Identification of Protein Quality Markers in Toad Venom from Bufo gargarizans
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Morphology of the Ear-Side Gland in the Toad
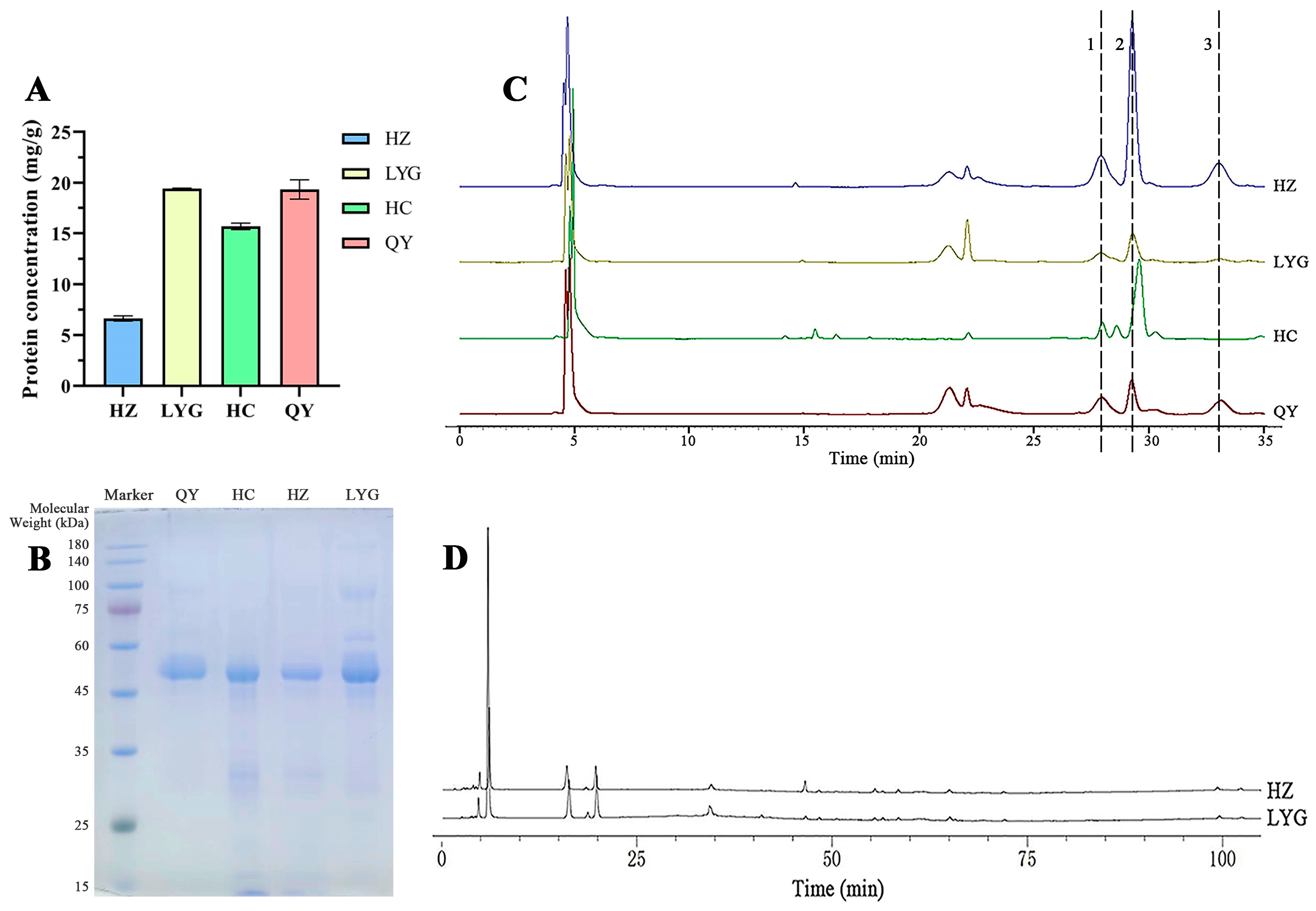
2.2. Composition of Venom from Toads from Different Areas
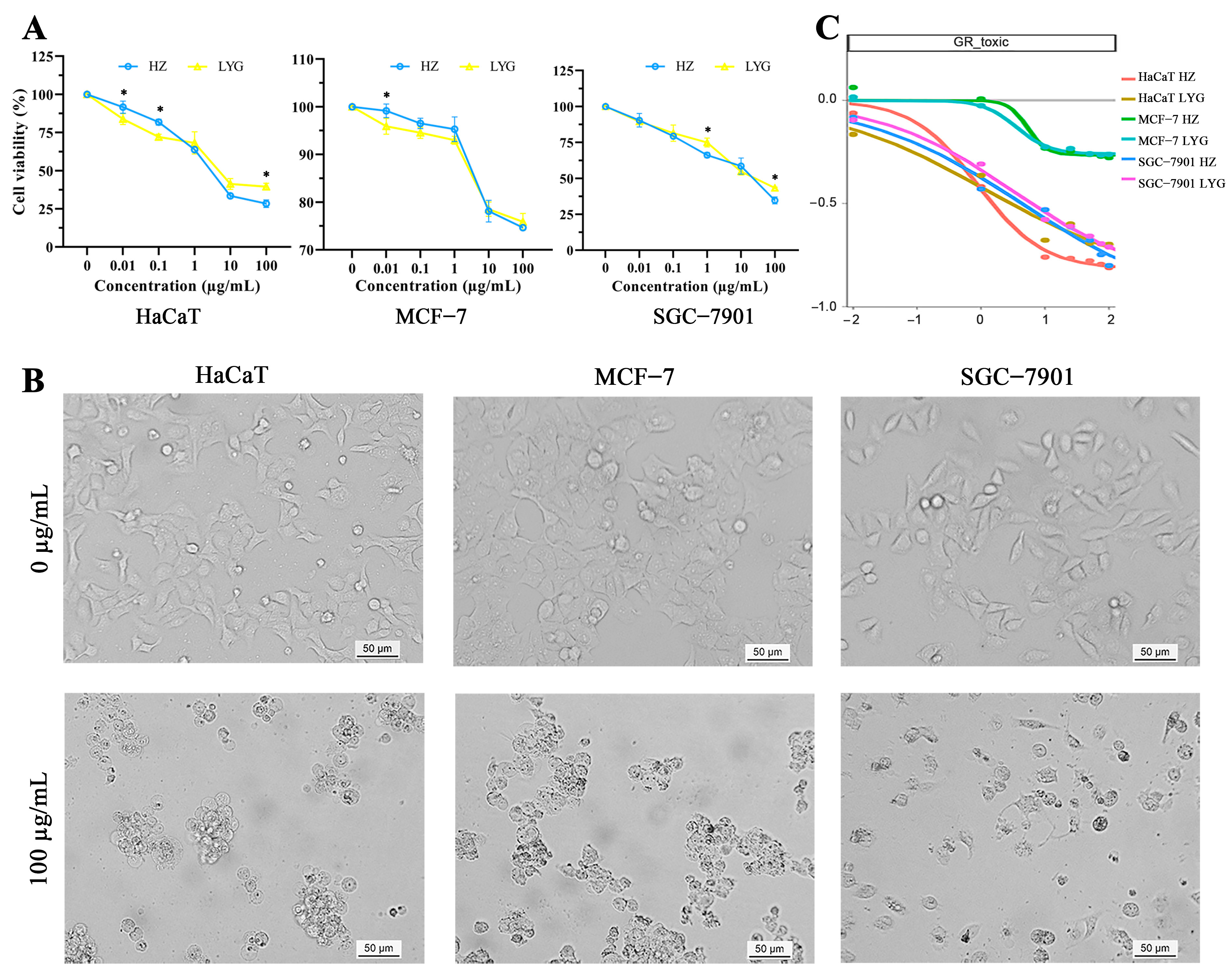
2.3. Cell Inhibitory Activity of Venom Proteins of Toads from Different Areas
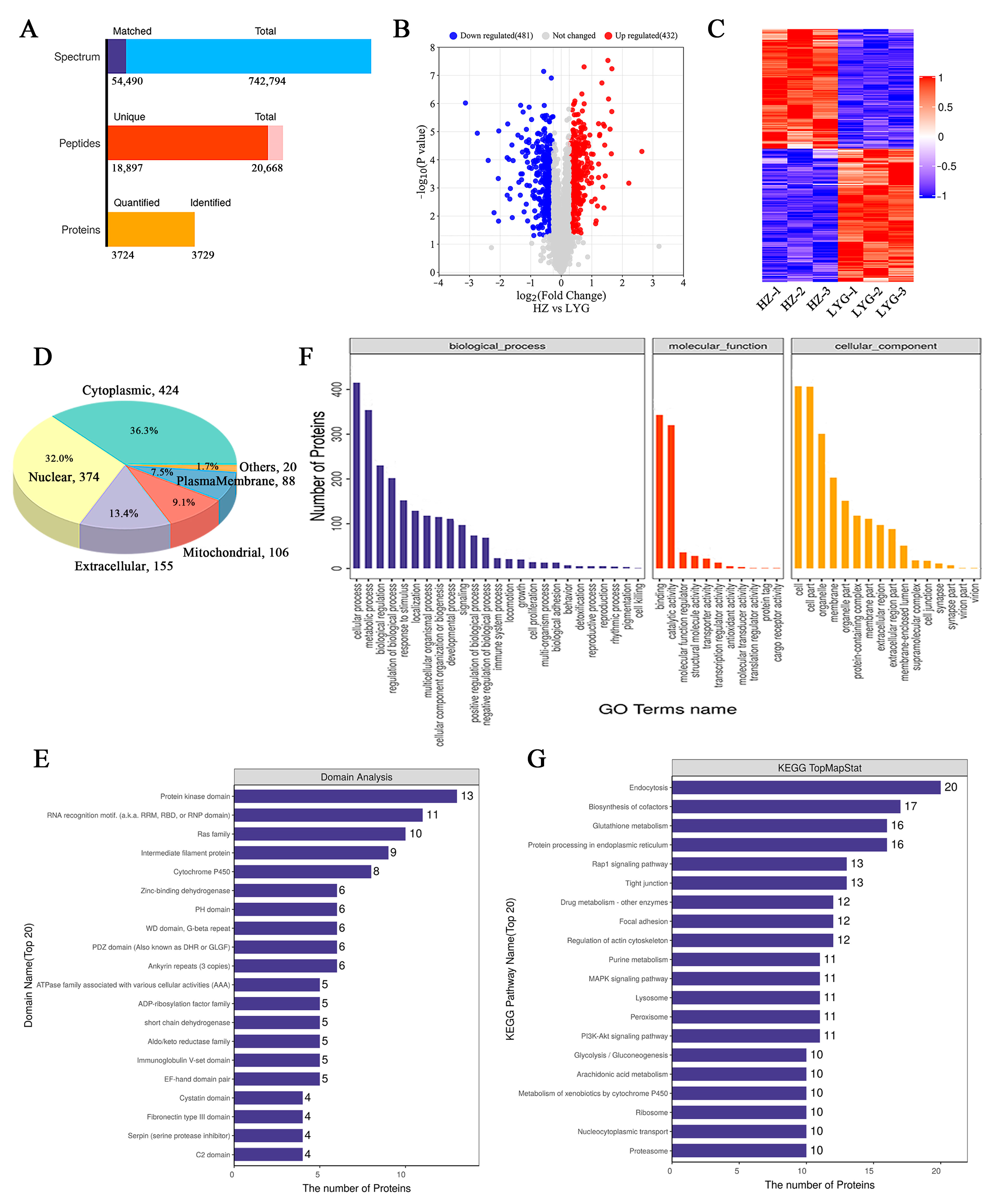
2.4. Proteomic Characterization of Toad Venom
2.5. Identification of Toad Venom Protein Quality Marker
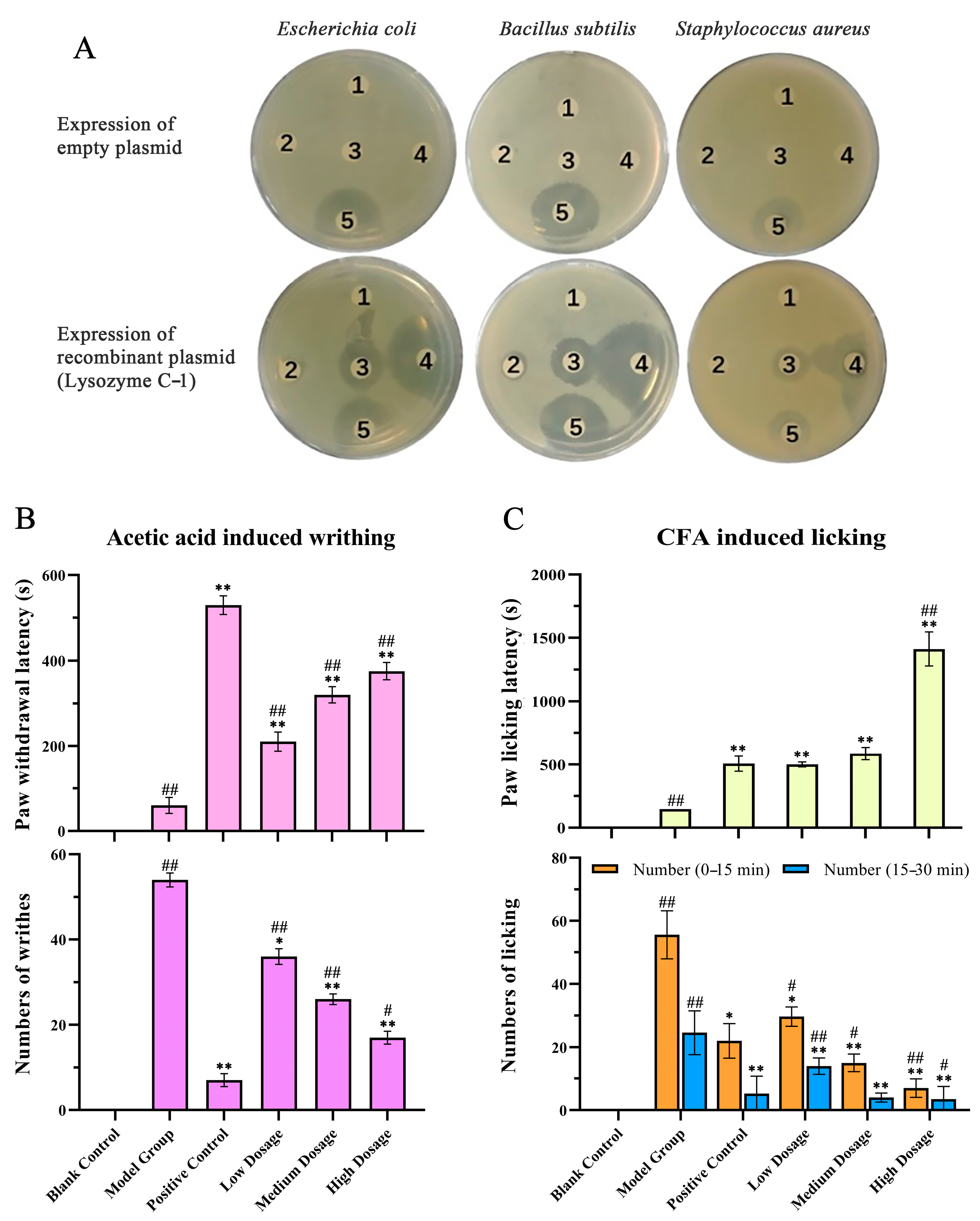
2.6. Functional Validation of Toad Venom Protein
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Toads and Toad Venom Samples
4.2. Ultrastructure of the Glands
4.3. Total Protein Extraction and Content Determination
4.4. SDS-PAGE Analysis
4.5. HPLC Analysis
4.6. Cytotoxic Activity and Growth Rate Inhibition
4.7. Transcriptomic and Proteomic Analyses
4.8. Protein Identification and Bioinformatic Analysis
4.9. Antimicrobial Assay
4.10. Anti-Inflammatory and Analgesic Assays
4.11. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Sample Availability
References
- Regueira, E.; Davila, C.; Hermida, G.N. Morphological Changes in Skin Glands During Development in Rhinella Arenarum (Anura: Bufonidae). Anat. Rec. 2016, 299, 141–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, F.; Wang, X.; Li, Z.; Zhou, A.; Tiffany-Castiglioni, E.; Xie, L.; Qian, Y. Identification of anti-tumor components from toad venom. Oncol. Lett. 2017, 14, 15–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Regueira, E.; Davila, C.; Sassone, A.G.; O’Donohoe, M.E.A.; Hermida, G.N. Post-metamorphic development of skin glands in a true toad: Parotoids versus dorsal skin. J. Morphol. 2017, 278, 652–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mailho-Fontana, P.L.; Antoniazzi, M.M.; Sciani, J.M.; Pimenta, D.C.; Barbaro, K.C.; Jared, C. Morphological and biochemical characterization of the cutaneous poison glands in toads (Rhinella marina group) from different environments. Front. Zool. 2018, 15, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O´Donohoe, M.; Luna, M.C.; Regueira, E.; Brunetti, A.E.; Basso, N.G.; Lynch, J.D.; Pereyra, M.O.; Hermida, G.N. Diversity and evolution of the parotoid macrogland in true toads (Anura: Bufonidae). Zool. J. Linn. Soc. 2019, 187, 453–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez, C.; Ibáñez, R.; Rollins-Smith, L.A.; Gutiérrez, M.; Durant-Archibold, A.A. Antimicrobial Secretions of Toads (Anura, Bufonidae): Bioactive Extracts and Isolated Compounds against Human Pathogens. Antibiotics 2020, 9, 843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, J.H.; Cao, Y.T.; Pan, H.Y.; Wang, L.H. Identification of Antitumor Constituents in Toad Venom by Spectrum-Effect Relationship Analysis and Investigation on Its Pharmacologic Mechanism. Molecules 2020, 25, 4269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.J.; Hu, J.H.; Ren, X.; Zhou, C.M.; Liu, Q.; Zhang, Y.Q. Toad venom: A comprehensive review of chemical constituents, anticancer activities, and mechanisms. Arch. Pharm. (Weinheim) 2021, 354, e2100060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, J.; Zulfiker, A.H.M.; Li, C.; Good, D.; Wei, M.Q. The Development of Toad Toxins as Potential Therapeutic Agents. Toxins 2018, 10, 336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yacoub, T.; Rima, M.; Karam, M.; Fajloun, J. Antimicrobials from Venomous Animals: An Overview. Molecules 2020, 25, 2402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huo, Y.; Xv, R.; Ma, H.; Zhou, J.; Xi, X.; Wu, Q.; Duan, J.; Zhou, M.; Chen, T. Identification of <10 KD peptides in the water extraction of Venenum Bufonis from Bufo gargarizans using Nano LC–MS/MS and De novo sequencing. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2018, 157, 156–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhan, X.; Wu, H.; Wu, H.; Wang, R.; Luo, C.; Gao, B.; Chen, Z.; Li, Q. Natural active constituents of Bufo bufo gargarizans cantor: A review of traditional uses, pharmacological activity, toxicity and quality control. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2020, 246, 112178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Guo, H.; Xu, D.; Yu, C.; Xv, R.; Wu, Q.; Di, L.; Cheng, H.; Duan, J.; Zhou, J.; et al. Cell affinity screening combined with nanoLC-MS/MS based peptidomics for identifying cancer cell binding peptides from Bufo Bufo gargarizans. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2021, 206, 114354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jo, S.; Yang, E.; Lee, Y.; Jeon, D.; Namkung, W. Cinobufagin Exerts Anticancer Activity in Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma Cells through Downregulation of ANO1. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 12037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Deng, L.; Cao, H.; Xu, N.; Zhang, D.; Tian, H.; Li, B.; Lu, Z.; Ye, W.; Yu, L.; et al. Screening of Bufadienolides from Toad Venom Identifies Gammabufotalin as a Potential Anti-inflammatory Agent. Planta Med. 2022, 88, 43–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, Q.; Liu, L.; Yuan, Y.; Turdu, G.; Mirzaakhmedov, S.; Aisa, H.A.; Yili, A. Two new polyamine alkaloids from the Bufo viridis toad venom. Nat. Prod. Res. 2022, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Lai, R. The chemistry and biological activities of peptides from amphibian skin secretions. Chem. Rev. 2015, 115, 1760–1846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shibao, P.Y.T.; Cologna, C.T.; Morandi-Filho, R.; Wiezel, G.A.; Fujimura, P.T.; Ueira-Vieira, C.; Arantes, E.C. Deep sequencing analysis of toad Rhinella schneideri skin glands and partial biochemical characterization of its cutaneous secretion. J. Venom. Anim. Toxins Incl. Trop. Dis. 2018, 24, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G. Bioinformatic Analysis of 1000 Amphibian Antimicrobial Peptides Uncovers Multiple Length—Dependent Correlations for Peptide Design and Prediction. Antibiotics 2020, 9, 491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, F.; Gao, F.; Yao, H.; Zhang, G.; Gao, B.; Lu, Y.; Wang, X.; Qian, Y. Identification of angiogenesis-inhibiting peptides from Chan Su. Protein Expr. Purif. 2019, 163, 105445–105450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, J.; He, X.; Hu, J.; Kamau, P.M.; Lai, R.; Rao, D.; Luo, L. Bv8-Like Toxin from the Frog Venom of Amolops jingdongensis Promotes Wound Healing via the Interleukin-1 Signaling Pathway. Toxins 2019, 12, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, J.; Zhao, M.; Xue, C.; Liang, J.; Huang, F. Analysis of the Composition of Deinagkistrodon acutus Snake Venom Based on Proteomics, and Its Antithrombotic Activity and Toxicity Studies. Molecules 2022, 27, 2229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jain, R.P.; Jayaseelan, B.F.; Wilson Alphonse, C.R.; Mahmoud, A.H.; Mohammed, O.B.; Ahmed Almunqedhi, B.M.; Rajaian Pushpabai, R. Mass spectrometric identification and denovo sequencing of novel conotoxins from vermivorous cone snail (Conus inscriptus), and preliminary screening of its venom for biological activities in vitro and in vivo. Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 2021, 28, 1582–1595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Zhang, Z.; Liao, Q.; Meng, E.; Mwangi, J.; Lai, R.; Rong, M. LCTX-F2, a Novel Potentiator of Coagulation Factors From the Spider Venom of Lycosa singoriensis. Front. Pharmacol. 2020, 11, 896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Q.; Long, C.; Wang, Z.; Wang, R.; Shi, W.; Qiu, J.; Mo, J.; Xie, Y. Hirudin, a thrombin inhibitor, attenuates TGF-β-induced fibrosis in renal proximal tubular epithelial cells by inhibition of protease-activated receptor 1 expression via S1P/S1PR2/S1PR3 signaling. Exp. Ther. Med. 2021, 23, 3–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erkoc, P.; von Reumont, B.M.; Lüddecke, T.; Henke, M.; Ulshöfer, T.; Vilcinskas, A.; Fürst, R.; Schiffmann, S. The Pharmacological Potential of Novel Melittin Variants from the Honeybee and Solitary Bees against Inflammation and Cancer. Toxins 2022, 14, 818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, F.; Xu, W.F.; Tang, L.P.; Wang, M.M.; Wang, X.J.; Qian, Y.C. Characteristics of cathelicidin-Bg, a novel gene expressed in the ear-side gland of Bufo gargarizans. Genet. Mol. Res. 2016, 15, gmr.15038481–gmr.15038490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, C.; Wang, Z.; Peng, X.; Liu, Y.; Lin, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Qiu, Y.; Jin, M.; Wang, R.; Kong, D. Discovery of two bombinin peptides with antimicrobial and anticancer activities from the skin secretion of Oriental fire-bellied toad, Bombina orientalis. Chem. Biol. Drug Des. 2018, 91, 50–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.; Cui, K.; Pan, H.; Wu, J.; Wang, L. The impact of multiple climatic and geographic factors on the chemical defences of Asian toads (Bufo gargarizans Cantor). Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 17236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Cui, Z.; Liu, Y.; Wang, D.; Liu, N.; Yoshikawa, M. Quality evaluation of traditional Chinese drug toad venom from different origins through a simultaneous determination of bufogenins and indole alkaloids by HPLC. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 2005, 53, 1582–1586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, T.; Dou, D.; Xu, L. Establishment of a quality marker (Q-marker) system for Chinese herbal medicines using burdock as an example. Phytomedicine 2019, 54, 339–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, W.; Huang, L.; Guo, D.; Liu, C. Approaches to establish Q-markers for the quality standards of traditional Chinese medicines. Acta Pharm. Sin. B 2017, 7, 439–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Wang, Q.; Liu, X.; Wang, X.; Xie, W.; Liu, K.; Jiang, W.; Mu, C.; Qi, H.; Wang, Q. An integrated approach to uncover quality markers of Traditional Chinese medicine underlying chemical profiling, network target selection and metabolomics approach: Guan-Xin-Jing capsule as a model. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2020, 190, 113413–113426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weiner, S.; Sauer, M.; Visser, P.J.; Tijms, B.M.; Vorontsov, E.; Blennow, K.; Zetterberg, H.; Gobom, J. Optimized sample preparation and data analysis for TMT proteomic analysis of cerebrospinal fluid applied to the identification of Alzheimer’s disease biomarkers. Clin. Proteom. 2022, 19, 13–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiong, L.; Pei, J.; Wu, X.; Bao, P.; Guo, X.; Yan, P. Explaining Unsaturated Fatty Acids (UFAs), Especially Polyunsaturated Fatty Acid (PUFA) Content in Subcutaneous Fat of Yaks of Different Sex by Differential Proteome Analysis. Genes 2022, 13, 790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdel-Hamid, M.; Yang, P.; Mostafa, I.; Osman, A.; Romeih, E.; Yang, Y.; Huang, Z.; Awad, A.A.; Li, L. Changes in Whey Proteome between Mediterranean and Murrah Buffalo Colostrum and Mature Milk Reflect Their Pharmaceutical and Medicinal Value. Molecules 2022, 27, 1575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Durrani, R.; Yang, M.; Yang, B.; Durand, E.; Delavault, A.; Hou, B.; Huan, W.; Long, Y.; Song, L.; Gao, F. Identification of novel bioactive proteins and their produced oligopeptides from Torreya grandis nuts using proteomic based prediction. Food Chem. 2023, 405, 134843–134852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.; Zhuang, X.X.; Qin, X.J.; Wei, L.B.; Gao, J.R. Identifying effective diagnostic biomarkers and immune infiltration features in chronic kidney disease by bioinformatics and validation. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 1069810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Câmara, G.A.; Nishiyama-Jr, M.Y.; Kitano, E.S.; Oliveira, U.C.; Silva, P.I.D.; Junqueira-de-Azevedo, I.L.; Tashima, A.K. A Multiomics Approach Unravels New Toxins With Possible In Silico Antimicrobial, Antiviral, and Antitumoral Activities in the Venom of Acanthoscurria rondoniae. Front. Pharmacol. 2020, 11, 1075–1089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, T.; Ge, Y.; Li, Y.; Xiang, Y.; Jiang, Y.; Hu, Y. Quality enhancement of large yellow croaker treated with edible coatings based on chitosan and lysozyme. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 120, 1072–1079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, L.; Li, Y.; Wang, L.; Guo, J.; Liu, W.; Meng, G.; Zhang, L.; Li, M.; Cong, L.; Sun, M. Recent Insights Into the Prognostic and Therapeutic Applications of Lysozymes. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 767642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habtewold, T.; Tapanelli, S.; Masters, E.K.G.; Windbichler, N.; Christophides, G.K. The circadian clock modulates Anopheles gambiae infection with Plasmodium falciparum. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0278484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, M.I.; Dowarha, D.; Katte, R.; Chou, R.H.; Filipek, A.; Yu, C. Lysozyme as the anti-proliferative agent to block the interaction between S100A6 and the RAGE V domain. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0216427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pandey, S.; Tuma, Z.; Peroni, E.; Monasson, O.; Papini, A.M.; Chottova Dvorakova, M. Identification of NPB, NPW and Their Receptor in the Rat Heart. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 7827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wojciechowicz, T.; Billert, M.; Jasaszwili, M.; Strowski, M.Z.; Nowak, K.W.; Skrzypski, M. The Role of Neuropeptide B and Its Receptors in Controlling Appetite, Metabolism, and Energy Homeostasis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 6632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, Y.; Liu, Y.; Deng, M.; Wang, H.P.; Abdul, M.; Zhang, F.F.; Zhang, Z.; Cao, J.L. The synergistic effects of opioid and neuropeptide B/W in rat acute inflammatory and neuropathic pain models. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2021, 898, 173979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antimycobacterial Susceptibility Testing Group. Updating the approaches to define susceptibility and resistance to anti-tuberculosis agents: Implications for diagnosis and treatment. Eur. Respir. J. 2022, 59, 2200166–2200177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Els, C.; Jackson, T.D.; Kunyk, D.; Lappi, V.G.; Sonnenberg, B.; Hagtvedt, R.; Sharma, S.; Kolahdooz, F.; Straube, S. Adverse events associated with medium- and long-term use of opioids for chronic non-cancer pain: An overview of Cochrane Reviews. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2017, 10, CD012509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sultana, N.; Chung, H.J.; Emon, N.U.; Alam, S.; Taki, M.T.I.; Rudra, S.; Tahamina, A.; Alam, R.; Ahmed, F.; Mamun, A.A. Biological Functions of Dillenia pentagyna Roxb. Against Pain, Inflammation, Fever, Diarrhea, and Thrombosis: Evidenced From in vitro, in vivo, and Molecular Docking Study. Front. Nutr. 2022, 9, 911274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clausen, M.L.; Slotved, H.C.; Krogfelt, K.A.; Agner, T. Tape Stripping Technique for Stratum Corneum Protein Analysis. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 19918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dżugan, M.; Miłek, M.; Kielar, P.; Stępień, K.; Sidor, E.; Bocian, A. SDS-PAGE Protein and HPTLC Polyphenols Profiling as a Promising Tool for Authentication of Goldenrod Honey. Foods 2022, 11, 2390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Girgih, A.T.; He, R.; Hasan, F.M.; Udenigwe, C.C.; Gill, T.A.; Aluko, R.E. Evaluation of the in vitro antioxidant properties of a cod (Gadus morhua) protein hydrolysate and peptide fractions. Food Chem. 2015, 173, 652–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mouna, R.; Broisat, A.; Ahmed, A.; Debiossat, M.; Boumendjel, A.; Ghezzi, C.; Kabouche, Z. Antiproliferative activity, cell-cycle arrest, apoptotic induction and LC-HRMS/MS analyses of extracts from two Linum species. Pharm. Biol. 2022, 60, 1491–1501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hafner, M.; Niepel, M.; Chung, M.; Sorger, P.K. Growth rate inhibition metrics correct for confounders in measuring sensitivity to cancer drugs. Nat. Methods 2016, 13, 521–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niu, J.; Shi, Y.; Huang, K.; Zhong, Y.; Chen, J.; Sun, Z.; Luan, M.; Chen, J. Integrative transcriptome and proteome analyses provide new insights into different stages of Akebia trifoliata fruit cracking during ripening. Biotechnol. Biofuels 2020, 13, 149–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Qi, X.; Chen, S.; Feng, J.; Chen, H.; Qin, Z.; Deng, Y. An integrated transcriptomic and proteomic approach to dynamically study the mechanism of pollen-pistil interactions during jasmine crossing. J. Proteom. 2021, 249, 104380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Van Vranken, J.G.; Pontano Vaites, L.; Schweppe, D.K.; Huttlin, E.L.; Etienne, C.; Nandhikonda, P.; Viner, R.; Robitaille, A.M.; Thompson, A.H.; et al. TMTpro reagents: A set of isobaric labeling mass tags enables simultaneous proteome-wide measurements across 16 samples. Nat. Methods 2020, 17, 399–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mai, L.; He, G.; Chen, J.; Zhu, J.; Chen, S.; Hou, X.; Yang, H.; Zhang, M.; Wu, Y.; Lin, Q.; et al. Proteomic Analysis of Hypoxia-Induced Senescence of Human Bone Marrow Mesenchymal Stem Cells. Stem Cells Int. 2021, 2021, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, G.; Yang, P.; Cui, J.; Gao, Y.; Yin, C.; Bai, Y.; Zhao, D.; Chang, J. Multiomics Analyses of Two Sorghum Cultivars Reveal the Molecular Mechanism of Salt Tolerance. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 13, 886805–886820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Cao, Z.; Sun, P.; Khan, A.; Guo, J.; Sun, Y.; Yu, X.; Fan, K.; Yin, W.; Li, E.; et al. A novel strategy for optimal component formula of anti-PRRSV from natural compounds using tandem mass tag labeled proteomic analyses. BMC Vet. Res. 2022, 18, 179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bo, C.; Zhang, J.; Sai, L.; Du, Z.; Yu, G.; Li, C.; Li, M.; Peng, C.; Jia, Q.; Shao, H. Integrative transcriptomic and proteomic analysis reveals mechanisms of silica-induced pulmonary fibrosis in rats. BMC Pulm. Med. 2022, 22, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, K.; Fu, M.; Zhao, Y.; Gerhard, E.; Li, Y.; Yang, J.; Guo, J. Anti-oxidant anti-inflammatory and antibacterial tannin-crosslinked citrate-based mussel-inspired bioadhesives facilitate scarless wound healing. Bioact. Mater. 2023, 20, 93–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, J.; Han, J.; Chen, J.; Zhang, Y.; Huang, Q.; Wang, Y.; Qi, X.; Liu, Z.; Leung, E.L.; Wang, D.; et al. Comparison of analgesic activities of aconitine in different mice pain models. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0249276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Wang, J.; He, Z.; Liu, X.; Liu, H.; Wang, X. Analgesic and Anxiolytic Effects of Gastrodin and Its Influences on Ferroptosis and Jejunal Microbiota in Complete Freund’s Adjuvant-Injected Mice. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 841662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fattori, V.; Pinho-Ribeiro, F.A.; Staurengo-Ferrari, L.; Borghi, S.M.; Rossaneis, A.C.; Casagrande, R.; Verri, W.A. The specialised pro-resolving lipid mediator maresin 1 reduces inflammatory pain with a long-lasting analgesic effect. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2019, 176, 1728–1744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Towns, J.M.; Leslie, D.E.; Denham, I.; Wigan, R.; Azzato, F.; Williamson, D.A.; Lee, D.; Chow, E.P.F.; Fairley, C.K.; Graves, S.R.; et al. Treponema pallidum detection in lesion and non-lesion sites in men who have sex with men with early syphilis: A prospective, cross-sectional study. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2021, 21, 1324–1331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Han, K.; Du, C.; Li, R.; Liu, J.; Zeng, H.; Zhu, L.; Li, A. Carboxypeptidase B blocks ex vivo activation of the anaphylatoxin-neutrophil extracellular trap axis in neutrophils from COVID-19 patients. Crit. Care 2021, 25, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Yao, Y.; Xu, Y.; Li, L.; Gong, Y.; Zhang, K.; Zhang, M.; Guan, Y.; Chang, L.; Xia, X.; et al. Pan-cancer circulating tumor DNA detection in over 10,000 Chinese patients. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Accession | Annotation | Activity | Fold Change | Regulation |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Comp52143_c1_seq21 | Lysozyme C-1 | Antimicrobial, Antitumor | 3.1136 | Up |
| Comp52065_c1_seq1 | E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase MYCBP2 | Antimicrobial, Antitumor | 1.5784 | Up |
| Comp25467_c0_seq2 | Mindbomb E3 ubiquitin protein ligase 1 | Antimicrobial | 1.4762 | Up |
| Comp52171_c0_seq2 | Sushi, von Willebrand factor type A, EGF, and pentraxin domain-containing protein 1 | Antimicrobial | 1.4248 | Up |
| Comp20546_c0_seq1 | E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase HERC2 | Antimicrobial, Antitumor | 1.2580 | Up |
| Comp59368_c0_seq1 | RanBP-type and C3HC4-type zinc finger-containing protein 1-like, partial | Antimicrobial | 1.2571 | Up |
| Comp51468_c0_seq2 | GLI pathogenesis-related 2 | Antimicrobial | 1.2232 | Up |
| Comp47732_c0_seq1 | GLI pathogenesis-related 2 | Antimicrobial | 1.2628 | Down |
| Comp30628_c0_seq1 | NHL repeat-containing protein 2 | Antimicrobial | 1.2907 | Down |
| Comp50754_c1_seq2 | Novel protein containing Sushi domain (SCR repeat) domain | Antimicrobial | 1.3641 | Down |
| Comp50084_c0_seq6 | E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase listerin | Antimicrobial, Antitumor | 1.6850 | Down |
| Comp47859_c0_seq1 | Cathepsin B | Antimicrobial | 2.4604 | Down |
| Comp43995_c0_seq5 | E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase Makorin-2 | Antimicrobial, Antitumor | 8.7779 | Down |
| Comp52833_c0_seq1 | Secretory phospholipase A2 DsM-S1 | Anti-inflammatory and Analgesic | 2.0525 | Down |
| Comp33502_c0_seq1 | Neuropeptide B isoform 2 (NPB) | Anti-inflammatory and Analgesic | 1.5847 | Up |
| Comp52379_c0_seq11 | Prostatic acid phosphatase | Anti-inflammatory and Analgesic | 1.4639 | Up |
| Comp80513_c0_seq1 | Arylacetamide deacetylase-like 3 | Anti-inflammatory and Analgesic | 1.2288 | Down |
| Comp40289_c0_seq1 | Serpin B6 | Antitumor | 1.2113 | Up |
| Comp39279_c0_seq1 | Insulin-like growth factor-binding protein 2 | Antitumor | 1.3578 | Down |
| Comp49982_c0_seq1 | Neurotrypsin-like | Antitumor | 1.2190 | Up |
| Comp51288_c0_seq3 | Leucine-rich repeat neuronal protein 1 | Antitumor | 1.2108 | Up |
| Comp44678_c0_seq2 | Galectin-9 | Antitumor | 1.6774 | Down |
| Comp51969_c1_seq1 | Transportin 3 | Antitumor | 1.2704 | Down |
| Comp47586_c0_seq2 | Immunoglobulin light chain type III | Antitumor | 1.3508 | Down |
| Comp22487_c0_seq1 | Glutathione S-transferase Mu 6 | Antitumor | 1.3454 | Up |
| Comp70215_c0_seq1 | Cytochrome P450 2C41 | Antitumor | 1.9139 | Up |
| Comp23296_c0_seq1 | Proteasome assembly chaperone 4 | Antitumor | 1.2332 | Down |
| Comp48235_c2_seq1 | Protein tyrosine phosphatase type IVA 3 | Antitumor | 1.2844 | Up |
| Comp702_c0_seq1 | Cytochrome P450 20A1 | Antitumor | 1.2398 | Up |
| Comp44914_c0_seq1 | Proteasome assembly chaperone 3 | Antitumor | 1.2478 | Up |
| Comp35535_c0_seq1 | DDB1- and CUL4-associated factor 11 homolog | Antitumor | 1.2019 | Up |
| Comp68566_c0_seq1 | Cytochrome P450, family 20, subfamily A, polypeptide 1 | Antitumor | 1.2497 | Down |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yang, M.; Huan, W.; Zhang, G.; Li, J.; Xia, F.; Durrani, R.; Zhao, W.; Lu, J.; Peng, X.; Gao, F. Identification of Protein Quality Markers in Toad Venom from Bufo gargarizans. Molecules 2023, 28, 3628. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28083628
Yang M, Huan W, Zhang G, Li J, Xia F, Durrani R, Zhao W, Lu J, Peng X, Gao F. Identification of Protein Quality Markers in Toad Venom from Bufo gargarizans. Molecules. 2023; 28(8):3628. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28083628
Chicago/Turabian StyleYang, Meiyun, Weiwei Huan, Guobing Zhang, Jie Li, Fengyan Xia, Rabia Durrani, Wei Zhao, Jidong Lu, Xinmeng Peng, and Fei Gao. 2023. "Identification of Protein Quality Markers in Toad Venom from Bufo gargarizans" Molecules 28, no. 8: 3628. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28083628
APA StyleYang, M., Huan, W., Zhang, G., Li, J., Xia, F., Durrani, R., Zhao, W., Lu, J., Peng, X., & Gao, F. (2023). Identification of Protein Quality Markers in Toad Venom from Bufo gargarizans. Molecules, 28(8), 3628. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28083628





