Deep Eutectic Solvent Coated Cerium Oxide Nanoparticles Based Polysulfone Membrane to Mitigate Environmental Toxicology
Abstract
:1. Introduction
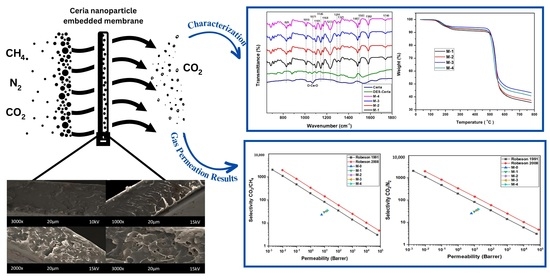
2. Results and Discussion
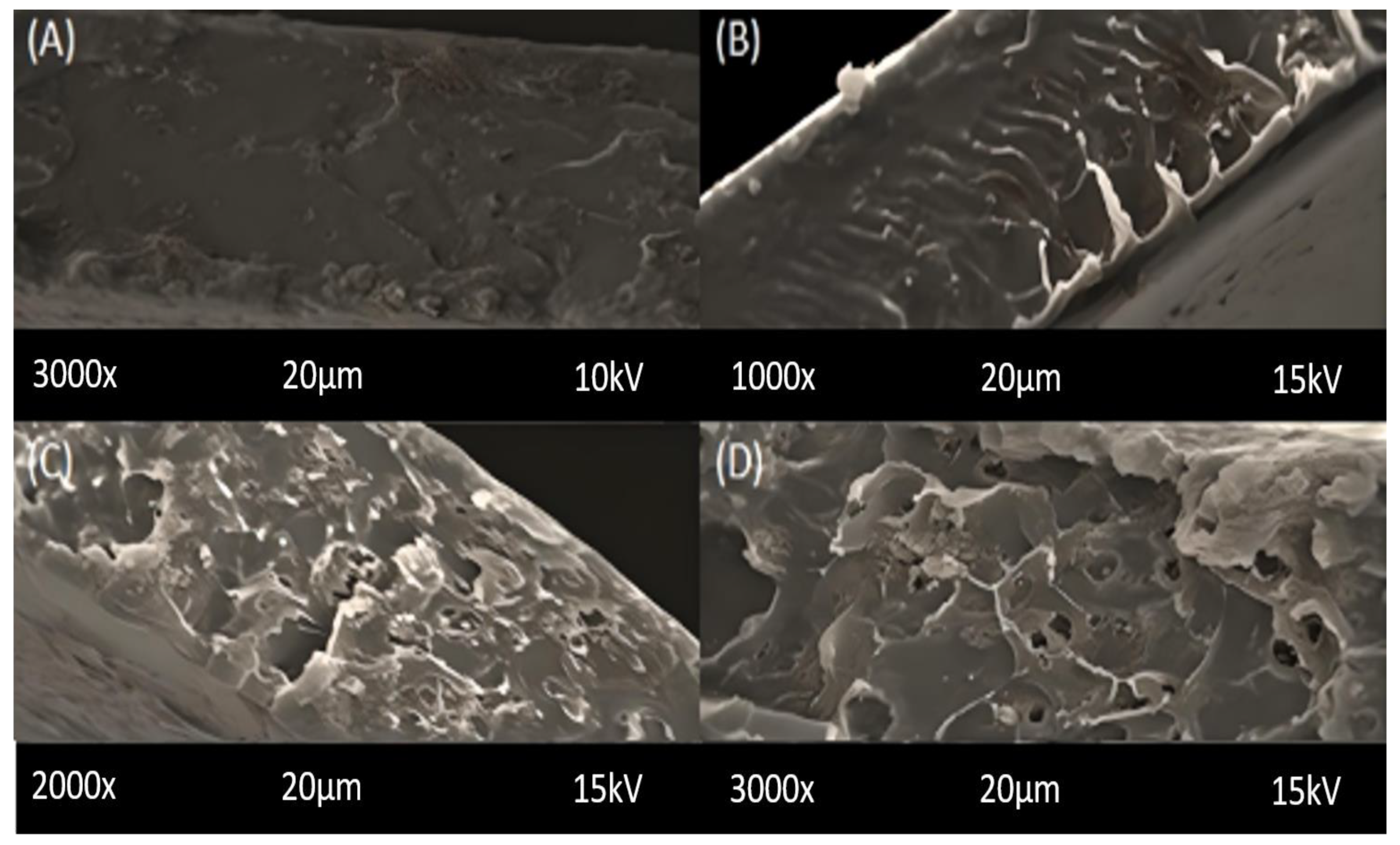
2.1. Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM)
2.2. Fourier Transform Infrared (FTIR) Spectroscopy
2.3. Thermogravimetric Analysis
2.4. Gas Permeation Analysis
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials
3.2. Deep Eutectic Solvent (DES) Preparation
3.3. Ceria Nanoparticles formation
3.4. Surface Modification of Cerium Oxide Nanoparticles by DES
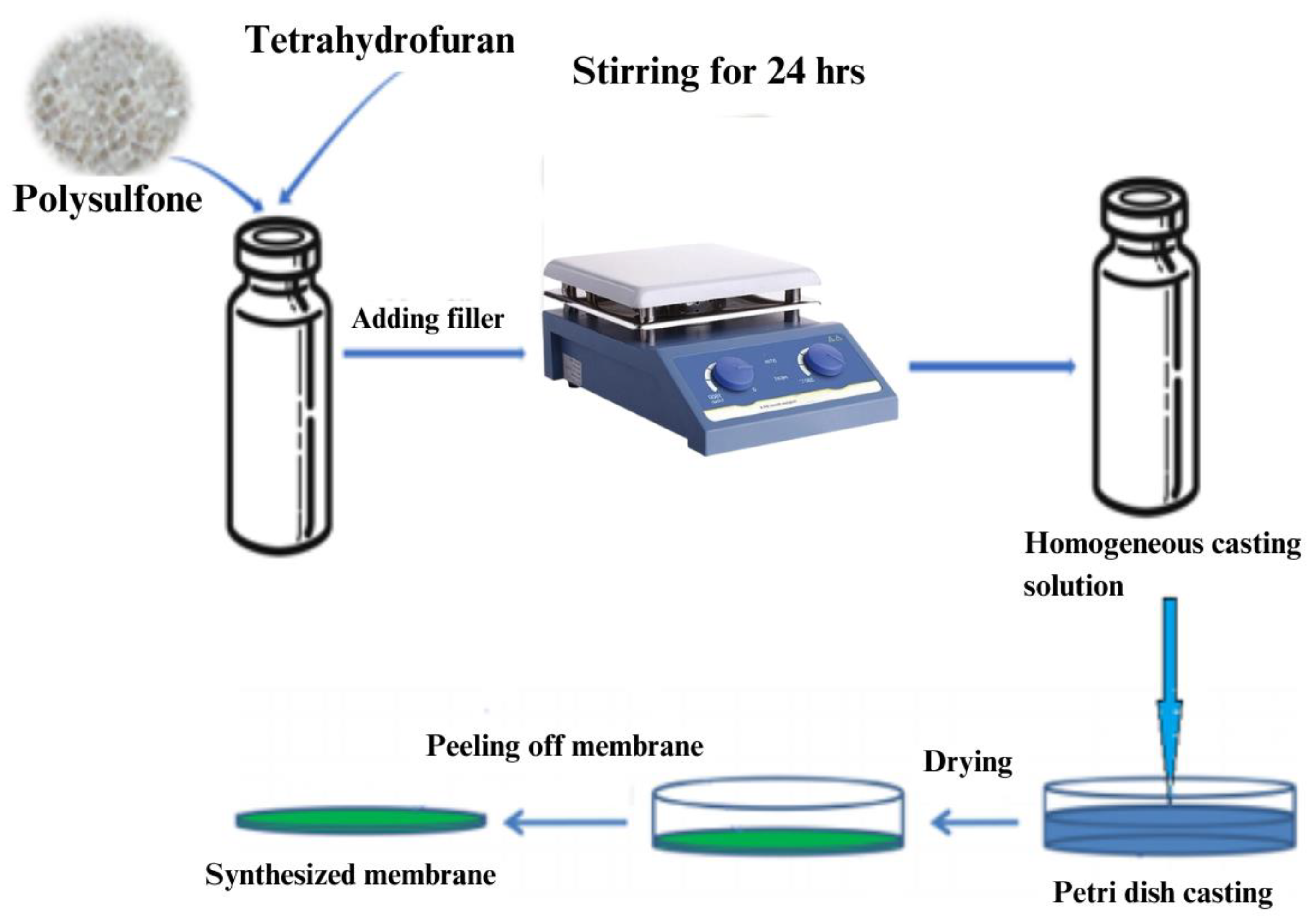
3.5. Mixed Matrix Membranes Fabrication
3.6. Characterization of Membrane Samples
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Sample Availability
References
- Chuah, C.Y.; Goh, K.; Yang, Y.; Gong, H.; Li, W.; Karahan, H.E.; Guiver, M.D.; Wang, R.; Bae, T.-H. Harnessing filler materials for enhancing biogas separation membranes. Chem. Rev. 2018, 118, 8655–8769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hua, Y.; Wang, H.; Li, Q.; Chen, G.; Liu, G.; Duan, J.; Jin, W. Highly efficient CH4 purification by LaBTB PCP-based mixed matrix membranes. J. Mater. Chem. A 2018, 6, 599–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norahim, N.; Yaisanga, P.; Faungnawakij, K.; Charinpanitkul, T.; Klaysom, C. Recent membrane developments for CO2 separation and capture. Chem. Eng. Technol. 2018, 41, 211–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, K.; Fu, Q.; Qiao, G.G.; Webley, P.A. Recent progress on fabrication methods of polymeric thin film gas separation membranes for CO2 capture. J. Membr. Sci. 2019, 572, 38–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olajire, A.A. CO2 capture and separation technologies for end-of-pipe applications—A review. Energy 2010, 35, 2610–2628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernardo, P.; Drioli, E.; Golemme, G. Membrane gas separation: A review/state of the art. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2009, 48, 4638–4663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koros, W.J.; Zhang, C. Materials for next-generation molecularly selective synthetic membranes. Nat. Mater. 2017, 16, 289–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.; Jin, W.; Xu, N. Two-dimensional-material membranes: A new family of high-performance separation membranes. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2016, 55, 13384–13397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, J.; Zhang, H.; Simon, G.P.; Wang, H. Polycrystalline advanced microporous framework membranes for efficient separation of small molecules and ions. Adv. Mater. 2020, 32, e1902009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kosinov, N.; Gascon, J.; Kapteijn, F.; Hensen, E.J. Recent developments in zeolite membranes for gas separation. J. Membr. Sci. 2016, 499, 65–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, M.; Wang, H.; Lin, Y. Inorganic membranes for carbon dioxide and nitrogen separation. Rev. Chem. Eng. 2012, 28, 101–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Li, X.; Wu, H.; Tian, Z.; Xin, Q.; He, G.; Peng, D.; Chen, S.; Yin, Y.; Jiang, Z.; et al. Advances in high permeability polymer-based membrane materials for CO2 separations. Energy Environ. Sci. 2016, 9, 1863–1890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galizia, M.; Chi, W.S.; Smith, Z.P.; Merkel, T.C.; Baker, R.W.; Freeman, B.D. 50th anniversary perspective: Polymers and mixed matrix membranes for gas and vapor separation: A review and prospective opportunities. Macromolecules 2017, 50, 7809–7843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robeson, L.M. The upper bound revisited. J. Membr. Sci. 2008, 320, 390–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dechnik, J.; Gascon, J.; Doonan, C.J.; Janiak, C.; Sumby, C. Mixed-matrix membranes. Angew. Int. Ed. 2017, 56, 9292–9310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, Y.; Wang, Z.; Zhao, D. Mixed matrix membranes for natural gas upgrading: Current status and opportunities. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2018, 57, 4139–4169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dorosti, F.; Omidkhah, M.; Abedini, R. Fabrication and characterization of Matrimid/MIL-53 mixed matrix membrane for CO2/CH4 separation. Chem. Eng. Res. Des. 2014, 92, 2439–2448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadeghi, Z.; Omidkhah, M.; Masoumi, M.E.; Abedini, R. Modification of existing permeation models of mixed matrix membranes filled with porous particles for gas separation. Can. J. Chem. Eng. 2016, 94, 547–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamshidi, M.; Pirouzfar, V.; Abedini, R.; Pedram, M.Z. The influence of nanoparticles on gas transport properties of mixed matrix membranes: An experimental investigation and modeling. Korean J. Chem. Eng. 2017, 34, 829–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Deng, Y. Nanoconfined ionic liquids. Chem. Rev. 2017, 117, 6755–6833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Wu, H.; Wu, S.; Song, S.; Guo, Z.; Ren, Y.; Zhao, R.; Yang, L.; Wu, Y.; Jiang, Z. Multifunctional covalent organic framework (COF)-Based mixed matrix membranes for enhanced CO2 separation. J. Membr. Sci. 2021, 618, 118693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Wang, Z.; Zhao, S.; Wang, J.; Wang, S. Recent advances on mixed matrix membranes for CO2 separation. Chin. J. Chem. Eng. 2017, 25, 1581–1597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; Lee, Y.M. High performance polymer membranes for CO2 separation. Curr. Opin. Chem. Eng. 2013, 2, 238–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aroon, M.; Ismail, A.; Matsuura, T.; Montazer-Rahmati, M. Performance studies of mixed matrix membranes for gas separation: A review. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2010, 75, 229–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasebe, S.; Aoyama, S.; Tanaka, M.; Kawakami, H. CO2 separation of polymer membranes containing silica nanoparticles with gas permeable nano-space. J. Membr. Sci. 2017, 536, 148–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raouf, M.; Abedini, R.; Omidkhah, M.; Nezhadmoghadam, E. A favored CO2 separation over light gases using mixed matrix membrane comprising polysulfone/polyethylene glycol and graphene hydroxyl nanoparticles. Process. Saf. Environ. Prot. 2020, 133, 394–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sainath, K.; Modi, A.; Bellare, J. In-situ growth of zeolitic imidazolate framework-67 nanoparticles on polysulfone/graphene oxide hollow fiber membranes enhance CO2/CH4 separation. J. Membr. Sci. 2020, 614, 118506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruhaimi, A.H.; Ab Aziz, M.A. Spherical CeO2 nanoparticles prepared using an egg-shell membrane as a bio-template for high CO2 adsorption. Chem. Phys. Lett. 2021, 779, 138842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farashi, Z.; Azizi, S.; Arzhandi, M.R.D.; Noroozi, Z.; Azizi, N. Improving CO2/CH4 separation efficiency of Pebax-1657 membrane by adding Al2O3 nanoparticles in its matrix. J. Nat. Gas Sci. Eng. 2019, 72, 103019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, R.; Wang, Z.; Wang, M.; Qiao, Z.; Wang, J. High nanoparticles loadings mixed matrix membranes via chemical bridging-crosslinking for CO2 separation. J. Membr. Sci. 2019, 573, 455–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taghizadeh, M.; Taghizadeh, A.; Vatanpour, V.; Ganjali, M.R.; Saeb, M.R. Deep eutectic solvents in membrane science and technology: Fundamental, preparation, application, and future perspective. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2020, 258, 118015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jablonský, M.; Škulcová, A.; Šima, J. Use of deep eutectic solvents in polymer chemistry–A review. Molecules 2019, 24, 3978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reed, K.; Cormack, A.; Kulkarni, A.; Mayton, M.; Sayle, D.; Klaessig, F.; Stadler, B. Exploring the properties and applications of nanoceria: Is there still plenty of room at the bottom? Environ. Sci. Nano 2014, 1, 390–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Y.; Han, G.; Chung, T.-S.; Weber, M.; Widjojo, N.; Maletzko, C. Effects of polyethylene glycol on membrane formation and properties of hydrophilic sulfonated polyphenylenesulfone (sPPSU) membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 2017, 531, 27–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elahi, B.; Mirzaee, M.; Darroudi, M.; Oskuee, R.K.; Sadri, K.; Amiri, M.S. Preparation of cerium oxide nanoparticles in Salvia MacrosiphonBoiss seeds extract and investigation of their photo-catalytic activities. Ceram. Int. 2019, 45, 4790–4797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sreekanth, T.; Dillip, G.; Lee, Y.R. Picrasmaquassioides mediated cerium oxide nanostructures and their post-annealing treatment on the microstructural, morphological and enhanced catalytic performance. Ceram. Int. 2016, 42, 6610–6618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; De Oliveira Vigier, K.; Royer, S.; Jérôme, F. Deep eutectic solvents: Syntheses, properties and applications. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2012, 41, 7108–7146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahbaz, K.; Mjalli, F.S.; Hashim, M.A.; AlNashef, I.M. Using deep eutectic solvents based on methyl triphenyl phosphunium bromide for the removal of glycerol from palm-oil-based biodiesel. Energy Fuels 2011, 25, 2671–2678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durand, E.; Lecomte, J.; Villeneuve, P. Deep eutectic solvents: Synthesis, application, and focus on lipase-catalyzed reactions. Eur. J. Lipid Sci. Technol. 2013, 115, 379–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lian, S.; Li, R.; Zhang, Z.; Liu, Q.; Song, C.; Lu, S. Improved CO2 separation performance and interfacial affinity of composite membranes by incorporating amino acid-based deep eutectic solvents. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2021, 272, 118953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muduli, S.K.; Wang, S.; Chen, S.; Ng, C.F.; Huan, C.H.A.; Sum, T.C.; Soo, H.S. Mesoporous cerium oxide nanospheres for the visible-light driven photocatalytic degradation of dyes. Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2014, 5, 517–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Zhang, S.; Wu, H.; Ye, C.; Liang, X.; Wang, S.; Wu, X.; Wu, Y.; Ren, Y.; Liu, Y.; et al. Porous organosilicon nanotubes in pebax-based mixed-matrix membranes for biogas purification. J. Membr. Sci. 2019, 573, 301–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, K.; Devi, S.; Bajaj, H.C.; Ingole, P.; Choudhari, J.; Bhrambhatt, H. Optical resolution of racemic mixtures of amino acids through nanofiltration membrane process. Sep. Sci. Technol. 2014, 49, 2630–2641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shan, M.; Seoane, B.; Andres-Garcia, E.; Kapteijn, F.; Gascon, J. Mixed-matrix membranes containing an azine-linked covalent organic framework: Influence of the polymeric matrix on post-combustion CO2-capture. J. Membr. Sci. 2018, 549, 377–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Ho, W.W. High-molecular-weight polyvinylamine/piperazine glycinate membranes for CO2 capture from flue gas. J. Membr. Sci. 2016, 514, 376–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, A.L.; Basu, S.; Cano-Odena, A.; Vankelecom, I.F. Novel high throughput equipment for membrane-based gas separations. J. Membr. Sci. 2010, 354, 32–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robeson, L.M. Correlation of separation factor versus permeability for polymeric membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 1991, 62, 165–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vakharia, V.; Salim, W.; Wu, D.; Han, Y.; Chen, Y.; Zhao, L.; Ho, W.W. Scale-up of amine-containing thin-film composite membranes for CO2 capture from flue gas. J. Membr. Sci. 2018, 555, 379–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]








| Sr No. | Wavenumber (cm−1) | Functional Groups |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 829 | Benzene ring bending |
| 2 | 1010 | C-H stretching in benzene ring |
| 3 | 1071 | O-Ce-O stretching vibration |
| 4 | 1101 | Symmetric elongating vibration of O=S=O |
| 5 | 1146 | Asymmetric stretching vibration of O=S=O |
| 6 | 1168 | Bending vibration of C-O |
| 7 | 1233 | Elongating vibration of -C6H4-O-C6H4- |
| 8 | 1291, 1321 | Symmetric stretching vibration of O=S=O |
| 9 | 1483 | Bending vibration of C-H |
| 10 | 1503, 1582 | Stretching mode of C=C in aromatics |
| 11 | 1740 | Symmetric stretching of C=O |
| Membrane Id | Membrane Type | PSF | Ceria | THF |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| M-0 | PSF | 4.8 | - | 95.2 |
| M-1 | 2% ceria membrane | 4.8 | 0.1 | 95.1 |
| M-2 | 4% ceria membrane | 4.8 | 0.2 | 95.0 |
| M-3 | 6% ceria membrane | 4.8 | 0.3 | 94.9 |
| M-4 | 8% ceria membrane | 4.8 | 0.4 | 94.8 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Saif-ur-Rehman; Shozab Mehdi, M.; Fakhar-e-Alam, M.; Asif, M.; Rehman, J.; A. Alshgari, R.; Jamal, M.; Uz Zaman, S.; Umar, M.; Rafiq, S.; et al. Deep Eutectic Solvent Coated Cerium Oxide Nanoparticles Based Polysulfone Membrane to Mitigate Environmental Toxicology. Molecules 2023, 28, 7162. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28207162
Saif-ur-Rehman, Shozab Mehdi M, Fakhar-e-Alam M, Asif M, Rehman J, A. Alshgari R, Jamal M, Uz Zaman S, Umar M, Rafiq S, et al. Deep Eutectic Solvent Coated Cerium Oxide Nanoparticles Based Polysulfone Membrane to Mitigate Environmental Toxicology. Molecules. 2023; 28(20):7162. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28207162
Chicago/Turabian StyleSaif-ur-Rehman, Muhammad Shozab Mehdi, Muhammad Fakhar-e-Alam, Muhammad Asif, Javed Rehman, Razan A. Alshgari, Muddasar Jamal, Shafiq Uz Zaman, Muhammad Umar, Sikander Rafiq, and et al. 2023. "Deep Eutectic Solvent Coated Cerium Oxide Nanoparticles Based Polysulfone Membrane to Mitigate Environmental Toxicology" Molecules 28, no. 20: 7162. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28207162
APA StyleSaif-ur-Rehman, Shozab Mehdi, M., Fakhar-e-Alam, M., Asif, M., Rehman, J., A. Alshgari, R., Jamal, M., Uz Zaman, S., Umar, M., Rafiq, S., Muhammad, N., bin Fawad, J., & Shafiee, S. A. (2023). Deep Eutectic Solvent Coated Cerium Oxide Nanoparticles Based Polysulfone Membrane to Mitigate Environmental Toxicology. Molecules, 28(20), 7162. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28207162