Abstract
Major depressive disorder (MDD) is a serious mental illness with a heavy social burden, but its underlying molecular mechanisms remain unclear. Mass spectrometry (MS)-based metabolomics is providing new insights into the heterogeneous pathophysiology, diagnosis, treatment, and prognosis of MDD by revealing multi-parametric biomarker signatures at the metabolite level. In this comprehensive review, recent developments of MS-based metabolomics in MDD research are summarized from the perspective of analytical platforms (liquid chromatography-MS, gas chromatography-MS, supercritical fluid chromatography-MS, etc.), strategies (untargeted, targeted, and pseudotargeted metabolomics), key metabolite changes (monoamine neurotransmitters, amino acids, lipids, etc.), and antidepressant treatments (both western and traditional Chinese medicines). Depression sub-phenotypes, comorbid depression, and multi-omics approaches are also highlighted to stimulate further advances in MS-based metabolomics in the field of MDD research.
1. Introduction
Major depressive disorder (MDD) is a debilitating and widespread psychiatric illness characterized by enduring and substantial feelings of sadness, inferiority, and despair [1]. Notably, the World Health Organization has listed depression as the third leading cause of disease burden across the world and has predicted that the disease will rank first by 2030 [2]. However, due to the complicated pathogenesis of depression and the lack of pathophysiological biomarkers, the diagnosis and treatment of MDD using subjective evaluation and “trial-and-error” approaches often involve considerable error rates [3].
Metabolites are the downstream products of transcription and translation, and changes in those closest to a given phenotype can reflect many pathological or internal changes in biochemical pathways [4]. Metabolic disorders are considered to be an etiological factor in MDD, and metabolite analysis can certainly improve our understanding of the many pathological processes involved in MDD [5,6]. Metabolomics is the culmination of the cascade of “omics” technologies. It combines advanced analytical instrumentations with pattern recognition algorithms to reveal and monitor changes in metabolite profiles in subjects based on their disease status or response to medical or other interventions [7]. Advances in metabolomics have opened new avenues for exploring mechanisms related to MDD.
The main analytical platforms in metabolomics are nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) and mass spectrometry (MS) [8]. NMR enables non-invasive analysis and relatively fast and straightforward metabolite annotation, but is less sensitive than MS. In-depth explanations and discussions of NMR-based metabolomics can be found in various excellent studies and reviews [9,10,11]. MS is widely used in metabolomics analyses. It combines rapidly developing separation technologies—primarily liquid chromatography (LC) and gas chromatography (GC)—to allow qualitative and quantitative analysis of multiple organic molecules in complex biological matrices (serum, plasma, urine, tissue, etc.) with high specificity, sensitivity, and throughput, and low sample consumption [12]. Given these advantages, the applications of MS in metabolomics research have grown exponentially in recent years.
This review focuses on advances in research into MDD using MS-based metabolomics. Common analytical procedures and key metabolic changes during pathogenesis and treatment are described, and current challenges and prospects are discussed with a view to enhancing research into this condition.
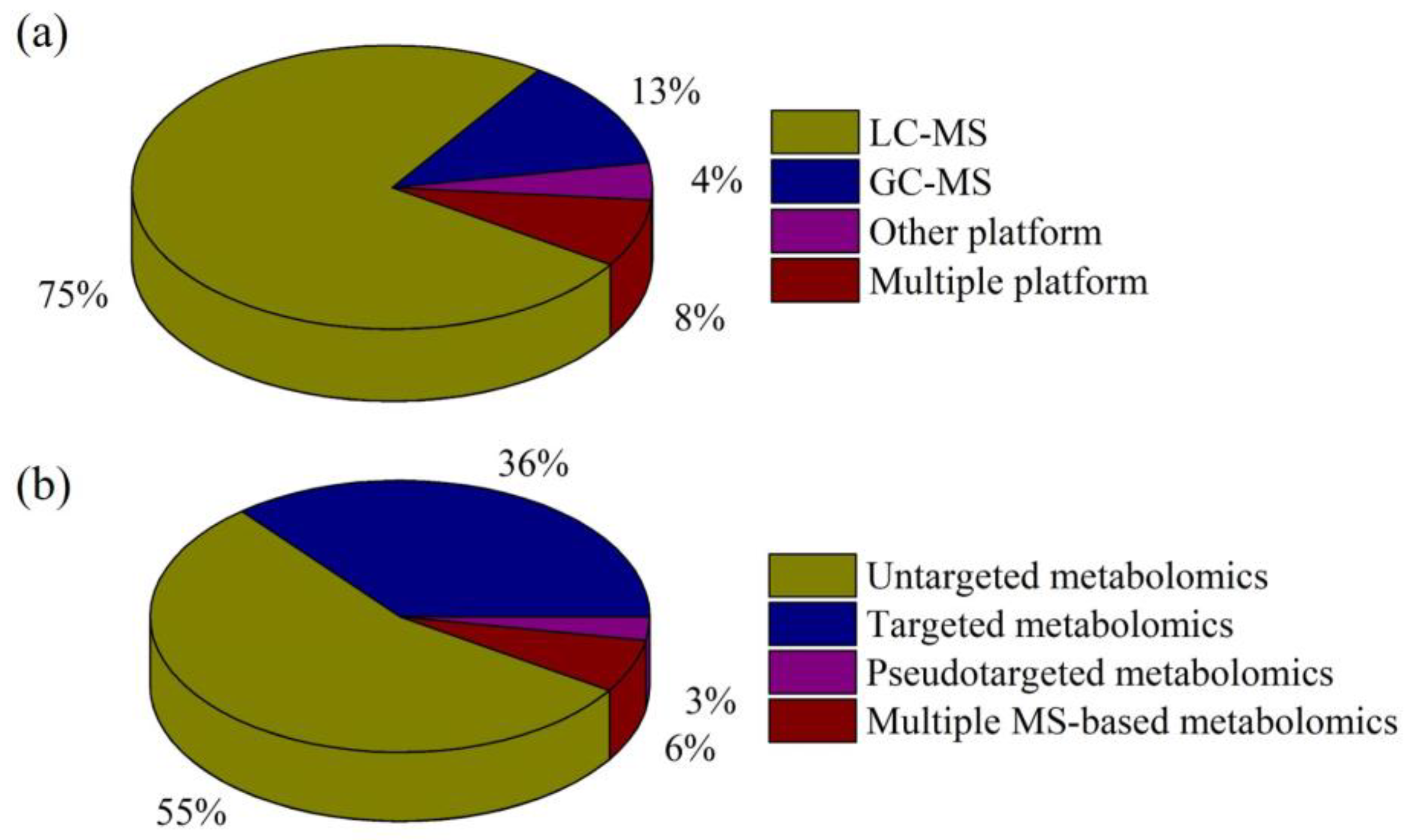
A search of electronic literature bases from 2020 to August 2023 (PubMed [n = 170] and Web of Science [n = 192]) was conducted using the keywords “depression”, “metabolomics”, and “mass spectrometry”. After a preliminary review of these studies, articles in which the disease studied was not depression or the research method was not metabolomics were excluded. In addition, the reference lists of all identified studies were manually searched to identify any additional studies. Finally, 142 studies that met our criteria were identified, and these reports were reviewed. Figure 1 summarizes the numbers of studies in our review for the different MS-based analytical platforms and metabolomics strategies.
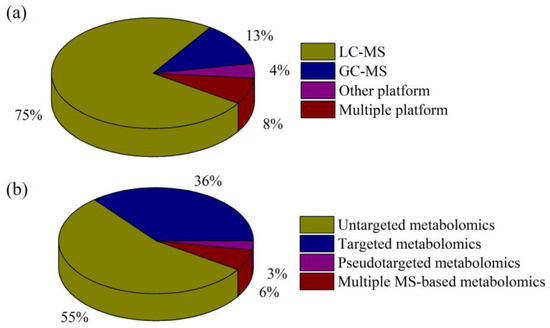
Figure 1.
Percentages of reviewed, published studies utilizing various (a) MS-based analytical platforms and (b) metabolomics strategies.
2. MS-Based Metabolomics Platforms in Depression Research
2.1. MS Platforms in Depression Research
Current state-of-the-art metabolomics technologies are mostly based on MS. Due to the need for measurement of isomers, isobars, and structurally similar analogs, chromatographic MS is preferred for metabolite profiling. LC-MS and GC-MS are the two primary platforms used in metabolomics research into depression, although other platforms, such as supercritical fluid chromatography-MS (SFC-MS) and capillary electrophoresis-MS (CE-MS), also play significant roles (Figure 1a).
2.1.1. LC-MS
LC-MS is capable of detecting most compounds, including non-volatile and thermally labile metabolites, with or without derivatization and is, thus, the most frequently used platform in metabolomics analysis of depression. LC-MS analysis uses various types of columns, including reverse phase (RP-LC-MS; e.g., C18, C8, and C30 columns), normal phase (NP-LC-MS), and hydrophilic interaction (HILIC-LC-MS). RP and HILIC are mainly used for separation of weakly polar and polar compounds, respectively. Recently, an all-in-one-injection HILIC-MS/MS method was developed for the simultaneous determination of 20 purine and pyrimidine metabolites and used to show greatly disturbed purine metabolism in the serum and hippocampus of depressed mice [13]. Our group established a convenient LC-MS/MS method for the simultaneous measurement of 18 amino acid enantiomers using a conventional octadecylsilane RP column and chiral derivatization reagent. Significant differences in glycine, l-threonine, and d-methionine between late-life depression patients and controls were revealed by this method [14]. Sensitive Profiling ChemoSelective Derivatization Carboxylomics (SPCSDCarboxyl) was proposed by Zhou’s group in 2023 for the analysis of carboxylic acids using 5-(diisopropylamino) amylamine derivatization and ultra-performance LC-quadrupole time-of-flight MS (UHPLC-Q-TOF/MS) [15]. Two hundred and eight metabolites were identified in the serum of depressed patients using SPCSDCarboxyl, and a combination of proline, 1-pyrroline-5-carboxylate, and glutamic acid could distinguish between patients and healthy controls. Mocking et al. measured 399 metabolites in patients with recurrent MDD using an established LC-MS/MS platform, and 80% of the recurring metabolic predictors belonged to the phospholipid, sphingomyelin, glycosphingolipid, eicosanoid, microbiome, or purine pathways [16].
2.1.2. GC-MS
GC-MS is suitable for the analysis of volatile organic compounds (VOCs), although derivatization is required to increase the thermal stability and volatility of non-volatile compounds and to reduce their polarity. Due to the high reproducibility of electron ionization in MS, GC-MS can utilize many mass spectra libraries, which enables relatively easy identification of peaks. Several studies have shown that urinary metabolite biomarkers identified by GC-MS can identify post-stroke depression (PSD) in stroke survivors [17]. A biomarker panel consisting of glyceric acid, tyrosine, and azelaic acid was identified in middle-aged and elderly patients with PSD [18,19]. Solid-phase microextraction and GC-MS were used to analyze urinary VOCs and semi-VOCs in patients with late-life major depressive and anxiety disorders. The combined indicators dimethylsulfone, phenethyl isothiocyanate, hexanoic acid, texanol, and texanol isomers showed excellent performance in evaluating MDD and/or agoraphobia in the elderly [20].
2.1.3. Other Chromatography-MS Platforms
Interest in SFC-MS in depression research has grown in recent years due to its excellent separation capabilities and environmental friendliness. It shows remarkable performance in the analysis of lipids. In-line supercritical fluid extraction coupled with SFC-MS/MS method was used to rapidly separate 23 inflammation-related lipids in brain tissue of depressed rats within 15 min. Six pro-inflammatory lipids increased in depressed rats, while six anti-inflammatory lipids decreased [21]. Analysis of VOCs in exhaled breath using proton-transfer-reaction MS (PTR-MS) is a hot topic in the field of depression research, given its advantageous real-time, in-line, and non-invasive attributes. Lueno et al. conducted the first PTR-MS study of the differences in VOCs in exhaled breath in MDD patients and healthy controls. There were significant differences in several masses between the groups, with m/z = 69, 74, 93, and 94 being identified as potential high-accuracy biomarkers [22]. This group then applied breathomics (one of the newest branches of metabolomics) using untargeted PTR-MS to explore changes in biochemical patterns and metabolic pathways related to MDD. A total of 23 differential exhaled metabolites were significantly altered in MDD patients, and these were mapped to five metabolic pathways [23]. Recently, an interesting study from Frodl’s group used PTR-MS to analyze gut–brain axis VOCs and distinguish between schizophrenia, MDD, and healthy controls [24]. CE-MS is a powerful tool that combines the high separation capability and low sample consumption of CE with the identification capabilities of MS. Okamoto et al. used CE and Fourier transform MS to identify differential patterns of serum metabolites in MDD patients with and without type 2 diabetes mellitus, indicating that this comorbidity can affect metabolic pathways and alter the distribution of serum metabolites in MDD patients [25].
2.1.4. Combined Chromatography-MS Platforms
A single analytical technique cannot encompass all metabolites, given their wide-ranging physicochemical properties and broad concentration ranges. For example, Xie’s group used GC-MS to characterize differential metabolites in the olfactory bulb (OB) of rats with chronic unpredictable mild stress (CUMS). Disruption of lipid and purine metabolisms was demonstrated, which may be related to dysfunction of the OB [26]. Subsequently, Zhou’s group used LC-MS to investigate metabolic changes in the OB of mice and, in contrast to the previous GC-MS results, demonstrated disruption of the tryptophan-5-hydroxytryptamine pathway [27]. These findings show that different analytical techniques can highlight different metabolic perspectives, and it is necessary to adopt multiple chromatography-MS platforms in the search for new depression biomarkers and molecular mechanisms. A combination of GC-MS and LC-MS/MS was used to analyze metabolite profiles in plasma, urine, and cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) of patients with treatment-refractory depression and suicidal behavior [28]. A significant proportion of patients showed treatable abnormalities, while no healthy controls exhibited metabolic abnormalities. A metabolome-wide association study using two separate UHPLC-MS/MS injections and one GC/MS injection of each sample found that the level of lauroylcarnitine in serum was decreased in patients with depression, which may indicate fatty acid oxidation and/or mitochondrial dysfunction in depression [29].
2.2. Metabolomics Strategies in Depression Research
Metabolomics is a branch of “omics” technology focusing on high-throughput identification and quantification of small molecule metabolites (<1500 Da). It can describe specific multi-parameter characteristics of the heterogeneous pathophysiological mechanisms underlying depression. There are three main MS-based metabolomics approaches in depression research: untargeted, targeted, and pseudotargeted analyses (Figure 1b).
2.2.1. Untargeted Metabolomics
Untargeted methods are typically used in metabolomics studies for the detection and discovery of small organic compounds, with high-resolution MS (HRMS) using Orbitrap or Q-TOF instruments providing full-scan information, accurate masses, and tandem MS details of the metabolites. Although untargeted metabolomics suffers from high complexity, poor repeatability, and limited linear range, it remains the first choice for the metabolite discovery stage because it is unbiased and has high coverage. Jiao et al. used the classic untargeted metabolomics technique (UHPLC-Q-TOF-MS) to investigate the antidepressant-like effects of Jiaotaiwan on rats [30]. Changes in the metabolite profile of rat serum before and after administration were analyzed using multiple statistical approaches. The most important biomarkers associated with depression were identified via principal component analysis, partial least squares discriminant analysis, and heatmap analysis. Pathway analysis then revealed that the therapeutic effect of Jiaotaiwan on depression may involve the regulation of amino acid, glycerophospholipid, and energy metabolisms. Untargeted metabolomics was also used to identify O-acetyl-l-carnitine, l-aspartic acid, fumarate, and alanine as peripheral biomarkers in patients with MDD [31]. To clarify the metabolites involved in specific pathways, a stable isotope-resolved metabolomics method was developed and applied in depression research for the first time by Qin’s group [32]. The stable isotope tracer 13C6-glucose was prepared and introduced into a CUMS rat model, and labeled metabolites were detected by LC-MS using HILIC and T3 chromatography columns. Twenty-eight of the 78 labeled metabolites related to energy metabolism in the model group differed significantly from the control group.
2.2.2. Targeted Metabolomics
Targeted metabolomics based on triple-quadrupole MS (TQMS) is generally used in the verification phase to confirm the identity of, and to quantify, compounds of interest. When using multiple reaction monitoring (MRM) mode, targeted analysis is characterized by high sensitivity, strong specificity, good repeatability, and wide linear range, but it is limited by its relatively narrow coverage of metabolites. However, continuous development of ionization efficiency, scanning rate, and other parameters has enabled the simultaneous analysis of dozens to hundreds of metabolites by TQMS. Energy-related metabolites, carnitine, amino acids, and biogenic amines were quantified in the ventral hippocampus of rats with chronic mild stress (CMS) using LC-MS/MS. Glycolysis and the tricarboxylic acid cycle were particularly involved in defining vulnerability to stress [33]. To avoid the addition of internal standards and corresponding analogs, Chen et al. developed a targeted metabolomics method involving relative quantification based on HILIC-MS/MS and the quality control-based random forest signal correction algorithm [34]. Nineteen metabolites were simultaneously determined in the serum of MDD patients, the changes in urocanic acid being reported for the first time.
2.2.3. Pseudotargeted Metabolomics
The recently developed pseudotargeted metabolomics approach combines the benefits of targeted and untargeted analyses. By extracting MRM transitions from biological samples, pseudotargeted profiling offers higher coverage of metabolites than targeted profiling. Furthermore, the use of selected ion monitoring (SRM) mode gives pseudotargeted profiling a wider linear range and better data quality than untargeted profiling. However, some limitations of pseudotargeted metabolomics still need to be addressed. For example, a combination of HRMS and TQMS is usually required, some detected metabolites cannot be identified, and it is only semi-quantitative [35]. There are many applications of targeted and untargeted metabolomics in studies of depression, but only a few studies have used pseudotargeted methods. In 2020, Yang et al. described a segment data-dependent acquisition (SDDA)-based pseudotargeted approach for analysis of depressed rats treated with liquiritin [36]. A total of 502 MRM transitions were detected, and five metabolic pathways were found to be related to depression. This same research group subsequently developed comprehensive pseudotargeted lipidomics methods based on SDDA and two- or three-phase liquid extraction to elucidate the differential lipids related to depression. Broadening the lipid coverage and addressing analyte co-elution enabled 53 and 61 differential variables to be identified in the plasma of depressed rats in these studies [37,38]. Yang et al. also described a green and efficient ultra-high performance supercritical fluid chromatography-MS (UHPSFC-MS/MS)-based pseudotargeted lipidomics method that detected 758 lipids within 8 min [39]. This method had a shorter analytical runtime, narrower peaks, higher sensitivity, and better separation of lipid isomers than the UHPLC-MS/MS-based pseudotargeted method. Applications of the pseudotargeted metabolomics approach in depression research are still in their infancy but show great potential.
2.2.4. Combined Metabolomics Strategies
Increasing attempts are being made to determine the complete metabolite profile for depression by combining multiple MS-based metabolomic approaches. Untargeted methods are often used as an initial screening assay in clinical biomarker discovery studies, with only those metabolites showing significant differences being confirmed using targeted, quantitative assays. Lee et al. profiled serum metabolites using an untargeted method, identifying 14 metabolites with differences between MDD and control groups [40]. The efficacy of endogenous acetylcarnitine for the diagnosis of depression and determination of remission status was then confirmed using a targeted SRM approach. Similarly, Wang et al. used untargeted serum metabolomics and pathway analysis to show that abnormal amino acid metabolism in mice with chronic social defeat stress (CSDS) is related to their abnormal behavior, and the reduction in leucine revealed by targeted metabolomics is specifically and positively related to the social interaction rate [41]. The antidepressant mechanism of the Chaihu–Baishao herb pair was investigated using combined untargeted and targeted analyses [42]. Twenty-one metabolic pathways that were synergistically regulated by Chaihu–Baishao were identified via cortex metabolomics based on UPLC-Q-Orbitrap/MS, and the crucial impact on the purine metabolism pathway was quantitatively confirmed by UPLC-MS/MS in MRM mode.
3. Key Metabolic Changes in Depression
Advances in MS-based metabolomics techniques have been crucial in driving the progress of research into depression. Recent applications of MS-based metabolomics in depression biomarker discovery and elucidation of pathogenic mechanisms are summarized below.
3.1. Monoamine Neurotransmitters
The “monoamine hypothesis” is important in the study of depression, and the development of the majority of clinical antidepressants has been based on monoamine neurotransmitters [43]. Although considerable progress has been made in this area, the underlying mechanisms remain unclear and treatments are increasingly controversial. Monoamine neurotransmitters can interact with other metabolic pathways in depression. The “monoamine (5-HT)-Glutamate/GABA long neural circuit”, proposed by Li, holds the view that monoaminergic and non-monoaminergic mechanisms form a long neural circuit that mediates rapid antidepressant effects [44]. Li et al., using LC-MS/MS, studied changes in neurotransmitters and their related metabolites in GABAergic, serotonergic, and catecholaminergic pathways in the nucleus accumbens of CUMS-induced anhedonia-like rats [45]. The level of 5-hydroxytryptamine in anhedonia-susceptible rats increased, while dopamine did not change significantly. Xu et al. found that gut microbiota (GM) can activate monoamines via stimulating the enteroendocrine cells to produce 5-hydroxytryptamine, dopamine, and norepinephrine, which can affect the central nervous system. The brain in turn can regulate gastrointestinal functions through the neuro-immune-endocrine system [46]. Using LC-MS/MS, Zhong’s group showed that Morinda officinalis oligosaccharides alleviated depression via the tryptophan-5-hydroxytryptophan-serotonin metabolic pathway in the GM [47]. In addition, monoamine neurotransmitters are intertwined with numerous new depression pathways, such as inflammation, oxidative stress, neurotrophins, and neurogenesis. In-depth explanation and discussion can refer to some excellent works and reviews [5,43].
3.2. Amino Acids
Amino acids and their metabolites are fundamental substrates and regulators in many metabolic pathways and some have been identified as biomarkers of depression. Untargeted GC-MS identified significant changes in l-alanine, l-glutamic acid, glycine, l-methionine, l-phenylalanine, l-valine, l-isoleucine, and l-norleucine in the main stress-targeted tissues of CUMS-induced mice [48]. High levels of glutamic acid, aspartic acid, and glycine and low levels of 3-hydroxykynurenine were quantified by LC-MS in serum of MDD patients, and the levels of glutamic acid and phenylalanine correlated with the severity of depression [49]. Significant negative associations of the branched-chain amino acids valine and leucine with depression were identified using untargeted metabolomics [50]. Increased glutamate, decreased dopamine, and altered trends in γ-aminobutyric acid in the habenula of CUMS-susceptible and -resilient rats were identified using LC-MS/MS [51].
Disruption of the tryptophan pathway plays a crucial role in MDD. Tryptophan is metabolized alongside the kynurenine, serotonin, and microbial pathways. Brum et al. found that levels of all tryptophan catabolites were reduced in the plasma of patients with MDD, bipolar depression (BD), and schizophrenia (SCZ), but these metabolites could not be used to distinguish between the disorders [52]. A similar conclusion was also reached by Liu et al. [53]. Yun et al. studied the relationship between the tryptophan–kynurenine pathway and the painful physical symptoms of MDD [54]. Patients with such symptoms exhibited higher kynurenine, quinolinic acid, and kynurenine/tryptophan ratios than those without. Tryptophan metabolism is central to communication between the GM and the brain in depression [55]. LC-MS/MS showed that kynurenine and 3-hydroxycaninuric acid increased significantly along the gut–brain axis of depressive-like rats subjected to chronic restraint stress (CRS) [56]. The tryptophan–kynurenine pathway is also linked to the inflammatory state of patients with MDD [57]. Haroon et al. analyzed kynurenine pathway metabolites and inflammatory markers in the plasma and CSF of depressed patients [58]. Kynurenine and kynurenine/tryptophan in plasma, and kynurenine, kynurenic acid, and quinolinic acid in CSF were closely related to plasma tumor necrosis factor. Pau et al. replicated and expanded upon these findings by evaluating more metabolites and suggesting that the levels of some peripheral kynurenine pathway metabolites might serve as proxies for central kynurenine pathway metabolites in patients with MDD [59]. Zheng et al. also found that C-reactive protein and kynurenic acid/quinolinic acid are independently associated with white matter integrity in MDD [60]. Some studies indicate that therapy can affect tryptophan metabolism. Tateishi et al. reported that levels of kynurenine, kynurenic acid, and kynurenine/tryptophan ratio in plasma of patients with treatment-resistant depression were unchanged after repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation treatment [61]; however, Ryan et al. reported that the kynurenic acid pathway was mobilized by electroconvulsive therapy [62].
3.3. Lipids
Lipids are a broad class of biomolecules with essential roles in many cellular processes, including molecular signal transduction, energy storage, and cell membrane formation. Advanced MS-based lipidomics methods have deepened our understanding of the lipidome in the central and peripheral nervous systems and its associations with depression [6]. Miao et al. identified lipid networks associated with the risk of depression using untargeted LC-MS lipid analysis [63]. For example, lower levels of sphingomyelins and glycerophospholipids and higher levels of lysophospholipids were associated with the incidence and/or prevalence of depression. An LC-MS lipidomics study identified 13 differentially expressed lipids in the plasma of adult female MDD and BD patients and could distinguish between these conditions with medium confidence (area under the curve [AUC] was 0.860) [64]. Similarly, a panel of 111 lipid species was capable of distinguishing SCZ from MDD (AUC = 0.920) [65]. Glycerophospholipids are critical components of neuronal membranes and eukaryote cellular membranes. LC-MS lipid metabolite profiling in the hippocampus of PSD rats showed 50 key metabolites were reduced, and these were mainly involved in glycerophospholipid metabolism (particularly cardiolipin metabolism) [66]. Glycerophospholipid metabolism was also associated with the pathogenesis of PSD in humans [67,68]. Various lipidomics studies have confirmed that peripheral and central glycerophospholipid metabolism disorders are involved in the pathogenesis of depression via the microbiome–gut–brain axis [69,70,71,72]. Jiang et al. used UHPLC-Q-TOF-MS to investigate plasma metabolite biomarkers in young MDD patients and identified phosphatidylcholine as a female-specific biomarker (AUC = 0.957) [73]. Schumacher et al. found that ceramide concentration in the plasma of MDD patients correlated with the severity of MDD, and neutralization of ceramides abrogated depressive behavior in mice [74]. Untargeted UHPLC-MS metabolomics revealed that phosphatidylserine (16:0/16:1) and phosphatidic acid (18:1/18:0) were significantly increased in plasma of MDD patients [75].
3.4. Energy Metabolism
Many studies have shown that energy metabolism is impaired in patients with depression. This may point towards new treatments for the condition. Most of the body’s energy comes from the tricarboxylic acid cycle, oxidative phosphorylation, and glycolysis [76]. Wang et al. demonstrated, using metabolomics, that the tricarboxylic acid cycle was inhibited in mice exposed to CSDS and in patients with first-episode depression [77]. The altered metabolism of acylcarnitines may link mitochondrial dysfunction to depression via impairment of fatty acid β-oxidation [78]. Lower levels of acetyl-l-carnitine and medium- and long-chain acylcarnitines and higher levels of l-carnitine and l-carnitine/acetyl-l-carnitine ratio were found in the plasma of depressed patients, but these differences disappeared after treatment [79,80]. Acylcarnitine profiles also help to distinguish different phenotypic subtypes of MDD, such as core depression, anxious depression, and neurovegetative symptoms of melancholia [81]. Given that glycogen is the main energy source for most higher organisms, Qin’s group used stable isotope-resolved metabolomics with a 13C6-glucose tracer to reveal the blockage of the tricarboxylic acid cycle and abnormal activation of gluconeogenesis in rats with CUMS and in corticosteroid-induced PC12 cells [82,83,84,85,86].
3.5. Gut Microbiota and Metabolomics
The relationship between the GM and depression is a particular focus of psychobiology research, but the underlying molecular mechanisms remain unclear [87]. A combination of 16S rRNA gene sequencing and MS-based metabolomics is often used to investigate these GM mechanisms in patients with depression and in CUMS, CSDS, and CRS mouse models [88]. Growing evidence from this toolkit of clinical studies and animal models suggests that GM compositions (e.g., the phylum Firmicutes and genera Bacteroides and Lactobacillus) and related metabolites (e.g., short-chain fatty acids and tryptophan metabolism) are disordered in depression along the brain–gut–microbiota axis. For example, Xie et al. found that two crucial tryptophan metabolism-related metabolites (tryptophan and 5-hydroxytryptophan) were reduced in the feces of CSDS mice, and these compounds were associated with Lactobacillus [89]. Zhang et al. showed that Bacteroides species enriched in the GM of MDD patients had differing effects on the susceptibility to depressive behaviors [90]. This was partly explained by the different changes in tryptophan pathway metabolites and neurotransmitters along the gut–brain axis. The relationship between microbial metabolites in feces and neurotransmitters in the prefrontal cortex of depressed mice was also explored using targeted metabolomics [91]. This suggested that the disruption of microbial metabolites may affect prefrontal cortex neurotransmitter levels, leading to depressive episodes. This same phenomenon—simultaneous changes in brain and gut metabolism in CUMS rats—was also observed by Hu et al. [92]. Our group used whole-genome shotgun metagenomic and untargeted metabolomic methods to identify disturbed microbial genes (in Bacteroides, Blautia, and Eubacterium) and fecal metabolites (γ-aminobutyrate, phenylalanine, and tryptophan) in MDD patients [93]. The antidepressant effect of chenodeoxycholic acid regulated by Blautia and Eubacterium has also been studied [94]. Table 1 summarizes the GM-related metabolites that have been reported to be associated with depression.

Table 1.
Examples of metabolites associated with gut microbiota that have been reported to be associated with depression.
4. Metabolomics in Antidepressant Treatment Response
Given the phenotypic complexity of patients’ responses to antidepressants, clinical symptoms and “trial-and-error” approaches are insufficient to guide treatment selection for individual patients. Pharmacotherapy is generally the first-choice treatment for MDD. Crucially, the metabolic status of MDD patients exhibiting a response to pharmacotherapy (including remission) appears to differ from non-responsive patients [106]. Pharmacometabolomics (the application of metabolomics in the study of drug effects) has been used to map the effects of antidepressants on metabolite profiles and has provided new insights into the mechanisms of action of various therapies. Some of the studies that have evaluated metabolite changes in animal models and clinical patients following antidepressant treatment are summarized in Table 2. Pharmacological medications have alleviated abnormalities of amino acid, energy, and lipid metabolisms and GM-derived metabolites induced by depression.

Table 2.
Applications of metabolomics in the analysis of treatments for depressive disorders.
4.1. Western Medicines
Several notable western medicines have contributed significantly to the management of depression, although their mechanisms of action are not fully understood. Escitalopram is one example. It is a commonly used antidepressant of the selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor (SSRI) class, but the response varies between individuals. The mechanism of citalopram/escitalopram was studied using metabolomics targeted at 180 metabolites, and changes in the profiles of acylcarnitine, lipids, and amino acids indicated that mitochondrial energetics and lipid membrane remodeling are implicated in the SSRI treatment response [107]. Recently, our group conducted an LC-MS/MS study on the relationship between plasma oxysterol levels and the effectiveness of escitalopram antidepressant treatment. Oxysterols, especially 27-hydroxycholesterol, decreased in responders and increased in non-responders following escitalopram treatment. This suggests that 27-hydroxycholesterol has potential as an escitalopram response indicator during MDD treatment [108]. We also explored the role of the GM in determining escitalopram treatment efficacy in MDD patients [109]. Such microbiota-centered perspective could potentially improve antidepressant efficacy in clinical practice. The antidepressant effects of ketamine have received increasing attention since the United States Food and Drug Administration approved (S)-ketamine nasal spray in March 2019 [151,152]. Zhou et al. analyzed changes in lipid compositions in mice with induced chronic variable stress (CVS) and found that disruption of sphingolipids, glycerolipids, and fatty acyls was partially corrected by administration of (S)-ketamine [113]. MS-based metabolomics has been used to analyze the efficacy of various synthetic antidepressants and has made a significant contribution to improving the treatment of depression.
4.2. Traditional Chinese Medicines
Traditional Chinese medicines (TCMs) exhibiting desirable antidepressive effects have gradually attracted more attention because of their strong safety profiles. However, due to the multi-component, multi-target, and multi-channel nature of TCMs, elucidation of their mechanisms of action is challenging. MS-based metabolomics provides a new way to elucidate these mechanisms holistically [153]. For the first time, in 2021, a combination of pharmacodynamics and urine metabolomics based on UPLC-Q-TOF-MS was used to investigate the antidepressant effect of Millettia speciosa Champ [154]. l-isoleucine, sebacic acid, and allantoin were identified as potential pharmacodynamic biomarkers related to the efficacy of this TCM. Similarly, LC-MS-based metabolomics of peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) was used to investigate the antidepressant mechanism of Chaigui granules [115]. Their antidepressant effects were attributed to improved immune function and regulation of the purine metabolic pathway in PBMCs. The metabolomics analysis of TCMs in Table 2 exhibits a systemic metabolic shift in amino acids (such as alanine, aspartate, glutamate, tryptophan, etc.), organic acids (oxalic acids, stearic acids, bile acid, etc.), and purine, phospholipid, etc. These differential metabolites are mainly involved in amino acid metabolism, lipid metabolism, energy metabolism, gut microbiota metabolism, etc. Such integration of metabolomics with other analytical strategies has provided new insights into the mechanisms of many TCMs and promoted their use as modern treatments for depression.
4.3. Other Treatments
Given the high proportion of refractory or treatment-resistant cases of depression, there is an urgent need for the development of new antidepressants. Metabolomics is an effective strategy in this field. l-theanine is a bioactive component of green tea and a food additive with health benefits. Zhu et al. systematically explored the antidepressant effects of l-theanine in a CUMS rat model using LC-MS/MS and enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) techniques [139]. Untargeted UPLC-Q-TOF-MS highlighted 28 metabolites that changed significantly during l-theanine treatment, while targeted HILIC-MS/MS identified these key amino acids and neurotransmitters and, consequently, their related pathways. By clarifying these preventive mechanisms, this study laid a foundation for the use of l-theanine in the treatment of children and adolescents with depression. Some probiotics also exhibit antidepressant effects and have fewer side effects, have less of an associated stigma, and are less addictive than conventional antidepressants [155]. The therapeutic effect of bifid triple viable probiotic capsules was evaluated in a CUMS rat model, and untargeted metabolomics revealed that the observed reduction in depression-like behavior may be related to endothelin-1 or CREB signaling [143].
5. Perspectives and Conclusions
MDD is a highly heterogeneous condition, but the use of metabolomics to identify specific biological characteristics of clinical sub-phenotypes is expected to improve personalized diagnostic capabilities. Brydges et al. used three metabolomics platforms to evaluate the correlation between metabolomic markers and three symptom dimensions of MDD (melancholic, anxious distress, and immunometabolic) [156]. These symptoms exhibited specific and minimally overlapping metabolomic signatures, suggesting that the multifaceted disruption of the delicate balance between the GM, dietary lipids, and host lipid metabolism may be a cause of specific MDD symptoms. It is clear that further detailed MS metabolomics studies of the various subtypes of depression are likely to improve clinical diagnosis.
In addition to subtypes of depression, increasing attention has been paid to metabolomics-based research of comorbid depression. Investigation of comorbid depression in mice under social fear conditions suggested that changes in sphingolipid metabolism in the brain may be related to the short- and long-term pathophysiology of social anxiety disorder [157]. The effects and mechanisms of Jiaotaiwan treatment of diabetes mellitus accompanied by depression, and of albiflorin and paeoniflorin in the treatment of cancer-related depression, have been evaluated using MS-based metabolomics, providing greater understanding of the mechanisms of antidepressant therapies [158,159]. Metabolomics is expected to be increasingly used in research into various diseases complicated by depression.
Due to the complexity of the pathogenesis of MDD, the integration of metabolomics with other “omics” technologies is becoming increasingly necessary. Recent studies have combined genomics and metabolomics to characterize various aspects of early- and adult-onset MDD, including adult MDD suicide attempts [160,161,162,163]. Integrated proteomics and metabolomics were used to explore antidepressant treatments in animal models and MDD patients [164,165]. Multi-omics methods will improve our understanding and treatment of MDD and enhance prevention strategies, enabling the considerable advancement of precision medicine [166].
Recent advances in MS-based metabolomics platforms have facilitated a more intensive study of depression. This review summarizes the main findings of the most recent studies in this field focusing on the applied platforms (LC-MS, GC-MS, SFC-MS, etc.) and strategies (untargeted, targeted, and pseudotargeted approaches). Key metabolic changes (in monoamine neurotransmitters, amino acids, lipids, energy metabolism, and GM-related metabolism) and the application of metabolomics in antidepressant treatments in western medicines and TCMs are also reviewed. Depression sub-phenotypes, comorbid depression, and multi-omics approaches are also discussed. We expect this review to stimulate new developments in MS-based metabolomics in the field of depression research.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, M.L. and Z.S.; writing—original draft preparation, M.L.; writing—review and editing, W.M. and Y.H.; supervision, Z.S. and J.Y.; funding acquisition, M.L., Z.S., J.Y. and W.M. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the R&D Program of Beijing Municipal Education Commission (KM202310025007), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 82171525, 82171526), Beijing Talents Project (2020A38), Beijing Key Laboratory of Mental Disorders, Code: 2021JSJB02.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Beurel, E.; Toups, M.; Nemeroff, C.B. The bidirectional relationship of depression and inflammation: Double trouble. Neuron 2020, 107, 234–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. Depression. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/ (accessed on 25 July 2021).
- Marwaha, S.; Palmer, E.; Suppes, T.; Cons, E.; Young, A.H.; Upthegrove, R. Novel and emerging treatments for major depression. Lancet 2023, 401, 141–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiu, S.; Guo, S.F.; Yang, Q.; Xie, Y.Q.; Tang, S.Q.; Zhang, A.H. Innovation in identifying metabolites from complex metabolome-Highlights of recent analytical platforms and protocols. Front. Chem. 2023, 11, 1129717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fries, G.R.; Saldana, V.A.; Finnstein, J.; Rein, T. Molecular pathways of major depressive disorder converge on the synapse. Mol. Psychiatry 2023, 28, 284–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pinto, B.; Conde, T.; Domingues, I.; Domingues, M.R. Adaptation of lipid profiling in depression disease and treatment: A critical review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 2032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, J.J.; Xie, P. The potential for metabolomics in the study and treatment of major depressive disorder and related conditions. Expert Rev. Proteom. 2020, 17, 309–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Letertre, M.P.M.; Dervilly, G.; Giraudeau, P. Combined nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy and mass spectrometryapproaches for metabolomics. Anal. Chem. 2021, 93, 500–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edison, A.S.; Colonna, M.; Gouveia, G.J.; Holderman, N.R.; Judge, M.T.; Shen, X.N.; Zhang, S.C. NMR: Unique strengths that enhance modern metabolomics research. Anal. Chem. 2021, 93, 478–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, X.F.; Shi, Y.; Ma, L.; Yang, W.Q.; Pu, J.C.; Shen, Y.Q.; Liu, Y.Y.; Zhang, H.P.; Lv, F.J.; Hu, L.B. Altered neurometabolite levels in the brains of patients with depression: A systematic analysis of magnetic resonance spectroscopy studies. J. Affect. Disord. 2023, 328, 95–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rydin, A.O.; Milaneschi, Y.; Quax, R.; Li, J.; Bosch, J.A.; Schoevers, R.A.; Giltay, E.J.; Penninx, B.W.J.H.; Lamers, F. A network analysis of depressive symptoms and metabolomics. Psychol. Med. 2023, 1–10, (Online ahead of print). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collins, S.L.; Koo, I.; Peters, J.M.; Smith, P.B.; Patterson, A.D. Current challenges and recent developments in mass spectrometry-based metabolomics. Annu. Rev. Anal. Chem. 2021, 14, 467–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Z.; Li, S.; Aa, N.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, R.; Xu, C.; Zhang, S.; Kong, X.; Wang, G.; Aa, J.; et al. Quantitative analysis of 20 purine and pyrimidine metabolites by HILIC-MS/MS in the serum and hippocampus of depressed mice. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2022, 219, 114886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; He, J.; Ruan, C.; Pan, W.; Mao, P.; Sun, Z.; Wang, G.; Yang, J. Simultaneous measurement of amino acid enantiomers in the serum of late-life depression patients using convenient LC-MS/MS method with N(alpha)-(5-fluoro-2,4-dinitrophenyl)-l-leucinamide derivatization. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2023, 230, 115387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bian, X.; Zhou, N.; Zhao, Y.; Fang, Y.; Li, N.; Zhang, X.; Wang, X.; Li, Y.; Wu, J.L.; Zhou, T. Identification of proline, 1-pyrroline-5-carboxylate and glutamic acid as biomarkers of depression reflecting brain metabolism using carboxylomics, a new metabolomics method. Psychiat. Clin. Neuros. 2023, 77, 196–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mocking, R.J.T.; Naviaux, J.C.; Li, K.; Wang, L.; Monk, J.M.; Bright, A.T.; Figueroa, C.A.; Schene, A.H.; Ruhé, H.G.; Assies, J.; et al. Metabolic features of recurrent major depressive disorder in remission, and the risk of future recurrence. Transl. Psychiatry 2021, 11, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, W.; Wang, X.F.; Wei, X.F.; Zhang, J.R.; Hu, C.; Ma, W.; Shen, W.D. Does urinary metabolite signature act as a biomarker of post-stroke depression? Front. Psychiatry 2022, 13, 928076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, J.; Han, Y.; Hong, Y.L.; Li, W.W.; Pei, Q.L.; Zhou, X.Y.; Zhang, B.B.; Wang, Y. Identification of potential metabolite markers for middle-aged patients with post-stroke depression using urine metabolomics. Neuropsych. Dis. Treat. 2020, 16, 2017–2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Lv, Y.N.; Li, X.B.; Xiong, J.J.; Liang, H.T.; Xie, L.; Wan, C.Y.; Chen, Y.Q.; Wang, H.S.; Liu, P.; et al. Urinary metabolite signatures for predicting elderly stroke survivors with depression. Neuropsychiatr. Dis. Treat. 2021, 17, 925–933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fujita, A.; Ihara, K.; Kawai, H.; Obuchi, S.; Watanabe, Y.; Hirano, H.; Fujiwara, Y.; Takeda, Y.; Tanaka, M.; Kato, K. A novel set of volatile urinary biomarkers for late-life major depressive and anxiety disorders upon the progression of frailty: A pilot study. Discov. Ment. Health 2022, 2, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, W.; Yang, J.; Liu, D.; Zhong, Q.; Zhou, T. Determination of inflammation-related lipids in depressive rats by on-line supercritical fluid extraction-supercritical fluid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2021, 203, 114210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lueno, M.; Dobrowolny, H.; Gescher, D.; Gbaoui, L.; Meyer-Lotz, G.; Hoeschen, C.; Frodl, T. Volatile organic compounds from breath differ between patients with major depression and healthy controls. Front. Psychiatry 2022, 13, 819607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gbaoui, L.; Fachet, M.; Luno, M.; Meyer-Lotz, G.; Frodl, T.; Hoeschen, C. Breathomics profiling of metabolic pathways affected by major depression: Possibilities and limitations. Front. Psychiatry 2022, 13, 1061326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henning, D.; Luno, M.; Jiang, C.; Meyer-Lotz, G.; Hoeschen, C.; Frodl, T. Gut-brain axis volatile organic compounds derived from breath distinguish between schizophrenia and major depressive disorder. J. Psychiatry Neurosci. 2023, 48, E117–E125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okamoto, N.; Hoshikawa, T.; Ikenouchi, A.; Natsuyama, T.; Fujii, R.; Igata, R.; Tesen, H.; Konishi, Y.; Honma, Y.; Harada, M.; et al. Comparison of serum metabolomics pathways and patterns between patients with major depressive disorder with and without type 2 diabetes mellitus: An exploratory study. J. Integr. Neurosci. 2023, 22, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Wang, Y.; Wu, Z.; Lan, T.; Tian, Y.; Chen, X.; Li, Y.; Dang, R.; Bai, M.; Cheng, K.; et al. Metabolomic abnormalities of purine and lipids implicated olfactory bulb dysfunction of CUMS depressive rats. Metab. Brain Dis. 2020, 35, 649–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.; Zhou, S.; Chen, Q.; Liu, M.; Dong, M.; Hou, J.; Zhou, B. Tryptophan-5-HT pathway disorder was uncovered in the olfactory bulb of a depression mice model by metabolomic analysis. Front. Mol. Neurosci. 2022, 15, 965697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, L.A.; Segreti, A.M.; Wrobleski, J.; Shaw, A.; Hyland, K.; Hughes, M.; Finegold, D.N.; Naviaux, R.K.; Brent, D.A.; Vockley, J.; et al. Metabolomic disorders: Confirmed presence of potentially treatable abnormalities in patients with treatment refractory depression and suicidal behavior. Psychol. Med. 2022, 11, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zacharias, H.U.; Hertel, J.; Johar, H.; Pietzner, M.; Lukaschek, K.; Atasoy, S.; Kunze, S.; Völzke, H.; Nauck, M.; Friedrich, N.; et al. A metabolome-wide association study in the general population reveals decreased levels of serum laurylcarnitine in people with depression. Mol. Psychiatry 2021, 26, 7372–7383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, Z.; Zhao, H.; Huang, W.; Liang, R.; Liu, Y.; Li, Z.; Li, L.; Xu, Y.; Gao, S.; Gao, S.; et al. An investigation of the antidepressant-like effect of Jiaotaiwan in rats by nontargeted metabolomics based on ultra-high-performance liquid chromatography quadrupole time-of-flight mass spectrometry. J. Sep. Sci. 2021, 44, 645–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Yu, H.; Tian, Y.; Wang, Y.; He, Y.; Lan, T.; Li, Y.; Bai, M.; Chen, X.; Chen, Z.; et al. Non-targeted metabolomics profiling of plasma samples from patients with major depressive disorder. Front. Psychiatry 2021, 12, 810302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Linghu, T.; Gao, Y.; Li, A.; Shi, B.; Tian, J.; Qin, X. A unique insight for energy metabolism disorders in depression based on chronic unpredictable mild stress rats using stable isotope-resolved metabolomics. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2020, 191, 113588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brivio, P.; Audano, M.; Gallo, M.T.; Gruca, P.; Lason, M.; Litwa, E.; Fumagalli, F.; Papp, M.; Mitro, N.; Calabrese, F. Metabolomic signature and mitochondrial dynamics outline the difference between vulnerability and resilience to chronic stress. Transl. Psychiatry 2022, 12, 87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Xie, H.; Huang, S.; Xiao, T.; Wang, Z.; Ni, X.; Deng, S.; Lu, H.; Hu, J.; Li, L.; et al. Development of mass spectrometry-based relatively quantitative targeted method for amino acids and neurotransmitters: Applications in the diagnosis of major depression. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2021, 194, 113773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, F.; Zhao, X.; Zeng, Z.; Wang, L.; Lv, W.; Wang, Q.; Xu, G. Development of a plasma pseudotargeted metabolomics method based on ultra-high-performance liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry. Nat. Protoc. 2020, 15, 2519–2537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.; Jin, W.; Liu, D.; Zhong, Q.; Zhou, T. Enhanced pseudotargeted analysis using a segment data dependent acquisition strategy by liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry for a metabolomics study of liquiritin in the treatment of depression. J. Sep. Sci. 2020, 43, 2088–2096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, M.; Zhou, T. Comprehensive pseudotargeted metabolomics analysis based on two-phase liquid extraction-UHPLC-MS/MS for the investigation of depressive rats. J. Sep. Sci. 2022, 45, 2977–2986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, D.; Yang, J.; Jin, W.; Zhong, Q.; Zhou, T. A high coverage pseudotargeted lipidomics method based on three-phase liquid extraction and segment data-dependent acquisition using UHPLC-MS/MS with application to a study of depression rats. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2021, 413, 3975–3986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.; Liu, D.; Jin, W.; Zhong, Q.; Zhou, T. A green and efficient pseudotargeted lipidomics method for the study of depression based on ultra-high performance supercritical fluid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2021, 192, 113646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.; Mun, S.; Lee, Y.R.; Choi, H.; Joo, E.J.; Kang, H.G.; Lee, J. Discovery and validation of acetyl-L-carnitine in serum for diagnosis of major depressive disorder and remission status through metabolomic approach. Front. Psychiatry 2022, 13, 1002828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Wu, Z.; Xiang, H.; Zhou, Y.; Qin, X.; Tian, J. Revealing the role of leucine in improving the social avoidance behavior of depression through a combination of untargeted and targeted metabolomics. Food Funct. 2023, 14, 6397–6409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Li, T.; Qin, X.; Du, G.; Zhou, Y. Integration of non-targeted metabolomics and targeted quantitative analysis to elucidate the synergistic antidepressant effect of Bupleurum Chinense DC-Paeonia Lactiflora Pall Herb Pair by regulating purine metabolism. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 900459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, Y.; Zou, D.; Li, Y.; Gu, S.; Dong, J.; Ma, X.; Xu, S.; Wang, F.; Huang, J.H. Monoamine neurotransmitters control basic emotions and affect major depressive disorders. Pharmaceuticals 2022, 15, 1203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.F. A hypothesis of monoamine (5-HT) – Glutamate/GABA long neural circuit: Aiming for fast-onset antidepressant discovery. Pharmacol. Therapeut. 2020, 208, 107494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Chen, Z.; Zhao, J.; Yu, H.; Chen, X.; He, Y.; Tian, Y.; Wang, Y.; Chen, C.; Cheng, K.; et al. Neurotransmitter and related metabolic profiling in the nucleus accumbens of chronic unpredictable mild stress-induced anhedonia-like rats. Front. Behav. Neurosci. 2022, 16, 862683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Q.Y.; Jiang, M.C.; Gu, S.M.; Zhang, X.L.; Feng, G.K.; Ma, X.J.; Xu, S.J.; Wu, E.X.; Huang, J.S.; Wang, F.S. Metabolomics changes in brain-gut axis after unpredictable chronic mild stress. Psychopharmacology 2022, 239, 729–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.W.; Gao, C.S.; Zhang, H.; Yang, J.; Wang, Y.P.; Pan, L.B.; Yu, H.; He, C.Y.; Luo, H.B.; Zhao, Z.X.; et al. Morinda officinalis oligosaccharides increase serotonin in the brain and ameliorate depression via promoting 5-hydroxytryptophan production in the gut microbiota. Acta Pharm. Sin. B 2022, 12, 3298–3312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geng, C.; Guo, Y.; Wang, C.; Liao, D.; Han, W.; Zhang, J.; Jiang, P. Systematic impacts of chronic unpredictable mild stress on metabolomics in rats. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, C.S.H.; Tay, G.W.N.; Wee, H.N.; Ching, J. The utility of amino acid metabolites in the diagnosis of major depressive disorder and correlations with depression severity. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 2231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whipp, A.M.; Heinonen-Guzejev, M.; Pietiläinen, K.H.; van Kamp, I.; Kaprio, J. Branched-chain amino acids linked to depression in young adults. Front. Neurosci. 2022, 16, 935858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Y.; Wu, Z.; Wang, Y.; Chen, C.; He, Y.; Lan, T.; Li, Y.; Bai, M.; Yu, H.; Chen, X.; et al. Alterations of neurotransmitters and related metabolites in the habenula from CUMS-susceptible and -resilient rats. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2021, 534, 422–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brum, M.; Nieberler, M.; Kehrwald, C.; Knopf, K.; Brunkhorst-Kanaan, N.; Etyemez, S.; Allers, K.A.; Bittner, R.A.; Slattery, D.A.; McNeill, R.V.; et al. Phase—And disorder-specific differences in peripheral metabolites of the kynurenine pathway in major depression, bipolar affective disorder and schizophrenia. World J. Biol. Psychiatry 2023, 24, 564–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.C.; Yu, H.; Li, R.; Zhou, C.H.; Shi, Q.Q.; Guo, L.; He, H. A preliminary comparison of plasma tryptophan metabolites and medium- and long-chain fatty acids in adult patients with major depressive disorder and schizophrenia. Medicina 2023, 59, 413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yun, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Zhao, W.; Ma, T.; Fan, H.; Bai, L.; Ma, B.; Qi, S.; Wang, Z.; An, H.; et al. Relationship between the tryptophan-kynurenine pathway and painful physical symptoms in patients with major depressive disorder. J. Psychosom. Res. 2022, 163, 111069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liaqat, H.; Parveen, A.; Kim, S.Y. Neuroprotective natural products’ regulatory effects on depression via gut-brain axis targeting tryptophan. Nutrients 2022, 14, 3270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, C.C.; Ye, F.; Xu, C.X.; Jiang, N.; Chang, Q.; Liu, X.M.; Pan, R.L. Tryptophan-kynurenine metabolic characterization in the gut and brain of depressive-like rats induced by chronic restraint stress. J. Affect. Disord. 2023, 328, 273–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arteaga-Henriquez, G.; Burger, B.; Weidinger, E.; Grosse, L.; Moll, N.; Schuetze, G.; Schwarz, M.; Wijkhuijs, A.; Op de Beeck, G.; Berghmans, R.; et al. Activation and deactivation steps in the tryptophan breakdown pathway in major depressive disorder: A link to the monocyte inflammatory state of patients. Prog. Neuropsychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry 2021, 107, 110226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haroon, E.; Welle, J.R.; Woolwine, B.J.; Goldsmith, D.R.; Baer, W.; Patel, T.; Felger, J.C.; Miller, A.H. Associations among peripheral and central kynurenine pathway metabolites and inflammation in depression. Neuropsychopharmacology 2020, 45, 998–1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paul, E.R.; Schwieler, L.; Erhardt, S.; Boda, S.; Trepci, A.; Kampe, R.; Asratian, A.; Holm, L.; Yngve, A.; Dantzer, R.; et al. Peripheral and central kynurenine pathway abnormalities in major depression. Brain Behav. Immun. 2022, 101, 136–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, H.; Teague, T.K.; Yeh, F.-C.; Burrows, K.; Figueroa-Hall, L.K.; Aupperle, R.L.; Khalsa, S.S.; Paulus, M.P.; Savitz, J. C-Reactive protein and the kynurenic acid to quinolinic acid ratio are independently associated with white matter integrity in major depressive disorder. Brain Behav. Immun. 2022, 105, 180–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tateishi, H.; Setoyama, D.; Kang, D.; Matsushima, J.; Kojima, R.; Fujii, Y.; Mawatari, S.; Kikuchi, J.; Sakemura, Y.; Fukuchi, J.; et al. The changes in kynurenine metabolites induced by rTMS in treatment-resistant depression: A pilot study. J. Psychiatr. Res. 2021, 138, 194–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryan, K.M.; Allers, K.A.; McLoughlin, D.M.; Harkin, A. Tryptophan metabolite concentrations in depressed patients before and after electroconvulsive therapy. Brain Behav. Immun. 2020, 83, 153–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, G.; Deen, J.; Struzeski, J.B.; Chen, M.; Zhang, Y.; Cole, S.A.; Fretts, A.M.; Lee, E.T.; Howard, B.V.; Fiehn, O.; et al. Plasma lipidomic profile of depressive symptoms: A longitudinal study in a large sample of community-dwelling American Indians in the strong heart study. Mol. Psychiatr. 2023, 28, 2480–2489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, T.; Guo, L.; Li, R.; Wang, F.; Yang, W.M.; Yang, J.B.; Cui, Z.Q.; Zhou, C.H.; Chen, Y.H.; Yu, H.; et al. Alterations of plasma lipids in adult women with major depressive disorder and bipolar depression. Front. Psychiatry 2022, 13, 927817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, F.; Guo, L.; Zhang, T.; Cui, Z.Q.; Wang, J.K.; Zhang, C.; Xue, F.; Zhou, C.H.; Li, B.J.; Tan, Q.R.; et al. Alterations in plasma lipidomic profiles in adult patients with schizophrenia and major depressive disorder. Medicina-Lithuania 2022, 58, 1509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, W.; Chen, J.; Gong, L.; Liu, F.; Zhao, H.; Mu, J. Alteration of glycerophospholipid metabolism in hippocampus of post-stroke depression rats. Neurochem. Res. 2022, 47, 2052–2063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, L.L.; Yan, C.M.; Zheng, W.C.; Li, Y.; Wang, Y.H.; Qu, M. Metabolic alterations and related biological functions of post-stroke depression in ischemic stroke patients. Neuropsych. Dis. Treat. 2023, 19, 1555–1564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, Q.; Tian, T.; Chen, J.; Guo, X.; Zhang, X.; Zou, T. Serum metabolic profiling of late-pregnant women with antenatal depressive symptoms. Front. Psychiatry 2021, 12, 679451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, P.; Wu, J.; Zhang, H.; Perry, S.W.; Yin, B.; Tan, X.; Chai, T.; Liang, W.; Huang, Y.; Li, Y.; et al. The gut microbiome modulates gut-brain axis glycerophospholipid metabolism in a region-specific manner in a nonhuman primate model of depression. Mol. Psychiatry 2021, 26, 2380–2392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, X.; Huang, C.; Yang, X.; Chen, J.; Pu, J.; He, Y.; Xie, P. Altered fecal metabolites and colonic glycerophospholipids were associated with abnormal composition of gut microbiota in a depression model of mice. Front. Neurosci. 2021, 15, 701355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, T.; Mao, Q.; Xie, J.; Wang, Y.; Shao, W.H.; Zhong, Q.; Chen, J.J. Multi-omics data reveals the disturbance of glycerophospholipid metabolism caused by disordered gut microbiota in depressed mice. J. Adv. Res. 2022, 39, 135–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, J.; Zhong, Q.; Wu, W.T.; Chen, J.J. Multi-omics data reveals the important role of glycerophospholipid metabolism in the crosstalk between gut and brain in depression. J. Transl. Med. 2023, 21, 93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, Y.; Qin, M.; Teng, T.; Li, X.; Yu, Y.; Wang, J.; Wu, H.; He, Y.; Zhou, X.; Xie, P. Identification of sex-specific plasma biomarkers using metabolomics for major depressive disorder in children and adolescents. Front. Psychiatry 2022, 13, 929207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schumacher, F.; Edwards, M.J.; Mühle, C.; Carpinteiro, A.; Wilson, G.C.; Wilker, B.; Soddemann, M.; Keitsch, S.; Scherbaum, N.; Müller, B.W.; et al. Ceramide levels in blood plasma correlate with major depressive disorder severity and its neutralization abrogates depressive behavior in mice. J. Biol. Chem. 2022, 298, 102185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Homorogan, C.; Nitusca, D.; Enatescu, V.; Schubart, P.; Moraru, C.; Socaciu, C.; Marian, C. Untargeted plasma metabolomic profiling in patients with major depressive disorder using ultra-high performance liquid chromatography coupled with mass spectrometry. Metabolites 2021, 11, 466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, X.; Ke, S.; Wang, Q.; Zhuang, T.; Xia, C.; Xu, Y.; Yang, L.; Zhou, M. Energy metabolism in major depressive disorder: Recent advances from omics technologies and imaging. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2021, 141, 111869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Cui, C.; Xu, P.; Zhu, L.; Xue, H.; Chen, B.; Jiang, P. Targeting PDK2 rescues stress-induced impaired brain energy metabolism. Mol. Psychiatry 2023. (Online ahead of print). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.; Deng, K.; Xue, Y.; Yang, R.; Yang, R.; Gong, Z.; Tang, M. Carnitine and depression. Front. Nutr. 2022, 9, 853058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ait Tayeb, A.E.K.; Colle, R.; El-Asmar, K.; Chappell, K.; Acquaviva-Bourdain, C.; David, D.J.; Trabado, S.; Chanson, P.; Feve, B.; Becquemont, L.; et al. Plasma acetyl-l-carnitine and l-carnitine in major depressive episodes: A case-control study before and after treatment. Psychol. Med. 2023, 53, 2307–2316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ait Tayeb, A.E.K.; Colle, R.; Chappell, K.; El-Asmar, K.; Acquaviva-Bourdain, C.; David, D.J.; Trabado, S.; Chanson, P.; Feve, B.; Becquemont, L.; et al. Metabolomic profiles of 38 acylcarnitines in major depressive episodes before and after treatment. Psychol. Med. 2023. (Online ahead of print). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, A.T.; MahmoudianDehkordi, S.; Bhattacharyya, S.; Arnold, M.; Liu, D.; Neavin, D.; Moseley, M.A.; Thompson, J.W.; Williams, L.S.J.; Louie, G.; et al. Acylcarnitine metabolomic profiles inform clinically-defined major depressive phenotypes. J. Affect. Disord. 2020, 264, 90–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linghu, T.; Zhao, Y.; Wu, W.; Gao, Y.; Tian, J.; Qin, X. Novel targets for ameliorating energy metabolism disorders in depression through stable isotope-resolved metabolomics. Biochim. Biophys. Acta. Bioenerg. 2022, 1863, 148578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ling-Hu, T.; Liu, S.B.; Gao, Y.; Han, Y.M.; Tian, J.S.; Qin, X.M. Stable isotope-resolved metabolomics reveals the abnormal brain glucose catabolism in depression based on chronic unpredictable mild stress rats. J. Proteome Res. 2021, 20, 3549–3558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, J.S.; Zhao, Y.H.; Ling-Hu, T.; Wu, W.Z.; Wang, X.X.; Ji, C.; Zhao, W.D.; Han, Y.M.; Qin, X.M. A novel insight for high-rate and low-efficiency glucose metabolism in depression through stable isotope-resolved metabolomics in CUMS-induced rats. J. Affect. Disord. 2023, 331, 121–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, J.S.; Wu, W.Z.; Liu, S.B.; Ling-Hu, T.; Zhao, Y.H.; Gao, Y.; Qin, X.M. Stable isotope-resolved metabolomics studies on corticosteroid-induced PC12 cells: A strategy for evaluating glucose catabolism in an in vitro model of depression. J. Proteome Res. 2022, 21, 788–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, C.; Zhao, W.D.; Zheng, J.; Zhou, S.; Tian, J.S.; Han, Y.M.; Qin, X.M. Mechanism of the effect of Xiaoyao powder treatment on exercise capacity of depressed rats-A stable isotope tracer metabolomic study. J. Liq. Chromatogr. R. T. 2022, 45, 143–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Wang, H.; Chen, X.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, H.; Xie, P. Gut microbiota and its metabolites in depression: From pathogenesis to treatment. EBioMedicine 2023, 90, 104527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Li, X.; Teng, T.; Jiang, Y.; Xiang, Y.; Fan, L.; Yu, Y.; Zhou, X.; Xie, P. Comparative analysis of gut microbiota and fecal metabolome features among multiple depressive animal models. J. Affect. Disord. 2022, 314, 103–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, J.; Wu, W.T.; Chen, J.J.; Zhong, Q.; Wu, D.; Niu, L.; Wang, S.; Zeng, Y.; Wang, Y. Tryptophan metabolism as bridge between gut microbiota and brain in chronic social defeat stress-induced depression mice. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2023, 13, 1121445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Fan, Q.; Hou, Y.; Zhang, X.; Yin, Z.; Cai, X.; Wei, W.; Wang, J.; He, D.; Wang, G.; et al. Bacteroides species differentially modulate depression-like behavior via gut-brain metabolic signaling. Brain Behav. Immun. 2022, 102, 11–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, J.; Wang, Y.; Zhong, Q.; Bai, S.J.; Zhou, C.J.; Tian, T.; Chen, J.J. Associations between disordered microbial metabolites and changes of neurotransmitters in depressed mice. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2022, 12, 906303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Z.Y.; Zhao, P.H.; Liao, A.M.; Pan, L.; Zhang, J.; Dong, Y.Q.; Huang, J.H.; He, W.W.; Ou, X.Q. Fermented wheat germ alleviates depression-like behavior in rats with chronic and unpredictable mild stress. Foods 2023, 12, 920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Zheng, P.; Li, Y.; Wu, J.; Tan, X.M.; Zhou, J.J.; Sun, Z.L.; Chen, X.; Zhang, G.F.; Zhang, H.P.; et al. Landscapes of bacterial and metabolic signatures and their interaction in major depressive disorders. Sci. Adv. 2020, 6, eaba8555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Zhu, X.; Xu, J.; Li, L.; Kan, W.; Bao, H.; Xu, J.; Wang, W.; Yang, Y.; Chen, P.; et al. The FXR mediated anti-depression effect of CDCA underpinned its therapeutic potentiation for MDD. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2023, 115, 109626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bai, S.J.; Xie, J.; Bai, H.L.; Tian, T.; Zou, T.; Chen, J.J. Gut microbiota-derived inflammation-related serum metabolites as potential biomarkers for major depressive disorder. J. Inflamm. Res. 2021, 14, 3755–3766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, M.; Tian, T.; Mao, Q.; Zou, T.; Zhou, C.J.; Xie, J.; Chen, J.J. Associations between disordered gut microbiota and changes of neurotransmitters and short-chain fatty acids in depressed mice. Transl. Psychiat. 2020, 10, 350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, W.; Chen, J.; Gong, L.; Liu, F.; Zhao, H.; Yan, Z.; Li, Y.; Zhang, J.; Xiao, M.; Mu, J. Microbiota-derived short-chain fatty acids may participate in post-stroke depression by regulating host’s lipid metabolism. J. Psychiatr. Res. 2023, 161, 426–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, W.; Gong, L.; Liu, F.; Ren, Y.; Mu, J. Alteration of gut microbiome and correlated lipid metabolism in post-sroke depression. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2021, 11, 663967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, J.; Wang, W.; Jiang, T.; Bai, X.; Liu, C. Viral metagenomics combined with metabolomics reveals the role of gut viruses in mouse model of depression. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 1046894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, K.; Liao, X.X.; Wu, X.Y.; Wang, R.; Hu, Z.W.; Liu, S.Y.; He, W.F.; Zhou, J.J. Effects of the lipid metabolites and the gut microbiota in ApoE-/- mice on atherosclerosis co-depression from the microbiota-gut-brain axis. Front. Mol. Biosci. 2022, 9, 786492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, N.; Zhang, J.; Wang, J.; Liu, Z.; Wang, X.; Kang, P.; Yang, C.; Liu, P.; Zhang, K. Abnormal gut microbiota and bile acids in patients with first-episode major depressive disorder and correlation analysis. Psychiatry Clin. Neurosci. 2022, 76, 321–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Jin, K.; Jiang, C.; Pan, F.; Wu, J.; Luan, H.; Zhao, Z.; Chen, J.; Mou, T.; Wang, Z.; et al. A pilot exploration of multi-omics research of gut microbiome in major depressive disorders. Transl. Psychiatry 2022, 12, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, H.; Yang, H.; Wang, Y.; Xing, Q.; Yan, L.; Chai, Y. Gut microbiome and fecal metabolic alteration in systemic lupus erythematosus patients with depression. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2022, 12, 1040211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Hou, Y.; Li, Y.; Wei, W.; Cai, X.; Shao, H.; Yuan, Y.; Zheng, X. Taxonomic and metabolic signatures of gut microbiota for assessing the severity of depression and anxiety in major depressive disorder patients. Neuroscience 2022, 496, 179–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Li, J.; Cheng, R.; Liu, H.; Zhao, Y.; Liu, Y.; Chen, Y.; Sun, Z.; Zhai, Z.; Wu, M.; et al. Alteration of the gut microbiome and correlated metabolism in a rat model of long-term depression. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2023, 13, 1116277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pu, J.; Liu, Y.; Gui, S.; Tian, L.; Yu, Y.; Wang, D.; Zhong, X.; Chen, W.; Chen, X.; Chen, Y.; et al. Effects of pharmacological treatment on metabolomic alterations in animal models of depression. Transl. Psychiatry 2022, 12, 175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MahmoudianDehkordi, S.; Ahmed, A.T.; Bhattacharyya, S.; Han, X.; Baillie, R.A.; Arnold, M.; Skime, M.K.; John-Williams, L.S.; Moseley, M.A.; Thompson, J.W.; et al. Alterations in acylcarnitines, amines, and lipids inform about the mechanism of action of citalopram/escitalopram in major depression. Transl. Psychiat. 2021, 11, 153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Z.; Yang, J.; Zhou, J.; Zhou, J.; Feng, L.; Feng, Y.; He, Y.; Liu, M.; Li, Y.; Wang, G.; et al. Tissue-specific oxysterols as predictors of antidepressant (Escitalopram) treatment response in patients with major depressive disorder. Biol. Psychiatry Glob. Open Sci. 2023, 3, 663–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhou, J.; Ye, J.; Sun, Z.; He, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Ren, S.; Zhang, G.; Liu, M.; Zheng, P.; et al. Multi-omics reveal microbial determinants impacting the treatment outcome of antidepressants in major depressive disorder. Microbiome 2023, 11, 195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abramova, O.; Zorkina, Y.; Syunyakov, T.; Zubkov, E.; Ushakova, V.; Silantyev, A.; Soloveva, K.; Gurina, O.; Majouga, A.; Morozova, A.; et al. Brain metabolic profile after intranasal vs. intraperitoneal clomipramine treatment in rats with ultrasound model of depression. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 9598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, D.; Zhao, H.; Gao, S.; Li, Y.; Cheng, Q.; Bi, C.; Zhou, Z.; Li, Y.; Yu, C. Clinical serum metabolomics study on fluoxetine hydrochloride for depression. Neurosci. Lett. 2021, 746, 135585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, B.; MahmoudianDehkordi, S.; Voort, J.L.V.; Han, X.; Port, J.D.; Frye, M.A.; Kaddurah-Daouk, R. Metabolomic signatures of intravenous racemic ketamine associated remission in treatment-resistant depression: A pilot hypothesis generating study. Psychiat. Res. 2022, 314, 114655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, C.; Zhao, X.; Ma, X.; Ma, H.; Li, R.; Hu, G.; Wang, H.; Peng, Z.; Cai, M. Effects of (S)-ketamine on depression-like behaviors in a chronic variable stress model: A role of brain lipidome. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2023, 17, 1114914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moaddel, R.; Zanos, P.; Farmer, C.A.; Kadriu, B.; Morris, P.J.; Lovett, J.; Acevedo-Diaz, E.E.; Cavanaugh, G.W.; Yuan, P.; Yavi, M.; et al. Comparative metabolomic analysis in plasma and cerebrospinal fluid of humans and in plasma and brain of mice following antidepressant-dose ketamine administration. Transl. Psychiat. 2022, 12, 179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, D.; Wang, L.; Wu, Y.; Qin, X.; Du, G.; Zhou, Y. Metabolomics based on peripheral blood mononuclear cells to dissect the mechanisms of chaigui granules for treating depression. ACS Omega 2022, 7, 8466–8482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, W.Z.; Ting, L.H.; Zhao, Y.H.; Zhao, W.D.; Ji, C.; Tian, J.S.; Ren, Y.; Qin, X.M. A unique insight for Xiaoyao San exerts antidepressant effects by modulating hippocampal glucose catabolism using stable isotope-resolved metabolomics. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2023, 300, 115702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Wei, F.; Liu, H.; Zhao, S.; Du, G.; Qin, X. Integrating hippocampal metabolomics and network pharmacology deciphers the antidepressant mechanisms of Xiaoyaosan. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2021, 268, 113549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Liu, C.; Tian, J.; Gao, X.; Li, K.; Du, G.; Qin, X. Plasma metabolomics of depressed patients and treatment with Xiaoyaosan based on mass spectrometry technique. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2020, 246, 112219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Yin, Q.; Tian, J.; Gao, X.; Qin, X.; Du, G.; Zhou, Y. Studies on the potential link between antidepressant effect of Xiaoyao San and its pharmacological activity of hepatoprotection based on multi-platform metabolomics. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2020, 249, 112432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.W.; Han, P.; Fu, J.; Yu, H.; Xu, H.; Hu, J.C.; Lu, J.Y.; Yang, X.Y.; Zhang, H.J.; Bu, M.M.; et al. Gut microbiota-based metabolites of Xiaoyao Pills (a typical Traditional Chinese medicine) ameliorate depression by inhibiting fatty acid amide hydrolase levels in brain. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2023, 313, 116555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, S.; Han, S.; Yu, L.; Du, L.; You, Y.; Chen, J.; Wang, M.; Wu, S.; Li, S.; Sun, X.; et al. Jia Wei Xiao Yao San ameliorates chronic stress-induced depression-like behaviors in mice by regulating the gut microbiome and brain metabolome in relation to purine metabolism. Phytomedicine 2022, 98, 153940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, S.; Li, Q.; Xu, Z.; Chen, Z.; Tao, Y.; Tong, Y.; Wang, T.; Chen, S.; Wang, P. Detection of the role of intestinal flora and tryptophan metabolism involved in antidepressant-like actions of crocetin based on a multi-omics approach. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 2022, 239, 3657–3677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Yan, T.; Gong, G.; Li, Y.; Zhang, J.; Wu, B.; Bi, K.; Jia, Y. Antidepressant-like effects of Schisandrin on lipopolysaccharide-induced mice: Gut microbiota, short chain fatty acid and TLR4/NF-kappaB signaling pathway. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2020, 89, 107029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Kan, Q.; Zhao, L.; Ye, G.; He, X.; Tang, H.; Shi, F.; Zou, Y.; Liang, X.; Song, X.; et al. Prophylactic effect of Tongxieyaofang polysaccharide on depressive behavior in adolescent male mice with chronic unpredictable stress through the microbiome-gut-brain axis. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2023, 161, 114525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, C.; Yuan, D.; Renaud, S.J.; Zhou, T.; Yang, F.; Liou, Y.; Qiu, X.; Zhou, L.; Guo, Y. Chaihu-shugan-san alleviates depression-like behavior in mice exposed to chronic unpredictable stress by altering the gut microbiota and levels of the bile acids hyocholic acid and 7-ketoDCA. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 1040591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Fang, Y.; Cui, L.; Wang, Z.; Luo, Y.; Gao, C.; Ge, W.; Huang, T.; Wen, J.; Zhou, T. Butyrate emerges as a crucial effector of Zhi-Zi-Chi decoctions to ameliorate depression via multiple pathways of brain-gut axis. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2022, 149, 112861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, X.X.; Hu, K.; Xie, X.H.; Wen, Y.L.; Wang, R.; Hu, Z.W.; Zhou, Y.L.; Li, J.J.; Wu, M.K.; Yu, J.X.; et al. Banxia Xiexin decoction alleviates AS co-depression disease by regulating the gut microbiome-lipid metabolic axis. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2023, 313, 116468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, C.; Chen, Z.; Fan, L.; Xue, Z.; Chen, J.; Wang, X.; Huang, Z.; Men, Y.; Yu, M.; Liu, Y.; et al. Integrating metabolomics and network analysis for exploring the mechanism underlying the antidepressant activity of Paeoniflorin in rats with CUMS-induced depression. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 904190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Q.S.; Yan, K.; Li, K.D.; Gao, L.N.; Wang, X.; Liu, H.B.; Zhang, Z.G.; Li, K.F.; Cui, Y.L. Targeting hippocampal phospholipid and tryptophan metabolism for antidepressant-like effects of albiflorin. Phytomedicine 2021, 92, 153735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Yang, X.; Chen, S.; Wu, L.; Zhou, J.; Jia, K.; Ju, W. Integrated network pharmacology and GC-MS-based metabolomics to investigate the effect of Xiang-Su volatile oil against menopausal depression. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 765638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qu, S.Y.; Li, X.Y.; Heng, X.; Qi, Y.Y.; Ge, P.Y.; Ni, S.j.; Yao, Z.Y.; Guo, R.; Yang, N.Y.; Cao, Y.; et al. Analysis of antidepressant activity of Huang-Lian Jie-Du decoction through network pharmacology and metabolomics. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 619268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, P.Y.; Qu, S.Y.; Ni, S.j.; Yao, Z.Y.; Qi, Y.Y.; Zhao, X.; Guo, R.; Yang, N.Y.; Zhang, Q.C.; Zhu, H.X. Berberine ameliorates depression-like behavior in CUMS mice by activating TPH1 and inhibiting IDO1-associated with tryptophan metabolism. Phytother. Res. 2022, 37, 342–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, M.; He, Y.; Tian, L.; Yu, L.; Cheng, Q.; Li, Z.; Gao, L.; Gao, S.; Yu, C. Gut microbiota-SCFAs-brain axis associated with the antidepressant activity of berberine in CUMS rats. J. Affect. Disord. 2023, 325, 141–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia, S.; Wang, R.; Zhang, D.; Guan, Z.; Ding, T.; Zhang, J.; Zhao, X. Quercetin modulates the liver metabolic profile in a chronic unpredictable mild stress rat model based on metabolomics technology. Food Funct. 2023, 14, 1726–1739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, X.Y.; Zhang, G.Y.; Wang, Q.X.; Song, J.; Li, Y.; Xia, C.Y.; Zhang, T.; Yang, L.; Sun, J.J.; Zhou, M.M. Integrated network pharmacology and hepatic metabolomics to reveal the mechanism of Acanthopanax senticosus against major depressive disorder. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2022, 10, 900637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Y.; Li, T.; Zhu, S.; Gong, W.; Qin, X.; Du, G. Study on antidepressant mechanism of Radix Bupleuri–Radix Paeoniae Alba herb pair by metabonomics combined with 1H nuclear magnetic resonance and ultra-high-performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry detection technology. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2021, 73, 1262–1273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Tian, J.; Gao, X.; Qin, X.; Du, G.; Zhou, Y. An integrated strategy to study the combination mechanisms of Bupleurum chinense DC and Paeonia lactiflora Pall for treating depression based on correlation analysis between serum chemical components profiles and endogenous metabolites profiles. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2023, 305, 116068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gu, S.; Mou, T.T.; Chen, J.; Wang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Cui, M.R.; Hao, W.Q.; Sun, Y.; Zhang, C.Q.; Zhao, T.T.; et al. Develop a stepwise integrated method to screen biomarkers of Baihe-Dihuang Tang on the treatment of depression in rats applying with composition screened, untargeted, and targeted metabolomics analysis. J. Sep. Sci. 2022, 43, 1656–1671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Wang, F.; Han, J.; Zhao, Y.; Yu, M.; Ma, M.; Yu, Z. Untargeted and targeted mass spectrometry reveal the effects of theanine on the central and peripheral metabolomics of chronic unpredictable mild stress-induced depression in juvenile rats. J. Pharm. Anal. 2023, 13, 73–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, L.; Zhou, X.; Tao, G.; Hao, W.; Wang, L.; Lan, Z.; Song, Y.; Wu, M.; Huang, J.Q. Ferulic acid and feruloylated oligosaccharides alleviate anxiety and depression symptom via regulating gut microbiome and microbial metabolism. Food Res. Int. 2022, 162, 111887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Wang, T.; Bai, S.; Chen, Z.; Qi, X.; Xie, P. Dl-3-n-butylphthalide attenuates mouse behavioral deficits to chronic social defeat stress by regulating energy metabolism via AKT/CREB signaling pathway. Transl. Psychiat. 2020, 10, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dang, R.; Wang, M.; Li, X.; Wang, H.; Liu, L.; Wu, Q.; Zhao, J.; Ji, P.; Zhong, L.; Licinio, J.; et al. Edaravone ameliorates depressive and anxiety-like behaviors via Sirt1/Nrf2/HO-1/Gpx4 pathway. J. Neuroinflamm. 2022, 19, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bu, Q.; Zhang, J.; Guo, X.; Feng, Y.; Yan, H.; Cheng, W.; Feng, Z.; Cao, M. The antidepressant effects and serum metabonomics of bifid triple viable capsule in a rat model of chronic unpredictable mild stress. Front. Nutr. 2022, 9, 947697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, P.; Chen, Y.; Zhu, H.; Wang, L.; Qian, X.; Zou, R.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, H.; Qian, L.; Wang, Q.; et al. Bifidobacterium breve CCFM1025 attenuates major depression disorder via regulating gut microbiome and tryptophan metabolism: A randomized clinical trial. Brain Behav. Immun. 2022, 100, 233–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Y.; Bu, F.; Chen, T.; Shi, G.; Yuan, X.; Feng, Z.; Duan, Z.; Wang, R.; Zhang, S.; Wang, Q.; et al. A next-generation probiotic: Akkermansia muciniphila ameliorates chronic stress-induced depressive-like behavior in mice by regulating gut microbiota and metabolites. Appl. Microbiol. Biot. 2021, 105, 8411–8426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, W.H.; Yeh, W.L.; Chou, C.H.; Wu, C.L.; Lai, C.H.; Yeh, Y.T.; Liao, C.A.; Wu, C.C. Suppressive effects of Lactobacillus on depression through regulating the gut microbiota and metabolites in C57BL/6J mice induced by Ampicillin. Biomedicines 2023, 11, 1068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, S.; Zhu, Z.; Li, H.; Wang, W.; Jiang, Z.; Pan, F.; Liu, D.; Ho, R.C.M.; Ho, C.S.H. Rifaximin ameliorates depression-like behaviour in chronic unpredictable mild stress rats by regulating intestinal microbiota and hippocampal tryptophan metabolism. J. Affect. Disord. 2023, 329, 30–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Satti, S.; Palepu, M.S.K.; Singh, A.A.; Jaiswal, Y.; Dash, S.P.; Gajula, S.N.R.; Chaganti, S.; Samanthula, G.; Sonti, R.; Dandekar, M.P. Anxiolytic- and antidepressant-like effects of Bacillus coagulans Unique IS-2 mediate via reshaping of microbiome gut-brain axis in rats. Neurochem. Int. 2023, 163, 105483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Han, Y.; Zhou, S.; Tian, J.; Qin, X.; Ji, C.; Zhao, W.; Chen, A. Serum metabolomic responses to aerobic exercise in rats under chronic unpredictable mild stress. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 4888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, C.H.; Chen, Y.H.; Xue, S.S.; Shi, Q.Q.; Guo, L.; Yu, H.; Xue, F.; Cai, M.; Wang, H.N.; Peng, Z.W. rTMS ameliorates depressive-like behaviors and regulates the gut microbiome and medium- and long-chain fatty acids in mice exposed to chronic unpredictable mild stress. CNS Neurosci. Ther. 2023, 29, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cristea, I.A.; Naudet, F. US Food and Drug Administration approval of esketamine and brexanolone. Lancet Psychiat. 2019, 6, 975–977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashimoto, K.; Chaki, S. Ketamine and its metabolites: Potential as novel treatments for depression. Neuropharmacology 2023, 230, 109492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, X.; Gao, X.; Cheng, J.; Xia, C.; Xu, Y.; Yang, L.; Zhou, M. Emerging application of metabolomics on Chinese herbal medicine for depressive disorder. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2021, 141, 111866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, C.; Mo, Y.Y.; Feng, S.S.; Meng, M.W.; Chen, S.Y.; Huang, H.M.; Ling, X.; Song, H.; Liang, Y.H.; Ou, S.F.; et al. Urinary metabonomics study of anti-depressive mechanisms of Millettia speciosa Champ on rats with chronic unpredictable mild stress-induced depression. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2021, 205, 114338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, Q.X.; Lim, Y.L.; Yaow, C.Y.L.; Ng, W.K.; Thumboo, J.; Liew, T.M. Effect of probiotic supplementation on gut microbiota in patients with major depressive disorders: A systematic review. Nutrients 2023, 15, 1351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brydges, C.R.; Bhattacharyya, S.; Dehkordi, S.M.; Milaneschi, Y.; Penninx, B.; Jansen, R.; Kristal, B.S.; Han, X.; Arnold, M.; Kastenmuller, G.; et al. Metabolomic and inflammatory signatures of symptom dimensions in major depression. Brain Behav. Immun. 2022, 102, 42–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zoicas, I.; Mühle, C.; Schumacher, F.; Kleuser, B.; Kornhuber, J. Development of comorbid depression after social fear conditioning in mice and its effects on brain sphingolipid metabolism. Cells 2023, 12, 1355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Y.; Su, H.; Wang, H.; Lu, F.; Nie, K.; Wang, Z.; Huang, W.; Dong, H. The effect and mechanism of Jiao-tai-wan in the treatment of diabetes mellitus with depression based on network pharmacology and experimental analysis. Mol. Med. 2021, 27, 154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, D.P.; Zhang, J.J.; Zhu, Y.; He, C.; Fei, W.T.; Yue, N.; Wang, C.L.; Wang, L.Y. Study of antidepressant-like effects of Albiflorin and Paeoniflorin through metabolomics from the perspective of cancer-related depression. Front. Neurol. 2022, 13, 828612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grant, C.W.; Barreto, E.F.; Kumar, R.; Kaddurah-Daouk, R.; Skime, M.; Mayes, T.; Carmody, T.; Biernacka, J.; Wang, L.; Weinshilboum, R.; et al. Multi-omics characterization of early- and adult-onset major depressive disorder. J. Pers. Med. 2022, 12, 412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grant, C.W.; Wilton, A.R.; Kaddurah-Daouk, R.; Skime, M.; Biernacka, J.; Mayes, T.; Carmody, T.; Wang, L.; Lazaridis, K.; Weinshilboum, R.; et al. Network science approach elucidates integrative genomic-metabolomic signature of antidepressant response and lifetime history of attempted suicide in adults with major depressive disorder. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 984383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joyce, J.B.; Grant, C.W.; Liu, D.; MahmoudianDehkordi, S.; Kaddurah-Daouk, R.; Skime, M.; Biernacka, J.; Frye, M.A.; Mayes, T.; Carmody, T.; et al. Multi-omics driven predictions of response to acute phase combination antidepressant therapy: A machine learning approach with cross-trial replication. Transl. Psychiatry 2021, 11, 513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernandez-Baixauli, J.; Puigbò, P.; Abasolo, N.; Palacios-Jordan, H.; Foguet-Romero, E.; Suñol, D.; Galofré, M.; Caimari, A.; Baselga-Escudero, L.; Bas, J.M.D.; et al. Alterations in metabolome and microbiome associated with an early stress stage in male wistar rats: A multi-omics approach. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 12931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamilton, P.J.; Chen, E.Y.; Tolstikov, V.; Peña, C.J.; Picone, J.A.; Shah, P.; Panagopoulos, K.; Strat, A.N.; Walker, D.M.; Lorsch, Z.S.; et al. Chronic stress and antidepressant treatment alter purine metabolism and beta oxidation within mouse brain and serum. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 18134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Zhang, L.; He, S.; Xie, Z.; Zhang, J.; Ge, C.; Sun, G.; Huang, J.; Li, H. Integrated module of multidimensional omics for peripheral biomarkers (iMORE) in patients with major depressive disorder: Rationale and design of a prospective multicentre cohort study. BMJ Open 2022, 12, e067447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sathyanarayanan, A.; Mueller, T.T.; Ali Moni, M.; Schueler, K.; Baune, B.T.; Lio, P.; Mehta, D.; Baune, B.T.; Dierssen, M.; Ebert, B.; et al. Multi-omics data integration methods and their applications in psychiatric disorders. Eur. Neuropsychopharm. 2023, 69, 26–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).