Advances on Hormones in Cosmetics: Illegal Addition Status, Sample Preparation, and Detection Technology
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Hormone Risk and Market Status in Cosmetics
2.1. Hormones and Their Risks in Cosmetics
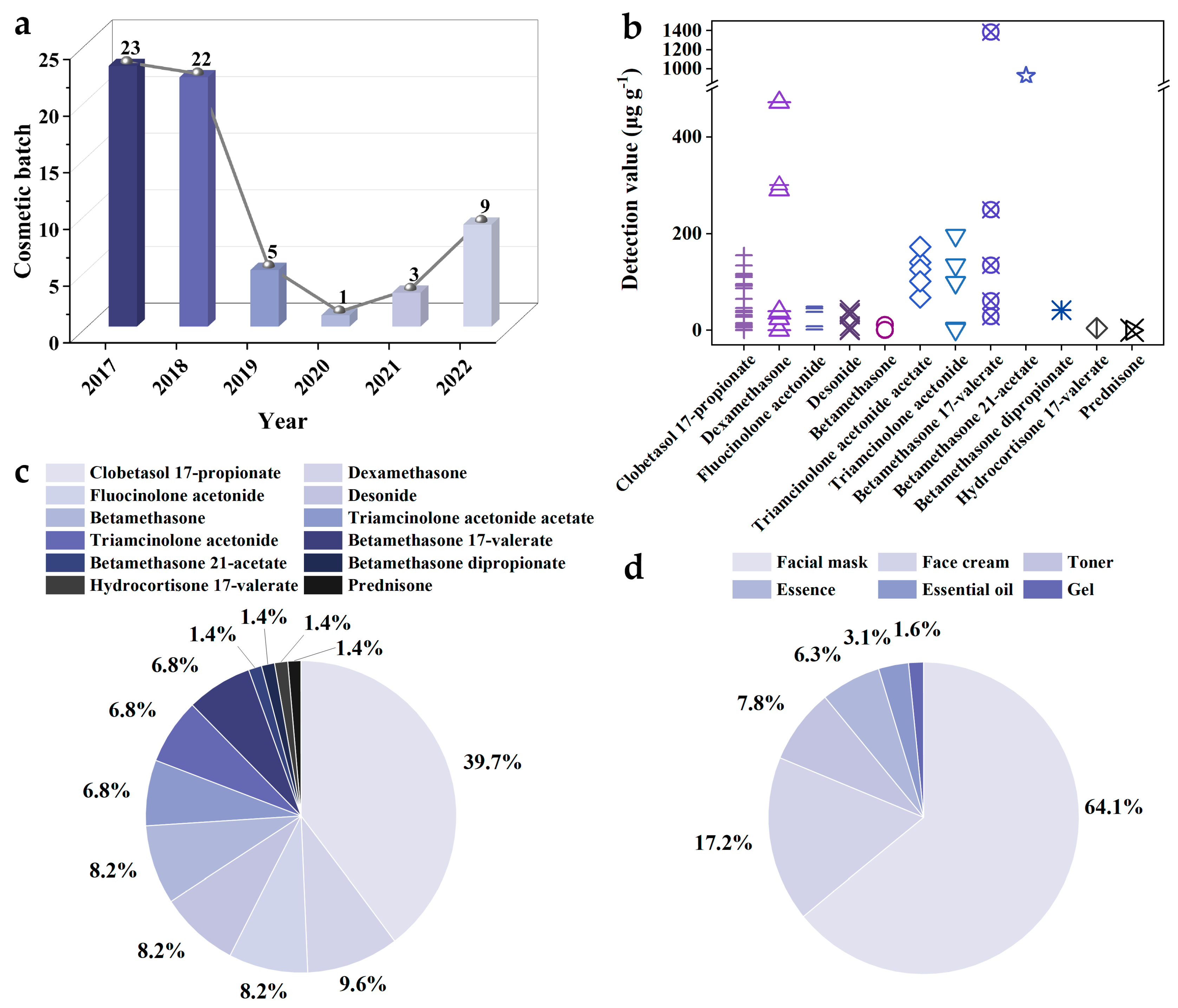
2.2. Hormone Addition Status in Cosmetics
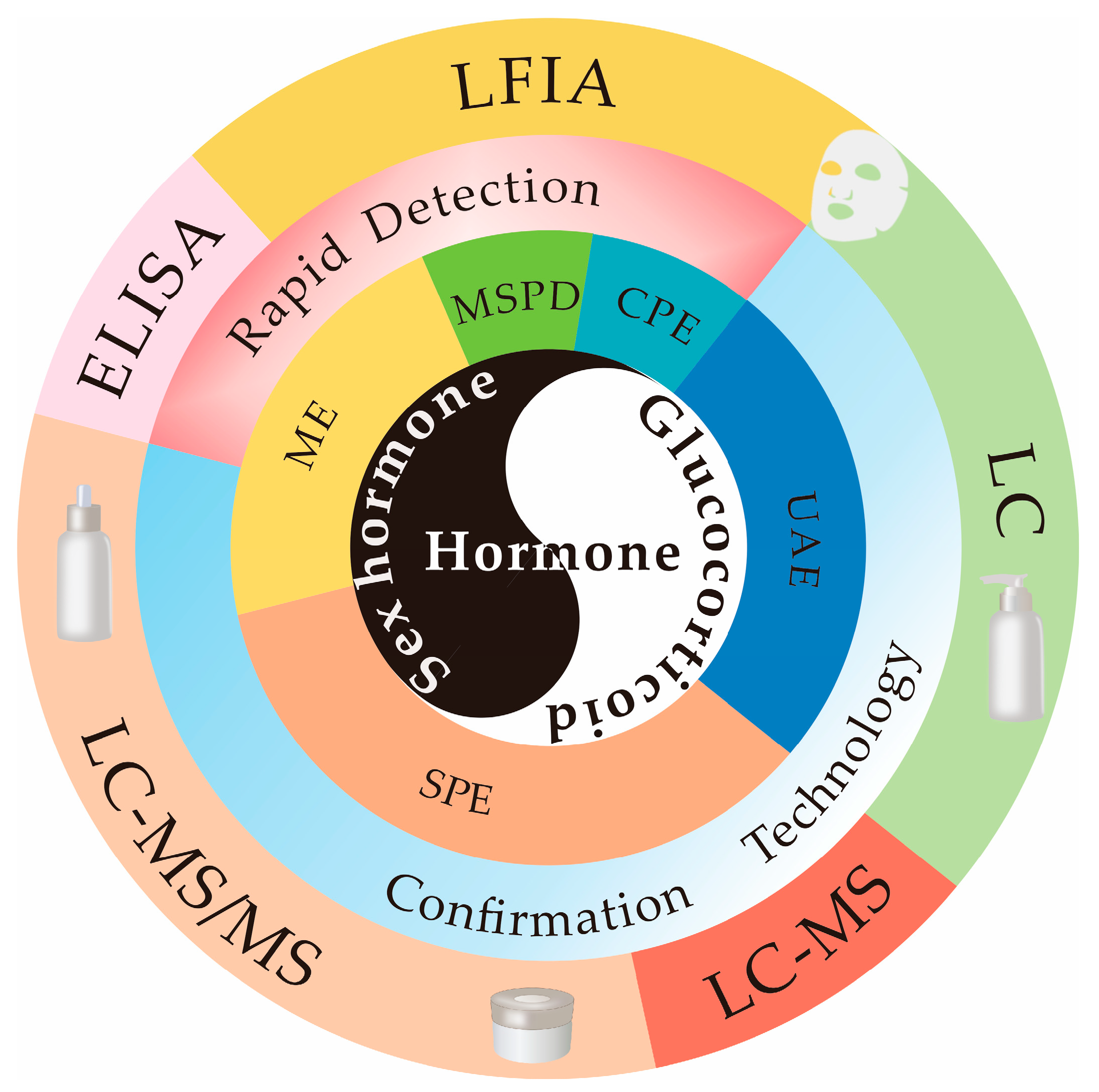
3. Cosmetic Sample Preparation Technologies
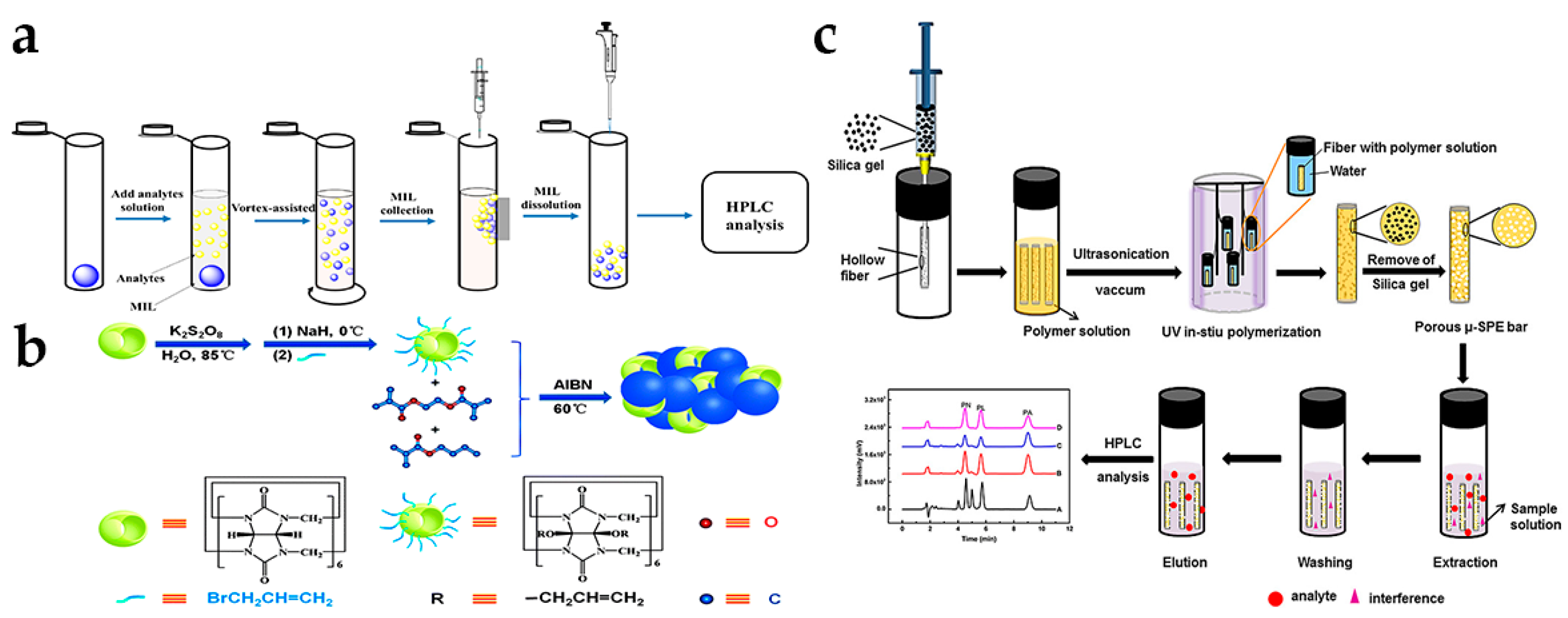
3.1. UAE
3.2. SPE
3.3. ME
3.4. Other Pretreatment Technologies
4. Analytical Technologies for Hormones in Cosmetics
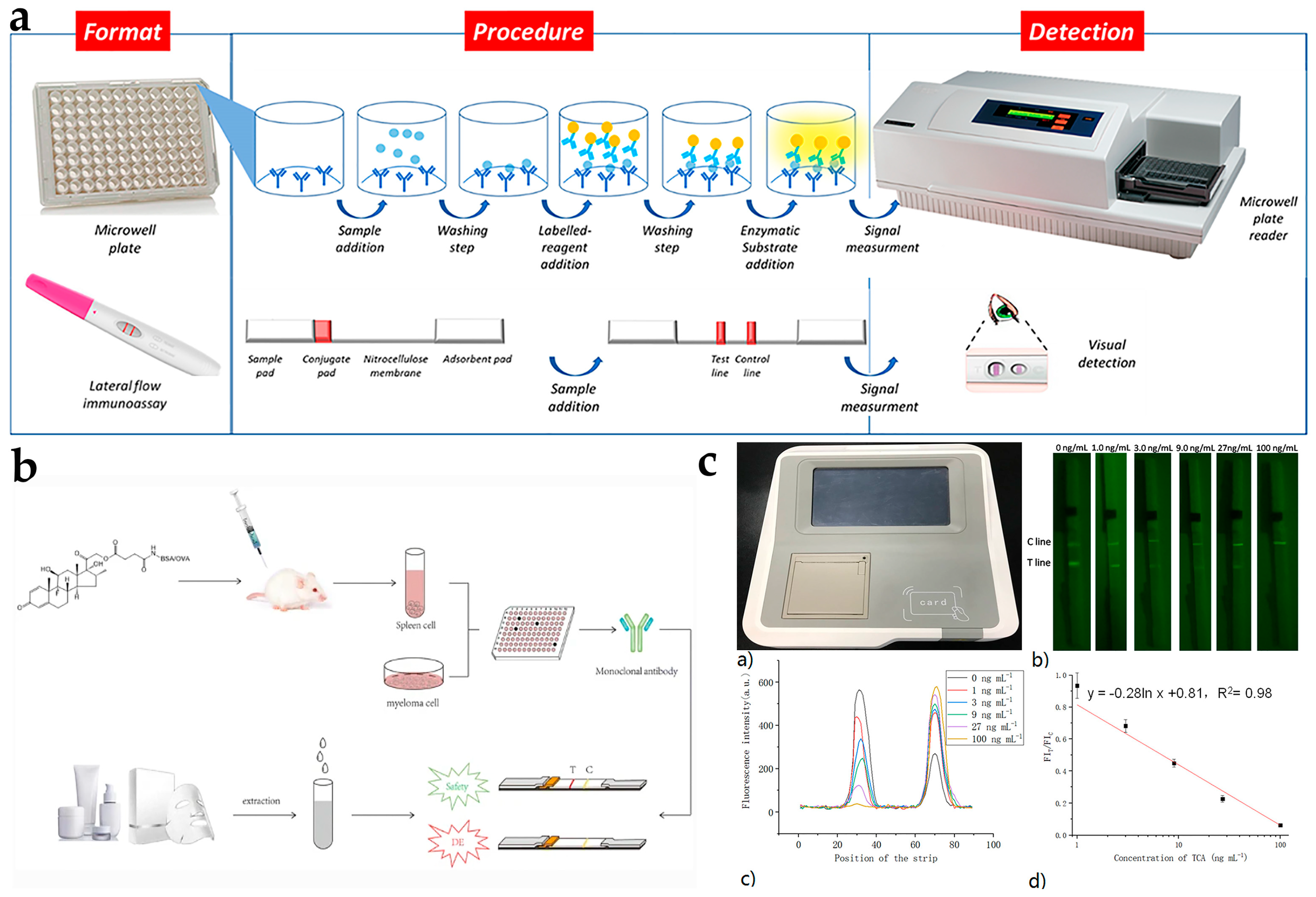
4.1. Confirmation Technologies
4.2. Rapid Detection Methods
5. Conclusions and Outlooks
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Su, Z.; Luo, F.Y.; Pei, X.R.; Zhang, F.L.; Xing, S.X.; Wang, G.L. Final Publication of the “Regulations on the Supervision and Administration of Cosmetics” and New Prospectives of Cosmetic Science in China. Cosmetics 2020, 7, 98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Xie, S.S.; Wu, Y.C.; Liang, Q.W.; Xie, X.T.; Luo, Z.H.; Liang, Z.H.; Liu, M.S. Research progress of detection technology for illegal addition of prohibited substances in cosmetics. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2020, 559, 012030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhan, J.; Ni, M.L.; Zhao, H.Y.; Ge, X.M.; He, X.Y.; Yin, J.Y.; Yu, X.J.; Fan, Y.M.; Huang, Z.Q. Multiresidue analysis of 59 nonallowed substances and other contaminants in cosmetics. J. Sep. Sci. 2014, 37, 3684–3690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gbetoh, M.H.; Amyot, M. Mercury, hydroquinone and clobetasol propionate in skin lightening products in West Africa and Canada. Environ. Res. 2016, 150, 403–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, S.; Zhou, P.; Hu, Y.; Li, G.; Xia, L. Triphenylbenzene functionalized polyhedral oligomeric silsesquioxane fluorescence sensor for the selective analysis of trace nitrofurazone in aquatic product and cosmetics. Anal. Chim. Acta 2022, 1225, 340249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, C.; Li, B.; Liu, M.; Mao, S. Demand, status, and prospect of antibiotics detection in the environment. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2022, 369, 132383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pratiwi, R.; Auliya As, N.N.; Yusar, R.F.; Shofwan, A.A. Analysis of Prohibited and Restricted Ingredients in Cosmetics. Cosmetics 2022, 9, 87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abad-Gil, L.; Lucas-S´anchez, S.; Gismera, M.J.; Sevilla, M.T.; Procopio, J.R. HPLC method with electrochemical detection on gold electrode for simultaneous determination of different antimicrobial agents in cosmetics. Microchem. J. 2022, 182, 107881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ingawale, D.K.; Mandlik, S.K. New insights into the novel anti-inflammatory mode of action of glucocorticoids. Immunopharmacol. Immunotoxicol. 2020, 42, 59–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mygind, N.; Andersson, M. Topical glucocorticosteroids in rhinitis: Clinical aspects. Acta Oto-Laryngol. 2006, 126, 1022–1029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.C.; Jin, J.K.; Qian, C.; Lou, J.N.; Lin, J.; Xu, A.K.; Xia, K.S.; Jin, L.B.; Liu, B.; Tao, H.M.; et al. Estrogen/ER in anti-tumor immunity regulation to tumor cell and tumor microenvironment. Cancer Cell Int. 2021, 21, 295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bleecker, E.R.; Menzies-Gow, A.N.; Price, D.B.; Bourdin, A.; Sweet, S.; Martin, A.L.; Alacqua, M.; Tran, T.N. Systematic Literature Review of Systemic Corticosteroid Use for Asthma Management. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2020, 201, 276–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tony, F.A.; Soliman, Y.M.A.; Salem, H.A. Effect of Oral Methyl Prednisolone on Different Radiological Patterns of Hypersensitivity Pneumonitis. J. Asthma Allergy 2021, 14, 501–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexander, T.; Maxim, E.; Cardwell, L.A.; Chawla, A.; Feldman, S.R. Prescriptions for atopic dermatitis: Oral corticosteroids remain commonplace. J. Dermatolog. Treat. 2018, 29, 238–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, Z.X.; Li, G.K. Current trends in sample preparation for cosmetic analysis. J. Sep. Sci. 2017, 40, 152–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Celeiro, M.; Garcia-Jares, C.; Llompart, M.; Lores, M. Recent Advances in Sample Preparation for Cosmetics and Personal Care Products Analysis. Molecules 2021, 26, 4900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabaleiro, N.; de la Calle, I.; Bendicho, C.; Lavilla, I. Current trends in liquid–liquid and solid–liquid extraction for cosmetic analysis: A review. Anal. Methods 2013, 5, 323–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grau, J.; Benede, J.L.; Chisvert, A. Use of Nanomaterial-Based (Micro)Extraction Techniques for the Determination of Cosmetic-Related Compounds. Molecules 2020, 25, 2586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lores, M.; Llompart, M.; Alvarez-Rivera, G.; Guerra, E.; Vila, M.; Celeiro, M.; Lamas, J.P.; Garcia-Jares, C. Positive lists of cosmetic ingredients: Analytical methodology for regulatory and safety controls-A review. Anal. Chim. Acta 2016, 915, 1–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aziz, A.A.; Nordin, F.N.M.; Zakaria, Z.; Abu Bakar, N.K. A systematic literature review on the current detection tools for authentication analysis of cosmetic ingredients. J. Cosmet. Dermatol. 2022, 21, 71–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abedi, G.; Talebpour, Z.; Jamechenarboo, F. The survey of analytical methods for sample preparation and analysis of fragrances in cosmetics and personal care products. Trends Anal. Chem. 2018, 102, 41–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabaleiro, N.; de la Calle, I.; Bendicho, C.; Lavilla, I. An overview of sample preparation for the determination of parabens in cosmetics. Trends Anal. Chem. 2014, 57, 34–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guerra, E.; Llompart, M.; Carmen, G.J. Analysis of Dyes in Cosmetics: Challenges and Recent Developments. Cosmetics 2018, 5, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin-Pozo, L.; Gomez-Regalado, M.D.C.; Moscoso-Ruiz, I.; Zafra-Gomez, A. Analytical methods for the determination of endocrine disrupting chemicals in cosmetics and personal care products: A review. Talanta 2021, 234, 122642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zangheri, M.; Calabretta, M.M.; Calabria, D.; Fiori, J.; Guardigli, M.; Michelini, E.; Melandri, S.; Maris, A.; Mirasoli, M.; Evangelisti, L. Immunological Analytical Techniques for Cosmetics Quality Control and Process Monitoring. Processes 2021, 9, 1982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahadir, E.B.; Sezginturk, M.K. Electrochemical biosensors for hormone analyses. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2015, 68, 62–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mpupa, A.; Selahle, S.K.; Mizaikoff, B.; Nomngongo, P.N. Recent Advances in Solid-Phase Extraction (SPE) Based on Molecularly Imprinted Polymers (MIPs) for Analysis of Hormones. Chemosensors 2021, 9, 151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arif, S.; Ata, S. Stability-indicating HPLC-DAD assay for simultaneous quantification of hydrocortisone 21 acetate, dexamethasone, and fluocinolone acetonide in cosmetics. Open Chem. 2020, 18, 962–973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giaccone, V.; Polizzotto, G.; Macaluso, A.; Cammilleri, G.; Ferrantelli, V. Determination of Ten Corticosteroids in Illegal Cosmetic Products by a Simple, Rapid, and High-Performance LC-MS/MS Method. Int. J. Anal. Chem. 2017, 2017, 3531649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niculet, E.; Bobeica, C.; Tatu, A.L. Glucocorticoid-Induced Skin Atrophy: The Old and the New. Clin. Cosmet. Investig. Dermatol. 2020, 13, 1041–1050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Timmermans, S.; Souffriau, J.; Libert, C. A General Introduction to Glucocorticoid Biology. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 1545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciampaglia, W.; Cognigni, G.E. Clinical use of progesterone in infertility and assisted reproduction. Acta Obstet. Gynecol. Scand. 2015, 94, 17–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taneja, A.; Chopra, I.; Kaur, H.; Naik, S.S.; Aggarwal, R.; Sachdeva, E.; Kaur, P. Successful management of abnormal uterine bleeding from uterine arteriovenous malformations with progesterone in postabortal patients. J. Obstet. Gynaecol. Res. 2019, 45, 1114–1117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, P.Q.; Xu, X.Y.; Xian, L.; Ge, Y.H.; Luo, Z.M.; Du, W.; Jing, W.H.; Zeng, A.G.; Chang, C.; Fu, Q. Development of molecularly imprinted column-on line-two dimensional liquid chromatography for rapidly and selectively monitoring estradiol in cosmetics. Talanta 2016, 161, 830–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vinatoru, M.; Mason, T.J.; Calinescu, I. Ultrasonically assisted extraction (UAE) and microwave assisted extraction (MAE) of functional compounds from plant materials. Trends Anal. Chem. 2017, 97, 159–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, C.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, H.; Dzah, C.S.; Zandile, M.; Duan, Y.; Ma, H.; Luo, X. Advances in ultrasound assisted extraction of bioactive compounds from cash crops—A review. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2018, 48, 538–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, D.P.; Zheng, J.; Zhou, Y.; Li, Y.; Li, S.; Li, H.B. Ultrasound-assisted extraction of natural antioxidants from the flower of Limonium sinuatum: Optimization and comparison with conventional methods. Food Chem. 2017, 217, 552–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chemat, F.; Rombaut, N.; Sicaire, A.G.; Meullemiestre, A.; Fabiano-Tixier, A.S.; Abert-Vian, M. Ultrasound assisted extraction of food and natural products. Mechanisms, techniques, combinations, protocols and applications. A review. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2017, 34, 540–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiori, J.; Andrisano, V. LC-MS method for the simultaneous determination of six glucocorticoids in pharmaceutical formulations and counterfeit cosmetic products. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2014, 91, 185–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golubovic, J.B.; Otasevic, B.M.; Protic, A.D.; Stankovic, A.M.; Zecevic, M.L. Liquid chromatography/tandem mass spectrometry for simultaneous determination of undeclared corticosteroids in cosmetic creams. Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 2015, 29, 2319–2327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.S.; Jin, Y.; Zhang, J.L.; Ren, Y.; Jia, Z.X. Simultaneous determination of seven prohibited substances in cosmetic products by liquid chromatography–tandem mass spectrometry. Chin. Chem. Lett. 2013, 24, 509–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.J.; Ni, X.J.; Cao, Y.H.; Zhuo, X.L.; Yang, X.X.; Cao, G.Q. Amphiphilic polymeric micelle as pseudostationary phase in electrokinetic chromatography for analysis of eight corticosteroids in cosmetics. Electrophoresis 2014, 35, 827–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Azzouz, A.; Kailasa, S.K.; Lee, S.S.; Rascon, A.J.; Ballesteros, E.; Zhang, M.; Kim, K.H. Review of nanomaterials as sorbents in solid-phase extraction for environmental samples. Trends Anal. Chem. 2018, 108, 347–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, F.N.; Wang, S.S.; She, Y.X.; Zhang, C.; Zheng, L.F.; Jin, M.J.; Shao, H.; Jin, F.; Du, X.W.; Wang, J. Subcritical water extraction combined with molecular imprinting technology for sample preparation in the detection of triazine herbicides. J. Chromatogr. A 2017, 1515, 17–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Priscilla, R.B.; Termopoli, V. Metal-Organic Frameworks in Solid-Phase Extraction Procedures for Environmental and Food Analyses. Chromatographia 2019, 82, 1191–1205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, H.L.; Li, N.; Lin, C.; Wang, X.; Zhao, R.S. Recent application of magnetic solid phase extraction for food safety analysis. Trends Anal. Chem. 2019, 120, 115632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capriotti, A.L.; Cavaliere, C.; Barbera, G.L.; Montone, C.M.; Piovesana, S.; Laganà, A. Recent Applications of Magnetic Solid-phase Extraction for Sample Preparation. Chromatographia 2019, 82, 1251–1274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arabi, M.; Ostovan, A.; Bagheri, A.R.; Guo, X.T.; Wang, L.Y.; Li, J.H.; Wang, X.Y.; Li, B.W.; Chen, L.X. Strategies of molecular imprinting-based solid-phase extraction prior to chromatographic analysis. Trends Anal. Chem. 2020, 128, 115923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, F.N.; She, Y.X.; Zhang, C.; Wang, S.S.; Du, X.W.; Jin, F.; Jin, M.J.; Shao, H.; Zheng, L.F.; Wang, J. Selective determination of chloramphenicol in milk samples by the solid-phase extraction based on dummy molecularly imprinted polymer. Food Anal. Methods 2017, 10, 2566–2575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, F.N.; She, Y.X.; Zhang, C.; Cao, X.L.; Wang, S.S.; Zheng, L.F.; Jin, M.J.; Shao, H.; Jin, F.; Wang, J. Selective solid-phase extraction based on molecularly imprinted technology for the simultaneous determination of 20 triazole pesticides in cucumber samples using high-performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. B 2017, 1064, 143–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Yan, M.; Feng, G.; Ying, Y.; Chen, G.; Shao, Y.; She, Y.; Wang, M.; Sun, J.; Zheng, L.; et al. An overview on molecular imprinted polymers combined with surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy chemical sensors toward analytical applications. Talanta 2021, 225, 122031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, F.; Li, X.Y.; Li, J.J.; Zhu, C.; Liu, M.; Wu, Z.Y.; Liu, L.; Tan, X.C.; Lei, F.H. Preparation and application of a molecular capture for safety detection of cosmetics based on surface imprinting and multi-walled carbon nanotubes. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2018, 527, 124–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meng, X.; Bai, H.; Guo, T.; Niu, Z.; Ma, Q. Broad screening of illicit ingredients in cosmetics using ultra-high-performance liquid chromatography-hybrid quadrupole-Orbitrap mass spectrometry with customized accurate-mass database and mass spectral library. J. Chromatogr. A 2017, 1528, 61–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Büyüktiryaki, S.; Keçili, R.; Hussain, C.M. Functionalized nanomaterials in dispersive solid phase extraction: Advances & prospects. Trends Anal. Chem. 2020, 127, 115893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.H.; Zhao, F.N.; Zhang, C.; Abd, E.I.A.M.; Baranenko, D.A.; Hacimuftuoglu, A.; She, Y.X. Assessment of magnetic core-shell mesoporous molecularly imprinted polymers for selective recognition of triazoles residual levels in cucumber. J. Chromatogr. B 2019, 1132, 121811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hemmati, M.; Rajabi, M.; Asghari, A. Magnetic nanoparticle based solid-phase extraction of heavy metal ions: A review on recent advances. Microchim. Acta 2018, 185, 160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.; Zhao, J.; Liang, N.; Zhao, L.S. Deep eutectic solvent-based magnetic colloidal gel assisted magnetic solid-phase extraction: A simple and rapid method for the determination of sex hormones in cosmetic skin care toners. Chemosphere 2020, 255, 127004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Chen, X.; Xia, L.; Xiao, X.; Li, G. Magnetic metal-organic frameworks-101 functionalized with graphite-like carbon nitride for the efficient enrichment of glucocorticoids in cosmetics. J. Chromatogr. A 2019, 1606, 460382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, W.; Zhang, B.L.; Guo, P.Q.; Chen, G.N.; Chang, C.; Fu, Q. Facile preparation of magnetic molecularly imprinted polymers for the selective extraction and determination of dexamethasone in skincare cosmetics using HPLC. J. Sep. Sci. 2018, 41, 2441–2452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Li, X.Y.; Li, J.J.; Wu, Z.Y.; Wang, F.; Liu, L.; Tan, X.C.; Lei, F.H. Selective separation and determination of glucocorticoids in cosmetics using dual-template magnetic molecularly imprinted polymers and HPLC. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2017, 504, 124–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jalili, V.; Barkhordari, A.; Ghiasvand, A. New extraction media in microextraction techniques. A review of reviews. Microchem. J. 2020, 153, 104386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, L.Q.; Cao, J. Modern microextraction techniques for natural products. Electrophoresis 2021, 42, 219–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chisvert, A.; Cárdenas, S.; Lucena, R. Dispersive micro-solid phase extraction. Trends Anal. Chem. 2019, 112, 226–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcinkowska, R.; Konieczna, K.; Marcinkowski, Ł.; Namieśnik, J.; Kloskowski, A. Application of ionic liquids in microextraction techniques: Current trends and future perspectives. Trends Anal. Chem. 2019, 119, 115614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, M.Q.; Sun, S.; Li, N.; Zhang, D.H.; Chen, M.Y.; Zhang, H.Q. Extraction and determination of hormones in cosmetics by homogeneous ionic liquid microextraction high-performance liquid chromatography. J. Sep. Sci. 2012, 35, 2032–2039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, X.; Xu, X.; Liu, Z.; Xue, S.; Zhang, L. Novel functionalized magnetic ionic liquid green separation technology coupled with high performance liquid chromatography: A rapid approach for determination of estrogens in milk and cosmetics. Talanta 2020, 209, 120542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, W.; Wang, Y.T.; Zhou, B.S.; Xu, Y.; Feng, Y.Q. Determination of Sexual Hormones in Liquid Cosmetics by Polymer Monolith Microextraction Coupled with High Performance Liquid Chromatography. Chin. J. Anal. Chem. 2007, 35, 681–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.F.; Song, N.Z.; Zheng, H.J.; Lv, X.J.; Hu, B.; Jia, Q. Preparation of an allyloxy-cucurbit[6]uril-modified polymer monolithic column for microextraction of estrogens in cosmetics. New J. Chem. 2015, 39, 9714–9721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, A.; Muhammad, T.; Aihebaier, S.; Muhammad, I.; Wu, B.; Ge, J.; Ayupbek, A. In-situ preparation of porous monolithic polymer inside hollow fiber as a micro-solid phase extraction device for glucocorticoids in cosmetics. J. Sep. Sci. 2020, 43, 936–945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barker, S.A. Matrix solid phase dispersion (MSPD). J. Biochem. Biophys. Methods 2007, 70, 151–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, X.J.; Chen, W.B. A Review on the Recent Progress in Matrix Solid Phase Dispersion. Molecules 2018, 23, 2767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, P.Q.; Chen, G.N.; Shu, H.; Li, P.; Yu, P.; Chang, C.; Wang, Y.T.; Fu, Q. Monodisperse molecularly imprinted microsphere cartridges coupled with HPLC for selective analysis of dexamethasone and hydrocortisone in cosmetics by using matrix solid-phase dispersion. Anal. Methods 2019, 11, 3687–3696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mortada, W.I. Recent developments and applications of cloud point extraction: A critical review. Microchem. J. 2020, 157, 105055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, X.H.; Chen, X.G.; Xu, X.F.; Li, G.K. Co-precipitation assisted cloud point extraction coupled with high performance liquid chromatography for the determination of estrogens in water and cosmetic samples. Anal. Methods 2013, 5, 6376–6381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- den Uijl, M.J.; Schoenmakers, P.J.; Pirok, B.W.J.; van Bommel, M.R. Recent applications of retention modelling in liquid chromatography. J. Sep. Sci. 2021, 44, 88–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanu, A.B. Recent developments in sample preparation techniques combined with high-performance liquid chromatography: A critical review. J. Chromatogr. A 2021, 1654, 462444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandes, C.; Lima, R.; Pinto, M.M.M.; Tiritan, M.E. Chromatographic supports for enantioselective liquid chromatography: Evolution and innovative trends. J. Chromatogr. A 2022, 1684, 463555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Gao, Y.; Zhong, D. Technologies to improve the sensitivity of existing chromatographic methods used for bioanalytical studies. Biomed. Chromatogr. 2020, 34, e4798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Yang, P.; Hou, X.D. Atomic spectrometry and atomic mass spectrometry in bioanalytical chemistry. Appl. Spectrosc. Rev. 2019, 54, 180–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urban, P.L. Quantitative mass spectrometry: An overview. Philos. Trans. A. Math. Phys. Eng. Sci. 2016, 374, 20150382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, N.S.; Yoo, G.J.; Lee, J.H.; Park, H.G.; Cho, S.; Shin, D.W.; Kim, Y.; Baek, S.Y. Determination of 43 prohibited glucocorticoids in cosmetic products using a simultaneous LC-MS/MS method. Anal. Methods 2017, 9, 2104–2115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jian, L.H.; Yuan, X.Q.; Han, J.; Zheng, R.; Peng, X.S.; Wang, K. Screening for illegal addition of glucocorticoids in adulterated cosmetic products using ultra-performance liquid chromatography/tandem mass spectrometry with precursor ion scanning. Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 2021, 35, e8999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tong, S.S.; Liu, Q.W.; Li, Y.C.; Zhou, W.H.; Jia, Q.; Duan, T.C. Preparation of porous polymer monolithic column incorporated with graphene nanosheets for solid phase microextraction and enrichment of glucocorticoids. J. Chromatogr. A 2012, 1253, 22–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, S.W.; Wu, Z.Y.; Zhou, K.; Luo, L.; Xu, Z.L. Development of a competitive indirect ELISA for high-throughput screening of hydrocortisone in cosmetic sample. Food Agric. Immunol. 2019, 30, 594–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Guo, L.Q.; Yu, M.; Zhao, H. The application of a lateral flow immunographic assay to rapidly test for dexamethasone in commercial facial masks. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2019, 411, 5703–5710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.W.; Sun, Y.Y.; Sun, Y.M.; Wang, H.; Shen, Y.D. Semiquantitative immunochromatographic colorimetric biosensor for the detection of dexamethasone based on up-conversion fluorescent nanoparticles. Microchim. Acta 2020, 187, 447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.W.; Yao, T.Q.; Wang, S.F.; Feng, R.H.; Chen, L.Q.; Zhu, V.V.; Hu, G.P.; Zhang, H.; Yang, G.W. Upconversion luminescence nanoparticles-based immunochromatographic assay for quantitative detection of triamcinolone acetonide in cosmetics. Spectrochim. Acta A 2019, 214, 302–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gang, S.; Wu, C.; Ohmiya, Y.; Kaul, S.C.; Wadhwa, R. Express ELISA for detection of mortalin. BioTechniques 2019, 67, 166–171. [Google Scholar]
- Tian, S.; Zeng, K.; Yang, A.; Wang, Q.; Yang, M. A copper based enzyme-free fluorescence ELISA for HER2 detection. J. Immunol. Methods 2017, 451, 78–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayin, Q.; Huang, L.; Ren, C.; Fu, Y.; Ma, X.; Guo, J. Anti-SARS-CoV-2 IgG and IgM detection with a GMR based LFIA system. Talanta 2021, 227, 122207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Q.; Lu, D.; Zhang, G.Y.; Zhang, D.; Shi, X.B. Recent improvements in enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays based on nanomaterials. Talanta 2021, 223, 121722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, K.Y.; Peng, J.; Shan, S.; Liu, D.F.; Huang, Y.N.; Lai, W.H. Green Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay Based on the Single-Stranded Binding Protein-Assisted Aptamer for the Detection of Mycotoxin. Anal. Chem. 2020, 92, 8422–8426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ince, B.; Sezginturk, M.K. Lateral flow assays for viruses diagnosis: Up-to-date technology and future prospects. Trends Anal. Chem. 2022, 157, 116725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, J.C.; Chen, S.Q.; Guo, J.H.; Ma, X. Nanomaterial Labels in Lateral Flow Immunoassays for Point-of-Care-Testing. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2021, 60, 90–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsiao, W.W.; Le, T.N.; Pham, D.M.; Ko, H.H.; Chang, H.C.; Lee, C.C.; Sharma, N.; Lee, C.K.; Chiang, W.H. Recent Advances in Novel Lateral Flow Technologies for Detection of COVID-19. Biosensors 2021, 11, 295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, X.; Li, L.; Dong, Y.; Dong, W.; Cui, H.X.; Xia, C.; Xu, T.; Wang, C.Z.; Zhang, J.; Liu, T.T.; et al. Rapid Detection of Five Estrogens Added Illegally to Dietary Supplements by Combining TLC with Raman Imaging Microscope. Molecules 2022, 27, 2650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, F.W.; Wang, C.; Yu, H.; Guo, Y.H.; Cheng, Y.L.; Yao, W.R.; Xie, Y.F. Establishment of the thin-layer chromatography-surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy and chemometrics method for simultaneous identification of eleven illegal drugs in anti-rheumatic health food. Food Biosci. 2022, 49, 101842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duarte, L.C.; Baldo, T.A.; Silva-Neto, H.A.; Figueredo, F.; Janegitz, B.C.; Coltro, W.K.T. 3D printing of compact electrochemical cell for sequential analysis of steroid hormones. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2022, 364, 131850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehennaoui, S.; Poorahong, S.; Jimenez, G.C.; Siaj, M. Selection of high affinity aptamer-ligand for dexamethasone and its electrochemical biosensor. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 6600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, T.; Wu, T.; Wei, S.; Wang, H.; Sun, M.; Yan, L.; Wei, Q.; Ju, H. Photoelectrochemical competitive immunosensor for 17β-estradiol detection based on ZnIn2S4@NH2-MIL-125(Ti) amplified by PDA NS/Mn:ZnCdS. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2020, 148, 111739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaya, S.I.; Cetinkaya, A.; Bakirhan, N.K.; Ozkan, S.A. Trends in sensitive electrochemical sensors for endocrine disruptive compounds. Trends Environ. Anal. 2020, 28, e00106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pu, H.B.; Xie, X.H.; Sun, D.W.; Wei, Q.Y.; Jiang, Y.F. Double strand DNA functionalized Au@Ag Nps for ultrasensitive detection of 17β-estradiol using surface-enhanced raman spectroscopy. Talanta 2019, 195, 419–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, X.; Sun, J.D.; Sun, X.L. Recent advances in biosensors for the detection of estrogens in the environment and food. Trends Anal. Chem. 2020, 127, 115882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Hormones | Typical Chemical Structures | Risks |
|---|---|---|
| Glucocorticoids | 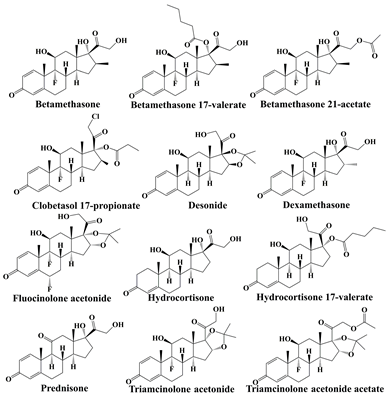 | skin thinning, inflammation, dryness and peeling, and even skin cancer [28,29,30] |
| Sex hormones | 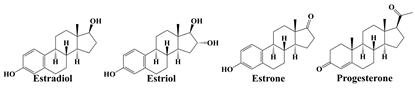 | skin thinning and atrophy, even hysteromyoma and breast cancer [34] |
| Hormones | Pretreatment Method | Condition/Material | Analytical Method | Mobile Phase | Stationary Phase | Linear Range μg L–1 | LOD μg L–1 | Sample | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Methylprednisolone beclomethasone flunisolide budesonide betamethasone 17-valerate beclomethasone dipropionate | UAE | UAE in THF for 20 min | LC–MS | 0.1% FA in ACN/0.1% FA in H2O | C18 | 300–10000 | 24.2 35.4 30.1 18.5 12.1 12.4 | Creams | [39] |
| Triamcinolone prednisolone methylprednisolone betamethasone dexamethasone fluocinolone acetonide prednisolone-21acetate hydrocortisone-21-acetate clobetasol propionate betamethasone dipropionate fluocinolone acetonide-21-acetate | UAE | UAE in ACN for 15 min at 50 °C | LC-MS/MS | ACN/0.1% FA in H2O | Atlantis T3 | 10–1000 | 0.25 1.0 0.3 0.3 0.25 1.0 0.25 1.0 0.25 1.0 1.0 | Creams | [40] |
| Hydrocortisone estrone canrenone triamcinolone acetonide progesterone | UAE | UAE in ACN for 15 min at 25 °C | LC–MS/MS | 0.2% FA in MeOH/0.2% FA in H2O | C18 | 10–1500 | <25 pg | Lotions, creams | [41] |
| Glucocorticoids (43) | UAE | UAE in MeOH for 30 min | UPLC-MS/MS | 0.1% FA in ACN/0.1% FA in H2O | C18 | 100–2000 | 0.33–30 | Solutions, lotions, creams, gels, powders | [81] |
| Glucocorticoids (47) | SPE | Oasis HLB SPE cartridge | UPLC–MS/MS | ACN/0.1% FA in H2O | C18 | – | 0.05–0.4 | Cream, gel, lotion, solution, powder, mask | [82] |
| Prednisone | SPE | plate@MWCNTs@MIPs | HPLC–UV | ACN/H2O | C18 | 1000–6000 | 5.0 | Mask, masque, milk, moisturizer | [52] |
| Glucocorticoids (12) Sex hormones (32) | dSPE | C18 and MgSO4 | UPLC–MS/MS | MeOH/1.5 mM NH4OAc in H2O | HSS-T3 | 0–480 | – | Cream, emulsion, shampoo | [3] |
| Glucocorticoids (40) Sex hormones (8) | UAE-dSPE | C18 and PSA | UPLC-MS/MS | ACN/NH4HCO3 solution | C18 | 3.6–2000 | 1.1–12.5 | Lotions, creams | [53] |
| Ethinylestradiol norgestrel megestrol acetate medroxyprogesterone acetate | MSPE | MMWCNTs | HPLC–DAD | ACN/0.1% phosphate aqueous solution | C18 | 200–20,000 | 330 60 80 80 | Toners | [57] |
| Hydrocortisone dexamethasone desonide fluocinonide flunisolide | MSPE | Fe3O4/g-C3N4/MIL-101 | UPLC–MS/MS | ACN/0.2% FA in H2O | C18 | 0.02–2.0 0.02–2.0 0.02–2.0 0.02–2.0 0.01–1.0 | 0.005 0.005 0.005 0.005 0.002 | Facial masks, toners | [58] |
| Dexamethasone | MSPE | Fe3O4@SiO2-MIPs | HPLC–UV | ACN/H2O | C18 | 500–50,000 | 50 | Cosmetics | [59] |
| Dexamethasone hydrocortisone | MSPE | Fe3O4@SiO2-MIPs | HPLC–UV | ACN/H2O | C18 | 500–15,000 | 15 | Lotions, toners, masks | [60] |
| 17α-Estradiol 17α-ethinylestradiol estrone 17α-hydroxyprogesterone medroxyprogesterone megestrol-17-acetate norethisterone acetate progesterone | HILME | [C6MIM][BF4] | HPLC–DAD | ACN/H2O | C18 | 0.625–125 0.625–125 0.625–125 0.25–50 0.25–50 0.125–100 0.25–125 0.125–125 | 0.24 0.19 0.18 0.08 0.09 0.03 0.05 0.03 | Liquid and gel-like cosmetics | [65] |
| Estrone estradiol 17-α-hydroxyprogesterone chloromadinone 17-acetate megestrol 17-acetate medroxyprogesterone 17-acetate | DLLME | MILs [P6,6,6,14+]2[CoCl4−] | HPLC–UV | ACN/H2O | C18 | 40–1000 40–1000 20–1000 30–1000 30–1000 40–1000 | 15 15 5.0 8.0 8.0 15 | Lotions | [66] |
| Estrone estradiol estriol progesterone diethylstilbestrol | PMME | ACB[6]@poly(BMA-EDMA) | HPLC–DAD | ACN/H2O | Shimpack PREP-ODS (H) and C18 | 1.0–1000 1.0–1000 1.0–1000 1.0–1000 1.0–700 | 0.012 0.022 0.053 0.017 0.019 | Cosmetics | [68] |
| Dexamethasone betamethasone prednisolone triamcinolone triamcinolone acetonide cortisone hydrocortisone fluocinonide beclomethasone dipropionate | PMME | P(BMA-EDMA-GN) | LC–MS | 0.3% FA in ACN/0.3% FA in H2O | C18 | 1.0–800 | 0.28 0.32 1.40 1.93 0.22 0.89 1.52 0.18 0.13 | Cosmetics | [83] |
| Prednisone prednisolone prednisolone acetate | μ-SPE | hollow fibers | HPLC–UV | MeOH/H2O | C18 | 5.0–2000 | 1.5 | Lotions | [69] |
| Dexamethasone hydrocortisone | MSPD | MIPs | HPLC–UV | ACN/H2O | C18 | 50–50,000 | 30 20 | Cosmetics | [72] |
| 17β-estradiol ethinyl estradiol estrone diethyl stilbestrol dihydro stilbestrol | CPE | AlCl3 and SDS | HPLC–UV | ACN/H2O | C18 | 2.0–50 | 0.2 0.7 0.4 0.4 0.2 | Toners | [74] |
| Hormones | Pretreatment Method | Condition | Detection Method | Nanomaterial | Recognition Element | Linear Range μg L–1 | LOD μg L–1 | Sample | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hydrocortisone | UAE | UAE for 10 min | ELISA | – | Antibody | 0.1–2.0 | 0.04 | Body lotions, moisture creams, toners | [84] |
| Dexamethasone | UAE | UAE in ACN and saturated NaCl solution for 10 min | LFIA | colloidal gold | Antibody | 10–200 | 10 | Facial masks | [85] |
| Dexamethasone | Dilution | 20-fold dilution by H2O | LFIA | UCNPs | Antibody | 0.1–9.0 | 2.0 | Cosmetics with skin whitening and acne treatment functions | [86] |
| Triamcinolone acetonide | Dilution | 20-fold dilution by H2O | LFIA | UCNPs | Antibody | 1.0–100 | 20 | Creams, masks, essences | [87] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, M.; Wang, L.; Wang, M.; Zhao, H.; Zhao, F. Advances on Hormones in Cosmetics: Illegal Addition Status, Sample Preparation, and Detection Technology. Molecules 2023, 28, 1980. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28041980
Li M, Wang L, Wang M, Zhao H, Zhao F. Advances on Hormones in Cosmetics: Illegal Addition Status, Sample Preparation, and Detection Technology. Molecules. 2023; 28(4):1980. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28041980
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Mengyue, Li Wang, Min Wang, Hua Zhao, and Fengnian Zhao. 2023. "Advances on Hormones in Cosmetics: Illegal Addition Status, Sample Preparation, and Detection Technology" Molecules 28, no. 4: 1980. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28041980
APA StyleLi, M., Wang, L., Wang, M., Zhao, H., & Zhao, F. (2023). Advances on Hormones in Cosmetics: Illegal Addition Status, Sample Preparation, and Detection Technology. Molecules, 28(4), 1980. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28041980







