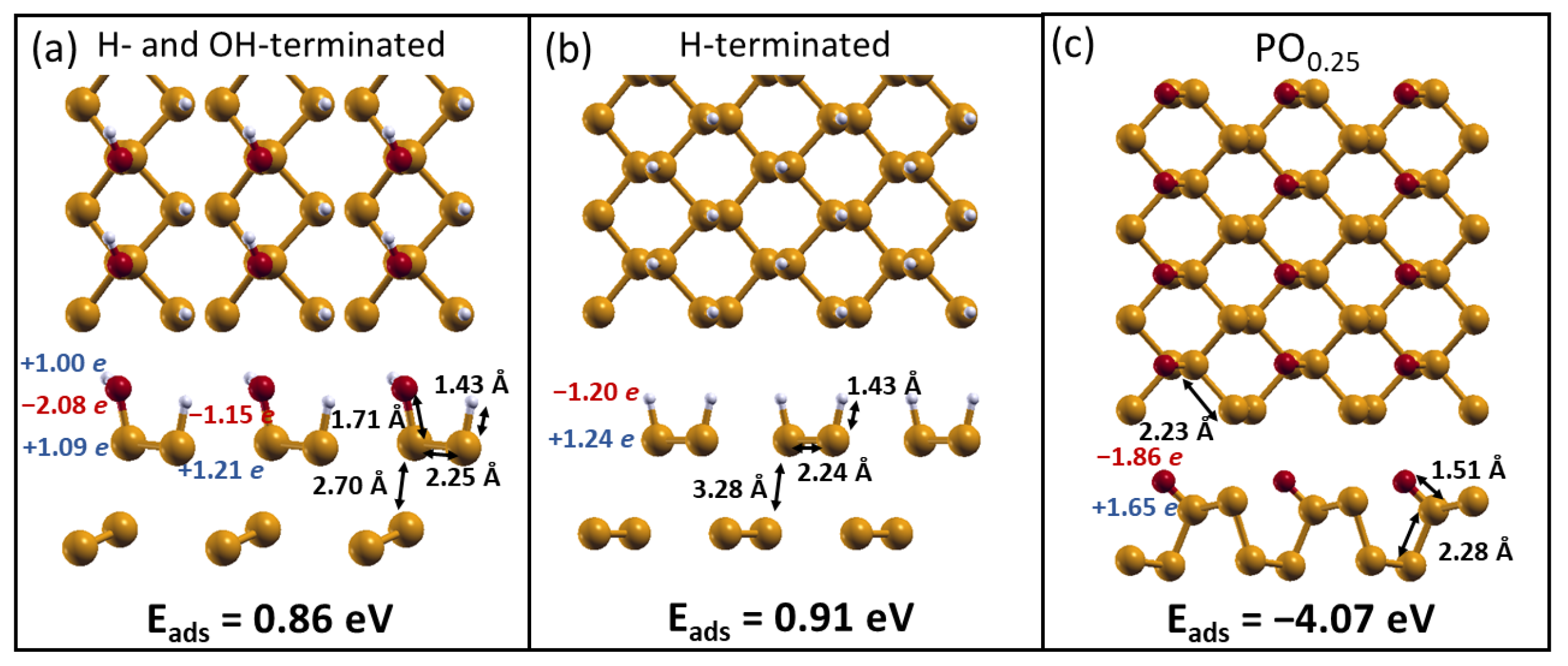
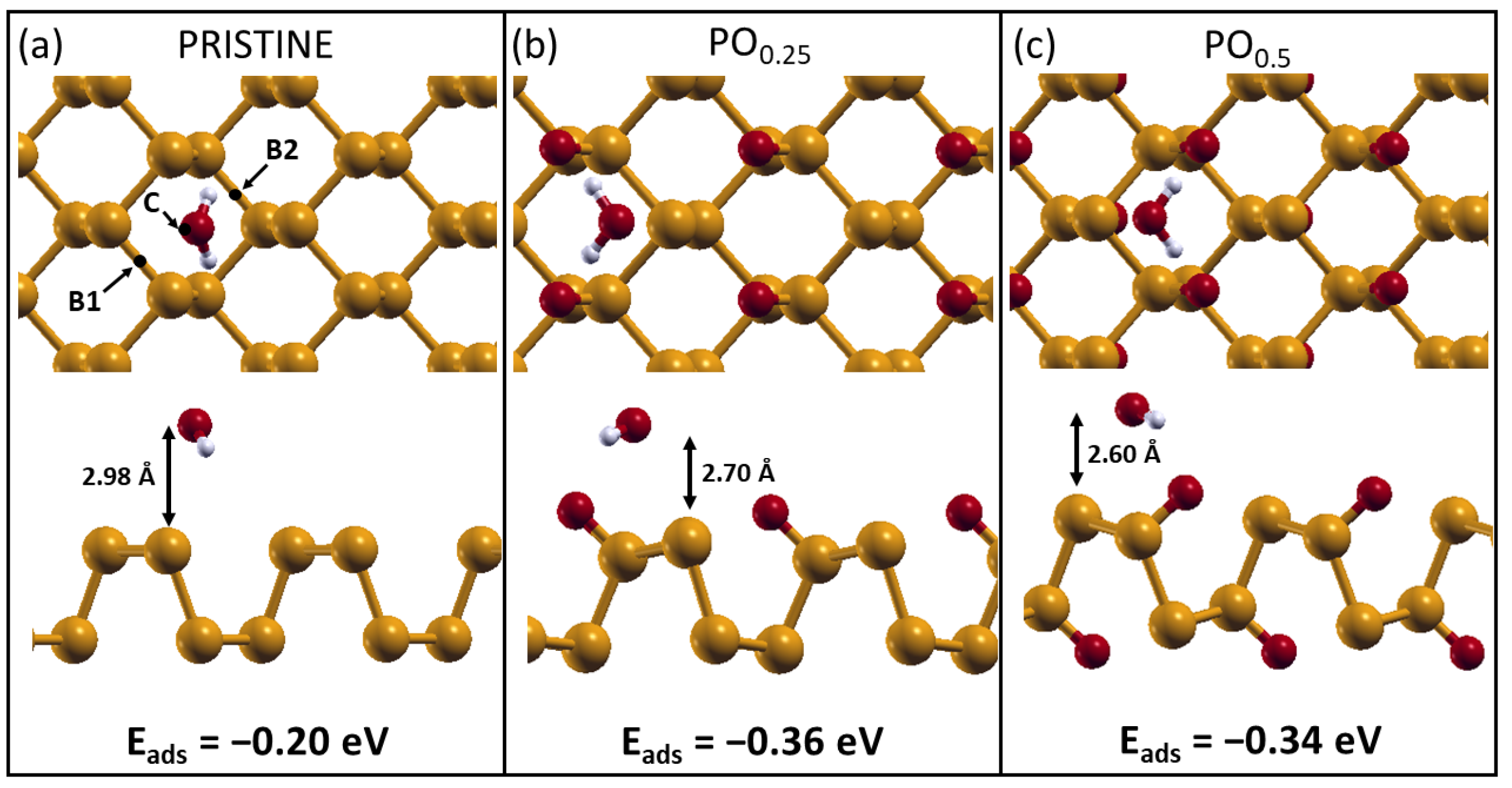
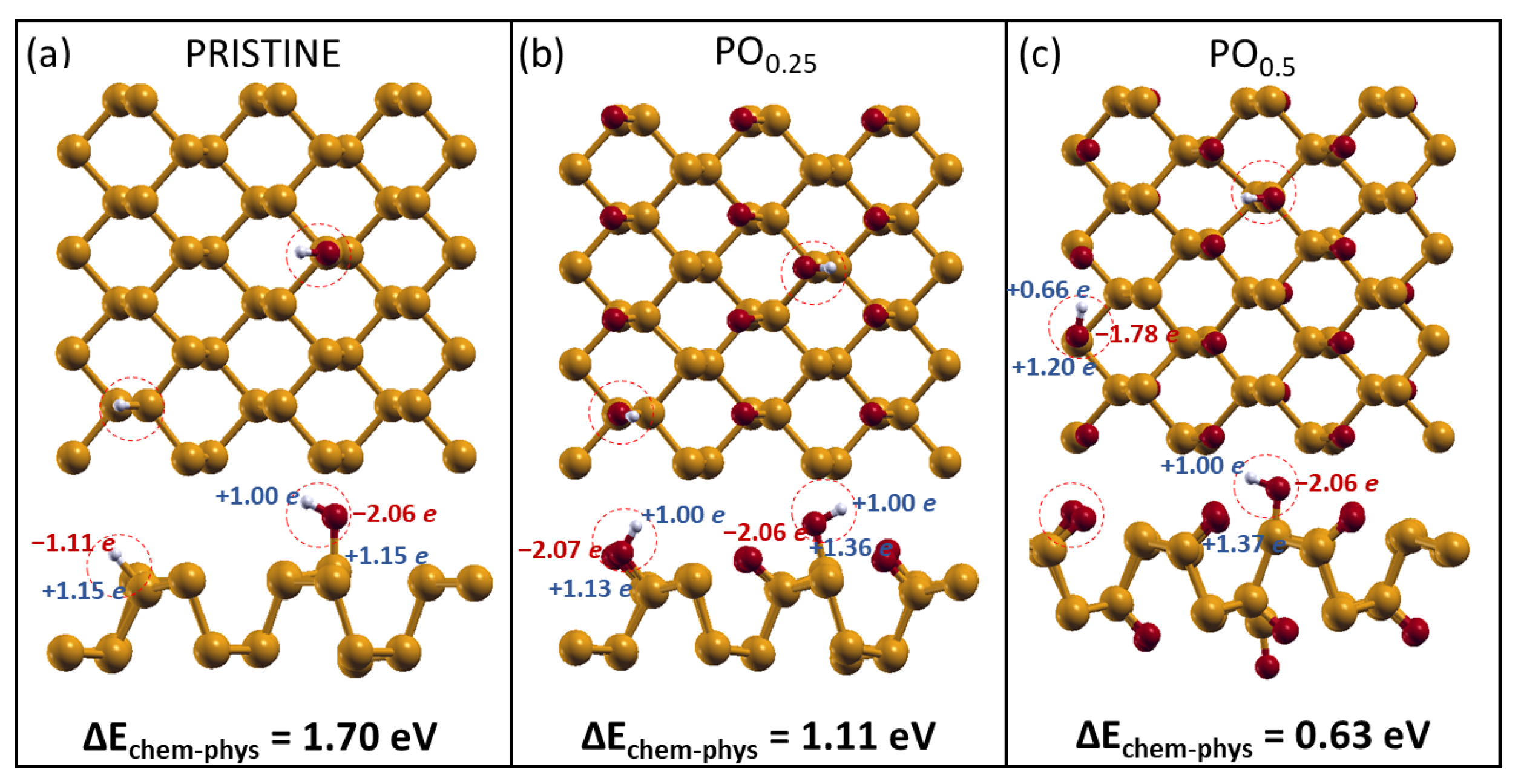
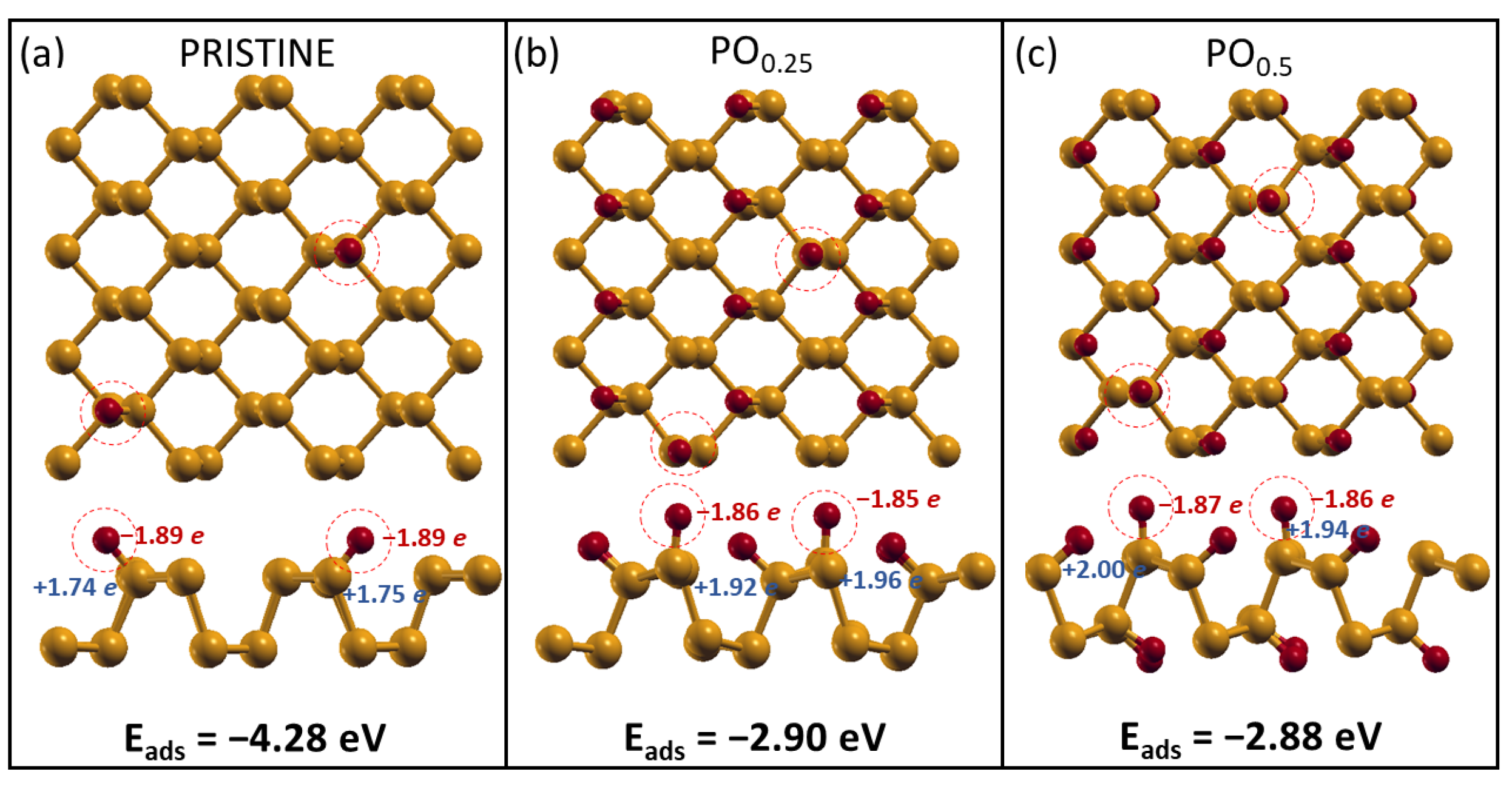
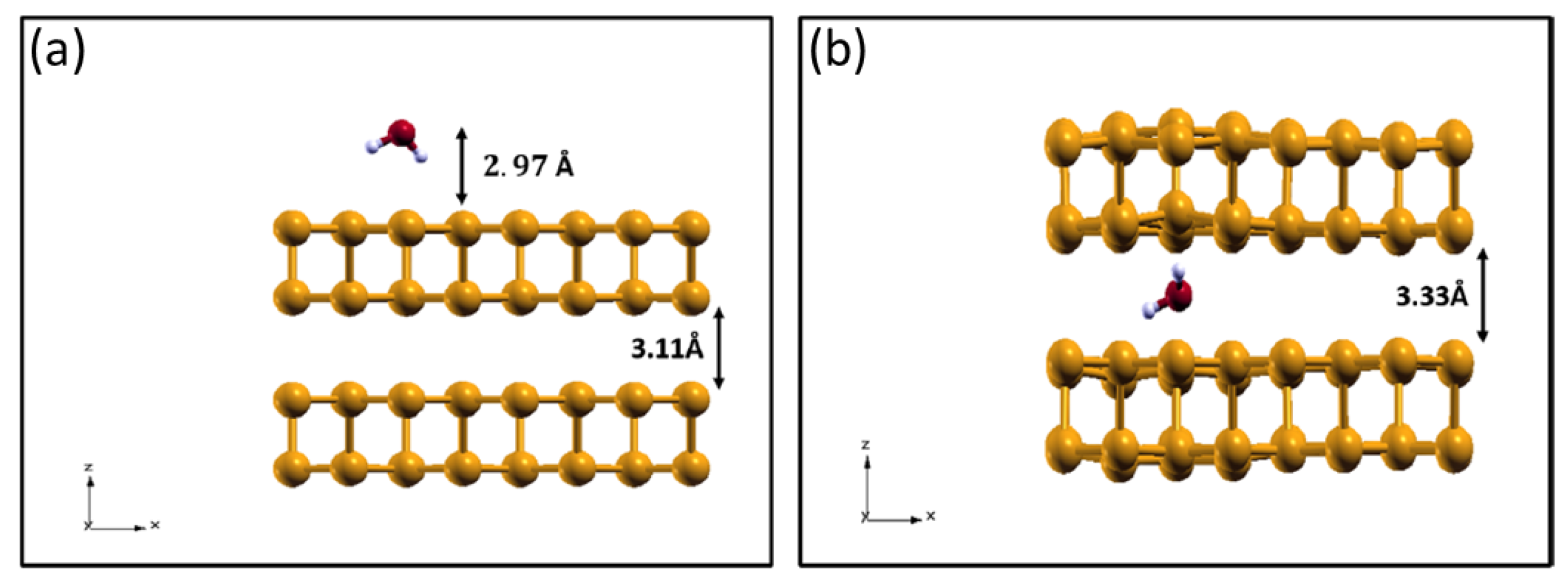
2.2. H2O Interacting with Oxidized Phosphorene
2.3. H2O and O2 Dissociation
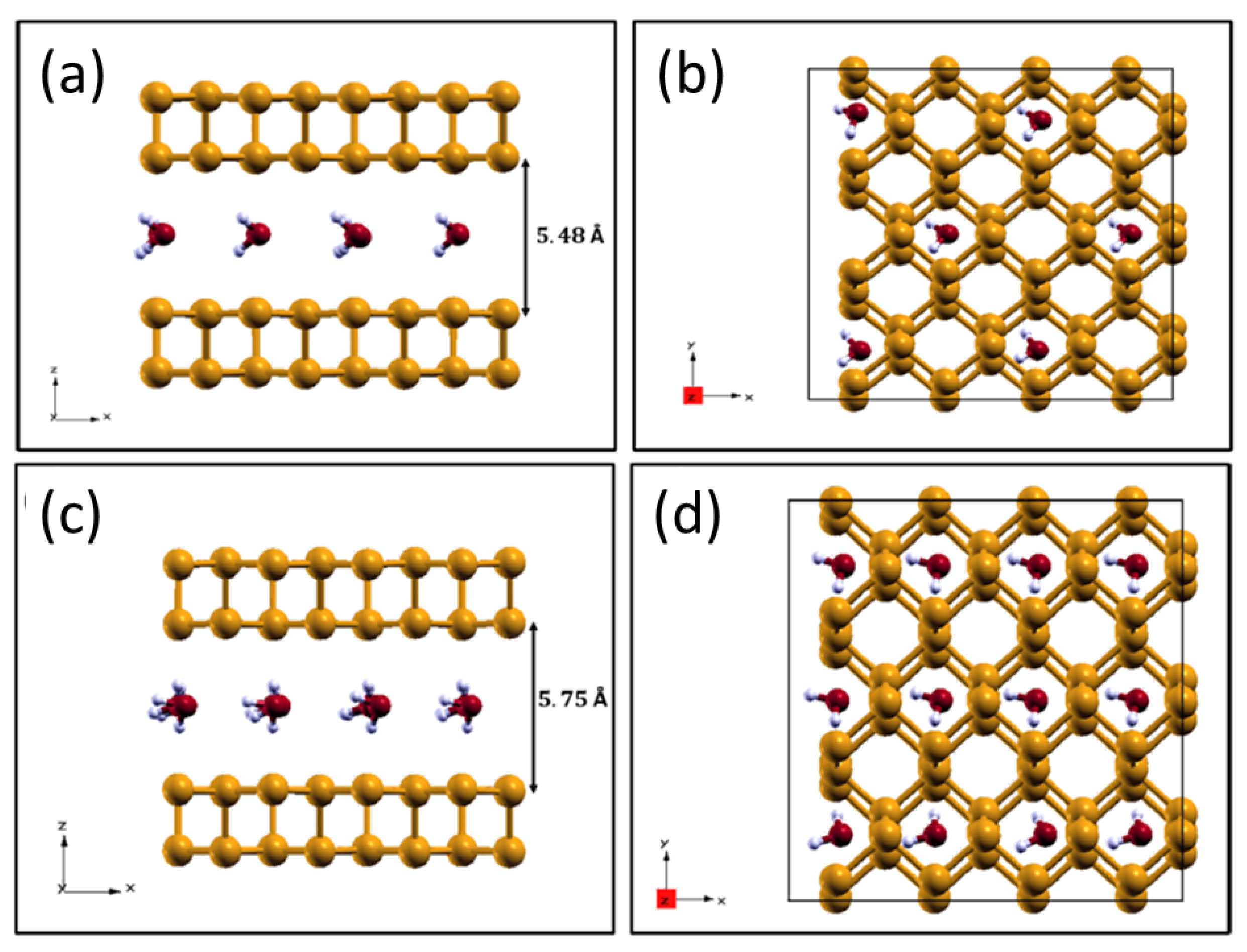
2.4. H2O Intercalation within Phosphorene Layers
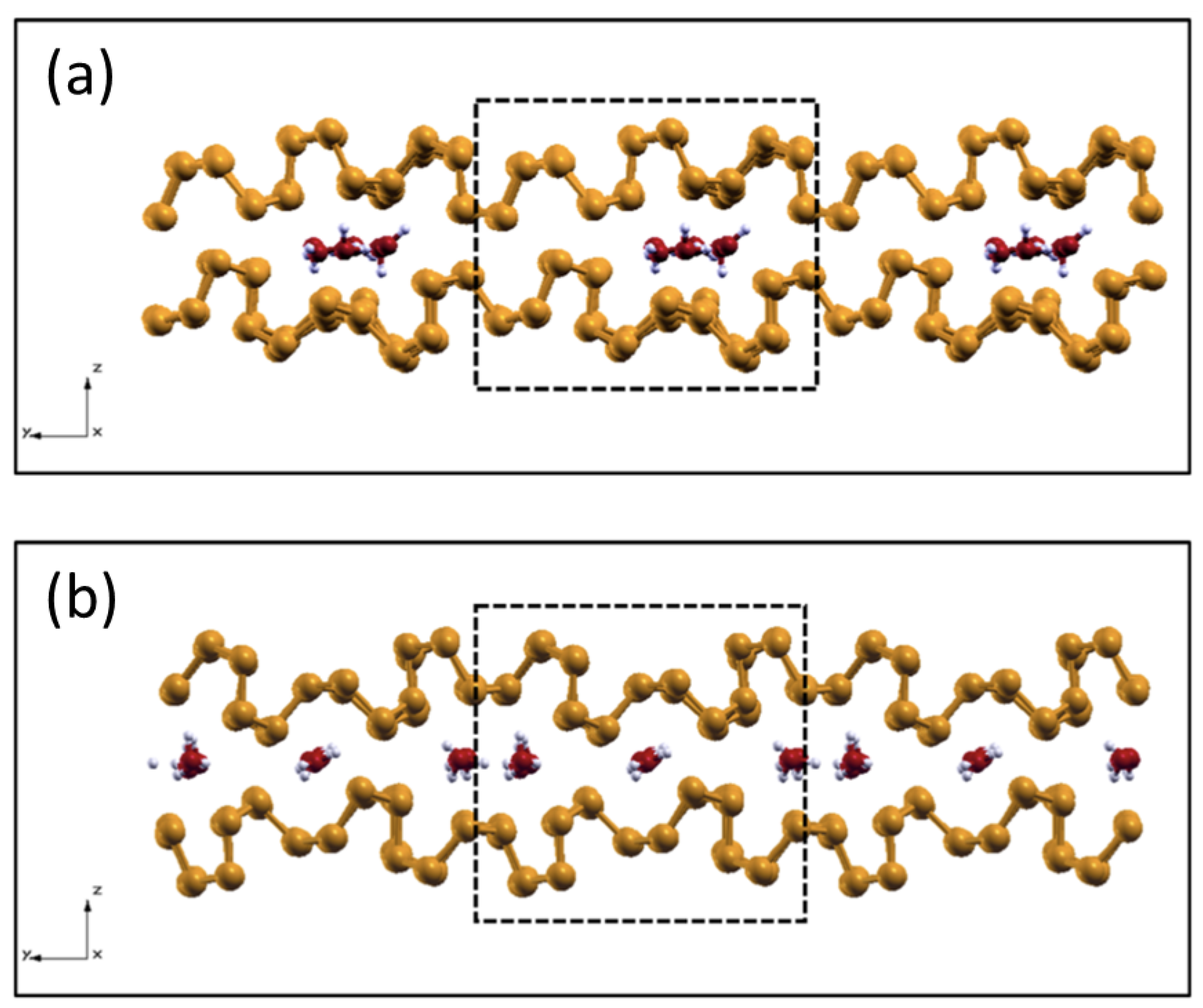
2.5. Intercalated Water in Harsh Tribological Conditions
3. Materials and Methods
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Sample Availability
References
- Churchill, H.O.; Jarillo-Herrero, P. Phosphorus joins the family. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2014, 9, 330–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Low, T.; Rodin, A.; Carvalho, A.; Jiang, Y.; Wang, H.; Xia, F.; Neto, A.C. Tunable optical properties of multilayer black phosphorus thin films. Phys. Rev. B 2014, 90, 075434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodin, A.; Carvalho, A.; Neto, A.C. Strain-induced gap modification in black phosphorus. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2014, 112, 176801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Du, Y.; Deng, Y.; Ye, P.D. Semiconducting black phosphorus: Synthesis, transport properties and electronic applications. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2015, 44, 2732–2743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elinski, M.B.; Liu, Z.; Spear, J.C.; Batteas, J.D. 2D or not 2D? The impact of nanoscale roughness and substrate interactions on the tribological properties of graphene and MoS2. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2017, 50, 103003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spear, J.C.; Ewers, B.W.; Batteas, J.D. 2D-nanomaterials for controlling friction and wear at interfaces. Nano Today 2015, 10, 301–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenkranz, A.; Liu, Y.; Yang, L.; Chen, L. 2D nano-materials beyond graphene: From synthesis to tribological studies. Appl. Nanosci. 2020, 10, 3353–3388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Z.; Xie, G.; He, F.; Wang, W.; Guo, D.; Wang, W. Atomic-scale friction of black phosphorus: Effect of thickness and anisotropic behavior. Adv. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 4, 1700998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galluzzi, M.; Zhang, Y.; Yu, X.F. Mechanical properties and applications of 2D black phosphorus. J. Appl. Phys. 2020, 128, 230903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.; He, F.; Xie, G.; Bian, Z.; Luo, J.; Wen, S. Black phosphorus: Degradation favors lubrication. Nano Lett. 2018, 18, 5618–5627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.; He, F.; Xie, G.; Bian, Z.; Ren, Y.; Liu, X.; Yang, H.; Guo, D.; Zhang, L.; Wen, S.; et al. Super-slippery degraded black phosphorus/silicon dioxide interface. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 7717–7726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Losi, G.; Cutini, M.; Restuccia, P.; Righi, M.C. Modeling phosphorene and MoS2 interacting with iron: Lubricating effects compared to graphene. J. Nanostruct. Chem. 2022, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, J.; Shen, W.; Wu, S.; Liu, L.; Feng, Z.; Wang, C.; Hu, C.; Yao, P.; Zhang, H.; Pang, W.; et al. Mechanical and electrical anisotropy of few-layer black phosphorus. ACS Nano 2015, 9, 11362–11370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, H.; Zhu, P.; Si, L.; Zhang, X.; Xie, G. “M-shape” nanoscale friction anisotropy of phosphorene. Comput. Mater. Sci. 2018, 150, 364–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Xie, G.; Luo, J. Superlubricity of black phosphorus as lubricant additive. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 43203–43210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Losi, G.; Restuccia, P.; Righi, M. Superlubricity in phosphorene identified by means of ab initio calculations. 2D Mater. 2020, 7, 025033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuriakose, S.; Ahmed, T.; Balendhran, S.; Bansal, V.; Sriram, S.; Bhaskaran, M.; Walia, S. Black phosphorus: Ambient degradation and strategies for protection. 2D Mater. 2018, 5, 032001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Qiao, J.; He, K.; Bliznakov, S.; Sutter, E.; Chen, X.; Luo, D.; Meng, F.; Su, D.; Decker, J.; et al. Interaction of black phosphorus with oxygen and water. Chem. Mater. 2016, 28, 8330–8339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Island, J.O.; Steele, G.A.; van der Zant, H.S.; Castellanos-Gomez, A. Environmental instability of few-layer black phosphorus. 2D Mater. 2015, 2, 011002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Utt, K.L.; Rivero, P.; Mehboudi, M.; Harriss, E.O.; Borunda, M.F.; Pacheco SanJuan, A.A.; Barraza-Lopez, S. Intrinsic defects, fluctuations of the local shape, and the photo-oxidation of black phosphorus. ACS Cent. Sci. 2015, 1, 320–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hyun, C.; Kim, J.H.; Lee, J.Y.; Lee, G.H.; Kim, K.S. Atomic scale study of black phosphorus degradation. RSC Adv. 2020, 10, 350–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, J.; Shrivastava, M. First-principles molecular dynamics insight into the atomic level degradation pathway of phosphorene. ACS Omega 2022, 7, 696–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziletti, A.; Carvalho, A.; Campbell, D.K.; Coker, D.F.; Castro Neto, A.H. Oxygen Defects in Phosphorene. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2015, 114, 046801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Slough, W.J.; Pandey, R.; Karna, S.P. Degradation of phosphorene in air: Understanding at atomic level. 2D Mater. 2016, 3, 025011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kistanov, A.A.; Cai, Y.; Zhou, K.; Dmitriev, S.V.; Zhang, Y.W. The role of H2O and O2 molecules and phosphorus vacancies in the structure instability of phosphorene. 2D Mater. 2016, 4, 015010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eslamibidgoli, M.J.; Eikerling, M.H. Mechanical and chemical stability of monolayer black phosphorous studied by density functional theory simulations. J. Phys. Chem. C 2018, 122, 22366–22373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- St Laurent, B.; Dey, D.; Yu, L.; Hollen, S. Atomic-Scale Investigation of Oxidation at the Black Phosphorus Surface. ACS Appl. Electron. Mater. 2021, 3, 4066–4072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Wan, Y.; Xie, H.; Mu, Y.; Du, P.; Wang, D.; Wu, X.; Ji, H.; Wan, L. Degradation chemistry and stabilization of exfoliated few-layer black phosphorus in water. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2018, 140, 7561–7567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Guo, W. Optimal water adsorption on phosphorene. J. Alloy. Compd. 2018, 737, 365–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foroutan, M.; Bavani, B.M.; Boudaghi, A. Controlled hydrophilization of black phosphorene: A reactive molecular dynamics simulation approach. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2022, 24, 27532–27547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Druenen, M. Degradation of Black Phosphorus and Strategies to Enhance Its Ambient Lifetime. Adv. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 7, 2001102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pei, J.; Gai, X.; Yang, J.; Wang, X.; Yu, Z.; Choi, D.Y.; Luther-Davies, B.; Lu, Y. Producing air-stable monolayers of phosphorene and their defect engineering. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 10450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanlon, D.; Backes, C.; Doherty, E.; Cucinotta, C.S.; Berner, N.C.; Boland, C.; Lee, K.; Harvey, A.; Lynch, P.; Gholamvand, Z.; et al. Liquid exfoliation of solvent-stabilized few-layer black phosphorus for applications beyond electronics. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 8563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Shin, H.; Lu, W. Highly ambient-stable few-layer black phosphorene by pulsed laser exfoliation and HEMM. Chem. Commun. 2019, 55, 2601–2604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rietsch, J.C.; Brender, P.; Dentzer, J.; Gadiou, R.; Vidal, L.; Vix-Guterl, C. Evidence of water chemisorption during graphite friction under moist conditions. Carbon 2013, 55, 90–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panitz, J.; Pope, L.; Lyons, J.; Staley, D. The tribological properties of MoS2 coatings in vacuum, low relative humidity, and high relative humidity environments. J. Vac. Sci. Technol. A Vac. Surfaces Film 1988, 6, 1166–1170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Perry, S.S. The role of water in modifying friction within MoS2 sliding interfaces. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2010, 2, 1444–1448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levita, G.; Restuccia, P.; Righi, M.C. Graphene and MoS2 interacting with water: A comparison by ab initio calculations. Carbon 2016, 107, 878–884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, X.; Yang, X.; Xie, G.; He, F.; Wang, R.; Zhang, C.; Guo, D.; Luo, J. Superlubricity under ultrahigh contact pressure enabled by partially oxidized black phosphorus nanosheets. npj 2D Mater. Appl. 2021, 5, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lü, T.Y.; Feng, H.; Zhang, Y.; Lu, Y.; Zheng, J.C. Regulate the polarity of phosphorene’s mechanical properties by oxidation. Comput. Mater. Sci. 2017, 139, 341–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reuter, K.; Scheffler, M. Composition, structure, and stability of RuO2(110) as a function of oxygen pressure. Phys. Rev. B 2001, 65, 035406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reuter, K.; Scheffler, M. Composition and structure of the RuO2(110) surface in an O2 and CO environment: Implications for the catalytic formation of CO2. Phys. Rev. B 2003, 68, 045407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stampfl, C. Surface processes and phase transitions from ab initio atomistic thermodynamics and statistical mechanics. Catal. Today 2005, 105, 17–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, E.; Chang, H.Y.; Kindi, M.; Joshi, G.; Cooper, K.; Lindsay, R.; Harrison, N. Corrosion Protection through Naturally Occurring Films: New Insights from Iron Carbonate. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 11, 33435–33441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soon, A.; Todorova, M.; Delley, B.; Stampfl, C. Thermodynamic stability and structure of copper oxide surfaces: A first-principles investigation. Phys. Rev. B 2007, 75, 125420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, S.; Liu, X.W.; Huo, C.F.; Li, Y.W.; Wang, J.; Jiao, H. Determining surface structure and stability of ε-Fe2C, χ-Fe5C2, θ-Fe3C and Fe4C phases under carburization environment from combined DFT and atomistic thermodynamic studies. Catal. Struct. React. 2015, 1, 44–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, S.; Liu, X.W.; Huo, C.F.; Li, Y.W.; Wang, J.; Jiao, H. Surface morphology of Hägg iron carbide (χ-Fe5C2) from ab initio atomistic thermodynamics. J. Catal. 2012, 294, 47–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zilibotti, G.; Righi, M.C.; Ferrario, M. Ab initio study on the surface chemistry and nanotribological properties of passivated diamond surfaces. Phys. Rev. B 2009, 79, 075420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Restuccia, P.; Ferrario, M.; Righi, M. Monitoring water and oxygen splitting at graphene edges and folds: Insights into the lubricity of graphitic materials. Carbon 2020, 156, 93–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Pandey, R.; Karna, S.P. Phosphorene oxide: Stability and electronic properties of a novel two-dimensional material. Nanoscale 2015, 7, 524–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, S.H.; Park, J.; Woo, S.; Kwon, Y.K. Two-dimensional dirac fermions on oxidized black phosphorus. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2019, 21, 24206–24211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kajita, S.; Righi, M.C. Insigths into the tribochemistry of silicon-doped carbon-based films by ab initio analysis of water–surface interactions. Tribol. Lett. 2016, 61, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levita, G.; Righi, M.C. Effects of water intercalation and tribochemistry on MoS2 lubricity: An ab initio molecular dynamics investigation. ChemPhysChem 2017, 18, 1475–1480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giannozzi, P.; Baroni, S.; Bonini, N.; Calandra, M.; Car, R.; Cavazzoni, C.; Ceresoli, D.; Chiarotti, G.L.; Cococcioni, M.; Dabo, I.; et al. QUANTUM ESPRESSO: A modular and open-source software project for quantum simulations of materials. J. Phys. Condens. Matter 2009, 21, 395502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giannozzi, P.; Andreussi, O.; Brumme, T.; Bunau, O.; Nardelli, M.B.; Calandra, M.; Car, R.; Cavazzoni, C.; Ceresoli, D.; Cococcioni, M.; et al. Advanced capabilities for materials modelling with Quantum ESPRESSO. J. Physics Condens. Matter 2017, 29, 465901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giannozzi, P.; Baseggio, O.; Bonfà, P.; Brunato, D.; Car, R.; Carnimeo, I.; Cavazzoni, C.; De Gironcoli, S.; Delugas, P.; Ferrari Ruffino, F.; et al. Quantum ESPRESSO toward the exascale. J. Chem. Phys. 2020, 152, 154105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perdew, J.P.; Burke, K.; Ernzerhof, M. Generalized gradient approximation made simple. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1996, 77, 3865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grimme, S. Semiempirical GGA-type density functional constructed with a long-range dispersion correction. J. Comput. Chem. 2006, 27, 1787–1799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monkhorst, H.J.; Pack, J.D. Special points for Brillouin-zone integrations. Phys. Rev. B 1976, 13, 5188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zilibotti, G.; Corni, S.; Righi, M.C. Load-Induced Confinement Activates Diamond Lubrication by Water. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2013, 111, 146101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, W.; Sanville, E.; Henkelman, G. A grid-based Bader analysis algorithm without lattice bias. J. Phys. Condens. Matter 2009, 21, 084204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanville, E.; Kenny, S.D.; Smith, R.; Henkelman, G. Improved grid-based algorithm for Bader charge allocation. J. Comput. Chem. 2007, 28, 899–908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, M.; Trinkle, D.R. Accurate and efficient algorithm for Bader charge integration. J. Chem. Phys. 2011, 134, 064111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Henkelman, G.; Arnaldsson, A.; Jónsson, H. A fast and robust algorithm for Bader decomposition of charge density. Comput. Mater. Sci. 2006, 36, 354–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ta, H.T.T.; Tran, N.V.; Tieu, A.K.; Zhu, H.; Yu, H.; Ta, T.D. Computational Tribochemistry: A Review from Classical and Quantum Mechanics Studies. J. Phys. Chem. C 2021, 125, 16875–16891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Benini, F.; Bassoli, N.; Restuccia, P.; Ferrario, M.; Righi, M.C. Interaction of Water and Oxygen Molecules with Phosphorene: An Ab Initio Study. Molecules 2023, 28, 3570. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28083570
Benini F, Bassoli N, Restuccia P, Ferrario M, Righi MC. Interaction of Water and Oxygen Molecules with Phosphorene: An Ab Initio Study. Molecules. 2023; 28(8):3570. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28083570
Chicago/Turabian StyleBenini, Francesca, Nicolò Bassoli, Paolo Restuccia, Mauro Ferrario, and Maria Clelia Righi. 2023. "Interaction of Water and Oxygen Molecules with Phosphorene: An Ab Initio Study" Molecules 28, no. 8: 3570. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28083570
APA StyleBenini, F., Bassoli, N., Restuccia, P., Ferrario, M., & Righi, M. C. (2023). Interaction of Water and Oxygen Molecules with Phosphorene: An Ab Initio Study. Molecules, 28(8), 3570. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28083570








