Rational Design of Nitrogen-Doped Carbon Dots for Inhibiting β-Amyloid Aggregation
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
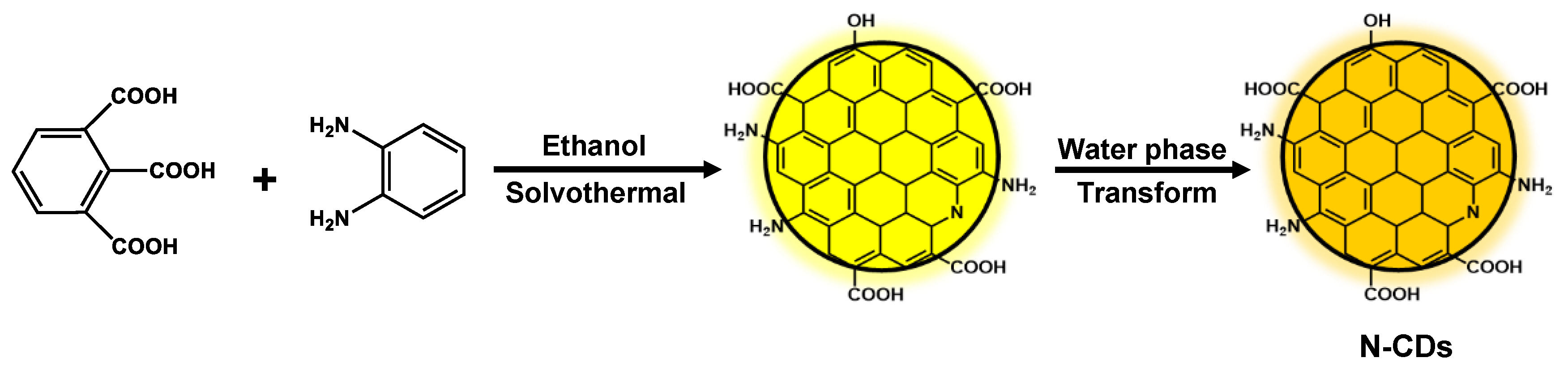
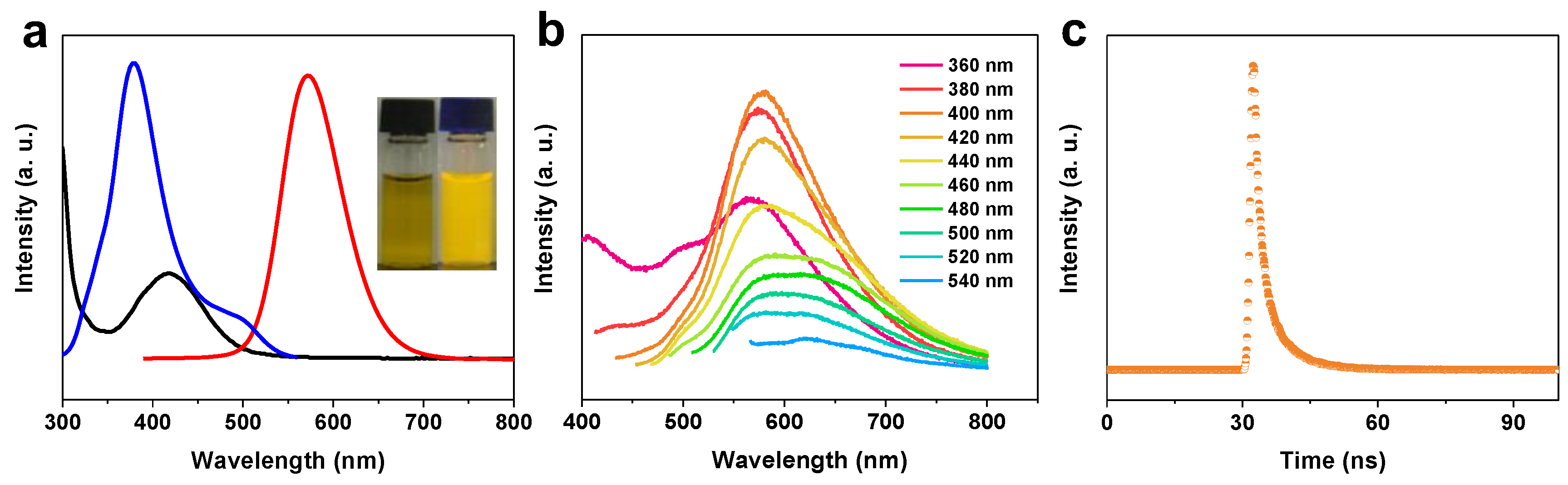
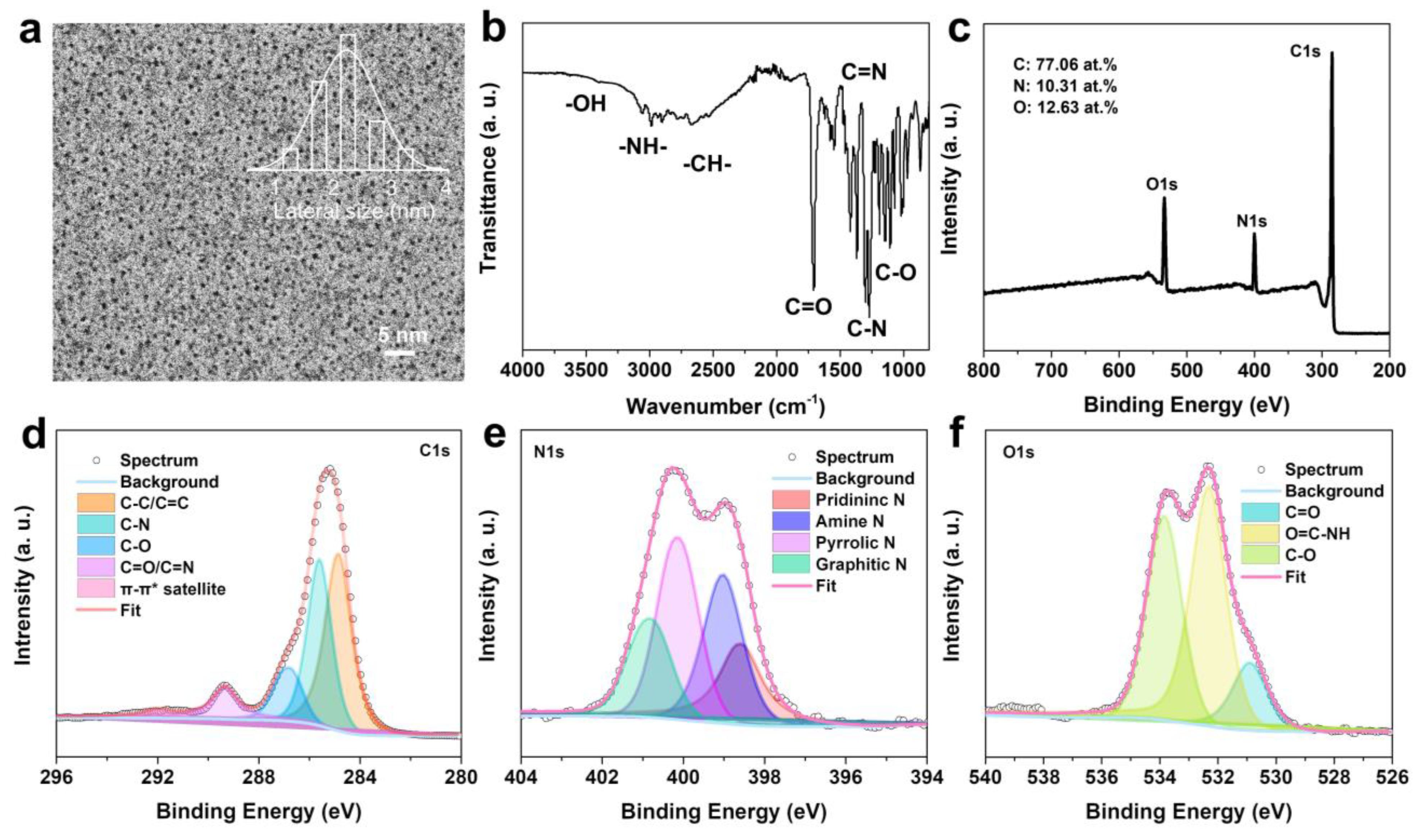
2.1. Characterization of N-CDs
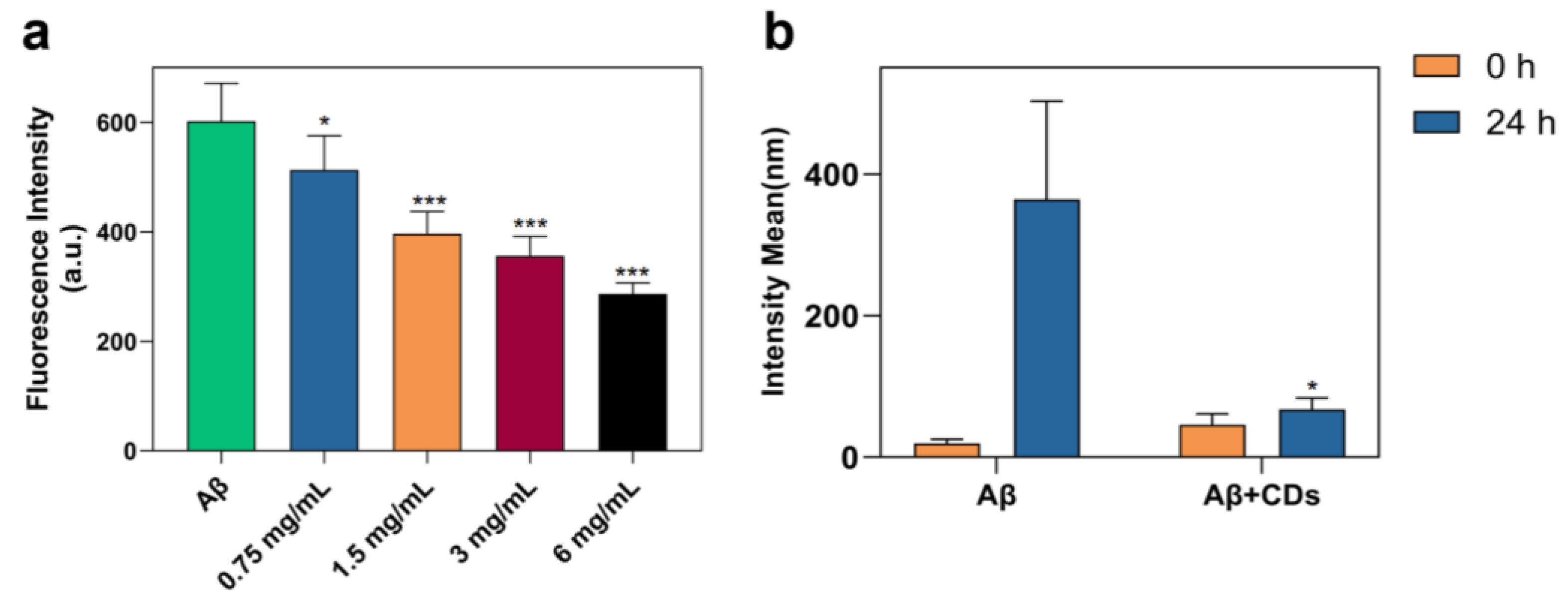
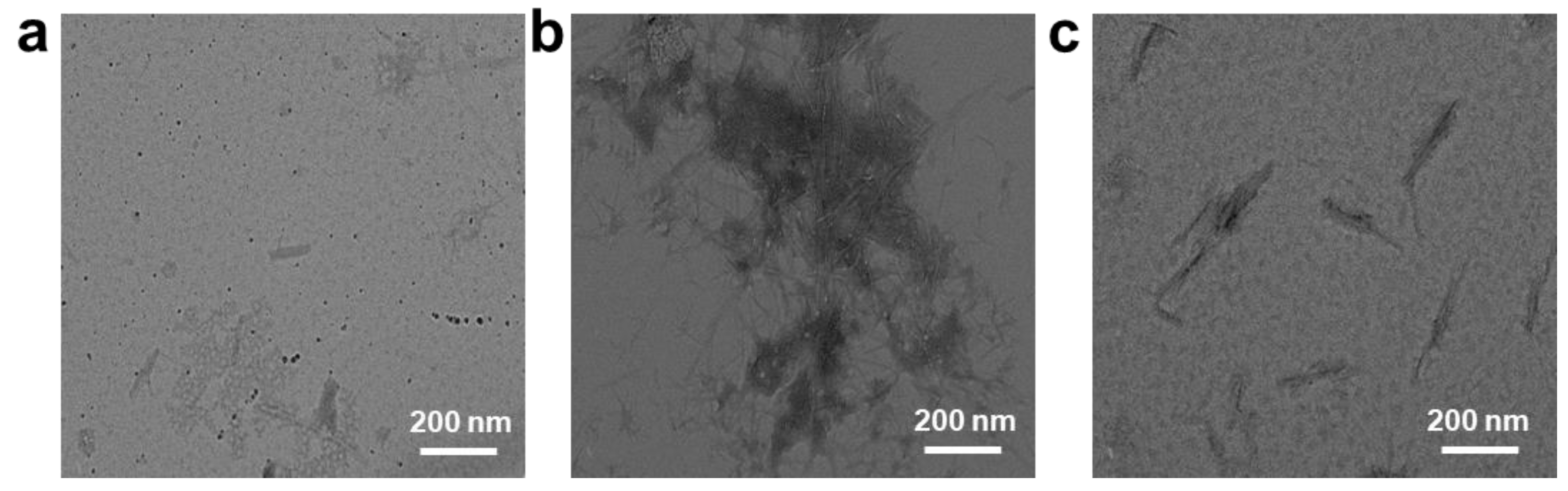
2.2. Inhibition on Aβ1–42 Aggregation Self-Assembly with N-CDs
2.3. Aβ-Induced Cell Viability Was Reversed by N-CDs
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials
3.2. Synthesis of N-CDs
3.3. Thioflavin T (ThT) Assay
3.4. Cell Viability Detected by MTT Assay
3.5. Characterization
3.6. Statistical Analysis
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hodson, R. Alzheimer’s disease. Nature 2018, 559, S1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mielke, M.M.; Vemuri, P.; Rocca, W.A. Clinical Epidemiology of Alzheimer’s Disease: Assessing Sex and Gender Differences. Clin. Epidemiol. 2014, 6, 37–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Serrano-Pozo, A.; Das, S.; Hyman, B.T. APOE and Alzheimer’s Disease: Advances in Genetics, Pathophysiology, and Therapeutic Approaches. Lancet Neurol. 2021, 20, 68–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Graff-Radford, J.; Yong, K.X.X.; Apostolova, L.G.; Bouwman, F.H.; Carrillo, M.; Dickerson, B.C.; Rabinovici, G.D.; Schott, J.M.; Jones, D.T.; Murray, M.E. New Insights into Atypical Alzheimer’s Disease in the Era of Biomarkers. Lancet Neurol. 2021, 20, 222–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiandaca, M.S.; Kapogiannis, D.; Mapstone, M.; Boxer, A.; Eitan, E.; Schwartz, J.B.; Abner, E.L.; Petersen, R.C.; Federoff, H.J.; Miller, B.L.; et al. Identification of Preclinical Alzheimer’s Disease by a Profile of Pathogenic Proteins in Neurally Derived Blood Exosomes: A Case-Control Study. Alzheimers Dement. 2015, 11, 600–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murakami, K.; Irie, K.; Morimoto, A.; Ohigashi, H.; Shindo, M.; Nagao, M.; Shimizu, T.; Shirasawa, T. Synthesis, Aggregation, Neurotoxicity, and Secondary Structure of Various A Beta 1-42 Mutants of Familial Alzheimer’s Disease at Positions 21–23. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2002, 294, 5–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roher, A.E.; Lowenson, J.D.; Clarke, S.; Woods, A.S.; Cotter, R.J.; Gowing, E.; Ball, M.J. Beta-Amyloid-(1-42) is a Major Component of Cerebrovascular Amyloid Deposits: Implications for the Pathology of Alzheimer Disease. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1993, 90, 10836–10840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kellar, D.; Craft, S. Brain Insulin Resistance in Alzheimer’s Disease and Related Disorders: Mechanisms and Therapeutic Approaches. Lancet Neurol. 2020, 19, 758–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tatulian, S.A. Challenges and Hopes for Alzheimer’s Disease. Drug Discov. Today 2022, 27, 1027–1043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weintraub, D.; Aarsland, D.; Chaudhuri, K.R.; Dobkin, R.D.; Leentjens, A.F.; Rodriguez-Violante, M.; Schrag, A. The Neuropsychiatry of Parkinson’s Disease: Advances and Challenges. Lancet Neurol. 2022, 21, 89–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, H.; Zhang, X.; Chen, Z.; Zhang, L.; Wang, L.; Xu, J.; Wu, M. High-Energy Short-Wave Blue Light Conversion Films Via Carbon Quantum Dots for Preventing Retinal Photochemical Damage. Carbon 2022, 199, 431–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Wang, B.; Zhang, M.; Zhang, J.; Li, Y.; Jia, P.; Zhang, H.; Duan, L.; Li, Y.; Li, Y.; et al. Carbon Dots as a Potential Therapeutic Agent for the Treatment of Cancer-Related Anemia. Adv. Mater. 2022, 34, e2200905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hou, L.; Chen, D.; Wang, R.; Wang, R.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, Z.; Nie, Z.; Lu, S. Transformable Honeycomb-Like Nanoassemblies of Carbon Dots for Regulated Multisite Delivery and Enhanced Antitumor Chemoimmunotherapy. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 2021, 60, 6581–6592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Guo, H.; Chen, C.; Quan, B.; Zeng, Z.; Xu, J.; Chen, Z.; Wang, L. Tunable Photoacoustic and Fluorescence Imaging of Nitrogen-Doped Carbon Quantum Dots. Appl. Mater. Today. 2023, 30, 101706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, H.; Liu, Z.; Shen, X.; Wang, L. One-Pot Synthesis of Orange Emissive Carbon Quantum Dots for All-Type High Color Rendering Index White Light-Emitting Diodes. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2022, 26, 8289–8296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Kong, T.; Xiong, H.M. Mulberry-Leaves-Derived Red-Emissive Carbon Dots for Feeding Silkworms to Produce Brightly Fluorescent Silk. Adv. Mater. 2022, 34, 2200152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Li, W.; Yin, L.; Liu, Y.; Guo, H.; Lai, J.; Han, Y.; Li, G.; Li, M.; Zhang, J.; et al. Full-Color Fluorescent Carbon Quantum Dots. Sci. Adv. 2020, 6, eabb6772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Wu, M.; Wang, Z.; Guo, H.; Wang, L.; Wu, M. Phosphorescence Tuning of Fluorine, Oxygen-Codoped Carbon Dots by Substrate Engineering. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2021, 48, 16262–16269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, W.; Guo, R.; Yuan, F.; Li, Y.; Li, X.; Zhang, Y.; Zhou, S.; Fan, L. Red-Emissive Carbon Quantum Dots for Nuclear Drug Delivery in Cancer Stem Cells. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 2020, 11, 1357–1363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Li, M.; Li, Y.; Wu, B.; Chen, H.; Wang, R.; Xu, T.; Guo, H.; Li, W.; Joyner, J.; et al. Designing a Sustainable Fluorescent Targeting Probe for Superselective Nucleus Imaging. Carbon 2021, 180, 48–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedone, D.; Moglianetti, M.; De Luca, E.; Bardi, G.; Pompa, P.P. Platinum Nanoparticles in Nanobiomedicine. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2017, 46, 4951–4975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.; Su, W.; Wu, H.; Yuan, T.; Yuan, C.; Liu, J.; Deng, G.; Gao, X.; Chen, Z.; Bao, Y.; et al. Targeted Tumour Theranostics in Mice via Carbon Quantum Dots Structurally Mimicking Large Amino Acids. Nat. Biomed. Eng. 2020, 4, 704–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, L.; Luo, Y.; Lin, D.; Xi, W.; Yang, X.; Wei, G. The Molecular Mechanism of Fullerene-Inhibited Aggregation of Alzheimer’s β-amyloid Peptide Fragment. Nanoscale 2014, 6, 9752–9762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daniyal, M.; Liu, B.; Wang, W. Comprehensive Review on Graphene Oxide for Use in Drug Delivery System. Curr. Med. Chem. 2020, 27, 3665–3685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, M.; Yang, X.; Ren, J.; Qu, K.; Qu, X. Using Graphene Oxide High Near-Infrared Absorbance for Photothermal Treatment of Alzheimer’s Disease. Adv. Mater. 2012, 24, 1722–1728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, H.; Li, X.; Zhu, L.; Wu, X.; Zhang, S.; Huang, F.; Feng, X.; Shi, L. Heat Shock Protein Inspired Nanochaperones Restore Amyloid-β Homeostasis for Preventative Therapy of Alzheimer’s Disease. Adv. Sci. 2019, 6, 1901844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, J.; Gonzalez-Carter, D.; Tockary, T.A.; Nakamura, N.; Xue, Y.; Nakakido, M.; Akiba, H.; Dirisala, A.; Liu, X.; Toh, K.; et al. Dual-Sensitive Nanomicelles Enhancing Systemic Delivery of Therapeutically Active Antibodies Specifically into the Brain. ACS Nano 2020, 14, 6729–6742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, L.; Wang, X.; Zhao, C.; Wang, H.; Du, W. Ruthenium Complexes as Novel Inhibitors of Human Islet Amyloid Polypeptide Fibril Formation. Metallomics 2013, 5, 1599–1603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsieh, S.; Chang, C.W.; Chou, H.H. Gold Nanoparticles as Amyloid-Like Fibrillogenesis Inhibitors. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2013, 112, 525–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Howson, S.E.; Dong, K.; Gao, N.; Ren, J.; Scott, P.; Qu, X. Chiral Metallohelical Complexes Enantioselectively Target Amyloid β for Treating Alzheimer’s Disease. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2014, 136, 11655–11663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, L.; Meziani, M.J.; Sahu, S.; Sun, Y.P. Photoluminescence Properties of Graphene Versus Other Carbon Nanomaterials. Acc. Chem. Res. 2013, 46, 171–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, G.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, R.; Tian, X.; Liu, Z.; Wang, A.; Liu, R.; Liu, B.; Han, M.Y.; Gao, X.; et al. Membrane-Penetrating Carbon Quantum Dots for Imaging Nucleic Acid Structures in Live Organisms. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2019, 58, 7087–7091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Y.; Peng, Z.; Seven, E.S.; Leblanc, R.M. Crossing the Blood-Brain Barrier with Nanoparticles. J. Control Release 2018, 70, 290–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Geng, Y.; Li, D.; Yao, H.; Huo, Z.; Li, Y.; Zhang, K.; Zhu, S.; Wei, H.; Xu, W.; et al. Deep Red Emissive Carbonized Polymer Dots with Unprecedented Narrow Full width at Half Maximum. Adv. Mater. 2020, 32, 1906641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, X.; Jing, Z.; Wu, W.; Zou, B.; Peng, Z.; Ren, P.; Wikramanayake, A.; Lu, Z.; Leblanc, R.M. Biocompatible and Blood-Brain Barrier Permeable Carbon Dots for Inhibition of Aβ Fibrillation and Toxicity, and BACE1 Activity. Nanoscale 2017, 9, 12862–12866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Y.; Liyanage, P.Y.; Devadoss, D.; Leblanc, R.M. Nontoxic Amphiphilic Carbon Dots as Promising Drug Nanocarriers Across the Blood-Brain Barrier and Inhibitors of β-amyloid. Nanoscale 2019, 11, 22387–22397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teleanu, R.I.; Gherasim, O.; Gherasim, T.G.; Grumezescu, V.; Grumezescu, A.M.; Teleanu, D.M. Nanomaterial-Based Approaches for Neural Rregeneration. Pharmaceutics 2019, 11, 266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norouzi, M.; Yasamineh, S.; Montazeri, M.; Dadashpour, M.; Sheervalilou, R.; Abasi, M.; Pilehvar-Soltanahmadi, Y. Recent Advances on Nanomaterials-Based Fluorimetric Approaches for MicroRNAs Detection. Mater. Sci. Eng. C. Mater. Biol. Appl. 2019, 104, 110007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LeVine, H., 3rd. Thioflavine T Interaction with Synthetic Alzheimer’s Disease Beta-Amyloid Peptides: Detection of Amyloid Aggregation in Solution. Protein Sci. 1993, 2, 404–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmoudi, M.; Akhavan, O.; Ghavami, M.; Rezaee, F.; Ghiasi, S.M. Graphene Oxide Strongly Inhibits Amyloid Beta Fibrillation. Nanoscale 2012, 4, 7322–7325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, J.; Wärmländer, S.K.; Yu, C.H.; Muhammad, K.; Gräslund, A.; Pieter Abrahams, J. The Aβ Peptide Forms Non-Amyloid Fibrils in the Presence of Carbon Nanotubes. Nanoscale 2014, 6, 6720–6726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Röhr, D.; Boon, B.D.C.; Schuler, M.; Kremer, K.; Hoozemans, J.J.M.; Bouwman, F.H.; El-Mashtoly, S.F.; Nabers, A.; Großerueschkamp, F.; Rozemuller, A.J.M. Label-Free Vibrational Imaging of Different Aβ Plaque Types in Alzheimer’s Disease Reveals Sequential Events in Plaque Development. Acta Neuropathol. Commun. 2020, 8, 222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, Y.M.; Park, S.; Choi, S.Y.; Oh, S.B.; Jung, M.; Pack, C.G.; Hwang, J.J.; Tak, E.; Lee, J.Y. Clusterin Binding Modulates the Aggregation and Neurotoxicity of Amyloid-β(1-42). Mol. Neurobiol. 2022, 59, 6228–6244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, D.; Guo, H.; Huang, K.; Zhang, H.; Chen, J.; Wang, L.; Lian, C.; Wang, Y. Carboxylated Carbon Quantum Dot-induced Binary Metal-organic Framework Nanosheet Synthesis to Boost the Electrocatalytic Performance. Mater. Today. 2022, 54, 42–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.; Tang, B.; Wang, L.; Bao, H.; Lu, Y.; Guan, C.; Zhang, L.; Le, M.; Liu, Z.; Wu, M. Machine Learning Driven Synthesis of Carbon Dots with Enhanced Quantum Yield. ACS Nano 2020, 14, 14761–14768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anand, A.; Unnikrishnan, B.; Wei, S.C.; Chou, C.P.; Zhang, L.Z.; Huang, C.C. Graphene Oxide and Carbon Dots as Broad-Spectrum Antimicrobial Agents-a Minireview. Nanoscale Horiz. 2019, 4, 117–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, G.; Li, L.; Wang, D.; Chen, M.; Zeng, Z.; Xiong, W.; Wu, X.; Guo, C. Carbon Dots: Synthesis, Properties and Biomedical Applications. J. Mater. Chem. B. 2021, 9, 6553–6575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, H.; Zhou, X.X.; Wei, J.S.; Li, X.B.; Qin, B.T.; Chen, X.B.; Xiong, H.M. Carbon Dots with Red/Near-Infrared Emissions and Their Intrinsic Merits for Biomedical Applications. Carbon 2020, 167, 322–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, H.; Guo, H.; Fang, Y.; Wang, L.; Li, P. Rational Design of Nitrogen-Doped Carbon Dots for Inhibiting β-Amyloid Aggregation. Molecules 2023, 28, 1451. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28031451
Liu H, Guo H, Fang Y, Wang L, Li P. Rational Design of Nitrogen-Doped Carbon Dots for Inhibiting β-Amyloid Aggregation. Molecules. 2023; 28(3):1451. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28031451
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Hong, Huazhang Guo, Yibin Fang, Liang Wang, and Peng Li. 2023. "Rational Design of Nitrogen-Doped Carbon Dots for Inhibiting β-Amyloid Aggregation" Molecules 28, no. 3: 1451. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28031451
APA StyleLiu, H., Guo, H., Fang, Y., Wang, L., & Li, P. (2023). Rational Design of Nitrogen-Doped Carbon Dots for Inhibiting β-Amyloid Aggregation. Molecules, 28(3), 1451. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28031451








