Authentication and Geographical Characterisation of Italian Grape Musts through Glucose and Fructose Carbon Isotopic Ratios Determined by LC-IRMS
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Method Validation
2.2. Geographical Characterization of Authentic Samples
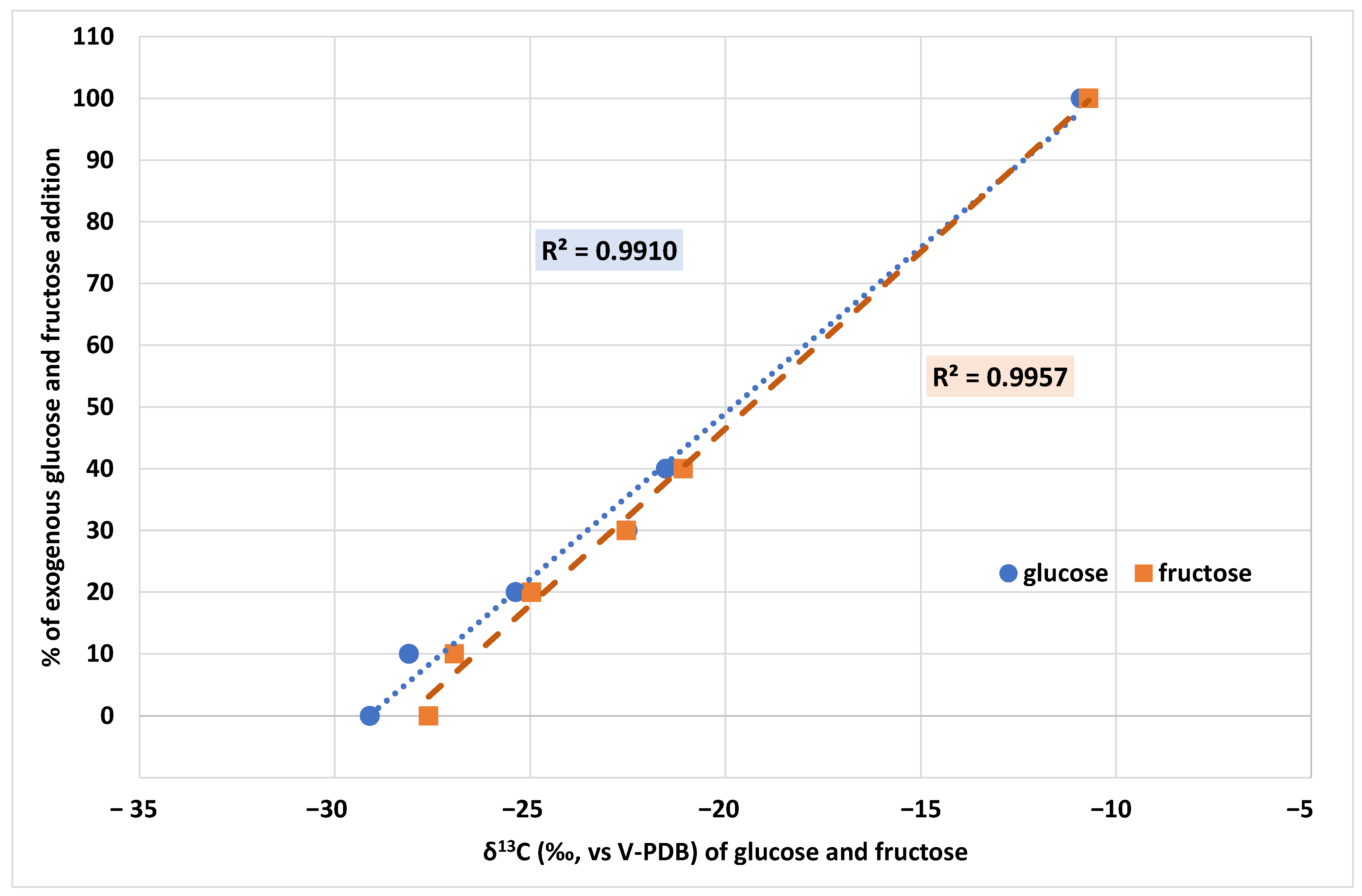
2.3. Authentication of Grape Musts
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Reagents
3.2. Samples
3.3. LC-IRMS
3.4. Stable Isotope Ratio Analysis and Data Correction
3.5. Statistical Analysis
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- International Organisation of Vine and Wine (OIV). Code International des Pratiques OEnologiques; OIV: Paris, France, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Johnson, H.; Robinson, J. The World Atlas of Wine, 8th ed.; Mitchell Beazley: London, UK, 2019; ISBN 9781784726188. [Google Scholar]
- Holmberg, L. Holmberg Wine Fraud. Int. J. Wine Res. 2010, 2, 105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Regulation, H.A.T. Commission Regulation (EEC) No. 2676/90 Determining Community Methods for the Analysis of Wines. Off. J. L 1990, 272, 1–192. [Google Scholar]
- O’Leary, M.H. Carbon Isotopes in Photosynthesis. BioScience 1988, 38, 328–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bauer-Christoph, C.; Wachter, H.; Christoph, N.; Rßmann, A.; Adam, L. Assignment of Raw Material and Authentication of Spirits by Gas Chromatography, Hydrogen- and Carbon-Isotope Ratio Measurements. Z. Lebensm. Forsch. A 1997, 204, 445–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christoph, N.; Hermann, A.; Wachter, H. 25 Years Authentication of Wine with Stable Isotope Analysis in the European Union—Review and Outlook. BIO Web Conf. 2015, 5, 02020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camin, F.; Dordevic, N.; Wehrens, R.; Neteler, M.; Delucchi, L.; Postma, G.; Buydens, L. Climatic and Geographical Dependence of the H, C and O Stable Isotope Ratios of Italian Wine. Anal. Chim. Acta 2015, 853, 384–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dordevic, N.; Wehrens, R.; Postma, G.J.; Buydens, L.M.C.; Camin, F. Statistical Methods for Improving Verification of Claims of Origin for Italian Wines Based on Stable Isotope Ratios. Anal. Chim. Acta 2012, 757, 19–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guyon, F.; Gaillard, L.; Salagoïty, M.-H.; Médina, B. Intrinsic Ratios of Glucose, Fructose, Glycerol and Ethanol 13C/12C isotopic ratio determined by HPLC-co-IRMS: Toward determining constants for wine authentication. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2011, 401, 1551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bisson, L.F. Stuck and Sluggish Fermentations. Am. J. Enol. Vitic. 1999, 50, 107–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabañero, A.I.; Recio, J.L.; Rupérez, M. Isotope Ratio Mass Spectrometry Coupled to Liquid and Gas Chromatography for Wine Ethanol Characterization. Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 2008, 22, 3111–3118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whiteman, J.; Smith, E.E.; Besser, A.; Newsome, S. A Guide to Using Compound-Specific Stable Isotope Analysis to Study the Fates of Molecules in Organisms and Ecosystems. Diversity 2019, 11, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.G. Compound-Specific Isotope Analysis; Encyclopedia of Earth Sciences Series Encyclopedia of Engineering Geology; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2017; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Tobias, H.J.; Sacks, G.L.; Brenna, J.T. Calibration and Data Processing in Gas Chromatography Combustion Isotope Ratio Mass Spectrometry. Drug Test. Anal. 2012, 4, 912–922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perini, M.; Strojnik, L.; Paolini, M.; Camin, F. Gas Chromatography Combustion Isotope Ratio Mass Spectrometry for Improving the Detection of Authenticity of Grape Must. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2020, 68, 3322–3329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perini, M.; Bontempo, L. Liquid Chromatography Coupled to Isotope Ratio Mass Spectrometry (LC-IRMS): A Review. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2022, 147, 116515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabañero, A.I.; Recio, J.L.; Rupérez, M. Simultaneous Stable Carbon Isotopic Analysis of Wine Glycerol and Ethanol by Liquid Chromatography Coupled to Isotope Ratio Mass Spectrometry. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2010, 58, 722–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elflein, L.; Raezke, K.-P. Improved Detection of Honey Adulteration by Measuring Differences between13C/12C Stable Carbon Isotope Ratios of Protein and Sugar Compounds with a Combination of Elemental Analyzer—Isotope Ratio Mass Spectrometry and Liquid Chromatography—Isotope Ratio Mass Spectrometry (δ13C-EA/LC-IRMS). Apidologie 2008, 39, 574–587. [Google Scholar]
- Cabañero, A.I.; Recio, J.L.; Rupérez, M. Liquid Chromatography Coupled to Isotope Ratio Mass Spectrometry: A New Perspective on Honey Adulteration Detection. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2006, 54, 9719–9727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camin, F.; Bontempo, L.; Heinrich, K.; Horacek, M.; Kelly, S.D.; Schlicht, C.; Thomas, F.; Monahan, F.J.; Hoogewerff, J.; Rossmann, A. Multi-Element (H,C,N,S) Stable Isotope Characteristics of Lamb Meat from Different European Regions. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2007, 389, 309–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbour, M.M.; Anthony Fischer, R.; Sayre, K.D.; Farquhar, G.D. Oxygen Isotope Ratio of Leaf and Grain Material Correlates with Stomatal Conductance and Grain Yield in Irrigated Wheat. Funct. Plant Biol. 2000, 27, 625–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaudillère, J.-P.; Van Leeuwen, C.; Ollat, N. Carbon Isotope Composition of Sugars in Grapevine, an Integrated Indicator of Vineyard Water Status. J. Exp. Bot. 2002, 53, 757–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walker, R.P.; Bonghi, C.; Varotto, S.; Battistelli, A.; Burbidge, C.A.; Castellarin, S.D.; Chen, Z.-H.; Darriet, P.; Moscatello, S.; Rienth, M.; et al. Sucrose Metabolism and Transport in Grapevines, with Emphasis on Berries and Leaves, and Insights Gained from a Cross-Species Comparison. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 7794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geng, K.; Zhang, Y.; Lv, D.; Li, D.; Wang, Z. Effects of Water Stress on the Sugar Accumulation and Organic Acid Changes in Cabernet Sauvignon Grape Berries. Hortic. Sci. 2022, 49, 164–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roßmann, A.; Schmidt, H.-L.; Reniero, F.; Versini, G.; Moussa, I.; Merle, M.H. Stable Carbon Isotope Content in Ethanol of EC Data Bank Wines from Italy, France and Germany. Z. Lebensm.-Unters. Forsch. 1996, 203, 293–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akamatsu, F.; Shimizu, H.; Igi, Y.; Kamada, A.; Koyama, K.; Yamada, O.; Goto-Yamamoto, N. Prediction Method for Determining the Carbon Stable Isotopic Composition of Berry Sugars in the Original Must of Chardonnay Wines. Food Chem. 2022, 369, 130854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thomas, F.; Randet, C.; Gilbert, A.; Silvestre, V.; Jamin, E.; Akoka, S.; Remaud, G.; Segebarth, N.; Guillou, C. Improved Characterization of the Botanical Origin of Sugar by Carbon-13 SNIF-NMR Applied to Ethanol. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2010, 58, 11580–11585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crittenden, R.G.; Andrew, A.S.; LeFournour, M.; Young, M.D.; Middleton, H.; Stockmann, R. Determining the Geographic Origin of Milk in Australasia Using Multi-Element Stable Isotope Ratio Analysis. Int. Dairy J. 2007, 17, 421–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bear, R.; Rintoul, D.; Snyder, B.; Smith-Caldas, M.; Herren, C.; Horne, E. Principles of Biology; Open Access Textbooks; New Prairie Press: Manhattan, KS, USA, 2016; Available online: https://newprairiepress.org/textbooks/1 (accessed on 1 December 2022).
- Prohaska, T.; Irrgeher, J.; Benefield, J.; Böhlke, J.K.; Chesson, L.A.; Coplen, T.B.; Ding, T.; Dunn, P.J.H.; Gröning, M.; Holden, N.E.; et al. Standard Atomic Weights of the Elements 2021 (IUPAC Technical Report). Chem. Int. 2022, 44, 32–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| δ13C (‰, vs. V-PDB) Glucose | δ13C (‰, vs. V-PDB) Fructose | δ13C (‰, vs. V-PDB) Glucose | δ13C (‰, vs. V-PDB) Fructose | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | −27.5 | −27.7 | Day 1 | −27.3 | −27.4 |
| 2 | −26.6 | −26.5 | Day 2 | −26.1 | −27.8 |
| 3 | −27.3 | −26.9 | Day 3 | −27.1 | −27.1 |
| 4 | −27.6 | −27.0 | |||
| 5 | −28.1 | −28.6 | |||
| 6 | −28.2 | −29.0 | |||
| 7 | −28.9 | −26.9 | |||
| 8 | −27.9 | −27.4 | |||
| Mean (‰) | −27.8 | −27.5 | Mean (‰) | −26.8 | −27.5 |
| Whitin-day RSD (%) | 2.5 | 3.2 | Between-day RSD (%) | 2.5 | 1.3 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Perini, M.; Pianezze, S.; Guardini, K.; Allari, L.; Larcher, R. Authentication and Geographical Characterisation of Italian Grape Musts through Glucose and Fructose Carbon Isotopic Ratios Determined by LC-IRMS. Molecules 2023, 28, 1411. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28031411
Perini M, Pianezze S, Guardini K, Allari L, Larcher R. Authentication and Geographical Characterisation of Italian Grape Musts through Glucose and Fructose Carbon Isotopic Ratios Determined by LC-IRMS. Molecules. 2023; 28(3):1411. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28031411
Chicago/Turabian StylePerini, Matteo, Silvia Pianezze, Katia Guardini, Letizia Allari, and Roberto Larcher. 2023. "Authentication and Geographical Characterisation of Italian Grape Musts through Glucose and Fructose Carbon Isotopic Ratios Determined by LC-IRMS" Molecules 28, no. 3: 1411. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28031411
APA StylePerini, M., Pianezze, S., Guardini, K., Allari, L., & Larcher, R. (2023). Authentication and Geographical Characterisation of Italian Grape Musts through Glucose and Fructose Carbon Isotopic Ratios Determined by LC-IRMS. Molecules, 28(3), 1411. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28031411







