Protective Effect of Ferulic Acid on Lipopolysaccharide-Induced BV2 Microglia Inflammation via AMPK/mTOR Signaling Pathway
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Effects of LPS and FA on the Viability of BV2 Microglia
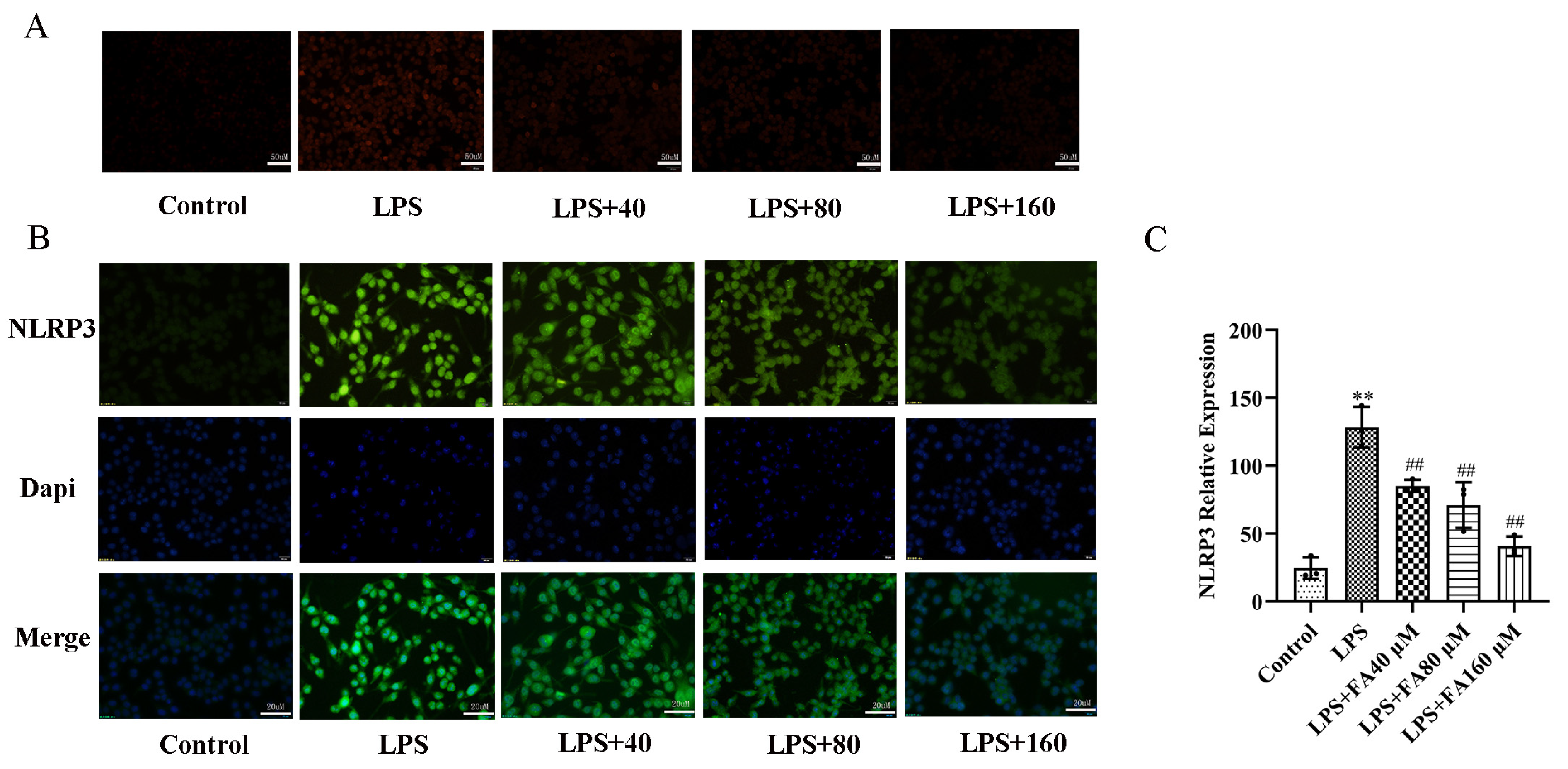
2.2. FA Inhibited LPS-Induced Oxidative Stress
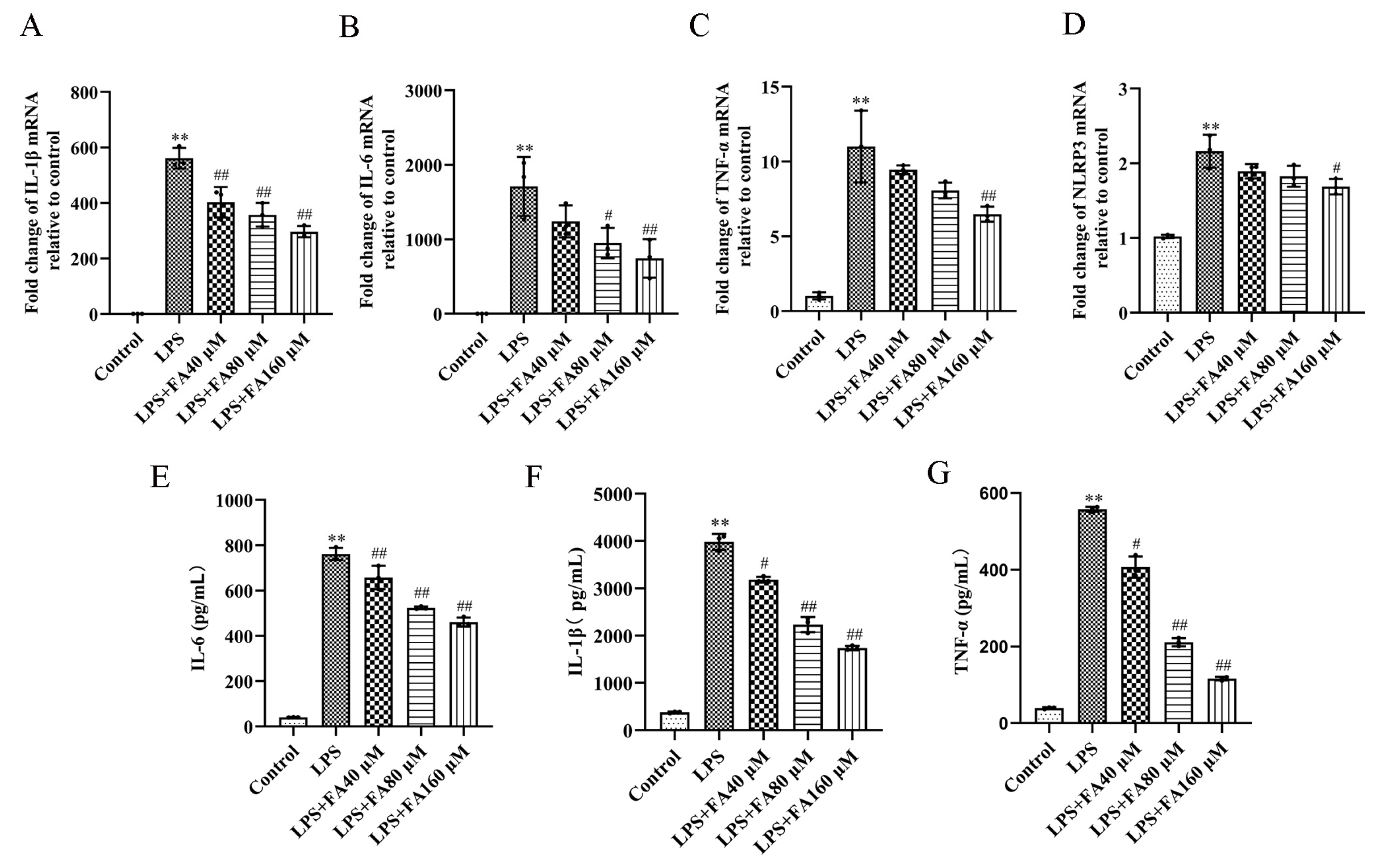
2.3. Effect of FA on Pro-Inflammatory Cytokines in LPS-Induced BV2 Microglia
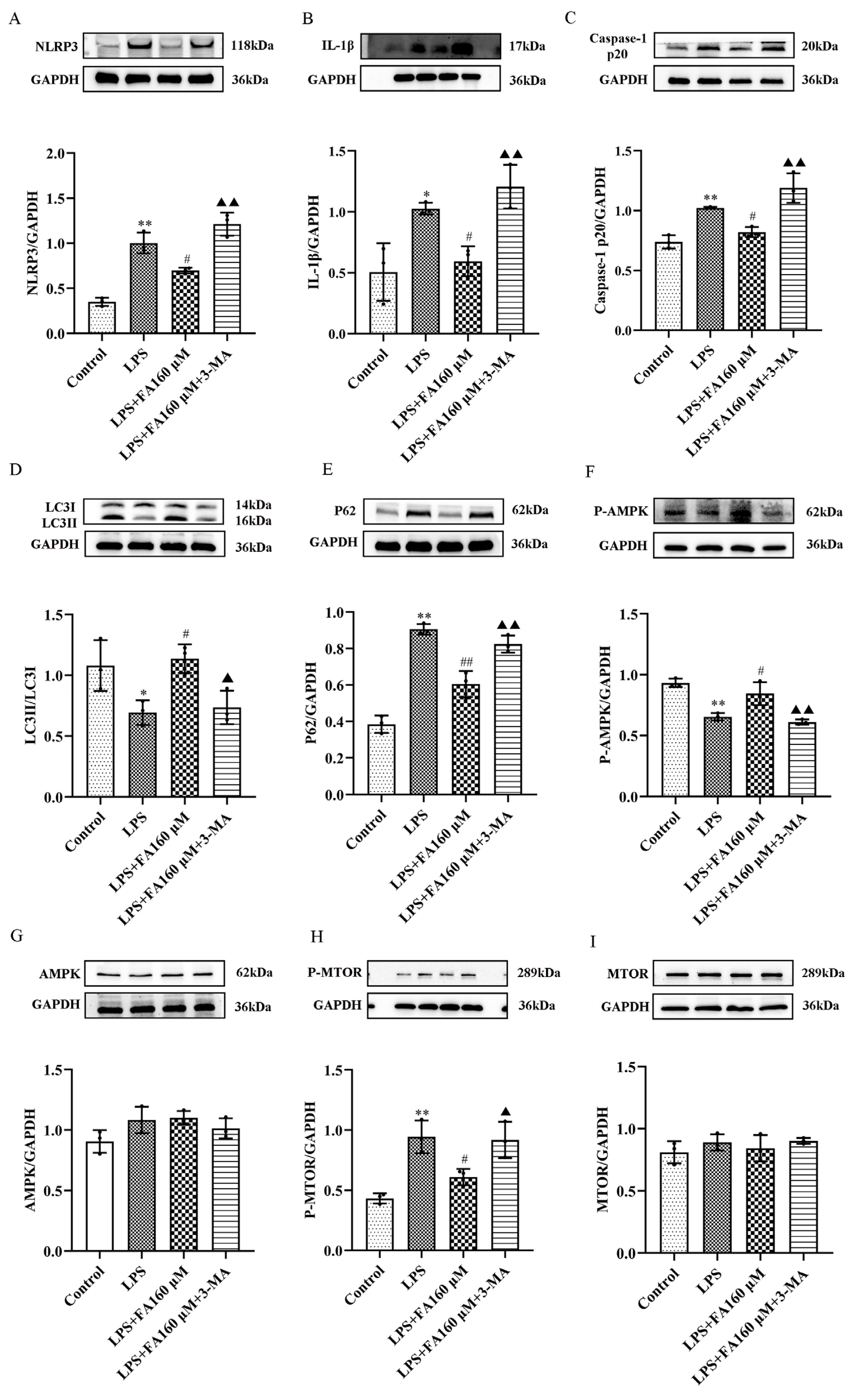
2.4. FA Can Reduce the Levels of Inflammatory Proteins in LPS-Treated BV2 Microglia, Restore Autophagy and Activate the AMPK/mTOR Pathway
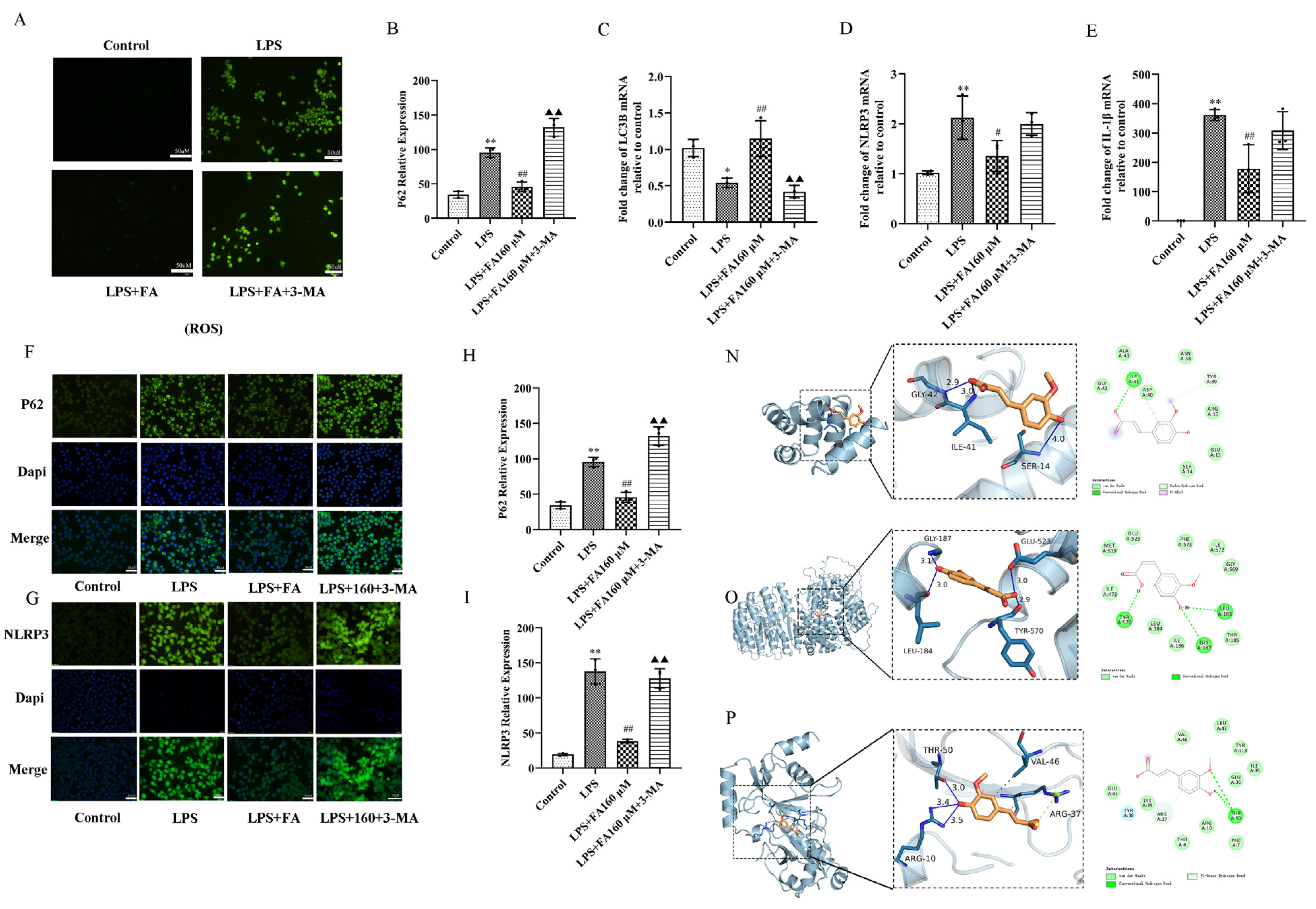
2.5. Autophagy Inhibitors (3-MA) Block the Neuroprotective Effect of FA
2.6. Autophagy Inhibitors (3-MA) Restore the Effects of LPS on Inflammatory Cytokines, Autophagy and the AMPK/mTOR Pathway
2.7. AMPK Inhibitors Block the Protective Effect of Neuroinflammation Induced by FA
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Cell Culture
4.2. Cell Treatment
4.3. Cell Viability Assay
4.4. Levels of ROS
4.5. Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA)
4.6. Quantitative Real-Time PCR (qRT-PCR)
4.7. Molecular Docking
4.8. Western Blot
4.9. Immunocytochemistry
4.10. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Sample Availability
References
- Kempuraj, D.; Thangavel, R.; Natteru, P.A.; Selvakumar, G.P.; Saeed, D.; Zahoor, H.; Zaheer, S.; Iyer, S.S.; Zaheer, A. Neuroinflammation Induces Neurodegeneration. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Spine 2016, 1, 1003. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Perry, V.H.; Nicoll, J.A.; Holmes, C. Microglia in neurodegenerative disease. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2010, 6, 193–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, T.; Yu, J.T.; Tan, L. Novel disease-modifying therapies for Alzheimer’s disease. J. Alzheimers Dis. 2012, 31, 475–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, X.; Zhu, M.; Che, X.; Wang, H.; Liang, X.-J.; Wu, C.; Xue, X.; Yang, J. Lipopolysaccharide induces neuroinflammation in microglia by activating the MTOR pathway and downregulating Vps34 to inhibit autophagosome formation. J. Neuroinflamm. 2020, 17, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; She, H.; Zhang, T.; Xu, H.; Cheng, L.; Yepes, M.; Zhao, Y.; Mao, Z. p38 MAPK inhibits autophagy and promotes microglial inflammatory responses by phosphorylating ULK1. J. Cell Biol. 2018, 217, 315–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bian, F.; Xiao, Y.; Zaheer, M.; Volpe, E.A.; Pflugfelder, S.C.; Li, D.-Q.; De Paiva, C.S. Inhibition of NLRP3 Inflammasome Pathway by Butyrate Improves Corneal Wound Healing in Corneal Alkali Burn. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.W.; Yang, S.J.; Na, J.M.; Hahn, H.G.; Cho, S.W. 3-(Naphthalen-2-yl(propoxy)methyl)azetidine hydrochloride attenuates NLRP3 inflammasome-mediated signaling pathway in lipopolysaccharide-stimulated BV2 microglial cells. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2018, 495, 151–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mori, T.; Koyama, N.; Tan, J.; Segawa, T.; Maeda, M.; Town, T. Combined treatment with the phenolics (−)-epigallocatechin-3-gallate and ferulic acid improves cognition and reduces Alzheimer-like pathology in mice. J. Biol. Chem. 2019, 294, 2714–2731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.-S.; Cho, J.-Y.; Kim, D.-H.; Yan, J.-J.; Lee, H.-K.; Suh, H.-W.; Song, D.-K. Inhibitory effects of long-term administration of ferulic acid on microglial activation induced by intracerebroventricular injection of beta-amyloid peptide (1-42) in mice. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2004, 27, 120–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sultana, R.; Ravagna, A.; Mohmmad-Abdul, H.; Calabrese, V.; Butterfield, D.A. Ferulic acid ethyl ester protects neurons against amyloid beta- peptide(1-42)-induced oxidative stress and neurotoxicity: Relationship to antioxidant activity. J. Neurochem. 2005, 92, 749–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, Y.; Chen, Q.; Xie, Y.; Tao, Z.; Jin, K.; Chen, S.; Bai, Y.; Yang, J.; Shan, S. Ferulic acid attenuates oxidative DNA damage and inflammatory responses in microglia induced by benzo(a)pyrene. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2019, 77, 105980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, Y.C.; Yeh, W.C.; Ohashi, P.S. LPS/TLR4 signal transduction pathway. Cytokine 2008, 42, 145–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuzmich, N.N.; Sivak, K.V.; Chubarev, V.N.; Porozov, Y.B.; Savateeva-Lyubimova, T.N.; Peri, F. TLR4 Signaling Pathway Modulators as Potential Therapeutics in Inflammation and Sepsis. Vaccines 2017, 5, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Shi, L.; Qiu, W.; Shi, Y. Ferulic acid exhibits anti-inflammatory effects by inducing autophagy and blocking NLRP3 inflammasome activation. Mol. Cell Toxicol. 2022, 18, 509–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamkanfi, M.; Dixit, V.M. Manipulation of host cell death pathways during microbial infections. Cell Host Microbe 2010, 8, 44–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, M.-M.; Wang, F.; Qi, D.; Liu, W.-W.; Gu, C.; Mao, C.-J.; Yang, Y.-P.; Zhao, Z.; Hu, L.-F.; Liu, C.-F. A Critical Role of Autophagy in Regulating Microglia Polarization in Neurodegeneration. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2018, 10, 378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voet, S.; Srinivasan, S.; Lamkanfi, M.; van Loo, G. Inflammasomes in neuroinflammatory and neurodegenerative diseases. EMBO Mol. Med. 2019, 11, e10248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knott, C.; Stern, G.; Wilkin, G.P. Inflammatory regulators in Parkinson’s disease: iNOS, lipocortin-1, and cyclooxygenases-1 and -2. Mol. Cell Neurosci. 2000, 16, 724–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, D.S.; Liu, W.G.; Yang, X.F.; Cao, F. Inhibitory effect of progesterone on inflammatory factors after experimental traumatic brain injury. Biomed. Environ. Sci. 2007, 20, 432–438. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.; Tan, L.; Wang, H.F.; Tan, C.C.; Meng, X.F.; Wang, C.; Tang, S.W.; Yu, J.T. Anti-inflammatory drugs and risk of Alzheimer’s disease: An updated systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Alzheimers Dis. 2015, 44, 385–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, J.; Yamashita, T.; Zhai, Y.; Nakano, Y.; Morihara, R.; Li, X.; Tian, F.; Liu, X.; Huang, Y.; Shi, X.; et al. Acceleration of NLRP3 inflammasome by chronic cerebral hypoperfusion in Alzheimer’s disease model mouse. Neurosci. Res. 2019, 143, 61–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoogland, I.C.; Houbolt, C.; van Westerloo, D.J.; van Gool, W.A.; van de Beek, D. Systemic inflammation and microglial activation: Systematic review of animal experiments. J. Neuroinflamm. 2015, 12, 114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rawat, C.; Kukal, S.; Dahiya, U.R.; Kukreti, R. Cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2) inhibitors: Future therapeutic strategies for epilepsy management. J. Neuroinflamm. 2019, 16, 197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iqbal, S.; Shah, F.A.; Naeem, K.; Nadeem, H.; Sarwar, S.; Ashraf, Z.; Imran, M.; Khan, T.; Anwar, T.; Li, S. Succinamide Derivatives Ameliorate Neuroinflammation and Oxidative Stress in Scopolamine-Induced Neurodegeneration. Biomolecules 2020, 10, 443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, S.; Mei, X. Role of NLRP3 Inflammasomes in Neuroinflammation Diseases. Eur. Neurol. 2020, 83, 576–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, Y.; Pan, M.; Zheng, B.; Chen, Y.; Li, W.; Yang, Q.; Zheng, Z.; Sun, N.; Zhang, Y.; Li, X. Autophagy Attenuates Angiotensin II-Induced Pulmonary Fibrosis by Inhibiting Redox Imbalance-Mediated NOD-Like Receptor Family Pyrin Domain Containing 3 Inflammasome Activation. Antioxid. Redox. Signal. 2019, 30, 520–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, M.-H.; Cho, K.; Kang, H.-J.; Jeon, E.-Y.; Kim, H.-S.; Kwon, H.-J.; Kim, H.-M.; Kim, D.-H.; Yoon, S.-Y. Autophagy in microglia degrades extracellular β-amyloid fibrils and regulates the NLRP3 inflammasome. Autophagy 2014, 10, 1761–1775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Zhang, T.; Wang, J.; Zhang, Z.; Zhai, Y.; Yang, G.-Y.; Sun, X. Rapamycin attenuates mitochondrial dysfunction via activation of mitophagy in experimental ischemic stroke. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2014, 444, 182–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Wang, D.; Zhang, T.; Lu, X.; Duan, F.; Ju, L.; Zhuang, X.; Jiang, X. Eugenol Attenuates Cerebral Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury by Enhancing Autophagy via AMPK-mTOR-P70S6K Pathway. Front. Pharmacol. 2020, 11, 84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Gene | Sense (5′-3′) | Anti-Sense (5′-3′) |
|---|---|---|
| IL-6 | ACCTGTCTATACCACTTCACAAGT | AGAATTGCCATTGCACAACTCT |
| IL-1β | AGGAGAACCAAGCAACGACA | TGCTTGGGATCCACACTCTC |
| TNF-α | CTTCTCATTCCTGCTTGTGGCA | GAGGCCATTTGGGAACTTCTCAT |
| NLRP3 | CAACAATGATCTTGGCGATCTGT | TACATTTCACCCAACTGTAGGCT |
| P62 | CTTCGGAAGTCAGCAAACCTGA | TCCCGACTCCATCTGTTCCTC |
| LC3B | GATACAAGGGGGAGAAGCAGCT | CTGCAAGCGCCGTCTGATT |
| β-actin | GGTCATCACTATTGGCAACGAGC | CCAGACAGCACTGTGTTGGCATA |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, X.; Zhou, X.; Cheng, X.; Lin, L.; Wang, Q.; Zhan, R.; Wu, Q.; Liu, S. Protective Effect of Ferulic Acid on Lipopolysaccharide-Induced BV2 Microglia Inflammation via AMPK/mTOR Signaling Pathway. Molecules 2023, 28, 3482. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28083482
Chen X, Zhou X, Cheng X, Lin L, Wang Q, Zhan R, Wu Q, Liu S. Protective Effect of Ferulic Acid on Lipopolysaccharide-Induced BV2 Microglia Inflammation via AMPK/mTOR Signaling Pathway. Molecules. 2023; 28(8):3482. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28083482
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Xingru, Xiaolan Zhou, Xiaoqing Cheng, Liting Lin, Qi Wang, Ruoting Zhan, Qingguang Wu, and Sijun Liu. 2023. "Protective Effect of Ferulic Acid on Lipopolysaccharide-Induced BV2 Microglia Inflammation via AMPK/mTOR Signaling Pathway" Molecules 28, no. 8: 3482. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28083482
APA StyleChen, X., Zhou, X., Cheng, X., Lin, L., Wang, Q., Zhan, R., Wu, Q., & Liu, S. (2023). Protective Effect of Ferulic Acid on Lipopolysaccharide-Induced BV2 Microglia Inflammation via AMPK/mTOR Signaling Pathway. Molecules, 28(8), 3482. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28083482







