Recent Advances of Marine Natural Indole Products in Chemical and Biological Aspects
Abstract
1. Introduction
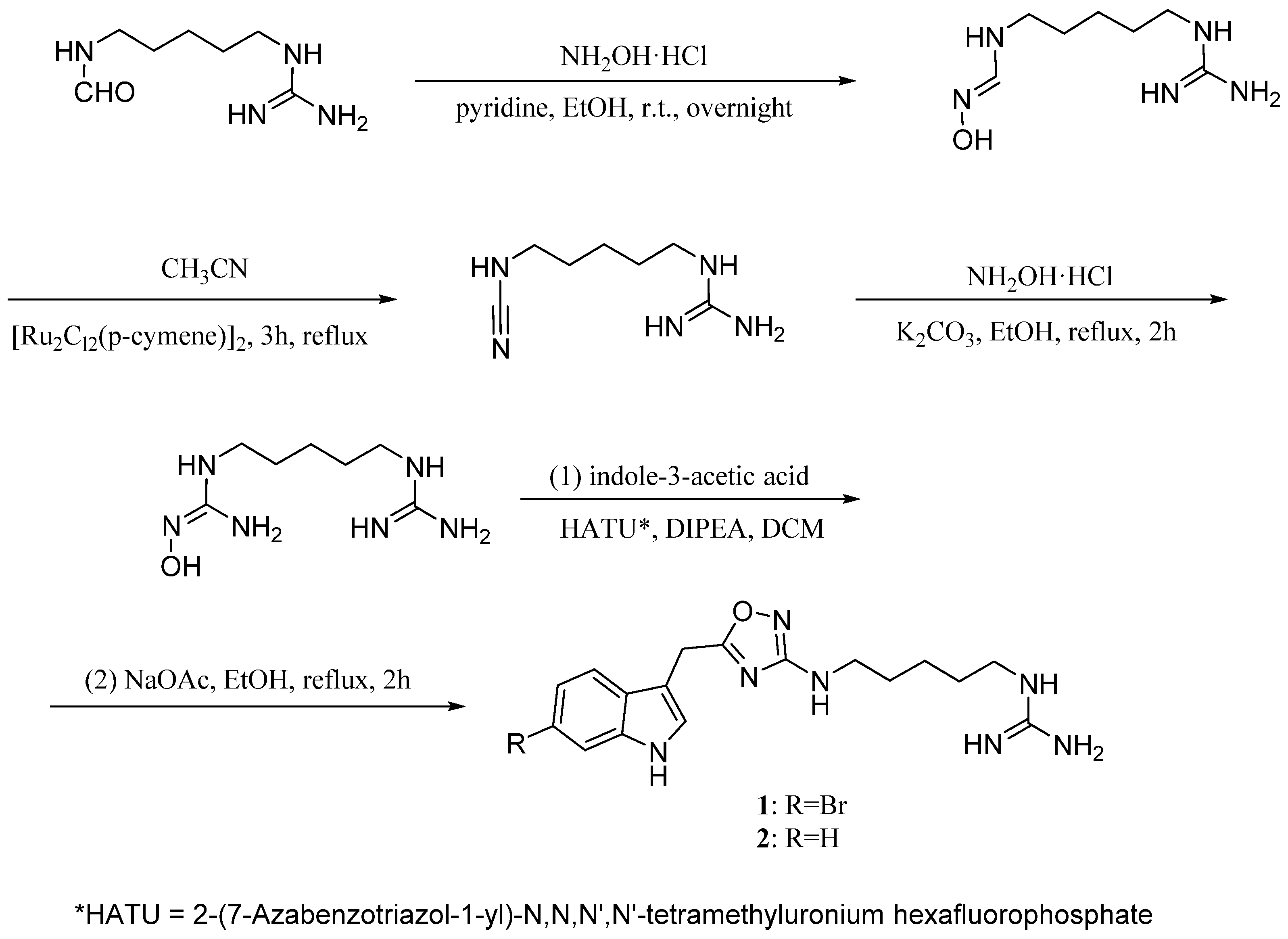
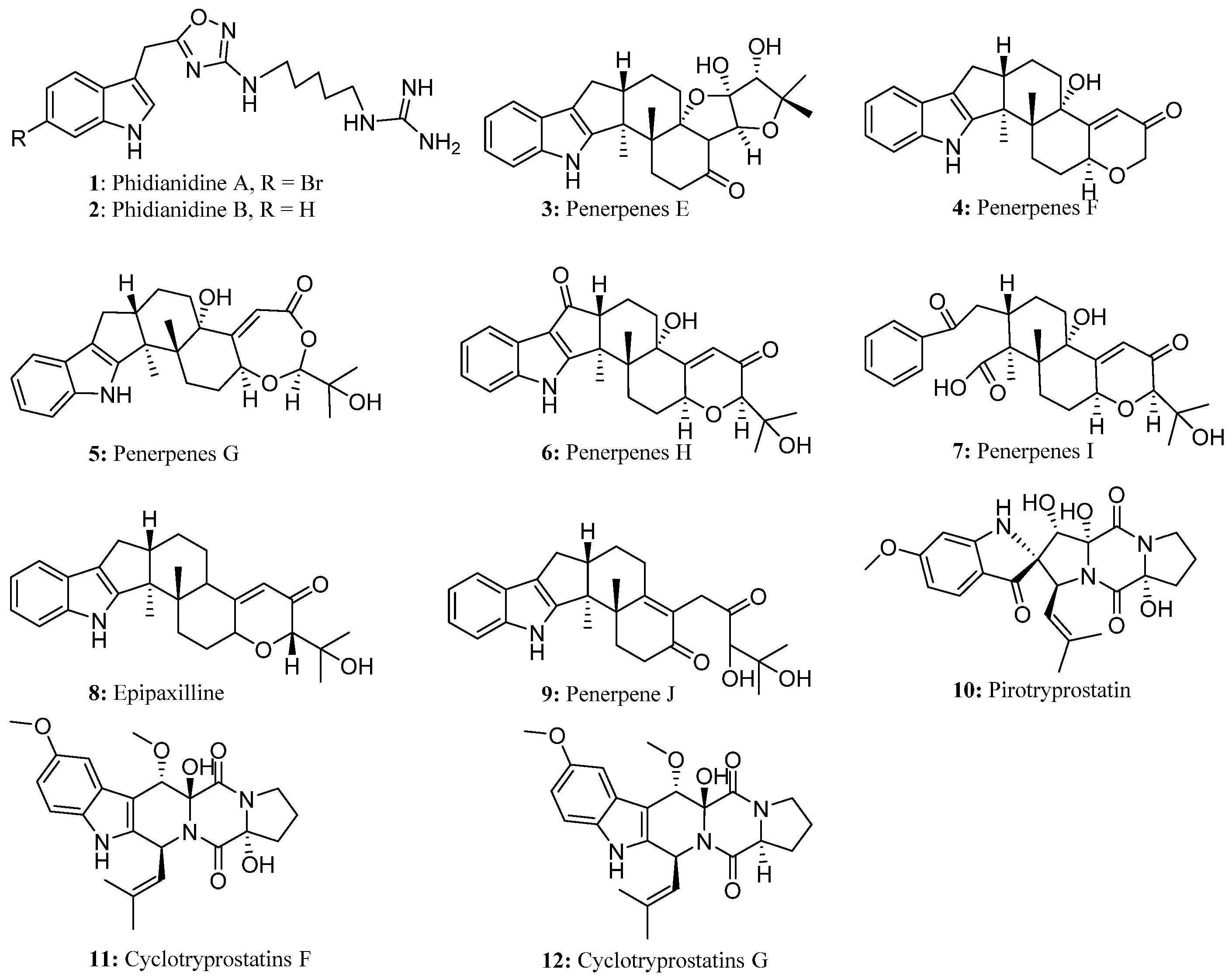
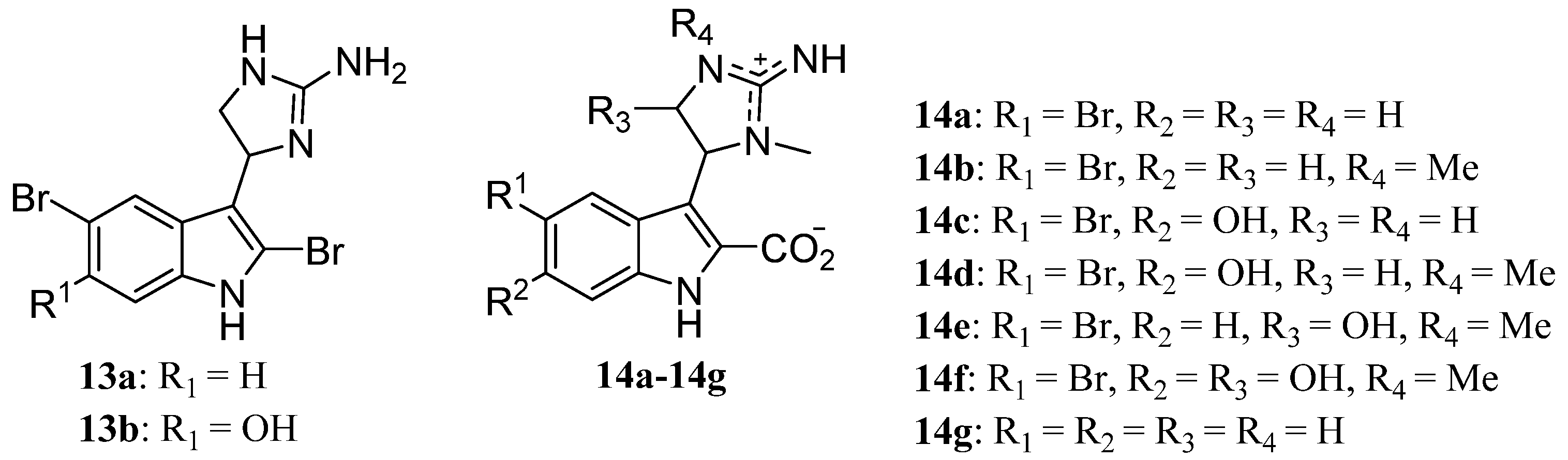
2. Monomeric Indoles and Annelated Indoles
3. Indolyl Peptides
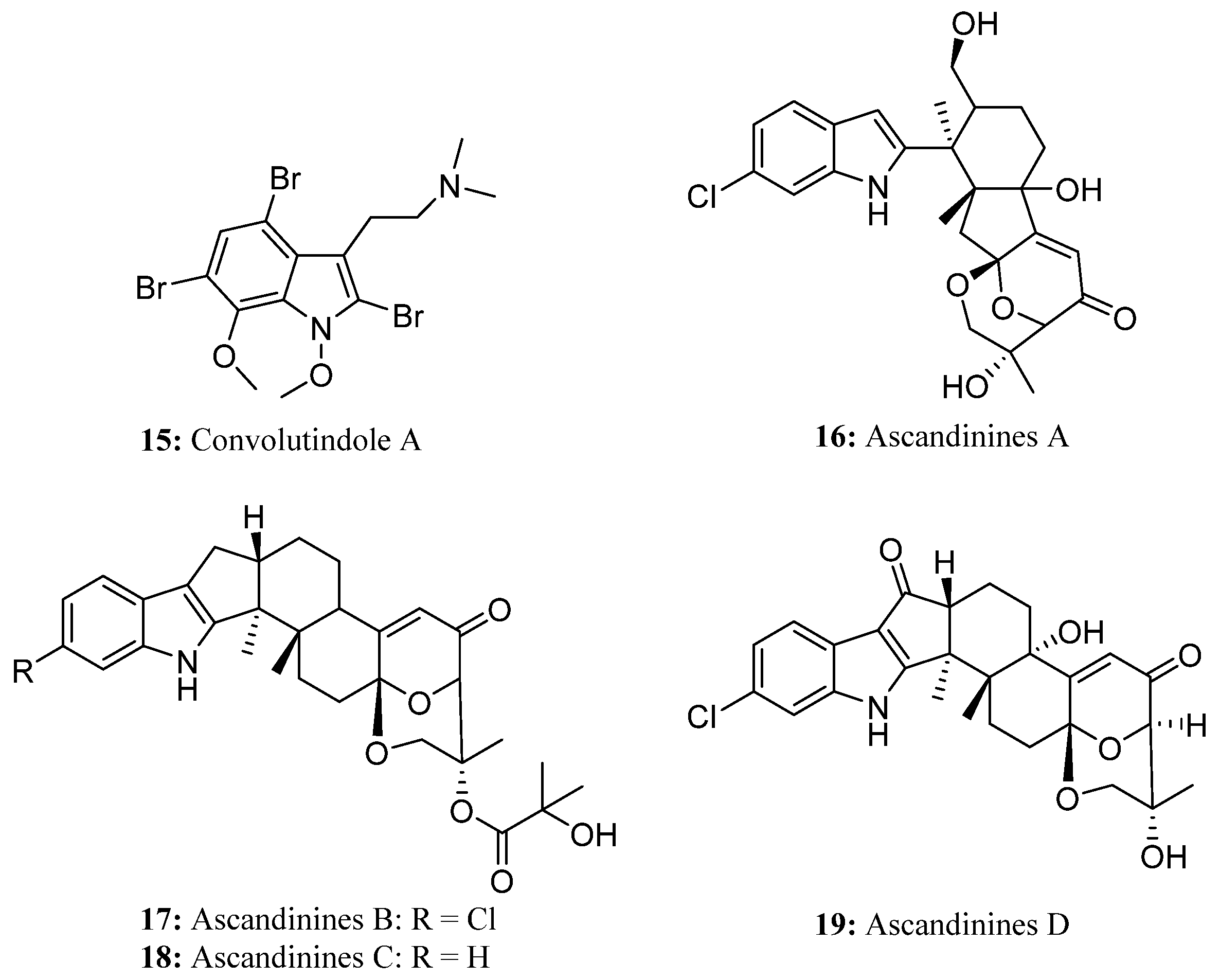
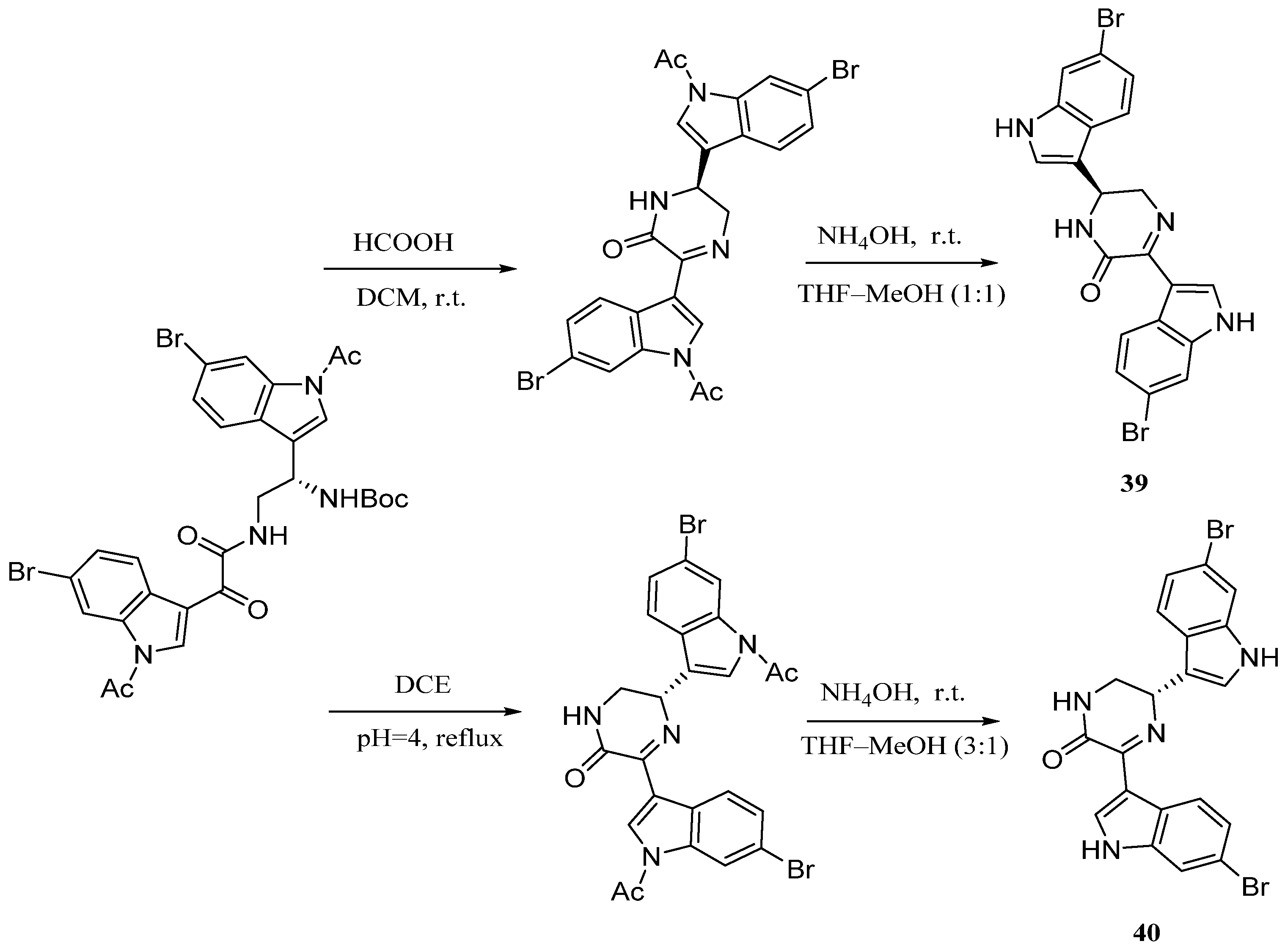
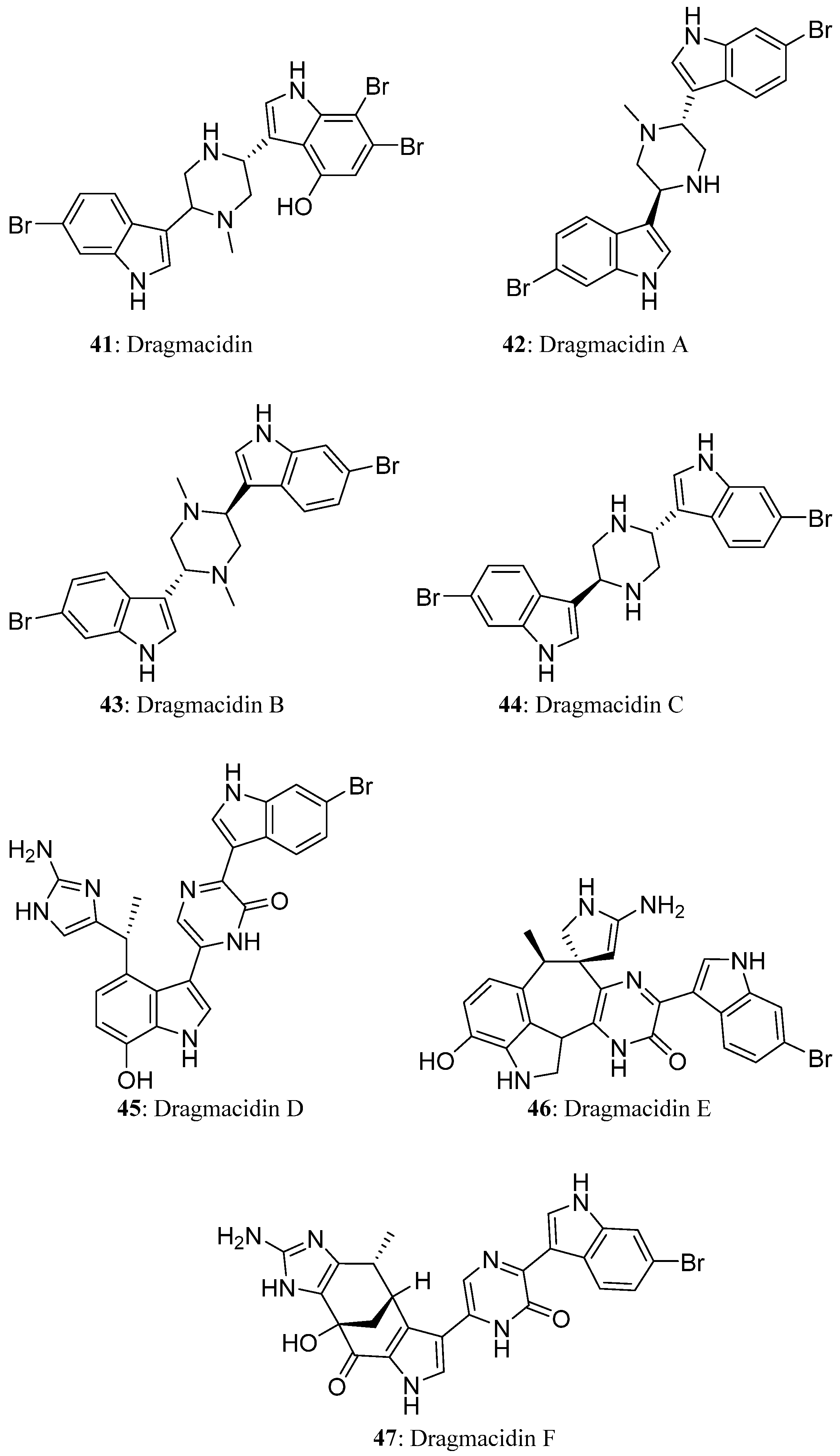
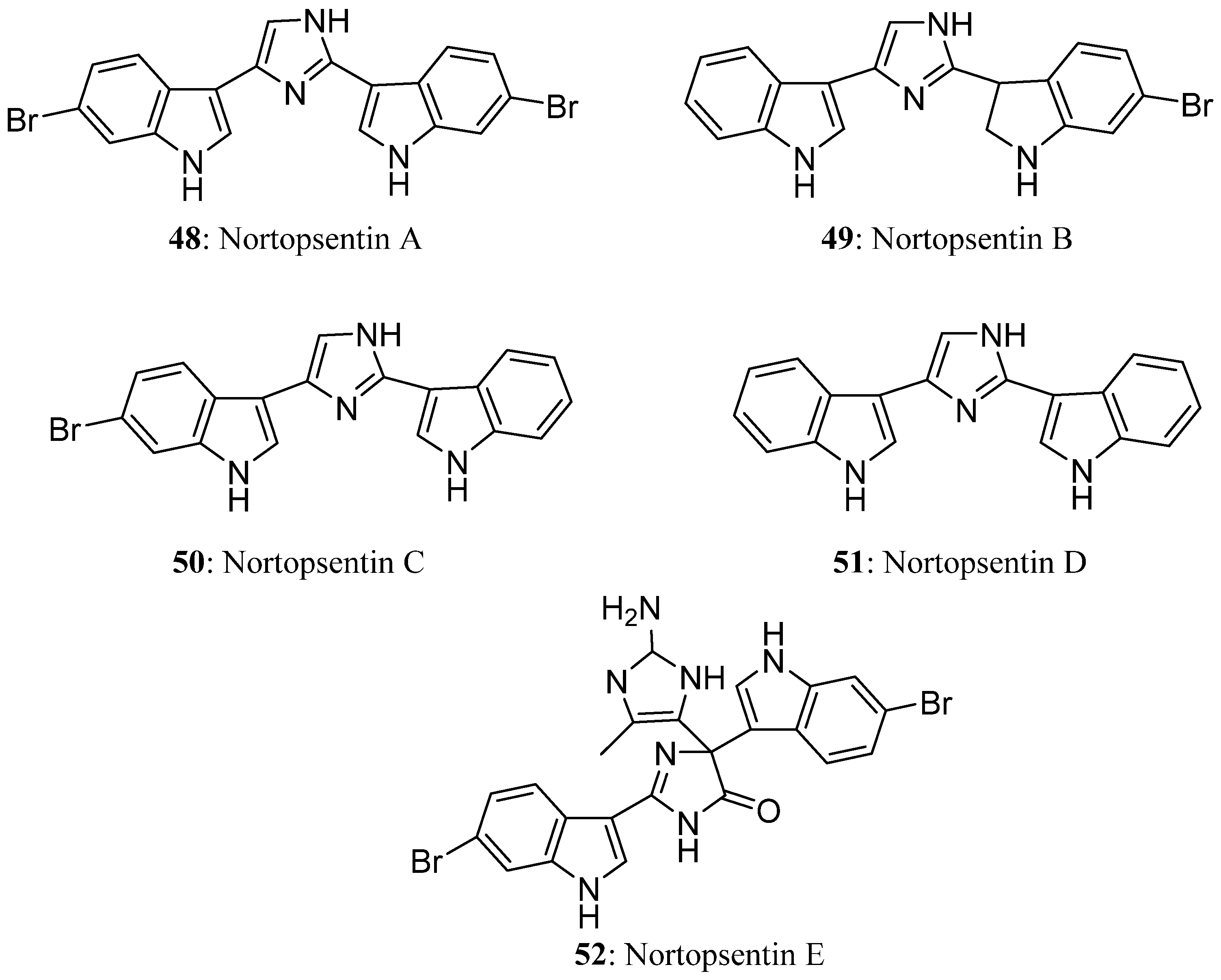
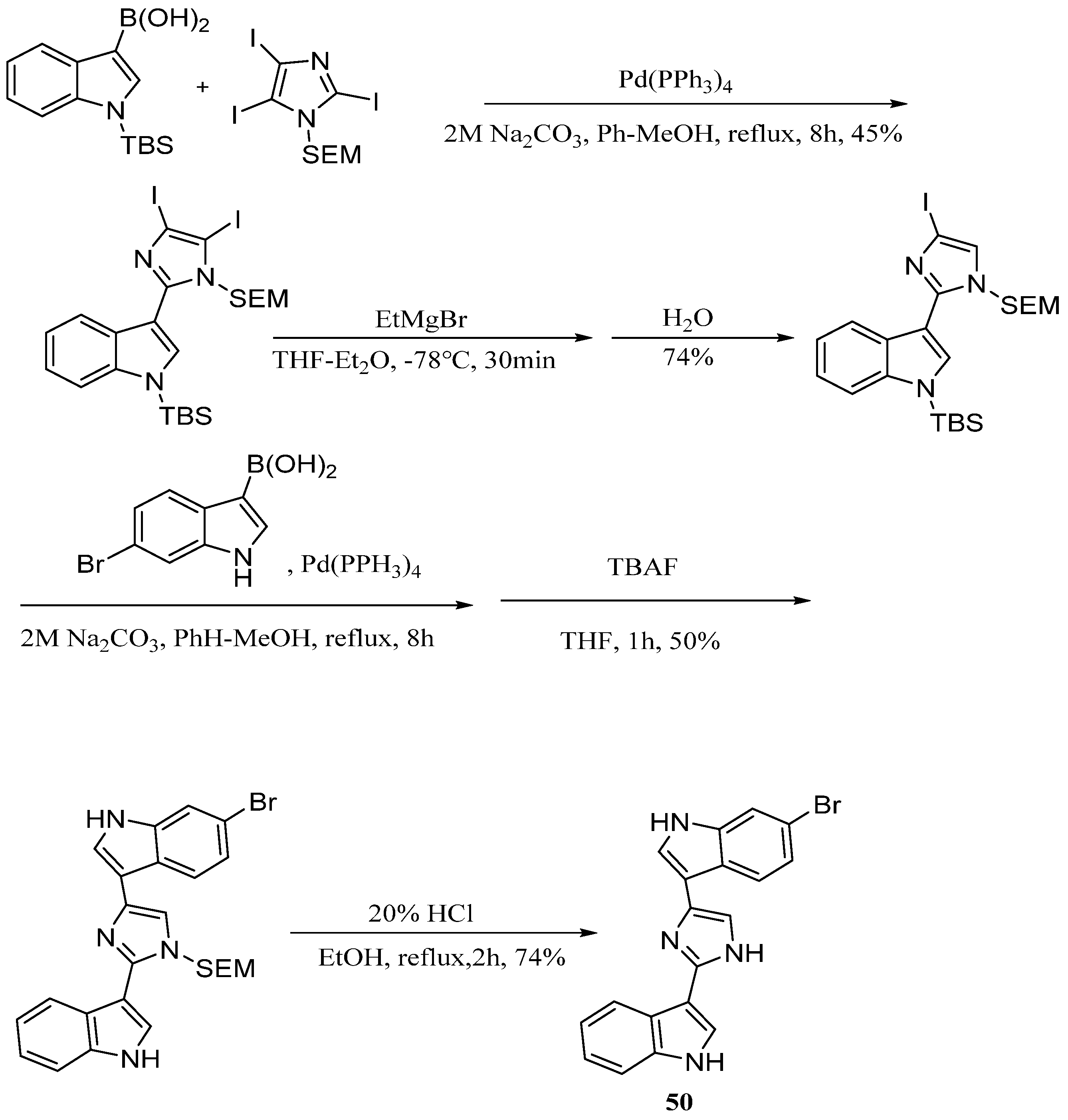
4. Bis-Indole Alkaloids
5. Conclusions and Prospect
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Fattorusso, E.; Taglialatela-Scafati, O. Modern Alkaloids: Structure, Isolation, Synthesis and Biology; Wiley-VCH: Weinheim, Germany, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Aygun, A.; Pindur, U. Chemistry and biology of new marine alkaloids from the indole and annelated indole series. Curr. Med. Chem. 2003, 13, 1113–1127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, C.S.; Fu, Y.; Zhang, L.; Gong, J.X.; Wang, Z.Z.; Xiao, W.; Zhang, H.Y.; Guo, Y.W. Synthesis and biological evaluation of novel marine-derived indole-based 1,2,4-oxadiazoles derivatives as multifunctional neuroprotective agents. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2015, 2, 216–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Li, H.; Chen, K.X.; Zuo, J.P.; Guo, Y.W.; Tang, W.; Li, X.W. Design and synthesis of marine phidianidine derivatives as potential immunosuppressive Agents. J. Med. Chem. 2018, 24, 11298–11308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brogan, J.T.; Stoops, S.L.; Lindsley, C.W. Total synthesis and biological evaluation of phidianidines A and B uncovers unique pharmacological profiles at CNS targets. ACS Chem. Neurosci. 2012, 9, 658–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vitale, R.M.; Gatti, M.; Carbone, M.; Barbieri, F.; Felicita, V.; Gavagnin, M.; Florio, T.; Amodeo, P. Minimalist hybrid ligand/receptor-based pharmacophore model for CXCR4 applied to a small-library of marine natural products led to the identification of phidianidine a as a new CXCR4 ligand exhibiting antagonist activity. ACS Chem. Biol. 2013, 12, 2762–2770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Labriere, C.; Elumalai, V.; Staffansson, J.; Cervin, G.; Le Norcy, T.; Denardou, H.; Rehel, K.; Moodie, L.W.K.; Hellio, C.; Pavia, H.; et al. Phidianidine A and synthetic analogues as naturally inspired marine antifoulants. J. Nat. Prod. 2020, 11, 3413–3423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.M.; Kong, F.D.; Fan, P.; Ma, Q.Y.; Xie, Q.Y.; Li, J.H.; Zheng, H.Z.; Zheng, Z.H.; Yuan, J.Z.; Dai, H.F.; et al. Indole-diterpenoids with protein tyrosine phosphatase inhibitory activities from the marine-derived fungus Penicillium sp. KFD28. J. Nat. Prod. 2019, 9, 2638–2644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.Y.; Xie, Q.Y.; Kong, F.D.; Ma, Q.Y.; Zhou, L.M.; Yuan, J.Z.; Dai, H.F.; Wu, Y.G.; Zhao, Y.X. Two new indole-diterpenoids from the marine-derived fungus Penicillium sp. KFD28. J. Asian Nat. Prod. Res. 2021, 11, 1030–1036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.H.; Geng, C.; Zhang, X.W.; Zhu, H.J.; Shao, C.L.; Cao, F.; Wang, C.Y. Discovery of bioactive indole-diketopiperazines from the marine-derived fungus penicillium brasilianum aided by genomic information. Mar. Drugs 2019, 9, 514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakemi, S.; Sun, H.H. Nortopsentins A, B, and C. Cytotoxic and antifungal imidazolediylbis[indoles] from the sponge Spongosorites ruetzleri. J. Org. Chem. 1991, 13, 4304–4307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paul, G.K.; Gunasekera, S.P.; Longley, R.E.; Pomponi, S.A. Theopederins K and L. Highly potent cytotoxic metabolites from a marine sponge Discodermia species. J. Nat. Prod. 2002, 1, 59–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Capon, R.J.; Peng, C.; Dooms, C. Trachycladindoles A-G: Cytotoxic heterocycles from an Australian marine sponge, Trachycladus laevispirulifer. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2008, 15, 2765–2771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narkowicz, C.K.; Blackman, A.J.; Lacey, E.; Gill, J.H.; Heiland, K. Convolutindole A and convolutamine H, new nematocidal brominated alkaloids from the marine bryozoan Amathia convoluta. J. Nat. Prod. 2002, 6, 938–941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, G.; Sun, C.; Hou, X.; Che, Q.; Zhang, G.; Gu, Q.; Liu, C.; Zhu, T.; Li, D. Ascandinines A-D, indole diterpenoids, from the Sponge-Derived Fungus Aspergillus candidus HDN15-152. J. Org. Chem. 2021, 3, 2431–2436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gompel, M.; Leost, M.; De Kier Joffe, E.B.; Puricelli, L.; Franco, L.H.; Palermo, J.; Meijer, L. Meridianins, a new family of protein kinase inhibitors isolated from the ascidian Aplidium meridianum. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2004, 7, 1703–1707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kruppa, M.; Sommer, G.A.; Muller, T.J.J. Concise syntheses of marine (bis)indole alkaloids meridianin C, D, F, and G and scalaridine A via one-pot Masuda borylation-Suzuki coupling sequence. Molecules 2022, 7, 2233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olsen, E.K.; Hansen, E.; Isaksson, J.; Sepcic, K.; Cergolj, M.; Svenson, J.; Andersen, J.H. Marine AChE inhibitors isolated from Geodia barretti: Natural compounds and their synthetic analogs. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2016, 5, 1629–1640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Longeon, A.; Copp, B.R.; Quevrain, E.; Roue, M.; Kientz, B.; Cresteil, T.; Petek, S.; Debitus, C.; Bourguet-Kondracki, M.L. Bioactive indole derivatives from the South Pacific marine sponges Rhopaloeides odorabile and Hyrtios sp. Mar. Drugs 2011, 5, 879–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Xu, W.; Li, S.; Chen, M.; Cheng, Y.; Yuan, W.; Cheng, Z.; Li, Q. Penicindopene A, a new indole diterpene from the deep-sea fungus Penicillium sp. YPCMAC1. Nat. Prod. Res. 2019, 20, 2988–2994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Youssef, D.T.; Shaala, L.A.; Asfour, H.Z. Bioactive compounds from the Red Sea marine sponge Hyrtios species. Mar. Drugs 2013, 4, 1061–1070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Limbadri, S.; Luo, X.; Lin, X.; Liao, S.; Wang, J.; Zhou, X.; Yang, B.; Liu, Y. Bioactive Novel Indole Alkaloids and Steroids from Deep Sea-Derived Fungus Aspergillus fumigatus SCSIO 41012. Molecules 2018, 23, 2379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akiyama, H.; Oku, N.; Kasai, H.; Shizuri, Y.; Matsumoto, S.; Igarashi, Y. Metabolites from thermophilic bacteria I: N-propionylanthranilic acid, a co-metabolite of the bacillamide class antibiotics and tryptophan metabolites with herbicidal activity from Laceyella sacchari. J. Antibiot. 2014, 11, 795–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gebhardt, K.; Schimana, J.; Muller, J.; Fiedler, H.P.; Kallenborn, H.G.; Holzenkampfer, M.; Krastel, P.; Zeeck, A.; Vater, J.; Holtzel, A.; et al. Screening for biologically active metabolites with endosymbiotic bacilli isolated from arthropods. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2002, 2, 199–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Socha, A.M.; Long, R.A.; Rowley, D.C. Bacillamides from a hypersaline microbial mat bacterium. J. Nat. Prod. 2007, 11, 1793–1795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Greshock, T.J.; Grubbs, A.W.; Jiao, P.; Wicklow, D.T.; Gloer, J.B.; Williams, R.M. Isolation, structure elucidation, and biomimetic total synthesis of versicolamide B, and the isolation of antipodal (-)-stephacidin A and (+)-notoamide B from Aspergillus versicolor NRRL 35600. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 2008, 19, 3573–3577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kagiyama, I.; Kato, H.; Nehira, T.; Frisvad, J.C.; Sherman, D.H.; Williams, R.M.; Tsukamoto, S. Taichunamides: Prenylated Indole Alkaloids from Aspergillus taichungensis (IBT 19404). Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 2016, 3, 1128–1132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Li, X.M.; Wang, J.N.; Li, X.; Wang, B.G. Prenylated indole alkaloids from the marine-derived fungus Paecilomyces variotii. Chin. Chem. Lett. 2015, 20, 3374–3376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Sun, W.; Deng, M.; Zhou, Q.; Wang, J.; Liu, J.; Chen, C.; Qi, C.; Luo, Z.; Xue, Y.; et al. Asperversiamides, Linearly Fused Prenylated Indole Alkaloids from the Marine-Derived Fungus Aspergillus versicolor. J. Org. Chem. 2018, 15, 8483–8492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, L.; Talwar, A.; Chauhan, P.M. Bis and tris indole alkaloids from marine organisms: New leads for drug discovery. Curr. Med. Chem. 2007, 16, 1789–1803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gunasekera, S.P.; McCarthy, P.J.; Kelly-Borges, M. Hamacanthins A and B, new antifungal bis indole alkaloids from the deep-water marine sponge, Hamacantha sp. J. Nat. Prod. 1994, 10, 1437–1441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, B.; Sun, Q.; Yao, X.; Hong, J.; Lee, C.O.; Sim, C.J.; Im, K.S.; Jung, J.H. Cytotoxic bisindole alkaloids from a marine sponge Spongosorites sp. J. Nat. Prod. 2005, 68, 711–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kouko, T.; Matsumura, K.; Kawasaki, T. Total synthesis of marine bisindole alkaloids, (+)-hamacanthins A, B and (−)-antipode of cis-dihydrohamacanthin B. Tetrahedron 2005, 9, 2309–2318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golantsov, N.E.; Festa, A.A.; Karchava, A.V.; Yurovskaya, M.A. ChemInform Abstract: Marine Indole Alkaloids Containing an 1-(Indol-3-yl)ethane-1,2-diamine Fragment. ChemInform 2013, 37, 1537–1540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, K.B.; Mar, W.; Kim, S.; Kim, J.Y.; Lee, T.H.; Kim, J.G.; Shin, D.; Sim, C.J.; Shin, J. Antimicrobial activity and cytotoxicity of bis(indole) alkaloids from the sponge Spongosorites sp. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2006, 3, 570–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kohmoto, S.; Kashman, Y.; McConnell, O.J.; Rinehart, K.L.J.; Wright, A.; Koehn, F. ChemInform Abstract: Dragmacidin, a New Cytotoxic Bis(indole) Alkaloid from a Deep Water Marine Sponge, Dragmacidon sp. ChemInform 1988, 13, 3116–3118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crooke, S.; Whitlock, C. A general synthesis of bis-indolylpiperazine-2,5-diones. Molecules 2012, 12, 14841–14845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morris, S.A.; Andersen, R.J. Brominated bis(indole) alkaloids from the marine sponge Hexadella sp. Tetrahedron 1990, 46, 715–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fahy, E.; Porn, B.; Smith, K. 6-bromotryptamine derivatives from the gulf of california tunicate dzdemnum candzdum. J. Nat. Prod. 1991, 46, 1192–1194. [Google Scholar]
- Murray, L.M.; Lim, T.K.; Hooper, J.N.A.; Capon, R.J. Isobromotopsentin: A New Bis(indole) Alkaloid From a Deep-Water Marine Sponge Spongosorites sp. Aust. J. Chem. 1995, 12, 2053–2058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cutignano, A.; Bifulco, G.; Bruno, I.; Casapullo, A.; Gomez-Paloma, L.; Riccio, R. Dragmacidin F: A new antiviral bromoindole alkaloid from the Mediterranean Sponge Halicortex sp. Tetrahedron 2000, 23, 3743–3748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, B.; Smallheer, J.M.; Amaral-Ly, C.; Wuonola, M.A. Total Synthesis of (.+−.)-Dragmacidin: A cytotoxic bis(indole)alkaloid of marine origin. J. Org. Chem. 2002, 22, 6823–6827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whitlock, C.R.; Cava, M.P. A total synthesis of dragmacidin B. Tetrahedron 1994, 3, 371–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyake, F.Y.; Yakushijin, K.; Horne, D.A. Biomimetic synthesis of grossularines-1. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 2005, 21, 3280–3282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawasaki, T.; Enoki, H.; Matsumura, K.; Ohyama, M.; Inagawa, M.; Sakamoto, M. First total synthesis of dragmacidin A via indolylglycines. Org. Lett. 2000, 19, 3027–3029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garg, N.K.; Stoltz, B.M. The formal total synthesis of Dragmacidin B, trans-Dragmacidin C, and cis- and trans-dihydrohamacanthins A. Tetrahedron Lett. 2005, 14, 2423–2426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capon, R.J.; Rooney, F.; Murray, L.M.; Collins, E.; Sim, A.T.R.; Rostas, J.A.P.; Butler, M.S.; Carroll, A.R. Dragmacidins: New protein phosphatase inhibitors from a southern australian deep-water marine sponge, Spongosorites sp. J. Nat. Prod. 1998, 5, 660–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mancini, I.; Guella, G.; Pietra, F.; Debitus, C.C.; Waikedre, J. From inactive nortopsentin D, a novel bis(indole) alkaloid isolated from the Axinellid Sponge Dragmacidon sp. from deep waters south of new caledonia, to a strongly cytotoxic derivative. Helv. Chim. Acta. 1996, 8, 2075–2082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.G.; Huang, H.; Jiang, B. Progress in studies of novel marine bis(indole) alkaloids. Curr. Org. Chem. 2004, 17, 1691–1720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramsden, C.A.; Moody, C.J.; Roffey, J.R.A. Synthesis of N-protected nortopsentins B and D. Arkivoc 2000, 3, 393–401. [Google Scholar]
- Fresneda, P.M.; Molina, P.; Sanz, M.A.J.S. The first synthesis of the bis(indole) marine alkaloid Rhopaladin D. Synlett. 2000, 7, 1691–1720. [Google Scholar]
- Braekman, J.C.; Daloze, D.; Stoller, C. Synthesis of Topsentin-A, abisindole alkaloid of the marine sponge topsentia genitrix. Bull. Des Sociétés Chim. Belg. 2010, 10, 809–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsujii, S.; Rinehart, K.L.; Gunasekera, S.P.; Kashman, Y.; Cross, S.S.; Lui, M.S.; Pomponi, S.A.; Diaz, M.C. Topsentin, bromotopsentin, and dihydrodeoxybromotopsentin: Antiviral and antitumor bis(indolyl)imidazoles from Caribbean deep-sea sponges of the family Halichondriidae. Structural and synthetic studies. J. Org. Chem. 2002, 23, 5446–5453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, J.; Seo, Y.; Cho, K.W.; Rho, J.R.; Sim, C.J. New Bis(Indole) alkaloids of the topsentin class from the sponge spongosorites genitrix. J. Nat. Prod. 1999, 4, 647–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wylie, B.L.; Ernst, N.B.; Grace, K.J.S.; Jacobs, R.S. Marine Natural Products as Phospholipase A2 Inhibitors. Prog. Surg. 1997, 24, 146–152. [Google Scholar]
- Hwang, J.; Kim, D.; Park, J.S.; Park, H.J.; Shin, J.; Lee, S.K. Photoprotective activity of Topsentin, A bis(indole) alkaloid from the marine sponge Spongosorites genitrix, by regulation of COX-2 and Mir-4485 expression in UVB-irradiated human keratinocyte cells. Mar. Drugs 2020, 18, 87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Casapullo, A.; Bifulco, G.; Bruno, I.; Riccio, R. New bisindole alkaloids of the topsentin and hamacanthin classes from the Mediterranean marine sponge Rhaphisia lacazei. J. Nat. Prod. 2000, 4, 447–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, J.Y.; Zhu, Y.; Zeng, L.M.; Xu, X.H. A new bisindole from Alga Caulerpa serrulata. J. Nat. Prod. 1997, 10, 1043–1044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pindur, U.; Lemster, T. Advances in marine natural products of the indole and annelated indole series: Chemical and biological aspects. Curr. Med. Chem. 2001, 13, 1681–1698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fresneda, P.M.; Molina, P.; Angeles Saez, M. The first synthesis of the bis(indole) marine alkaloid Caulersin. Synlett 1999, 10, 1651–1653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maiti, B.C.; Thomson, R.H.; Mahendran, M. Structure of Caulerpin, a Pigmet from Caulerpa Algae. J. Chem. Res. 1978, 4, 126–127. [Google Scholar]
- Lunagariya, J.; Bhadja, P.; Zhong, S.; Vekariya, R.; Xu, S. Marine natural product bis-indole alkaloid Caulerpin: Chemistry and biology. MiniRev. Med. Chem. 2019, 9, 751–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wahlström, N.; Stensland, B.; Bergman, J. Synthesis of the marine alkaloid Caulersin. Tetrahedron 2004, 9, 2147–2153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miki, Y.; Aoki, Y.; Miyatake, H.; Minematsu, T.; Hibino, H. Synthesis of caulersin and its isomers by reaction of indole-2,3-dicarboxylic anhydrides with methyl indoleacetates. Tetrahedron Lett. 2006, 29, 5215–5218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canche Chay, C.I.; Gomez Cansino, R.; Espitia Pinzon, C.I.; Torres-Ochoa, R.O.; Martinez, R. Synthesis and anti-tuberculosis activity of the marine natural product Caulerpin and its analogues. Mar. Drugs 2014, 4, 1757–1772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, S.C.; Guo, Y.W.; Shen, X. Two novel aromatic valerenane-type sesquiterpenes from the Chinese green alga Caulerpa taxifolia. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2006, 11, 2947–2950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Souza, E.T.; de Lira, D.P.; de Queiroz, A.C.; da Silva, D.J.; de Aquino, A.B.; Mella, E.A.; Lorenzo, V.P.; de Miranda, G.E.; de Araujo-Junior, J.X.; Chaves, M.C.; et al. The antinociceptive and anti-inflammatory activities of caulerpin, a bisindole alkaloid isolated from seaweeds of the genus Caulerpa. Mar. Drugs 2009, 7, 689–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavalcante-Silva, L.H.; de Carvalho Correia, A.C.; Barbosa-Filho, J.M.; da Silva, B.A.; de Oliveira Santos, B.V.; de Lira, D.P.; Sousa, J.C.; de Miranda, G.E.; de Andrade Cavalcante, F.; Alexandre-Moreira, M.S. Spasmolytic effect of caulerpine involves blockade of Ca2+ influx on guinea pig ileum. Mar. Drugs 2013, 5, 1553–1564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Morgan, J.B.; Coothankandaswamy, V.; Liu, R.; Jekabsons, M.B.; Mahdi, F.; Nagle, D.G.; Zhou, Y.D. The Caulerpa pigment caulerpin inhibits HIF-1 activation and mitochondrial respiration. J. Nat. Prod. 2009, 12, 2104–2109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alarif, W.M.; Abou-Elnaga, Z.S.; Ayyad, S.E.N.; Al-lihaibi, S.S. Insecticidal metabolites from the Green Alga Caulerpa racemosa. CLEAN-Soil Air Water 2010, 38, 548–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.J.; Lee, D.G.; Rho, H.S.; Krasokhin, V.B.; Shin, H.J.; Lee, J.S.; Lee, H.S. Cytotoxic 5-hydroxyindole alkaloids from the marine sponge Scalarispongia sp. J. Heterocycl. Chem. 2013, 6, 1400–1404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, F.D.; Zhang, S.L.; Zhou, S.Q.; Ma, Q.Y.; Xie, Q.Y.; Chen, J.P.; Li, J.H.; Zhou, L.M.; Yuan, J.Z.; Hu, Z.; et al. Quinazoline-containing indole alkaloids from the marine-derived fungus Aspergillus sp. HNMF114. J. Nat. Prod. 2019, 12, 3456–3463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, P.; Zhang, M.; Li, H.; Wang, R.; Hou, H.; Li, X.; Liu, K.; Chen, H. New prenylated indole homodimeric and pteridine alkaloids from the marine-derived fungus Aspergillus austroafricanus Y32-2. Mar. Drugs 2021, 19, 98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.L.; Chen, D.; Huang, L.; Ni, M.; Zhao, Y.; Fan, H.; Bao, X. Antichlamydial dimeric indole derivatives from marine actinomycete Rubrobacter radiotolerans. Planta Med. 2017, 9, 805–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.B.; Lauro, G.; O’Connor, R.D.; Lohith, K.; Kelly, M.; Colin, P.; Bifulco, G.; Bewley, C.A. Tulongicin, an antibacterial tri-indole alkaloid from a deep-water Topsentia sp. Sponge. J. Nat. Prod. 2017, 9, 2556–2560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, Y.; Yang, J.; Yu, J.; Li, J.; Yuan, J.; Wong, N.K.; Ju, J. Chlorinated bis-indole alkaloids from deep-sea derived Streptomyces sp. SCSIO 11791 with antibacterial and cytotoxic activities. J. Antibiot. 2020, 8, 542–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

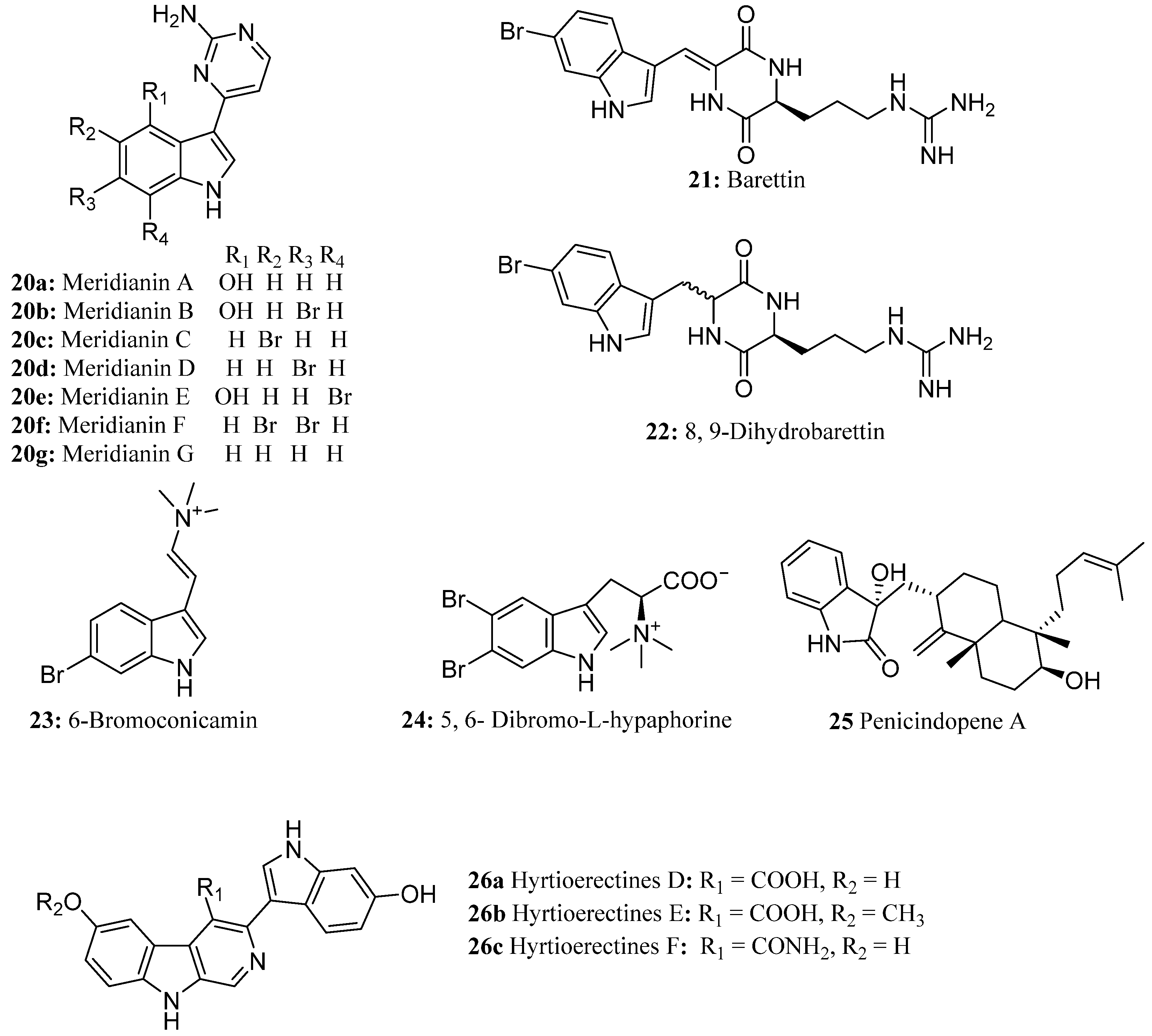

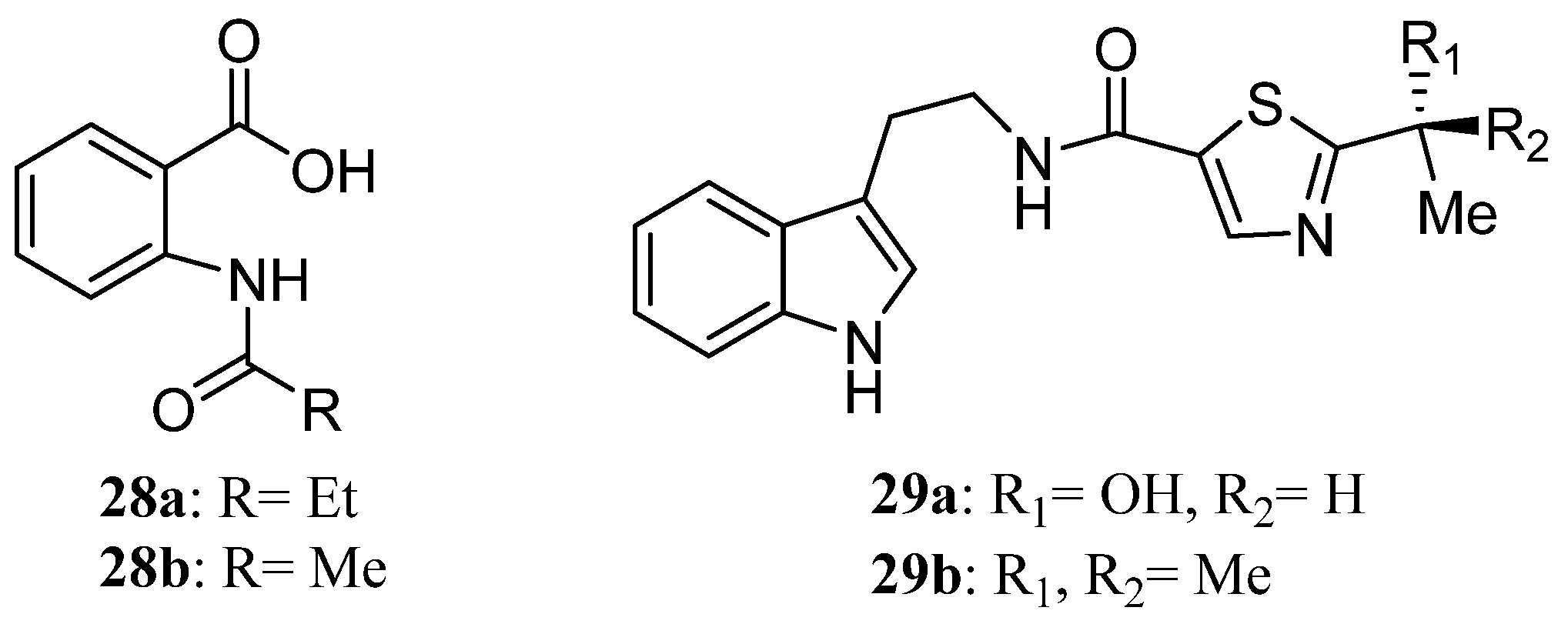
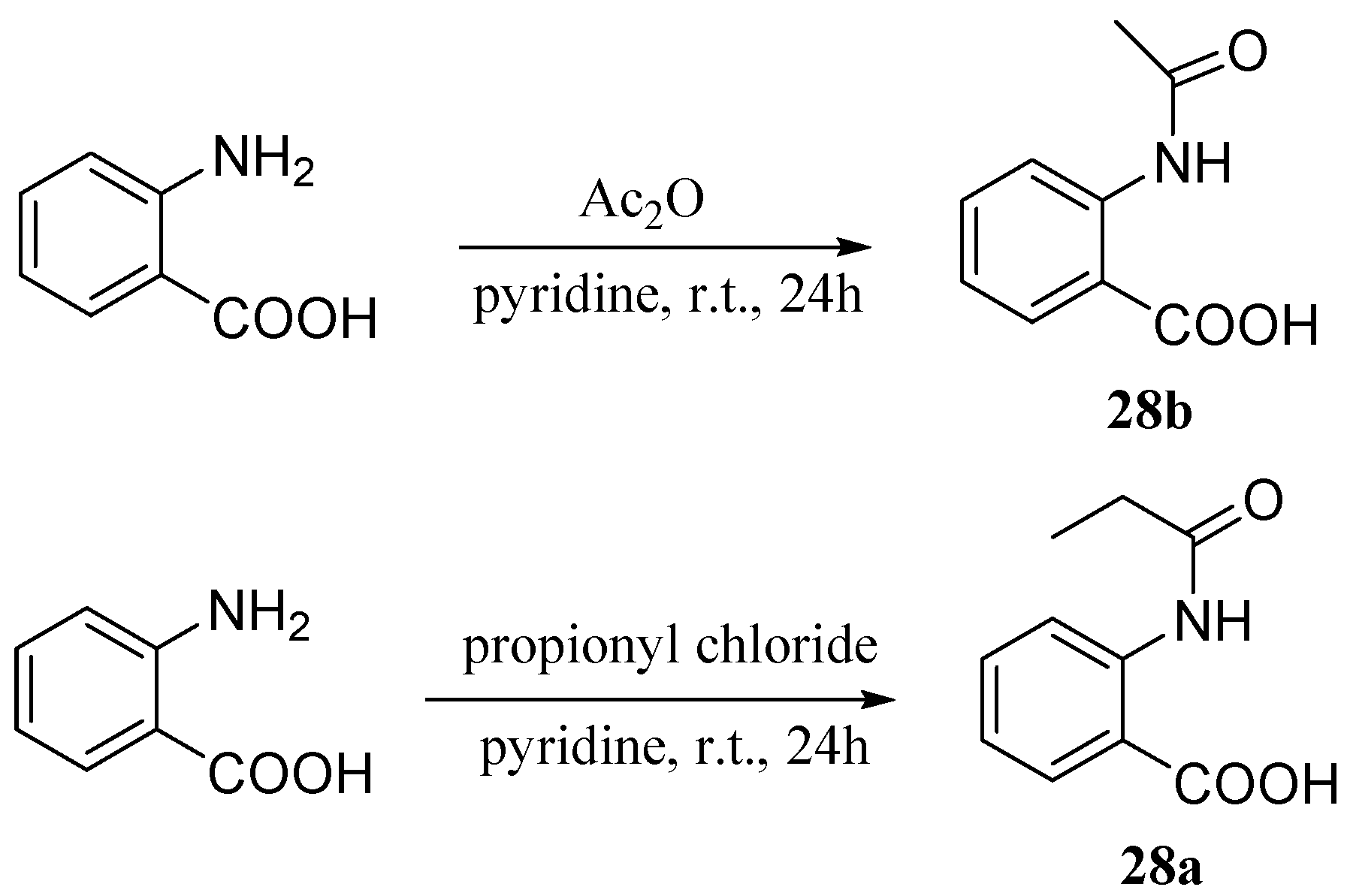

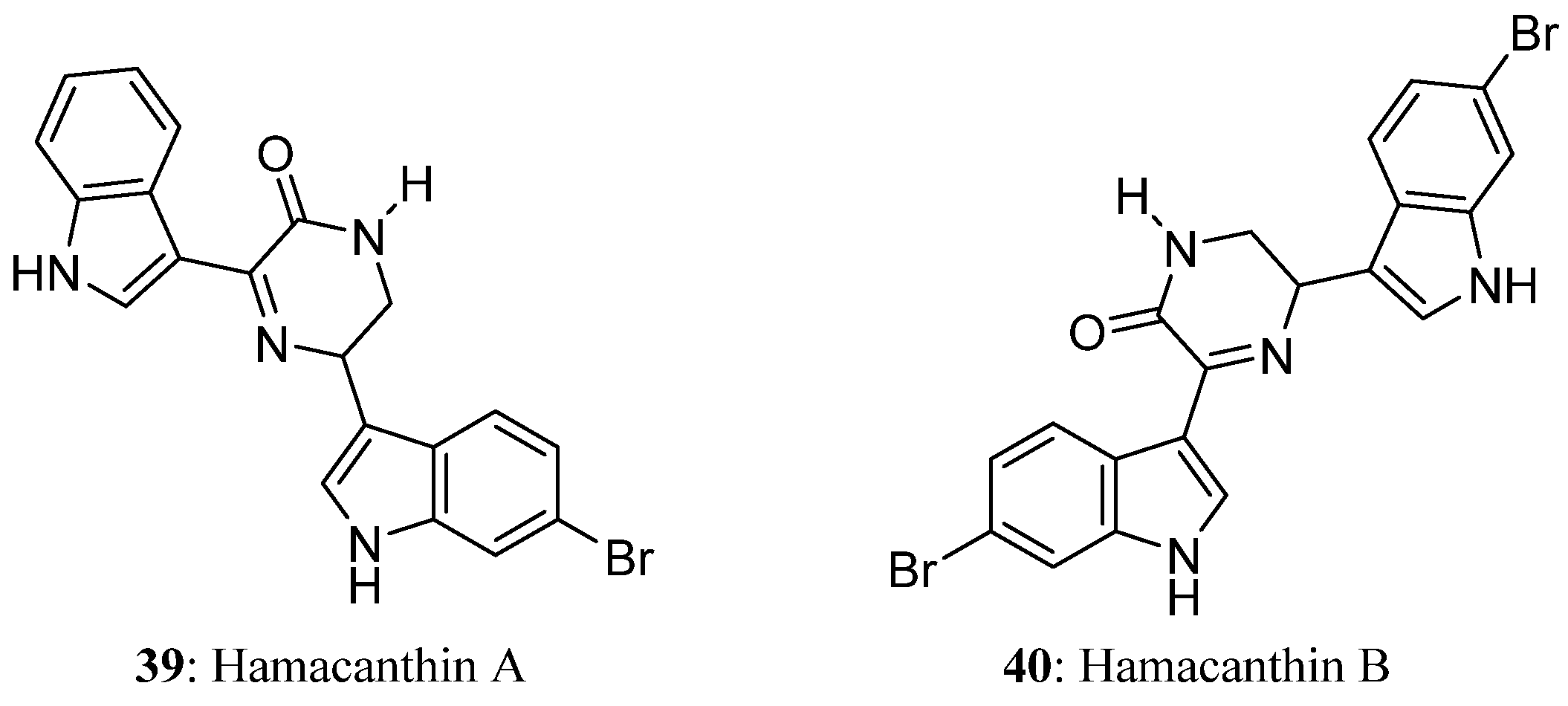


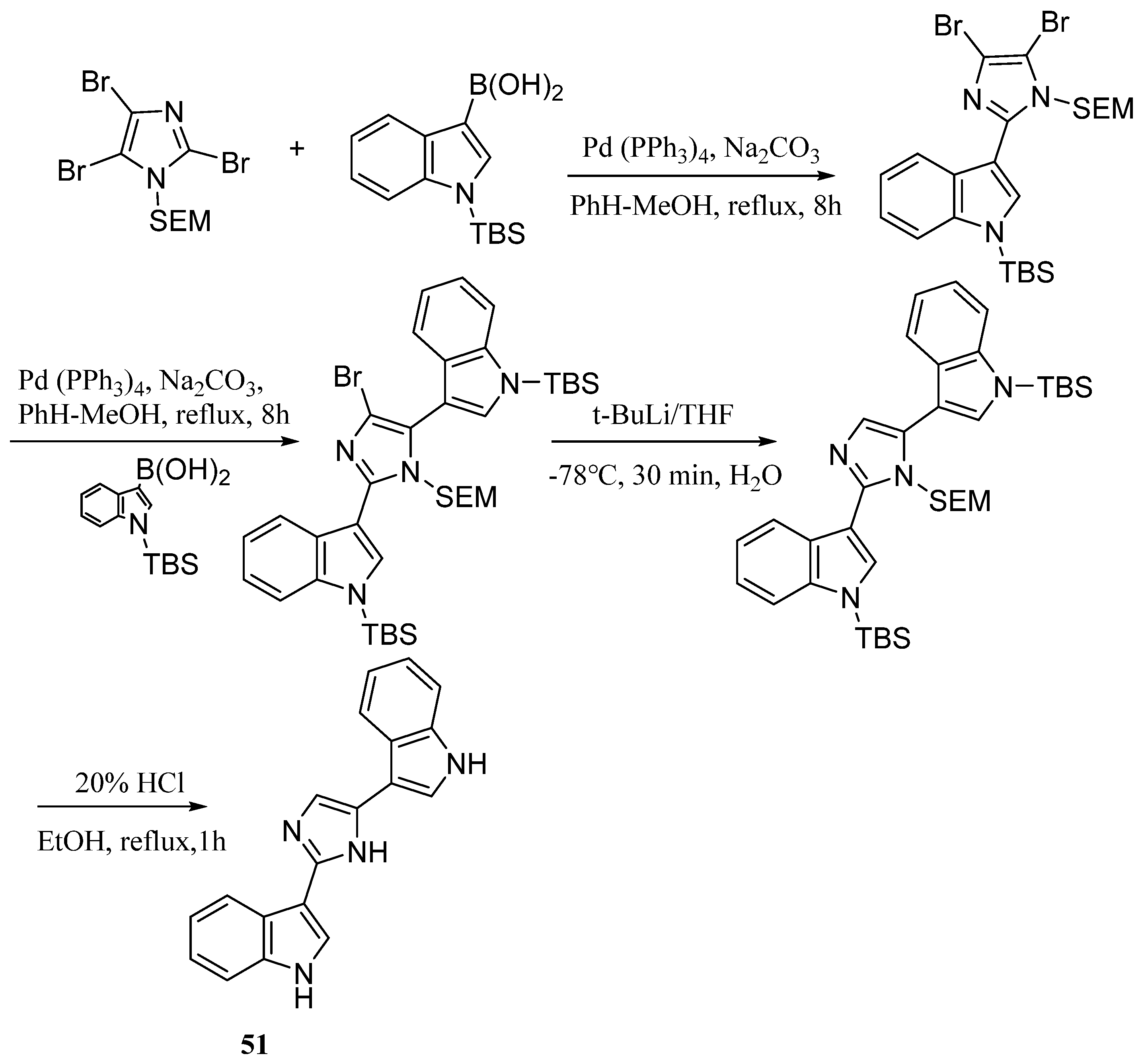

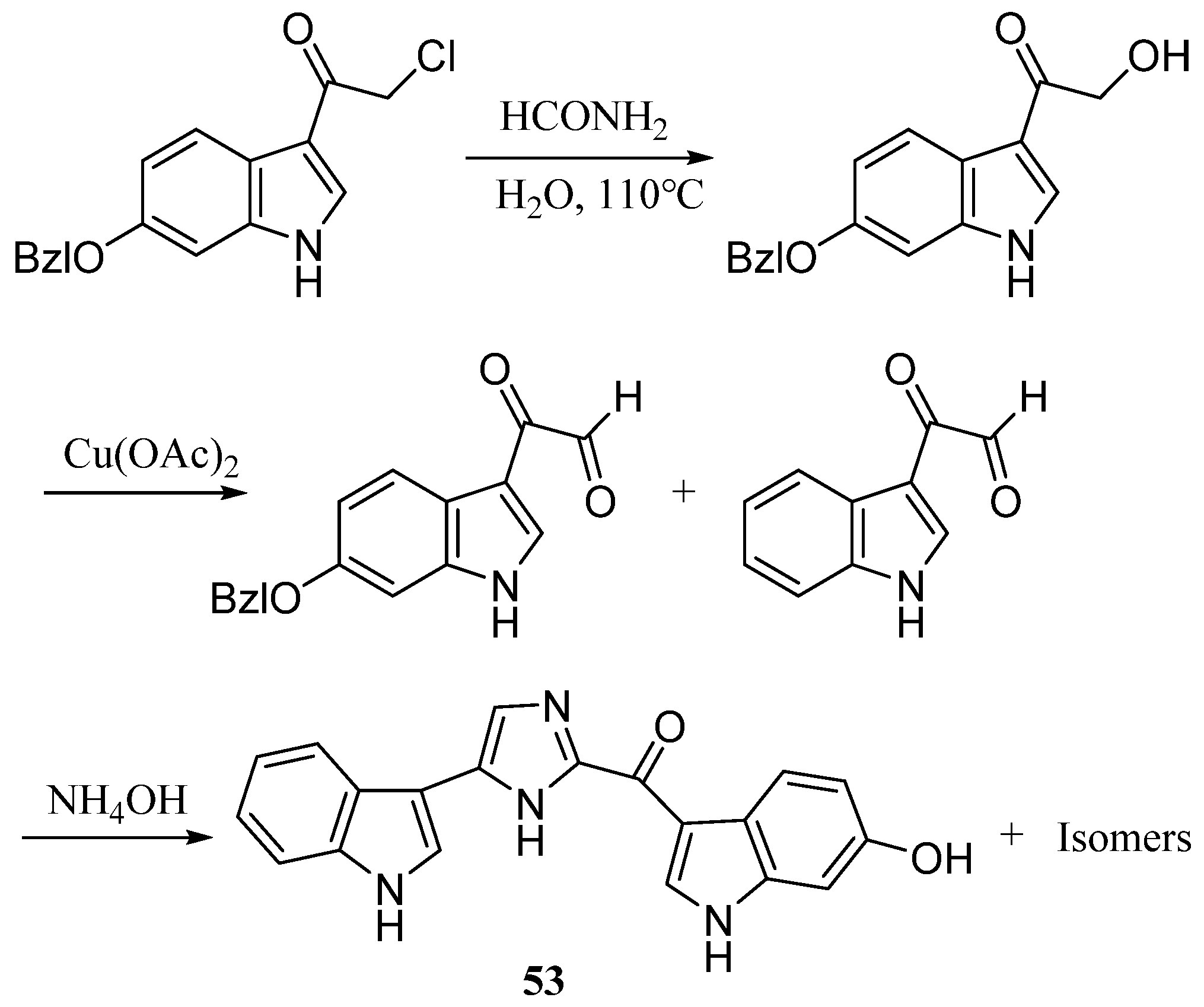
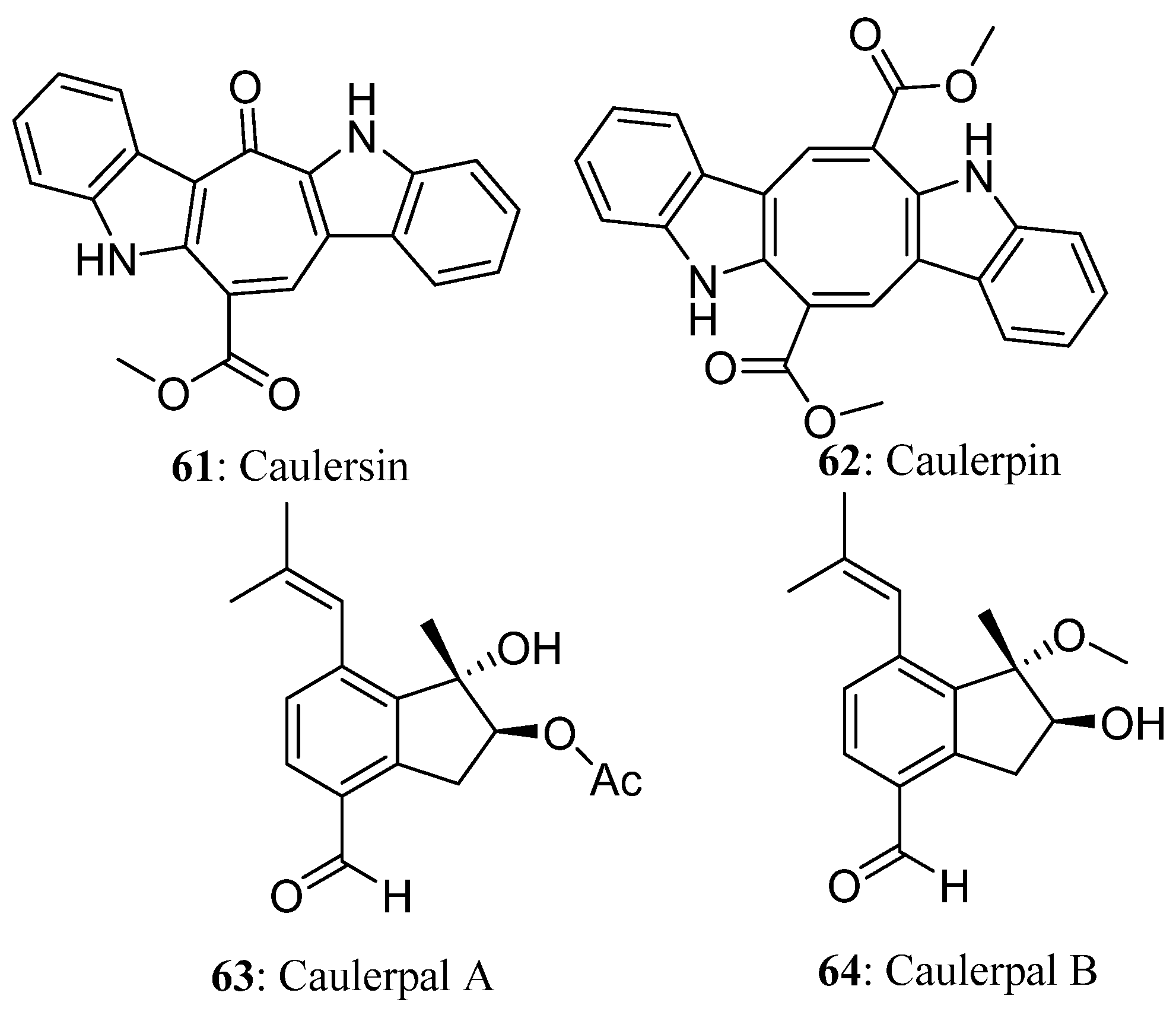

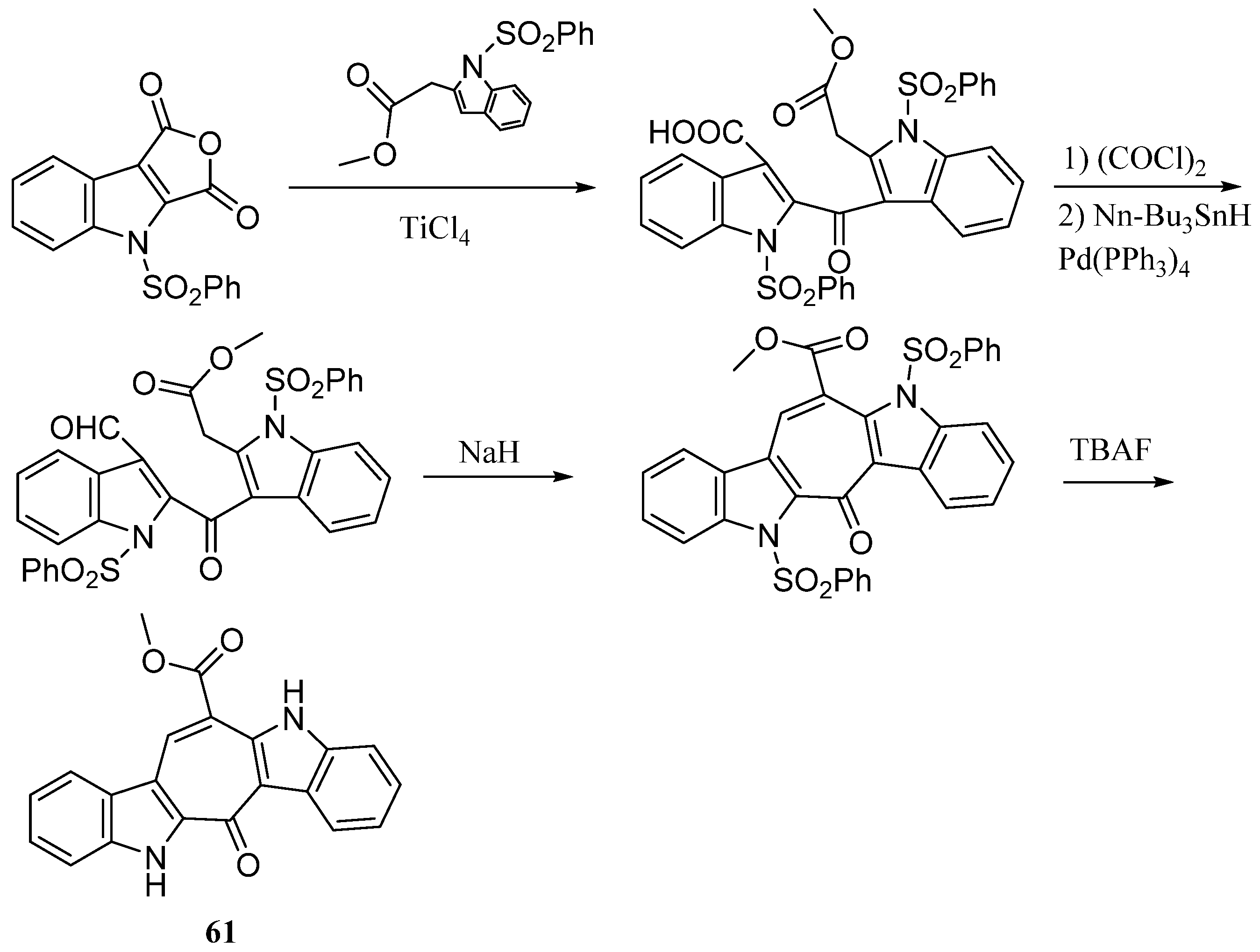

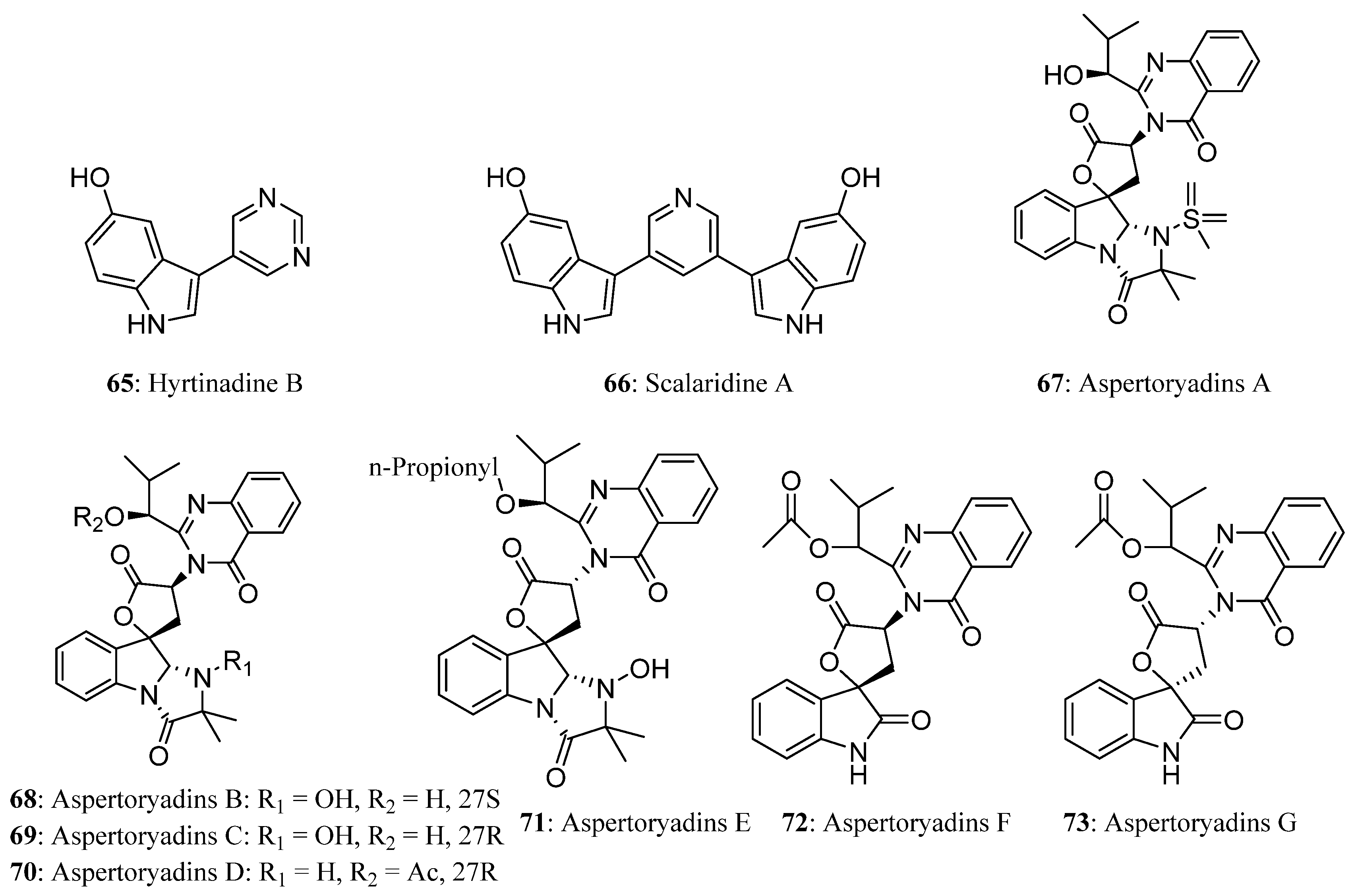
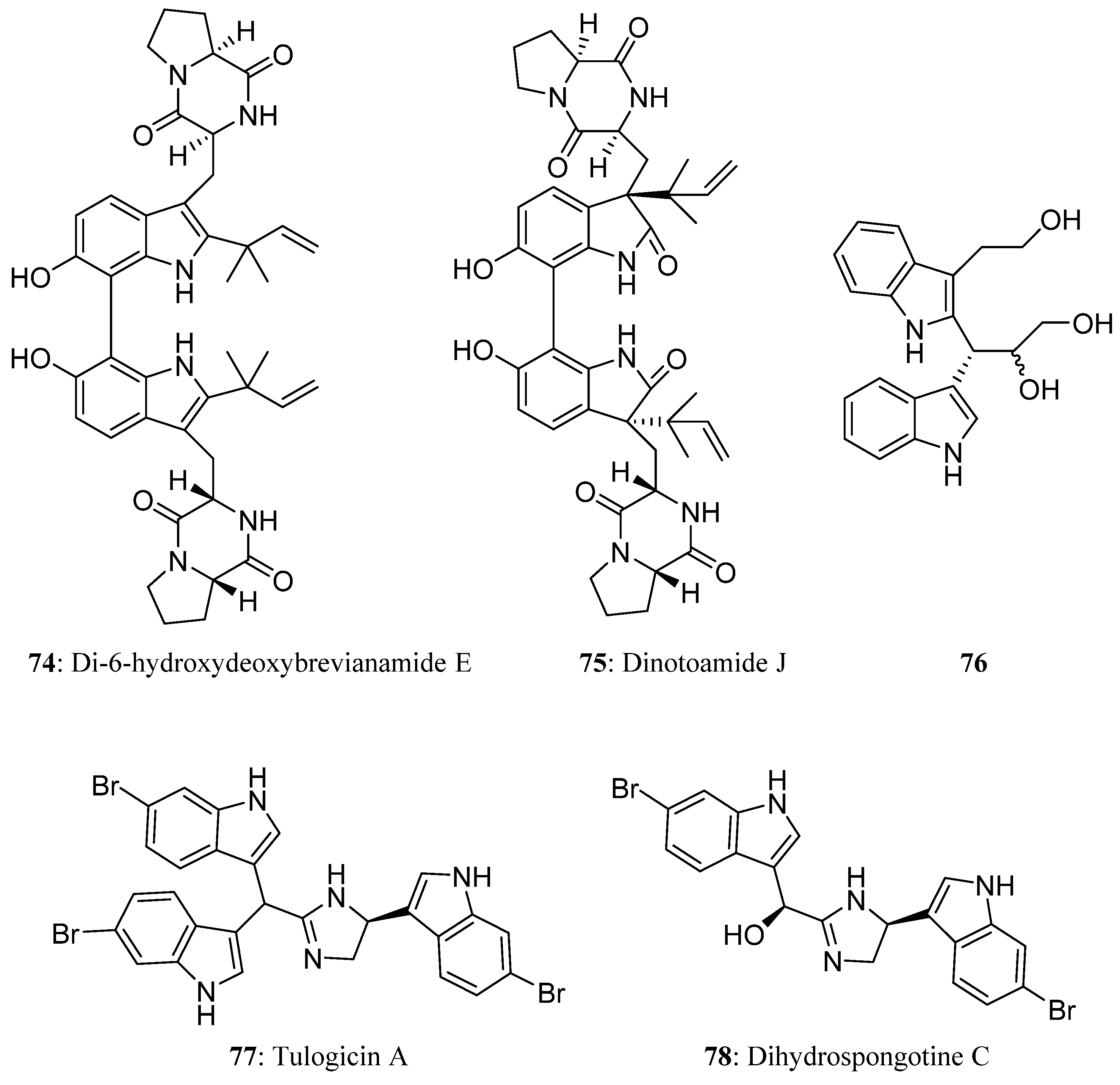
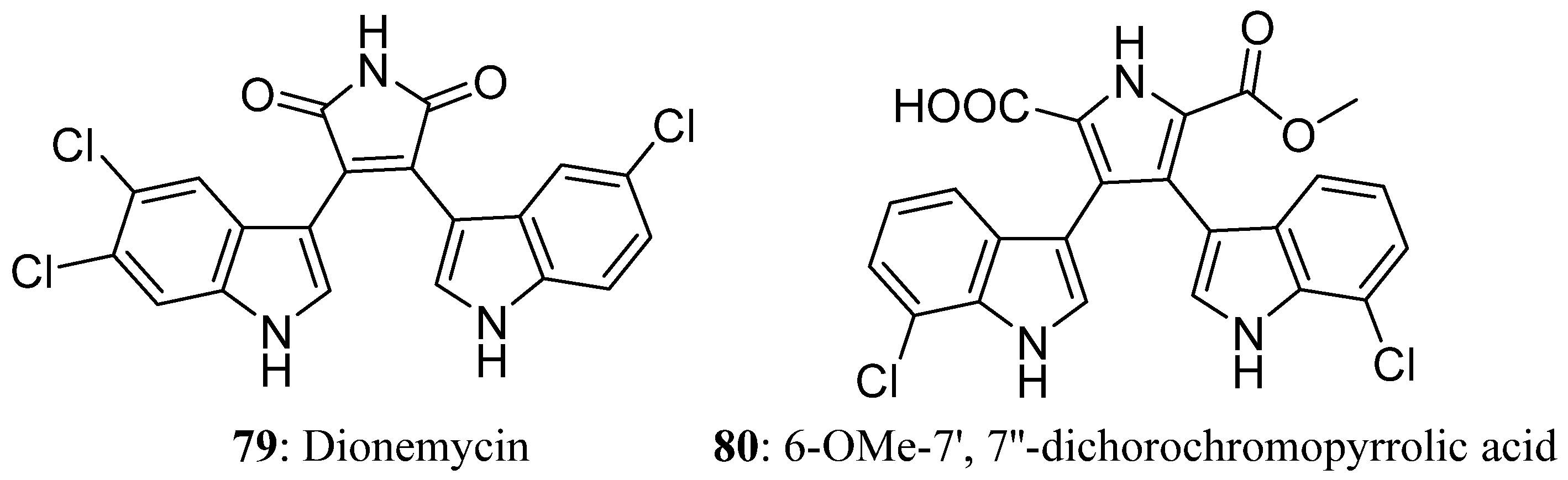
| Compound | Cell Line (GI50 (μM)) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| MDA-MB-231 | A549 | HT-29 | |
| 26a | 25 | 30 | 28 |
| 26b | 90 | 100 | 85 |
| 26c | 42 | 35 | 45 |
| Doxorubicin a | 0.30 | 0.35 | 0.40 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sun, H.; Sun, K.; Sun, J. Recent Advances of Marine Natural Indole Products in Chemical and Biological Aspects. Molecules 2023, 28, 2204. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28052204
Sun H, Sun K, Sun J. Recent Advances of Marine Natural Indole Products in Chemical and Biological Aspects. Molecules. 2023; 28(5):2204. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28052204
Chicago/Turabian StyleSun, Haoyi, Kangping Sun, and Jingyong Sun. 2023. "Recent Advances of Marine Natural Indole Products in Chemical and Biological Aspects" Molecules 28, no. 5: 2204. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28052204
APA StyleSun, H., Sun, K., & Sun, J. (2023). Recent Advances of Marine Natural Indole Products in Chemical and Biological Aspects. Molecules, 28(5), 2204. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28052204






