Multifunctional Fe3O4 Nanoparticles Filled Polydopamine Hollow Rods for Antibacterial Biofilm Treatment
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
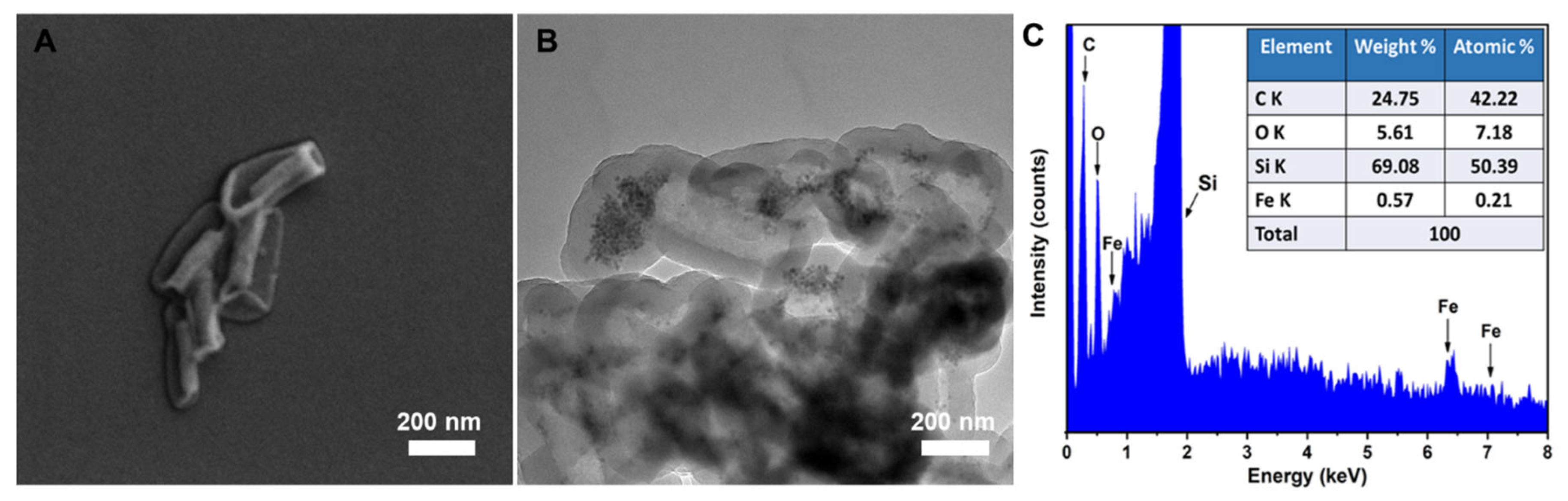
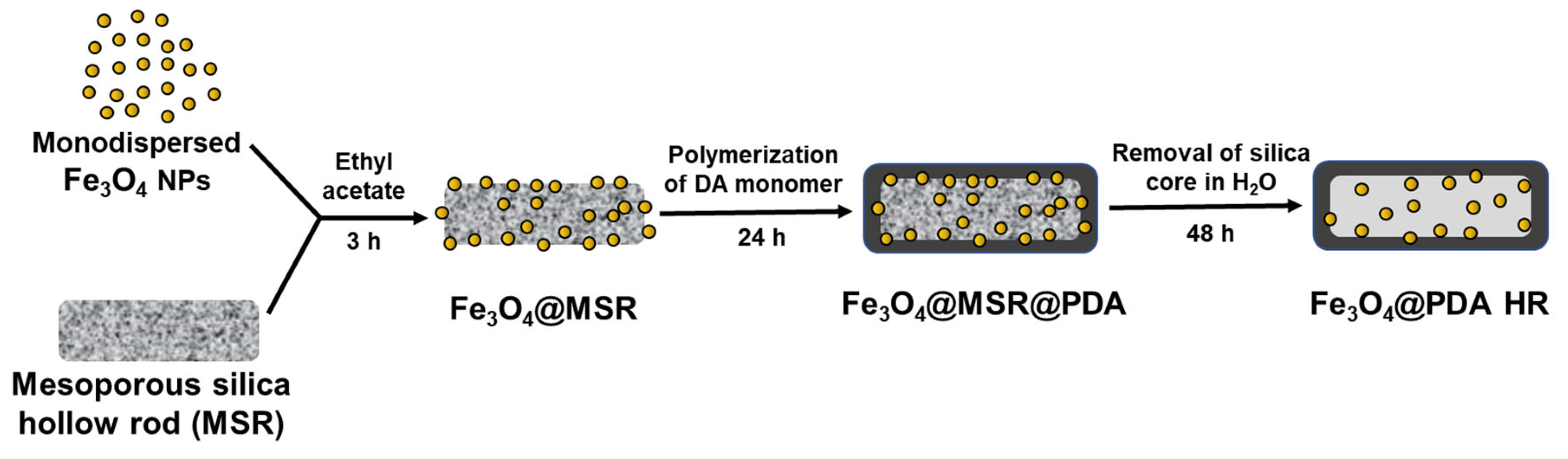
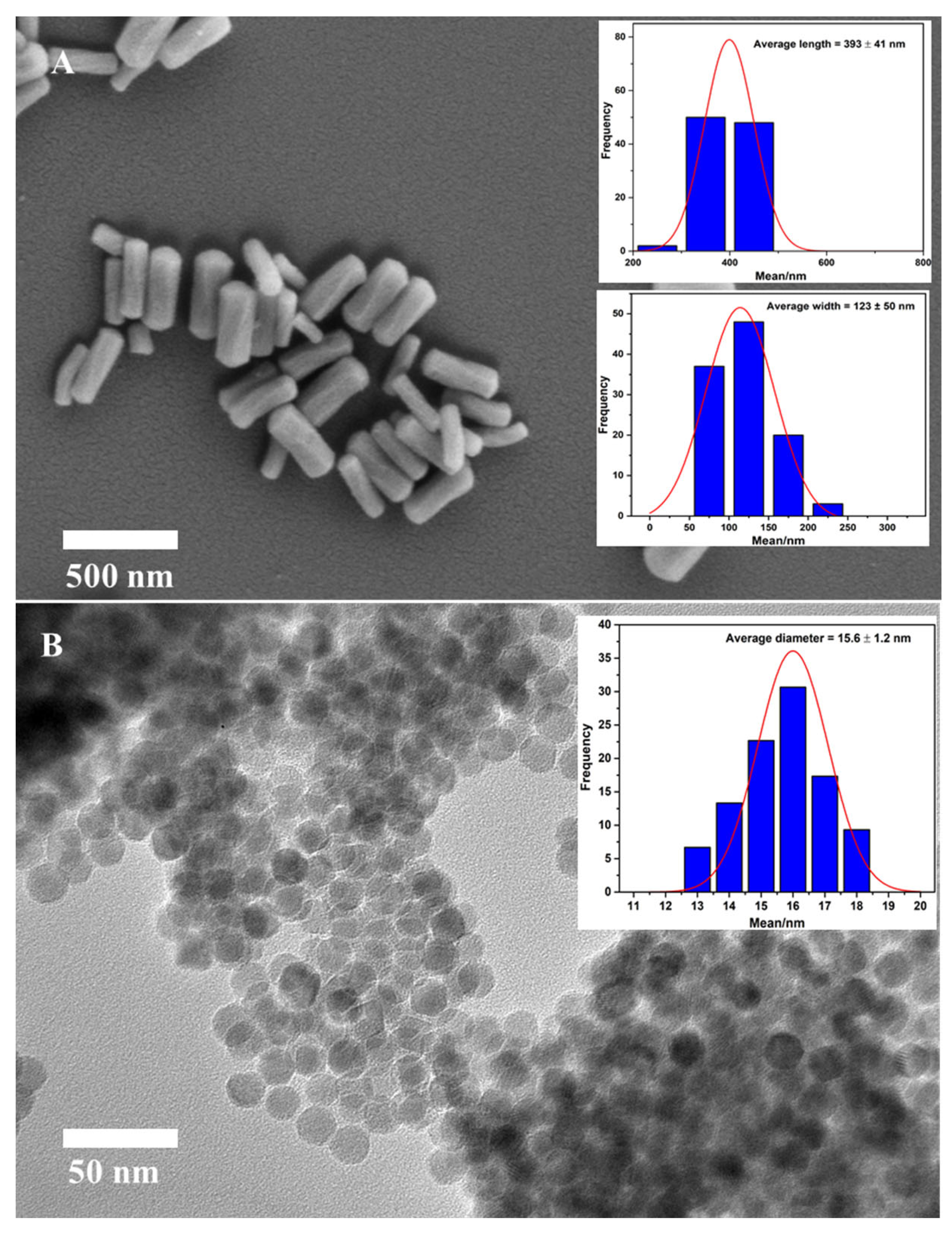
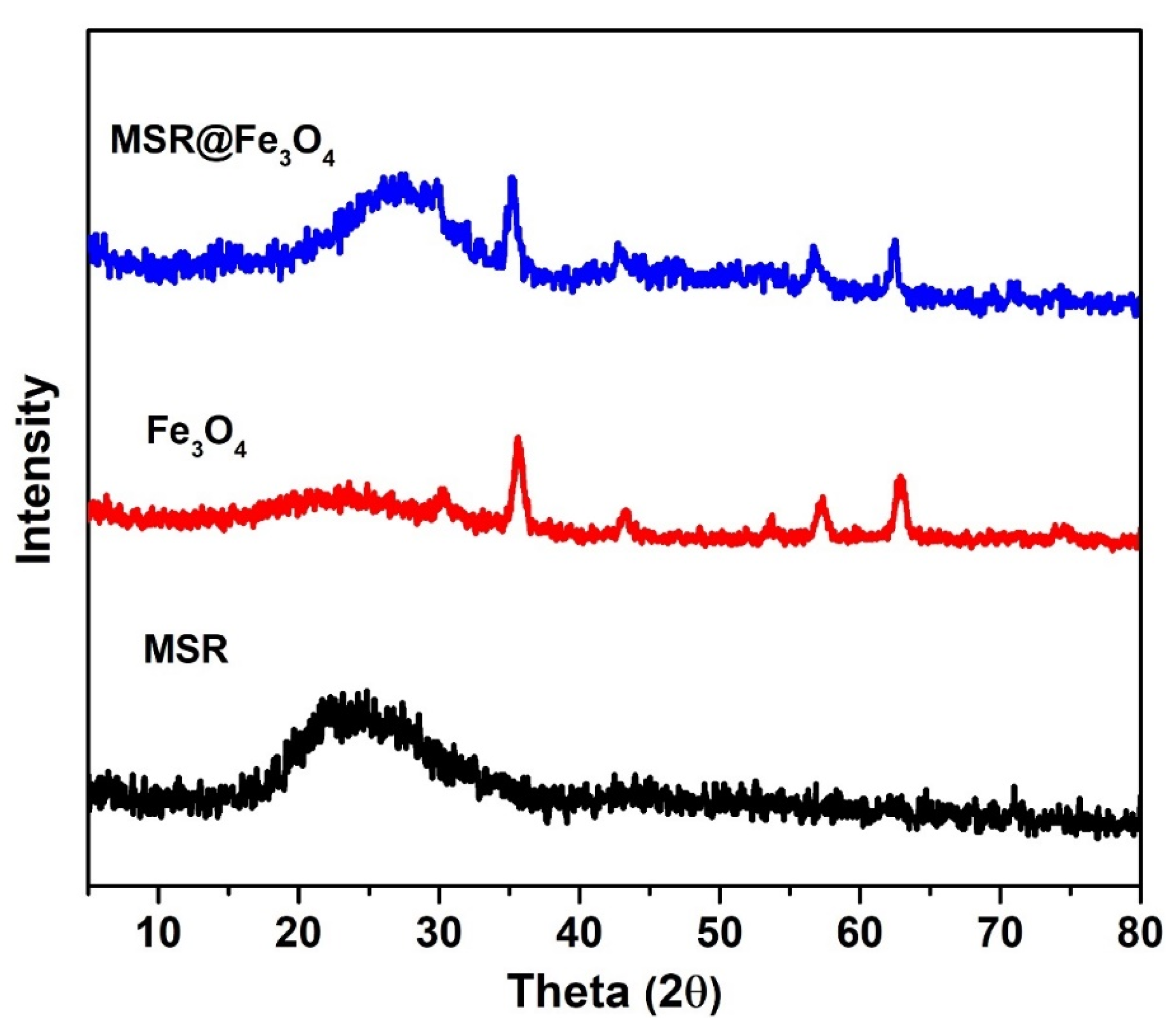
2.1. Synthesis of Monodisperse Fe3O4 NPs and Its Grafting onto MSR
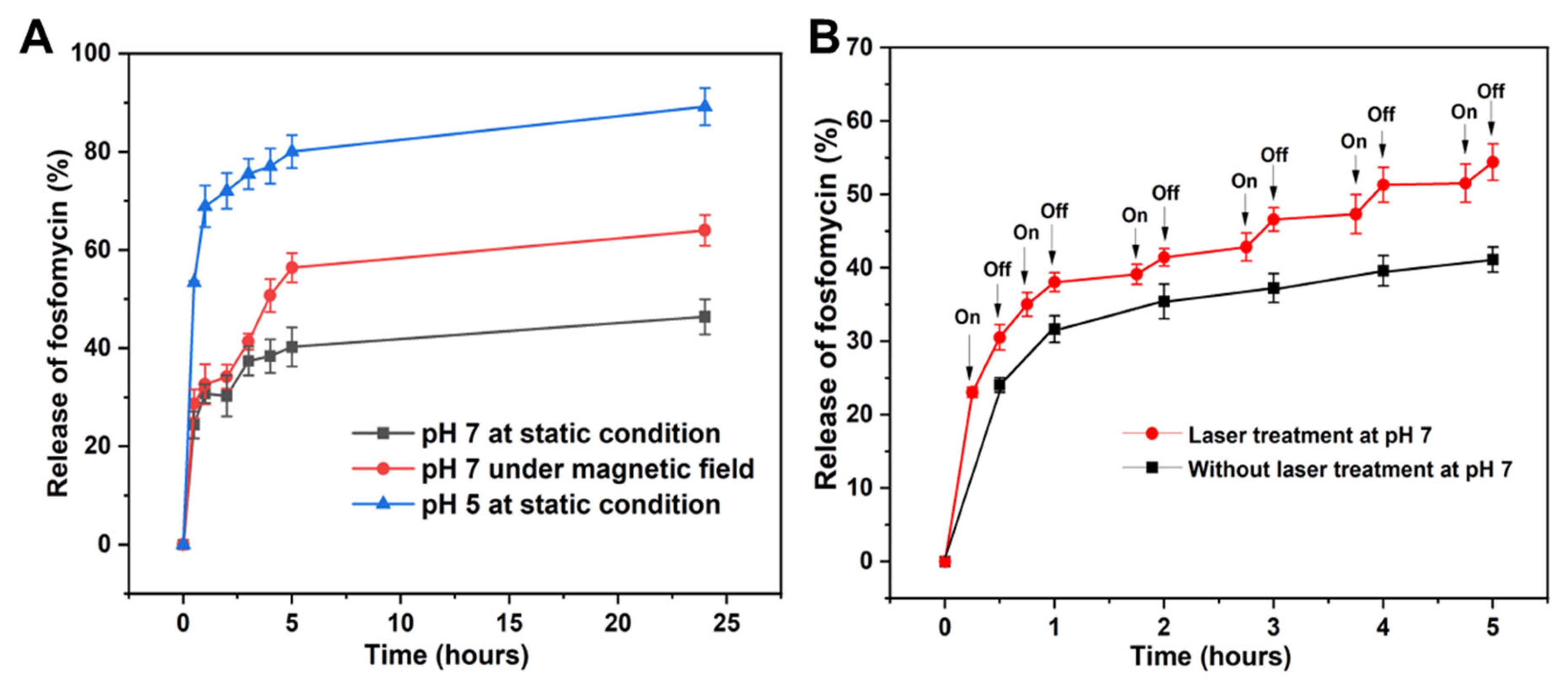
2.2. Loading and Controlled Release of Fosfomycin from Fe3O4@PDA HR
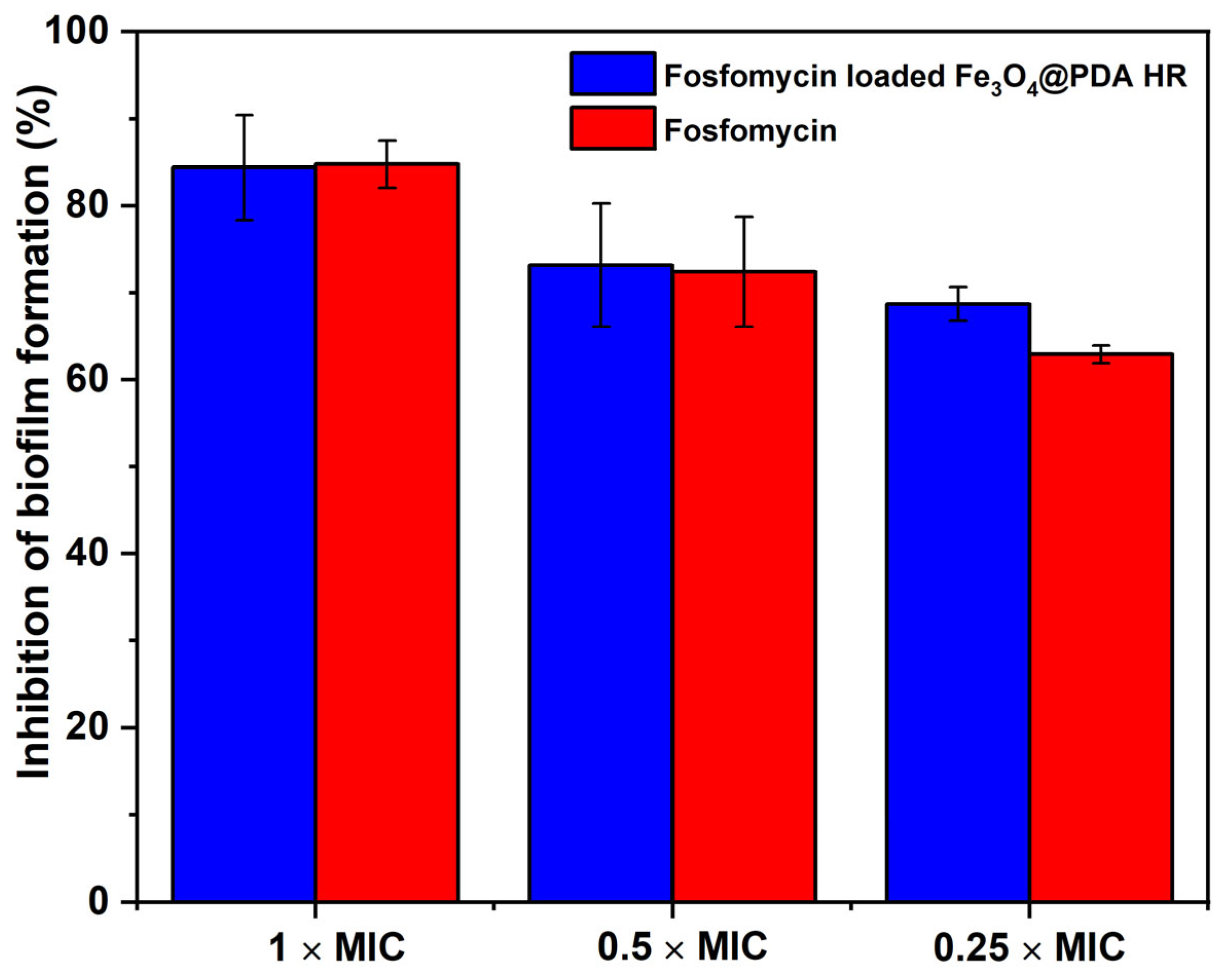
2.3. Fosfomycin Loaded Fe3O4@PDA HR for Biofilm Inhibition
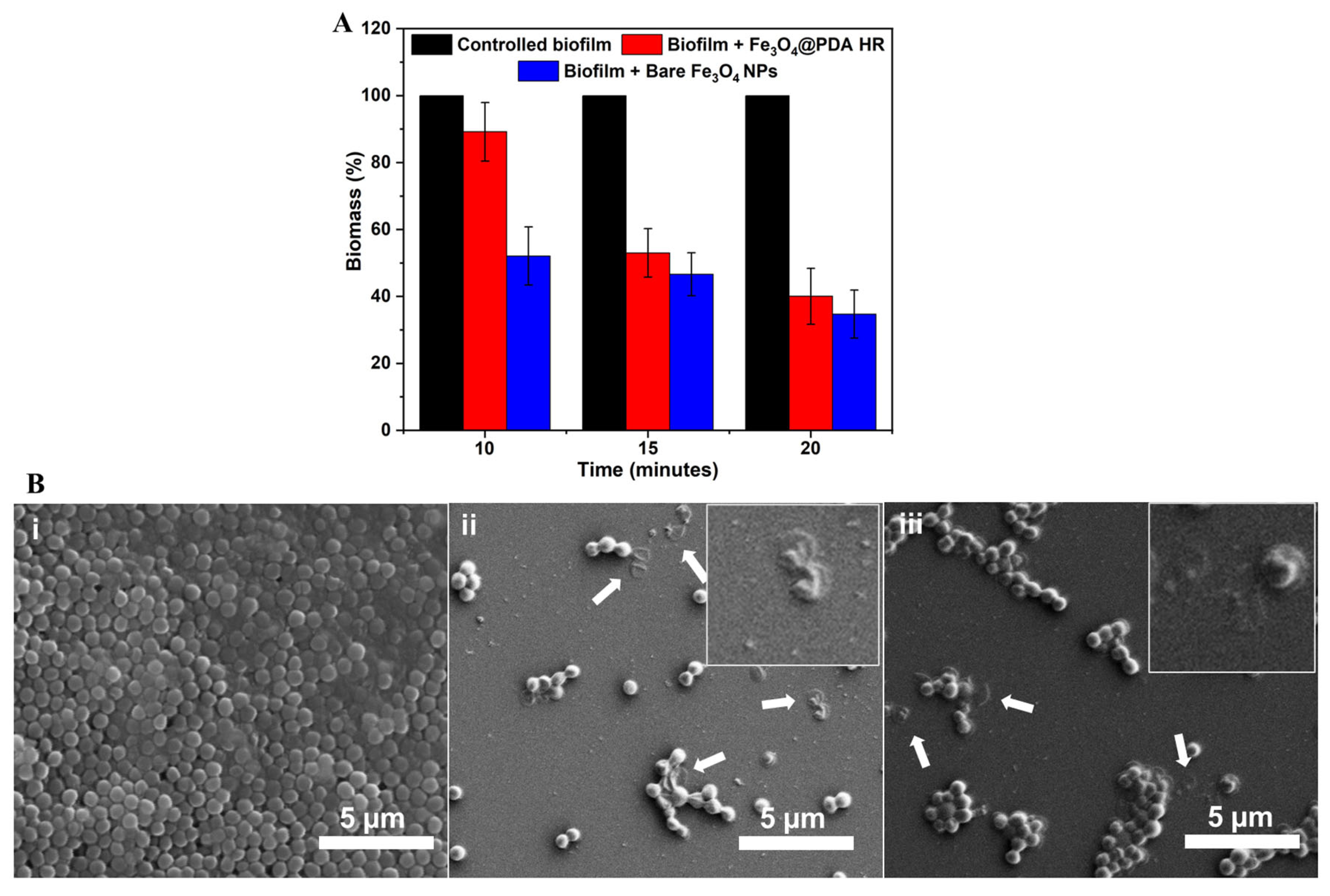
2.4. Fe3O4@PDA HR as Physico-Mechanical Means against Bacterial Preformed Biofilm
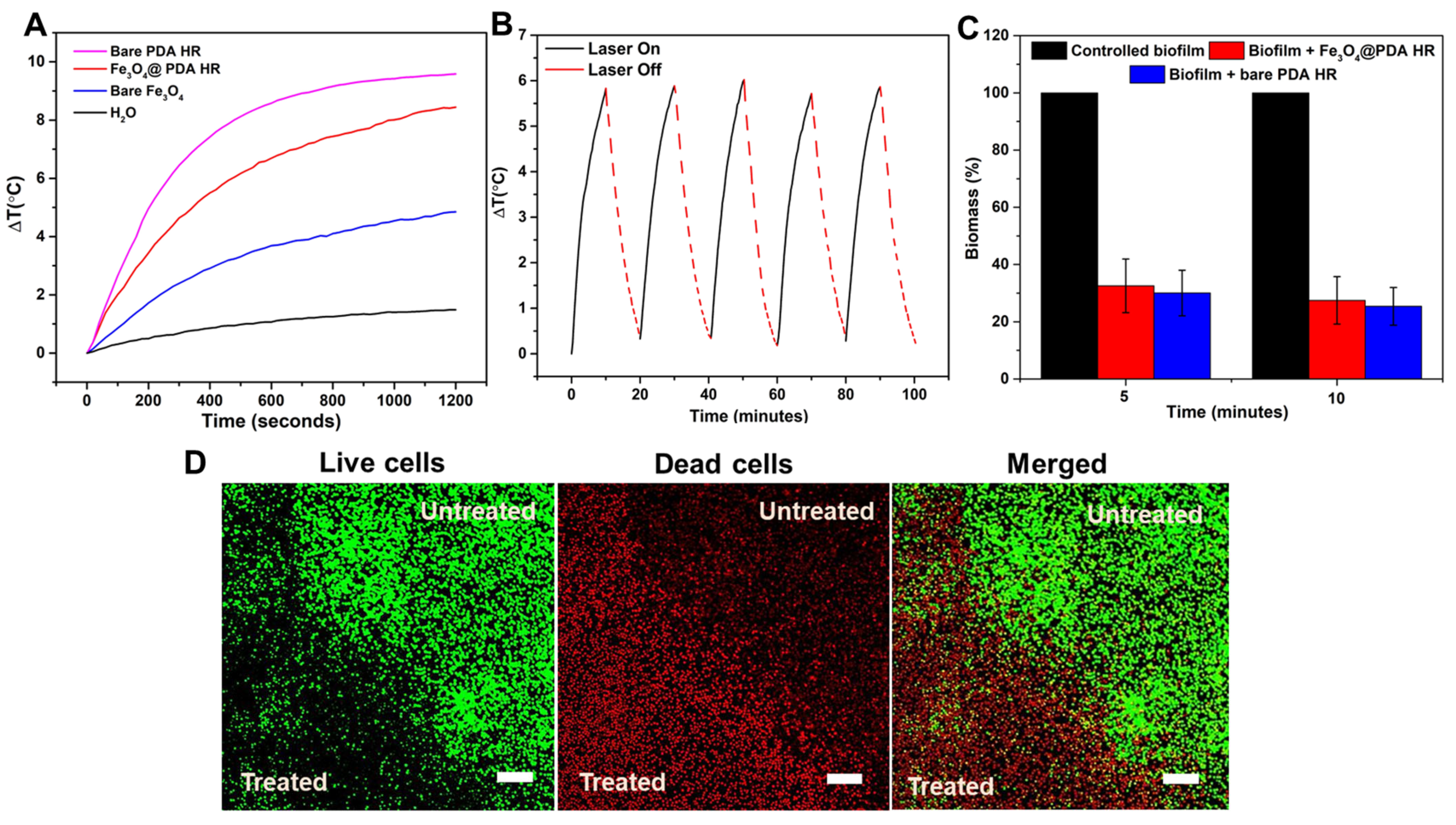
2.5. Fe3O4@PDA HR against Pre-Formed Biofilm under NIR Laser Irradiation
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials and Reagents
3.2. Synthesis of Mesoporous Silica Rods (MSR) and Its Carboxylic Functionalization
Synthesis of Amine Functionalized Monodisperse Fe3O4 NPs
3.3. Grafting Amine Functionalized Fe3O4 onto Carboxylic Functionalized MSR
3.4. Fabrication of Fe3O4 NPs Filled PDA HR
3.5. Loading Fosfomycin to Fe3O4@PDA HR
3.6. Stimuli Triggered Release of Fosfomycin
3.6.1. pH Mediated Drug Release Profile
3.6.2. NIR Laser Irradiation Mediated Drug Release Profile
3.6.3. Release of Fosfomycin under Exposure to Rotational Magnetic Field
3.7. Determination of Minimal Inhibitory Concentration of Free Fosfomycin and Fosfomycin Loaded Fe3O4@PDA HR against S. aureus
Evaluating Anti-Biofilm Formation Activity of Fosfomycin Loaded Fe3O4@PDA HR via Metabolic Assay
3.8. Evaluating the Effect of Fe3O4@ PDA HR against Pre-Formed Biofilm under Magnetic Rotation Field
Evaluating the Effect of Fe3O4@ PDA HR against Pre-Formed Biofilm upon Laser Irradiation
3.9. Live/Dead Cell Staining for Antibiofilm Effect
3.10. Material Characterization
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Sample Availability
References
- Manzano, M.; Vallet-Regí, M. Mesoporous silica nanoparticles for drug delivery. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2020, 30, 1902634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Fernández, A.; Aznar, E.; Martínez-Máñez, R.; Sancenón, F. New advances in in vivo applications of gated mesoporous silica as drug delivery nanocarriers. Small 2020, 16, 1902242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Feng, N. Mesoporous silica nanoparticles: Synthesis, classification, drug loading, pharmacokinetics, biocompatibility, and application in drug delivery. Expert Opin. Drug Deliv. 2019, 16, 219–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Appelhans, D.; Voit, B. Hollow capsules with multiresponsive valves for controlled enzymatic reactions. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2018, 140, 16106–16114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, X.; González, K.S.; Lynn, D.M. Templated synthesis of polymer-based yolk/shell particles with tunable morphologies. Chem. Mater. 2019, 31, 7443–7452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, R.K.; Kim, T.H.; Patel, K.D.; Knowles, J.C.; Kim, H.W. Biocompatible magnetite nanoparticles with varying silica-coating layer for use in biomedicine: Physicochemical and magnetic properties, and cellular compatibility. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part A 2012, 100, 1734–1742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taimoory, S.M.; Rahdar, A.; Aliahmad, M.; Sadeghfar, F.; Hajinezhad, M.R.; Jahantigh, M.; Shahbazi, P.; Trant, J.F. The synthesis and characterization of a magnetite nanoparticle with potent antibacterial activity and low mammalian toxicity. J. Mol. Liq. 2018, 265, 96–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.; Liu, Q.; Wang, L.; Jiang, W.; Zhang, W.; Song, X. Multifunctional triple-porous Fe3O4@SiO2 superparamagnetic microspheres for potential hyperthermia and controlled drug release. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 32049–32057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Javanbakht, S.; Shadi, M.; Mohammadian, R.; Shaabani, A.; Ghorbani, M.; Rabiee, G.; Amini, M.M. Preparation of Fe3O4@ SiO2@ Tannic acid double core-shell magnetic nanoparticles via the Ugi multicomponent reaction strategy as a pH-responsive co-delivery of doxorubicin and methotrexate. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2020, 247, 122857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Gaus, K.; Tilley, R.D.; Gooding, J.J. The impact of nanoparticle shape on cellular internalisation and transport: What do the different analysis methods tell us? Mater. Horiz. 2019, 6, 1538–1547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Guo, W.; Su, X.; Ou-Yang, L.; Dang, M.; Tao, J.; Lu, G.; Teng, Z. Small size mesoporous organosilica nanorods with different aspect ratios: Synthesis and cellular uptake. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2018, 512, 134–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, N.; Li, J.; Xu, C.; Xu, L.; Li, S.; Xu, L. Mesoporous silica nanorods for improved oral drug absorption. Artif. Cells Nanomed. Biotechnol. 2018, 46, 1132–1140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gopichand, P.; Agarwal, G.; Natarajan, M.; Mandal, J.; Deepanjali, S.; Parameswaran, S.; Dorairajan, L. In vitro effect of fosfomycin on multi-drug resistant gram-negative bacteria causing urinary tract infections. Infect. Drug Resist. 2019, 12, 2005. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ibrahim, Y.M.; Abu El-Wafa, W.M. Evaluation of fosfomycin combined with vancomycin against vancomycin-resistant coagulase negative staphylococci. J. Chemother. 2020, 32, 411–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trinh, T.D.; Smith, J.R.; Rybak, M.J. Parenteral Fosfomycin for the treatment of multidrug resistant bacterial infections: The rise of the epoxide. Pharmacother. J. Hum. Pharmacol. Drug Ther. 2019, 39, 1077–1094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheeseman, S.; Christofferson, A.J.; Kariuki, R.; Cozzolino, D.; Daeneke, T.; Crawford, R.J.; Truong, V.K.; Chapman, J.; Elbourne, A. Antimicrobial metal nanomaterials: From passive to stimuli-activated applications. Adv. Sci. 2020, 7, 1902913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elbourne, A.; Cheeseman, S.; Atkin, P.; Truong, N.P.; Syed, N.; Zavabeti, A.; Mohiuddin, M.; Esrafilzadeh, D.; Cozzolino, D.; McConville, C.F. Antibacterial liquid metals: Biofilm treatment via magnetic activation. ACS Nano 2020, 14, 802–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quan, K.; Zhang, Z.; Chen, H.; Ren, X.; Ren, Y.; Peterson, B.W.; van der Mei, H.C.; Busscher, H.J. Artificial channels in an infectious biofilm created by magnetic nanoparticles enhanced bacterial killing by antibiotics. Small 2019, 15, 1902313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghorbani-Choghamarani, A.; Tahmasbi, B.; Noori, N.; Faryadi, S. Pd–S-methylisothiourea supported on magnetic nanoparticles as an efficient and reusable nanocatalyst for Heck and Suzuki reactions. Comptes Rendus Chim. 2017, 20, 132–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shagholani, H.; Ghoreishi, S.M.; Mousazadeh, M. Improvement of interaction between PVA and chitosan via magnetite nanoparticles for drug delivery application. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2015, 78, 130–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Dai, W.; Yin, Z.-Z.; Gao, J.; Wu, D.; Kong, Y. Synthesis of oxidized pullulan coated mesoporous silica for pH-sensitive drug delivery. Eur. Polym. J. 2020, 122, 109399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, Z.U.; Wei, N.; Li, Z.; Sun, W.; Wang, D. Preparation of hollow mesoporous silica nanospheres: Controllable template synthesis and their application in drug delivery. New J. Chem. 2017, 41, 14122–14129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, H.Q.; Bhave, M.; Xu, G.; Sun, C.; Yu, A. Synthesis of polydopamine hollow capsules via a polydopamine mediated silica water dissolution process and its application for enzyme encapsulation. Front. Chem. 2019, 7, 468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, D.; Gao, Y.; Wang, L.; Liu, G.; Chen, Y.; Wang, T.; Tao, W.; Mei, L.; Huang, L.; Zeng, X. Polydopamine-based surface modification of mesoporous silica nanoparticles as pH-sensitive drug delivery vehicles for cancer therapy. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2016, 463, 279–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, W.; Liu, C.; Chen, Y. Stability of polydopamine coatings on gold substrates inspected by surface plasmon resonance imaging. Langmuir 2018, 34, 3565–3571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Hong, W.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, T.T.; Chen, Z.; Yuan, S.; Peng, P.; Xiao, M.; Xu, L. Photothermally triggered cytosolic drug delivery of glucose functionalized polydopamine nanoparticles in response to tumor microenvironment for the GLUT1-targeting chemo-phototherapy. J. Control. Release 2020, 317, 232–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ambekar, R.S.; Kandasubramanian, B. A polydopamine-based platform for anti-cancer drug delivery. Biomater. Sci. 2019, 7, 1776–1793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aksoy, I.; Kucukkececi, H.; Sevgi, F.; Metin, O.; Hatay Patir, I. Photothermal antibacterial and antibiofilm activity of black phosphorus/gold nanocomposites against pathogenic bacteria. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 26822–26831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-Melcón, C.; Riesco-Peláez, F.; Carballo, J.; García-Fernández, C.; Capita, R.; Alonso-Calleja, C. Structure and viability of 24-and 72-h-old biofilms formed by four pathogenic bacteria on polystyrene and glass contact surfaces. Food Microbiol. 2018, 76, 513–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robertson, J.; McGoverin, C.; Vanholsbeeck, F.; Swift, S. Optimisation of the protocol for the LIVE/DEAD® BacLightTM bacterial viability kit for rapid determination of bacterial load. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGoverin, C.; Robertson, J.; Jonmohamadi, Y.; Swift, S.; Vanholsbeeck, F. Species Dependence of SYTO 9 Staining of Bacteria. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 2149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, Q.; Deng, T.; Lin, F.-C.; Zhang, B.; Zink, J.I. Supramolecular assemblies of heterogeneous mesoporous silica nanoparticles to co-deliver antimicrobial peptides and antibiotics for synergistic eradication of pathogenic biofilms. ACS Nano 2020, 14, 5926–5937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Choi, C.K.K.; Hong, H.; Xiao, Y.; Kwok, M.L.; Liu, H.; Tian, X.Y.; Choi, C.H.J. Dopamine Receptor-Mediated Binding and Cellular Uptake of Polydopamine-Coated Nanoparticles. ACS Nano 2021, 15, 13871–13890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, G.; Gong, H.; Qian, X.; Tan, P.; Li, Z.; Liu, T.; Liu, J.; Li, Y.; Liu, Z. Mesoporous silica nanorods intrinsically doped with photosensitizers as a multifunctional drug carrier for combination therapy of cancer. Nano Res. 2015, 8, 751–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, Y.; Chen, M.; Xue, Q.; Liu, W. Preparation and self-assembly of carboxylic acid-functionalized silica. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2007, 311, 507–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, J.; An, K.; Hwang, Y.; Park, J.-G.; Noh, H.-J.; Kim, J.-Y.; Park, J.-H.; Hwang, N.-M.; Hyeon, T. Ultra-large-scale syntheses of monodisperse nanocrystals. Nat. Mater. 2004, 3, 891–895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Z.; Zhou, Z.; Bao, J.; Wang, Z.; Hu, J.; Chi, X.; Ni, K.; Wang, R.; Chen, X.; Chen, Z. Octapod iron oxide nanoparticles as high-performance T 2 contrast agents for magnetic resonance imaging. Nat. Commun. 2013, 4, 2266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tran, H.Q.; Alam, H.; Goff, A.; Daeneke, T.; Bhave, M.; Yu, A. Multifunctional Fe3O4 Nanoparticles Filled Polydopamine Hollow Rods for Antibacterial Biofilm Treatment. Molecules 2023, 28, 2325. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28052325
Tran HQ, Alam H, Goff A, Daeneke T, Bhave M, Yu A. Multifunctional Fe3O4 Nanoparticles Filled Polydopamine Hollow Rods for Antibacterial Biofilm Treatment. Molecules. 2023; 28(5):2325. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28052325
Chicago/Turabian StyleTran, Huy Quang, Husna Alam, Abigail Goff, Torben Daeneke, Mrinal Bhave, and Aimin Yu. 2023. "Multifunctional Fe3O4 Nanoparticles Filled Polydopamine Hollow Rods for Antibacterial Biofilm Treatment" Molecules 28, no. 5: 2325. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28052325
APA StyleTran, H. Q., Alam, H., Goff, A., Daeneke, T., Bhave, M., & Yu, A. (2023). Multifunctional Fe3O4 Nanoparticles Filled Polydopamine Hollow Rods for Antibacterial Biofilm Treatment. Molecules, 28(5), 2325. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28052325






