Efficient Adsorption of Tebuconazole in Aqueous Solution by Calcium Modified Water Hyacinth-Based Biochar: Adsorption Kinetics, Mechanism, and Feasibility
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Characterization of Biochar
2.1.1. SEM–EDS Analysis
2.1.2. Brunauer–Emmett–Teller Analysis
2.1.3. X-ray Diffraction Analysis
2.1.4. Fourier Transform Infrared Spectral Analysis
2.2. Adsorption Capacity
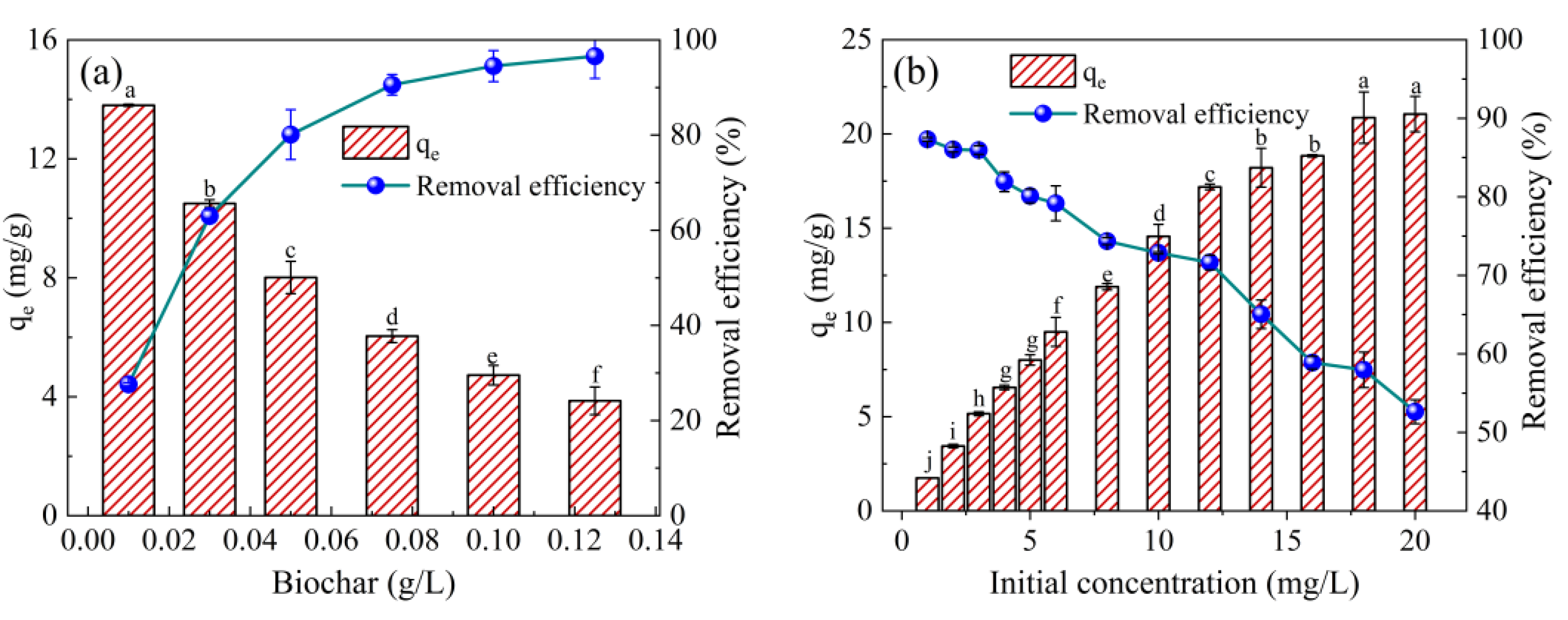
2.2.1. Effect of Biochar Dosages and Initial TE Concentration
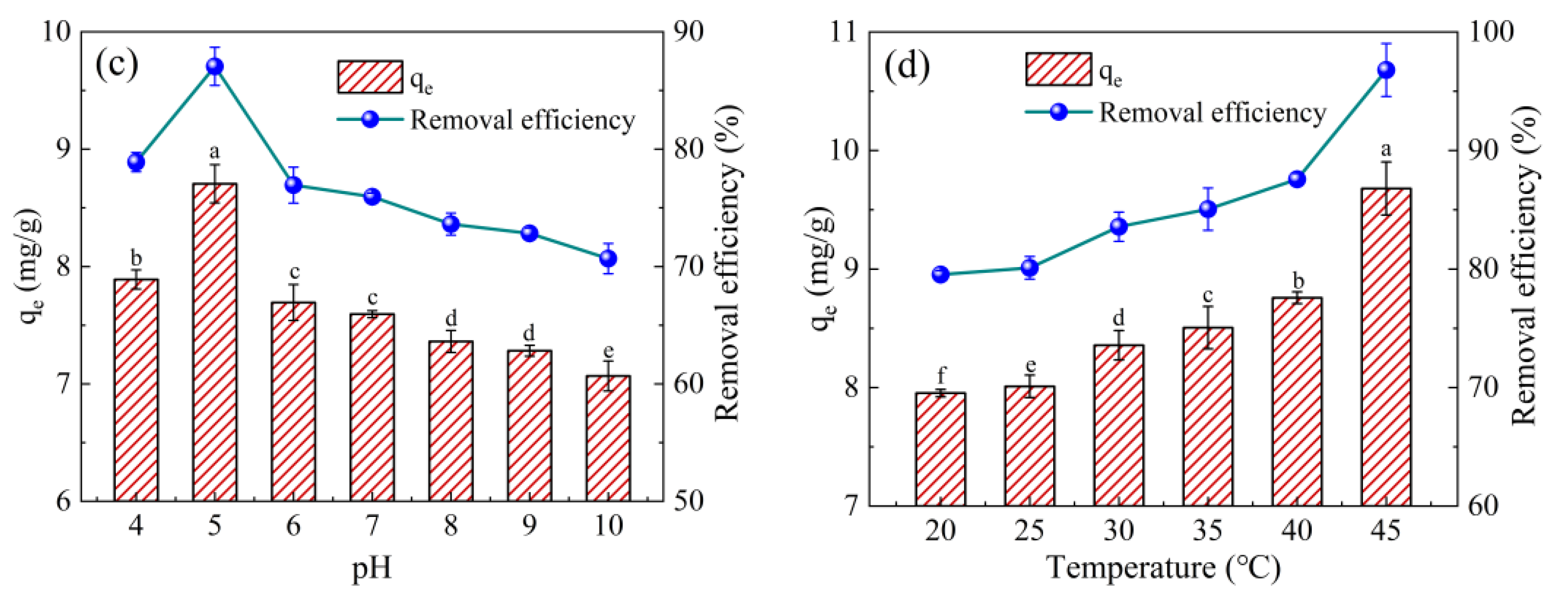
2.2.2. Effect of Initial pH and Temperature
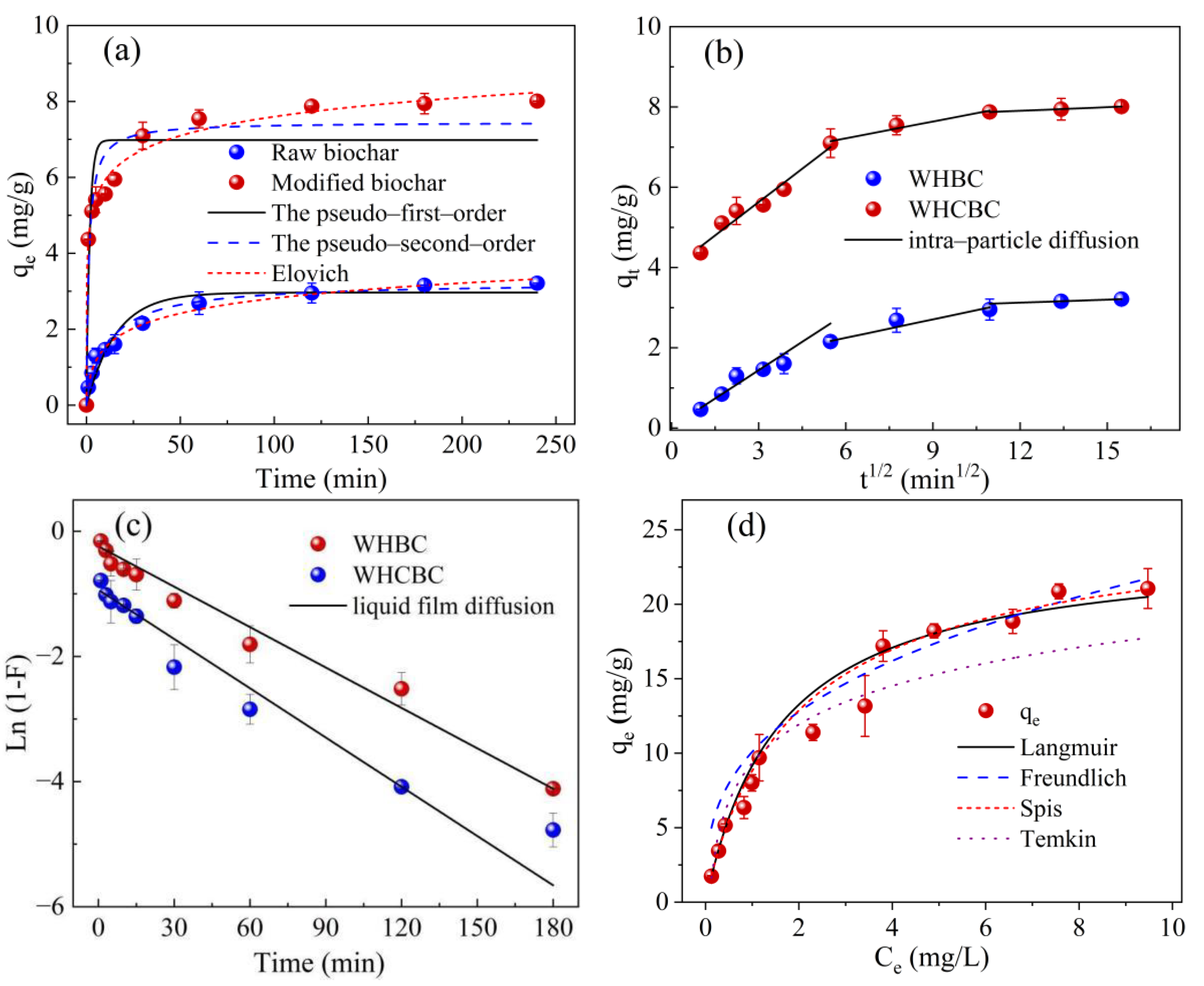
2.3. Adsorption Kinetics
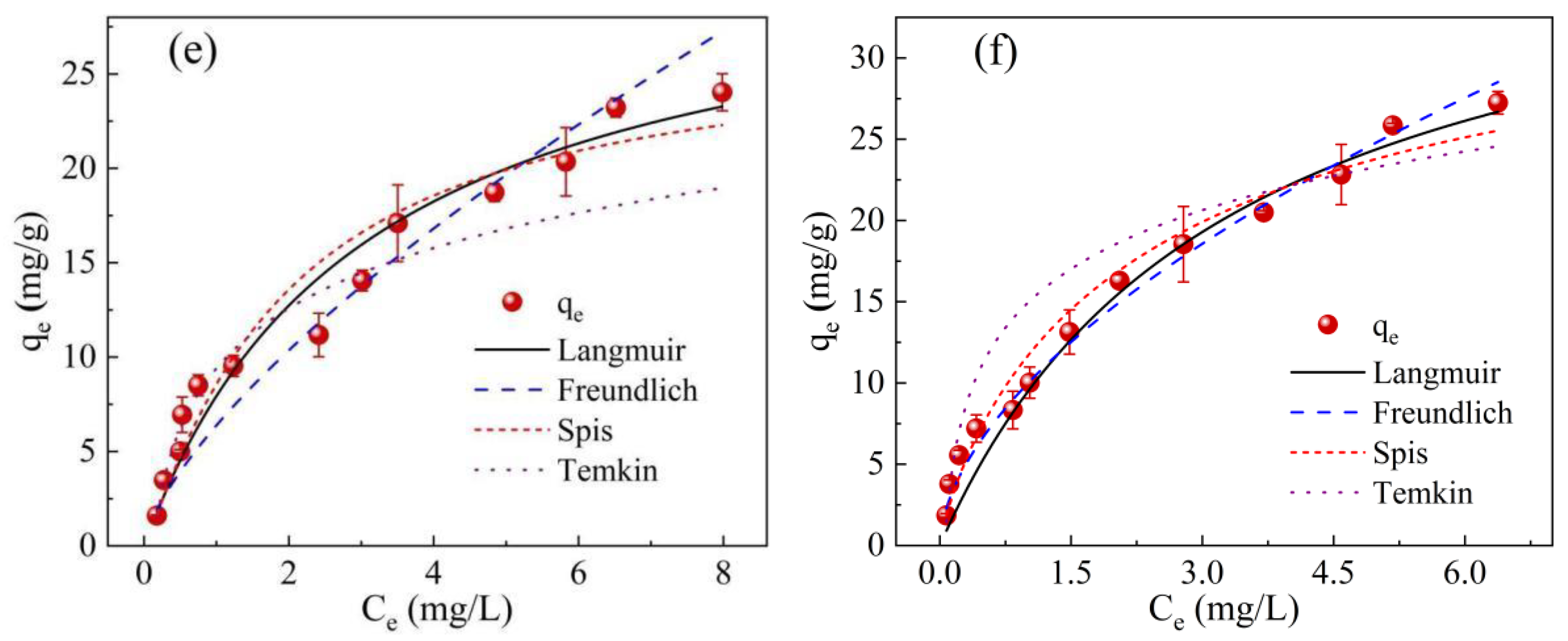
2.4. Adsorption Isotherms
2.5. Adsorption Mechanism
2.6. Effect of Coexisting Substances, Leaching, and Renewability
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Reagents and Materials
3.2. Preparation of Biochar
3.3. Characterization
3.4. Adsorption Experiments
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Li, S.Y.; Sun, Q.Q.; Wu, Q.; Gui, W.J.; Zhu, G.N.; Schlenk, D. Endocrine disrupting effects of tebuconazole on different life stages of zebrafish (Danio rerio). Environ. Pollut. 2019, 249, 1049–1059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, N.N.; Ruan, H.C.; Chen, F.R.; Zhang, Y.L.; Yang, X.J.; Dai, Y.L.; Gan, L.; Du, Y.X. Development and application of an allele–specific PCR assay for detecting T409C mutation of cyp51 gene linked with tebuconazole resistance in Villosiclava virens (rice false smut). Can. J. Plant Pathol. 2017, 39, 318–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bollmann, U.E.; Tang, C.; Eriksson, E.; Jönsson, K.; Vollertsen, J.; Bester, K. Biocides in urban wastewater treatment plant influent at dry and wet weather: Concentrations, mass flows and possible sources. Water Res. 2014, 60, 64–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ku, T.T.; Zhou, M.M.; Hou, Y.W.; Xie, Y.Y.; Li, G.K.; Sang, N. Tebuconazole induces liver injury coupled with ROS–mediated hepatic metabolism disorder. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2021, 220, 112309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.H.; Zhang, J.Y.; Li, F.X.; Liu, J. Triazole fungicide tebuconazole disrupts human placental trophoblast cell functions. J. Hazard. Mater. 2016, 308, 294–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vieira, R.S.F.; Venâncio, C.A.S.; Félix, L.M. Behavioural impairment and oxidative stress by acute exposure of zebrafish to a commercial formulation of tebuconazole. Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol 2022, 91, 103823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Xia, W.; Wan, Y.J.; Xu, S.Q. Azole and strobilurin fungicides in source, treated, and tap water from Wuhan, central China: Assessment of human exposure potential. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 801, 149733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saleh, I.A.; Zouari, N.; Al–Ghouti, M.A. Removal of pesticides from water and wastewater: Chemical, physical and biological treatment approaches. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2020, 19, 101026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.C.; Zhu, K.; Su, M.M.; Zhu, H.Y.; Lu, J.B.; Wang, Y.X.; Dong, J.K.; Qin, H.; Wang, Y.; Zang, Y. Influence of solution pH on degradation of atrazine during UV and UV/H2O2 oxidation: Kinetics, mechanism, and degradation pathways. RSC Adv. 2019, 9, 35847–35861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kane, A.; Assadi, A.A.; Jery, A.E.; Badawi, A.K.; Kenfoud, H.; Baaloudj, O.; Assadi, A.A. Advanced photocatalytic treatment of wastewater using immobilized titanium dioxide as a photocatalyst in a pilot–scale reactor: Process intensification. Materials 2022, 15, 4547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Figueredo, F.D.A.A.; de Souza Lucas, F.W.; Fill, T.P.; Rodrigues-Filho, E.; Mascaro, L.H.; da Silva Casciano, P.N.; de Lima-Neto, P.; Correia, A.N. Insights into electrodegradation mechanism of tebuconazole pesticide on Bi–doped PbO2 electrodes. Electrochim. Acta 2015, 154, 278–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crini, G.; Exposito Saintemarie, A.; Rocchi, S.; Fourmentin, M.; Jeanvoine, A.; Millon, L.; Morin-Crini, N. Simultaneous removal of five triazole fungicides from synthetic solutions on activated carbons and cyclodextrin–based adsorbents. Heliyon 2017, 3, e00380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, Y.L.; Guo, W.S.; Ngo, H.H.; Nghiem, L.D.; Hai, F.I.; Zhang, J.; Liang, S.; Wang, X.C. A review on the occurrence of micropollutants in the aquatic environment and their fate and removal during wastewater treatment. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 473–474, 619–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baaloudj, O.; Nasrallah, N.; Kenfoud, H.; Bourkeb, K.W.; Badawi, A.K. Polyaniline/Bi12TiO20 hybrid system for cefixime removal by combining adsorption and photocatalytic degradation. ChemEngineering 2023, 7, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahzad, W.; Badawi, A.K.; Rehan, Z.A.; Khan, A.M.; Khan, R.A.; Shah, F.; Ali, S.; Ismail, B. Enhanced visible light photocatalytic performance of Sr0.3(Ba,Mn)0.7ZrO3 perovskites anchored on graphene oxide. Ceram. Int. 2022, 48, 24979–24988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malakootian, M.; Shahesmaeili, A.; Faraji, M.; Amiri, H.; Silva Martinez, S. Advanced oxidation processes for the removal of organophosphorus pesticides in aqueous matrices: A systematic review and meta–analysis. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2020, 134, 292–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barquilha, C.E.R.; Braga, M.C.B. Adsorption of organic and inorganic pollutants onto biochars: Challenges, operating conditions, and mechanisms. Bioresour. Technol. Rep. 2021, 15, 100728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.K.; Zhang, J.Y.; Hu, B.C.; Yu, J.; Wang, J.; Guo, X.J. Graphene/Fe3O4 nanocomposite for effective removal of ten triazole fungicides from water solution: Tebuconazole as an example for investigation of the adsorption mechanism by experimental and molecular docking study. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 2019, 95, 635–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Z.H.; Lv, D.Z.; Zhou, D.D.; Yang, Z.H.; Wang, M.Y.; Abdelhai Senosy, I.; Liu, X.; Chen, M.; Zhuang, L.Y. Enhanced removal efficiency towards azole fungicides from environmental water using a metal organic framework functionalized magnetic lignosulfonate. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2021, 279, 119785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cha, J.S.; Park, S.H.; Jung, S.C.; Ryu, C.; Jeon, J.K.; Shin, M.C.; Park, Y.K. Production and utilization of biochar: A review. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2016, 40, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hung, C.M.; Chen, C.W.; Huang, C.P.; Dong, C.D. Degradation of 4–nonylphenol in marine sediments using calcium peroxide activated by water hyacinth (Eichhornia crassipes)–derived biochar. Environ. Res. 2022, 211, 113076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hung, C.M.; Huang, C.P.; Hsieh, S.L.; Chen, Y.T.; Chen, C.W.; Dong, C.D. Water hyacinth derived biochar for polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons removal and oxidative stress study. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2023, 29, 103027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saleh, T.S.; Badawi, A.K.; Salama, R.S.; Mostafa, M.M.M. Design and development of novel composites containing nickel ferrites supported on activated carbon derived from agricultural wastes and its application in water remediation. Materials 2023, 16, 2170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Creamer, A.E.; Gao, B. Carbon–based adsorbents for postcombustion CO2 capture: A critical review. Sci. Technol. 2016, 50, 7276–7289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Islam, M.N.; Rahman, F.; Papri, S.A.; Faruk, M.O.; Das, A.K.; Adhikary, N.; Debrot, A.; Ahsan, M.N. Water hyacinth (Eichhornia crassipes (Mart.) Solms.) as an alternative raw material for the production of bio–compost and handmade paper. J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 294, 11306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emam, A.A.; Abo Faraha, S.A.; Kamal, F.H.; Gamal, A.M.; Basseem, M. Modification and characterization of Nano cellulose crystalline from Eichhornia crassipes using citric acid: An adsorption study. Carbohydr. Polym. 2020, 240, 116202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viswanathan, S.P.; Njazhakunnathu, G.V.; Neelamury, S.P.; Padmakumar, B.; Ambatt, T.P. The efficiency of aquatic weed–derived biochar in enhanced removal of cationic dyes from aqueous medium. Biomass Convers. Biorefin. 2022, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramirez–Muñoz, A.; Pérez, S.; Flórez, E.; Acelas, N. Recovering phosphorus from aqueous solutions using water hyacinth (Eichhornia crassipes) toward sustainability through its transformation to apatite. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 106225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amalina, F.; Razak, A.S.A.; Krishnan, S.; Zularisam, A.W.; Nasrullah, M. Water hyacinth (Eichhornia crassipes) for organic contaminants removal in water—A review. J. Hazard. Mater. Adv 2022, 7, 100092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Z.H.; Wang, M.Y.; Zhou, D.D.; Senosy, I.A.; Yang, Z.H.; Lv, D.Z.; Liu, X.; Zhuang, L.Y.; Chen, M. Integration of bimetallic organic frameworks and magnetic biochar for azole fungicides removal. Environ. Adv. 2022, 7, 100152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Miao, J.; Saleem, M.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, Q.M. Enhanced adsorptive removal of carbendazim from water by FeCl3–modified corn straw biochar as compared with pristine, HCl and NaOH modification. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2022, 10, 107024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, M.; Li, Z.W.; Luo, N.L.; Ren, Y.; Wen, J.J.; Huang, B.; Zeng, G.M. Application potential of biochar in environment: Insight from degradation of biochar–derived DOM and complexation of DOM with heavy metals. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 646, 220–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, Y.Y.; Luo, Y.; He, Q.P.; Zhao, D.; Zhang, K.Q.; Shen, S.Z.; Wang, F. Performance and mechanism of a biochar–based Ca–La composite for the adsorption of phosphate from water. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 105267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuo, S.N.; Dai, T.C.; Ren, H.Y.; Liu, B.F. Simultaneous adsorption of phosphate and tetracycline by calcium modified corn stover biochar: Performance and mechanism. Bioresour. Technol. 2022, 359, 127477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wallace Anna, R.; Su, C.; Choi, Y.K.; Kan, E.; Sun, W. Removal of fluoride from water using a calcium–modified dairy manure–derived biochar. J. Environ. Eng. 2020, 146, 04020128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.C.; Ji, X.G.; Wang, Y.; Zang, Y.; Zang, Y.X.; Li, W.; Yuan, J.; Ma, D.; Sun, H.W.; Duan, J.M. A stable Fe–Zn modified sludge–derived biochar for diuron removal: Kinetics, isotherms, mechanism, and practical research. Molecules 2023, 6, 2628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, H.W.; He, J.J.; Liu, Y.C.; Ji, X.G.; Wang, G.; Yang, X.Y.; Zhang, Y.X. Removal performance and mechanism of emerging pollutant chloroquine phosphate from water by iron and magnesium co–modified rape straw biochar. Molecules 2023, 8, 3290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.B.; Su, L.; Cheng, C.P.; Cheng, H.Y.; Chang, M.C.; Liu, F.W.; Liu, N.; Oh, K. A new type of calcium–rich biochars derived from spent mushroom substrates and their efficient adsorption properties for cationic dyes. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2022, 10, 1007630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.Q.; He, F.F.; Shen, X.Y.; Hu, D.W.; Huang, Q. Pyrolyzed fabrication of N/P co–doped biochars from (NH4)3PO4–pretreated coffee shells and appraisement for remedying aqueous Cr(VI) contaminants. Bioresour. Technol. 2020, 315, 123840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, S.; Irshad, M.K.; Ibrahim, M.; Chen, Q.; Shang, J.Y.; Zhang, Q. The distinctive role of nano–hydroxyapatite modified biochar for alleviation of cadmium and arsenic toxicity in aqueous system. J. Water Process. Eng. 2022, 49, 103054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, L.J.; Li, S.B.; Jin, Y.F.; Hu, B.W.; Sheng, G.D. Enhanced adsorption of Eu(III) from wastewater using Solidago canadensis–derived biochar functionalized by Ca/Al–LDH and hydroxyapatite. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2021, 567, 150794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sayin, F.; Akar, S.T.; Akar, T. From green biowaste to water treatment applications: Utilization of modified new biochar for the efficient removal of ciprofloxacin. Sustain. Chem. Pharm. 2021, 24, 100522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.M.; Xu, J.L.; Luo, X.X.; Shi, J.X. Efficient adsorption of dyes from aqueous solution using a novel functionalized magnetic biochar: Synthesis, kinetics, isotherms, adsorption mechanism, and reusability. Bioresour. Technol. 2022, 360, 127526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhen, X.T.; Yu, Y.L.; Shi, M.Z.; Zhu, S.C.; Yan, T.C.; Yue, Z.X.; Gu, Y.X.; Zheng, H.; Cao, J. Activated carbon derived from hawthorn kernel waste for rapid adsorption of fungicides. Surf. Interfaces 2022, 28, 101700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Čadková, E.; Komárek, M.; Debord, J.; Della Puppa, L.; Bordas, F.; Bollinger, J.C. pKa constant determination of two triazole pesticides: Tebuconazole and penconazole. J. Solution Chem. 2013, 42, 1075–1082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iamsaard, K.; Weng, C.H.; Yen, L.T.; Tzeng, J.H.; Poonpakdee, C.; Lin, Y.T. Adsorption of metal on pineapple leaf biochar: Key affecting factors, mechanism identification, and regeneration evaluation. Bioresour. Technol. 2022, 344, 126131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.Z.; Li, Y.F.; Cao, Y.Y.; Han, L.J. Characteristics of tetracycline adsorption by cow manure biochar prepared at different pyrolysis temperatures. Bioresour. Technol. 2019, 285, 121348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.; Jiang, S.Q.; Zhang, Y.N.; Xu, J.; Qiu, L.W.; Wang, L.P. Investigation into adsorption characteristics and mechanism of atrazine on nano–MgO modified fallen leaf biochar. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 105727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mei, Y.L.; Xu, J.; Zhang, Y.; Li, B.; Fan, S.S.; Xu, H.C. Effect of Fe–N modification on the properties of biochars and their adsorption behavior on tetracycline removal from aqueous solution. Bioresour. Technol. 2021, 325, 124732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.J.; Sun, H.W.; Liu, Y.C.; Wang, X.H.; Valizadeh, K. The sorption of Tebuconazole and Linuron from an aqueous environment with a modified sludge–based biochar: Effect, mechanisms, and its persistent free radicals study. J. Chem. 2021, 2021, 2912054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, T.B.; Nguyen, T.K.T.; Chen, W.H.; Chen, C.W.; Bui, X.T.; Patel, A.K.; Dong, C.D. Hydrothermal and pyrolytic conversion of sunflower seed husk into novel porous biochar for efficient adsorption of tetracycline. Bioresour. Technol. 2023, 373, 128711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.M.; Shi, J.X.; Luo, X.X. Enhanced adsorption of rhodamine B from water by Fe–N co–modified biochar: Preparation, performance, mechanism and reusability. Bioresour. Technol. 2022, 343, 126103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, Z.T.; Ye, S.J.; Wu, H.P.; Xiao, R.; Zeng, G.M.; Liang, J.; Zhang, C.; Yu, J.F.; Fang, Y.L.; Song, B. Research on the sustainable efficacy of g–MoS2 decorated biochar nanocomposites for removing tetracycline hydrochloride from antibiotic–polluted aqueous solution. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 648, 206–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, C.; Zhang, H.X. Modified–biochar adsorbents (MBAs) for heavy–metal ions adsorption: A critical review. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2022, 10, 107393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Gao, M.; Cao, M.B.; Dan, J.M.; Yang, H.B. Self–propagating synthesis of Zn–loaded biochar for tetracycline elimination. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 759, 143542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Z.Q.; Zhao, L.; Liu, C.H.; Zhen, Y.F.; Ma, J. Fast adsorption of BPA with high capacity based on π–π electron donor–acceptor and hydrophobicity mechanism using an in–situ sp2 C dominant N–doped carbon. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 381, 122510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.L.; Xiao, Y.; Wang, L.Y.; Xing, Y.H.; Bai, F.Y.; Shi, Z. Oriented construction of the Mixed–metal organic framework with triazine hexacarboxylic acid and fluorescence detection: Fe3+, Cr2O72– and TNP. Polyhedron 2022, 214, 115648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, H.; Yang, D.S.; Zhang, C.H.; Liu, W.; Zhang, L.P.; Dong, Y.B. Selective removal behavior of lead and cadmium from calcium–rich solution by MgO loaded soybean straw biochars and mechanism analysis. Chemosphere 2023, 319, 138010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.Y.; Liu, X.C.; Xiang, Y.J.; Wang, P.; Zhang, J.C.; Zhang, F.F.; Wei, J.H.; Luo, L.; Lei, M.; Tang, L. Modification of biochar derived from sawdust and its application in removal of tetracycline and copper from aqueous solution: Adsorption mechanism and modelling. Bioresour. Technol. 2017, 245, 266–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, X.S.; Hu, Y.J.; Tang, J.; Sheng, T.T.; Jiang, G.M.; Xu, X.H. Effects of co–existing ions and natural organic matter on removal of chromium(VI) from aqueous solution by nanoscale zero valent iron (nZVI)–Fe3O4 nanocomposites. Chem. Eng. J. 2013, 218, 55–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, V.T.; Nguyen, T.B.; Dat, N.D.; Huu, B.T.; Nguyen, X.C.; Tran, T.; Bui, M.H.; Dong, C.D.; Bui, X.T. Adsorption of norfloxacin from aqueous solution on biochar derived from spent coffee ground: Master variables and response surface method optimized adsorption process. Chemosphere 2022, 288, 132577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, Y.D.; Zheng, J.J.; Jiang, C.; Zhang, F.; Wei, L.C.; Zhu, L. Hydrochloric acid–modified algal biochar for the removal of Microcystis aeruginosa: Coagulation performance and mechanism. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2022, 10, 108903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, M.B.; Zhou, J.L.; Ngo, H.H.; Guo, W.S.; Chen, M.F. Progress in the preparation and application of modified biochar for improved contaminant removal from water and wastewater. Bioresour. Technol. 2016, 214, 836–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, J.D.; Jiang, C.Y.; Guan, Q.Q.; Ning, P.; Gu, J.J.; Chen, Q.L.; Zhang, J.M.; Miao, R.R. Enhanced removal of Cr(VI) from aqueous solution by supported ZnO nanoparticles on biochar derived from waste water hyacinth. Chemosphere 2018, 195, 632–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

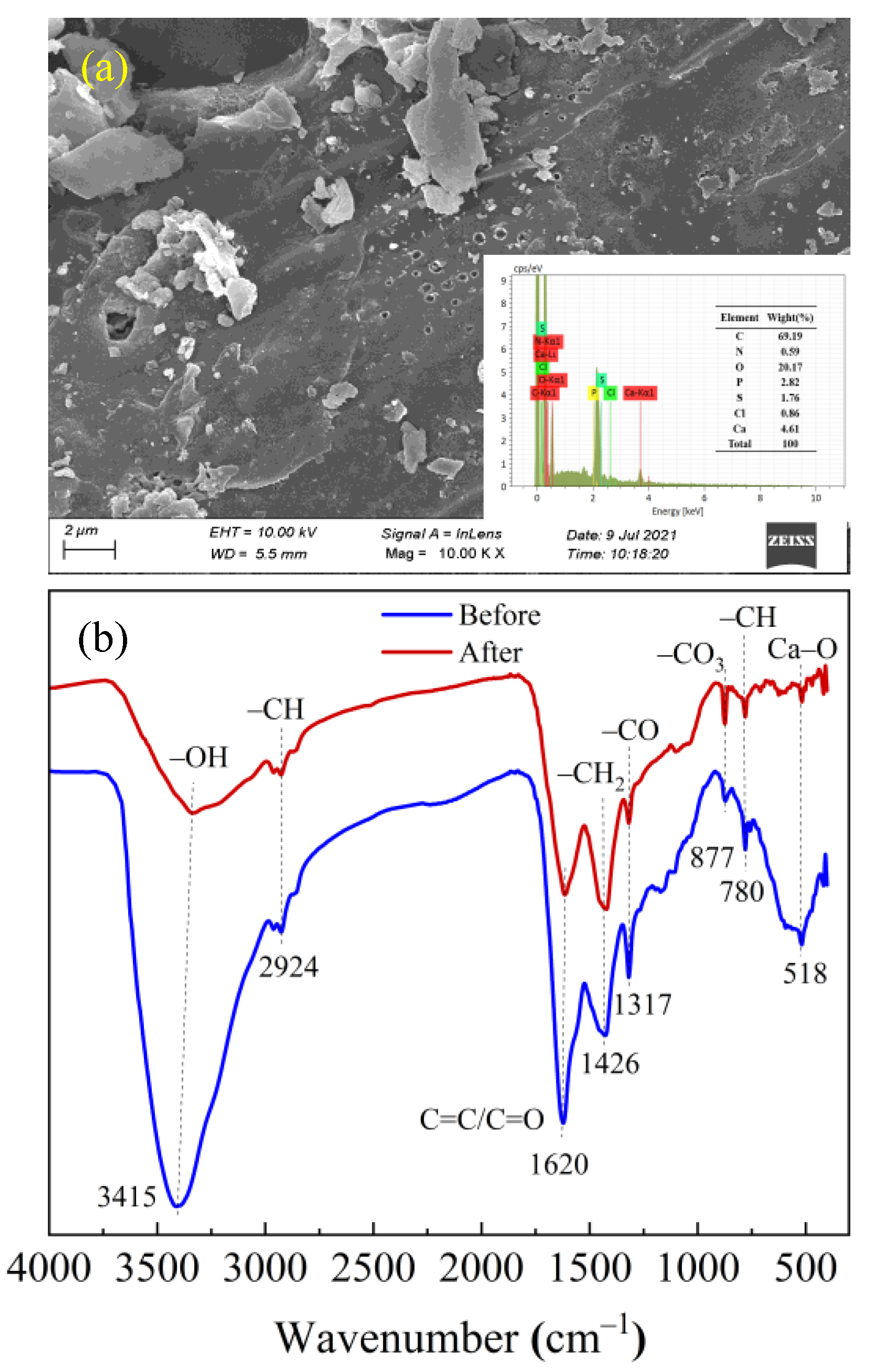
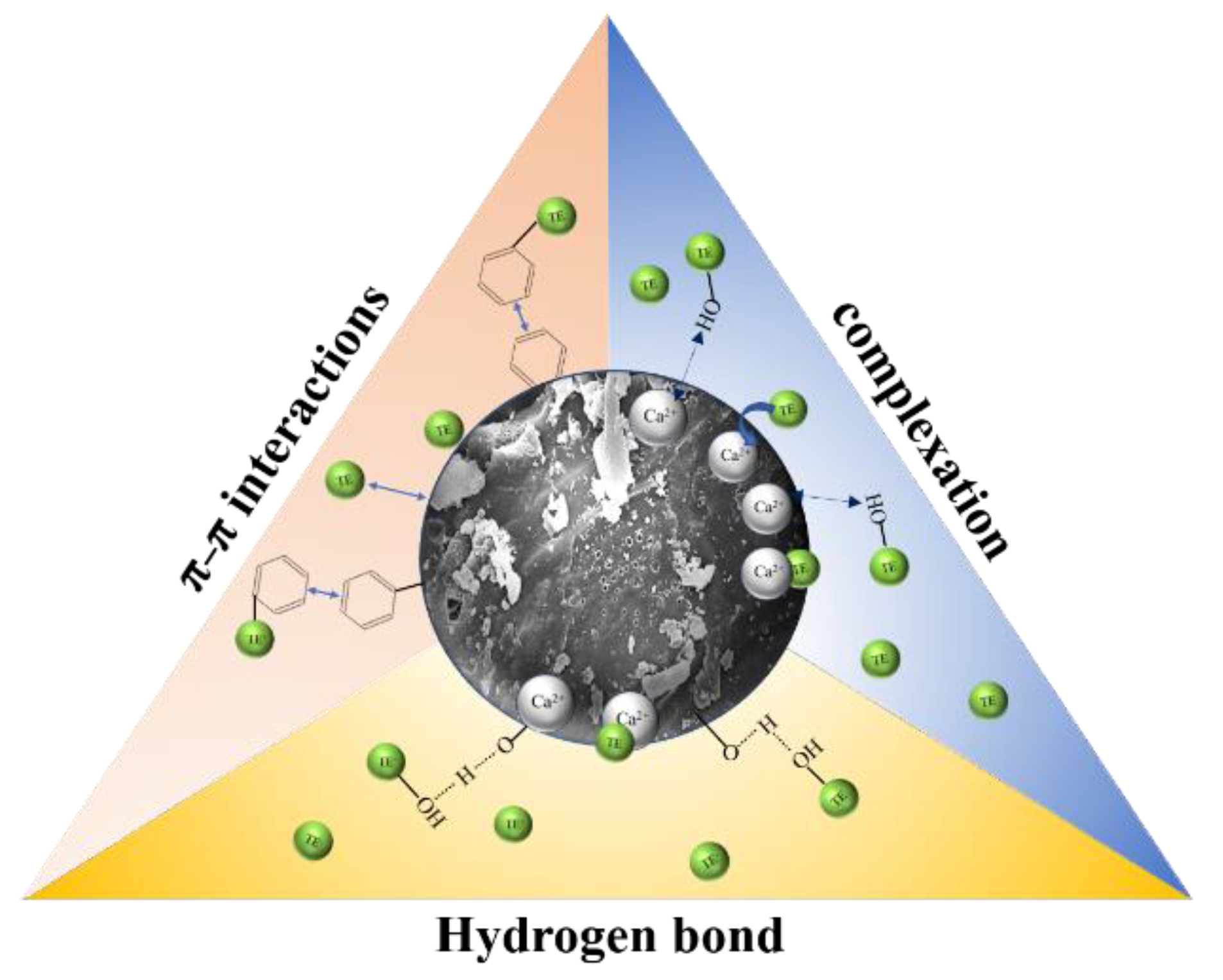
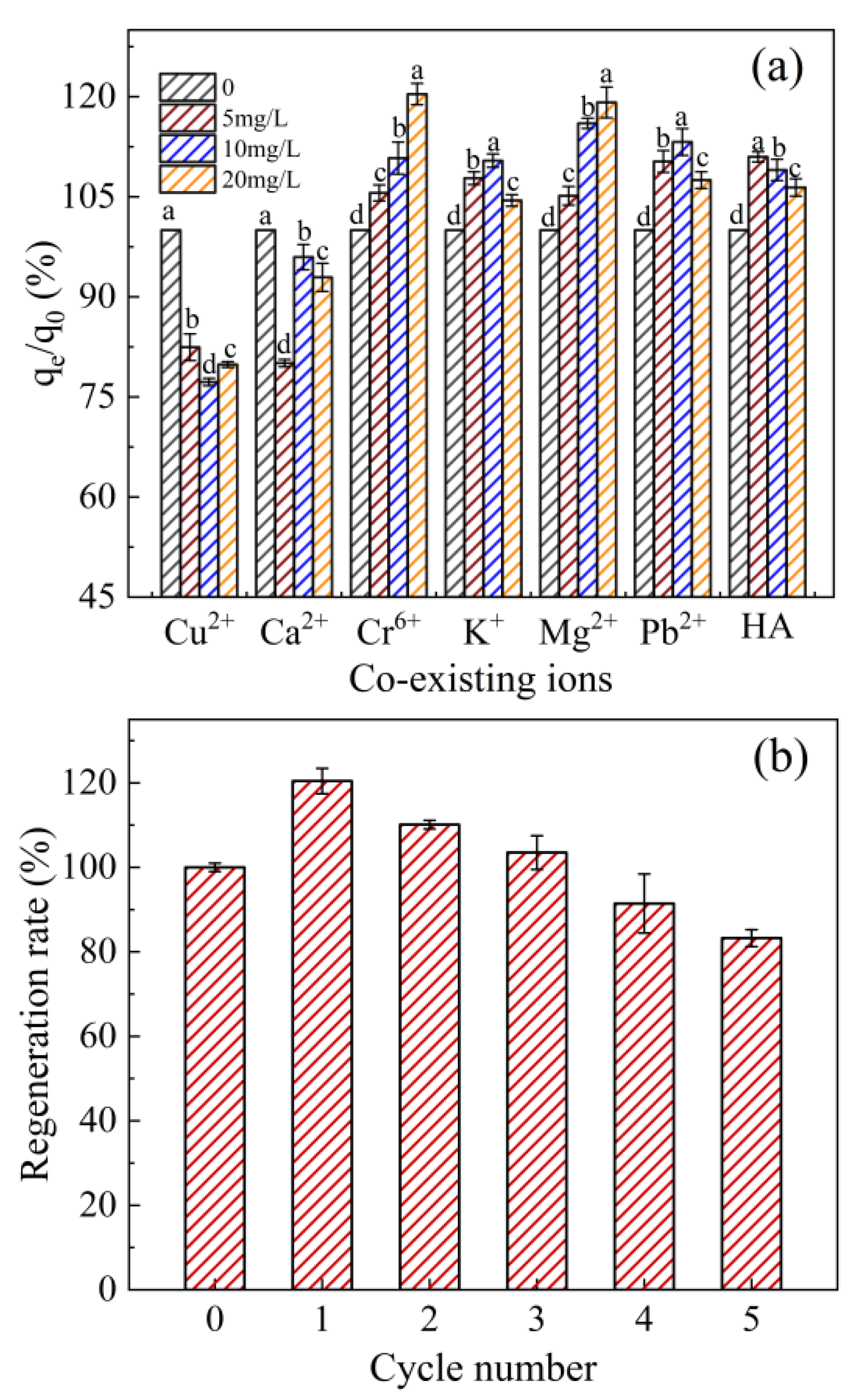
| Biochar | Specific Surface Area (m2/g) | Total Pore Volume (cm3/g) | Average Pore Diameter (nm) |
|---|---|---|---|
| WHBC | 3.30 | 0.00430 | 5.22 |
| WHCBC | 5.29 | 0.00812 | 6.63 |
| Model | Parameter | WHBC | WHCBC |
|---|---|---|---|
| Experimental adsorption capacity | qm (mg/g) | 3.21 | 8.01 |
| Pseudo-first-order model | qm (mg/g) | 2.95 | 6.98 |
| K1 (min–1) | 0.0575 | 0.586 | |
| R2 | 0.807 | 0.805 | |
| Pseudo-second-order model | qm (mg/g) | 3.26 | 7.45 |
| K2 (g/(mg·min)) | 0.0239 | 0.105 | |
| R2 | 0.926 | 0.911 | |
| Elovich model | α (g/(mg·min) | 0.740 | 261 |
| β (g/mg) | 1.72 | 1.38 | |
| R2 | 0.992 | 0.989 | |
| Intra-particle diffusion model | kid1 (g/(mg·min1/2) | 0.471 | 0.554 |
| c1 (mg/g) | 0.0300 | 3.97 | |
| R12 | 0.985 | 0.952 | |
| kid2 (g/(mg·min1/2) | 0.153 | 0.140 | |
| c2 (mg/g) | 1.33 | 6.38 | |
| R22 | 0.919 | 0.932 | |
| kid3 (g/(mg·min1/2) | 0.0253 | 0.0300 | |
| c3 (mg/g) | 2.82 | 7.54 | |
| R32 | 1.00 | 0.997 | |
| Liquid film diffusion model | Kfd | 0.0215 | 0.0262 |
| R2 | 1.00 | 1.00 |
| Model | Parameter | Temperature (°C) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 25 | 35 | 45 | ||
| Langmuir isotherm | qm (mg/g) | 24.0 | 32.2 | 40.5 |
| KL (L/mg) | 0.618 | 0.327 | 0.304 | |
| R2 | 0.989 | 0.980 | 0.981 | |
| Freundlich isotherm | KF (mg/g(L/mg)1/n) | 10.1 | 6.38 | 9.94 |
| n | 2.93 | 1.43 | 1.76 | |
| R2 | 0.954 | 0.949 | 0.995 | |
| Sips isotherm | qm (mg/g) | 26.0 | 26.9 | 37.54 |
| Ks (L/mg) | 0.492 | 0.510 | 0.385 | |
| m | 0.937 | 1.13 | 0.839 | |
| R2 | 0.989 | 0.980 | 0.985 | |
| Temkin isotherm | Kt (L/mg) | 12.2 | 7.71 | 17.4 |
| B | 663 | 556 | 507 | |
| R2 | 0.942 | 0.937 | 0.973 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, Y.; Gao, Z.; Ji, X.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Sun, H.; Li, W.; Wang, L.; Duan, J. Efficient Adsorption of Tebuconazole in Aqueous Solution by Calcium Modified Water Hyacinth-Based Biochar: Adsorption Kinetics, Mechanism, and Feasibility. Molecules 2023, 28, 3478. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28083478
Liu Y, Gao Z, Ji X, Wang Y, Zhang Y, Sun H, Li W, Wang L, Duan J. Efficient Adsorption of Tebuconazole in Aqueous Solution by Calcium Modified Water Hyacinth-Based Biochar: Adsorption Kinetics, Mechanism, and Feasibility. Molecules. 2023; 28(8):3478. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28083478
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Yucan, Zhonglu Gao, Xianguo Ji, Ying Wang, Yan Zhang, Hongwei Sun, Wei Li, Lide Wang, and Jinming Duan. 2023. "Efficient Adsorption of Tebuconazole in Aqueous Solution by Calcium Modified Water Hyacinth-Based Biochar: Adsorption Kinetics, Mechanism, and Feasibility" Molecules 28, no. 8: 3478. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28083478
APA StyleLiu, Y., Gao, Z., Ji, X., Wang, Y., Zhang, Y., Sun, H., Li, W., Wang, L., & Duan, J. (2023). Efficient Adsorption of Tebuconazole in Aqueous Solution by Calcium Modified Water Hyacinth-Based Biochar: Adsorption Kinetics, Mechanism, and Feasibility. Molecules, 28(8), 3478. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28083478







