Untargeted Metabolomics Using UHPLC-HRMS Reveals Metabolic Changes of Fresh-Cut Potato during Browning Process
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
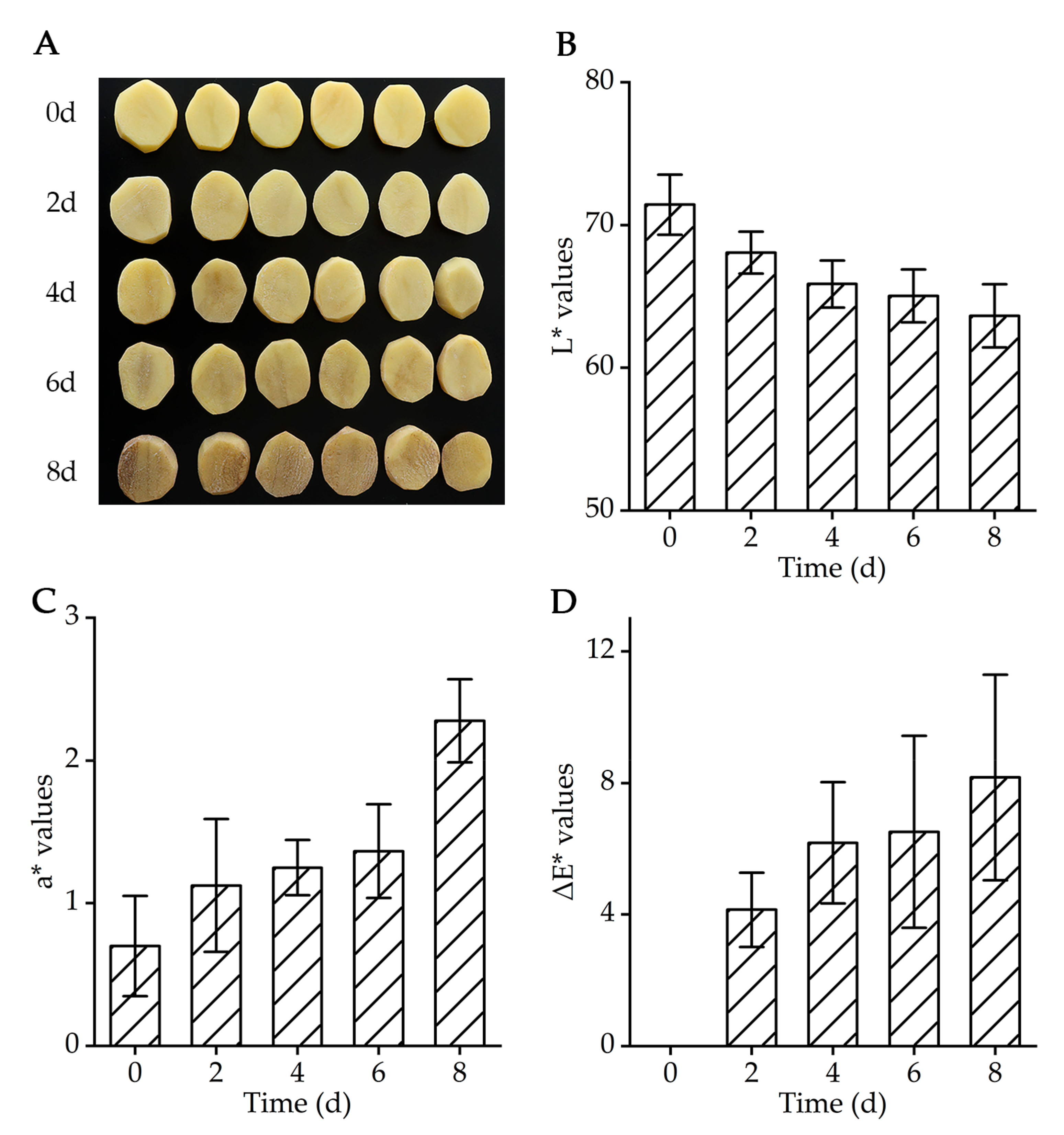
2.1. Color Analysis
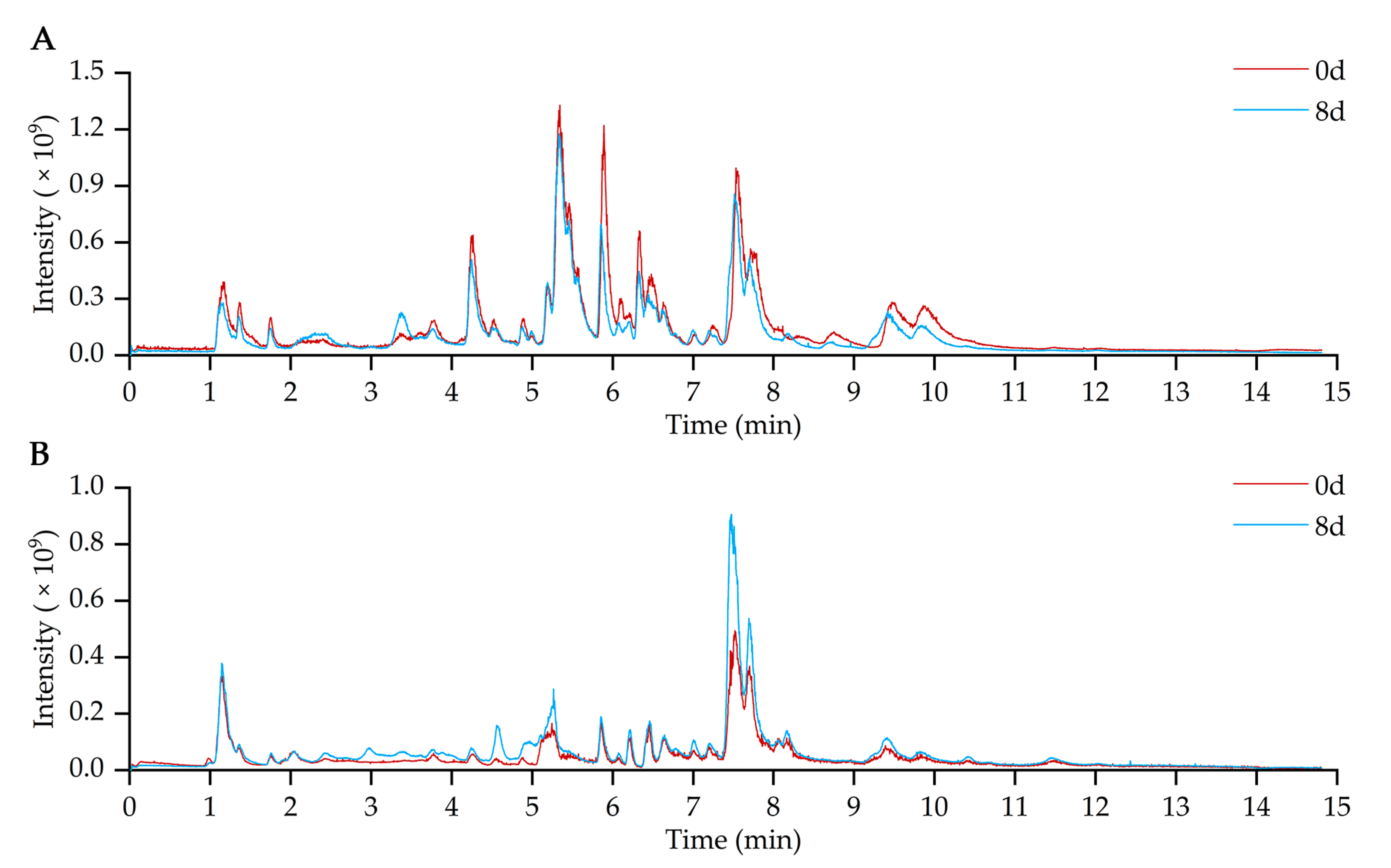
2.2. Metabolites Profiling
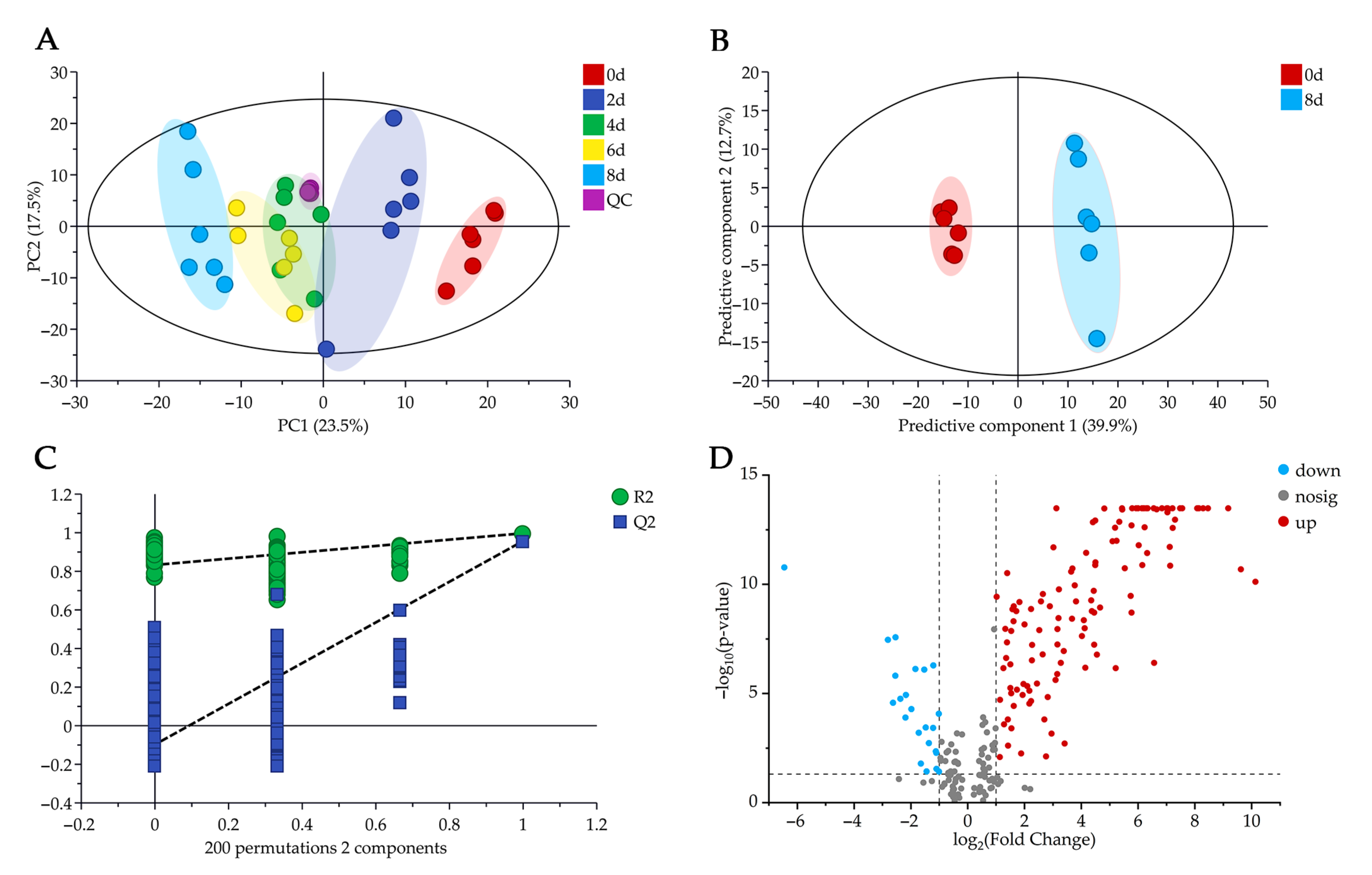
2.3. Multivariate Statistical Analysis
2.4. Key Metabolites Analysis
2.5. Changes of Key Metabolites during Browning Process
2.5.1. Amino Acids and Derivative
2.5.2. Lipids and Derivative
2.5.3. Nucleotides and Derivative
2.6. Limitations
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Chemical and Reagents
3.2. Fresh-Cut Processing
3.3. Color Measurement
3.4. Metabolite Extraction
3.5. UHPLC-HRMS Acquisition
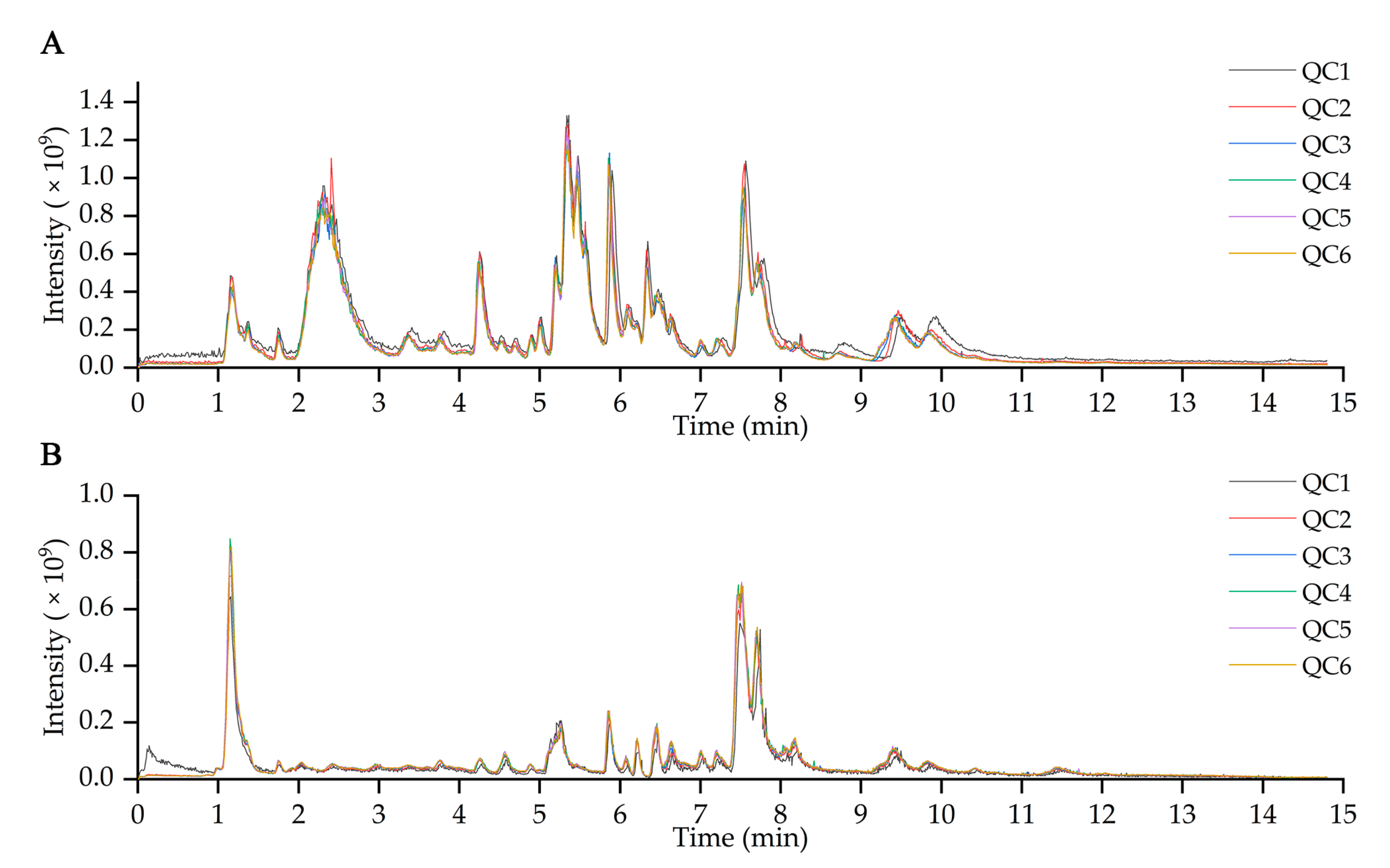
3.6. Data Processing and Statistical Analysis
3.7. Metabolites Confirmation
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Sample Availability
References
- Dourado, C.; Pinto, C.; Barba, F.J.; Lorenzo, J.M.; Delgadillo, I.; Saraiva, J.A. Innovative non-thermal technologies affecting potato tuber and fried potato quality. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2019, 88, 274–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akyol, H.; Riciputi, Y.; Capanoglu, E.; Caboni, M.F.; Verardo, V. Phenolic compounds in the potato and its byproducts: An overview. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiao, L.; Gao, M.; Wang, Y.; Tian, X.; Lu, L.; Liu, X. Integrated transcriptomic and metabolomic analysis of cultivar differences provides insights into the browning mechanism of fresh-cut potato tubers. Postharvest Biol. Technol. 2022, 188, 111905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, L.; Gao, M.; Zheng, J.; Zhang, J.; Lu, L.; Liu, X. Novel browning alleviation technology for fresh-cut products: Preservation effect of the combination of Sonchus oleraceus L. extract and ultrasound in fresh-cut potatoes. Food Chem. 2021, 348, 129132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toivonen, P.M.A.; Brummell, D.A. Biochemical bases of appearance and texture changes in fresh-cut fruit and vegetables. Postharvest Biol. Technol. 2008, 48, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Serrano, M.; Barceló, A.R. Comparative study of the products of the peroxidase-catalyzed and the polyphenoloxidase-catalyzed (+)-catechin oxidation. Their possible implications in strawberry (Fragaria × ananassa) browning reactions. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2002, 50, 1218–1224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, E.Y.; Moon, J.H.; Park, H.Y.; Lee, H.J.; Kim, J.-Y. Effect of thermal shock cycling on storage stability and quality of fresh-cut potato. LWT Food Sci. Technol. 2020, 121, 108972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Wang, J.; Zhang, X.; Shi, Q.; Xin, L.; Fu, H.; Wang, Y. Effects of radio frequency assisted blanching on polyphenol oxidase, weight loss, texture, color and microstructure of potato. Food Chem. 2018, 248, 173–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rizzo, V.; Amoroso, L.; Licciardello, F.; Mazzaglia, A.; Muratore, G.; Restuccia, C.; Lombardo, S.; Pandino, G.; Strano, M.G.; Mauromicale, G. The effect of Sous vide packaging with rosemary essential oil on storage quality of fresh-cut potato. LWT Food Sci. Technol. 2018, 94, 111–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, X.; Zhang, M.; Devahastin, S.; Guo, Z. Effects of pressurized argon and nitrogen treatments in combination with modified atmosphere on quality characteristics of fresh-cut potatoes. Postharvest Biol. Technol. 2019, 149, 159–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Yang, Q.; Lu, Y.; Li, Y.; Li, T.; Zhou, B.; Qiao, L. Effect of purslane (Portulaca oleracea L.) extract on anti-browning of fresh-cut potato slices during storage. Food Chem. 2019, 283, 445–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Y.; Wang, D.; Zhao, W.; Zheng, Y.; Wang, Y.; Wang, P.; Ma, Y.; Zhao, X. Low frequency ultrasound treatment enhances antibrowning effect of ascorbic acid in fresh-cut potato slices. Food Chem. 2022, 380, 132190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wolfender, J.L.; Marti, G.; Thomas, A.; Bertrand, S. Current approaches and challenges for the metabolite profiling of complex natural extracts. J. Chromatogr. A 2015, 1382, 136–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, P.; Ng, Q.X.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, B.; Ong, C.N.; He, Y. Metabolite changes behind faster growth and less reproduction of Daphnia similis exposed to low-dose silver nanoparticles. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2018, 163, 266–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; Kim, J.; Yun, E.J.; Kim, K.H. Food metabolomics: From farm to human. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2016, 37, 16–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lacalle-Bergeron, L.; Izquierdo-Sandoval, D.; Sancho, J.V.; López, F.J.; Hernández, F.; Portolés, T. Chromatography hyphenated to high resolution mass spectrometry in untargeted metabolomics for investigation of food (bio)markers. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2021, 135, 116161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Utpott, M.; Rodrigues, E.; Rios, A.O.; Mercali, G.D.; Flôres, S.H. Metabolomics: An analytical technique for food processing evaluation. Food Chem. 2022, 366, 130685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Q.; Pan, H.; Shao, H.; Qian, C.; Han, J.; Li, Y.; Lou, Y. UPLC/MS-based untargeted metabolomics reveals the changes in muscle metabolism of electron beam irradiated Solenocera melantho during refrigerated storage. Food Chem. 2022, 367, 130713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galeano Garcia, P.; Neves Dos Santos, F.; Zanotta, S.; Eberlin, M.N.; Carazzone, C. Metabolomics of Solanum lycopersicum infected with phytophthora infestans leads to early detection of late blight in asymptomatic plants. Molecules 2018, 23, 3330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.X.; Pan, Y.G.; He, F.P.; Yuan, M.Q.; Li, S.B. Pathway Analysis and metabolites identification by metabolomics of etiolation substrate from fresh-cut Chinese water chestnut (Eleocharis tuberosa). Molecules 2016, 21, 1648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, F.; Cai, F.; Luo, B.; Gu, R.; Ahmed, S.; Long, C. Variation of microbiological and biochemical profiles of Laowo dry-cured ham, an indigenous fermented food, during ripening by GC-TOF-MS and UPLC-QTOF-MS. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2020, 68, 8925–8935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, W.C.; Chen, Y.T.; Chen, H.J.; Hsieh, C.W.; Liao, P.C. Comparative UHPLC-Q-Orbitrap HRMS-based metabolomics unveils biochemical changes of black garlic during aging process. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2020, 68, 14049–14058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- An, T.; Chen, M.; Zu, Z.; Chen, Q.; Lu, H.; Yue, P.; Gao, X. Untargeted and targeted metabolomics reveal changes in the chemical constituents of instant dark tea during liquid-state fermentation by Eurotium cristatum. Food Res. Int. 2021, 148, 110623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- García, C.J.; García-Villalba, R.; Gil, M.I.; Tomas-Barberan, F.A. LC-MS untargeted metabolomics to explain the signal metabolites inducing browning in fresh-cut lettuce. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2017, 65, 4526–4535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García, C.J.; Gil, M.I.; Tomas-Barberan, F.A. LC–MS untargeted metabolomics reveals early biomarkers to predict browning of fresh-cut lettuce. Postharvest Biol. Technol. 2018, 146, 9–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Sun, J.; Teng, Z.; Luo, Y.; Yu, L.; Simko, I.; Chen, P. Identification of marker compounds for predicting browning of fresh-cut lettuce using untargeted UHPLC-HRMS metabolomics. Postharvest Biol. Technol. 2021, 180, 111626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Xiao, K.; Zhang, A.; Zhu, W.; Zhang, H.; Tan, F.; Huang, Q.; Wu, X.; Zha, D. Metabolomic analysis, combined with enzymatic and transcriptome assays, to reveal the browning resistance mechanism of fresh-cut eggplant. Foods 2022, 11, 1174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Zhang, A.; Shang, J.; Zhu, Z.; Li, Y.; Wu, X.; Zha, D. Study on browning mechanism of fresh-cut eggplant (Solanum melongena L.) based on metabolomics, enzymatic assays and gene expression. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 6937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuo, W.; Lu, L.; Su, M.; Zhang, J.; Li, Y.; Huang, S.; Li, C.; Wang, N.; Zhang, Z.; Chen, X. Analysis of differentially expressed genes and differentially abundant metabolites associated with the browning of Meihong red-fleshed apple fruit. Postharvest Biol. Technol. 2021, 174, 111437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarpong, F.; Oteng-Darko, P.; Golly, M.K.; Amenorfe, L.P.; Rashid, M.T.; Zhou, C. Comparative study of enzymes inactivation and browning pigmentation of apple (Malus domestica) slices by selected gums during low temperature storage. J. Food Biochem. 2018, 42, e12681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, F.; Jiang, A.; Feng, K.; Gu, S.; Xu, D.; Hu, W. Effect of methyl jasmonate on wound healing and resistance in fresh-cut potato cubes. Postharvest Biol. Technol. 2019, 157, 110958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lever, J.; Krzywinski, M.; Altman, N. Principal component analysis. Nat. Methods 2017, 14, 641–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Westerhuis, J.A.; Hoefsloot, H.C.J.; Smit, S.; Vis, D.J.; Smilde, A.K.; van Velzen, E.J.J.; van Duijnhoven, J.P.M.; van Dorsten, F.A. Assessment of PLSDA cross validation. Metabolomics 2008, 4, 81–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, T.; Zhu, M.; Chen, Y.; Yan, X.; Chen, Q.; Wu, X.; Lin, J.; Xie, M. 1H NMR combined with chemometrics for the rapid detection of adulteration in camellia oils. Food Chem. 2018, 242, 308–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toyota, M.; Spencer, D.; Sawai-Toyota, S.; Jiaqi, W.; Zhang, T.; Koo, A.J.; Howe, G.A.; Gilroy, S. Glutamate triggers long-distance, calcium-based plant defense signaling. Science 2018, 361, 1112–1115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Wang, H.; Yan, H.; Malik, A.U.; Dong, T.; Wang, Q. Pre-cut NaCl solution treatment effectively inhibited the browning of fresh-cut potato by influencing polyphenol oxidase activity and several free amino acids contents. Postharvest Biol. Technol. 2021, 178, 111543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baxter, A.; Mittler, R.; Suzuki, N. ROS as key players in plant stress signalling. J. Exp. Bot. 2014, 65, 1229–1240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiménez, A.; Hernández, J.A.; Del Rio, L.A.; Sevilla, F. Evidence for the presence of the ascorbate-glutathione cycle in mitochondria and peroxisomes of pea leaves. Plant Physiol. 1997, 114, 275–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S. Glutathione suppresses the enzymatic and non-enzymatic browning in grape juice. Food Chem. 2014, 160, 8–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laxalt, A.M.; Munnik, T. Phospholipid signalling in plant defence. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 2002, 5, 332–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scherer, G.F.E. Phospholipid signalling and lipid-derived second messengers in plants. Plant Growth Regul. 1996, 18, 125–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christeller, J.T.; Galis, I. α-linolenic acid concentration and not wounding per se is the key regulator of octadecanoid (oxylipin) pathway activity in rice (Oryza sativa L.) leaves. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2014, 83, 117–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uchiyama, A.; Yaguchi, T.; Nakagawa, H.; Sasaki, K.; Kuwata, N.; Matsuura, H.; Takahashi, K. Biosynthesis and in vitro enzymatic synthesis of the isoleucine conjugate of 12-oxo-phytodienoic acid from the isoleucine conjugate of α-linolenic acid. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2018, 28, 1020–1023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, S.; Hu, H.; Wang, Y.; Zhou, H.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, L.; Li, P. The role of melatonin in alleviating the postharvest browning of lotus seeds through energy metabolism and membrane lipid metabolism. Postharvest Biol. Technol. 2020, 167, 111243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Huber, D.J.; Hu, M.; Jiang, G.; Gao, Z.; Xu, X.; Jiang, Y.; Zhang, Z. Delay of postharvest browning in litchi fruit by melatonin via the enhancing of antioxidative processes and oxidation repair. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2018, 66, 7475–7484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.; Chen, M.; Lin, H.; Lin, M.; Hung, Y.C.; Lin, Y.; Chen, Y.; Wang, H.; Ritenour, M.A. Phomopsis longanae-induced pericarp browning and disease development of longan fruit can be alleviated or aggravated by regulation of ATP-mediated membrane lipid metabolism. Food Chem. 2018, 269, 644–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katahira, R.; Ashihara, H. Profiles of purine biosynthesis, salvage and degradation in disks of potato (Solanum tuberosum L.) tubers. Planta 2006, 225, 115–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Cao, Y.; Zhou, L.; Jiang, C.Z.; Feng, Y.; Wei, S. Effects of postharvest curing treatment on flesh colour and phenolic metabolism in fresh-cut potato products. Food Chem. 2015, 169, 246–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, J.X.; Ramli, S.; Desa, S.; Chen, S.N. Use of Centella asiatica extract in reducing microbial contamination and browning effect in fresh cut fruits and vegetables during storage: A potential alternative of synthetic preservatives. LWT Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 151, 112229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schymanski, E.L.; Jeon, J.; Gulde, R.; Fenner, K.; Ruff, M.; Singer, H.P.; Hollender, J. Identifying small molecules via high resolution mass spectrometry: Communicating confidence. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 48, 2097–2098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becerra-Martínez, E.; Florentino-Ramos, E.; Pérez-Hernández, N.; Gerardo Zepeda-Vallejo, L.; Villa-Ruano, N.; Velázquez-Ponce, M.; García-Mendoza, F.; Bañuelos-Hernández, A.E. 1H NMR-based metabolomic fingerprinting to determine metabolite levels in serrano peppers (Capsicum annum L.) grown in two different regions. Food Res. Int. 2017, 102, 163–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, X.; Yu, Q.; Li, B.; Kan, J. Comparative analysis of carotenoids and metabolite characteristics in discolored red pepper and normal red pepper based on non-targeted metabolomics. LWT Food Sci. Technol. 2022, 153, 112398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Name | Formula | Molecular Weight (Da) | Mass Error (ppm) | Retention Time (min) | VIP Score (0d/8d) | p-Value (0d/8d) | Log2 FC (0d/8d) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Amino acids and derivatives | |||||||
| Ornithine | C5H12N2O2 | 132.0896 | −1.90 | 10.12 | 1.46 | 9.81 × 10−6 | 1.53 |
| Glutamic acid | C5H9NO4 | 147.0527 | −3.04 | 7.61 | 1.49 | 2.86 × 10−2 | −1.10 |
| 1-Methylhistidine | C7H11N3O2 | 169.0847 | −2.46 | 9.33 | 1.19 | 8.16 × 10−7 | −1.53 |
| Glutathione | C10H17N3O6S | 307.0829 | −2.91 | 7.93 | 1.57 | 2.70 × 10−8 | −2.54 |
| Lipids and derivatives | |||||||
| Linolenic acid | C18H30O2 | 278.2238 | −2.89 | 1.27 | 1.43 | 3.60 × 10−4 | −1.48 |
| 12-OPDA | C18H28O3 | 292.2028 | −3.67 | 2.39 | 1.49 | 1.10 × 10−13 | 7.30 |
| Phytosphingosine | C18H39NO3 | 317.2919 | −3.59 | 4.85 | 1.49 | 1.19 × 10−13 | 4.49 |
| Nucleotides and derivatives | |||||||
| Cytosine | C4H5N3O | 111.0432 | −0.47 | 5.85 | 1.46 | 2.32 × 10−8 | 4.02 |
| Adenine | C5H5N5 | 135.0541 | −2.71 | 3.37 | 1.57 | 3.70 × 10−10 | 1.02 |
| Cytidine | C9H13N3O5 | 243.0846 | −3.63 | 5.86 | 1.42 | 1.70 × 10−9 | 4.37 |
| AMP | C10H14N5O7P | 347.0621 | −2.86 | 7.92 | 1.52 | 3.75 × 10−9 | 3.67 |
| S-Adenosylmethionine | C15H22N6O5S | 398.1363 | −2.26 | 10.76 | 1.57 | 1.12 × 10−8 | 3.16 |
| Vitamins | |||||||
| Pyridoxamine | C8H12N2O2 | 168.0894 | −2.66 | 7.25 | 1.43 | 5.22 × 10−3 | −1.11 |
| Pyridoxine | C8H11NO3 | 169.0734 | −2.97 | 3.89 | 1.35 | 3.76 × 10−2 | −1.01 |
| Sugar | |||||||
| Maltose | C12H22O11 | 342.1151 | −3.26 | 7.46 | 1.56 | 1.10 × 10−8 | 1.32 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, B.; Fu, Y.; Xi, H.; Liu, S.; Zhao, W.; Li, P.; Fan, W.; Wang, D.; Sun, S. Untargeted Metabolomics Using UHPLC-HRMS Reveals Metabolic Changes of Fresh-Cut Potato during Browning Process. Molecules 2023, 28, 3375. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28083375
Li B, Fu Y, Xi H, Liu S, Zhao W, Li P, Fan W, Wang D, Sun S. Untargeted Metabolomics Using UHPLC-HRMS Reveals Metabolic Changes of Fresh-Cut Potato during Browning Process. Molecules. 2023; 28(8):3375. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28083375
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Baohong, Yingjie Fu, Hui Xi, Shan Liu, Wuduo Zhao, Peng Li, Wu Fan, Dingzhong Wang, and Shihao Sun. 2023. "Untargeted Metabolomics Using UHPLC-HRMS Reveals Metabolic Changes of Fresh-Cut Potato during Browning Process" Molecules 28, no. 8: 3375. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28083375
APA StyleLi, B., Fu, Y., Xi, H., Liu, S., Zhao, W., Li, P., Fan, W., Wang, D., & Sun, S. (2023). Untargeted Metabolomics Using UHPLC-HRMS Reveals Metabolic Changes of Fresh-Cut Potato during Browning Process. Molecules, 28(8), 3375. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28083375






