Laser Pyrolysis of Iron Oxide Nanoparticles and the Influence of Laser Power
Abstract
:1. Introduction
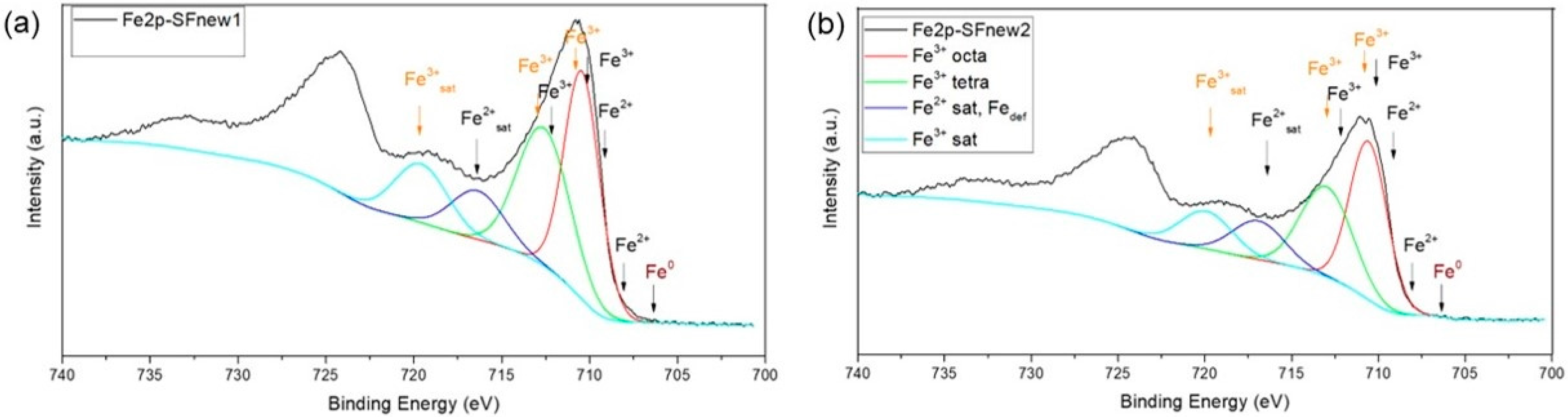
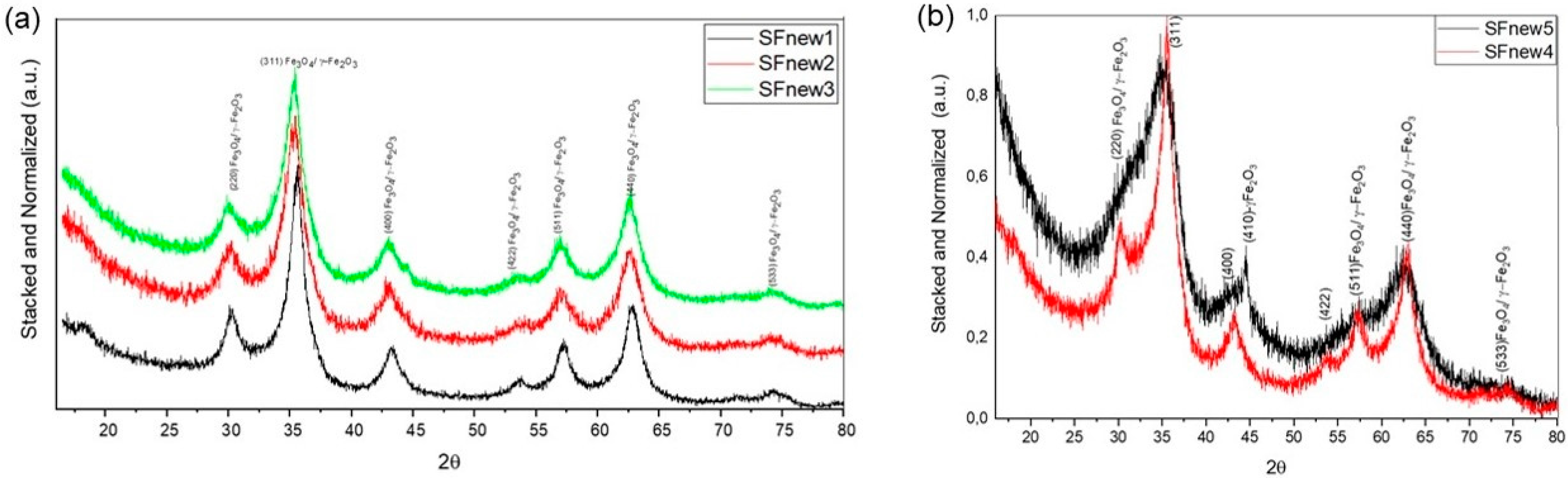
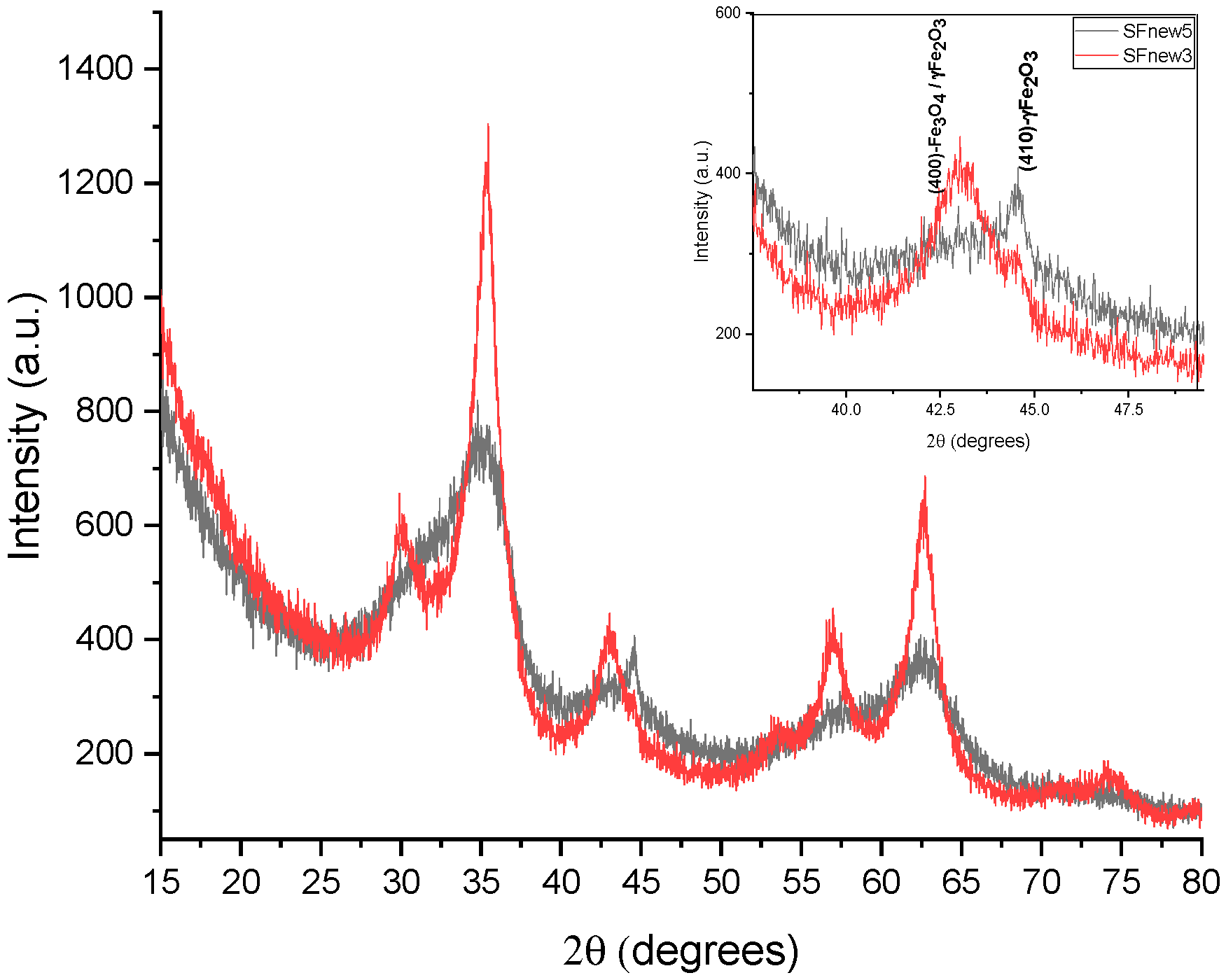
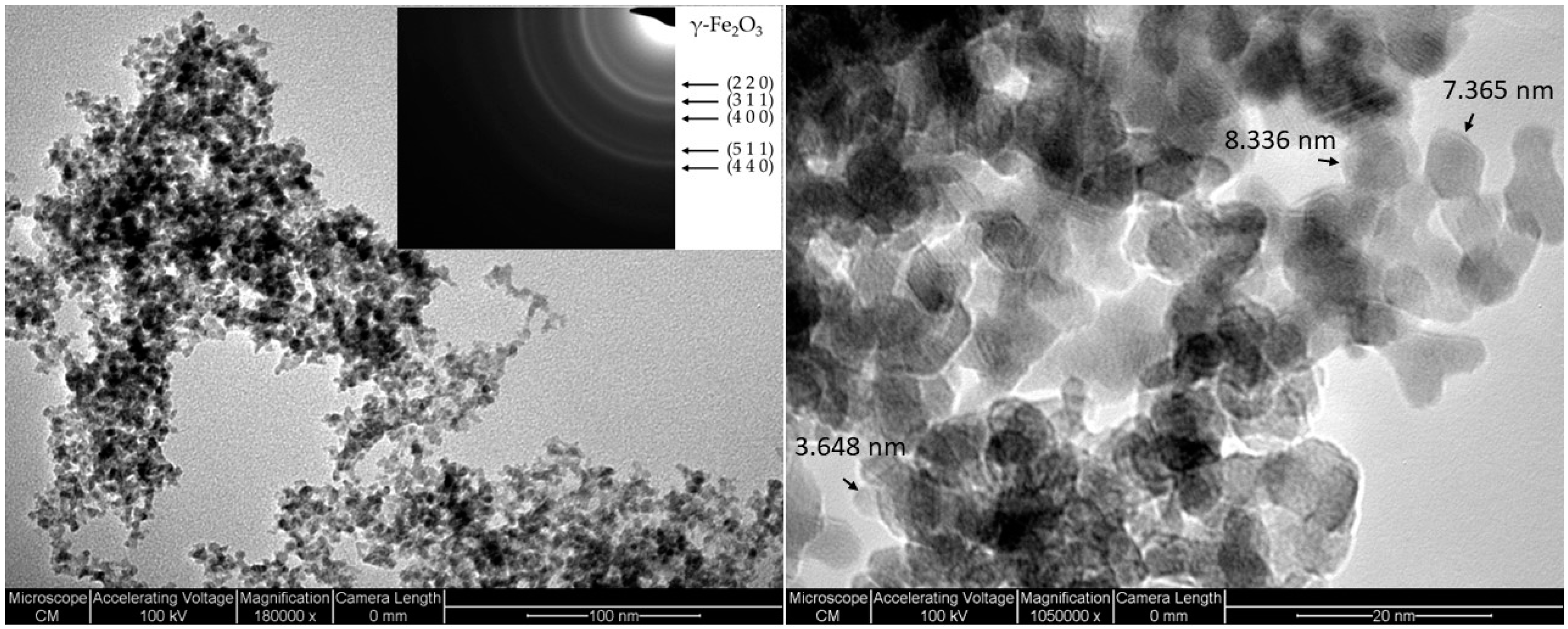
2. Results and Discussions
3. Experimental Part
3.1. Materials and Methods
Nanoparticle Synthesis
3.2. Nanoparticle Characterisation
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Sample Availability
References
- Faraji, M.; Yamini, Y.; Rezaee, M. Magnetic nanoparticles: Synthesis, stabilization, functionalization, characterization, and applications. J. Iran. Chem. Soc. 2010, 7, 1–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Materón, E.M.; Miyazaki, C.M.; Carr, O.; Joshi, N.; Picciani, P.H.; Dalmaschio, C.J.; Davis, F.; Shimizu, F.M. Magnetic nanoparticles in biomedical applications: A review. Appl. Surf. Sci. Adv. 2021, 6, 100163. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Q.; Kartikowati, C.W.; Horie, S.; Ogi, T.; Iwaki, T.; Okuyama, K. Correlation between particle size/domain structure and magnetic properties of highly crystalline Fe3O4 nanoparticles. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 9894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malumbres, A.; Martínez, G.; Mallada, R.; Hueso, J.L.; Bomatí-Miguel, O.; Santamaría, J. Continuous production of iron-based nanocrystals by laser pyrolysis. Effect of operating variables on size, composition and magnetic response. Nanotechnology 2013, 24, 325603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, W.; He, Q.; Jiang, C. Magnetic Iron Oxide Nanoparticles: Synthesis and Surface Functionalization Strategies. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2008, 3, 397. [Google Scholar]
- Ion, M.; Alexandrescu, R. New Advances in the Production of Iron-Based Nanostructures Manufactured by Laser Pyrolysis. In Upscaling of Bio-Nano-Processes: Selective Bioseparation by Magnetic Particles; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2014; pp. 15–37. [Google Scholar]
- Etemadi, H.; Buchanan, J.K.; Kandile, N.G.; Plieger, P.G. Iron Oxide Nanoparticles: Physicochemical Characteristics and Historical Developments to Commercialization for Potential Technological Applications. ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. 2021, 7, 5432–5450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bomatí-Miguel, O.; Tartaj, P.; Morales, M.P.; Bonville, P.; Golla-Schindler, U.; Zhao, X.Q.; Veintemillas-Verdaguer, S. Core–Shell Iron–Iron Oxide Nanoparticles Synthesized by Laser-Induced Pyrolysis. Small 2006, 2, 1476–1483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alexandrescu, R.; Morjann, I.; Crunteanu, A.; Cojocaru, S.; Petcu, S.; Teodorescu, V.; Huisken, F.; Koh, B.; Ehbrecht, M. Iron-oxide-based nanoparticles produced by pulsed infrared laser pyrolysis of Fe(CO)5. Mater. Chem. Phys. 1998, 55, 115–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Sahoo, Y.; Wang, S.; Luo, H.; Prasad, P.N.; Swihart, M.T. Laser-driven synthesis and magnetic properties of iron nanoparticles. J. Nanoparticle Res. 2006, 8, 335–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García, M.A.; Bouzas, V.; Costo, R.; Veintemillas, S.; Morales, P.; García-Hernández, M.; Alexandrescu, R.; Morjan, I.; Gasco, P. Magnetic Properties of Fe Oxide Nanoparticles Produced by Laser Pyrolysis for Biomedical Applications. AIP Conf. Proc. 2010, 1275, 26–29. [Google Scholar]
- Costo, R.; Bello, V.; Robic, C.; Port, M.; Marco, J.F.; Morales, M.P.; Veintemillas-Verdaguer, S. Ultrasmall Iron Oxide Nanoparticles for Biomedical Applications: Improving the Colloidal and Magnetic Properties. Langmuir 2011, 28, 178–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bomatí-Miguel, O.; Morales, M.P.; Tartaj, P.; Ruiz-Cabello, J.; Bonville, P.; Santos, M.; Zhao, X.; Veintemillas-Verdaguer, S. Fe-based nanoparticulate metallic alloys as contrast agents for magnetic resonance imaging. Biomaterials 2005, 26, 5695–5703. (In English) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kandasamy, G.; Maity, D. Recent advances in superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles (SPIONs) for in vitro and in vivo cancer nanotheranostics. Int. J. Pharm. 2015, 496, 191–218. (In English) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bautista, M.C.; Bomati-Miguel, O.; Morales, M.d.P.; Serna, C.J.; Veintemillas-Verdaguer, S. Surface characterisation of dextran-coated iron oxide nanoparticles prepared by laser pyrolysis and coprecipitation. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2005, 293, 20–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morales, M.P.; Bomati-Miguel, O.; de Alejo, R.P.; Ruiz-Cabello, J.; Veintemillas-Verdaguer, S.; O’Grady, K. Contrast agents for MRI based on iron oxide nanoparticles prepared by laser pyrolysis. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2003, 266, 102–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ténégal, F.; Voicu, I.; Armand, X.; Herlin-Boime, N.; Reynaud, C. Residence time effect on fullerene yield in butadiene-based laser pyrolysis flame. Chem. Phys. Lett. 2003, 379, 40–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bomatí-Miguel, O.; Mazeina, L.; Navrotsky, A.; Veintemillas-Verdaguer, S. Calorimetric Study of Maghemite Nanoparticles Synthesized by Laser-Induced Pyrolysis. Chem. Mater. 2008, 20, 591–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dumitrache, F.; Morjan, I.; Fleaca, C.; Badoi, A.; Manda, G.; Pop, S.; Marta, D.; Huminic, G.; Vekas, L.; Daia, C.; et al. Highly magnetic Fe2O3 nanoparticles synthesized by laser pyrolysis used for biological and heat transfer applications. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2015, 336, 297–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radu, T.; Iacovita, C.; Benea, D.; Turcu, R. X-Ray Photoelectron Spectroscopic Characterization of Iron Oxide Nanoparticles. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2017, 405, 337–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grosvenor, A.P.; Kobe, B.A.; McIntyre, N.S. Examination of the oxidation of iron by oxygen using X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy and QUASESTM. Surf. Sci. 2004, 565, 151–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wirecka, R.; Lachowicz, D.; Berent, K.; Marzec, M.M.; Bernasik, A. Ion distribution in iron oxide, zinc and manganese ferrite nanoparticles studied by XPS combined with argon gas cluster ion beam sputtering. Surf. Interfaces 2022, 30, 101865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chowdhury, S.R.; Yanful, E.K.; Pratt, A.R. Chemical states in XPS and Raman analysis during removal of Cr(VI) from contaminated water by mixed maghemite–magnetite nanoparticles. J. Hazard. Mater. 2012, 235–236, 246–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nistorescu, S.; Udrea, A.-M.; Badea, M.A.; Lungu, I.; Boni, M.; Tozar, T.; Dumitrache, F.; Maraloiu, V.-A.; Popescu, R.G.; Fleaca, C.; et al. Low Blue Dose Photodynamic Therapy with Porphyrin-Iron Oxide Nanoparticles Complexes: In Vitro Study on Human Melanoma Cells. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 2130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- National Institute of Standards and Technology. Iron Pentacarbonyl. Available online: https://webbook.nist.gov/cgi/cbook.cgi?ID=C13463406&Mask=4&Type=ANTOINE&Plot=on (accessed on 15 September 2023).

| Sample | Gas Flow Rates | Laser Power | Other Parameters |
|---|---|---|---|
| SFnew1 | DC2H4 = 33 sccm Dair = 33 sccm DFe(CO)5 ≅ 4.78 sccm | PLar = 157 W PLab = 150 W | Tfl = 670 °C |
| SFnew2 | DC2H4 = 33 sccm Dair = 33 sccm DFe(CO)5 ≅ 4.78 sccm | PLar = 80 W PLab = 75 W | Tfl = 485 °C |
| SFnew3 | DC2H4 = 33 sccm Dair = 33 sccm DFe(CO)5 ≅ 4.78 sccm | PLar = 125 W PLab = 120 W | Tfl = 680 °C |
| SFnew4 | DC2H4 = 100 sccm Dair = 100 sccm DFe(CO)5 ≅ 14.50 sccm | PLar = 88 W PLab = 86 W | Tfl = 608 °C |
| SFnew5 | DC2H4 = 100 sccm Dair = 100 sccm DFe(CO)5 ≅ 14.50 sccm | PLar = 40 W PLab = 35 W | Tfl = 400 °C |
| Sample | SFnew1 | SFnew2 | SFnew3 | SFnew4 | SFnew5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| τ (msec) | 0.449 | 0.559 | 0.445 | 0.158 | 0.208 |
| Sample | C (at.%) | O (at.%) | Fe (at.%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| SFnew1 | 28.8 | 50.3 | 20.9 |
| SFnew2 | 30.1 | 50.2 | 19.7 |
| SFnew3 | 28.0 | 47.1 | 24.9 |
| SFnew4 | 28.8 | 46.1 | 25.1 |
| SFnew5 | 30.0 | 46.3 | 23.7 |
| Sample | Z-Average (nm) | PDI | Z-Potential (mV) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean | SD | Mean | SD | Mean | SD | |
| SFnew1 | 228.56 | 5.275 | 0.403 | 0.027 | 53.33 | −0.543 |
| SFnew2 | 181.5 | 6.481 | 0.465 | 0.063 | 61.43 | 0.418 |
| SFnew3 | 135.6 | 1.070 | 0.359 | 0.009 | 61.9 | 0.989 |
| SFnew4 | 141.6 | 1.608 | 0.416 | 0.051 | 58.93 | 1.172 |
| SFnew5 | 162.26 | 5.441 | 0.398 | 0.006 | 60 | 0.355 |
| Sample | C (at.%) | O (at.%) | Fe (at.%) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Element | ||||
| SFnew1 | 0.63 | 53.2 | 46.17 | |
| SFnew4 | 0.91 | 42.72 | 56.37 | |
| Sample | NPs Crystallographic Parameters | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Dmed (nm) | A (Å) | Volcell | |
| SFnew1 | 5.7 | 8.368 | 583.02 |
| SFnew2 | 4.3 | 8.394 | 591.35 |
| SFnew3 | 4.4 | 8.377 | 587.77 |
| SFnew4 | 5.3 | 8.365 | 585.41 |
| SFnew5 | 2.3 | 8.373 | 587.85 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lungu, I.I.; Andronescu, E.; Dumitrache, F.; Gavrila-Florescu, L.; Banici, A.M.; Morjan, I.; Criveanu, A.; Prodan, G. Laser Pyrolysis of Iron Oxide Nanoparticles and the Influence of Laser Power. Molecules 2023, 28, 7284. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28217284
Lungu II, Andronescu E, Dumitrache F, Gavrila-Florescu L, Banici AM, Morjan I, Criveanu A, Prodan G. Laser Pyrolysis of Iron Oxide Nanoparticles and the Influence of Laser Power. Molecules. 2023; 28(21):7284. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28217284
Chicago/Turabian StyleLungu, Iulia Ioana, Ecaterina Andronescu, Florian Dumitrache, Lavinia Gavrila-Florescu, Ana Maria Banici, Iuliana Morjan, Anca Criveanu, and Gabriel Prodan. 2023. "Laser Pyrolysis of Iron Oxide Nanoparticles and the Influence of Laser Power" Molecules 28, no. 21: 7284. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28217284
APA StyleLungu, I. I., Andronescu, E., Dumitrache, F., Gavrila-Florescu, L., Banici, A. M., Morjan, I., Criveanu, A., & Prodan, G. (2023). Laser Pyrolysis of Iron Oxide Nanoparticles and the Influence of Laser Power. Molecules, 28(21), 7284. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28217284








