A Fluorescent Molecularly Imprinted Polymer-Coated Paper Sensor for On-Site and Rapid Detection of Glyphosate
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Reagents and Apparatus
2.2. Synthesis of Fluorescent Monomers
2.3. Synthesis of Fluorescent MIPs
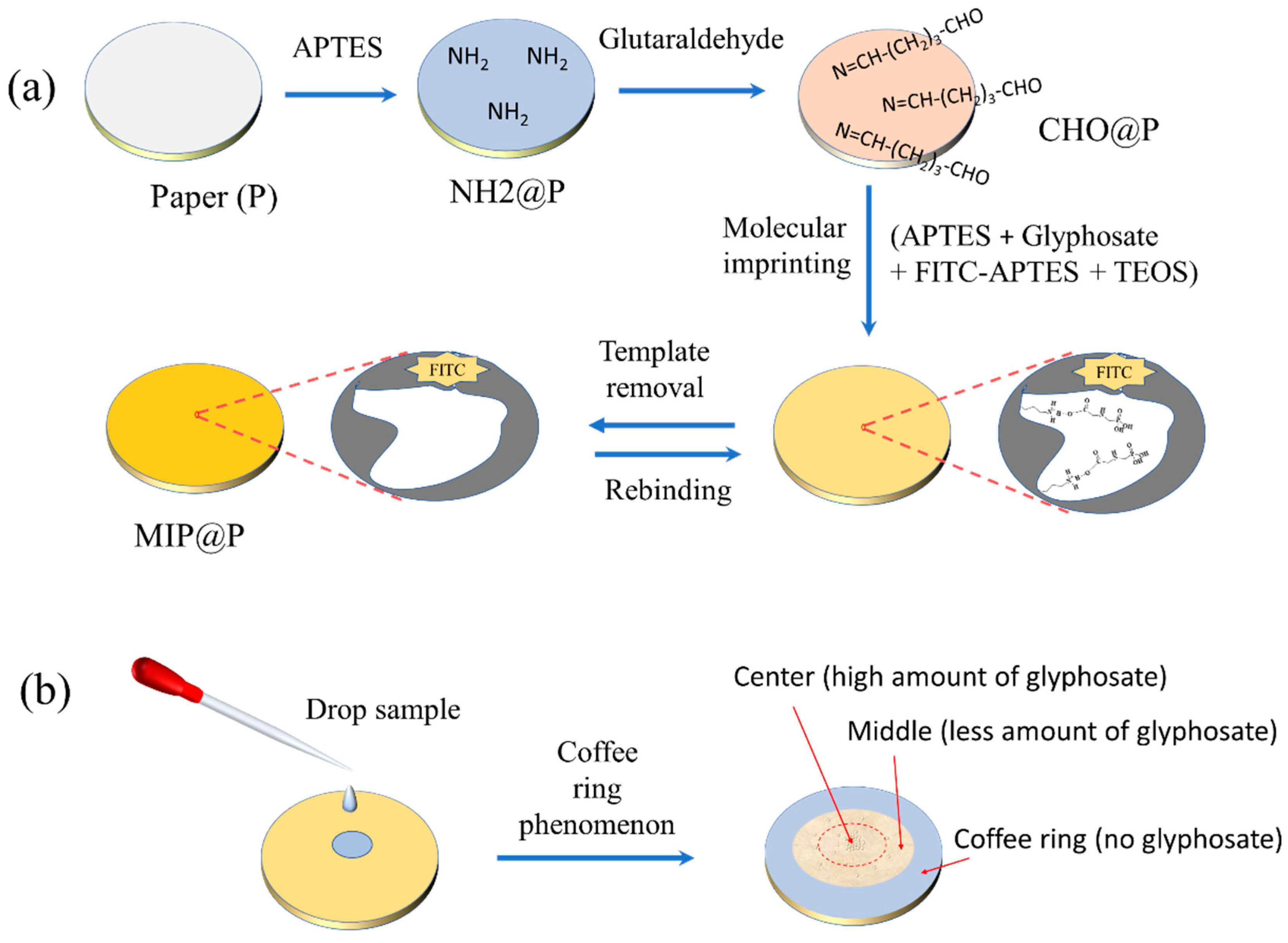
2.4. Preparation of Fluorescent MIP Coated Paper (MIP@P)
2.5. Fluorescence Test of MIP Particles
2.6. Fluorescence Test of the Fluorescent Papers
2.7. Specificity Tests of MIP1 and MIP@P
2.8. Application in Real Samples
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Preparation of MIP@P
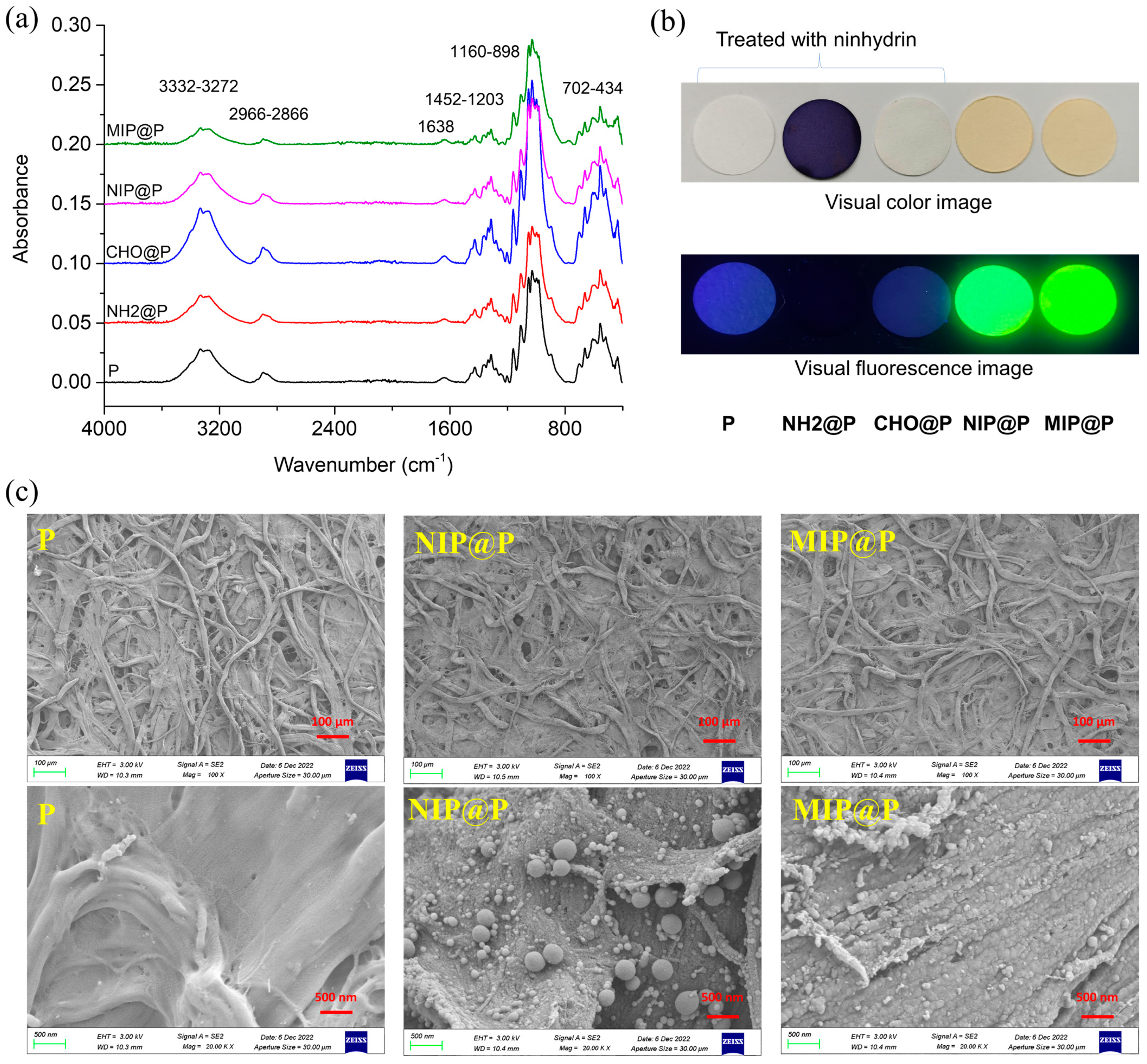
3.2. Characterization
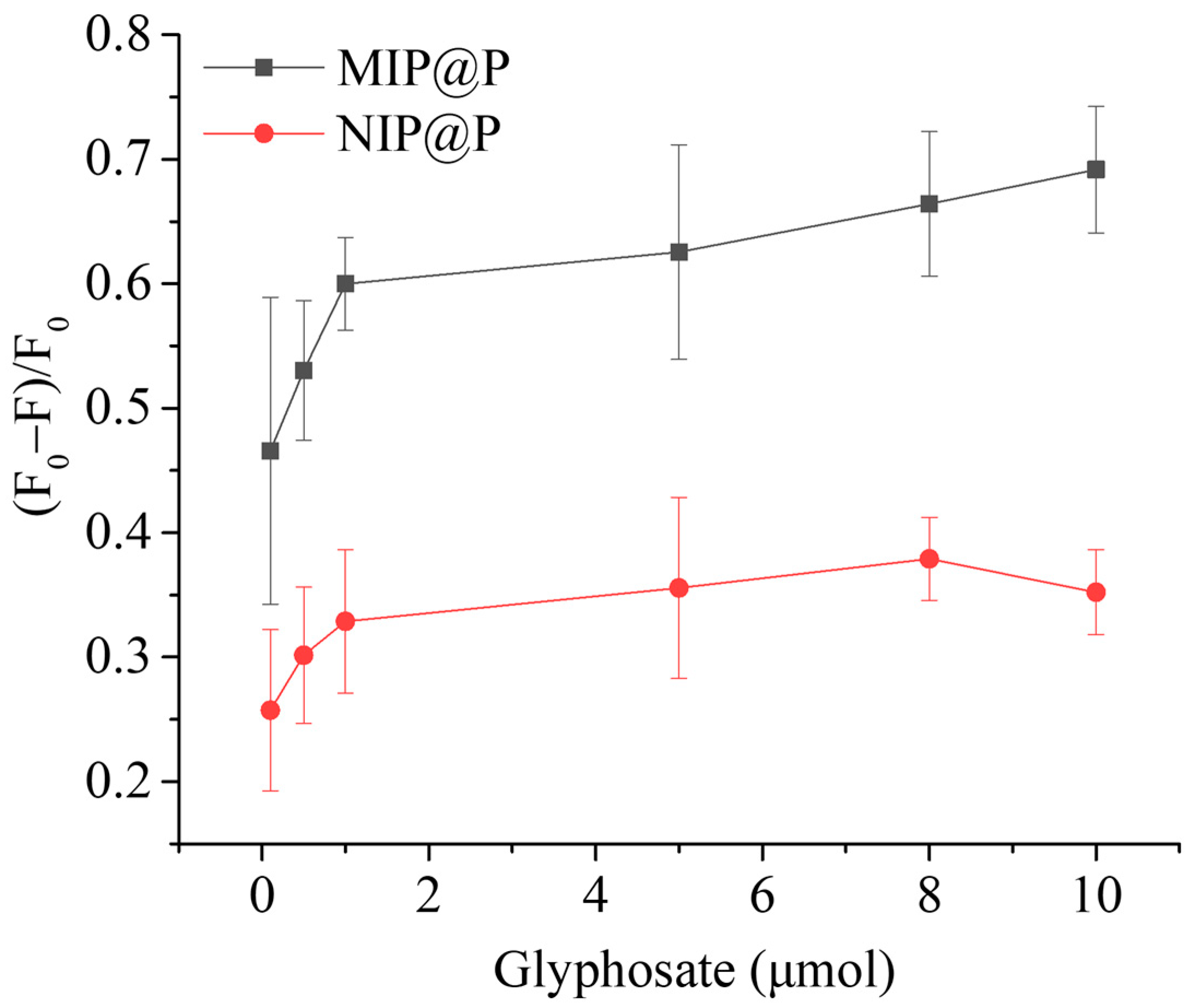
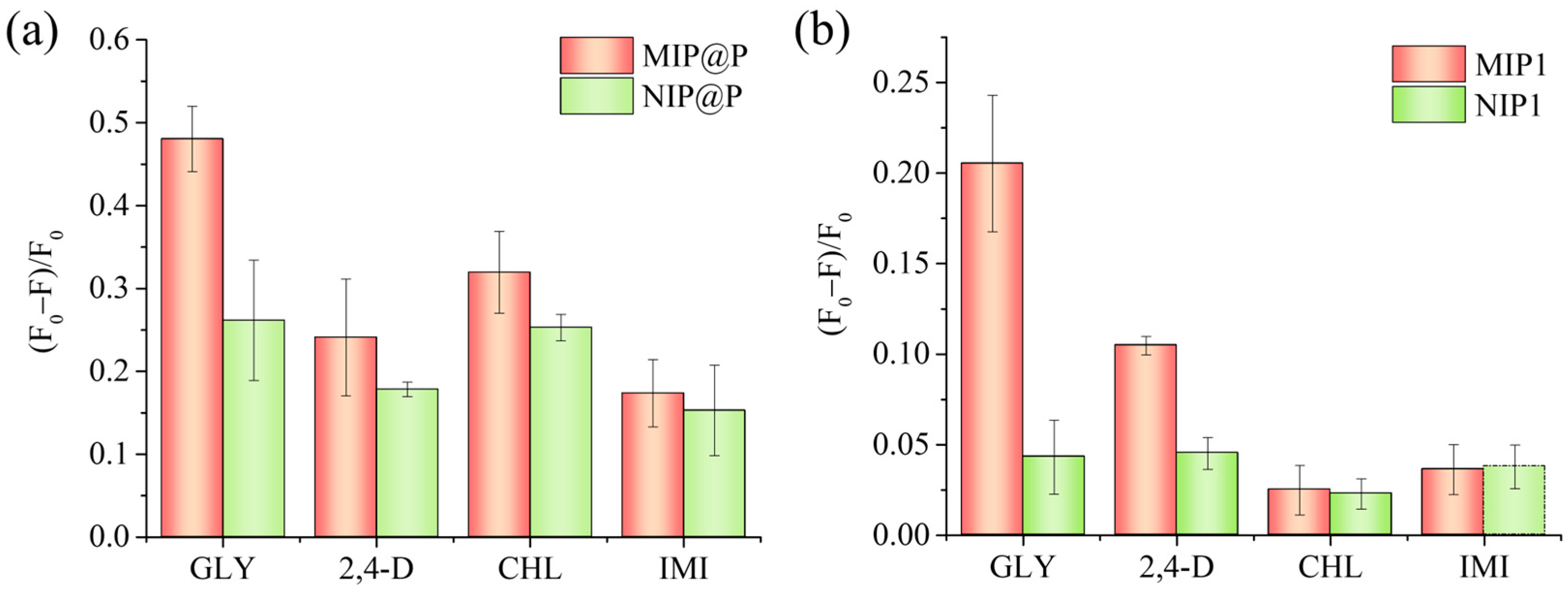
3.3. Selectivity and Specificity of MIP@P
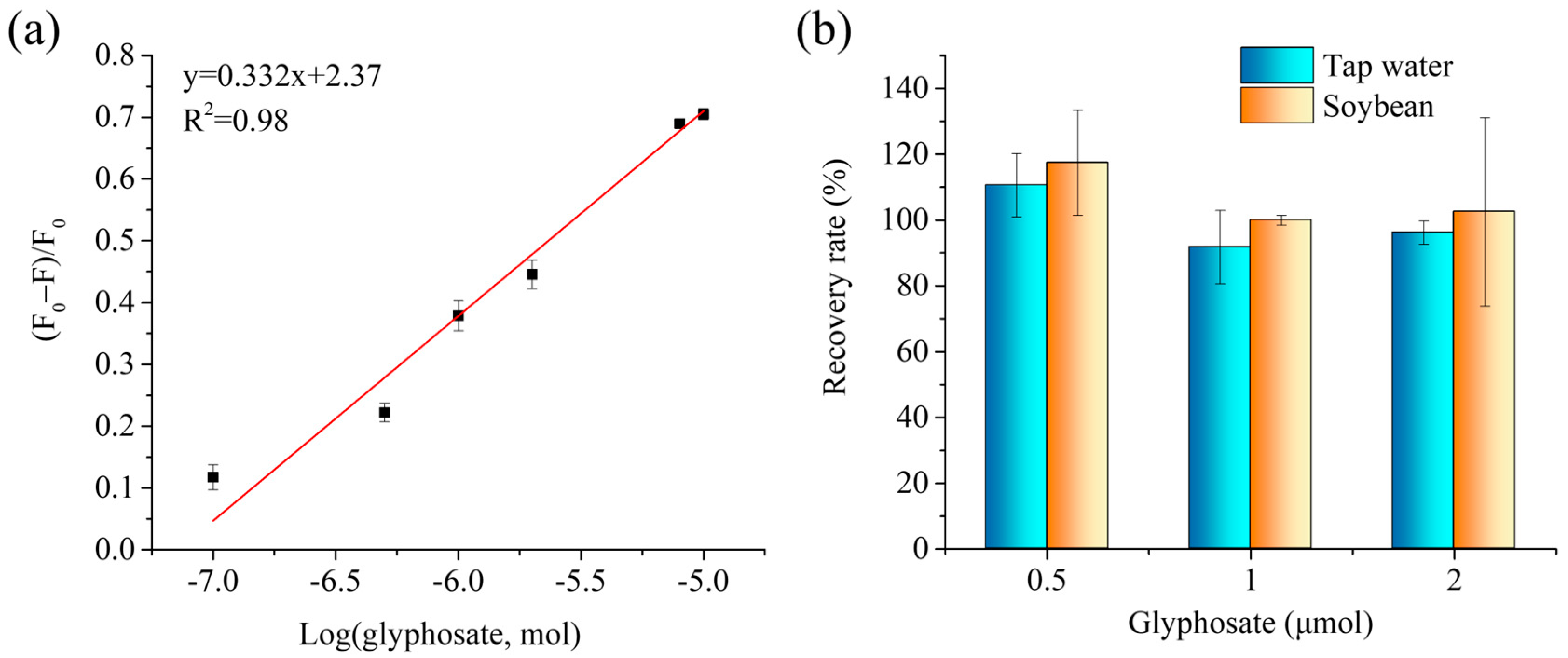
3.4. Application in Real Samples
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Sample Availability
References
- Gomez-Caballero, A.; Diaz-Diaz, G.; Bengoetxea, O.; Quintela, A.; Unceta, N.; Goicolea, M.A.; Barrio, R.J. Water compatible stir-bar devices imprinted with underivatised glyphosate for selective sample clean-up. J. Chromatogr. A 2016, 1451, 23–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santos, J.S.; Pontes, M.S.; Santiago, E.F.; Fiorucci, A.R.; Arruda, G.J. An efficient and simple method using a graphite oxide electrochemical sensor for the determination of glyphosate in environmental samples. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 749, 142385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Do, M.H.; Florea, A.; Farre, C.; Bonhomme, A.; Bessueille, F.; Vocanson, F.; Tran-Thi, N.-T.; Jaffrezic-Renault, N. Molecularly imprinted polymer-based electrochemical sensor for the sensitive detection of glyphosate herbicide. Int. J. Environ. Anal. Chem. 2015, 95, 1489–1501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Smith, S.; Smith, G.; Wang, W.; Li, Y. Glyphosate contamination in grains and foods: An overview. Food Control 2019, 106, 106710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saunders, L.E.; Pezeshki, R. Glyphosate in Runoff Waters and in the Root-Zone: A Review. Toxics 2015, 3, 462–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rigobello-Masini, M.; Pereira, E.A.O.; Abate, G.; Masini, J.C. Solid-Phase Extraction of Glyphosate in the Analyses of Environmental, Plant, and Food Samples. Chromatographia 2019, 82, 1121–1138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zouaoui, F.; Bourouina-Bacha, S.; Bourouina, M.; Alcacer, A.; Bausells, J.; Jaffrezic-Renault, N.; Zine, N.; Errachid, A. Experimental Study and Mathematical Modeling of a Glyphosate Impedimetric Microsensor Based on Molecularly Imprinted Chitosan Film. Chemosensors 2020, 8, 104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wirth, M.A.; Schulz-Bull, D.E.; Kanwischer, M. The challenge of detecting the herbicide glyphosate and its metabolite AMPA in seawater—Method development and application in the Baltic Sea. Chemosphere 2021, 262, 128327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gotti, R.; Fiori, J.; Bosi, S.; Dinelli, G. Field-amplified sample injection and sweeping micellar electrokinetic chromatography in analysis of glyphosate and aminomethylphosphonic acid in wheat. J. Chromatogr. A 2019, 1601, 357–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berry, C. Glyphosate and cancer: The importance of the whole picture. Pest Manag. Sci. 2020, 76, 2874–2877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zouaoui, F.; Bourouina-Bacha, S.; Bourouina, M.; Zine, N.; Errachid, A.; Jaffrezic-Renault, N. Mathematical Modelling of Glyphosate Molecularly Imprinted Polymer-Based Microsensor with Multiple Phenomena. Molecules 2022, 27, 493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- GB2763-2021; National Standard of China. National Food Safety Standard-Maximum Residue Limits for Pesticides in Food. China Agriculture Press: Beijing, China, 2021; pp. 57–58.
- European Food Safety, A. Review of the existing maximum residue levels for glyphosate according to Article 12 of Regulation (EC) No 396/2005. Eur. Food Saf. Auth. EF 2018, 16, 5263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perez-Mayan, L.; Castro, G.; Ramil, M.; Cela, R.; Rodriguez, I. Approaches to liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry assessment of glyphosate residues in wine. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2022, 414, 1445–1455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sawetwong, P.; Chairam, S.; Jarujamrus, P.; Amatatongchai, M. Enhanced selectivity and sensitivity for colorimetric determination of glyphosate using Mn–ZnS quantum dot embedded molecularly imprinted polymers combined with a 3D-microfluidic paper-based analytical device. Talanta 2021, 225, 122077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibarra Bouzada, L.M.E.; Hernández, S.R.; Kergaravat, S.V. Glyphosate detection from commercial formulations: Comparison of screening analytic methods based on enzymatic inhibition. Int. J. Environ. Anal. Chem. 2019, 101, 1821–1835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viirlaid, E.; Ilisson, M.; Kopanchuk, S.; Mäeorg, U.; Rinken, A.; Rinken, T. Immunoassay for rapid on-site detection of glyphosate herbicide. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2019, 191, 507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchís, J.; Kantiani, L.; Llorca, M.; Rubio, F.; Ginebreda, A.; Fraile, J.; Garrido, T.; Farré, M. Determination of glyphosate in groundwater samples using an ultrasensitive immunoassay and confirmation by on-line solid-phase extraction followed by liquid chromatography coupled to tandem mass spectrometry. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2012, 402, 2335–2345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaghela, C.; Kulkarni, M.; Haram, S.; Aiyer, R.; Karve, M. A novel inhibition based biosensor using urease nanoconjugate entrapped biocomposite membrane for potentiometric glyphosate detection. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 108, 32–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, X.; Yang, K.L. Development of an oligopeptide functionalized surface plasmon resonance biosensor for online detection of glyphosate. Anal. Chem. 2013, 85, 5727–5733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, S.; Lyu, Z.; Li, S.; Ruan, X.; Fei, M.; Zhou, Y.; Niu, X.; Zhu, W.; Du, D.; Lin, Y. Molecularly imprinted polypyrrole nanotubes based electrochemical sensor for glyphosate detection. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2021, 191, 113434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majdinasab, M.; Daneshi, M.; Louis Marty, J. Recent developments in non-enzymatic (bio)sensors for detection of pesticide residues: Focusing on antibody, aptamer and molecularly imprinted polymer. Talanta 2021, 232, 122397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Wang, Y.; Pei, Y.; Fan, Z.; Cao, J.; Wu, J. Application of immunoassay techniques in glyphosate residue detection. Chin. J. Immunol. 2018, 34, 291–295. [Google Scholar]
- Melnikov, P.; Bobrov, A.; Marfin, Y. On the Use of Polymer-Based Composites for the Creation of Optical Sensors: A Review. Polymers 2022, 14, 4448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanwar, S.; Mathur, D. Graphene-based nanocomposites as sensing elements for the electrochemical detection of pesticides: A review. J. Solid State Electrochem. 2021, 25, 2145–2159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Kamra, T.; Ye, L. Nanoparticle-enhanced fluorescence emission for non-separation assays of carbohydrates using a boronic acid-alizarin complex. Chem. Commun. 2016, 52, 3701–3704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Jiang, L.; Kamra, T.; Ye, L. Synthesis of fluorescent molecularly imprinted nanoparticles for turn-on fluorescence assay using one-pot synthetic method and a preliminary microfluidic approach. Polymer 2018, 138, 352–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, J.; Chen, W.; Ma, Y.; Pan, G. Molecularly imprinted polymers as receptor mimics for selective cell recognition. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2018, 47, 5574–5587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, L.; Mosbach, K. Molecular Imprinting: Synthetic Materials As Substitutes for Biological Antibodies and Receptors. Chem. Mater. 2008, 20, 859–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, R.R.; Guo, Z.C.; Lu, H.F.; Zhang, Q.; Liu, Z. Molecular imprinting and cladding produces antibody mimics with significantly improved affinity and specificity. Sci. Bull. 2021, 67, 278–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, K.; Zhang, L.; Ge, S.; Yu, J. A molecularly imprinted polypyrrole for ultrasensitive voltammetric determination of glyphosate. Microchim. Acta 2017, 184, 1959–1967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Da, L.; Yang, L.; Chu, S.; Yang, F.; Yu, S.; Jiang, C. Colorimetric fluorescent paper strip with smartphone platform for quantitative detection of cadmium ions in real samples. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 392, 122506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mampallil, D.; Eral, H.B. A review on suppression and utilization of the coffee-ring effect. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2018, 252, 38–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Huang, C.Z.; Li, Y.F. Fluorescence assay based on preconcentration by a self-ordered ring using berberine as a model analyte. Anal. Chem. 2002, 74, 5564–5568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, T.; Li, Q.; Wang, M.; Xu, J.; Li, J.; Wang, F. Synthesis of fluorescent artificial receptors with high specificity for simultaneous detection of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. Food Chem. 2023, 410, 135419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Wang, D.; Wang, T.; Jin, Y.; Ling, B.; Li, Q.; Li, J. A simple approach to prepare fluorescent molecularly imprinted nanoparticles. RSC Adv. 2021, 11, 7732–7737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Y.; Wang, T.; Li, Q.; Wang, F.; Li, J. A microfluidic approach for rapid and continuous synthesis of glycoprotein-imprinted nanospheres. Talanta 2022, 239, 123084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, R.; Dai, S.; Dou, M.; Yang, J.; Wang, X.; Liu, X.; Wei, C.; Li, Q.; Li, J. Simultaneous, Label-Free and High-throughput SERS Detection of Multiple Pesticides on Ag@Three-Dimensional Silica Photonic Microsphere Array. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2023, 71, 3050–3059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Ling, B.; Li, Q.; Abouhany, R. Dual roles of 3-aminopropyltriethoxysilane in preparing molecularly imprinted silica particles for specific recognition of target molecules. RSC Adv. 2020, 10, 20368–20373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, L.; Cormack, P.A.G.; Mosbach, K. Molecular imprinting on microgel spheres. Anal. Chim. Acta 2001, 435, 187–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimani, M.; Pérez-Padilla, V.; Valderrey, V.; Gawlitza, K.; Rurack, K. Red-Emitting Polymerizable Guanidinium Dyes as Fluorescent Probes in Molecularly Imprinted Polymers for Glyphosate Detection. Chemosensors 2022, 10, 99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimani, M.; Kislenko, E.; Gawlitza, K.; Rurack, K. Fluorescent molecularly imprinted polymer particles for glyphosate detection using phase transfer agents. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 14151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.; Lee, J.; Shin, I.S. Advanced method for fabrication of molecularly imprinted mesoporous organosilica with highly sensitive and selective recognition of glyphosate. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 10293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zouaoui, F.; Bourouina-Bacha, S.; Bourouina, M.; Abroa-Nemeir, I.; Ben Halima, H.; Gallardo-Gonzalez, J.; El Alami El Hassani, N.; Alcacer, A.; Bausells, J.; Jaffrezic-Renault, N.; et al. Electrochemical impedance spectroscopy determination of glyphosate using a molecularly imprinted chitosan. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2020, 309, 127753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thimoonnee, S.; Somnet, K.; Ngaosri, P.; Chairam, S.; Karuwan, C.; Kamsong, W.; Tuantranont, A.; Amatatongchai, M. Fast, sensitive and selective simultaneous determination of paraquat and glyphosate herbicides in water samples using a compact electrochemical sensor. Anal. Methods 2022, 14, 820–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uka, B.; Kieninger, J.; Urban, G.A.; Weltin, A. Electrochemical Microsensor for Microfluidic Glyphosate Monitoring in Water Using MIP-Based Concentrators. ACS Sens. 2021, 6, 2738–2746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Y.; Yan, Y.; Liu, C.; Zhang, D.; Wang, D.; Ispas, A.; Bund, A.; Du, B.; Zhang, Z.; Schaaf, P.; et al. Plasma-Assisted Fabrication of Molecularly Imprinted NiAl-LDH Layer on Ni Nanorod Arrays for Glyphosate Detection. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2022, 14, 35704–35715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, C.; She, Y.; Li, T.; Zhao, F.; Jin, M.; Guo, Y.; Zheng, L.; Wang, S.; Jin, F.; Shao, H.; et al. A highly selective electrochemical sensor based on molecularly imprinted polypyrrole-modified gold electrode for the determination of glyphosate in cucumber and tap water. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2017, 409, 7133–7144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazouz, Z.; Rahali, S.; Fourati, N.; Zerrouki, C.; Aloui, N.; Seydou, M.; Yaakoubi, N.; Chehimi, M.M.; Othmane, A.; Kalfat, R. Highly Selective Polypyrrole MIP-Based Gravimetric and Electrochemical Sensors for Picomolar Detection of Glyphosate. Sensors 2017, 17, 2586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balciunas, D.; Plausinaitis, D.; Ratautaite, V.; Ramanaviciene, A.; Ramanavicius, A. Towards electrochemical surface plasmon resonance sensor based on the molecularly imprinted polypyrrole for glyphosate sensing. Talanta 2022, 241, 123252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Polymer Name | Template, 0.1 mmol | Functional Monomer, 0.6 mmol | Fluorescent Functional Monomer, 2 μmol |
|---|---|---|---|
| MIP1 | Glyphosate | APTES | APTES-FITC |
| NIP1 | / | APTES | APTES-FITC |
| MIP2 | Glyphosate | AAPTMS | AAPTMS-FITC |
| NIP2 | / | AAPTMS | AAPTMS-FITC |
| MIP3 | Glyphosate | AAAPTMS | AAAPTMS-FITC |
| NIP3 | / | AAAPTMS | AAAPTMS-FITC |
| MIP | IF | Cross-Reactivity Factor | Analysis Time | LOD | Linear Range | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Guanidinium dyes-based fluorescent MIP particle | 1.9 | 2.1, 2.1 | 2 min | 4.8/0.6 µM | 7.9–40.8 µM | [41] |
| MIP@Au electrochemical sensor | 14.5 | 7.9, 43.5, 14.5 | 30 min | 5.9 × 10−6 nM | 1.8 × 10−3–296 nM | [44] |
| MIP@nanotube electrochemical sensor | 8 | 4.1, 5.8, 6.1, 8 | 5 min | 11.4 nM | 14.8–2071 nM | [21] |
| MIP nanoparticle-coated electrochemical sensor | / | / | / | 4.0 nM | 0.025–500 mM | [45] |
| Fluorescent MIP mesoporous silica particles | 2.9 | 1.4 | 2–3 min | 1.45 µM | 5–55 µM | [42] |
| Mn–ZnS QDs-based MIP-modified paper sensor | / | / | 5 min | 11.83 nM | 29.6 nM–296 µM | [15] |
| Graphene QDs-based fluorescent MIP nanoparticle | / | / | / | 0.1 nM | 0–800 µM | [43] |
| MIP-based microfluidic electrochemical sensor | / | / | 15 s | 247/188 nM | 0–50 µM | [46] |
| Inorganic framework MIP-based on Ni nanorod arrays | 2.2 | / | / | 3.1 nM | 0.01–1 µM | [47] |
| Polypyrrole MIP electrochemical sensor | 9 | / | 18 min | 1.6 µM | 0.03–4.73 µM | [48] |
| MIP@ Au and Prussian Blue electrochemical sensor | 3 | 2, 2.1, 4.3, 4 | 10 min | 0.5 µM | 2.4–7.1 µM | [31] |
| Polypyrrole MIP-based gravimetric and electrochemical sensors | / | / | 30 min | 1 pM | 1 pM–1 nM | [49] |
| Polypyrrole MIP-based electrochemical surface plasmon resonance sensor | 2.8 | / | 5 min | 1.1/3.4 nM | 0.05–0.5 mM | [50] |
| Fluorescent MIP silica particle | 7.6 | 2.0, 8.2, 5.7 | 5 min | 0.41 µM | 0.5–20 μM | This work |
| Fluorescent MIP-coated paper sensor | 2.0 | 2.0, 1.5, 2.8 | 5 min | 0.29 µmol | 0.5–10 μmol | This work |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, M.; Qiu, J.; Zhu, C.; Hua, Y.; Yu, J.; Jia, L.; Xu, J.; Li, J.; Li, Q. A Fluorescent Molecularly Imprinted Polymer-Coated Paper Sensor for On-Site and Rapid Detection of Glyphosate. Molecules 2023, 28, 2398. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28052398
Wang M, Qiu J, Zhu C, Hua Y, Yu J, Jia L, Xu J, Li J, Li Q. A Fluorescent Molecularly Imprinted Polymer-Coated Paper Sensor for On-Site and Rapid Detection of Glyphosate. Molecules. 2023; 28(5):2398. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28052398
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Meng, Jun Qiu, Chennuo Zhu, Yunyan Hua, Jie Yu, Lulu Jia, Jianhong Xu, Jianlin Li, and Qianjin Li. 2023. "A Fluorescent Molecularly Imprinted Polymer-Coated Paper Sensor for On-Site and Rapid Detection of Glyphosate" Molecules 28, no. 5: 2398. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28052398
APA StyleWang, M., Qiu, J., Zhu, C., Hua, Y., Yu, J., Jia, L., Xu, J., Li, J., & Li, Q. (2023). A Fluorescent Molecularly Imprinted Polymer-Coated Paper Sensor for On-Site and Rapid Detection of Glyphosate. Molecules, 28(5), 2398. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28052398







