Efficacy of Hydroponically Cultivated Saffron in the Preservation of Retinal Pigment Epithelium
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Chemical Composition of Saffron Samples
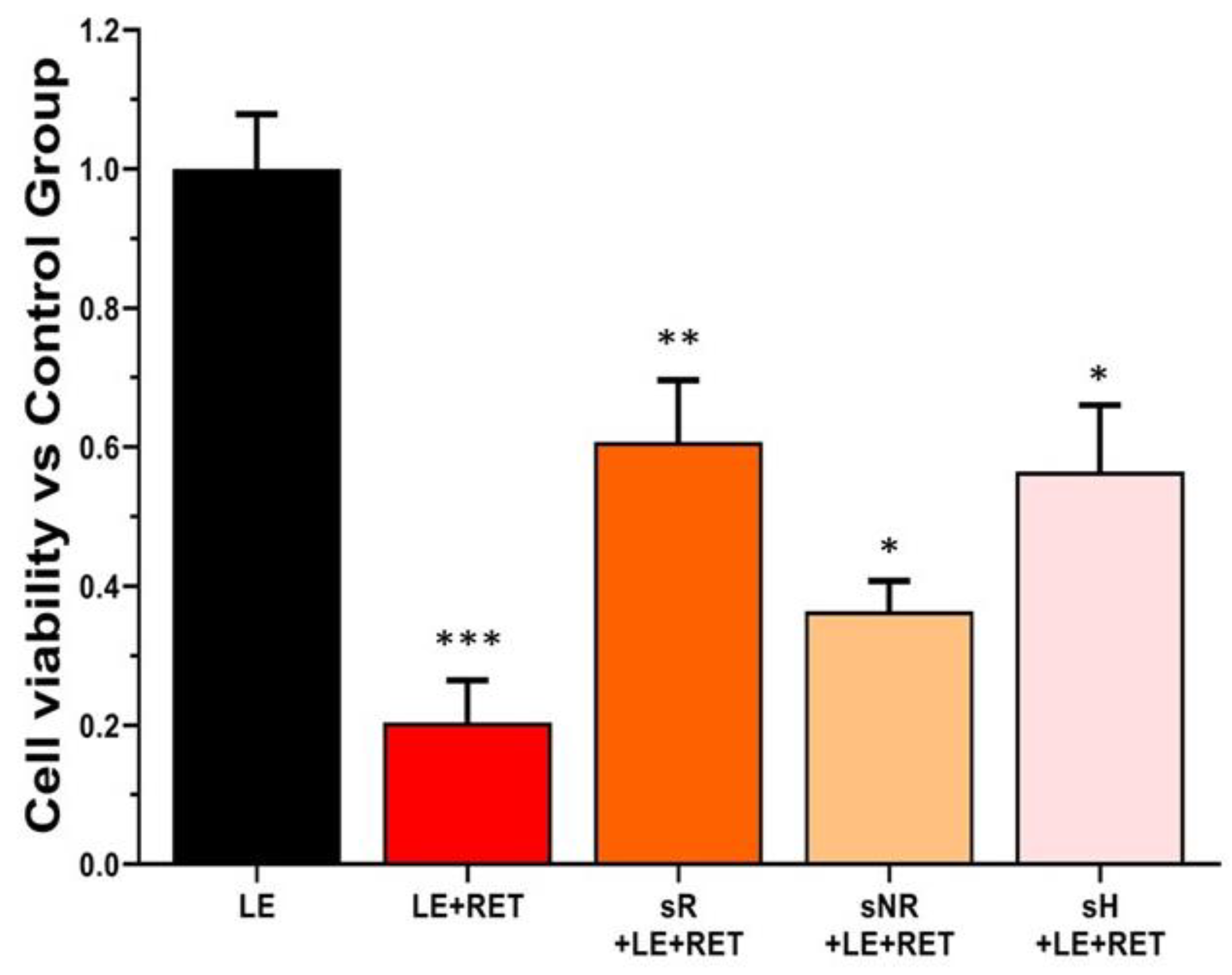
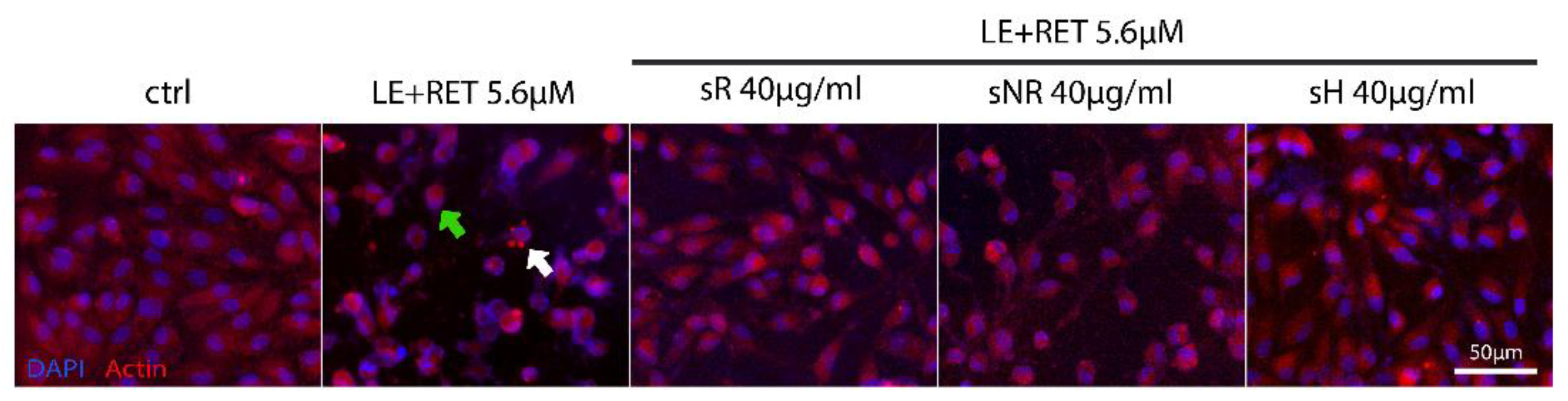
2.2. Saffron Treatment Improves Cell Viability and Preserves Cell Morphology in Retinol + Light-Induced RPE Degeneration
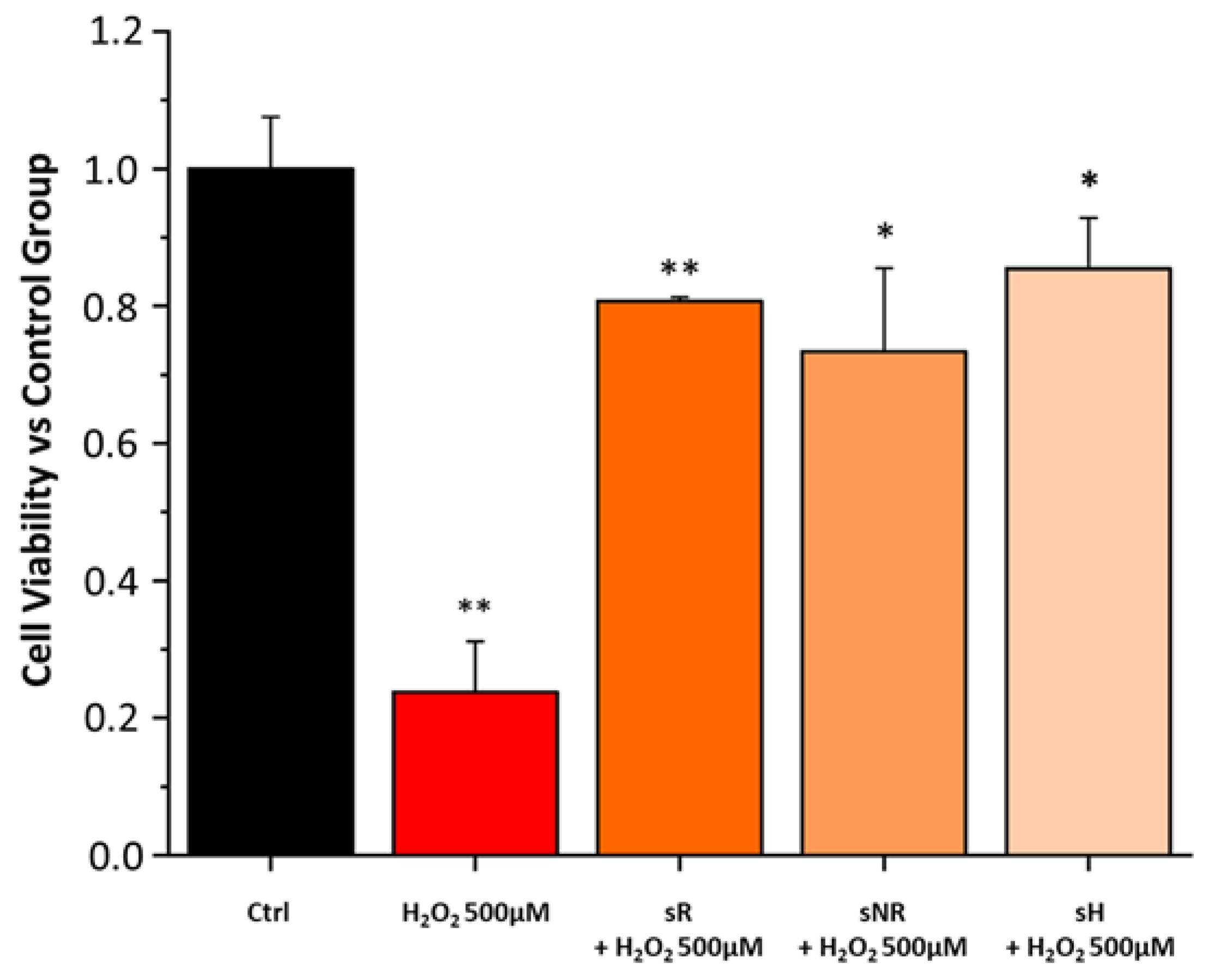
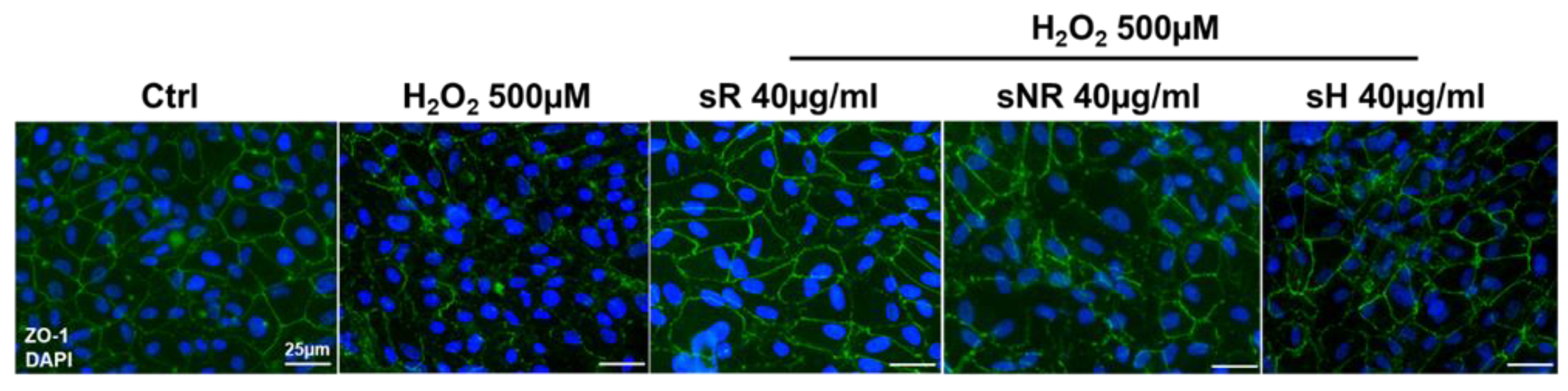
2.3. Saffron Treatment Improves Cell Viability and Gap Junction Integrity in H2O2-Induced RPE Degeneration
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. High-Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) and Spectrophotometry
4.2. Cell Culture
4.3. Cell Viability
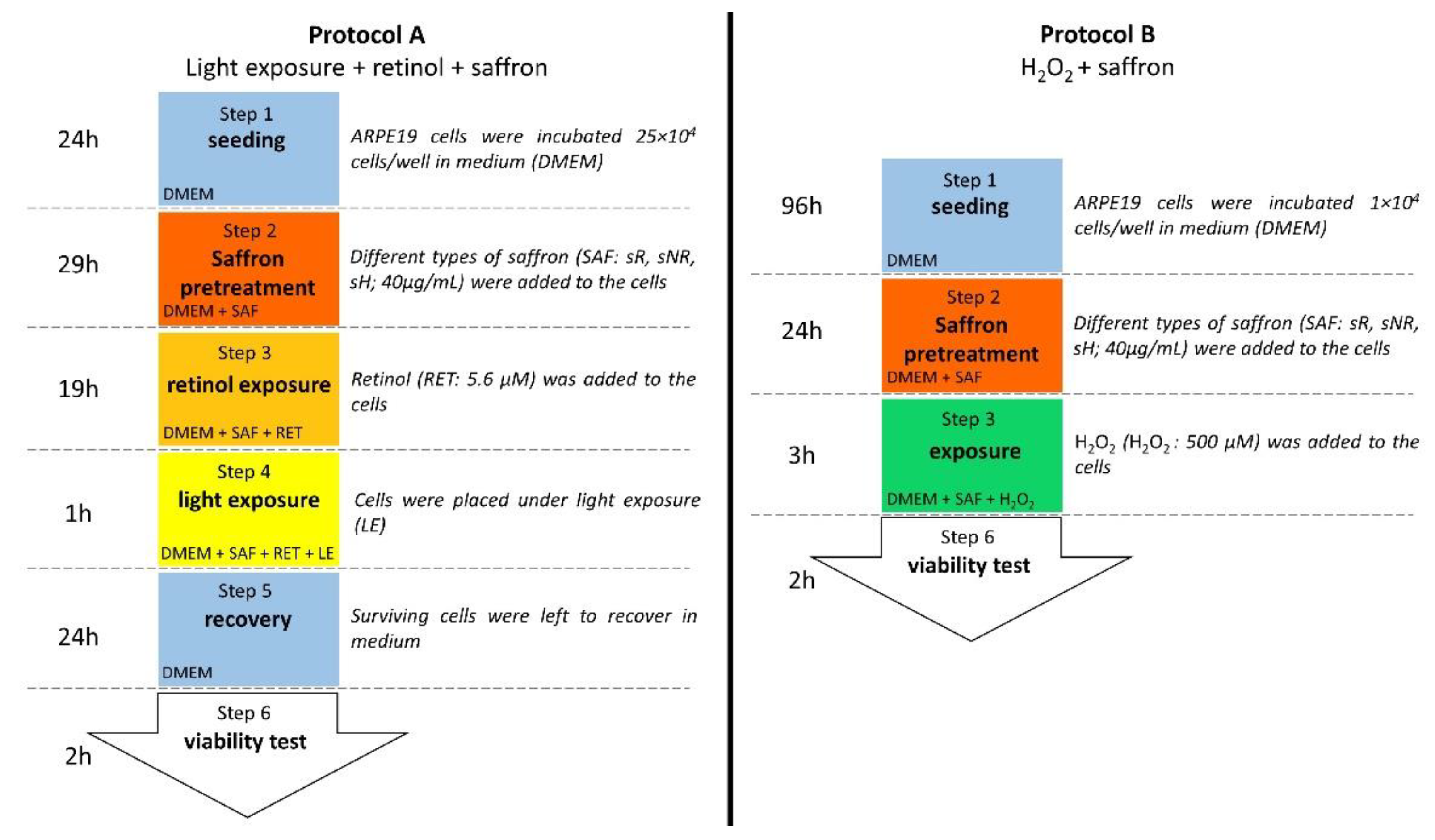
4.4. Light Exposure + Retinol + Saffron Protocol
4.5. H2O2 + Saffron Protocol
4.6. Immunofluorescence
4.7. Statistical Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Sample Availability
References
- Bisti, S.; Di Marco, S.; Maggi, M.A.; Di Paolo, M.; Piccardi, M.F.B. Saffron shifts the degenerative and inflammatory phenotype in photoreceptor degeneration. In Saffron: The Age-Old Panacea in New Light, 1st ed.; Sarwat, M., Sumaiya, S., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2020; pp. 163–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bathaie, S.Z.; Farajzade, A.; Hoshyar, R. A review of the chemistry and uses of crocins and crocetin, the carotenoid natural dyes in saffron, with particular emphasis on applications as colorants including their use as biological stains. Biotech. Histochem. 2014, 89, 401–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rubert, J.; Lacina, O.; Zachariasova, M.; Hajslova, J. Saffron authentication based on liquid chromatography high resolution tandem mass spectrometry and multivariate data analysis. Food Chem. 2016, 204, 201–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, J.; Wanrooij, J.; van Bommel, M.; Quye, A. Characterisation of chemical components for identifying historical Chinese textile dyes by ultra high performance liquid chromatography—photodiode array—electrospray ionisation mass spectrometer. J. Chromatogr. A 2017, 1479, 87–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moras, B.; Loffredo, L.; Rey, S. Quality assessment of saffron (Crocus sativus L.) extracts via UHPLC-DAD-MS analysis and detection of adulteration using gardenia fruit extract (Gardenia jasminoides Ellis). Food Chem. 2018, 257, 325–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- D’Archivio, A.A.; Di Donato, F.; Foschi, M.; Maggi, M.A.; Ruggieri, F. UHPLC Analysis of Saffron (Crocus sativus L.): Optimization of Separation Using Chemometrics and Detection of Minor Crocetin Esters. Molecules 2018, 23, 1851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouvier, F.; Suire, C.; Mutterer, J.; Camara, B. Oxidative remodeling of chromoplast carotenoids identification of the carotenoid dioxygenase CsCCD and CsZCD genes involved in Crocus secondary metabolite biogenesis. Plant Cell 2003, 15, 47–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moraga, A.R.; Nohales, P.F.; Pérez, J.A.F.; Gómez-Gómez, L. Glucosylation of the saffron apocarotenoid crocetin by a glucosyltransferase isolated from Crocus sativus stigmas. Planta 2004, 219, 955–966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Himeno, H.; Sano, K. Synthesis of Crocin, Picrocrocin and Safranal by Saffron Stigma-like Structures Proliferatedin Vitro. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 1987, 51, 2395–2400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maggi, M.A.; Bisti, S.; Picco, C. Saffron: Chemical Composition and Neuroprotective Activity. Molecules 2020, 25, 5618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maggi, M.A.; Consonni, R.; Cagliani, L.R.; Prestipino, G.; Bisti, S.; Picco, C. Saffron and retinal neurodegenerative diseases: Relevance of chemical composition. J. Anat. 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sambo, P.; Nicoletto, C.; Giro, A.; Pii, Y.; Valentinuzzi, F.; Mimmo, T.; Lugli, P.; Orzes, G.; Mazzetto, F.; Astolfi, S.; et al. Hydroponic Solutions for Soilless Production Systems: Issues and Opportunities in a Smart Agriculture Perspective. Front. Plant Sci. 2019, 10, 923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, Y.; Xu, C.L.; Breazzano, M.P.; Tanaka, A.J.; Ryu, J.; Levi, S.R.; Yao, K.; Sparrow, J.R.; Tsang, S.H. Progressive RPE atrophy and photoreceptor death in KIZ-associated autosomal recessive retinitis pigmentosa. Ophthalmic Genet. 2020, 41, 26–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, Y.; Wang, S. Not All Stressors Are Equal: Mechanism of Stressors on RPE Cell Degeneration. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2020, 8, 591067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liao, Y.; Zhang, H.; He, D.; Wang, Y.; Cai, B.; Chen, J.; Ma, J.; Liu, Z.; Wu, Y. Retinal Pigment Epithelium Cell Death Is Associated With NLRP3 Inflammasome Activation by All-trans Retinal. Investig. Opthalmology Vis. Sci. 2019, 60, 3034–3045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Archivio, A.A.; Giannitto, A.; Maggi, M.A.; Ruggieri, F. Geographical classification of Italian saffron (Crocus sativus L.) based on chemical constituents determined by high-performance liquid-chromatography and by using linear discriminant analysis. Food Chem. 2016, 212, 110–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez, A.M.; Carmona, M.; Zalacain, A.; Carot, J.M.; Jabaloyes, J.M.; Alonso, G.L. Rapid Determination of Crocetin Esters and Picrocrocin from Saffron Spice (Crocus sativus L.) Using UV–Visible Spectrophotometry for Quality Control. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2008, 56, 3167–3175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- ISO 3632-2; Spices—Saffron (Crocus sativus L.)—Part 2: Test Methods. International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2010.
- Islam, R.; Corraya, R.M.; Pasovic, L.; Khan, A.Z.; Aass, H.C.D.; Eidet, J.R.; Utheim, T.P. The Effects of Prolonged Storage on ARPE-19 Cells Stored at Three Different Storage Temperatures. Molecules 2020, 25, 5809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, C.-H.; Wu, M.-R.; Li, C.-H.; Cheng, H.-W.; Huang, S.-H.; Tsai, C.-H.; Lin, F.-L.; Ho, J.-D.; Kang, J.-J.; Hsiao, G.; et al. Editor’s Highlight: Periodic Exposure to Smartphone-Mimic Low-Luminance Blue Light Induces Retina Damage Through Bcl-2/BAX-Dependent Apoptosis. Toxicol. Sci. 2017, 157, 196–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piccardi, M.; Fadda, A.; Martelli, F.; Marangoni, D.; Magli, A.; Minnella, A.M.; Bertelli, M.; Di Marco, S.; Bisti, S.; Falsini, B. Antioxidant Saffron and Central Retinal Function in ABCA4-Related Stargardt Macular Dystrophy. Nutrients 2019, 11, 2461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piccardi, M.; Marangoni, D.; Minnella, A.M.; Savastano, M.C.; Valentini, P.; Ambrosio, L.; Capoluongo, E.; Maccarone, R.; Bisti, S.; Falsini, B. A Longitudinal Follow-Up Study of Saffron Supplementation in Early Age-Related Macular Degeneration: Sustained Benefits to Central Retinal Function. Evid.-Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2012, 2012, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Datta, S.; Cano, M.; Ebrahimi, K.; Wang, L.; Handa, J.T. The impact of oxidative stress and inflammation on RPE degeneration in non-neovascular AMD. Prog. Retin. Eye Res. 2017, 60, 201–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feldman, T.; Ostrovskiy, D.; Yakovleva, M.; Dontsov, A.; Borzenok, S.; Ostrovsky, M. Lipofuscin-Mediated Photic Stress Induces a Dark Toxic Effect on ARPE-19 Cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 12234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trevino, S.G.; Schuschereba, S.T.; Bowman, P.D.; Tsin, A. Lecithin:retinol acyltransferase in ARPE-19. Exp. Eye Res. 2005, 80, 897–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tolleson, W.H.; Cherng, S.-H.; Xia, Q.; Boudreau, M.; Yin, J.J.; Wamer, W.G.; Howard, P.C.; Yu, H.; Fu, P.P. Photodecomposition and Phototoxicity of Natural Retinoids. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2005, 2, 147–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

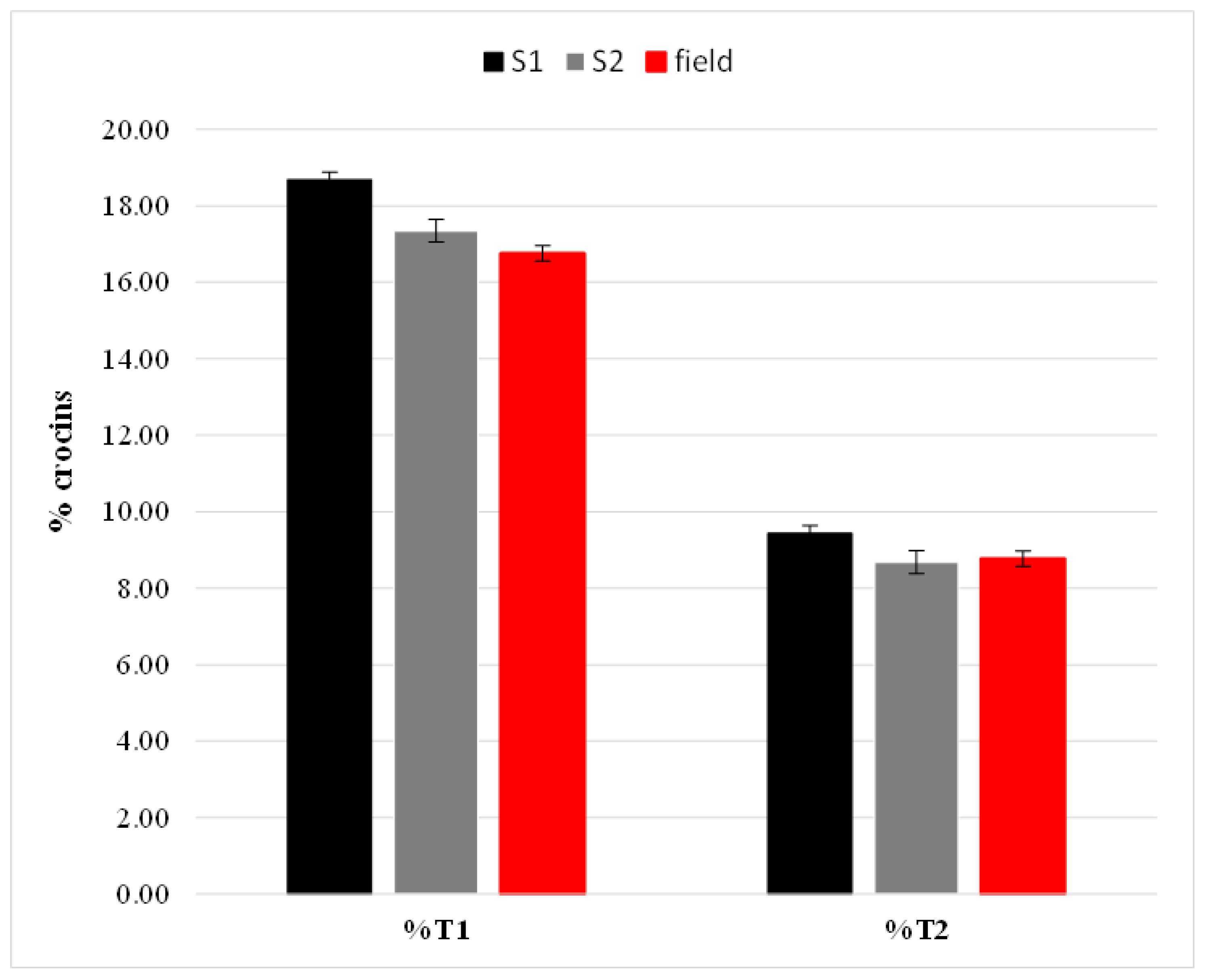
| Sample | E440 | E257 | E330 | Moisture |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| S1 | 282 | 122 | 40 | 10% |
| S2 | 257 | 91 | 35 | 9% |
| Field Saffron | 247 | 109 | 29 | 10% |
| Reference value for saffron of class 1 (dry weight) included | Greater/equal to 200 | Greater/equal to 70 | Between 20 and 50 | Less than 12% for saffron in stigmas |
| Experimental Groups | Tag |
|---|---|
| ARPE19 cells | Ctrl |
| ARPE19 cells + light exposure | LE |
| ARPE19 cells + light exposure + retinol | LE + RET |
| ARPE19 cells + light exposure + retinol + REPRON saffron | sR + LE + RET |
| ARPE19 cells + light exposure + retinol + non-REPRON saffron | sNR + LE + RET |
| ARPE19 cells + light exposure + retinol + hydroponic ENEA saffron | sH + LE + RET |
| ARPE19 cells + H2O2 500 µM | H2O2 500 µM |
| ARPE19 cells + H2O2 500 µM + REPRON saffron | sR + H2O2 500 µM |
| ARPE19 cells + H2O2 500 µM + non-REPRON saffron | sNR + H2O2 500 µM |
| ARPE19 cells + H2O2 500 µM + hydroponic ENEA saffron | sH + H2O2 500 µM |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Di Paolo, M.; Corsi, F.; Maggi, M.; Nardi, L.; Bisti, S.; Piano, I.; Gargini, C. Efficacy of Hydroponically Cultivated Saffron in the Preservation of Retinal Pigment Epithelium. Molecules 2023, 28, 1699. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28041699
Di Paolo M, Corsi F, Maggi M, Nardi L, Bisti S, Piano I, Gargini C. Efficacy of Hydroponically Cultivated Saffron in the Preservation of Retinal Pigment Epithelium. Molecules. 2023; 28(4):1699. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28041699
Chicago/Turabian StyleDi Paolo, Mattia, Francesca Corsi, Maria Maggi, Luca Nardi, Silvia Bisti, Ilaria Piano, and Claudia Gargini. 2023. "Efficacy of Hydroponically Cultivated Saffron in the Preservation of Retinal Pigment Epithelium" Molecules 28, no. 4: 1699. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28041699
APA StyleDi Paolo, M., Corsi, F., Maggi, M., Nardi, L., Bisti, S., Piano, I., & Gargini, C. (2023). Efficacy of Hydroponically Cultivated Saffron in the Preservation of Retinal Pigment Epithelium. Molecules, 28(4), 1699. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28041699








