Alkaloids and Styryl lactones from Goniothalamus ridleyi King and Their α-Glucosidase Inhibitory Activity
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
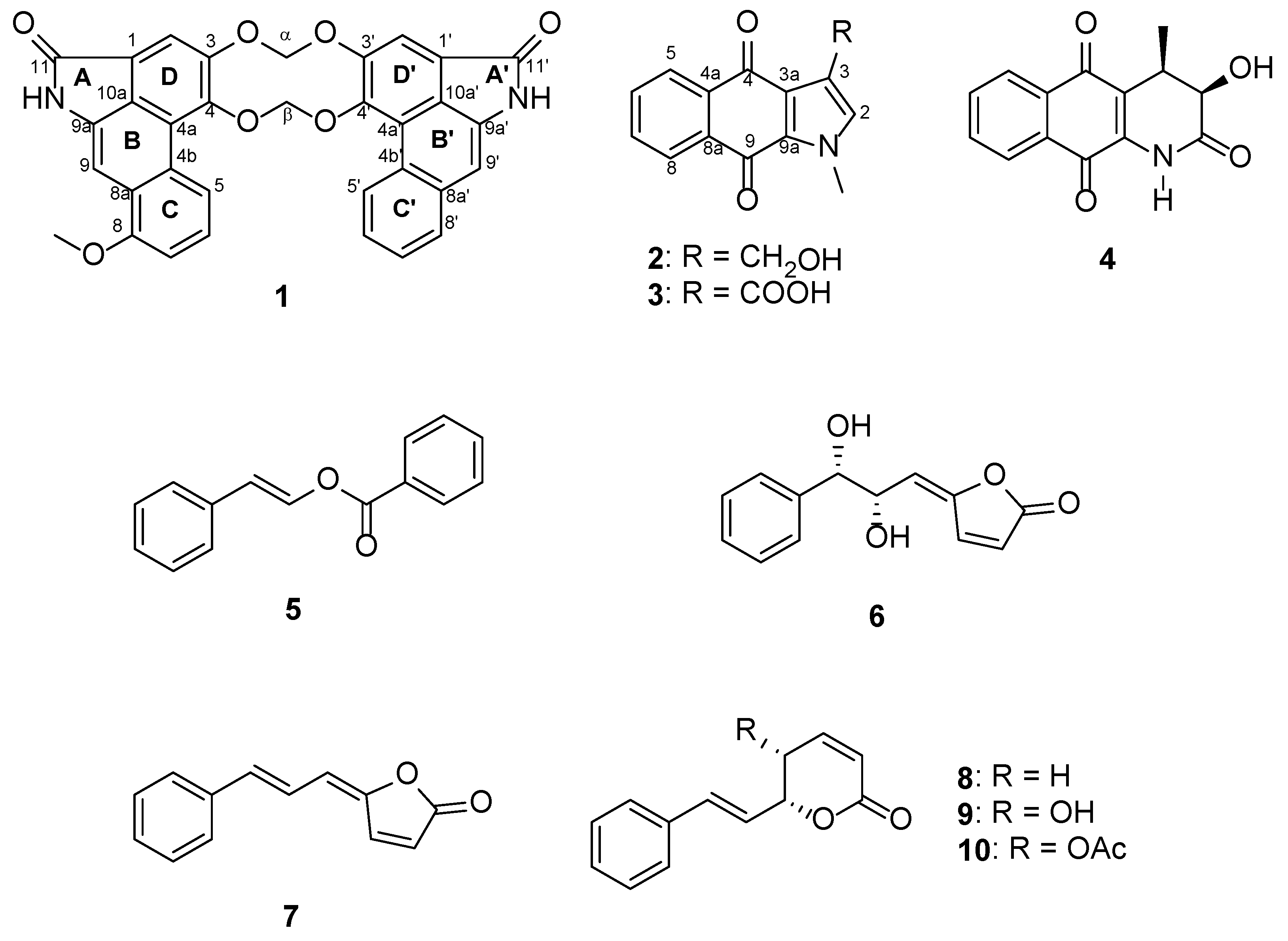
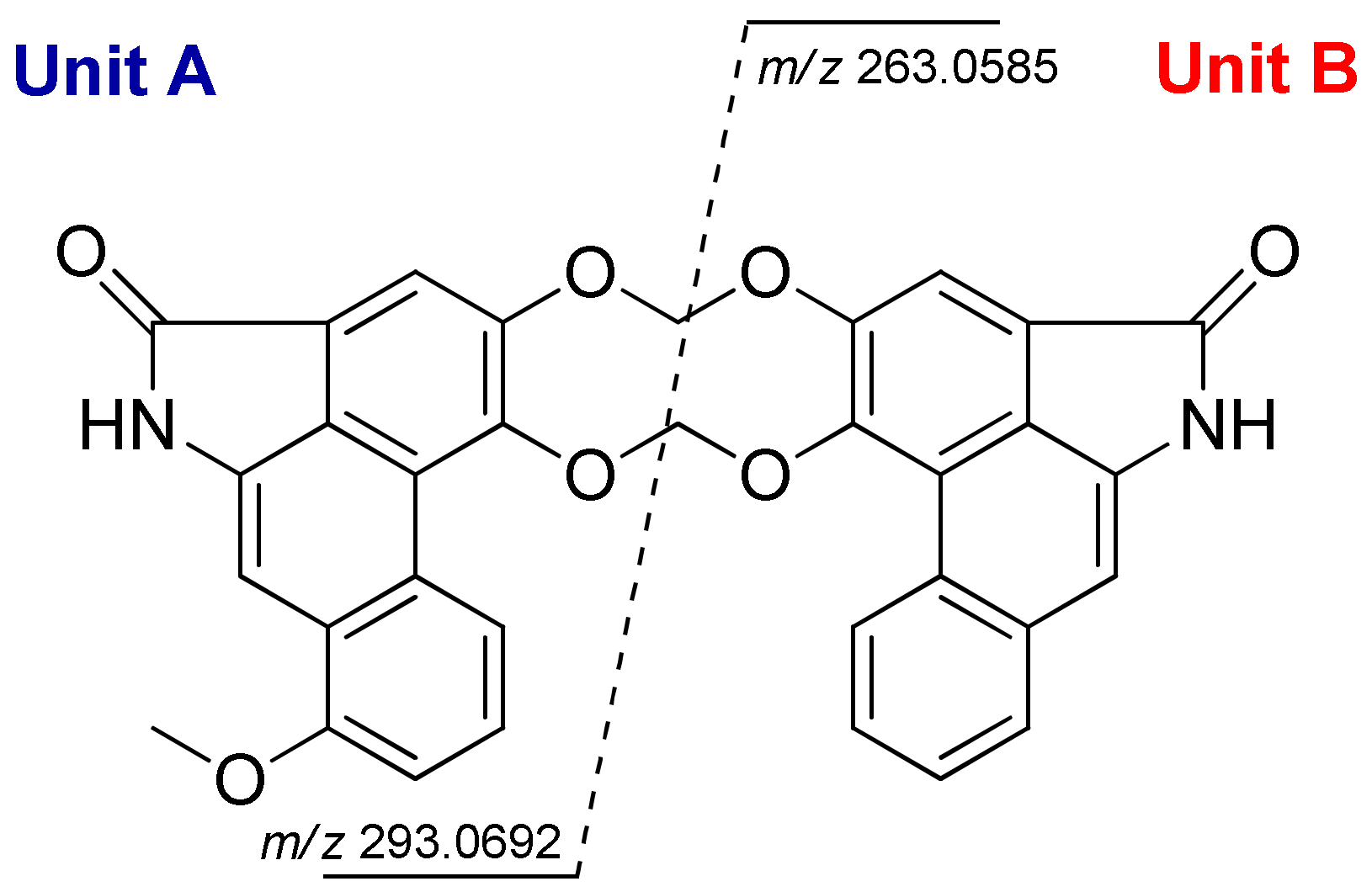
2.1. Structural Elucidation
2.2. α-Glucosidase Inhibitory Activity
3. Conclusions
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. General Experimental Procedures
4.2. Plant Material
4.3. Extraction and Isolation
4.3.1. Gonioridleylactam (1)
4.3.2. Gonioridleyindole (3-Hydroxymethyl-1-methyl-1H-benz[f]indole-4,9-dione, 2)
4.4. α-Glucosidase Inhibitory Activity
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Sample Availability
References
- Blázquez, M.A.; Bermejo, A.; Zafra-Polo, M.C.; Cortes, D. Styryl-lactones from Goniothalamus species–A review. Phytochem. Anal. 1999, 10, 161–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aslam, M.S.; Ahmad, M.S.; Mamat, A.S.; Ahmad, M.Z.; Salam, F. Goniothalamus: Phytochemical and ethnobotanical review. Recent Adv. Biol. Med. 2016, 2, 34–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaidee, W.; Andersen, R.J.; Patrick, B.O.; Pyne, S.G.; Muanprasat, C.; Borwornpinyo, S.; Laphookhieo, S. Alkaloids and styryllactones from Goniothalamus cheliensis. Phytochemistry 2019, 157, 8–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meesakul, P.; Jaidee, W.; Richardson, C.; Andersen, R.J.; Patrick, B.O.; Willis, A.C.; Muanprasat, C.; Wang, J.; Lei, X.G.; Hadsadee, S.; et al. Styryllactones from Goniothalamus tamirensis. Phytochemistry 2020, 171, 112248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lian Ee, G.C.; Lee, H.L.; Goh, S.H. Larvicidal activity of Malaysian Goniothalamus species. Nat. Prod. Lett. 1999, 13, 137–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noor-Zarina, A.W.; Saleha, S.; Halimah, A.S.; Azimahtol, H.L.P.; Nazlina, I. Antioxidant, antibacterial and antiviral properties of Goniothalamus umbrosus leaves methanolic extract. Afr. J. Microbiol. Res. 2011, 5, 3138–3143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macabeo, A.P.G.; Lopez, A.D.A.; Schmidt, S.; Heilmann, J.; Dahse, H.M.; Alejandro, G.J.D.; Franzblau, S.G. Antitubercular and cytotoxic constituents from Goniothalamus gitingensis. Rec. Nat. Prod. 2014, 8, 41–45. [Google Scholar]
- Lekphrom, R.; Kanokmedhakul, S.; Kanokmedhakul, K. Bioactive styryllactones and alkaloid from flowers of Goniothalamus laoticus. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2009, 125, 47–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jusoh, S.; Din, L.B.; Zakaria, Z.; Khaledi, H. 5-Hydroxy-6-[(E)-2-phenylethenyl]-5, 6-dihydro-2H-pyran-2-one isolated from Goniothalamus ridleyi. Acta Cryst. 2012, 68, 2274. [Google Scholar]
- Jusoh, S.; Zakaria, Z.; Ahmad, F.B.; Din, L.B. Isolation and characterization of styryl lactone of Goniothalamus ridleyi. Sains Malays. 2015, 44, 365–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.J.; Kong, M.; Chen, R.Y.; Yu, D.Q. Alkaloids from the roots of Goniothalamus griffithii. J. Nat. Prod. 1999, 62, 1050–1052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, S.; Leong, W.K. Regio- and stereoselective addition of carboxylic acids to phenylacetylene catalyzed by cyclopentadienyl ruthenium complexes. J. Organomet. Chem. 2006, 691, 1117–1120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, X.P.; Anderson, J.E.; Chang, C.J.; McLaughlin, J.L. Three new bioactive styryllactones from Goniothalamus giganteus (Annonaceae). Tetrahedron 1991, 47, 9751–9758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, D.T.; Thi Mai, H.D.; Pham, V.C.; Nguyen, V.H.; Litaudon, M.; Guéritte, F.; Nguyen, Q.V.; Tran, T.A.; Chau, V.M. Alkaloids and styryllactones from the leaves of Goniothalamus tamirensis. Phytochem. Lett. 2013, 6, 79–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fátima, Â.; Kohn, L.K.; Carvalho, J.E.; Pillia, R.A. Cytotoxic activity of (S)–goniothalamin and analogues against human cancer cells. Bioorgan. Med. Chem. 2006, 14, 622–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goh, S.H.; Ee, G.C.L.; Chuah, C.H.; Mak, T.C.W. 5β-Hydroxygoniothalamin, a styrylpyrone derivative from Goniothalamus dolichocarpus (Annonaceae). Nat. Prod. Lett. 2006, 5, 255–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, F.B.; Tukol, W.A.; Omar, S.; Sharif, A.M. 5-Acetyl goniothalamin, a styryl dihydropyrone from Goniothalamus uvaroides. Phytochemistry 1991, 30, 2430–2431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inman, M.; Visconti, A.; Yan, C.; Siegel, D.; Ross, D.; Moody, C.J. Antitumour indolequinones: Synthesis and activity against human pancreatic cancer cells. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2014, 12, 4848–4861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trinh, D.H.; Tran, P.T.; Trinh, B.T.; Nguyen, H.T.; Nguyen, H.D.; Ha, L.D.; Nguyen, L.H.D. Coumarins and acridone alkaloids with α-glucosidase inhibitory and antioxidant activity from the roots of Paramignya trimera. Phytochem. Lett. 2006, 35, 94–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le, T.K.D.; Danova, A.; Aree, T.; Duong, T.H.; Koketsu, M.; Ninomiya, M.; Chavasiri, W. α-Glucosidase inhibitors from the stems of Knema globularia. J. Nat. Prod. 2022, 85, 776–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rangel-Grimaldo, M.; Rivero-Cruz, I.; Madariaga-Mazón, A.; Figueroa, M.; Mata, R. α-Glucosidase inhibitors from Preussia minimoides. J. Nat. Prod. 2017, 80, 582–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghani, U.; Nur-e-Alam, M.; Yousaf, M.; Ul-Haq, Z.; Noman, O.M.; Al-Rehaily, A.J. Natural flavonoid α-glucosidase inhibitors from Retama raetam: Enzyme inhibition and molecular docking reveal important interactions with the enzyme active site. Bioorg. Chem. 2019, 87, 736–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dang, P.H.; Nguyen, H.X.; Duong, T.T.T.; Tran, T.K.T.; Nguyen, P.T.; Vu, T.K.T.; Awale, S. α-Glucosidase inhibitory and cytotoxic taxane diterpenoids from the stem bark of Taxus wallichiana. J. Nat. Prod. 2017, 80, 1087–1095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saunders, R.M.K.; Chalermglin, P. A synopsis of Goniothalamus species (Annonaceae) in Thailand, with descriptions of three new species. Bot. J. Linn. 2008, 156, 355–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kittiwisut, S.; Amnuoypol, S.; Pathompak, P.; Setharaksa, S. α-Glucosidase and α-amylase inhibitory effects with anti-oxidative activity of Tetracera loureiri (Finet & Gagnep.) Pierre ex Craib leaf extracts. Pharm. Sci. Asia 2021, 48, 175–184. [Google Scholar]

| Position | δC | δH [mult, J in Hz] | HMBC (1H→13C) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 119.8 | ||
| 2 | 105.0 | 7.58 (s) | 1, 3, 4, 4a, 11 |
| 3 | 147.3 | ||
| 4 | 149.2 | ||
| 4a | 111.8 | ||
| 4b | 124.7 | ||
| 5 | 119.2 | 8.25 (d, 8.2) | 4b, 6, 7, 8 |
| 6 | 125.6 | 7.52 (t, 8.2) | 5, 7, 8 |
| 7 | 108.0 | 7.20 (d, 8.2) | 5, 6, 8 |
| 8 | 155.9 | ||
| 8a | 104.2 | ||
| 9 | 98.1 | 7.54 (s) | 8, 9a,10a |
| 9a | 134.6 | ||
| 10a | 125.5 | ||
| 11 | 167.9 | ||
| 1′ | 119.8 | ||
| 2′ | 105.3 | 7.57 (s) | 1′, 3′, 4′, 10a′, 11′ |
| 3′ | 147.5 | ||
| 4′ | 149.3 | ||
| 4a′ | 111.8 | ||
| 4b′ | 124.8 | ||
| 5′ | 126.8 | 8.63 (dd, 7.8, 1.5) | 4a′, 7′, 8a′ |
| 6′ | 125.2 | 7.58 (td, 7.8, 1.5) | 8′ |
| 7′ | 127.6 | 7.61 (td, 7.8, 1.5) | 5′, 8a′ |
| 8′ | 128.7 | 7.92 (dd, 7.8, 1.5) | 4b′, 6′, 9′ |
| 8a′ | 134.7 | ||
| 9′ | 104.2 | 7.16 (s) | 4a′, 8′, 9a′, 10a′ |
| 9a′ | 135.5 | ||
| 10a′ | 125.5 | ||
| 11′ | 167.9 | ||
| α | 103.3 | 6.49 (s) | 3, 3′ |
| β | 103.3 | 6.50 (s) | 4, 4′ |
| N-H | 9.76 (s) | ||
| N-H′ | 9.74 (s) | ||
| 8-OMe | 55.3 | 4.05 (s) | 8′ |
| Position | δC | δH [mult, J in Hz] | HMBC (1H→13C) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2 | 129.3 | 6.85 (s) | 3, 3a, 9a, 1′, N-CH3 |
| 3 | 126.2 | ||
| 3a | 162.2 | ||
| 4 | 183.0 | ||
| 4a | 133.9 | ||
| 5 | 126.8 | 7.70 (m) | 4, 6 |
| 6 | 133.6 | 8.16 (m) | 4a, 5 |
| 7 | 133.3 | 8.16 (m) | 8, 8a |
| 8 | 126.7 | 7.70 (m) | 7, 9 |
| 8a | 133.8 | ||
| 9 | 176.4 | ||
| 9a | 131.8 | ||
| 1′ | 36.8 | 4.72 (s) | 2, 3, 3a |
| N-CH3 | 57.1 | 4.07 (s) | 2, 9a |
| Compounds | %Inhibition at 250 µg/mL | IC50, µM |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 99.6 | 138.9 ± 0.9 |
| 2 | 99.3 | inactive |
| 3 | 99.5 | inactive |
| 4 | 98.0 | inactive |
| 7 | 98.6 | 1.25 ± 0.4 |
| 9 | 99.8 | inactive |
| Acarbose | 88.1 | 185.7 ± 0.3 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Polbuppha, I.; Teerapongpisan, P.; Phukhatmuen, P.; Suthiphasilp, V.; Maneerat, T.; Charoensup, R.; Andersen, R.J.; Laphookhieo, S. Alkaloids and Styryl lactones from Goniothalamus ridleyi King and Their α-Glucosidase Inhibitory Activity. Molecules 2023, 28, 1158. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28031158
Polbuppha I, Teerapongpisan P, Phukhatmuen P, Suthiphasilp V, Maneerat T, Charoensup R, Andersen RJ, Laphookhieo S. Alkaloids and Styryl lactones from Goniothalamus ridleyi King and Their α-Glucosidase Inhibitory Activity. Molecules. 2023; 28(3):1158. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28031158
Chicago/Turabian StylePolbuppha, Isaraporn, Passakorn Teerapongpisan, Piyaporn Phukhatmuen, Virayu Suthiphasilp, Tharakorn Maneerat, Rawiwan Charoensup, Raymond J. Andersen, and Surat Laphookhieo. 2023. "Alkaloids and Styryl lactones from Goniothalamus ridleyi King and Their α-Glucosidase Inhibitory Activity" Molecules 28, no. 3: 1158. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28031158
APA StylePolbuppha, I., Teerapongpisan, P., Phukhatmuen, P., Suthiphasilp, V., Maneerat, T., Charoensup, R., Andersen, R. J., & Laphookhieo, S. (2023). Alkaloids and Styryl lactones from Goniothalamus ridleyi King and Their α-Glucosidase Inhibitory Activity. Molecules, 28(3), 1158. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28031158








